Orion (constellation): Difference between revisions
reffed |
Fixed (again) linguistic hiccup |
||
| Line 86: | Line 86: | ||
The [[Seri people]] of northwestern Mexico call the three stars in the belt of this constellation ''Hapj'' (a name denoting a hunter) which consists of three stars: ''Hap'' (mule deer), ''Haamoja'' (pronghorn), and ''Mojet'' (bighorn sheep). ''Hap'' is in the middle and has been shot by the hunter; its blood has dripped onto [[Tiburón Island]].<ref>{{cite book |last=Moser |first=Mary B. |coauthors=Stephen A. Marlett |title=Comcáac quih yaza quih hant ihíip hac: Diccionario seri-español-inglés |url=http://lengamer.org/admin/language_folders/seri/user_uploaded_files/links/File/DiccionarioSeri2005.pdf |year=2005 |publisher=Universidad de Sonora and Plaza y Valdés Editores |location=Hermosillo, Sonora and Mexico City|language=Spanish and English}}</ref> |
The [[Seri people]] of northwestern Mexico call the three stars in the belt of this constellation ''Hapj'' (a name denoting a hunter) which consists of three stars: ''Hap'' (mule deer), ''Haamoja'' (pronghorn), and ''Mojet'' (bighorn sheep). ''Hap'' is in the middle and has been shot by the hunter; its blood has dripped onto [[Tiburón Island]].<ref>{{cite book |last=Moser |first=Mary B. |coauthors=Stephen A. Marlett |title=Comcáac quih yaza quih hant ihíip hac: Diccionario seri-español-inglés |url=http://lengamer.org/admin/language_folders/seri/user_uploaded_files/links/File/DiccionarioSeri2005.pdf |year=2005 |publisher=Universidad de Sonora and Plaza y Valdés Editores |location=Hermosillo, Sonora and Mexico City|language=Spanish and English}}</ref> |
||
The same three stars are known in Latin America as "[[The Three Marys]] |
The same three stars are known in Spain and most of Latin America as "Las tres Marías" (Spanish for "[[The Three Marys]]"). |
||
The [[Ojibwa]] (Chippewa) Native Americans call this constellation Kabibona'kan, the Winter Maker, as its presence in the night sky heralds winter.{{citation needed|date=September 2012}} |
The [[Ojibwa]] (Chippewa) Native Americans call this constellation Kabibona'kan, the Winter Maker, as its presence in the night sky heralds winter.{{citation needed|date=September 2012}} |
||
Revision as of 20:12, 27 March 2013
| Constellation | |
 | |
| Abbreviation | Ori |
|---|---|
| Genitive | Orionis |
| Pronunciation | /ɒˈraɪ.ən/ |
| Symbolism | Orion, the Hunter |
| Right ascension | 5 |
| Declination | +5 |
| Quadrant | NQ1 |
| Area | 594 sq. deg. (26th) |
| Main stars | 7 |
| Bayer/Flamsteed stars | 81 |
| Stars with planets | 8 |
| Stars brighter than 3.00m | 8 |
| Stars within 10.00 pc (32.62 ly) | 8 |
| Brightest star | Rigel (β Ori) (0.12m) |
| Messier objects | 3 |
| Meteor showers | Orionids Chi Orionids |
| Bordering constellations | Gemini Taurus Eridanus Lepus Monoceros |
| Visible at latitudes between +85° and −75°. Best visible at 21:00 (9 p.m.) during the month of January.  | |
Orion, sometimes subtitled The Hunter, is a prominent constellation located on the celestial equator and visible throughout the world. It is one of the most conspicuous and most recognizable constellations in the night sky.[1] Its name refers to Orion, a hunter in Greek mythology. Its brightest stars are Beta (Rigel) and Alpha (Betelgeuse), a blue-white and red supergiant respectively. Many other of the brightest stars in the constellation are hot blue supergiant stars.
History and mythology

The distinctive pattern of Orion has been recognized in numerous cultures around the world, and many myths have been associated with it. It has also been used as a symbol in the modern world.
