Extermination camp: Difference between revisions
→Background: Removed paragraph on extermination, this is not supported by the Wansee document at all and is conjecture by the author. Everything in the third paragraph is pure author conjecture and not supported by any documentation. |
→Background: This background section on Action T4 must be removed, the T4 document does not say anything at all how this is being represented it clearly does not direct the murder of healthy people Tag: section blanking |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
While not on the same scale as that perpetrated by the Nazis, the [[Fascism|fascist]] [[Ustaše]] forces of the [[Independent State of Croatia]] also operated extermination camps. |
While not on the same scale as that perpetrated by the Nazis, the [[Fascism|fascist]] [[Ustaše]] forces of the [[Independent State of Croatia]] also operated extermination camps. |
||
== Background == |
|||
{{Main|Nisko Plan}} |
|||
[[File:Birkenau25August1944.jpg|thumb|U.S. aerial photograph of Auschwitz II (Birkenau) showing crematoria II and III]] |
|||
Initiated in 1939 by the [[Action T4]] programme to exterminate "[[life unworthy of life]]" (in German: "Lebensunwertes Leben") a Nazi designation for the segments of populace which had no [[right to life]] and thus were to be "[[euthanized]]". Initially [[Jews]] along with numerous other groups, were interned in [[concentration camps]] or restricted to ghettos. However, in 1941 the Nazis 'solved' ''die Endlösung der Judenfrage'' ([[Final Solution|The Final Solution of the Jewish Question]]) by the systematic killing of Europe's Jews. This adaption of the [[Action T4]] programme by Nazi leaders during the first half of 1941, was derived from the then accepted ideas of [[racial hygiene]] and [[racial science]]. The initial, formal killings of the Final Solution were undertaken by the SS ''[[Einsatzgruppen]]'' (Task Forces) death squads who followed the [[Wehrmacht]] during the ''[[Operation Barbarossa]]'' invasion of the USSR in June 1941. |
|||
== Definitions == |
== Definitions == |
||
Revision as of 14:39, 10 December 2014
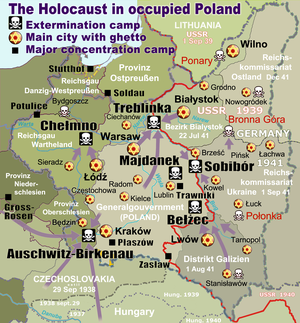
Extermination camps (or death camps) were camps during World War II (1939–45) built by Nazi Germany to systematically kill millions of people by execution (primarily by gassing) and extreme work under starvation conditions:(. Initiated with the Action T4 programme, it was adapted, expanded and applied to victims from many groups; however, Jews became the main Nazi targets. This genocide of the Jewish people was the Third Reich's "Final Solution to the Jewish question".[1] The Nazi attempts at Jewish genocide are now collectively known as the Holocaust.[2]
While not on the same scale as that perpetrated by the Nazis, the fascist Ustaše forces of the Independent State of Croatia also operated extermination camps.
Definitions
The Nazis distinguished between extermination camps and concentration camps.
The terms extermination camp (Vernichtungslager) and death camp (Todeslager) are interchangeable usages, each referring to camps whose primary function was genocide, not for punishing crime or containing political prisoners, but for the systematic killing of the prisoners delivered there. The Nazis did not expect the majority of prisoners taken to the Belzec, Sobibór or Treblinka extermination camps to survive more than a few hours beyond arrival.[3] The first extermination camps were under the direct command of SS–Polizei-führer Globocnik, and operated by SS Police battalions and Trawnikis – volunteers from Eastern Europe.
These differed from concentration camps, such as Dachau and Belsen, which were initially prison camps for people defined as socially or politically undesirable in Nazi society. The SS-Totenkopfverbände managed the Nazi concentration camps such as Dachau and Ravensbrück. As early as September 1942, Dr. Johann Paul Kremer, M.D., an SS physician, witnessed a gassing of prisoners, and in his diary wrote: "They don't call Auschwitz the camp of annihilation [das Lager der Vernichtung] for nothing!"[4] The distinction was evident during the Nuremberg trials, when Dieter Wisliceny (a deputy to Adolf Eichmann) was asked to name the extermination camps, and he identified Auschwitz and Majdanek as such. Then, when asked "How do you classify the camps Mauthausen, Dachau, and Buchenwald?" he replied, "They were normal concentration camps, from the point of view of the department of Eichmann."[5]
Extermination camps are distinguished from the Arbeitslager (forced labor camps) established in German-occupied countries to use the prisoners, including prisoners of war, as slave labor. In most camps (excepting PoW camps for the non-Soviet soldiers and certain labor camps), the high death rates resulted from execution, starvation, disease, exhaustion, and physical brutality.
