Leadership: Difference between revisions
m Reverted edits by 66.172.229.202 (talk) to last version by E.w.bullock |
|||
| Line 437: | Line 437: | ||
{{Commons category}} |
{{Commons category}} |
||
*{{dmoz|Business/Management/Leadership/}} |
*{{dmoz|Business/Management/Leadership/}} |
||
*[http://byrnesconsulting.com/2010/04/27/how-leaders-soar-above-the-rest/ 15 behaviors of successful leaders] |
|||
[[Category:Emergency laws]] |
[[Category:Emergency laws]] |
||
Revision as of 05:53, 27 April 2010
This article needs additional citations for verification. (September 2009) |
This article may require copy editing for grammar, style, cohesion, tone, or spelling. (February 2010) |
Leadership is stated as the “process of social influence in which one person can enlist the aid and support of others in the accomplishment of a common task.”[1] Definitions more inclusive of followers have also emerged. Alan Keith of Genentech stated that, "Leadership is ultimately about creating a way for people to contribute to making something extraordinary happen."[2] Tom DeMarco says that leadership needs to be distinguished from posturing.[3]
Leadership remains one of the most relevant aspects of the organizational context. However, defining leadership has been challenging and definitions can vary depending on the situation. According to Ann Marie E. McSwain, Assistant Professor at Lincoln University, “leadership is about capacity: the capacity of leaders to listen and observe, to use their expertise as a starting point to encourage dialogue between all levels of decision-making, to establish processes and transparency in decision-making, to articulate their own value and visions clearly but not impose them. Leadership is about setting and not just reacting to agendas, identifying problems, and initiating change that makes for substantial improvement rather than managing change.”
The following sections discuss several important aspects of leadership including a description of what leadership is and a description of several popular theories and styles of leadership. This article also discusses topics such as the role of emotions and vision, as well as leadership effectiveness and performance, leadership in different contexts, how it may differ from related concepts (i.e., management), and some critiques of leadership as generally conceived.
Theories of leadership
Students of leadership have produced theories involving traits [4], situational interaction, function, behavior, power, vision and values [5], charisma, and intelligence among others.
Trait Theory
Trait theory tries to describe the characteristics associated with effective leadership.
Early History
The search for the characteristics or traits of leaders has been ongoing for centuries. History’s greatest philosophical writings from Plato’s Republic to Plutarch’s Lives have explored the question of “What qualities distinguish an individual as a leader?” Underlying this search was the early recognition of the importance of leadership and the assumption that leadership is rooted in the characteristics that certain individuals possess. This idea that leadership is based on individual attributes is known as the “trait theory of leadership.”
This view of leadership, the trait theory, was explored at length in a number of works in the previous century. Most notable are the writings of Thomas Carlyle and Francis Galton, whose works have prompted decades of research. In Heroes and Hero Worship (1841), Carlyle identified the talents, skills, and physical characteristics of men who rose to power. In Galton’s (1869) Hereditary Genius, he examined leadership qualities in the families of powerful men. After showing that the numbers of eminent relatives dropped off when moving from first degree to second degree relatives, Galton concluded that leadership was inherited. In other words, leaders were born, not developed. Both of these notable works lent great initial support for the notion that leadership is rooted in characteristics of the leader.
For decades, this trait-based perspective dominated empirical and theoretical work in leadership[6]. Using early research techniques, researchers conducted over a hundred studies proposing a number of characteristics that distinguished leaders from nonleaders: intelligence, dominance, adaptability, persistence, integrity, socioeconomic status, and self-confidence just to name a few[7].
The Rise of Alternative Leadership Theories
In the late 1940s and early 1950s, however, a series of qualitative reviews of these studies (e.g., Bird, 1940[8]; Stogdill, 1948[9]; Mann, 1959[10]) prompted researchers to take a drastically different view of the driving forces behind leadership. In reviewing the extant literature, Stogdill and Mann found that while some traits were common across a number of studies, the overall evidence suggested that persons who are leaders in one situation may not necessarily be leaders in other situations. Subsequently, leadership was no longer characterized as an enduring individual trait, as situational approaches (see alternative leadership theories below) posited that individuals can be effective in certain situations, but not others. This approach dominated much of the leadership theory and research for the next few decades.
The Reemergence of the Trait Theory
New methods and measurements were developed after these influential reviews that would ultimately reestablish the trait theory as a viable approach to the study of leadership. For example, improvements in researchers’ use of the round robin research design methodology allowed researchers to see that individuals can and do emerge as leaders across a variety of situations and tasks[11]. Additionally, during the 1980s statistical advances allowed researchers to conduct meta-analyses, in which they could quantitatively analyze and summarize the findings from a wide array of studies. This advent allowed trait theorists to create a comprehensive and parsimonious picture of previous leadership research rather than rely on the qualitative reviews of the past. Equipped with new methods, leadership researchers revealed the following:
- Individuals can and do emerge as leaders across a variety of situations and tasks[11]
- Significant relationships exist between leadership and such individual traits as:
- intelligence[12]
- adjustment[12]
- extraversion[12]
- conscientiousness[13][14][15]
- openness to experience[14][16]
- general self-efficacy[17][18]
Current Criticisms of the Trait Theory
While the trait theory of leadership has certainly regained popularity, its reemergence has not been accompanied by a corresponding increase in sophisticated conceptual frameworks[6].
Specifically, Zaccaro (2007)[6] noted that trait theories still:
- Focus on a small set of individual attributes such as Big Five personality traits, to the neglect of cognitive abilities, motives, values, social skills, expertise, and problem-solving skills
- Fail to consider patterns or integrations of multiple attributes
- Do not distinguish between those leader attributes that are generally not malleable over time and those that are shaped by, and bound to, situational influences
- Do not consider how stable leader attributes account for the behavioral diversity necessary for effective leadership
Leader Attribute Pattern Approach
Considering the criticisms of the trait theory outlined above, several researchers have begun to adopt a different perspective of leader individual differences - the leader attribute pattern approach[19][20][21][22][23]. In contrast to the traditional approach, the leader attribute pattern approach is based on theorists’ arguments that the influence of individual characteristics on outcomes is best understood by considering the person as an integrated totality rather than a summation of individual variables[22][24]. In other words, the leader attribute pattern approach argues that integrated constellations or combinations of individual differences may explain substantial variance in both leader emergence and leader effectiveness beyond that explained by single attributes, or by additive combinations of multiple attributes.