Mediterranean
Ancient Near East
The Babylonian star catalogues of the Late Bronze Age name Orion MULSIPA.ZI.AN.NA,[note 1] "The Heavenly Shepherd" or "True Shepherd of Anu" - Anu being the chief god of the heavenly realms.[2] The Babylonian constellation was sacred to Papshukal and Ninshubur, both minor gods fulfilling the role of 'messenger to the gods'. Papshukal was closely associated with the figure of a walking bird on Babylonian boundary stones, and on the star map the figure of the Rooster was located below and behind the figure of the True Shepherd—both constellations represent the herald of the gods, in his bird and human forms respectively.[3]
The stars of Orion were associated with Osiris, the sun-god of rebirth and afterlife, by the ancient Egyptians.[4][5][6]
Orion has also been identified with the Egyptian Pharaoh of the Fifth Dynasty called Unas who, according to the Pyramid Texts, became great by eating the flesh of his mortal enemies and then slaying and devouring the gods themselves. This was based on a belief in contiguous magic whereby consuming the flesh of great people would bring inheritance of their power.[5] After devouring the gods and absorbing their spirits and powers, Unas journeys through the day and night sky to become the star Sahu, or Orion.[4] The Pyramid Texts also show that the dead Pharaoh was identified with the god Osiris, whose form in the stars was often said to be the constellation Orion.[4]
The Armenians identified their forefather Hayk with Orion. Hayk is also the name of the Orion constellation in the Armenian translation of the Bible.[7]
The Bible mentions Orion three times, naming it "Kesil" (כסיל, literally - fool). Though, this name perhaps is etymologically connected with "Kislev", the name for the ninth month of the Hebrew calendar (i.e. November–December), which, in turn, may derive from the Hebrew root K-S-L as in the words "kesel, kisla" (כֵּסֶל, כִּסְלָה, hope, positiveness), i.e. hope for winter rains.): Job 9:9 ("He is the maker of the Bear and Orion"), Job 38:31 ("Can you loosen Orion`s belt?"), and Amos 5:8 ("He who made the Pleiades and Orion"). In ancient Aram, the constellation was known as Nephîlā′, the Nephilim may have been Orion's descendants.[8]
Greco-Roman antiquity

Orion's current name derives from Greek mythology, in which Orion was a gigantic hunter of primordial times.[9] Some of these myths relate to the constellation; one story tells that Orion was killed by a giant scorpion; the gods raised him and the Scorpion to the skies, as Scorpio/Scorpius. Yet other stories say Orion was chasing the Pleiades.[10]
The constellation is mentioned in Horace's Odes (Ode 3.27.18), Homer's Odyssey (Book 5, line 283) and Iliad, and Virgil's Aeneid (Book 1, line 535)
Africa
In ancient Egypt, the constellation of Orion was known to represent Osiris, who, after being killed by his evil brother Set, was revived by his wife Isis to live immortal among the stars.[11]
Middle East
In medieval Muslim astronomy, Orion was known as al-jabbar "the giant".[citation needed]
Asian antiquity
In China, Orion was one of the 28 lunar mansions Sieu (Xiu) (宿). It is known as Shen (參), literally meaning "three", for the stars of Orion's Belt. (See Chinese constellations)
The Chinese character 參 (pinyin shēn) originally meant the constellation Orion (Chinese: 參宿; pinyin: shēnxiù); its Shang dynasty version, over three millennia old, contains at the top a representation of the three stars of Orion's belt atop a man's head (the bottom portion representing the sound of the word was added later).[12]
The Rig Veda refers to the Orion Constellation as Mriga (The Deer).[13]
The Malay called Orion' Belt Bintang Tiga Beradik (the "Three Brother Star").[citation needed]
European folklore

In old Hungarian tradition, "Orion" is known as (magic) Archer (Íjász), or Reaper (Kaszás). In recently rediscovered myths he is called Nimrod (Hungarian "Nimród"), the greatest hunter, father of the twins "Hunor" and "Magor"). The "π" and "o" stars (on upper right) form together the reflex bow or the lifted scythe. In other Hungarian traditions, "Orion's belt" is known as "Judge's stick" (Bírópálca).[14]
In Scandinavian tradition, "Orion's belt" was known as Frigg's Distaff (Friggerock) or Freyja's distaff.[15]
The Finns call the Orion's belt and the stars below it as Väinämöisen viikate (Väinämöinen's scythe).[16] Another name for the asterism of Alnilam, Alnitak and Minkata is Väinämöisen vyö' (Väinämöinen's Belt) and the stars "hanging" from the belt as Kalevanmiekka (Kaleva's sword).