The death camps

In the early years of the Holocaust, the Jews were primarily sent to concentration camps, but from 1942 onwards they were mostly deported to the extermination camps. For political and logistical reasons, the most infamous extermination camps Nazi Germany built were in Occupied Poland, where most of the intended victims lived; Poland had the greatest European Jewish populace.[6] On top of that, the camps outside of the Third Reich proper could be kept secret from the German civil populace.[7]
Operationally, there were two types of death camp.
Pure extermination camps

Gas vans producing poisonous carbon monoxide exhaust fumes were initially developed at the Chełmno extermination camp, before being used elsewhere.[8]
The camps at Treblinka, Bełżec, and Sobibór were constructed during Operation Reinhard (October 1941 – November 1943), for the extermination of Poland's Jews. Prisoners were promptly killed upon arrival. Initially, the camps used carbon monoxide gas chambers; at first, the corpses were buried, but then incinerated atop pyres. Later, gas chambers and crematoria were built in Treblinka and Belzec; Zyklon-B was used in Belzec.[9]
Whereas the Auschwitz II (Auschwitz–Birkenau) and Majdanek camps were parts of a labor camp complex, the Operation Reinhard camps and the Chełmno camp were exclusively for the quick extermination of many people (primarily Jews) within hours of their arrival.[10] Some able-bodied prisoners delivered to the death camp were not immediately killed, but were forced into labor units (Sonderkommando) to work at the extermination process, removing corpses from the gas chambers and burning them. Because the extermination camps were physically small (only several hundred metres long and wide) and equipped with minimal housing and support installations, the Nazis deceived the prisoners upon their arrival, telling them that they were at a temporary transit stop, and soon would continue to an Arbeitslager (work camp) farther east.
Concentration–extermination camps
Nazi
Some prisoners were selected for slave labor, instead of immediate death; they were kept alive as camp inmates, available to work wherever the rulers required. Three extermination camps – Auschwitz, Majdanek, and the Ustaše run Jasenovac – were later retrofitted with Zyklon-B gas chambers and crematoria, remaining operational until war's end in 1945.[9]
Maly Trostenets extermination camp in the USSR initially operated as a prison camp. It became an extermination camp later in the war with victims initially undergoing mass shootings. This was supplemented with exhaust fume gassing in a van from October 1943.
Sajmište concentration camp operated by the Nazis in Yugoslavia had a gas van stationed for use from March to June 1942. Once the industrial killings were completed, the van was returned to Berlin. After a refit the van was then sent to Maly Trostinets for use at the camp there.
Janowska concentration camp near Lwow in Poland operated a selection process for the detainees. Some prisoners were assigned to work. Others were either transported to Belzec or victims of mass shootings on two slopes in the Piaski sand-hills behind the camp.
The Warsaw concentration camp was an associated group of the German Nazi concentration camps, possibly including an extermination camp, located in German-occupied Warsaw. The various details regarding the camp are very controversial and remain subject of historical research and public debate.
Ustaše

On 10 April 1941, the Independent State of Croatia (NDH) was established, supported by Nazi Germany and fascist Italy, and adopted similar racial and political doctrines. Camps were established by the fascist Ustaše government for contributing to the Nazi "final solution" to the "Jewish problem", the killing of Roma people and the elimination of political opponents, but most significantly to achieve the destruction of the Serbian population of the NDH.[11][12] The degree of cruelty with which the Serb population was persecuted shocked even the Germans.[13] The sadistic brutality of the Ustaše shocked even the Nazis.[14]
Jadovno concentration camp was located in a secluded area about 20 kilometres (12 mi) from the town of Gospić. It held thousands of Serbs and Jews over a period of 122 days from May to August 1941. Prisoners were usually but by no means exclusively killed by being pushed into deep ravines located near the camp.
