Flanders: Difference between revisions
| Line 286: | Line 286: | ||
The standard language in Flanders is [[Dutch language|Dutch]]; a single authority, the [[Nederlandse Taalunie]], comprising appointees of the Belgian and Netherlands governments, sets standards for spelling and grammar. The term [[Flemish]] can be applied to the Dutch spoken in Flanders; it shows many regional and local variants. |
The standard language in Flanders is [[Dutch language|Dutch]]; a single authority, the [[Nederlandse Taalunie]], comprising appointees of the Belgian and Netherlands governments, sets standards for spelling and grammar. The term [[Flemish]] can be applied to the Dutch spoken in Flanders; it shows many regional and local variants. |
||
At first sight, ''Flemish culture'' is defined by its [[language]] and its gourmandic mentality, as compared to the more Calvinistic Dutch culture. |
At first sight, ''Flemish culture'' is defined by its [[language]] and its gourmandic mentality, as compared to the more Calvinistic Dutch culture. Although Flanders has never existed as an independent country, a tradition of [[Flemish Literature|Flemish literature]] has existed for centuries; with writers and poets such as [[Guido Gezelle]], who not only explicitly referred to his writings as Flemish, but actually used it in many of his poems, and strongly defended it: |
||
{{col-begin}}{{col-2}} |
{{col-begin}}{{col-2}} |
||
'''Original'''<br> |
'''Original'''<br> |
||
Revision as of 05:57, 8 December 2009
Flanders (Dutch: , French: Flandre) is the (political) community of the Flemings but also one of the institutions in Belgium, and a geographical region located in parts of present-day Belgium, France, and the Netherlands. Over the course of history, the geographical territory that was called "Flanders" has varied.
In contemporary Belgium, Flanders might be understood as the 'country of the Flemings'. This covers the north of Belgium Flemish Region and includes the Brussels Capital Region, the latter being shared with French speakers.
For the last few decades, with the legal establishment of the Flemish Community (Dutch: de Vlaamse Gemeenschap), the Flemings have their own political institutions. The parliament and government are the governing institutions of Flanders. There is also a geographical, political and administrative entity called the Flemish Region (Dutch: het Vlaams Gewest) but it has ceded all its competencies to the Flemish Community. Thus, the institutions of the Community govern both the Community and the Region. The capital city of Flanders is Brussels.
Previously, Flanders formed a county, the County of Flanders, which extended over:
- The Belgian provinces of West Flanders and East Flanders
- The French region French Flanders in the department Nord-Pas de Calais
- The Dutch region Zeelandic Flanders (Zeeuws-Vlaanderen) in the province of Zeeland
Related to these geographical or political uses of the noun 'Flanders', and the adjective 'Flemish', they may also be used to describe several other distinct (but inter-connected) cultural, geographical, historical, linguistic or political items or entities.
The term "Flanders"
In Belgium
The term "Flanders" has several main meanings:
- the social, cultural and linguistic, scientific and educational, economical and political community of the Flemings; generally called the "Flemish community" (small "c") (others refer to this as the "Flemish nation"). It has over 6 million inhabitants, or about 60% of the population of Belgium.
- the constituent governing institution of the federal Belgian state through the institutions named the Flemish Community (capital "C"), exercising the powers in most of those domains for the aforementioned community, and the officially Dutch-speaking Flemish Region which has powers mainly on economical matters. The Community absorbed the Region, leading to a single operative body: the Flemish government and a single legislative organ: the Flemish parliament;
- the geographical region in the north of Belgium coinciding with the federal Belgian state's Flemish Region but excluding the bilingual Capital Region;
- the geographical area comprising the two westernmost provinces of the Flemish Region, West Flanders and East Flanders, parts of a former county named Flanders.
In France
In the Netherlands
Evolution of the term
Vlaanderen literally means Flooded Land[citation needed] or Lowland. The name appeared first around the 8th century. The precise geographical area denominated by "Flanders" has evolved a great deal over the centuries.
In the Middle Ages, the term Flanders was applied to an area in western Europe, the County of Flanders, spread over:
- Belgium:
- the area that is now approximately the Flemish provinces of East Flanders and West Flanders
- the French-speaking area to the west of the Scheldt river, called Tournaisis (from the town of Tournai in the province of Hainaut)
- France (French Flanders):
- in the French language: La Flandre Lilloise comprising the arrondissements of Lille and Douai, in the north of France, to which country it was ceded in the 14th century. Because French was spoken there, the area was also called la Flandre romane (Romance Flanders) or la Flandre gallicante (Gallic Flanders), or incorrectly Flandre-wallonne (Walloon Flanders) though its language was not Walloon but Picard. The city of Lille manifests itself as "Flemish", for instance by the large TGV station Lille-Flandres.
- the originally Dutch-speaking remainder of what is now the département Nord (Nord-Pas de Calais), called Westhoek or Maritime Flanders, ceded to France in the 17th and early 18th century, during most of which latter century the area was the province of Flanders and that of Artois.