New World
The Seri people of northwestern Mexico call the three stars in the belt of this constellation Hapj (a name denoting a hunter) which consists of three stars: Hap (mule deer), Haamoja (pronghorn), and Mojet (bighorn sheep). Hap is in the middle and has been shot by the hunter; its blood has dripped onto Tiburón Island.[17]
The same three stars are known in Spain and most of Latin America as "Las tres Marías" (Spanish for "The Three Marys").
The Ojibwa (Chippewa) Native Americans call this constellation Kabibona'kan, the Winter Maker, as its presence in the night sky heralds winter.[citation needed]
To the Lakota Native Americans, Tayamnicankhu (Orion’s Belt) is the spine of a bison. The great rectangle of Orion are the bison's ribs; Orion's belt forms the bison's spine; The Pleiades star cluster in nearby Taurus is the bison’s head and Sirius in Canis Major, known as Tayamnisinte, is its tail.
Contemporary symbolism
The imagery of the belt and sword has found its way into popular western culture, for example in the form of the shoulder insignia of the 27th Infantry Division of the United States Army during both World Wars, probably owing to a pun on the name of the division's first commander, Major General John F. O'Ryan.[citation needed]
The defunct film distribution company Orion Pictures used the constellation as its logo.[citation needed]
In fiction
In J. R. R. Tolkien's mythology surrounding Middle-earth, Orion is known as Menelvagor, which is Sindarin for "The Swordsman in the Sky."[18]
In J.K. Rowling's Harry Potter series, one of the main Death Eater characters, Bellatrix Lestrange, is named after the gamma star in Orion.[citation needed]
Depictions
In artistic renderings, the surrounding constellations are sometimes related to Orion: he is depicted standing next to the river Eridanus with his two hunting dogs Canis Major and Canis Minor, fighting Taurus the bull. He is sometimes depicted hunting Lepus the hare. He also sometimes is depicted to have a lion's hide in his hand.
There are alternative ways to visualise Orion. From the Southern Hemisphere, Orion is oriented south-upward, and the belt and sword are sometimes called the saucepan or pot in Australia and New Zealand. Orion's Belt is called Drie Konings (Three Kings) or the Drie Susters (Three Sisters) by Afrikaans speakers in South Africa[19] and are referred to as les Trois Rois (the Three Kings) in Daudet's Lettres de Mon Moulin (1866). The appellation Driekoningen (the Three Kings) is also often found in 17th- and 18th-century Dutch star charts and seaman's guides. The same three stars are known in Spain and Latin America as "Las Tres Marías".
Characteristics
Orion is bordered by Taurus to the northwest, Eridanus to the southwest, Lepus to the south, Monoceros to the east, and Gemini to the northeast. Covering 594 square degrees, Canis Minor ranks twenty-sixth of the 88 constellations in size. The constellation boundaries, as set by Eugène Delporte in 1930, are defined by a polygon of 26 sides. In the equatorial coordinate system, the right ascension coordinates of these borders lie between 04h 43.3m and 06h 25.5m , while the declination coordinates are between 22.87° and −10.97°.[20] The constellation's three-letter abbreviation, as adopted by the International Astronomical Union in 1922, is "Ori".[21]
Orion is most visible in the evening sky from January to March,[22] winter in the Northern Hemisphere, and summer in the Southern Hemisphere. In the tropics (less than about 8° from the equator), the constellation transits at the zenith.
In the period May–July (summer in the Northern Hemisphere, winter in the Southern Hemisphere), Orion is in the daytime sky and thus not visible at most latitudes. However, for much of Antarctica in the Southern Hemisphere's winter months, the Sun is below the horizon even at midday. Stars (and thus Orion) are then visible at twilight for a few hours around local noon, low in the North. At the same time of day at the South Pole itself (Amundsen–Scott South Pole Station), Rigel is only 8° above the horizon, and the Belt sweeps just along it. In the Southern Hemisphere's summer months, when Orion is normally visible in the night sky, the constellation is actually not visible in Antarctica because the sun does not set at that time of year south of the Antarctic Circle.[23][24]
In countries close to the equator (e.g. Kenya, Indonesia, Colombia, Ecuador), Orion appears overhead in December around midnight and in the February evening sky.