Jasenovac concentration camp was a complex of five sub-camps that replaced Jadovno. Many inmates arriving at Jasenovac were scheduled for systematic extermination. An important criterion for selection was the duration of a prisoner's anticipated detention. Strong men capable of labour and sentenced to less than three years of incarceration were allowed to live. All inmates with indeterminate sentences or sentences of three years or more were immediately scheduled for execution, regardless of their fitness.[15] Some of the mass executions were mechanical following Nazi methodology. Others were performed manually utilising tools such as mallets and agricultural knives and often in conjunction with throwing the victims off the end of a ramp into the River Sava.
Soviet Union
Robert Conquest[16] argues that the regime in labour camps in the Soviet Union, principally those in Siberia, was designed to bring about the death of prisoners after extracting 3–6 months' labour from them. Aleksandr Solzhenitsyn [17] concurs with him.
Other
More recently the Khmer Rouge regime in Cambodia made extensive use of camps in which a high proportion of the inmates perished. High inmate death rates are a reported feature of internment camps for political prisoners in North Korea.
Extermination
Nazi
Development


Heinrich Himmler visited the outskirts of Minsk in 1941 to witness mass shooting. He was told by the commanding officer there that the shootings were proving psychologically damaging to those being asked to pull the triggers. Thus Himmler knew another method of mass killing was required.[18] After the war, the diary of the Auschwitz Commandant, Rudolf Höss, revealed that psychologically "unable to endure wading through blood any longer", many Einsatzkommandos – the killers – either went mad or killed themselves.[19]
The Nazis had first used gassing with carbon monoxide cylinders to kill 70,000 disabled people in Germany in what they called a 'euthanasia programme' to disguise that mass murder was taking place. Despite the lethal effects of carbon monoxide, this was seen as unsuitable for use in the East due to the cost of transporting the carbon monoxide in cylinders.[18]
Each extermination camp operated differently, yet each had designs for quick and efficient industrialized killing. While Höss was away on an official journey in late August 1941 his deputy, Karl Fritzsch, tested out an idea. At Auschwitz clothes infected with lice were treated with crystallised prussic acid. The crystals were made to order by the IG Farben chemicals company for which the brand name was Zyklon-B. Once released from their container, Zyklon-B crystals in the air released a lethal cyanide gas. Fritzch tried out the effect of Zyklon B on Soviet POWs, who were locked up in cells in the basement of the bunker for this experiment. Höss on his return was briefed and impressed with the results and this became the camp strategy for extermination as it was also to be at Majdanek. Besides gassing, the camp guards continued killing prisoners via mass shooting, starvation, torture, etc.[20]
Operation
SS Obersturmführer Kurt Gerstein, of the Institute for Hygiene of the Waffen-SS, during the war told a Swedish diplomat of life in a death camp, of how, on 19 August 1942, he arrived at Belzec extermination camp (which was equipped with carbon monoxide gas chambers) and was shown the unloading of 45 train cars filled with 6,700 Jews, many already dead, but the rest were marched naked to the gas chambers, where:
Unterscharführer Hackenholt was making great efforts to get the engine running. But it doesn't go. Captain Wirth comes up. I can see he is afraid, because I am present at a disaster. Yes, I see it all and I wait. My stopwatch showed it all, 50 minutes, 70 minutes, and the diesel [engine] did not start. The people wait inside the gas chambers. In vain. They can be heard weeping, "like in the synagogue", says Professor Pfannenstiel, his eyes glued to a window in the wooden door. Furious, Captain Wirth lashes the Ukrainian [prisoner] assisting Hackenholt twelve, thirteen times, in the face. After 2 hours and 49 minutes – the stopwatch recorded it all – the diesel started. Up to that moment, the people shut up in those four crowded chambers were still alive, four times 750 persons, in four times 45 cubic meters. Another 25 minutes elapsed. Many were already dead, that could be seen through the small window, because an electric lamp inside lit up the chamber for a few moments. After 28 minutes, only a few were still alive. Finally, after 32 minutes, all were dead ... Dentists [then] hammered out gold teeth, bridges, and crowns. In the midst of them stood Captain Wirth. He was in his element, and, showing me a large can full of teeth, he said: "See, for yourself, the weight of that gold! It's only from yesterday, and the day before. You can't imagine what we find every day – dollars, diamonds, gold. You'll see for yourself!" [21]

Auschwitz Camp Commandant Rudolf Höss reported that the first time Zyklon B gas was used on the Jews, many suspected they were to be killed – despite having been deceived into believing they were to be deloused and then returned to the camp. As a result, the Nazis identified and isolated "difficult individuals" who might alert the prisoners, and removed them from the mass – lest they incite revolt among the deceived majority of prisoners en route to the gas chambers. The "difficult" prisoners were led to a site out of view to be killed off discreetly.