Behavioral and style theories
In response to the early criticisms of the trait approach, theorists began to research leadership as a set of behaviors, evaluating the behavior of 'successful' leaders, determining a behavior taxonomy and identifying broad leadership styles.[25] David McClelland, for example, Leadership takes a strong personality with a well developed positive ego. Not so much as a pattern of motives, but a set of traits is crucial. To lead; self-confidence and a high self-esteem is useful, perhaps even essential.[26][Kevin Mick]
Kurt Lewin, Ronald Lipitt, and Ralph White developed in 1939 the seminal work on the influence of leadership styles and performance. The researchers evaluated the performance of groups of eleven-year-old boys under different types of work climate. In each, the leader exercised his influence regarding the type of group decision making, praise and criticism (feedback), and the management of the group tasks (project management) according to three styles: (1) authoritarian, (2) democratic and (3) laissez-faire.[27] Authoritarian climates were characterized by leaders who make decisions alone, demand strict compliance to his orders, and dictate each step taken; future steps were uncertain to a large degree. The leader is not necessarily hostile but is aloof from participation in work and commonly offers personal praise and criticism for the work done. Democratic climates were characterized by collective decision processes, assisted by the leader. Before accomplishing tasks, perspectives are gained from group discussion and technical advice from a leader. Members are given choices and collectively decide the division of labor. Praise and criticism in such an environment are objective, fact minded and given by a group member without necessarily having participated extensively in the actual work. Laissez faire climates gave freedom to the group for policy determination without any participation from the leader. The leader remains uninvolved in work decisions unless asked, does not participate in the division of labor, and very infrequently gives praise.[27] The results seemed to confirm that the democratic climate was preferred.[28]
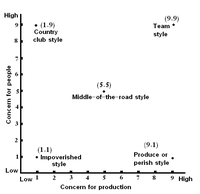
The managerial grid model is also based on a behavioral theory. The model was developed by Robert Blake and Jane Mouton in 1964 and suggests five different leadership styles, based on the leaders' concern for people and their concern for goal achievement.[29]
B.F. Skinner is the father of Behavior Modification and developed the concept of positive reinforcement. Positive reinforcement occurs when a stimulus is presented contingent upon a behavior which results in a higher probability of that behavior increasing in the future[30]. The following is an example of how positive reinforcement can be used in a business setting. Assume praise is a positive reinforcer for a particular employee. This employee does not show up to work on time every day. The manager of this employee decides to praise the employee for showing up on time every day the employee actually shows up to work on time. As a result, the employee comes to work on time more often because the employee likes to be praised. In this example, praise (i.e. stimulus) is a positive reinforcer for this employee because the employee arrives (i.e. behavior) to work on time more frequently after being praised for showing up to work on time.
The use of positive reinforcement is a successful and growing technique used by leaders to motivate and attain desired behaviors from subordinates. Organizations such as Frito-Lay, 3M, B.F. Goodrich, Michigan Bell, and Emery Air Freight have all used reinforcement to increase productivity[31]. Empirical research covering the last 20 years suggests that reinforcement theory has a 17 percent increase in performance. Additionally, many reinforcement techniques such as the use of praise are inexpensive which can result in higher performances for low monetary costs.
Situational and contingency theories
Situational theory also appeared as a reaction to the trait theory of leadership. Social scientists argued that history was more than the result of intervention of great men as Carlyle suggested. Herbert Spencer (1884) said that the times produce the person and not the other way around.[32] This theory assumes that different situations call for different characteristics; according to this group of theories, no single optimal psychographic profile of a leader exists. According to the theory, "what an individual actually does when acting as a leader is in large part dependent upon characteristics of the situation in which he functions."[33]
Some theorists started to synthesize the trait and situational approaches. Building upon the research of Lewin et al., academics began to normatize the descriptive models of leadership climates, defining three leadership styles and identifying in which situations each style works better. The authoritarian leadership style, for example, is approved in periods of crisis but fails to win the "hearts and minds" of their followers in the day-to-day management; the democratic leadership style is more adequate in situations that require consensus building; finally, the laissez faire leadership style is appreciated by the degree of freedom it provides, but as the leader does not "take charge", he can be perceived as a failure in protracted or thorny organizational problems.[34] Thus, theorists defined the style of leadership as contingent to the situation, which is sometimes classified as contingency theory. Four contingency leadership theories appear more prominently in the recent years: Fiedler contingency model, Vroom-Yetton decision model, the path-goal theory, and the Hersey-Blanchard situational theory.
The Fiedler contingency model bases the leader’s effectiveness on what Fred Fiedler called situational contingency. This results from the interaction of leadership style and situational favorableness (later called "situational control"). The theory defined two types of leader: those who tend to accomplish the task by developing good-relationships with the group (relationship-oriented), and those who have as their prime concern carrying out the task itself (task-oriented).[35] According to Fiedler, there is no ideal leader. Both task-oriented and relationship-oriented leaders can be effective if their leadership orientation fits the situation. When there is a good leader-member relation, a highly structured task, and high leader position power, the situation is considered a "favorable situation". Fiedler found that task-oriented leaders are more effective in extremely favourable or unfavourable situations, whereas relationship-oriented leaders perform best in situations with intermediate favourability.
Victor Vroom, in collaboration with Phillip Yetton (1973)[36] and later with Arthur Jago (1988),[37] developed a taxonomy for describing leadership situations, taxonomy that was used in a normative decision model where leadership styles where connected to situational variables, defining which approach was more suitable to which situation.[38] This approach was novel because it supported the idea that the same manager could rely on different group decision making approaches depending on the attributes of each situation. This model was later referred as situational contingency theory.[39]
The path-goal theory of leadership was developed by Robert House (1971) and was based on the expectancy theory of Victor Vroom.[40] According to House, the essence of the theory is "the meta proposition that leaders, to be effective, engage in behaviors that complement subordinates' environments and abilities in a manner that compensates for deficiencies and is instrumental to subordinate satisfaction and individual and work unit performance.[41] The theory identifies four leader behaviors, achievement-oriented, directive, participative, and supportive, that are contingent to the environment factors and follower characteristics. In contrast to the Fiedler contingency model, the path-goal model states that the four leadership behaviors are fluid, and that leaders can adopt any of the four depending on what the situation demands. The path-goal model can be classified both as a contingency theory, as it depends on the circumstances, but also as a transactional leadership theory, as the theory emphasizes the reciprocity behavior between the leader and the followers.
The situational leadership model proposed by Hersey and Blanchard suggests four leadership-styles and four levels of follower-development. For effectiveness, the model posits that the leadership-style must match the appropriate level of followership-development. In this model, leadership behavior becomes a function not only of the characteristics of the leader, but of the characteristics of followers as well.[42]
Functional theory
Functional leadership theory (Hackman & Walton, 1986; McGrath, 1962) is a particularly useful theory for addressing specific leader behaviors expected to contribute to organizational or unit effectiveness. This theory argues that the leader’s main job is to see that whatever is necessary to group needs is taken care of; thus, a leader can be said to have done their job well when they have contributed to group effectiveness and cohesion (Fleishman et al., 1991; Hackman & Wageman, 2005; Hackman & Walton, 1986). While functional leadership theory has most often been applied to team leadership (Zaccaro, Rittman, & Marks, 2001), it has also been effectively applied to broader organizational leadership as well (Zaccaro, 2001). In summarizing literature on functional leadership (see Kozlowski et al. (1996), Zaccaro et al. (2001), Hackman and Walton (1986), Hackman & Wageman (2005), Morgeson (2005)), Klein, Zeigert, Knight, and Xiao (2006) observed five broad functions a leader performs when promoting organisation's effectiveness. These functions include: (1) environmental monitoring, (2) organizing subordinate activities, (3) teaching and coaching subordinates, (4) motivating others, and (5) intervening actively in the group’s work.