- The Netherlands:
- a part of what is now Zeeland in south-western Netherlands, called Zeelandic Flanders (Zeeuws-Vlaanderen)
The significance of the County and its counts eroded through time, but the designation remained in a very broad sense. In the Early Modern, the term Flanders was associated with the southern part of the Low Countries, the Southern Netherlands. During the 19th and 20th centuries, it became increasingly commonplace to refer to the area from De Panne to Maasmechelen, including the Belgian parts of the Duchy of Brabant and Limburg, as "Flanders".
The ambiguity between this eastwardly much wider area and that of the Countship (or the Belgian parts thereof), still remains. In most present-day contexts however, the term Flanders is generally taken to refer to either the political, social, cultural and linguistic community (and the corresponding official institution, the Flemish Community), or the geographical area, one of the three institutional regions in Belgium, namely the Flemish Region.
In history of art and other fields, the adjectives Flemish and Netherlandish are commonly used to designate all the artistic production in this area before about 1580, after which it refers specifically to the southern Netherlands. For example the term Flemish Primitives, now outdated in English but used in French, Flemish and other languages, is a synonym for Early Netherlandish painting, and it is not uncommon to see Mosan art categorized as Flemish art. In music the Franco-Flemish School is also known as the Dutch School
History
Early history
The area roughly encompassing the later geographical meanings of Flanders, had been inhabited by Celts until Germanic people began immigrating by crossing the Rhine, either gradually driving them south- or westwards, or rather merging with them. By the first century BC Germanic languages had become prevalent, and the inhabitants were called Belgæ while the area was the coastal district of Gallia Belgica, the most northeastern province of the Roman Empire at its height. The boundaries were the Marne and Seine in the West, with Armorica (Brittany), and the Rhine in the East, with Frisia. This changed upon the Count of Rouen's settlement with the King of France, which made a cession of western Flanders and eastern Armorica to the Normans.
Historical Flanders: County of Flanders
Created in the year 862 as a feudal fief in West Francia, the County of Flanders was divided when its western districts fell under French rule in the late 12th century. The remaining parts of Flanders came under the rule of the counts of neighbouring Hainaut in 1191. The entire area passed in 1384 to the dukes of Burgundy, in 1477 to the Habsburg dynasty, and in 1556 to the kings of Spain. The western districts of Flanders came finally under French rule under successive treaties of 1659 (Artois), 1668, and 1678.
During the late Middle Ages Flanders' trading towns (notably Ghent, Bruges and Ypres) made it one of the richest and most urbanised parts of Europe, weaving the wool of neighbouring lands into cloth for both domestic use and export. As a consequence, a very sophisticated culture developed, with impressive achievements in the arts and architecture, rivalling those of Northern Italy.
Increasingly powerful from the 12th century, the territory's autonomous urban communes were instrumental in defeating a French attempt at annexation (1300–1302), finally defeating the French in the Battle of the Golden Spurs (July 11, 1302), near Kortrijk. Two years later, the uprising was defeated and Flanders remained part of the French Crown. Flemish prosperity waned in the following century, however, owing to widespread European population decline following the Black Death of 1348, the disruption of trade during the Anglo-French Hundred Years' War (1338–1453), and increased English cloth production. Flemish weavers had gone over to Worstead and North Walsham in Norfolk in the 12th century and established the woollen industry.
Flanders in the Low Countries
The Reformation
Martin Luther's 95 Theses, published in 1517, had a profound effect on the Low Countries. Among the wealthy traders of Antwerp, the Lutheran beliefs of the German Hanseatic traders found appeal, perhaps partly for economic reasons in Dutch. The spread of Protestantism in this city was aided by the presence of an Augustinian cloister (founded 1514) in the St. Andries quarter. Luther, an Augustinian himself, had taught some of the monks, and his works were in print by 1518. Charles V ordered the closing of this cloister around 1525. The first Lutheran martyrs came from Antwerp. The Reformation resulted in consecutive but overlapping waves of reform: a Lutheran, followed by a militant Anabaptist, then a Mennonite, and finally a Calvinistic movement. These movements existed independently of each other.
The Pragmatic Sanction of 1549, issued by Charles V, established the Low Countries as the Seventeen Provinces (or Spanish Netherlands in its broad sense) as an entity separate from the Holy Roman Empire and from France. The schism between the southern Roman Catholics and northern Calvinists resulted in the Union of Atrecht and the Union of Utrecht, respectively.
Beeldenstorm

One hallmark of the Reformation was the belief that excessive commemoration of the saints and their images had become idolatry. Efforts to end it led to the iconoclasm of 1566 (the Beeldenstorm) – the demolition of statues and paintings depicting saints. This was associated with the ensuing religious war between Catholics and Protestants, especially the Anabaptists. The Beeldenstorm started in what is now the arrondissement of Dunkirk in French Flanders, with open-air sermons (Dutch: hagepreken) . The first took place on the Cloostervelt near Hondschoote. The first large sermon was held near Boeschepe on July 12, 1562. These open-air sermons, mostly of Anabaptist or Mennonite signature, spread through the country. On August 10, 1566 at the end of the pilgrimage from Hondschoote to Steenvoorde, the chapel of the Sint-Laurensklooster (Monastery of Saint Lawrence) was defaced by Protestants. The iconoclasm resulted not only in the destruction of Catholic art, but also cost the lives of many priests. It next spread to Antwerp, and on August 22, to Ghent. One cathedral, eight churches, twenty-five cloisters, ten hospitals and seven chapels were attacked. From there, it further spread east and north, but in total lasted not even a month.