Navigational aid
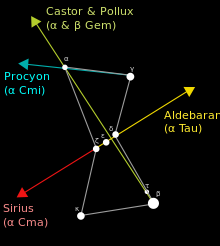
Orion is very useful as an aid to locating other stars. By extending the line of the Belt southeastward, Sirius (α CMa) can be found; northwestward, Aldebaran (α Tau). A line eastward across the two shoulders indicates the direction of Procyon (α CMi). A line from Rigel through Betelgeuse points to Castor and Pollux (α Gem and β Gem). Additionally, Rigel is part of the Winter Circle. Sirius and Procyon, which may be located from Orion by following imaginary lines (see map), also are points in both the Winter Triangle and the Circle.[25]
Major features

Orion's seven brightest stars form a distinctive hourglass-shaped asterism, or pattern, in the night sky. Four stars—Rigel, Betelgeuse, Bellatrix and Saiph—form a large roughly rectangular shape, in the centre of which lie the three stars of Orion's Belt—Alnitak, Alnilam and Mintaka. Descending from the 'belt' is a smaller line of three stars (the middle of which is in fact not a star but the Orion Nebula), known as the hunter's 'sword'.
Many of the stars are luminous hot blue supergiants, with the stars of the belt and sword forming the Orion OB1 Association. Standing out by its red hue, Betelgeuse may nevertheless be a runaway member of the same group.
Stars
- Betelgeuse, known alternatively by its Bayer designation Alpha Orionis, is a massive M-type red supergiant star nearing the end of its life. When it explodes it will even be visible during the day. It is the second brightest star in Orion, and is a semiregular variable star.[26] It serves as the "right shoulder" of the hunter it represents (assuming that he is facing the observer), and is the eighth brightest star in the night sky.[27]
- Rigel, which is also known as Beta Orionis, is a B-type blue supergiant that is the sixth brightest star in the night sky. Similar to Betelgeuse, Rigel is fusing heavy elements in its core and will pass its supergiant stage soon (on an astronomical timescale), either collapsing in the case of a supernova or shedding its outer layers and turning into a white dwarf. It serves as the left foot of Orion, the hunter.[28]
- Bellatrix was designated Gamma Orionis by Johann Bayer, but is known colloquially as the "Amazon Star". It is the twenty-seventh brightest star in the night sky.[29] Bellatrix is considered a B-type blue giant, though it is too small to explode in a supernova. Bellatrix's luminosity is derived from its high temperature rather than its radius,[30] a factor that defines Betelgeuse.[26] Bellatrix serves as Orion's left shoulder.[30]
- Mintaka garnered the name Delta Orionis from Bayer, even though it is the faintest of the three stars in Orion's Belt. It is a multiple star system, composed of a large B-type blue giant and a more massive O-type white star. The Mintaka system constitutes an eclipsing binary variable star, where the eclipse of one star over the other creates a dip in brightness. Mintaka is the westernmost of the three stars of Orion's Belt.[31]

- Alnilam was named Epsilon Orionis, a consequence of Bayer's wish to name the three stars in Orion's Belt (from north to south) in alphabetical order. Alnilam is a B-type blue supergiant; despite being nearly twice as far from the Sun as Mintaka and Alnitak, the other two belt stars, its luminosity makes it nearly equal in magnitude. Alnilam is losing mass quickly, a consequence of its size; it is approximately four million years old.[32]
- Alnitak was designated Zeta Orionis by Bayer, and is the easternmost star in Orion's Belt. It is a triple star some 800 light years distant, with the primary star being a hot blue supergiant and the brightest class O star in the night sky.
- Saiph was designated Kappa Orionis by Bayer, and serves as Orion's right foot. It is of a similar distance and size to Rigel, but appears much fainter, as its hot surface temperature (46,000°F or 26,000°C) causes it to emit most of its light in the ultraviolet region of the spectrum.