A variety of leadership behaviors are expected to facilitate these functions. In initial work identifying leader behavior, Fleishman (1953) observed that subordinates perceived their supervisors’ behavior in terms of two broad categories referred to as consideration and initiating structure. Consideration includes behavior involved in fostering effective relationships. Examples of such behavior would include showing concern for a subordinate or acting in a supportive manner towards others. Initiating structure involves the actions of the leader focused specifically on task accomplishment. This could include role clarification, setting performance standards, and holding subordinates accountable to those standards.
Transactional and transformational theories
Eric Berne[43] first analyzed the relations between a group and its leadership in terms of Transactional Analysis.
The transactional leader (Burns, 1978)[44] is given power to perform certain tasks and reward or punish for the team’s performance. It gives the opportunity to the manager to lead the group and the group agrees to follow his lead to accomplish a predetermined goal in exchange for something else. Power is given to the leader to evaluate, correct and train subordinates when productivity is not up to the desired level and reward effectiveness when expected outcome is reached.
The transformational leader (Burns, 1978)[44] motivates its team to be effective and efficient. Communication is the base for goal achievement focusing the group on the final desired outcome or goal attainment. This leader is highly visible and uses chain of command to get the job done. Transformational leaders focus on the big picture, needing to be surrounded by people who take care of the details. The leader is always looking for ideas that move the organization to reach the company’s vision.
Leadership and emotions
Leadership can be perceived as a particularly emotion-laden process, with emotions entwined with the social influence process[45]. In an organization, the leaders’ mood has some effects on his/her group. These effects can be described in 3 levels[46]:
- The mood of individual group members. Group members with leaders in a positive mood experience more positive mood than do group members with leaders in a negative mood.The leaders transmit their moods to other group members through the mechanism of emotional contagion[46].Mood contagion may be one of the psychological mechanisms by which charismatic leaders influence followers[47].
- The affective tone of the group. Group affective tone represents the consistent or homogeneous affective reactions within a group. Group affective tone is an aggregate of the moods of the individual members of the group and refers to mood at the group level of analysis. Groups with leaders in a positive mood have a more positive affective tone than do groups with leaders in a negative mood [46].
- Group processes like coordination, effort expenditure, and task strategy. Public expressions of mood impact how group members think and act. When people experience and express mood, they send signals to others. Leaders signal their goals, intentions, and attitudes through their expressions of moods. For example, expressions of positive moods by leaders signal that leaders deem progress toward goals to be good.The group members respond to those signals cognitively and behaviorally in ways that are reflected in the group processes [46].
In research about client service, it was found that expressions of positive mood by the leader improve the performance of the group, although in other sectors there were other findings[48].
Beyond the leader’s mood, her/his behavior is a source for employee positive and negative emotions at work. The leader creates situations and events that lead to emotional response. Certain leader behaviors displayed during interactions with their employees are the sources of these affective events. Leaders shape workplace affective events. Examples – feedback giving, allocating tasks, resource distribution. Since employee behavior and productivity are directly affected by their emotional states, it is imperative to consider employee emotional responses to organizational leaders[49]. Emotional intelligence, the ability to understand and manage moods and emotions in the self and others, contributes to effective leadership in organizations[48]. Leadership is about being responsible.
Neo-emergent theory
The Neo-emergent leadership theory (from the Oxford school of leadership) espouses that leadership is created through the emergence of information by the leader or other stakeholders, not through the true actions of the leader himself. In other words, the reproduction of information or stories form the basis of the perception of leadership by the majority. It is well known that the great naval hero Lord Nelson often wrote his own versions of battles he was involved in, so that when he arrived home in England he would receive a true hero's welcome. In modern society, the press, blogs and other sources report their own views of a leader which may be based on reality, but may also be based on a political command, a payment or an inherent interest of the author, media or leader. Therefore, it can be contended that the perception of all leaders is created and in fact does not reflect their true leadership qualities at all.
Environmental leadership theory
The Environmental leadership model (Carmazzi) describes leadership from a Group dynamics perspective incorporating group psychology and self awareness to nurture “Environments” that promote self sustaining group leadership based on personal emotional gratification from the activities of the group. The Environmental Leader creates the psychological structure by which employees can find and attain this gratification through work or activity.
It stems from the idea that each individual has various environments that bring out different facets from their own Identity, and each facet is driven by emotionally charged perceptions within each environment… The Environmental Leader creates a platform through education and awareness where individuals fill each others emotional needs and become more conscious of when, and how they affect personal and team emotional gratifications. This is accomplished by knowing why people “react” to their environment instead of act intelligently.
“Environmental Leadership is not about changing the mindset of the group or individual, but in the cultivation of an environment that brings out the best and inspires the individuals in that group. It is not the ability to influence others to do something they are not committed to, but rather to nurture a culture that motivates and even excites individuals to do what is required for the benefit of all. It is not carrying others to the end result, but setting the surrounding for developing qualities in them to so they may carry each other.” Carmazzi
The role of an Environmental Leader is to instill passion and direction to a group and the dynamics of that group. This leader implements a psychological support system within a group that fills the emotional and developmental needs of the group.
Leadership styles
Leadership style refers to a leader’s behaviour. It is the result of the philosophy, personality and experience of the leader.
Kurt Lewin's Leadership styles
Kurt Lewin and colleagues identified different styles of leadership [50]:
- Dictator
- Autocratic
- Participative
- Laissez-Faire
Autocratic or Authoritarian Leaders
Under the autocratic leadership style, all decision-making powers are centralized in the leader, as with dictator leaders.
They do not entertain any suggestions or initiatives from subordinates. The autocratic management has been successful as it provides strong motivation to the manager. It permits quick decision-making, as only one person decides for the whole group and keeps each decision to themself until they feel it is needed by the rest of the group.
Participative or Democratic Leaders
The democratic leadership style favors decision-making by the group as shown, such as leader gives instruction after consulting the group.
They can win the cooperation of their group and can motivate them effectively and positively. The decisions of the democratic leader are not unilateral as with the autocrat because they arise from consultation with the group members and participation by them.
Laissez-Faire or Free Rein Leaders
The phrase is French and literally means "let do", but, in a leadership context, can be roughly translated as "free rein".
A free rein leader does not lead, but leaves the group entirely to itself as shown; such a leader allows maximum freedom to subordinates, i.e., they are given a free hand in deciding their own policies and methods.