Charles' son, King Philip II of Spain, a devout Catholic and self-proclaimed protector of the Counter-Reformation who was also the duke, count or lord of each of the Seventeen Provinces, suppressed Calvinism in Flanders, Brabant and Holland. What is now approximately Belgian Limburg was part of the Bishopric of Liège and was Catholic de facto. Part of what is now Dutch Limburg supported the Union of Atrecht, but did not sign it.
The Eighty Years' War and its consequences
In 1568 the Seventeen Provinces that signed the Union of Utrecht started a revolt against Philip II: the Eighty Years' War. Spanish troops quickly started fighting the rebels, but before the revolt could be completely defeated, a war between England and Spain had broken out, forcing Philip's Spanish troops to halt their advance. Meanwhile, the Spanish armies had already conquered the important trading cities of Bruges and Ghent. Antwerp, which was then arguably the most important port in the world, also had to be conquered. On August 17, 1585, Antwerp fell. This ended the Eighty Years' War for the (from now on) Southern Netherlands. The United Provinces (the Netherlands proper) fought on until 1648 – the Peace of Westphalia.
While Spain was at war with England, the rebels from the north, strengthened by refugees from the south, started a campaign to reclaim areas lost to Philips II's Spanish troops. They managed to conquer a considerable part of Brabant (the later Noord-Brabant of the Netherlands), and the south bank of the Scheldt estuary (Zeeuws-Vlaanderen), before being stopped by Spanish troops. The front line at the end of this war stabilized and became the current border between present-day Belgium and the Netherlands. The Dutch (as they later became known) had managed to reclaim enough of Spanish-controlled Flanders to close off the river Scheldt, effectively cutting Antwerp off from its trade routes.
First the fall of Antwerp to the Spanish and later also the closing of the Scheldt were causes of a considerable emigration of Antverpians.[2] Many of the Calvinist merchants of Antwerp and also of other Flemish cities left Flanders and emigrated to the north. A large number of them settled in Amsterdam, which was at the time a smaller port, only of significance in the Baltic trade. In the following years Amsterdam was rapidly transformed into one of the world's most important ports. Because of the contribution of the Flemish exiles to this transformation, the exodus is sometimes described as "creating a new Antwerp".
Flanders and Brabant, due to these events, went into a period of relative decline from the time of the Thirty Years War.[3] In the Northern Netherlands however, the mass emigration from Flanders and Brabant became an important driving force behind the Dutch Golden Age.
1581–1795: The Southern Netherlands

Although arts remained at a relatively impressive level for another century with Peter Paul Rubens (1577–1640) and Anthony van Dyck, Flanders experienced a loss of its former economic and intellectual power under Spanish, Austrian, and French rule, with heavy taxation and rigid imperial political control compounding the effects of industrial stagnation and Spanish-Dutch and Franco-Austrian conflict.
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (June 2008) |
1795–1815: French Revolution and Napoleonic France
In 1794 the French Republican Army started using Antwerp as the northernmost naval port of France,[3] which country officially annexed Flanders the following year as the départements of Lys, Escaut, Deux-Nèthes, Meuse-Inférieure and Dyle. Obligatory (French) army service for all men aged 16–25 was one of the main reasons for the people's uprising against the French in 1798, known as the Boerenkrijg (Peasants' War), with the heaviest fighting in the Campine area.
1815–1830: United Kingdom of the Netherlands
After the defeat of Napoleon Bonaparte at the 1815 Battle of Waterloo in Waterloo, Brabant, sovereignty over the Austrian Netherlands – Belgium minus the East Cantons and Luxembourg – was given by the Congress of Vienna (1815) to the United Netherlands (Dutch: Verenigde Nederlanden), the state that briefly existed under Sovereign Prince William I of Orange Nassau, the latter King William I of the United Kingdom of the Netherlands, after the French Empire was driven out of the Dutch territories. The United Kingdom of the Netherlands was born. The Protestant King of the Netherlands, William I rapidly started the industrialisation of the southern parts of the Kingdom. The political system that was set up however, slowly but surely failed to forge a true union between the northern and the southern parts of the Kingdom. The southern bourgeoisie mainly was Roman Catholic, in contrast to the mainly Protestant north; large parts of the southern bourgeoisie also primarily spoke French rather than Dutch.
