2007 Kenyan presidential election: Difference between revisions
removed Category:Elections in Kenya; added Category:Presidential elections in Kenya using HotCat |
Cyberbot II (talk | contribs) Rescuing 3 sources, flagging 0 as dead, and archiving 66 sources. #IABot |
||
| Line 65: | Line 65: | ||
* [[Economy of Kenya|Economy]] |
* [[Economy of Kenya|Economy]] |
||
* Infrastructure |
* Infrastructure |
||
* Corruption (see Wikileaks Kenya entry<ref>[http://www.wikileaks.org/wiki/Category:Kenya ]{{ |
* Corruption (see Wikileaks Kenya entry<ref>[http://www.wikileaks.org/wiki/Category:Kenya ] {{wayback|url=http://www.wikileaks.org/wiki/Category:Kenya |date=20071218171251 |df=y }}</ref>) |
||
* [[Majimbo]]/[[Ugatuzi]] (federalism & devolution) |
* [[Majimbo]]/[[Ugatuzi]] (federalism & devolution) |
||
* Free High school Education |
* Free High school Education |
||
| Line 229: | Line 229: | ||
Odinga held a strong lead in vote counting on 28 December,<ref name=Jeff>Jeffrey Gettleman, [http://www.nytimes.com/2007/12/31/world/africa/31kenya.html?_r=1&hp&oref=slogin "Disputed Vote Plunges Kenya Into Bloodshed"], ''The New York Times'', 31 December 2007.</ref> and the ODM declared victory for Odinga on 29 December;<ref name=Opp>[http://www.int.iol.co.za/index.php?set_id=1&click_id=68&art_id=nw20071229123805553C415151 "Kenya opposition declares victory"], AFP (''IOL''), 29 December 2007.</ref> however, as more results were announced on the same day, the gap between the two candidates narrowed.<ref name=Jeff/><ref name=Opp/> Early on 30 December, Odinga accused the government of fraud, urged Kibaki to concede defeat, and called for a recount.<ref>Stephen Ndegwa, [http://allafrica.com/stories/200712300020.html "Kenya: Raila Calls for Vote Recount"], ''The East African Standard'' (allAfrica.com), 30 December 2007.</ref> The Electoral Commission declared Kibaki the winner later on 30 December, placing him ahead of Odinga by about 232,000 votes.<ref>Barney Jopson, [http://us.ft.com/ftgateway/superpage.ft?news_id=fto010320080354570443&page=2 "Kenyan police try to block opposition rally"], Reuters (''Financial Times''), 3 January 2008.</ref><ref name=Victor>[http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/africa/7164890.stm "Kibaki named victor in Kenya vote"], BBC News, 20 December 2007.</ref> According to Odinga, at least 300,000 votes for Kibaki were falsely included in his total.<ref>[http://www.theage.com.au/news/world/kenyans-riot-after-rigged-election/2007/12/31/1198949705836.html?page=fullpage#contentSwap1 "Kenyans riot after 'rigged' election"], AFP (theage.com.au), 31 December 2007.</ref> The Chairman of the Electoral Commission, [[Samuel Kivuitu]], said that while irregularities did occur, they were a matter for the courts, not the Electoral Commission.<ref>Jeffrey Gettleman, [http://www.iht.com/articles/2007/12/30/africa/kenya.php "Tribal violence breaks out in Kenya over disputed election result"], ''International Herald Tribune'', 30 December 2007.</ref> Following the Commission's declaration of his victory, Kibaki was sworn in for his second term later on the same day,<ref name=Victor/><ref>Stephanie McCrummen, [http://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2007/12/30/AR2007123002506_pf.html "Incumbent Declared Winner in Kenya's Disputed Election"], ''The Washington Post'', 31 December 2007, page A11.</ref> saying that he had been told by his people that he had won, calling for the "verdict of the people" to be respected and for "healing and reconciliation" to begin.<ref name=Victor/> |
Odinga held a strong lead in vote counting on 28 December,<ref name=Jeff>Jeffrey Gettleman, [http://www.nytimes.com/2007/12/31/world/africa/31kenya.html?_r=1&hp&oref=slogin "Disputed Vote Plunges Kenya Into Bloodshed"], ''The New York Times'', 31 December 2007.</ref> and the ODM declared victory for Odinga on 29 December;<ref name=Opp>[http://www.int.iol.co.za/index.php?set_id=1&click_id=68&art_id=nw20071229123805553C415151 "Kenya opposition declares victory"], AFP (''IOL''), 29 December 2007.</ref> however, as more results were announced on the same day, the gap between the two candidates narrowed.<ref name=Jeff/><ref name=Opp/> Early on 30 December, Odinga accused the government of fraud, urged Kibaki to concede defeat, and called for a recount.