Almohad Caliphate: Difference between revisions
Omar-Toons (talk | contribs) |
Undid revision 403260427 by Omar-Toons (talk)consensually does not mean unanimously |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
|common_name = Almohads |
|common_name = Almohads |
||
|continent=Africa & Europe |
|continent=Africa & Europe |
||
|region = North Africa & |
|region = North Africa & Iberian Peninsula |
||
|country = Morocco |
|country = Algeria, Gibraltar, Lybia, Morocco, Portugal, Spain, Tunisia |
||
|status=Empire |
|status=Empire |
||
|year_start = 1121 |
|year_start = 1121 |
||
|year_end = 1269 |
|year_end = 1269 |
||
|p1 = Almoravid dynasty |
|p1 = Almoravid dynasty |
||
|s1 = |
|s1 = Abdalwadid |
||
|s2 = Emirate of Granada |
|s2 = Emirate of Granada |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
|s4 = Hafsid dynasty |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
|s5 = Crown of Castile |
|||
|s6 = Kingdom of Portugal |
|||
|s7 = Crown of Aragon |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
|flag_s1 = Dz tlem2.gif |
|||
|flag_s2 = Royal Standard of Nasrid Dynasty Kingdom of Grenade.svg |
|||
|flag_s3 = Marinid emblem.png |
|||
|flag_s4 = Tunis hafsid flag.png |
|||
|flag_s5 = Banner of arms crown of Castille Habsbourg style.svg |
|||
|flag_s6 = Kingdom of the Algarve CoA.png |
|||
|flag_s7 = Estandarte de la Corona de Aragon.png |
|||
|image_flag = Flag of Almohad Dynasty.svg |
|image_flag = Flag of Almohad Dynasty.svg |
||
|image_map = Almohads1200.png |
|image_map = Almohads1200.png |
||
|image_map_caption = The Almohad dynasty (green) at its greatest extent, c. 1200. |
|image_map_caption = The Almohad dynasty (green) at its greatest extent, c. 1200. |
||
|common_languages = [[Classical Arabic]], [[Berber languages]], [[Medieval Hebrew|Hebrew]], [[Mozarabic language|Mozarabic]], [[African Romance]] & [[Andalusian Arabic]]. |
|||
|common_languages = |
|||
|religion = [[Islam]] ([[History of Christianity#High Middle Ages (800–1299)|Catholicism]], [[History of the Jews under Muslim rule|Judaism]]) |
|||
|religion = [[Sunni Islam]] |
|||
|capital = [[Marrakesh]] |
|capital = [[Marrakesh]] & [[Seville]]. |
||
|government_type = [[Monarchy]] |
|government_type = [[Monarchy]] |
||
|title_leader = [[Caliph]] |
|title_leader = [[Caliph]] |
||
| Line 28: | Line 39: | ||
|stat_area1 = 1621393.5 |
|stat_area1 = 1621393.5 |
||
|currency = [[Dinar]], [[Dobla almohad]] |
|currency = [[Dinar]], [[Dobla almohad]] |
||
|today = {{flag|Algeria}}</br>{{flag|Gibraltar}}</br>{{flag|Libya}}</br>{{flag|Morocco}}</br>{{flag|Portugal}}</br>{{flag|Spain}}</br>{{flag|Tunisia}}</br> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | The '''Almohad Dynasty''' ([[Berber languages|Berber]]: '''Imweḥḥden''', from [[Arabic]] الموحدون ''[[Al-Muwahhidūn|al-Muwahhidun]]'', i.e., "[[monotheist|the monotheists]]" or "the Unitarians"), was a [[Berber people|Berber]], [[Muslim]] dynasty that was founded in the 12th century, which conquered most of [[northern Africa]] as far as [[Libya]], together with [[Al-Andalus]] ([[Moors|Moorish]] [[Iberian Peninsula|Iberia]], now southern Spain and Portugal). |
||
Between 1130 and his death in 1163, [[Abd al-Mu'min]] al-Kumi defeated the ruling [[Almoravid]]s and extended his power over all northern Africa as far as [[Libya]] becoming Emir of [[Marrakesh]] in 1149. |
Between 1130 and his death in 1163, [[Abd al-Mu'min]] al-Kumi defeated the ruling [[Almoravid]]s and extended his power over all northern Africa as far as [[Libya]] becoming Emir of [[Marrakesh]] in 1149. |
||