In 1815 the Dutch Senate was reinstated (Dutch: Eerste Kamer der Staaten Generaal). The nobility, mainly coming from the south, became more and more estranged from their northern colleagues. Resentment grew both among the Roman Catholics from the south and the Protestants from the north and among the powerful liberal bourgeoisie from the south and their more moderate colleagues from the north. On August 25, 1830 (after the showing of the opera 'La Muette de Portici' of Daniel Auber in Brussels) the Belgian Revolution sparked off and became a fact. On October 4, 1830, the Provisional Authority (Dutch: Voorlopig Bewind) proclaimed the independence which was later confirmed by the National Congress that issued a new Liberal Constitution and declared the new state a Constitutional Monarchy, under the House of Saxe-Coburg. Flanders now became part of the Kingdom of Belgium, which was recognized by the major European Powers on January 20, 1831. The de facto dissidence was only finally recognized by the United Kingdom of the Netherlands on April 19, 1839.
Kingdom of Belgium
In 1830, the Belgian Revolution led to the splitting up of the two countries. Belgium was confirmed as an independent state by the Treaty of London of 1839, but deprived of the eastern half of Limburg (now Dutch Limburg), and the Eastern half of Luxembourg (now the Grand-Duchy of Luxembourg) . Sovereignty over Zeeuws Vlaanderen, south of the Westerscheldt river delta, was left with the Kingdom of the Netherlands, which was allowed to levy a toll on all traffic to Antwerp harbour until 1863.[3]
Rise of the Flemish Movement
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (June 2008) |
The Belgian Revolution was not well supported in Flanders and even on the 4th of October 1830, when the Belgian independence was eventually declared, Flemish authorities refused to take orders from the new Belgian government in Brussels. Only after Flanders was subdued with the aid of a large French military force one month later, under the leadership of the Count de Pontécoulant, Flanders became a true part of Belgium.
The French-speaking bourgeoisie showed very little respect for the Flemish part of the population. French became the only official language in Belgium and all secondary and higher education in the Flemish language was abolished. Belgium's co-founder, Charles Rogier, wrote in 1832 to Jean-Joseph Raikem, the minister of justice:
"Les premiers principes d'une bonne administration sont basés sur l'emploi exclusif d'une langue, et il est évident que la seule langue des Belges doit être le français. Pour arriver à ce résultat, il est nécessaire que toutes les fonctions civiles et militaires soient confiées à des Wallons et à des Luxembourgeois; de cette manière, les Flamands, privés temporairement des avantages attachés à ces emplois, seront contraints d'apprendre le français, et l'on détruira ainsi peu à peu l'élément germanique en Belgique."
"The first principles of a good administration are based upon the exclusive use of one language, and it is evident that the only language of the Belgians should be French. In order to achieve this result, it is necessary that all civil and military functions are entrusted to Walloons and Luxemburgers; this way, the Flemish, temporarily deprived of the advantages of these offices, will be constrained to learn French, and we will hence destroy bit by bit the Germanic element in Belgium."
In 1838, another co-founder, senator Alexandre Gendebien, even declared that the Flemish were "one of the more inferior races on the Earth, just like the negroes".
In 1834, all people even remotely suspected of being "Flemish minded" or calling for the reunification of the Netherlands were prosecuted and their houses looted and burnt. Flanders, until then a very prosperous European region, was not considered worthwhile for investment and scholarship. A study in 1918 demonstrated that in the first 88 years of its existence, 80% of the Belgian GNP was invested in Wallonia. This led to a widespread poverty in Flanders, forcing roughly 300.000 Flemish to emigrate to Wallonia to start working there in the heavy industry.
All of these events led to a silent uprising in Flanders against the French-speaking domination. But it was not until 1878 that Dutch was allowed to be used for official purposes in Flanders, although French remained the only official language in Belgium.
A remarkable case happened in 1872. Jozef Schoep, a Fleming, presented himself at the town hall of Sint-Jans Molenbeek to declare the birth of his son. The civil servant noted the declarations made in Dutch by Schoep in French and also addressed him in French. Schoep didn't understand the language and left the town hall as a sign of protest, without having signed the necessary documents. The Brussels' court condemned him to a fine of 50 Francs plus tax. Schoep rejected this verdict, accompanied by two solicitors who both stated that they would plead in Dutch. The president of the court at first didn't allow this, but afterwards changed his mind. Eventually, the pleaders were allowed to use Dutch on the condition that their pleas would be translated into French by an official interpreter because the judges didn't know a single word of Dutch. Schoep's sollicitors also demanded that the State would have its plea translated, but this was again rejected by the court. Eventually the case went to the supreme court, which ruled that pleading in Dutch would be forbidden. Its verdict was based on the so-called freedom of language and that no-one could ask from any judge to know any other language but French. Mr. Schoep's son had to wait until 1882 before he'd receive a legal birth certificate. His father had died in the mean time.
One year later, Dutch was again allowed in secondary schools; the first of which reopened in 1889. The Flemings had to wait until 1919—after many Flemish soldiers died in the trenches of World War I—to have their language officially recognised and until 1930 before the first Flemish university was reopened.
The first translation of the Belgian constitution in Dutch was not published until 1967.