A prisoner Sonderkommando (Special Detachment) effected the most of the processes of extermination; they accompanied the Jews into the gas chamber (a chamber room, usually outfitted to appear as a large shower room, with (nonworking) water nozzles, tile walls, etc.) and remained with them until just before the chamber door closed. To psychologically maintain the "calming effect" of the delousing deception, an SS guard stood at the door, as if awaiting the prisoners. The Sonderkommando hurried them to undress and enter the "shower room" as quickly as possible; to that effect, they also assisted the aged and the very young in undressing.[22]
To further persuade the prisoners that nothing harmful was happening, the Sonderkommando deceived them with small talk about camp life. Fearing that the delousing "disinfectant" might harm their children, many mothers hid their infants beneath their piled clothes. Camp Commandant Höss reported that the "men of the Special Detachment were particularly on the look-out for this", and encouraged the women to take their children into the "shower room". Likewise, the Sonderkommando comforted older children who might cry "because of the strangeness of being undressed in this fashion".[23]
Yet, not every prisoner was deceived by such psychological warfare tactics; Commandant Höss reported of Jews "who either guessed, or knew, what awaited them, nevertheless ... [they] found the courage to joke with the children, to encourage them, despite the mortal terror visible in their own eyes". Some women would suddenly "give the most terrible shrieks while undressing, or tear their hair, or scream like maniacs"; the Sonderkommando immediately took them away for execution by shooting.[24] In such circumstances, others, meaning to save themselves at the gas chamber's threshold, betrayed the identities and "revealed the addresses of those members of their race still in hiding".[25]
Once the door of the filled gas chamber was sealed, pellets of Zyklon B were dropped through special holes in the roof. Nazi regulations required that the Camp Commandant supervise the preparations, the gassing (through a peephole), and the aftermath looting of the corpses. Commandant Höss reported that the gassed victims "showed no signs of convulsion"; the Auschwitz camp physicians attributed that to the "paralyzing effect on the lungs" of the Zyklon-B gas, which killed before the victim began suffering convulsions.[26]
As a matter of political training, some high-ranked Nazi Party leaders and SS officers were sent to Auschwitz–Birkenau to witness the gassings; Höss reported that "all were deeply impressed by what they saw ... [yet some] ... who had previously spoken most loudly, about the necessity for this extermination, fell silent once they had actually seen the 'final solution of the Jewish problem'." As the Auschwitz Camp Commandant Rudolf Höss justified the extermination by explaining the need for "the iron determination with which we must carry out Hitler's orders"; yet saw that even "[Adolf] Eichmann, who certainly [was] tough enough, had no wish to change places with me."[27]
Corpse disposal
After the gassings, the Sonderkommando removed the corpses from the gas chamber, then extracted any gold teeth, and – to minimize the distinct smell of burning human hair – they shaved the corpses, before delivering them to the crematoria or to the fire pits, thus maintaining secret the existence of the extermination camp. The Sonderkommando were responsible for burning the corpses, and stoking the fires, draining body fat, and turning over the "mountain of burning corpses" for even combustion and a peak fire-temperature. Commandant Höss was impressed by the diligence of the Sonderkommando prisoners, despite their being "well aware that ... they, too, would meet exactly the same fate", yet always doing their jobs "in such a matter-of-course manner that they might, themselves, have been the exterminators". Höss further reported that the men ate and smoked "even when engaged in the grisly job of burning corpses", in the course of which they occasionally encountered the corpse of a relative, but, although they "were obviously affected by this ... it never led to any incident" of revolt, as in the case of a Sonderkommando who so encountered the corpse of his wife, yet behaved "as though nothing had happened".[28]
The corpses were incinerated in crematoria and the ashes either buried or scattered; yet, at Sobibór, Treblinka, Belzec, and Chełmno, the corpses were incinerated on pyres. The efficiency of industrialised killing at Auschwitz-Birkenau produced too many corpses to adequately burn or bury, so the crematoria (manufactured to specification by Topf und Söhne) were put into use to handle the disposals around the clock, day and night.[29]
Ustaše


Most commonly Jadovno victims were bound together in a line and the first few victims were murdered with rifle butts or other objects. Afterwards, an entire row of inmates were pushed into the ravine. Hand grenades were hurtled inside in order to kill off the victims. Dogs would also be thrown in to feed on the wounded and the dead.[30][31] In some cases, inmates were also killed by gunfire, as well as with knives and blunt objects.
