Coronary artery aneurysm: Difference between revisions
Content deleted Content added
Citation bot (talk | contribs) Alter: doi-broken-date. | You can use this bot yourself. Report bugs here. | Suggested by AManWithNoPlan | Category:Pages_with_DOIs_inactive_as_of_2020_January | via #UCB_Category |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
| duration = |
| duration = |
||
| types = |
| types = |
||
| causes = |
| causes = atherosclerosis, Kawasaki disease, coronary catheterization. |
||
| risks = |
| risks = |
||
| diagnosis = |
| diagnosis = [[coronary angiography]] |
||
| differential = |
| differential = |
||
| prevention = |
| prevention = |
||
| treatment = medical management, surgical excision, [[Coronary artery bypass surgery|coronary bypass grafting]] (CABG), and [[percutaneous coronary intervention]]s<ref name="JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions 2018 pp. 1211–1223">{{cite journal | title=Management of Coronary Artery Aneurysms | journal=JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions | volume=11 | issue=13 | date=2018-07-09 | issn=1936-8798 | doi=10.1016/j.jcin.2018.02.041 | pages=1211–1223 | url=https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1936879818308598?via%3Dihub | access-date=2020-09-19}}</ref> |
|||
| treatment = |
|||
| medication = |
| medication = |
||
| prognosis = |
| prognosis = |
||
Revision as of 21:18, 19 September 2020
| Coronary artery aneurysm | |
|---|---|
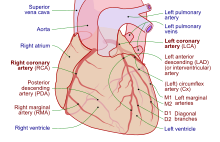 | |
| Coronary arteries | |
| Specialty | Cardiology |
| Causes | atherosclerosis, Kawasaki disease, coronary catheterization. |
| Diagnostic method | coronary angiography |
| Treatment | medical management, surgical excision, coronary bypass grafting (CABG), and percutaneous coronary interventions[1] |
Coronary artery aneurysm is an abnormal dilatation of part of the coronary artery.
Causes
Acquired causes include atherosclerosis,[2] Kawasaki disease[3] and coronary catheterization.
It can also be congenital.[4][5]
Diagnosis
It is often found coincidentally on coronary angiography.[6]
Treatment
This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (September 2017) |
Prognosis
Generally, it has a good prognosis.[6] In Kawasaki's disease, untreated, there is a 1–2% death rate, from cardiac causes.
See also
References
- ^ "Management of Coronary Artery Aneurysms". JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions. 11 (13): 1211–1223. 2018-07-09. doi:10.1016/j.jcin.2018.02.041. ISSN 1936-8798. Retrieved 2020-09-19.
- ^ Nichols L, Lagana S, Parwani A (May 2008). "Coronary artery aneurysm: a review and hypothesis regarding etiology". Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 132 (5): 823–8. doi:10.1043/1543-2165(2008)132[823:CAAARA]2.0.CO;2 (inactive 2020-09-10). PMID 18466032.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of September 2020 (link) - ^ Fukazawa R, Ikegam E, Watanabe M, et al. (May 2007). "Coronary artery aneurysm induced by Kawasaki disease in children show features typical senescence". Circ. J. 71 (5): 709–15. doi:10.1253/circj.71.709. PMID 17456996.
- ^ Seabra-Gomes R, Somerville J, Ross DN, Emanuel R, Parker DJ, Wong M (April 1974). "Congenital coronary artery aneurysms". Br Heart J. 36 (4): 329–35. doi:10.1136/hrt.36.4.329. PMC 1020027. PMID 4842623.
- ^ Meinert D, Mohammed Z (March 2000). "MRI of congenital coronary artery aneurysm". Br J Radiol. 73 (867): 322–4. doi:10.1259/bjr.73.867.10817051. PMID 10817051.
- ^ a b Pahlavan PS, Niroomand F (October 2006). "Coronary artery aneurysm: a review". Clin Cardiol. 29 (10): 439–43. doi:10.1002/clc.4960291005. PMC 6654377. PMID 17063947.