World War I and its consequences
Flanders (and Belgium as a whole) saw some of the greatest loss of life on the Western Front of the First World War, in particular from the three battles of Ypres. Due to the hundreds of thousands of casualties at Ypres, the poppies that sprang up from the battlefield afterwards, later immortalised in the Canadian poem "In Flanders Fields", written by John McCrae, have become a symbol for lives lost in war.
Flemish feeling of identity and consciousness grew through the events and experiences of war. The German occupying authorities had taken several Flemish-friendly measures. More importantly, the experiences of many Dutch-speaking soldiers on the front led by French speaking officers catalysed Flemish emancipation. The French speaking officers barked the orders in French, followed by "et pour les Flamands, la même chose", which basically meant, "Same thing for the Flemish", which obviously did not help the Flemish conscripts, who were mostly uneducated farmers and workers, who didn't speak French at all. [citation needed] The resulting suffering is still remembered by Flemish organizations during the yearly Yser pilgrimage in Diksmuide at the monument of the Yser Tower.
Right-Wing Nationalism in the interbellum and World War II
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (June 2008) |
During the interbellum and World War II, several right-wing fascist and/or national-socialistic parties emerged in Belgium, of which the Flemish ones drew unto the feeling of discrimination by the Wallonians against the Flemish. Since these parties were promised more rights for the Flemings by the German government during World War II, some of them collaborated with the Nazi regime. After the war, collaborators (or people who were "Zwart", "Black" during the war) were of course prosecuted and punished, and amongst those were much Flemish Nationalists, whose main goal was more rights for Flanders. As a result, up until this day Flemish Nationalism is often wrongly associated with right wing and fascist ideologies.
Communautary quibbles and the Egmont pact
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (June 2008) |
Recent events
Fake revolution
On 13 December 2006, a spoof news broadcast by the Belgian Francophone public broadcasting station RTBF declared that Flanders had decided to declare independence from Belgium, and that the King and Queen of Belgium had already left the country by plane. Images were shown of people celebrating and waving flags in the background. Within minutes of the beginning of the broadcast, the news station was flooded with calls from concerned French speaking Belgians. It was only half an hour after the beginning of the broadcast that the disclaimer "This is fiction" was displayed. It was revealed that the programme had been broadcast to stimulate discussion of this subject[4].
Belgian federal elections
The 2007 elections showed an extraordinary outcome in terms of support for Flemish autonomy. All the political parties that advocated a significant increase of Flemish autonomy increased their share of the votes and seats in the Belgian parliament. This was especially the case for CD&V and N-VA (forming a cartel). In addition, the very assertive Lijst Dedecker gained a spectacular entry in parliament. It got even slightly ahead of the greens (Groen!). The outright secessionist Vlaams Belang remained strong, but stalled. The main parties advocating more or less the current Belgian institutions and only modest increases in Flemish autonomy severely lost (Groen!, OpenVLD, and especially SP.A). The 2009 regional elections have strengthened the parties in favor a significant increase of Flemish autonomy: CD&V and N-VA were the clear winners, while LDD consolidated its position, whereas openVLD, SP.A and Groen! further decreased their voters' share.
These victories for the advocates of much more Flemish autonomy are very much in parallel with opinion polls that show a structural increase in popular support for their agenda. Since 2006, certain polls have started showing a majority in favor of Flemish independence. Those polls are not yet representative, but they point to a significant long-term trend.
Several negotiators having come and gone since the last federal elections of 10 June 2007 without diminishing the disagreements between Flemish and Walloon politicians regarding a further State reform, continues to prevent the formation of the federal government.
Government and politics
Both the Flemish Community and the Flemish Region are constitutional institutions of the Kingdom of Belgium with precise geographical boundaries. In practice, the Flemish Community and Region together form a single body, with its own parliament and government, as the Community legally absorbed the competences of the Region.
The area of the Flemish Community is represented on the maps above, including the area of the Brussels-Capital Region (hatched on the relevant map). Roughly, the Flemish Community exercises competences originally oriented towards the individuals of the Community's language: culture (including audiovisual media), education, and the use of the language. Extensions to personal matters less directly associated with language comprise sports, health policy (curative and preventive medicine), and assistance to individuals (protection of youth, social welfare, aid to families, immigrant assistance services, etc.).[5]
The area of the Flemish Region is represented on the maps above. It has a population of around 6 million (excluding the Dutch-speaking community in the Brussels Region, grey on the map for it is not a part of the Flemish Region). Roughly, the Flemish Region is responsible for territorial issues in a broad sense, including economy, employment, agriculture, water policy, housing, public works, energy, transport, the environment, town and country planning, nature conservation, credit, and foreign trade. It supervises the provinces, municipalities, and intercommunal utility companies.[6]
The number of Dutch-speaking Flemish people in the Capital Region is estimated to be between 11% and 15% (official figures do not exist as there is no language census and no official subnationality). According to a survey conducted by the Université Catholique de Louvain in Louvain-La-Neuve and published in June 2006, 51% of respondents from Brussels claimed to be bilingual, even if they do not have Dutch as their first language.[7][8] They are governed by the Brussels Region for economics affairs and by the Flemish Community for educational and cultural issues.