The Jasenovac mechanical means of mass killing included following Nazi methods and the use initially of gas vans and later Zyklon B in stationary gas chambers. The Jasenovac guards have also been reported to have cremated living inmates in the crematorium. A notable difference of the Ustaše guards compared to the SS at the Nazi camps was the widespread use of manual methods in the mass killings. These involved instruments such as mallets and agricultural knives which evolved to often to be done in a manner where still alive victims were thrown off the end of a ramp into the River Sava.
Death toll
Nazi
The estimated total number of people executed in the Nazi camps in the table below is over three million:
| Camp | Estimated deaths |
Operational | Occupied territory | Current country of location | Primary means for mass killings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Auschwitz–Birkenau | 1,100,000[32] | May 1940 – January 1945 | Province of Upper Silesia | Poland | Zyklon B gas chambers |
| Bełżec | 600,000[33] | 17 March 1942 – end of June 1943 | General Government district | Poland | Carbon monoxide gas chambers |
| Chełmno | 320,000[34] | 8 December 1941 – March 1943, June 1944 – 18 January 1945 |
District of Reichsgau Wartheland | Poland | Carbon monoxide vans |
| Majdanek | 80,000 [35] | October 1, 1941 — July 22, 1944 | General Government district | Poland | Zyklon B gas chambers |
| Maly Trostinets | 200,000[36] | Summer of 1941 to 28 June 1944 | District of Reichskommissariat Ostland | Belarus | Mass shootings, Carbon monoxide van |
| Sajmište | 23,000– 47,000 |
28 October 1941–July 1944 | Independent State of Croatia | Serbia | Carbon monoxide van |
| Sobibór | 250,000[37] | 16 May 1942 – 17 October 1943 | General Government district | Poland | Carbon monoxide gas chambers |
| Treblinka | 800,000[38] | 22 July 1942 – 19 October 1943 | General Government district | Poland | Carbon monoxide gas chambers |
| Total | 3,115,000–3,215,000 [39][40] | ||||
At the Maly Trostenets extermination camp in Belarus, USSR, some 65,000 Jews were executed, whilst the estimated number of gentiles (non-Jews, i.e. communists, priests, soldiers, etc.) varies between 100,000 to 400,000.[41]
Ustaše
Death toll estimates vary for a number of reasons such as lack of records and political bias. Estimates for Jadovno concentration camp generally offer a range of 10,000 – 72,000 deaths at the camp over a period of 122 days (May to August 1941). The United States Holocaust Memorial Museum (USHMM) in Washington, D.C. presently estimates that the Ustaša regime murdered between 77,000 and 99,000 people at Jasenovac concentration camp between 1941 and 1945.[42] The Jasenovac Memorial Site quotes a similar figure of between 80,000 and 100,000 victims.[43] The television documentary, "Nazi Collaborators" on Dinko Sakic stated that over 300,000 people were killed at Jasenovac.[14]
The post-war period

In 1944, as the Red Army advanced into eastern Poland, the Nazis either partly or completely dismantled the eastern-most extermination camps to conceal the mass killings done there, and the buried remains (excepting Auschwitz–Birkenau, which was partially demolished in 1947). Because most of the death camps in the far east of the country (Belzec and Sobibór) had been constructed with local lumber, the physical installations were quickly deteriorated, eroded, and destroyed, by the natural elements.
In the post-war period, the Communist government of the People's Republic of Poland (1944–90) created monuments at the extermination camp sites, that mentioned no ethnic, religious, or national particulars of the Nazi victims. The extermination camps sites have been accessible to Western visitors to Poland; the camps are tourist attractions, especially the most-infamous Nazi death camp, Auschwitz concentration camp, near the town of Oświęcim (Auschwitz). March of the Living is organized yearly since 1988. In the early 1990s, Jewish Holocaust organisations disputed with Polish Catholic groups about: "What religious symbols of martyrdom are appropriate as memorials in a Nazi death camp such as Auschwitz?" The Jews opposed to the erection of Christian memorials at a quarry adjacent to the Auschwitz camp, wherein featured the Auschwitz cross – a Roman cross erected near death camp Auschwitz I, where mostly Poles were killed, rather than at Auschwitz II (Auschwitz-Birkenau), where mostly Jews were killed.