| Line 45: | Line 58: | ||
After his return to Magreb at the age of twenty-eight, Ibn Tumart began preaching and agitating, heading riotous attacks on wine-shops and on other manifestations of laxity. He even went so far as to assault the sister{{citation needed|date=December 2009}} of the [[Almoravid]] (Murabit) amir `Ali III, in the streets of [[Fez, Morocco|Fez]], because she was going about unveiled, after the manner of Berber women. `Ali III allowed him to escape unpunished. |
After his return to Magreb at the age of twenty-eight, Ibn Tumart began preaching and agitating, heading riotous attacks on wine-shops and on other manifestations of laxity. He even went so far as to assault the sister{{citation needed|date=December 2009}} of the [[Almoravid]] (Murabit) amir `Ali III, in the streets of [[Fez, Morocco|Fez]], because she was going about unveiled, after the manner of Berber women. `Ali III allowed him to escape unpunished. |
||
Ibn Tumart, who had been driven from several other towns for exhibitions of reforming zeal, now took refuge among his own people, the [[Masmuda]], in the [[Atlas Mountains|Atlas]]. It is highly probable that his influence would not have outlived him, if he had not found a lieutenant in [[Abd al-Mu'min]] al-Kumi, another Berber, from [[Algeria]], who was undoubtedly a soldier and statesman of a high order. When Ibn Tumart died in 1128 at the monastery or [[ribat]] which he had founded in the Atlas at [[Tinmel]], after suffering a severe defeat by the [[Almoravids]], Abd al-Mu'min kept his death secret for two years, till his own influence was established. He then came forward as the lieutenant of the [[Mahdi]] Ibn Tumart. |
Ibn Tumart, who had been driven from several other towns for exhibitions of reforming zeal, now took refuge among his own people, the [[Masmuda]], in the [[Atlas Mountains|Atlas]]. It is highly probable that his influence would not have outlived him, if he had not found a lieutenant in [[Abd al-Mu'min]] al-Kumi, another Berber, from [[Algeria]], who was undoubtedly a soldier and statesman of a high order. When Ibn Tumart died in 1128 at the monastery or [[ribat]] which he had founded in the Atlas at [[Tinmel]], after suffering a severe defeat by the [[Almoravids]], Abd al-Mu'min kept his death secret for two years, till his own influence was established. He then came forward as the lieutenant of the [[Mahdi]] Ibn Tumart. Between 1130 and his death in 1163, `Abd-el-Mumin not only rooted out the Murabits and in 1130 try to conquest Marrakech<ref>[http://unesdoc.unesco.org/images/0000/000043/004350sb.pdf National Comission of the Kingdom of Morocco to Unesco in 1973]</ref>, but extended his power over all northern Africa as far as [[Egypt]], becoming amir of [[Marrakesh]] in 1149. [[Al-Andalus]] followed the fate of Africa, and in 1170 the Almohads transferred their capital to [[Seville]], a step followed by the founding of the great mosque (now superseded by the cathedral), the tower of which, the [[Giralda]], they erected in 1184 to mark the accession of [[Abu Yusuf Ya'qub al-Mansur]]. From the time of Yusuf II, however, they governed their co-religionists in Iberia and Central North [[Africa]] through lieutenants, their dominions outside [[Morocco]] being treated as provinces. When their amirs crossed the Straits it was to lead a jihad against the Christians and to return to their capital, [[Marrakesh]]. |
||
[[Image:Safi minaret.png|400px|thumb|left|The Almohad minaret in Safi]] |
[[Image:Safi minaret.png|400px|thumb|left|The Almohad minaret in Safi]] |
||
| Line 51: | Line 64: | ||