As of 2005, Flemish institutions such as Flanders' government, parliament, etc. represent the Flemish Community and the Flemish region. The region and the community thus de facto share the same parliament and the same government. All these institutions are based in Brussels. Nevertheless, both bodies (the Community and the Region) still exist and the distinction between both is important for the people living in Brussels. Members of the Flemish parliament who were elected in the Brussels Region cannot vote on affairs belonging to the competences of the Flemish Region.
The official language for all Flemish institutions is Dutch. French enjoys a limited official recognition in a dozen municipalities along the borders with French-speaking Wallonia, and a large recognition in the bilingual Brussels Region. French is widely known in Flanders, with 59% claiming to know French according to a survey conducted by the Université catholique de Louvain in Louvain-La-Neuve and published in June 2006.[9][10]
Politics
Many new political parties during the last half century were founded in Flanders: the nationalist Volksunie of which the right nationalist Vlaams Blok (Vlaams Belang) split off, and which later dissolved into the former SPIRIT (now SLP), moderate nationalism rather left of the spectrum, and the NVA, more conservative moderate nationalism; the leftist alternative/ecological Groen!; the short-lived anarchistic libertarian spark ROSSEM and more recently the conservative-right liberal Lijst Dedecker, founded by Jean-Marie Dedecker.
Flemish nation
For many Flemings, Flanders is more than just a geographical area or the federal institutions (Flemish Community and Region). Some even call it a nation: a people of over 6 million living in the Flemish Region and in the Brussels-Capital Region. Flemings share many political, cultural, scientific, social and educational views. Although most Flemings identify themselves more with Flanders than with Belgium, the largest group defines itself as both Flemish and Belgian. The idea of an independent Flanders finds its root in the romantic nationalism of the 19th century.[citation needed]
Administrative divisions
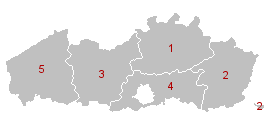
The Flemish Region covers 13,522 km2 (5,221 sq mi) and contains over 300 municipalities. It is divided into 5 provinces:
- Antwerp (Antwerpen)
- Limburg (Limburg)
- East Flanders (Oost-Vlaanderen)
- Flemish Brabant (Vlaams-Brabant)
- West Flanders (West-Vlaanderen)
Independently from the provinces, Flanders has its own local institutions in the Brussels-Capital Region, being the Vlaamse GemeenschapsCommissie (VGC), and its municipal antennae (Gemeenschapscentra, community centers for the Flemish community in Brussels). These institutions are independent from the educational, cultural and social institutions which depend directly on the Flemish government. They exert, among others, all those cultural competences that outside Brussels fall under the provinces.
Geography and climate
Antwerp, Ghent, Bruges and Leuven are the largest cities of the Flemish Region. Antwerp has a population of more than 470,000 citizens and is the largest city, Ghent has a population of 240,000 citizens, followed by Bruges with 100,000 citizens and Leuven counts almost 100,000 citizens. Brussels is a part of Flanders as far as community matters are concerned, but does not belong to the Flemish Region.
Flanders has two main geographical regions: the coastal Yser basin plain in the north-west and a central plain. The first consists mainly of sand dunes and clayey alluvial soils in the polders. Polders are areas of land, close to or below sea level that have been reclaimed from the sea, from which they are protected by dikes or, a little further inland, by fields that have been drained with canals. With similar soils along the lowermost Scheldt basin starts the central plain, a smooth, slowly rising fertile area irrigated by many waterways that reaches an average height of about five metres (16.4 ft) above sea level with wide valleys of its rivers upstream as well as the Campine region to the east having sandy soils at altitudes around thirty metres[11] Near its southern edges close to Wallonia one can find slightly rougher land richer of calcium with low hills reaching up to 150 m (492 ft) and small valleys, and at the eastern border with the Netherlands, in the Meuse basin, there are marl caves (mergelgrotten). Its exclave around Voeren between the Dutch border and the Walloon province of Liège attains a maximum altitude of 288 m (945 ft) above sea level.[12][13]
The climate is maritime temperate, with significant precipitation in all seasons (Köppen climate classification: Cfb; the average temperature is 3 °C (37 °F) in January, and 18 °C (64 °F) in July; the average precipitation is 65 millimetres (2.6 in) in January, and 78 millimetres (3.1 in) in July).
Economy
Total GDP of the Flemish Region in 2004 was € 165,847 million (Eurostat figures). Per capita GDP at purchasing power parity was 23% above the EU average.