Different situations call for different leadership styles. In an emergency when there is little time to converge on an agreement and where a designated authority has significantly more experience or expertise than the rest of the team, an autocratic leadership style may be most effective; however, in a highly motivated and aligned team with a homogeneous level of expertise, a more democratic or laissez-faire style may be more effective. The style adopted should be that which most effectively achieves the objectives of the group while balancing the interests of its individual members.
Leadership performance
In the past, some researchers have argued that the actual influence of leaders on organizational outcomes is overrated and romanticized as a result of biased attributions about leaders (Meindl & Ehrlich, 1987). Despite these assertions however, it is largely recognized and accepted by practitioners and researchers that leadership is important, and research supports the notion that leaders do contribute to key organizational outcomes (Day & Lord, 1988; Kaiser, Hogan, & Craig, 2008). To facilitate successful performance it is important to understand and accurately measure leadership performance.
Job performance generally refers to behavior that is expected to contribute to organizational success (Campbell, 1990). Campbell identified a number of specific types of performance dimensions; leadership was one of the dimensions that he identified. There is no consistent, overall definition of leadership performance (Yukl, 2006). Many distinct conceptualizations are often lumped together under the umbrella of leadership performance, including outcomes such as leader effectiveness, leader advancement, and leader emergence (Kaiser et al., 2008). For instance, leadership performance may be used to refer to the career success of the individual leader, performance of the group or organization, or even leader emergence. Each of these measures can be considered conceptually distinct. While these aspects may be related, they are different outcomes and their inclusion should depend on the applied/research focus.
Contexts of leadership
Leadership in organizations
An organization that is established as an instrument or means for achieving defined objectives has been referred to as a formal organization. Its design specifies how goals are subdivided and reflected in subdivisions of the organization. Divisions, departments, sections, positions, jobs, and tasks make up this work structure. Thus, the formal organization is expected to behave impersonally in regard to relationships with clients or with its members. According to Weber's definition, entry and subsequent advancement is by merit or seniority. Each employee receives a salary and enjoys a degree of tenure that safeguards her/him from the arbitrary influence of superiors or of powerful clients. The higher his position in the hierarchy, the greater his presumed expertise in adjudicating problems that may arise in the course of the work carried out at lower levels of the organization. It is this bureaucratic structure that forms the basis for the appointment of heads or chiefs of administrative subdivisions in the organization and endows them with the authority attached to their position.[51]
In contrast to the appointed head or chief of an administrative unit, a leader emerges within the context of the informal organization that underlies the formal structure. The informal organization expresses the personal objectives and goals of the individual membership. Their objectives and goals may or may not coincide with those of the formal organization. The informal organization represents an extension of the social structures that generally characterize human life — the spontaneous emergence of groups and organizations as ends in themselves.
In prehistoric times, humanity was preoccupied with personal security, maintenance, protection, and survival. Now humanity spends a major portion of waking hours working for organizations. Her/His need to identify with a community that provides security, protection, maintenance, and a feeling of belonging continues unchanged from prehistoric times. This need is met by the informal organization and its emergent, or unofficial, leaders.[52]
Leaders emerge from within the structure of the informal organization. Their personal qualities, the demands of the situation, or a combination of these and other factors attract followers who accept their leadership within one or several overlay structures. Instead of the authority of position held by an appointed head or chief, the emergent leader wields influence or power. Influence is the ability of a person to gain co-operation from others by means of persuasion or control over rewards. Power is a stronger form of influence because it reflects a person's ability to enforce action through the control of a means of punishment.[52]
A leader is a person who influences a group of people towards a specific result. It is not dependent on title or formal authority. (elevos, paraphrased from Leaders, Bennis, and Leadership Presence, Halpern & Lubar). Leaders are recognized by their capacity for caring for others, clear communication, and a commitment to persist.[53] An individual who is appointed to a managerial position has the right to command and enforce obedience by virtue of the authority of his position. However, she or he must possess adequate personal attributes to match his authority, because authority is only potentially available to him. In the absence of sufficient personal competence, a manager may be confronted by an emergent leader who can challenge her/his role in the organization and reduce it to that of a figurehead. However, only authority of position has the backing of formal sanctions. It follows that whoever wields personal influence and power can legitimize this only by gaining a formal position in the hierarchy, with commensurate authority.[52] Leadership can be defined as one's ability to get others to willingly follow. Every organization needs leaders at every level.[54]
Leadership versus management
Over the years the philosophical terminology of "management" and "leadership" have, in the organisational context, been used both as synonyms and with clearly differentiated meanings. Debate is fairly common about whether the use of these terms should be restricted, and generally reflects an awareness of the distinction made by Burns (1978) between "transactional" leadership (characterised by eg emphasis on procedures, contingent reward, management by exception) and "transformational" leadership (characterised by eg charisma, personal relationships, creativity).[44]
Leadership by a group
In contrast to individual leadership, some organizations have adopted group leadership. In this situation, more than one person provides direction to the group as a whole. Some organizations have taken this approach in hopes of increasing creativity, reducing costs, or downsizing. Others may see the traditional leadership of a boss as costing too much in team performance. In some situations, the maintenance of the boss becomes too expensive - either by draining the resources of the group as a whole, or by impeding the creativity within the team, even unintentionally.[citation needed]
A common example of group leadership involves cross-functional teams. A team of people with diverse skills and from all parts of an organization assembles to lead a project. A team structure can involve sharing power equally on all issues, but more commonly uses rotating leadership. The team member(s) best able to handle any given phase of the project become(s) the temporary leader(s). Additionally, as each team member has the opportunity to experience the elevated level of empowerment, it energizes staff and feeds the cycle of success.[55]
Leaders who demonstrate persistence, tenacity, determination and synergistic communication skills will bring out the same qualities in their groups. Good leaders use their own inner mentors to energize their team and organizations and lead a team to achieve success.[56]
According to the National School Boards Association (USA) [57]
These Group Leadership or Leadership Teams have specific characteristics:
Characteristics of a Team
- There must be an awareness of unity on the part of all its members.
- There must be interpersonal relationship. Members must have a chance to contribute, learn from and work with others.
- The member must have the ability to act together toward a common goal.
Ten characteristics of well-functioning teams:
- Purpose: Members proudly share a sense of why the team exists and are invested in accomplishing its mission and goals.
- Priorities: Members know what needs to be done next, by whom, and by when to achieve team goals.
- Roles: Members know their roles in getting tasks done and when to allow a more skillful member to do a certain task.
- Decisions: Authority and decision-making lines are clearly understood.
- Conflict: Conflict is dealt with openly and is considered important to decision-making and personal growth.
- Personal traits: members feel their unique personalities are appreciated and well utilized.
- Norms: Group norms for working together are set and seen as standards for every one in the groups.
- Effectiveness: Members find team meetings efficient and productive and look forward to this time together.
- Success: Members know clearly when the team has met with success and share in this equally and proudly.