The Almohad princes had a longer and a more distinguished career than the Murabits (or [[Almoravids]]). Yusuf I or [[Abu Yaqub Yusuf]] (1163–1184), and Ya'qub I or [[Yaqub al-Mansur]] (1184-1199), the successors of Abd al-Mumin, were both able men. Initially their government drove many Jewish and Christian subjects to take refuge in the growing Christian states of Portugal, Castile and Aragon. But in the end they became less fanatical than the [[Almoravids]], and Ya'qub al-Mansur was a highly accomplished man, who wrote a good [[Arabic language|Arabic]] style and who protected the philosopher [[Averroes]]. His title of al-Mansur, "The Victorious," was earned by the defeat he inflicted on [[Alfonso VIII of Castile]] in the [[Battle of Alarcos]] (1195). |
The Almohad princes had a longer and a more distinguished career than the Murabits (or [[Almoravids]]). Yusuf I or [[Abu Yaqub Yusuf]] (1163–1184), and Ya'qub I or [[Yaqub al-Mansur]] (1184-1199), the successors of Abd al-Mumin, were both able men. Initially their government drove many Jewish and Christian subjects to take refuge in the growing Christian states of Portugal, Castile and Aragon. But in the end they became less fanatical than the [[Almoravids]], and Ya'qub al-Mansur was a highly accomplished man, who wrote a good [[Arabic language|Arabic]] style and who protected the philosopher [[Averroes]]. His title of al-Mansur, "The Victorious," was earned by the defeat he inflicted on [[Alfonso VIII of Castile]] in the [[Battle of Alarcos]] (1195). |
||
At the end of XIII century [[Banu Hilal]] and [[Banu Sulaym]] controled some parts<ref>[http://www.settat-chaouia.ma/Histoire/histoire/id-menu-164.html History of Settat]</ref> |
|||
===Loss of Iberia=== |
===Loss of Iberia=== |
||
[[Image:Mapa reconquista almohades-en.svg|thumb|right|300px|Map showing the area of Almohad control in Spain and the paths of counter-attacks from Castile (C) and Aragón (A). ((L) Leon, (P) Portugal, (N) Navarre)]]However, the Christian states in Iberia were becoming too well organized to be overrun by the Muslims, and the Almohads made no permanent advance against them. |
[[Image:Mapa reconquista almohades-en.svg|thumb|right|300px|Map showing the area of Almohad control in Spain and the paths of counter-attacks from Castile (C) and Aragón (A). ((L) Leon, (P) Portugal, (N) Navarre)]]However, the Christian states in Iberia were becoming too well organized to be overrun by the Muslims, and the Almohads made no permanent advance against them. |
||
In 1212 [[Muhammad an-Nasir|Muhammad III, "al-Nasir"]] (1199–1214), the successor of al-Mansur, after an initially successful advance north, was defeated by an alliance of the four Christian princes of [[Kingdom of Castile|Castile]], [[Aragón]], [[Kingdom of Navarre]] and [[Portugal]], at the [[Battle of Las Navas de Tolosa]] in the [[Sierra Morena]]. The battle destroyed Almohad dominance. Nearly all of the Moorish dominions in Iberia were lost soon after, with the great Moorish cities of [[Córdoba, Spain|Córdoba]] and [[Seville]] falling to the Christians in 1236 and 1248 respectively. |
In 1212 [[Muhammad an-Nasir|Muhammad III, "al-Nasir"]] (1199–1214), the successor of al-Mansur, after an initially successful advance north, was defeated by an alliance of the four Christian princes of [[Kingdom of Castile|Castile]], [[Aragón]], [[Kingdom of Navarre]] and [[Portugal]], at the [[Battle of Las Navas de Tolosa]] in the [[Sierra Morena]]. The battle destroyed Almohad dominance. Nearly all of the Moorish dominions in Iberia were lost soon after, with the great Moorish cities of [[Córdoba, Spain|Córdoba]] and [[Seville]] falling to the Christians in 1236 and 1248 respectively. In 1216 Marinids conquest Taza<ref>[http://unesdoc.unesco.org/images/0000/000043/004350sb.pdf National Comission of the Kingdom of Morocco in Unesco in 1973]</ref> and in marinids conquest Taza in 1248 again<ref>Historia de España musulmana, de Anwar G. Chejne</ref> |