Flanders was one of the first continental European areas to undergo the Industrial Revolution, in the 19th century. Initially, the modernization relied heavily on food processing and textile. However, by the 1840s the textile industry of Flanders was in severe crisis and there was famine in Flanders (1846–50). After World War II, Antwerp and Ghent experienced a fast expansion of the chemical and petroleum industries. Flanders also attracted a large majority of foreign investments in Belgium, among others thanks to its well-educated and industrious labour force.[citation needed] The 1973 and 1979 oil crises sent the economy into a recession. The steel industry remained in relatively good shape. In the 1980s and 90s, the economic centre of the Belgium continued to shift further to Flanders. Nowadays, the Flemish economy is mainly service-oriented, although its diverse industry remains a crucial force.[citation needed] Flemish productivity per capita is between 20 and 25% higher than that in Wallonia.[citation needed]
Flanders has developed an excellent transportation infrastructure of ports, canals, railways and highways.[citation needed] The Port of Antwerp is the second-largest in Europe, after Rotterdam.[14]
In 1999, the euro, the single European currency, was introduced in Flanders. It replaced the Belgian franc in 2002. The Flemish economy is strongly export oriented, in particular of high value-added goods.[citation needed] The main imports are food products, machinery, rough diamonds, petroleum and petroleum products, chemicals, clothing and accessories, and textiles. The main exports are automobiles, food and food products, iron and steel, finished diamonds, textiles, plastics, petroleum products, and nonferrous metals. Since 1922, Belgium and Luxembourg have been a single trade market within a customs and currency union—the Belgium-Luxembourg Economic Union. Its main trading partners are Germany, the Netherlands, France, the United Kingdom, Italy, the United States and Spain.[citation needed]
Demographics
The highest population density is found in the area circumscribed by the Brussels-Antwerp-Ghent-Leuven agglomerations that surround Mechelen and is known as the Flemish Diamond, in other important urban centres as Bruges and Kortrijk to the west, and notable centres Turnhout and Hasselt to the east. In April 2005 the Flemish Region had a population of 6,058,368, and about 15% of the 1,018,029 people in the Brussels Region are also considered Flemish.[15]
The (Belgian) laicist constitution provides for freedom of religion, and the various government generally respects this right in practice. Since independence, Catholicism, counterbalanced by strong freethought movements, has had an important role in Belgium's politics, since the 20th century in Flanders mainly via the Christian trade union (ACV) and the Christian Democrat party (CD&V). According to the 2001 Survey and Study of Religion,[16] about 47 percent of the Belgian population identify themselves as belonging to the Catholic Church, while Islam is the second-largest religion at 3.5 percent. A 2006 inquiry in Flanders, considered more religious than Wallonia, showed that 55% considered themselves religious, and 36% believed that God created the world.[17] (See also Religion in Belgium).
Education is compulsory from the ages of six to 18, but most Flemings continue to study until around 23. Among the OECD countries in 1999, Flanders had the third-highest proportion of 18–21-year-olds enrolled in postsecondary education. Flanders also scores very high in international comparative studies on education. Its secondary school students consistently rank among the top three for mathematics and science. However, the success is not evenly spread: ethnic minority youth score consistently lower, and the difference is larger than in most comparable countries.
Mirroring the historical political conflicts between the freethought and Catholic segments of the population, the Flemish educational system is split into a laïque branch controlled by the communities, the provinces, or the municipalities, and a subsidised religious—mostly Catholic—branch controlled by both the communities and the religious authorities—usually the dioceses. It should however be noted that—at least for the Catholic schools—the religious authorities have very limited power over these schools. Smaller school systems follow 'methodical pedagogies' (Steiner, Montessori, Freinet, ...) or serve the Jewish and Protestant minorities. During the school year 2003-2004, 68.30% of the total population of children between the ages of six and 18 went to subsidized private schools (both religious schools or 'methodical pedagogies' schools). [18]
Language and culture
The standard language in Flanders is Dutch; a single authority, the Nederlandse Taalunie, comprising appointees of the Belgian and Netherlands governments, sets standards for spelling and grammar. The term Flemish can be applied to the Dutch spoken in Flanders; it shows many regional and local variants.
At first sight, Flemish culture is defined by its language and its gourmandic mentality, as compared to the more Calvinistic Dutch culture. Although Flanders has never existed as an independent country, a tradition of Flemish literature has existed for centuries; with writers and poets such as Guido Gezelle, who not only explicitly referred to his writings as Flemish, but actually used it in many of his poems, and strongly defended it:
|
Original |
Translation |
This distinction in literature is also made by some experts such as Kris Humbeeck, professor of Literature at the University of Antwerp [1]. Nevertheless, the near totality of Dutch-language literature read (and appreciated to varying degrees) in Flanders is the same as in the Netherlands.
Influential Flemish writers include Ernest Claes, Stijn Streuvels and Felix Timmermans; their novels mostly describe rural life in Flanders in the 19th and beginning of the 20th century. They were widely read by the elder generation but are considered somewhat old-fashioned by present day critics. Some famous Flemish writers from the early 20th century wrote in French, like Nobel Prize winners (1911) Maurice Maeterlinck and Emile Verhaeren. Still widely read and translated into other languages (including English) are the novels of authors like Willem Elsschot, Louis Paul Boon and Hugo Claus. The younger generation is represented by novelists like Tom Lanoye, Herman Brusselmans and the poet Herman de Coninck.