Holocaust denial
Holocaust deniers are people and organisations who assert that the Holocaust did not occur, or that it did not occur in the historically recognized manner and extent.
Extermination camp research is difficult because of extensive attempts by the SS and Nazi regime to conceal the existence of the extermination camps. As a result of Sonderaktion 1005, camps were dismantled, records destroyed, and mass graves were dug up. Furthermore, extermination camps that remained uncleared were liberated by Soviet troops, who had different standards of documentation and openness than the Western allies. The existence of the extermination camps is firmly established by testimonies of camp survivors and Final Solution perpetrators, material evidence (the remaining camps, etc.), Nazi photographs and films of the killings,[citation needed] and camp administration records.
Holocaust deniers often start by pointing out legitimate public misconceptions about the extermination camps. For example, widely published images in America were mostly of typhoid victims and Soviet POWs at the Buchenwald and Dachau concentration camps – the first to be liberated by American troops and the most available imagery in America. In early news reports and for years afterwards these images were often used by the news media somewhat inaccurately in conjunction with descriptions of extermination camps and Jewish suffering. Holocaust deniers, after pointing out such common errors, put it forward as evidence that extermination camps did not exist and the limited evidence about them is mostly a hoax arising out of a deliberate Jewish conspiracy.
Holocaust denial is highly discredited by scholars and is a criminal offence in Austria, Belgium, France, Germany, Lithuania, the Netherlands, Poland, and Switzerland.
See also
- German camps in occupied Poland during World War II
- Soap made from human corpses
- World War II crimes in Poland
References
- ^ " Die Endlösung der Judenfrage" – Adolf Hitler (In English, "The final solution of the Jewish problem"). Furet, François. Unanswered Questions: Nazi Germany and the Genocide of the Jews. Schocken Books (1989), p. 182; ISBN 978-0-8052-4051-1
- ^ Doris Bergen, Germany and the Camp System, part of Auschwitz: Inside the Nazi State, Community Television of Southern California, 2004-2005
- ^ Minerbi, Alessandra (2005). A New Illustrated History of the Nazis: Rare Photographs of the Third Reich. David & Charles. p. 168.
- ^ "Diary of Johann Paul Kremer (September 5, 1942)". Holocaust-history.org. March 2, 1999. Retrieved August 27, 2013.
- ^ Overy, Richard. Interrogations, p. 356–7. Penguin 2002. ISBN 978-0-14-028454-6
- ^ "The evacuation of Jews to Poland", Jewish Virtual Library.'.' Retrieved 2009-07-28.
- ^ Ellen Land-Weber, "Conditions for Polish Jews During WWII" in To Save a Life: Stories of Holocaust Rescue.'.' Retrieved 2009-07-28.
- ^ Lifshitz, pp. 101–102
- ^ a b See: M. Lifshitz, "Zionism" (משה ליפשיץ, "ציונות") p. 304. Compare with H. Abraham, "History of Israel and the nations in the era of Holocaust and uprising (חדד אברהם, "תולדות ישראל והעמים בתקופת השואה והתקומה")"
- ^ Aktion Reinhard: Belzec, Sobibór & Treblinka, Nizkor Project
- ^ Genocide and Fascism; The Eliminationist Drive in Fascist Europe by Aristotle Kallis, Routledge, New York, NY 2009 pages 236-244
- ^ M. Shelach (ed.), "History of the holocaust: Yugoslavia".
- ^ Cox 2007, p. 225.
- ^ a b "Nazi Collaborators", Yesterday TV, UK, 12.00, 11 Jan 2014
- ^ State Commission, 1946, pp. 9-11, 46-47
- ^ Conquest, Robert. Kolyma: The Arctic Death Camps.
- ^ Solzhenitsyn, Aleksandr. The Gulag Archipelago.
- ^ a b "Auschwitz: The Nazis and the Final Solution" Yesterday television channel, 18:00, 18 November 2013
- ^ Hoss [sic], Rudolf (2005). "I, the Commandant of Auschwitz," in Lewis, Jon E. (ed.), True War Stories, p. 321. Carroll & Graf Publishers. ISBN 978-0-7867-1533-6.