||
All that remained, thereafter, was the Moorish state of [[Granada]], which after an internal Muslim revolt, survived as a tributary state of the Christian kingdoms on Iberia's southern periphery. The [[Nasrid dynasty]] or ''Banu Nazari'' ({{lang-ar|بنو نصر}}) rose to power there after the defeat of the Almohads dynasty in 1212. Twenty different Muslim kings ruled [[Granada]] from the founding of the dynasty in 1232 by [[Muhammed I ibn Nasr, Sultan of Granada|Muhammed I ibn Nasr]] until January 2, 1492, when [[Boabdil|Sultan Boabdil]] surrendered to the Christian Spanish kingdom. Today, the most visible evidence of the Nasrids is the [[Alhambra]] palace complex built under their rule. |
All that remained, thereafter, was the Moorish state of [[Granada]], which after an internal Muslim revolt, survived as a tributary state of the Christian kingdoms on Iberia's southern periphery. The [[Nasrid dynasty]] or ''Banu Nazari'' ({{lang-ar|بنو نصر}}) rose to power there after the defeat of the Almohads dynasty in 1212. Twenty different Muslim kings ruled [[Granada]] from the founding of the dynasty in 1232 by [[Muhammed I ibn Nasr, Sultan of Granada|Muhammed I ibn Nasr]] until January 2, 1492, when [[Boabdil|Sultan Boabdil]] surrendered to the Christian Spanish kingdom. Today, the most visible evidence of the Nasrids is the [[Alhambra]] palace complex built under their rule. |
||
[[File:Almohads after 1212.jpg|right|300px]] |
|||
In their African holdings, the Almohads encouraged the establishment of Christians even in [[Fez, Morocco|Fez]], and after the [[Battle of Las Navas de Tolosa]] they occasionally entered into alliances with the kings of [[Kingdom of Castile|Castile]]. They were successful in expelling the garrisons placed in some of the coast towns by the [[Normans|Norman]] kings of [[Sicily]]. The history of their decline differs from that of the [[Almoravids]], whom they had displaced. They were not assailed by a great religious movement, but lost territories, piecemeal, by the revolt of tribes and districts. Their most effective enemies were the Beni Marin ([[Marinid]]s) who founded the next dynasty. The last representative of the line, Idris II, "El Wathiq"' was reduced to the possession of [[Marrakesh]], where he was murdered by a slave in 1269. |
In their African holdings, the Almohads encouraged the establishment of Christians even in [[Fez, Morocco|Fez]], and after the [[Battle of Las Navas de Tolosa]] they occasionally entered into alliances with the kings of [[Kingdom of Castile|Castile]]. They were successful in expelling the garrisons placed in some of the coast towns by the [[Normans|Norman]] kings of [[Sicily]]. The history of their decline differs from that of the [[Almoravids]], whom they had displaced. They were not assailed by a great religious movement, but lost territories, piecemeal, by the revolt of tribes and districts. Their most effective enemies were the Beni Marin ([[Marinid]]s) who founded the next dynasty. The last representative of the line, Idris II, "El Wathiq"' was reduced to the possession of [[Marrakesh]], where he was murdered by a slave in 1269. |
||
==Religious fundamentalism== |