Of the lesser stars, Hatsya (or Iota Orionis) forms the tip of Orion's sword, whilst Meissa (or Lambda Orionis) forms Orion's head. In common with many other bright stars, the names Betelgeuse, Rigel, Saiph, Alnitak, Mintaka, Alnilam, Hatsya, and Meissa originate from the Arabic language.
| Proper Name |
Solar Radii | Apparent Magnitude |
~Distance (L Yrs) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Betelgeuse | 667 | 0.43 | 643 |
| Rigel | 78 | 0.18 | 772 |
| Bellatrix | 7.0 | 1.62 | 243 |
| Mintaka | ? | 2.23 (3.2/3.3) / 6.85 / 14.0 | 900 |
| Alnilam | 26 | 1.68 | 1359 |
| Alnitak | ? | 1.70/~4/4.21 | 800 |
| Saiph | 11 | 2.06 | 724 |
Belt
Orion's Belt or The Belt of Orion is an asterism within the constellation. It consists of the three bright stars ζ Ori (Alnitak), ε Ori (Alnilam), and δ Ori (Mintaka). Alnitak is approximately 800 light years away from earth and, including ultraviolet radiation, which the human eye cannot see, Alnitak is 100,000 times more luminous than the Sun.[33] Alnilam is approximately 1340 light years away from Earth, shines with magnitude 1.70, and with ultraviolet light is 375,000 times more luminous than the Sun.[32] Mintaka is 915 light years away and shines with magnitude 2.21. It is 90,000 times more luminous than the Sun and is a double star: the two orbit each other every 5.73 days.[31] Looking for Orion's Belt in the night sky is the easiest way to locate the constellation. In the Northern Hemisphere, Orion's Belt is best visible in the night sky during the month of January around 9:00 pm, when it is approximately around the local meridian.[1]
Just southwest of Alnitak lies Sigma Orionis, a multiple star system composed of five stars that have a combined apparent magnitude of 3.7 and lying 1150 light years distant. Southwest of Mintaka lies the quadruple star Eta Orionis.
Head
Three stars compose a small triangle that marks the head. The apex is marked by Meissa (Lambda Orionis), a hot blue giant of spectral type O8 III and apparent magnitude 3.54, which lies some 1100 light years distant. Phi-1 and Phi-2 Orionis make up the base. Also nearby is the very young star FU Orionis.
North Arrow
Together the 'Alnitak, Alnilam, & Almintaka', the 'Eta Orionis' form an arrow head, and with the 'M42, M43' at the lower end form the tail of an arrow. All together form an arrow that always points 'NORTH'. Therefore, it is used as navigational guide at night especially in the Sahara desert where there are not many natural signs.
Club
Stretching north from Betelgeuse are the stars that make up Orion's club. Mu Orionis marks the elbow, Nu and Xi mark the handle of the club, and Chi1 and Chi2 mark the end of the club. Just east of Chi1 is the Mira-type variable red giant U Orionis.
Shield
West from Bellatrix lie six stars all designated Pi Orionis (π1 Ori, π2 Ori, π3 Ori, π4 Ori, π5 Ori and π6 Ori) which make up Orion's shield.