- Training: Opportunities for feedback and updating skills are provided and taken advantage of by team members.
Leadership among primates
Richard Wrangham and Dale Peterson, in Demonic Males: Apes and the Origins of Human Violence present evidence that only humans and chimpanzees, among all the animals living on earth, share a similar tendency for a cluster of behaviors: violence, territoriality, and competition for uniting behind the one chief male of the land.[58] This position is contentious. Many animals beyond apes are territorial, compete, exhibit violence, and have a social structure controlled by a dominant male (lions, wolves, etc.), suggesting Wrangham and Peterson's evidence is not empirical. However, we must examine other species as well, including elephants (which are matriarchal and follow an alpha female), meerkats (who are likewise matriarchal), and many others.
It would be beneficial, to examine that most accounts of leadership over the past few millennia (since the creation of Christian religions) are through the perspective of a patriarchal society, founded on Christian literature. If one looks before these times, it is noticed that Pagan and Earth-based tribes in fact had female leaders. It is important also to note that the peculiarities of one tribe cannot necessarily be ascribed to another, as even our modern-day customs differ. The current day patrilineal custom is only a recent invention in human history and our original method of familial practices were matrilineal (Dr. Christopher Shelley and Bianca Rus, UBC). The fundamental assumption that has been built into 90% of the world's countries is that patriarchy is the 'natural' biological predisposition of homo sapiens. Unfortunately, this belief has led to the widespread oppression of women in all of those countries, but in varying degrees. (Whole Earth Review, Winter, 1995 by Thomas Laird, Michael Victor). The Iroquoian First Nations tribes are an example of a matrilineal tribe, along with Mayan tribes, and also the society of Meghalaya, India. (Laird and Victor, ).
By comparison, bonobos, the second-closest species-relatives of man, do not unite behind the chief male of the land. The bonobos show deference to an alpha or top-ranking female that, with the support of her coalition of other females, can prove as strong as the strongest male in the land. Thus, if leadership amounts to getting the greatest number of followers, then among the bonobos, a female almost always exerts the strongest and most effective leadership. However, not all scientists agree on the allegedly "peaceful" nature of the bonobo or its reputation as a "hippie chimp".[1]
Historical views on leadership
This section needs additional citations for verification. (September 2009) |
Sanskrit literature identifies ten types of leaders. Defining characteristics of the ten types of leaders are explained with examples from history and mythology.[59]
Aristocratic thinkers have postulated that leadership depends on one's blue blood or genes: monarchy takes an extreme view of the same idea, and may prop up its assertions against the claims of mere aristocrats by invoking divine sanction: see the divine right of kings. Contrariwise, more democratically-inclined theorists have pointed to examples of meritocratic leaders, such as the Napoleonic marshals profiting from careers open to talent.
In the autocratic/paternalistic strain of thought, traditionalists recall the role of leadership of the Roman pater familias. Feminist thinking, on the other hand, may object to such models as patriarchal and posit against them emotionally-attuned, responsive, and consensual empathetic guidance, which is sometimes associated with matriarchies.
Comparable to the Roman tradition, the views of Confucianism on "right living" relate very much to the ideal of the (male) scholar-leader and his benevolent rule, buttressed by a tradition of filial piety.
Leadership is a matter of intelligence, trustworthiness, humaneness, courage, and discipline . . . Reliance on intelligence alone results in rebelliousness. Exercise of humaneness alone results in weakness. Fixation on trust results in folly. Dependence on the strength of courage results in violence. Excessive discipline and sternness in command result in cruelty. When one has all five virtues together, each appropriate to its function, then one can be a leader. — Sun Tzu[60]
In the 19th century, the elaboration of anarchist thought called the whole concept of leadership into question. (Note that the Oxford English Dictionary traces the word "leadership" in English only as far back as the 19th century.) One response to this denial of élitism came with Leninism, which demanded an élite group of disciplined cadres to act as the vanguard of a socialist revolution, bringing into existence the dictatorship of the proletariat.
Other historical views of leadership have addressed the seeming contrasts between secular and religious leadership. The doctrines of Caesaro-papism have recurred and had their detractors over several centuries. Christian thinking on leadership has often emphasized stewardship of divinely-provided resources - human and material - and their deployment in accordance with a Divine plan. Compare servant leadership.
For a more general take on leadership in politics, compare the concept of the statesman.
Action Oriented Team Leadership Skills
This is a unique approach to team leadership that is aimed at action oriented environments where effective functional leadership is required to achieve critical or reactive tasks by small teams deployed into the field. In other words leadership of small groups often created to respond to a situation or critical incident.
In most cases these teams are tasked to operate in remote and changeable environments with limited support or backup (action environments). Leadership of people in these environments requires a different set of skills to that of front line management. These leaders must effectively operate remotely and negotiate both the needs of the individual, team and task within a changeable environment. This has been termed Action Oriented Leadership. Some example action oriented leadership is demonstrated in the following ways: extinguishing a rural fire, locating a missing person, leading a team on an outdoor expedition or rescuing a person from a potentially hazardous environment.
Titles emphasizing authority
This section may require copy editing for grammar, style, cohesion, tone, or spelling. (February 2010) |
At certain stages in their development, the hierarchies of social ranks implied different degrees or ranks of leadership in society. Thus a knight led fewer men in general than did a duke; a baronet might in theory control less land than an earl. See peerage for a systematization of this hierarchy, and order of precedence for links to various systems.
In the course of the 18th and 20th centuries, several political operators took non-traditional paths to become dominant in their societies. They or their systems often expressed a belief in strong individual leadership, but existing titles and labels ("King", "Emperor", "President" and so on) often seemed inappropriate, insufficient or downright inaccurate in some circumstances. The formal or informal titles or descriptions they or their flunkies employ express and foster a general veneration for leadership of the inspired and autocratic variety. The definite article when used as part of the title (in languages that use definite articles) emphasizes the existence of a sole "true" leader.
Critical Thought on the concept of leadership
Noam Chomsky[61] and others[62] have brought critical thinking to the very concept of leadership and have provided an analysis which asserts that people abrogate their responsibility to think and will actions for themselves. While the conventional view of leadership is rather satisfying to people who "want to be told what to do", these critics say that one should question why they are being subjected to a will or intellect other than their own if the leader is not a Subject Matter Expert (SME).
The fundamentally anti-democratic nature of the leadership principle is challenged by the introduction of concepts such as autogestion, employeeship, common civic virtue, etc., which stress individual responsibility and/or group authority in the work place and elsewhere by focusing on the skills and attitudes that a person needs in general rather than separating out leadership as the basis of a special class of individuals.
Similarly various historical calamities are attributed to a misplaced reliance on the principle of leadership.
See also
|
|
|
|
References
- Notes
- ^ Chemers, M. M. (2002). Meta-cognitive, social, and emotional intelligence of transformational leadership: Efficacy and Effectiveness. In R. E. Riggio, S. E. Murphy, F. J. Pirozzolo (Eds.), Multiple Intelligences and Leadership.