==Religious fundamentalism== |
||
The Almohads, who had taken control of the [[Almoravid]]s' Maghribi and Andalusian territories by 1147,<ref name=islamicworldeb>Islamic world. (2007). In Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved September 2, 2007, from [http://www.britannica.com/eb/article-26925 Encyclopædia Britannica Online].</ref> far surpassed the [[Almoravids]] in fundamentalist outlook, and they treated the [[dhimmi]]s (non-Muslims) harshly. Faced with the choice of either death or conversion, most Jews and Christians emigrated.<ref>[http://www.theforgottenrefugees.com/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=66&Itemid=39 The Forgotten Refugees]</ref> A few, like the family of [[Maimonides]], eventually fled east to more tolerant Muslim lands,<ref name=frank>Frank and Leaman, 2003, p. 137-138.</ref> while most of them went northward to settle in the growing Christian kingdoms.<ref>[http://www.jewishvirtuallibrary.org/jsource/Judaism/Sephardim.html Sephardim]</ref><ref>Kraemer, 2005, pp. 16-17.</ref>{{Citation broken|date=September 2008}} |
The Almohads, who had taken control of the [[Almoravid]]s' Maghribi and Andalusian territories by 1147,<ref name=islamicworldeb>Islamic world. (2007). In Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved September 2, 2007, from [http://www.britannica.com/eb/article-26925 Encyclopædia Britannica Online].</ref> far surpassed the [[Almoravids]] in fundamentalist outlook, and they treated the [[dhimmi]]s (non-Muslims) harshly. Faced with the choice of either death or conversion, most Jews and Christians emigrated.<ref>[http://www.theforgottenrefugees.com/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=66&Itemid=39 The Forgotten Refugees]</ref> A few, like the family of [[Maimonides]], eventually fled east to more tolerant Muslim lands,<ref name=frank>Frank and Leaman, 2003, p. 137-138.</ref> while most of them went northward to settle in the growing Christian kingdoms.<ref>[http://www.jewishvirtuallibrary.org/jsource/Judaism/Sephardim.html Sephardim]</ref><ref>Kraemer, 2005, pp. 16-17.</ref>{{Citation broken|date=September 2008}} |
||
[[File:La Giralda, Seville, Spain - Sep 2009.jpg|right|thumb|200px|La [[Giralda]].]] |
|||
[[File:Koutbia.jpg|right|thumb|200px|[[Koutoubia Mosque]].]] |
|||
==List of Almohad caliphs (1121–1269)== |
==List of Almohad caliphs (1121–1269)== |
||
*[[Muhammad ibn Abdallah ibn Tumart|Ibn Tumart]] 1121-1130 |
*[[Muhammad ibn Abdallah ibn Tumart|Ibn Tumart]] 1121-1130 |
||
| Line 79: | Line 94: | ||
*[[Abu al-Ula al-Wathiq Idris|Idris II]] 1266–1269 |
*[[Abu al-Ula al-Wathiq Idris|Idris II]] 1266–1269 |
||
==List of Sufi writers of the Almohad caliphate== |
== List of Sufi writers of the Almohad caliphate == |
||
*[[Abu Madyan|Sidi Abu Madyan Choaïb ben al-Houssein al-Ansari]] (1126–1198) |
*[[Abu Madyan|Sidi Abu Madyan Choaïb ben al-Houssein al-Ansari]] (1126–1198) |
||
*[[Ali ibn Harzihim]] ( |
*[[Ali ibn Harzihim]] (d.1164) |
||
*[[Abi Mohammed Salih]] (1153–1234) |
*[[Abi Mohammed Salih]] (1153–1234) |
||
*[[Abu Abdallah ibn Harzihim]] ( |
*[[Abu Abdallah ibn Harzihim]] (d.1235) |
||
*[[Abu-l-Hassan ash-Shadhili]] (1197–1258) |
*[[Abu-l-Hassan ash-Shadhili]] (1197–1258) |
||
*[[Abdelwahid al-Marrakushi]] (b. 1185) historian and writer |
*[[Abdelwahid al-Marrakushi]] (b. 1185) historian and writer |
||
| Line 103: | Line 118: | ||
{{reflist}} |
{{reflist}} |
||
{{S-start}} |
|||
{{Succession box| |
|||
before= [[Almoravid Dynasty]]| |
|||
title=Almohad Dynasty| |
|||
years=1121–1269 | |
|||