Meteor showers
Around 20 October each year the Orionid meteor shower (Orionids) reaches its peak. Coming from the border with the constellation Gemini as many as 20 meteors per hour can be seen. The shower's parent body is Halley's Comet.[34]
Deep-sky objects
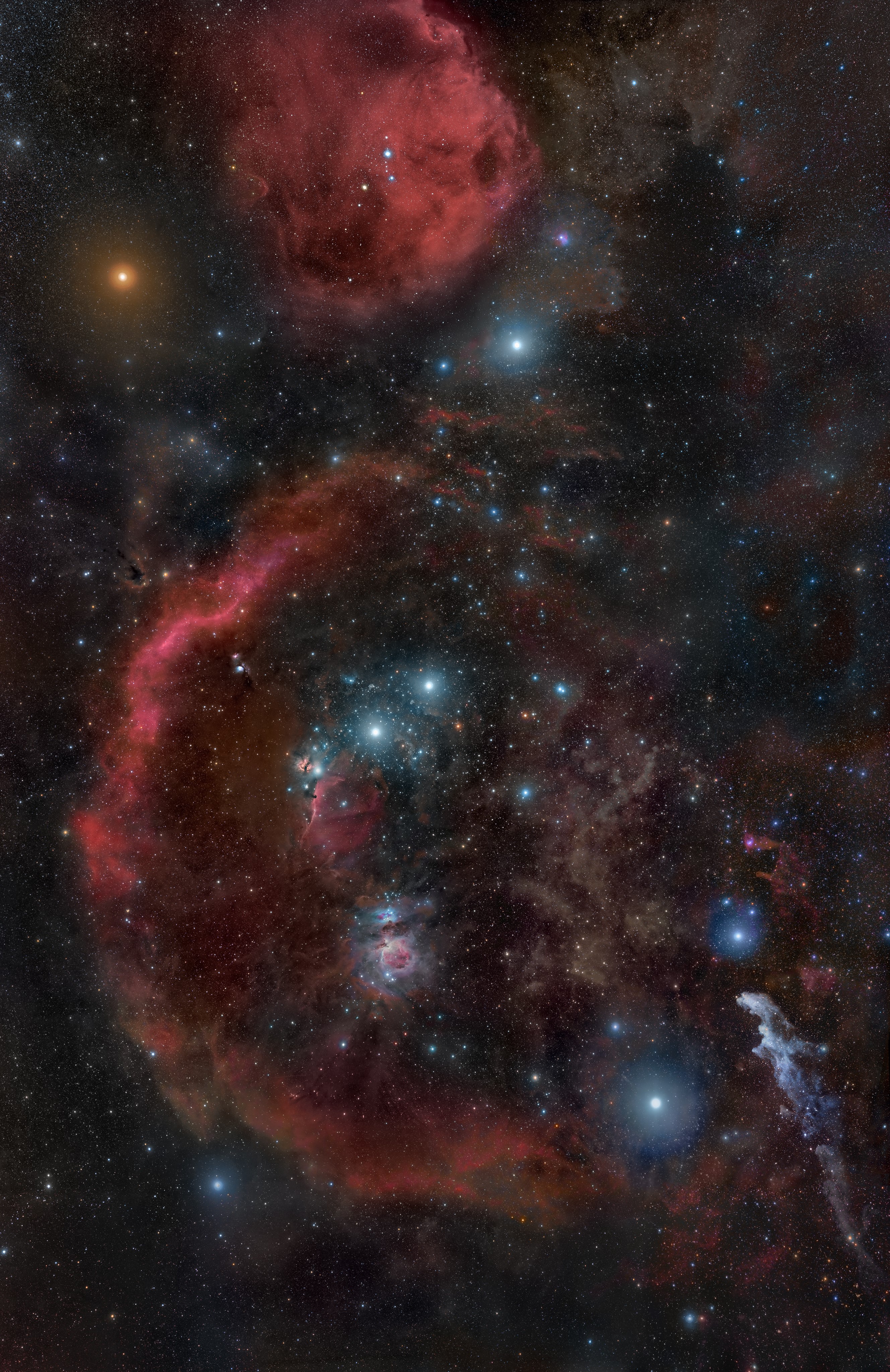

Hanging from Orion's belt is his sword, consisting of the multiple stars θ1 and θ2 Orionis, called the Trapezium and the Orion Nebula (M42). This is a spectacular object that can be clearly identified with the naked eye as something other than a star. Using binoculars, its clouds of nascent stars, luminous gas, and dust can be observed. The Trapezium cluster has many newborn stars, including several brown dwarfs, all of which are at an approximate distance of 1,500 light-years. Named for the four bright stars that form a trapezoid, it is largely illuminated by the brightest stars, which are only a few hundred thousand years old. Observations by the Chandra X-ray Observatory show both the extreme temperatures of the main stars—up to 60,000 Kelvin—and the star forming regions still extant in the surrounding nebula.[35]
M78 (NGC 2068) is a nebula in Orion. With an overall magnitude of 8.0, it is significantly dimmer than the Great Orion Nebula that lies to its south; however, it is at approximately the same distance, at 1600 light-years from Earth. It can easily be mistaken for a comet in the eyepiece of a telescope. M78 is associated with the variable star V351 Orionis, whose magnitude changes are visible in very short periods of time.[36] Another fairly bright nebula in Orion is NGC 1999, also close to the Great Orion Nebula. It has an integrated magnitude of 10.5 and is 1500 light-years from Earth. The variable star V380 Orionis is embedded in NGC 1999.[37]
Another famous nebula is IC 434, the Horsehead Nebula, near ζ Orionis. It contains a dark dust cloud whose shape gives the nebula its name.