Flanders is also famous for its Flemish art.
See also
- Burgundian Netherlands
- Count of Flanders
- Flemish education
- Flemish Movement
- Flemish Parliament
- Flemish Primitives
- List of Minister-Presidents of Flanders
- List of political parties in Flanders
- Science and technology in Flanders
- Seventeen Provinces
- VRT, the Flemish publicly-funded broadcaster
- vtm, the biggest Flemish commercial TV-station
References
- ^ The birth and growth of Utrecht
- ^ Footnote: An Antverpian, derived from Antverpia, the Latin name of Antwerp, is an inhabitant of this city; the term is also the adjective expressing that its substantive is from or in that city or belongs to it.
- ^ a b c
"Antwerp — History". Find it in Flanders. Tourism Flanders & Brussels, Flanders House, London, UK. Retrieved 2007-01-02.
{{cite web}}: External link in|publisher= - ^ http://en.wikinews.org/wiki/Fictional_documentary_about_Flemish_independence_causes_consternation_in_Belgium
- ^ "The Communities". .be Portal. Belgian Federal Government. Retrieved 2007-05-23.
- ^ "The Regions". .be Portal. Belgian Federal Government. Retrieved 2007-05-23.
- ^ Template:Fr icon Report of study by the Université Catholique de Louvain
- ^ Template:Nl icon Article at Taaluniversum.org summarising report
- ^ *Report of study by Universite Catholique de Louvain (in French)
- ^ *Article at Taaluniversum.org summarising report (in Dutch)
- ^ The altitude of Mechelen, approximately in the middle of the central plain forming the large part of Flanders, is 7 m (23 ft) above sea level. Already closer to the higher southern Wallonia, the more eastern Leuven and Hasselt reach altitudes up to about 40 m (131 ft)
"Kingdom of Belgium map (politically outdated)". Retrieved 15 May 2007.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dateformat=ignored (help) - ^
Ir. Jan Strubbe in collaboration with Dr. Frank Mostaert and Ir. Koen Maeghe. "Flood management in Flanders with special focus on navigable waterways" (PDF). Ministry of the Flemish Community, department Environment and Infrastructure (Waterbouwkundig Laboratorium, Flanders Hydraulics Research, Administratie Waterwegen en Zeewezen). Retrieved 2007.
Flanders is covered by the three major catchment basins (Yser, Scheldt and Meuse). This rather lowlying nearly flat region (2 to 150 m/6–492 ft altitude above sea-level) ...
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help); Unknown parameter|accessmmonthday=ignored (help); line feed character in|quote=at position 104 (help) - ^
Myriam Dumortier, Luc De Bruyn, Maarten Hens, Johan Peymen, Anik Schneiders, Toon Van Daele, Wouter Van Reeth, Gisèle Weyembergh and Eckhart Kuijken (2006). "Biodiversity Indicators 2006 - State of Nature in Flanders (Belgium)" (PDF). Research Institute for Nature and Forest (INBO), Brussels. ISBN 90-403-0251-0. Retrieved 2007.
The altitude ranges from a few meters above sea-level in the Polders to 288 m (945 ft) above sea-level in the south eastern exclave.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help); Unknown parameter|accessmmonthday=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Focus on the port". Port of Antwerp. Retrieved September 27, 2009.
- ^ Official statistics of Belgium
- ^ "Belgium". International Religious Freedom Report 2004. US Department of State, Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights, and Labor. 2004. Retrieved 2007-05-28.
- ^ Inquiry by 'Vepec', 'Vereniging voor Promotie en Communicatie' (Organisation for Promotion and Communication), published in Knack magazine 22 November 2006 p. 14 [The Dutch language term 'gelovig' is in the text translated as 'religious', more precisely it is a very common word for believing in particular in any kind of God in a monotheistic sense, and/or in some afterlife.
- ^ "Education in Flanders" (PDF). A broad view of the Flemish educational landscape. Ministry of the Flemish Community. 2005. Retrieved 2009-11-02.
External links
- Transclusion error: {{En}} is only for use in File namespace. Use {{langx|en}} or {{in lang|en}} instead. Flemish authorities (Dutch: Vlaamse overheid)
- Template:Nl Flemish authorities (Dutch: Vlaamse overheid)
- Flemish government (Dutch: Vlaamse regering)
- Flemish Community Council in Brussels (Dutch: Vlaamse Gemeenschapscommissie (VGC))
- Transclusion error: {{En}} is only for use in File namespace. Use {{langx|en}} or {{in lang|en}} instead. Visit Flanders
- Transclusion error: {{En}} is only for use in File namespace. Use {{langx|en}} or {{in lang|en}} instead. Flanders Today (Weekly independent magazine on Flanders)
- Toerisme Vlaanderen
- Dag Vlaanderen
- Template:Fr French Flanders
- Template:Nl Flanders reaches 6 million inhabitants