after=[[Marinid Dynasty]] | |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
{{S-end}} |
|||
{{Morocco topics}} |
|||
{{Empires}} |
{{Empires}} |
||
| ⚫ | |||
[[Category:History of North Africa]] |
[[Category:History of North Africa]] |
||
[[Category:History of Algeria]] |
[[Category:History of Algeria]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
[[Category:History of Gibraltar]] |
[[Category:History of Gibraltar]] |
||
[[Category:History of Libya]] |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
[[Category:History of Tunisia]] |
[[Category:History of Tunisia]] |
||
[[Category:Medieval Portugal]] |
[[Category:Medieval Portugal]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
[[Category:Almohad dynasty]] |
[[Category:Almohad dynasty]] |
||
[[Category:Berber people]] |
[[Category:Berber people]] |
||
Revision as of 02:17, 20 December 2010
Almohad dynasty الموَحدون al-Muwahhidūn | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1121–1269 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
Flag | |||||||||||||||||||||
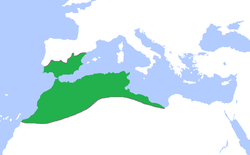 The Almohad dynasty (green) at its greatest extent, c. 1200. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Capital | Marrakesh & Seville. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Common languages | Classical Arabic, Berber languages, Hebrew, Mozarabic, African Romance & Andalusian Arabic. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Religion | Islam (Catholicism, Judaism) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Caliph | |||||||||||||||||||||
• 1121-1130 | Abd al-Mumin | ||||||||||||||||||||
• 1266–1269 | Abu al-Ula al-Wathiq Idris | ||||||||||||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||||||||||||
• Established | 1121 | ||||||||||||||||||||
• Disestablished | 1269 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 1,621,393.5 km2 (626,023.5 sq mi) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Currency | Dinar, Dobla almohad | ||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| Today part of | |||||||||||||||||||||
The Almohad Dynasty (Berber: Imweḥḥden, from Arabic الموحدون al-Muwahhidun, i.e., "the monotheists" or "the Unitarians"), was a Berber, Muslim dynasty that was founded in the 12th century, which conquered most of northern Africa as far as Libya, together with Al-Andalus (Moorish Iberia, now southern Spain and Portugal).
Between 1130 and his death in 1163, Abd al-Mu'min al-Kumi defeated the ruling Almoravids and extended his power over all northern Africa as far as Libya becoming Emir of Marrakesh in 1149.
Al-Andalus, Moorish Iberia, followed the fate of Africa, and in 1170 the Almohads transferred their capital to Seville. However, by 1212 Muhammad III, "al-Nasir" (1199–1214) was defeated by an alliance of the four Christian princes of Castile, Aragón, Navarre and Portugal, at the Battle of Las Navas de Tolosa in the Sierra Morena. The battle destroyed Almohad dominance. Nearly all of the Moorish dominions in Iberia were lost soon after, with the great Moorish cities of Córdoba and Seville falling to the Christians in 1236 and 1248 respectively.
The Almohads continued to rule in Africa until the piecemeal loss of territory through the revolt of tribes and districts enabled their most effective enemies, the Marinids in 1215. The last representative of the line, Idris II, "El Wathiq"' was reduced to the possession of Marrakesh, where he was murdered by a slave in 1269.
Today the holy place and the tomb of the Almohads are present in Morocco, as is the tomb of their rivals and enemies the Almoravids.