Besides these nebulae, surveying Orion with a small telescope will reveal a wealth of interesting deep-sky objects, including M43, M78, as well as multiple stars including Iota Orionis and Sigma Orionis. A larger telescope may reveal objects such as Barnard's Loop and the Flame Nebula (NGC 2024), as well as fainter and tighter multiple stars and nebulae.
All of these nebulae are part of the larger Orion Molecular Cloud Complex, which is located approximately 1,500 light-years away and is hundreds of light-years across. It is one of the most intense regions of stellar formation visible in our galaxy.
Future
Orion is located on the celestial equator, but it will not always be so located due to the effects of precession of the Earth's axis. Orion lies well south of the ecliptic, and it only happens to lie on the celestial equator because the point on the ecliptic that corresponds to the June solstice is close to the border of Gemini and Taurus, to the north of Orion. Precession will eventually carry Orion further south, and by AD 14000 Orion will be far enough south that it will become invisible from the latitude of Great Britain.[38]
Further in the future, Orion's stars will gradually move away from the constellation due to proper motion. However, Orion's brightest stars all lie at a large distance from the Earth on an astronomical scale—much farther away than Sirius, for example. Orion will still be recognizable long after most of the other constellations—composed of relatively nearby stars—have distorted into new configurations, with the exception of a few of its stars eventually exploding as supernovae, for example Betelgeuse, which is predicted to explode sometime in the next million years.[39]
See also
- EURion constellation
- Orvandil
- Urania
- Orion Nebula in fiction
- Orion correlation theory
- Hubble 3D (2010), an IMAX film with an elaborate CGI "fly-through" of the Orion Nebula
References
- Explanatory notes
- ^ The determiner glyph for "constellation" or "star" in these lists is MUL (𒀯). See Babylonian star catalogues.
- Citations
- ^ a b Dolan, Chris. "Orion". Archived from the original on 2011-11-28. Retrieved 2011-11-28.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ John H. Rogers, "Origins of the ancient contellations: I. The Mesopotamian traditions", Journal of the British Astronomical Association 108 (1998) 9–28
- ^ Babylonian Star-lore by Gavin White, Solaria Pubs, 2008, page 218ff & 170
- ^ a b c The Oxford Guide: Essential Guide to Egyptian Mythology, Edited by Donald B. Redford, p302-307, Berkley, 2003, ISBN 0-425-19096-X
- ^ a b Mackenzie, Donald A. (1907). "Triumph of the Sun God". Egyptian Myth and Legend. Gresham Pub. Co. pp. 167–168. ISBN 0-517-25912-5.
{{cite book}}: External link in|chapterurl=|chapterurl=ignored (|chapter-url=suggested) (help) - ^ http://www.coldwaterschools.org/lms/planetarium/myth/orion.html;[dead link] http://www.constellationsofwords.com/Constellations/Orion.html
- ^ Vahan Kurkjian, "History of Armenia," Michigan, 1968
- ^ Peake's commentary on the Bible, 1962, page 260 section 221f.
- ^ Star Tales – Orion
- ^ Chandra :: Photo Album :: Constellation Orion
- ^ Mystery of the Sphinx. Documentary 2005. Morningstar Entertainment.
- ^ 漢語大字典 Hànyǔ Dàzìdiǎn (in Chinese), 1992 (p.163). 湖北辭書出版社和四川辭書出版社 Húbĕi Cishu Chūbǎnshè and Sìchuān Cishu Chūbǎnshè, re-published in traditional character form by 建宏出版社 Jiànhóng Publ. in Taipei, Taiwan; ISBN 957-813-478-9
- ^ Holay, P. V. "Vedic astronomers". Bulletin of the Astronomical Society of India. 26: 91–106. Bibcode:1998BASI...26...91H.