- ^ Kouzes, J., and Posner, B. (2007). The Leadership Challenge. CA: Jossey Bass.
- ^ Slack: Getting Past Burnout, Busywork, and the Myth of Total Efficiency
- ^ Locke et al. 1991
- ^ (Richards & Engle, 1986, p.206)
- ^ a b c Zaccaro, S. J. (2007). Trait-based perspectives of leadership. American Psychologist, 62, 6-16.
- ^ Bass, B.M. & Bass, R. (2008). The Bass handbook of leadership: Theory, research, and managerial applications (4th ed.). New York: Free Press.
- ^ Bird, C. (1940). Social Psychology. New York: Appleton-Century.
- ^ Stogdill, R.M. (1948). Personal factors associated with leadership: A survey of the literature. Journal of Psychology, 25, 35-71.
- ^ Mann, R.D. (1959). A review of the relationship between personality and performance in small groups. Psychological Bulletin, 56, 241-270.
- ^ a b Kenny, D.A. & Zaccaro, S.J. (1983). An estimate of variance due to traits in leadership. Journal of Applied Psychology, 68, 678-685.
- ^ a b c Lord, R.G., De Vader, C.L., & Alliger, G.M. (1986). A meta-analysis of the relation between personality traits and leader perceptions: An application of validity generalization procedures. Journal of Applied Psychology, 71, 402-410.
- ^ Arvey, R.D., Rotundo, M., Johnson, W., Zhang, Z., & McGue, M. (2006). The determinants of leadership role occupancy: Genetic and personality factors. The Leadership Quarterly, 17, 1-20.
- ^ a b Judge, T.A., Bono, J.E., Ilies, R., & Gerhardt, M.W. (2002). Personality and leadership: A qualitative and quantitative review. Journal of Applied Psychology, 87, 765-780.
- ^ Tagger, S., Hackett, R., Saha, S. (1999). Leadership emergence in autonomous work teams: Antecedents and outcomes. Personnel Psychology, 52, 899-926.
- ^ Kickul, J., & Neuman, G. (2000). Emergence leadership behaviors: The function of personality and cognitive ability in determining teamwork performance and KSAs. Journal of Business and Psychology, 15, 27-51.
- ^ Smith, J.A., & Foti, R.J. (1998). A pattern approach to the study of leader emergence. The Leadership Quarterly, 9, 147-160.
- ^ Foti, R.J., & Hauenstein, N.M.A. (2007). Pattern and variable approaches in leadership emergence and effectiveness. Journal of Applied Psychology, 92, 347-355.
- ^ Zaccaro, S. J., Gulick, L.M.V. & Khare, V.P. (2008). Personality and leadership. In C. J. Hoyt, G. R. Goethals & D. R. Forsyth (Eds.), Leadership at the crossroads (Vol 1) (pp. 13-29). Westport, CT: Praeger.
- ^ Foti, R. J., & Hauenstein, N. M. A. (2007). Pattern and variable approaches in leadership emergence and effectiveness. Journal of Applied Psychology, 92, 347-355.
- ^ Gershenoff, A. G., & Foti, R. J. (2003). Leader emergence and gender roles in all-female groups: A contextual examination. Small Group Research, 34, 170-196.
- ^ a b Mumford, M. D., Zaccaro, S. J., Harding, F. D., Jacobs, T. O., & Fleishman, E. A. (2000). Leadership skills for a changing world solving complex social problems. The Leadership Quarterly, 11, 11-35.
- ^ Smith, J.A., & Foti R.J. (1998). A pattern approach to the study of leader emergence, Leadership Quarterly, 9, 147-160.
- ^ Magnusson, D. (1995). Holistic interactionism: A perspective for research on personality development. In L. A. Pervin & O. P. John (Eds.), Handbook of personality: Theory and research (pp. 219-247). New York: Guilford Press.
- ^ Spillane (2004)
- ^ Horton, Thomas. New York The CEO Paradox (1992
- ^ a b Lewin et al. (1939)
- ^ Miner (2005) pp. 39-40
- ^ Blake et al. (1964)
- ^ Miltenberger, R.G., (2004). Behavior Modification Principles and Procedures (3rd ed). Belmont, CA: Wadsworth/Thomson Learning.
- ^ Lussier, R.N., & Achua, C.F., (2010). Leadership, Theory, Application, & Skill Development.(4th ed). Mason, OH: South-Western Cengage Learning.
- ^ Spencer (1884), apud Heifetz (1994), pp. 16
- ^ Hemphill (1949)
- ^ Wormer et al. (2007), pp: 198
- ^ Fiedler (1967)
- ^ Vroom, Yetton (1973)
- ^ Vroom, Jago (1988)
- ^ Sternberg, Vroom (2002)
- ^ Lorsch (1974)
- ^ House (1971)
- ^ House (1996)
- ^ Hersey et al. (2008)
- ^ The Structure and Dynamics of Organizations and Groups, Eric Berne, ISBN 0-345-28473-9
- ^ a b c Burns, J. M. (1978). Leadership. New York: Harper and Row Publishers Inc.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ George J.M. 2000. Emotions and leadership: The role of emotional intelligence, Human Relations 53 (2000), pp. 1027–1055
- ^ a b c d Sy, T.; Cote, S.; Saavedra, R. (2005). "The contagious leader: Impact of the leader's mood on the mood of group members, group affective tone, and group processes" (PDF). Journal of Applied Psychology. 90 (2): 295–305.
- ^ Bono J.E. & Ilies R. 2006 Charisma, positive emotions and mood contagion. The Leadership Quarterly 17(4): pp. 317-334
- ^ a b George J.M. 2006. Leader Positive Mood and Group Performance: The Case of Customer Service. Journal of Applied Social Psychology :25(9) pp. 778 - 794
- ^ Dasborough M.T. 2006.Cognitive asymmetry in employee emotional reactions to leadership behaviors. The Leadership Quarterly 17(2):pp. 163-178
- ^ Lewin, K.; Lippitt, R.; White, R.K. (1939). "Patterns of aggressive behavior in experimentally created social climates". Journal of Social Psychology. 10: 271–301.
- ^ Cecil A Gibb (1970). Leadership (Handbook of Social Psychology). Reading, Mass.: Addison-Wesley. pp. 884–89. ISBN 0140805176 9780140805178. OCLC 174777513.
{{cite book}}: Check|isbn=value: length (help) - ^ a b c Henry P. Knowles; Borje O. Saxberg (1971). Personality and Leadership Behavior. Reading, Mass.: Addison-Wesley. pp. 884–89. ISBN 0140805176 9780140805178. OCLC 118832.
{{cite book}}: Check|isbn=value: length (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Hoyle, John R. Leadership and Futuring: Making Visions Happen. Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin Press, Inc., 1995.