History
Origins
The dynasty originated with Ibn Tumart, a member of the Masmuda, a Berber tribe of the Atlas Mountains of Morocco. Ibn Tumart was the son of a lamplighter in a mosque and had been noted for his piety from his youth; he was small, and misshapen and lived the life of a devotee-beggar. As a youth he performed the hajj to Mecca (or "Makkah"), whence he was expelled on account of his severe strictures on the laxity of others, and thence wandered to Baghdad, where he attached himself to the school of the orthodox doctor al-Ash'ari. But he made a system of his own by combining the teaching of his master with parts of the doctrines of others, and with mysticism imbibed from the great teacher Ghazali. His main principle was a strict Unitarianism which denied the independent existence of the attributes of God, as being incompatible with his unity, and therefore a polytheistic idea. Ibn Tumart in fact represented a revolt against what he perceived as anthropomorphism in the Muslim orthodoxy.
Conquests
After his return to Magreb at the age of twenty-eight, Ibn Tumart began preaching and agitating, heading riotous attacks on wine-shops and on other manifestations of laxity. He even went so far as to assault the sister[citation needed] of the Almoravid (Murabit) amir `Ali III, in the streets of Fez, because she was going about unveiled, after the manner of Berber women. `Ali III allowed him to escape unpunished.
Ibn Tumart, who had been driven from several other towns for exhibitions of reforming zeal, now took refuge among his own people, the Masmuda, in the Atlas. It is highly probable that his influence would not have outlived him, if he had not found a lieutenant in Abd al-Mu'min al-Kumi, another Berber, from Algeria, who was undoubtedly a soldier and statesman of a high order. When Ibn Tumart died in 1128 at the monastery or ribat which he had founded in the Atlas at Tinmel, after suffering a severe defeat by the Almoravids, Abd al-Mu'min kept his death secret for two years, till his own influence was established. He then came forward as the lieutenant of the Mahdi Ibn Tumart. Between 1130 and his death in 1163, `Abd-el-Mumin not only rooted out the Murabits and in 1130 try to conquest Marrakech[1], but extended his power over all northern Africa as far as Egypt, becoming amir of Marrakesh in 1149. Al-Andalus followed the fate of Africa, and in 1170 the Almohads transferred their capital to Seville, a step followed by the founding of the great mosque (now superseded by the cathedral), the tower of which, the Giralda, they erected in 1184 to mark the accession of Abu Yusuf Ya'qub al-Mansur. From the time of Yusuf II, however, they governed their co-religionists in Iberia and Central North Africa through lieutenants, their dominions outside Morocco being treated as provinces. When their amirs crossed the Straits it was to lead a jihad against the Christians and to return to their capital, Marrakesh.

The Almohad princes had a longer and a more distinguished career than the Murabits (or Almoravids). Yusuf I or Abu Yaqub Yusuf (1163–1184), and Ya'qub I or Yaqub al-Mansur (1184-1199), the successors of Abd al-Mumin, were both able men. Initially their government drove many Jewish and Christian subjects to take refuge in the growing Christian states of Portugal, Castile and Aragon. But in the end they became less fanatical than the Almoravids, and Ya'qub al-Mansur was a highly accomplished man, who wrote a good Arabic style and who protected the philosopher Averroes. His title of al-Mansur, "The Victorious," was earned by the defeat he inflicted on Alfonso VIII of Castile in the Battle of Alarcos (1195).
At the end of XIII century Banu Hilal and Banu Sulaym controled some parts[2]
Loss of Iberia

However, the Christian states in Iberia were becoming too well organized to be overrun by the Muslims, and the Almohads made no permanent advance against them.
In 1212 Muhammad III, "al-Nasir" (1199–1214), the successor of al-Mansur, after an initially successful advance north, was defeated by an alliance of the four Christian princes of Castile, Aragón, Kingdom of Navarre and Portugal, at the Battle of Las Navas de Tolosa in the Sierra Morena. The battle destroyed Almohad dominance. Nearly all of the Moorish dominions in Iberia were lost soon after, with the great Moorish cities of Córdoba and Seville falling to the Christians in 1236 and 1248 respectively. In 1216 Marinids conquest Taza[3] and in marinids conquest Taza in 1248 again[4]
All that remained, thereafter, was the Moorish state of Granada, which after an internal Muslim revolt, survived as a tributary state of the Christian kingdoms on Iberia's southern periphery. The Nasrid dynasty or Banu Nazari (Arabic: بنو نصر) rose to power there after the defeat of the Almohads dynasty in 1212. Twenty different Muslim kings ruled Granada from the founding of the dynasty in 1232 by Muhammed I ibn Nasr until January 2, 1492, when Sultan Boabdil surrendered to the Christian Spanish kingdom. Today, the most visible evidence of the Nasrids is the Alhambra palace complex built under their rule.