- ^ Toroczkai-Wigand Ede : Öreg csillagok ("Old stars"), Hungary (1915) reedited with Műszaki Könyvkiadó METRUM (1988).
- ^ Schön, Ebbe. (2004). Asa-Tors hammare, Gudar och jättar i tro och tradition. Fält & Hässler, Värnamo. p. 228.
- ^ http://www.ursa.fi/yhd/uranus/luennot%202004/perusteet/tahdet.htm
- ^ Moser, Mary B. (2005). Comcáac quih yaza quih hant ihíip hac: Diccionario seri-español-inglés (PDF) (in Spanish and English). Hermosillo, Sonora and Mexico City: Universidad de Sonora and Plaza y Valdés Editores.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^ "Encyclopedia of Arda: Swordsman of the Sky". Glyphweb.com. 1999-11-27. Retrieved 2012-05-16.
- ^ Three Kings and the Cape Clouds at psychohistorian.org
- ^ "Orion, Constellation Boundary" (Document). International Astronomical Union.
{{cite document}}: Unknown parameter|accessdate=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|url=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|work=ignored (help) - ^ Russell, Henry Norris (1922). "The New International Symbols for the Constellations". Popular Astronomy. 30: 469–71. Bibcode:1922PA.....30..469R.
- ^ Ellyard, David; Tirion, Wil (2008) [1993]. The Southern Sky Guide (3rd ed.). Port Melbourne, Victoria: Cambridge University Press. p. 4. ISBN 978-0-521-71405-1.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ A Beginner's Guide to the Heavens in the Southern Hemisphere
- ^ The Evening Sky Map Southern Hemisphere Edition
- ^ Orion Constellation
- ^ a b "Variable Star of the Month, Alpha Ori". Variable Star of the Season. American Association of Variable Star Observers. 2000. Retrieved 2009-02-26. [dead link]
- ^ "Betelgeuse". Chris Dolan's Constellations. University of Wisconsin. 2009. Retrieved 2009-02-26.
- ^ "Rigel". Jim Kaler's Stars. University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign Campus. 2009. Retrieved 2009-02-26.[dead link]
- ^ "Bellatrix". Chris Dolan's Constellations. University of Wisconsin. 2009. Retrieved 2009-02-26.
- ^ a b "Bellatrix". Jim Kaler's Stars. University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign Campus. 2009. Retrieved 2009-02-26.[dead link]
- ^ a b "Mintaka". Jim Kaler's Stars. University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign Campus. 2009. Archived from the original on 2011-11-28. Retrieved 2011-11-28.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b "Alnilam". Jim Kaler's Stars. University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign Campus. 2009. Archived from the original on 2011-11-28. Retrieved 2011-11-28.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Alnitak". Stars.astro.illinois.edu. Retrieved 2012-05-16.
- ^ Jenniskens, Peter (September 2012). "Mapping Meteoroid Orbits: New Meteor Showers Discovered". Sky & Telescope: 22.
- ^ Wilkins, Jamie; Dunn, Robert (2006). 300 Astronomical Objects: A Visual Reference to the Universe (1st ed.). Buffalo, New York: Firefly Books. ISBN 978-1-55407-175-3.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help) - ^ Levy 2005, pp. 99–100.
- ^ Levy 2005, p. 107.
- ^ "Precession". Myweb.tiscali.co.uk. Retrieved 2012-05-16.
- ^ Wilkins, Alasdair. "Earth may soon have a second sun". io9. Space Porn.
- Bibliography
- Levy, David H. (2005). Deep Sky Objects. Prometheus Books. ISBN 1-59102-361-0.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help)
- Ian Ridpath and Wil Tirion (2007). Stars and Planets Guide, Collins, London. ISBN 978-0-00-725120-9. Princeton Universitl Press, Princeton. ISBN 978-0-691-13556-4.
External links
- The Deep Photographic Guide to the Constellations: Orion
- Melbourne Planetarium: Orion Sky Tour
- Views of Orion from other places in our Galaxy
- The clickable Orion
- Star Tales – Orion
- Deep Widefield image of Orion
- Constellations of Words. Orion
- APOD - Orion: Head to Toe
- Orion Constellation at Constellation Guide
- Beautiful Astrophoto: Zoom Into Orion