- ^ Borkin, Joseph (1978). The Crime and Punishment of IG Farben. New York: Free Press. ISBN 978-0-02-904630-2.
- ^ The Nazi Sourcebook: An Anthology of Texts. Routledge. 2002. p. 354. ISBN 978-0-415-22213-6.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|authors=ignored (help) - ^ Höss, pp. 321–322.
- ^ Höss, pp. 322–323.
- ^ Höss, p. 323.
- ^ Höss, p. 324.
- ^ Höss, pp. 320, 328.
- ^ Höss, p. 328.
- ^ Höss, pp. 325–326.
- ^ Berenbaum, Michael; Yisrael Gutman (1998). Anatomy of the Auschwitz Death Camp. Indiana University Press. p. 199. ISBN 978-0-253-20884-2.
- ^ Mojzes 2011, p. 60.
- ^ Mojzes 2009, p. 160.
- ^ "It is estimated that the SS and police deported at a minimum 1.3 million people to Auschwitz complex between 1940 and 1945. Of these, the camp authorities murdered 1.1 million." (Number includes victims killed in other Auschwitz camps.) Template:WebCite
- ^ Between March and December 1942, the Germans deported some 434,500 Jews, and an indeterminate number of Poles and Roma (Gypsies) to Belzec, to be killed. http://www.ushmm.org/wlc/article.php?lang=en&ModuleId=10005191
- ^ In total, the SS and the police killed some 152,000 people in Chełmno. http://www.ushmm.org/wlc/en/article.php?ModuleId=10005194
- ^ A recent study reduced the estimated number of deaths at Majdanek, in "Majdanek Victims Enumerated", by Pawel P. Reszka, Lublin, in the Gazeta Wyborcza 12 December 2005, reproduced on the site of the Auschwitz–Birkenau Museum, Lublin scholar Tomasz Kranz established that figure, which the Majdanek museum staff consider authoritative. Earlier calculations were greater: ca. 360,000, in a much-cited 1948 publication by Judge Zdzisław Łukaszkiewicz, of the Main Commission for the Investigation of Nazi Crimes in Poland; and ca. 235,000, in a 1992 article by Dr. Czesaw Rajca, formerly of the Majdanek museum.
- ^ Yad Vashem, "Maly Trostinets" (PDF). Retrieved September 1, 2013.
- ^ In all, the Germans and their auxiliaries killed at least 167,000 people at Sobibór. http://www.ushmm.org/wlc/article.php?lang=en&ModuleId=10005192
- ^ The Höfle Telegram indicates some 700,000 killed by 31 December 1942, yet the camp functioned until 1943, hence the true deaths total likely is greater. "Reinhard: Treblinka Deportations". Nizkor.org. Retrieved 2012-12-20.
- ^ Holocaust Encyclopedia, NAZI CAMPS. United States Holocaust Memorial Museum.
- ^ Terese Pencak Schwartz, The Holocaust: Non-Jewish Victims. Jewish Virtual Library.
- ^ See Maly Trostinec at the camps Yad Vashem website
- ^ US Holocaust Memorial Museum: Jasenovac
- ^ "Official Website of the Jasenovac Memorial Site".
Bibliography
- Bartov, Omer (ed.). The Holocaust: origins, implementation, aftermath. London: Routledge, 2000 ISBN 0-415-15035-3
- Gilbert, Martin. Holocaust Journey: travelling in search of the past, Phoenix, 1997. An account of the sites of the extermination camps as they are today, plus historical information about them and about the fate of the Jews of Poland.
- Klee, Ernst. "'Turning the tap on was no big deal': the gassing doctors during the Nazi period and afterwards," in Dachau Review, vol. 2, 1990.
- Levi, Primo. The Drowned and the Saved. London: Michael Joseph, 1986 ISBN 0-7181-3063-4
External links
- The Implementation of the Final Solution: The Death Camps on the Yad Vashem website
- The Holocaust History Project
- Holocaust and concentration camps information
- The Holocaust Education & Archive Research Team
- Official U.S. National Archive Footage of Nazi camps
- Belzec, Sobibor, Treblinka. Holocaust Denial and Operation Reinhard.