- ^ The Top 10 Leadership Qualities - HR World
- ^ Ingrid Bens (2006). Facilitating to Lead. Jossey-Bass.
- ^ Dr. Bart Barthelemy (1997). The Sky Is Not The Limit - Breakthrough Leadership. St. Lucie Press.
- ^ National School Boards Association
- ^ Richard Wrangham and Dale Peterson (1996). Demonic Males. Apes and the Origins of Human Violence. Mariner Books
- ^ KSEEB. Sanskrit Text Book -9th Grade. Governament of Karnataka, India.
- ^ THE 100 GREATEST LEADERSHIP PRINCIPLES OF ALL TIME, EDITED BY LESLIE POCKELL WITH ADRIENNE AVILA, 2007, Warner Books
- ^ Profit over People: neoliberalism and global order, N. Chomsky, 1999 Ch. Consent without Consent, p. 53
- ^ The Relationship between Servant Leadership, Follower Trust, Team Commitment and Unit Effectiveness, Zani Dannhauser, Doctoral Thesis, Stellenbosch University 2007
- Books
- Blake, R.; Mouton, J. (1964). The Managerial Grid: The Key to Leadership Excellence. Houston: Gulf Publishing Co.
- Carlyle, Thomas (1841). On Heroes, Hero-Worship, and the Heroic History. Boston, MA: Houghton Mifflin.
- Fiedler, Fred E. (1967). A theory of leadership effectiveness. McGraw-Hill: Harper and Row Publishers Inc.
- Heifetz, Ronald (1994). Leadership without Easy Answers. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press. ISBN 0-674-51858-6.
- Hemphill, John K. (1949). Situational Factors in Leadership. Columbus: Ohio State University Bureau of Educational Research.
- Hersey, Paul; Blanchard, Ken; Johnson, D. (2008). Management of Organizational Behavior: Leading Human Resources (9th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education.
- Miner, J. B. (2005). Organizational Behavior: Behavior 1: Essential Theories of Motivation and Leadership. Armonk: M.E. Sharpe.
- Spencer, Herbert (1841). The Study of Sociology. New York: D. A. Appleton.
- Tittemore, James A. (2003). Leadership at all Levels. Canada: Boskwa Publishing. ISBN 0973291400.
- Vroom, Victor H.; Yetton, Phillip W. (1973). Leadership and Decision-Making. Pittsburgh: University of Pittsburgh Press.
- Vroom, Victor H.; Jago, Arthur G. (1988). The New Leadership: Managing Participation in Organizations. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall.
- Van Wormer, Katherine S.; Besthorn, Fred H.; Keefe, Thomas (2007). Human Behavior and the Social Environment: Macro Level: Groups, Communities, and Organizations. US: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0195187547.
- Journal articles
- House, Robert J. (1971). "A path-goal theory of leader effectiveness". Administrative Science Quarterly. 16: 321–339. doi:10.2307/2391905.
- House, Robert J. (1996). "Path-goal theory of leadership: Lessons, legacy, and a reformulated theory". Leadership Quarterly. 7 (3): 323–352. doi:10.1016/S1048-9843(96)90024-7.
- Lewin, Kurt; Lippitt, Ronald; White, Ralph (1939). "Patterns of aggressive behavior in experimentally created social climates". Journal of Social Psychology: 271–301.
- Kirkpatrick, S.A., (1991). "Leadership: Do traits matter?". Academy of Management Executive. 5 (2).
{{cite journal}}:|first1=missing|last1=(help)CS1 maint: extra punctuation (link) CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Lorsch, Jay W. (Spring 1974). "Review of Leadership and Decision Making". Sloan Management Review.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: year (link) - Spillane, James P.; et al. (2004). "Towards a theory of leadership practice". Journal of Curriculum Studies. 36 (1): 3–34.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|last2=(help) - Vroom, Victor; Sternberg, Robert J. (2002). "Theoretical Letters: The person versus the situation in leadership". The Leadership Quarterly. 13: 301–323.
Further Reading
- Argyris, C. (1976) Increasing Leadership Effectiveness, Wiley, New York, 1976 (even though published in 1976, this still remains a "standard" reference text)
- Avolio, B. J., Sosik, J. J., Jung, D. I., & Berson, Y. (2003). Leadership models, methods, and applications. In W. C. Borman, D. R. Ilgen & R. J. *Klimoski (Eds.), Handbook of psychology: Industrial and organizational psychology, Vol. 12. (pp. 277-307): John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
- Avolio, B. J., Walumbwa, F., & Weber, T. J. (in press). Leadership: Current theories, research, and future directions. Annual Review of Psychology.
- Bass, B.M. & Avolio, B.J. (1995). MLQ Multifactor Leadership Questionnaire for Research: Permission Set. Redwood City, CA: Mindgarden.
- Bass, B. M. (1990). Bass & Stogdill's handbook of leadership: Theory, research, and managerial applications (3rd ed.). New York, NY, US: Free Press.
- Bennis, W. (1989) On Becoming a Leader, Addison Wesley, New York, 1989
- Borman, W. C., & Brush, D. H. (1993). More progress toward a taxonomy of managerial performance requirements. Human Performance, 6(1), 1-21.
- Bray, D. W., Campbell, R. J., & Grant, D. L. (1974). Formative years in business: a long-term AT&T study of managerial lives: Wiley, New York.
- Campbell, J. (1990). An overview of the Army selection and classification project. Personnel Psychology, 43, 231-240.
- Campbell, J., McCloy, R., Oppler, S., & Sager, C. (1993). A theory of performance. In N. Schmitt & W. Borman (Eds.), Personnel Selection in organizations (pp. 35-71). San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
- Crawford, C. J. (2005). Corporate rise the X principles of extreme personal leadership. Santa Clara, CA: XCEO. ISBN 0-976-90190-0 9780976901907
- Day, D. V., & Lord, R. G. (1988). Executive leadership and organizational performance: suggestions for a new theory and methodology. Journal of Management, 14(3), 453-464.
- Den Hartog, D. N., & Koopman, P. L. (2002). Leadership in organizations. In N. Anderson, D. S. Ones, H. K. Sinangil & C. Viswesvaran (Eds.), Handbook of industrial, work and organizational psychology, Volume 2: Organizational psychology. (pp. 166-187): Sage Publications, Inc.
- Fleishman, E. A. (1953). The description of supervisory behavior. Journal of Applied Psychology, 37(1), 1-6.
- Fleishman, E. A., Mumford, M. D., Zaccaro, S. J., Levin, K. Y., Korotkin, A. L., & Hein, M. B. (1991). Taxonomic efforts in the description of leader behavior: A synthesis and functional interpretation. Leadership Quarterly, 2(4), 245-287.
- Greiner, K. (2002). The inaugural speech. ERIC Accession Number ED468083 [2].
- Hackman, J. R., & Wageman, R. (2005). A Theory of Team Coaching. Academy of Management Review, 30(2), 269-287.