<ref>Stephen Ndegwa, [http://allafrica.com/stories/200712300020.html "Kenya: Raila Calls for Vote Recount"], ''The East African Standard'' (allAfrica.com), 30 December 2007.</ref> The Electoral Commission declared Kibaki the winner later on 30 December, placing him ahead of Odinga by about 232,000 votes.<ref>Barney Jopson, [http://us.ft.com/ftgateway/superpage.ft?news_id=fto010320080354570443&page=2 "Kenyan police try to block opposition rally"], Reuters (''Financial Times''), 3 January 2008.</ref><ref name=Victor>[http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/africa/7164890.stm "Kibaki named victor in Kenya vote"], BBC News, 20 December 2007.</ref> According to Odinga, at least 300,000 votes for Kibaki were falsely included in his total.<ref>[http://www.theage.com.au/news/world/kenyans-riot-after-rigged-election/2007/12/31/1198949705836.html?page=fullpage#contentSwap1 "Kenyans riot after 'rigged' election"], AFP (theage.com.au), 31 December 2007.</ref> The Chairman of the Electoral Commission, [[Samuel Kivuitu]], said that while irregularities did occur, they were a matter for the courts, not the Electoral Commission.<ref>Jeffrey Gettleman, [http://www.iht.com/articles/2007/12/30/africa/kenya.php "Tribal violence breaks out in Kenya over disputed election result"], ''International Herald Tribune'', 30 December 2007.</ref> Following the Commission's declaration of his victory, Kibaki was sworn in for his second term later on the same day,<ref name=Victor/><ref>Stephanie McCrummen, [http://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2007/12/30/AR2007123002506_pf.html "Incumbent Declared Winner in Kenya's Disputed Election"], ''The Washington Post'', 31 December 2007, page A11.</ref> saying that he had been told by his people that he had won, calling for the "verdict of the people" to be respected and for "healing and reconciliation" to begin.<ref name=Victor/> |
||
Kivuitu said that there were some problems in the vote counting, noting that in one constituency voter turnout was reported as 115%,<ref>[http://www.sabcnews.com/africa/east_africa/0,2172,161636,00.html "Kenya election results expected today"], SABC News, 30 December 2007.</ref> this was later clarified by Kivuitu appearing in an interview by [[NTV (Kenya)|Nation Television]] due to a double entry of one polling station in [[Maragua Constituency]] on the parliamentary tally and not the presidential tally. According to the [[European Union]]'s head observer in the election, [[Alexander Graf Lambsdorff]], the election was "flawed"<ref name=Jeff/> and the Electoral Commission failed to establish "the credibility of the tallying process to the satisfaction of all parties and candidates."<ref>[http://us.ft.com/ftgateway/superpage.ft?news_id=fto123020071125520138&page=2 "Kibaki re-elected as president of Kenya"], Reuters (''Financial Times''), 30 December 2008.</ref> The United Kingdom's Foreign Secretary, [[David Miliband]], said that his country had "real concerns" about the election. While the United States initially congratulated Kibaki and called for the results to be respected,<ref name=Reject>[http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/africa/7165406.stm "Odinga rejects Kenya poll result"], BBC News, 31 December 2007.</ref> it also expressed concern,<ref>Mike Pflanz, [http://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/main.jhtml?xml=/news/2007/12/31/wkenya431.xml "Kenya election riots leave more than 120 dead"], Telegraph.co.uk, 31 December 2007.</ref> and on 2 January 2008 a spokesman for the [[United States Department of State|US State Department]] declined to confirm US recognition of Kibaki's victory.<ref>David Gollust, [http://www.voanews.com/english/2008-01-02-voa73.cfm "US in Diplomatic Push to End Kenya Violence"], VOA News, 2 January 2007.</ref> Kivuitu said on 2 January that he had been pressured by PNU and ODM-K (Kibaki's and Kalonzo Musyoka's parties) into announcing the results without delay, declaring Kibaki as elected winner; claiming that he did not personally know who really won.<ref>{{cite web|url= |