In their African holdings, the Almohads encouraged the establishment of Christians even in Fez, and after the Battle of Las Navas de Tolosa they occasionally entered into alliances with the kings of Castile. They were successful in expelling the garrisons placed in some of the coast towns by the Norman kings of Sicily. The history of their decline differs from that of the Almoravids, whom they had displaced. They were not assailed by a great religious movement, but lost territories, piecemeal, by the revolt of tribes and districts. Their most effective enemies were the Beni Marin (Marinids) who founded the next dynasty. The last representative of the line, Idris II, "El Wathiq"' was reduced to the possession of Marrakesh, where he was murdered by a slave in 1269.
Religious fundamentalism
The Almohads, who had taken control of the Almoravids' Maghribi and Andalusian territories by 1147,[5] far surpassed the Almoravids in fundamentalist outlook, and they treated the dhimmis (non-Muslims) harshly. Faced with the choice of either death or conversion, most Jews and Christians emigrated.[6] A few, like the family of Maimonides, eventually fled east to more tolerant Muslim lands,[7] while most of them went northward to settle in the growing Christian kingdoms.[8][9][full citation needed]


List of Almohad caliphs (1121–1269)
- Ibn Tumart 1121-1130
- Abd al-Mu'min 1130–1163
- Abu Ya'qub Yusuf I 1163–1184
- Abu Yusuf Ya'qub al-Mansur 1184–1199
- Muhammad an-Nasir 1199–1213
- Abu Ya'qub Yusuf II 1213–1224
- Abd al-Wahid I 1224
- Abdallah al-Adil 1224–1227
- Yahya 1227–1235
- Idris I 1227–1232
- Abdul-Wahid II 1232–1242
- Ali 1242–1248
- Umar 1248–1266
- Idris II 1266–1269
List of Sufi writers of the Almohad caliphate
- Sidi Abu Madyan Choaïb ben al-Houssein al-Ansari (1126–1198)
- Ali ibn Harzihim (d.1164)
- Abi Mohammed Salih (1153–1234)
- Abu Abdallah ibn Harzihim (d.1235)
- Abu-l-Hassan ash-Shadhili (1197–1258)
- Abdelwahid al-Marrakushi (b. 1185) historian and writer
- Salih ben Sharif al-Rundi (1204–1285)
References
Bibliography
- History of the Almonades, Reinhart Dozy, (second edition, 1881)
- Conquest of Spain by the Arab-Moors, Coppée, (Boston, 1881)
- Le livre d'Ibn Tumart, I. Goldziher, (1903)
- Les Benou Ghanya, Bel, (1903)
- Mica Enciclopedie de Istorie Universala, Marcel D. Popa, Horia C. Matei, (Bucharest, Editura Politica 1988)
External links
- Almohads Dynasty : Islamic Architecture
- Abd al-Mumin life among Masmudas: Encyclopædia Britannica
Notes
- ^ National Comission of the Kingdom of Morocco to Unesco in 1973
- ^ History of Settat
- ^ National Comission of the Kingdom of Morocco in Unesco in 1973
- ^ Historia de España musulmana, de Anwar G. Chejne
- ^ Islamic world. (2007). In Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved September 2, 2007, from Encyclopædia Britannica Online.
- ^ The Forgotten Refugees
- ^ Frank and Leaman, 2003, p. 137-138.
- ^ Sephardim
- ^ Kraemer, 2005, pp. 16-17.