- Hackman, J. R., & Walton, R. E. (1986). Leading groups in organizations. In P. S. Goodman (Ed.), Designing effective work groups (pp. 72-119). San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
- Hogan, R., Curphy, C. J., & Hogan, J. (1994). What we know about leadership: effectiveness and personality. American Psychologist, 49(6), 493-504.
- House, R. J. (2004) Culture, Leadership, and Organizations: The GLOBE Study of 62 Societies, SAGE Publications, Thousand Oaks, 2004 [3].
- Howard, A., & Bray, D. W. (1988). Managerial lives in transition: advancing age and changing times: New York: Guilford Press.
- Jacobs, T. O., & Jaques, E. (1987). Leadership in Complex Systems In Praeger (Ed.), Human Productivity Enhancement (Vol. 2, pp. 7-65). New York.
- Jacobs, T. O., & Jaques, E. (1990). Military executive leadership. Measures of leadership, 281-295.
- Judge, T. A., Bono, J. E., Ilies, R., & Gerhardt, M. W. (2002). Personality and leadership: A qualitative and quantitative review. Journal of Applied Psychology, 87(4), 765-780.
- Kaiser, R. B., Hogan, R., & Craig, S. B. (2008). Leadership and the Fate of Organizations. American Psychologist, 63(2), 96.
- Klein, K. J., Ziegert, J. C., Knight, A. P., & Xiao, Y. (2006). Dynamic delegation: Shared, hierarchical, and deindividualized leadership in extreme action teams. Administrative Science Quarterly, 51(4), 590-621.
- Kouzes, J. M. and Posner, B. Z. (2002). The leadership challenge. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
- Kozlowski, S. W. J., Gully, S. M., Salas, E., Cannon-Bowers, J. A., Beyerlein, M. M., Johnson, D. A., et al. (1996). Team leadership and development: *Theory, principles, and guidelines for training leaders and teams. In Advances in interdisciplinary studies of work teams: Team leadership, Vol. 3. (pp. 253-291): Elsevier Science/JAI Press.
- Laubach, R. (2005) Leadership is Influence
- Lord, R. G., De Vader, C. L., & Alliger, G. M. (1986). A meta-analysis of the relation between personality traits and leadership perceptions: An application of validity generlization procedures. Journal of Applied Psychology, 71(3), 402-410.
- Machiavelli, Niccolo (1530) The Prince
- Maxwell, J. C. & Dornan, J. (2003) Becoming a Person of Influence
- McGovern, George S., Donald C. Simmons, Jr. and Daniel Gaken (2008) Leadership and Service: An Introduction, Kendall/Hunt Publishing. ISBN 978-0-7575-5109-3.
- McGrath, J. E. (1962). Leadership behavior: Some requirements for leadership training. Washington, D.C.: U.S. Civil Service Commission.
- Meindl, J. R., & Ehrlich, S. B. (1987). The romance of leadership and the evaluation of organizational performance. Academy of Management Journal, 30(1), 91-109.
- Morgeson, F. P. (2005). The External Leadership of Self-Managing Teams: Intervening in the Context of Novel and Disruptive Events. Journal of Applied Psychology, 90(3), 497-508.
- Motowidlo, S. J. (2003). Job performance. Borman, Walter C (Ed); Ilgen, Daniel R (Ed); et al, (2003). Handbook of psychology: Industrial and organizational psychology, NY, US: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
- Mumford, M. D. (1986). Leadership in the organizational context: Conceptual approach and its application. Journal of Applied Social Psychology, 16(6), 508-531.
- Mumford, M. D., Zaccaro, S. J., Harding, F. D., Jacobs, T. O., & Fleishman, E. A. (2000). Leadership skills for a changing world solving complex social problems. The Leadership Quarterly, 11(1), 11-35.
- Nanus, Burt (1995) The visionary leadership
- Ogbonnia, SKC. (2007). Political Parties and Effective Leadership: A contingency Approach
- Pitcher, P. (1994 French) Artists, Craftsmen, and Technocrats: The dreams realities and illusions of leadership, Stoddart Publishing, Toronto, 2nd English edition, 1997. ISBN 0-7737-5854-2
- Renesch, John (1994) Leadership in a New Era: Visionary Approaches to the Biggest Crisis of Our Time, San Francisco, New Leaders Press (paperback 2002, New York, Paraview Publishing
- Renesch, John (2001) "Conscious Leadership: Taking Responsibility for Our Better Future," LOHAS Weekly Newsletter, March 1, 2001 [4]
- Roberts, W. (1987) Leadership Secrets of Attila the Hun
- Stacey, R. (1992) Managing Chaos, Kogan-Page, London, 1992
- Stogdill, R. M. (1974). Handbook of leadership: A survey of the literature. New York: Free Press
- Stogdill, R.M. (1950) 'Leadership, membership and organization', Psychological Bulletin, 47: 1-14
- Terry, G. (1960) The Principles of Management, Richard Irwin Inc, Homewood Ill, pg 5.
- Torbert, W. (2004) Action Inquiry: the Secret of Timely and Transforming Leadership, San Francisco, CA: Berrett-Koehler Publishers.
- Warneka, P and Warneka, T. (2007). The Way of Leading People: Unlocking Your Integral Leadership Skills with the Tao Te Ching. Asogomi Publications Intl. Cleveland, Ohio. website
- Warneka, T. (2006). Leading People the Black Belt Way: Conquering the Five Core Problems Facing Leaders Today. Asogomi Publications Intl. Cleveland, Ohio. website
- Warneka, T. (2008). Black Belt Leader, Peaceful Leader: An Introduction to Catholic Servant Leadership. website
- Yukl, G. A. (2006). Leadership in Organizations. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice-Hall.
- Zaccaro, S. J. (2001). The nature of executive leadership: A conceptual and empirical analysis of success. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
- Zaccaro, S. J., & Klimoski, R. J. (2001). The nature of organizational leadership: An introduction. In S. J. Zaccaro & R. J. Klimoski (Eds.), The nature of organizational leadership: Understanding the performance imperatives confronting today’s leaders (pp. 3-41). San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass.
- Zaccaro, S. J., Rittman, A. L., & Marks, M. A. (2001). Team leadership. Leadership Quarterly, 12(4), 451-483.
- Zaccaro, S. J. (2007). Trait-based perspective. American Psychology , 62 (1), 7-16.
- Zaleznik, A. (1977) "Managers and Leaders: Is there a difference?", Harvard Business Review, May-June, 1977
External links
- Articles needing cleanup from February 2010
- Cleanup tagged articles without a reason field from February 2010
- Wikipedia pages needing cleanup from February 2010
- Wikipedia articles needing copy edit from February 2010
- Emergency laws
- Strategic management
- Management
- Business theory
- Organizational studies and human resource management
- Political philosophy
- Political science terms
- Positions of authority
- Positive psychology
- Social psychology
- Sociology
- Leadership