Kivuitu said that there were some problems in the vote counting, noting that in one constituency voter turnout was reported as 115%,<ref>[http://www.sabcnews.com/africa/east_africa/0,2172,161636,00.html "Kenya election results expected today"], SABC News, 30 December 2007.</ref> this was later clarified by Kivuitu appearing in an interview by [[NTV (Kenya)|Nation Television]] due to a double entry of one polling station in [[Maragua Constituency]] on the parliamentary tally and not the presidential tally. According to the [[European Union]]'s head observer in the election, [[Alexander Graf Lambsdorff]], the election was "flawed"<ref name=Jeff/> and the Electoral Commission failed to establish "the credibility of the tallying process to the satisfaction of all parties and candidates."<ref>[http://us.ft.com/ftgateway/superpage.ft?news_id=fto123020071125520138&page=2 "Kibaki re-elected as president of Kenya"], Reuters (''Financial Times''), 30 December 2008.</ref> The United Kingdom's Foreign Secretary, [[David Miliband]], said that his country had "real concerns" about the election. While the United States initially congratulated Kibaki and called for the results to be respected,<ref name=Reject>[http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/africa/7165406.stm "Odinga rejects Kenya poll result"], BBC News, 31 December 2007.</ref> it also expressed concern,<ref>Mike Pflanz, [http://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/main.jhtml?xml=/news/2007/12/31/wkenya431.xml "Kenya election riots leave more than 120 dead"], Telegraph.co.uk, 31 December 2007.</ref> and on 2 January 2008 a spokesman for the [[United States Department of State|US State Department]] declined to confirm US recognition of Kibaki's victory.<ref>David Gollust, [http://www.voanews.com/english/2008-01-02-voa73.cfm "US in Diplomatic Push to End Kenya Violence"], VOA News, 2 January 2007.</ref> Kivuitu said on 2 January that he had been pressured by PNU and ODM-K (Kibaki's and Kalonzo Musyoka's parties) into announcing the results without delay, declaring Kibaki as elected winner; claiming that he did not personally know who really won.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.eastandard.net/news/?id=1143979833 |title=The Standard | Online Edition | I acted under a pressure, says Kivuitu |publisher=Eastandard.net (Internet Archive) |date=2 January 2008 |accessdate=2013-03-30 |deadurl=yes |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/20130529032850/http://eastandard.net/news/?id=1143979833 |archivedate=29 May 2013 }}</ref> |
||
Within minutes of the Commission's declaration of Kibaki's victory, tribe-based rioting and violence, primarily directed against Kikuyus, broke out across Kenya,<ref name=Jeff/> and the government suspended live television coverage for some days.<ref name=Jeff/><ref name=Reject/><ref>The Nation, [http://allafrica.com/stories/200712310011.html "Kenya: Violence Erupts After Kibaki Sworn in"], The Nation (allafrica.com), 30 December 2007.</ref><ref>The Nation, [http://allafrica.com/stories/200712310456.html "Kenya: Death and Chaos After Kibaki Win"], The Nation (allafrica.com), 31 December 2007.</ref> Odinga alleged that "a clique of people around Kibaki" sought to rig the election, but said that democracy "is unstoppable like the flow of the Nile". The ODM announced its intention to hold a ceremony on 31 December in which Odinga would be declared the "people's president", but police said that this could incite violence and that Odinga could be arrested if the ceremony occurred.<ref name=Reject/> Odinga then delayed this, but called for a million-strong rally on 3 January 2008<ref>[http://web.archive.org/web/20080105055743/http://www.cbsnews.com/stories/2007/12/31/ap/world/main3658458.shtml "Kenya: Police Claim Shoot To Kill Orders"], Associated Press (CBS News), 31 December 2007.</ref> and for his supporters to wear black armbands as a show of mourning.<ref>Nick Wadhams, [http://www.time.com/time/world/article/0,8599,1699123,00.html "Will Kenya's Vote Lead to Tribal War?"], TIME.com, 31 December 2007.</ref> |
Within minutes of the Commission's declaration of Kibaki's victory, tribe-based rioting and violence, primarily directed against Kikuyus, broke out across Kenya,<ref name=Jeff/> and the government suspended live television coverage for some days.<ref name=Jeff/><ref name=Reject/><ref>The Nation, [http://allafrica.com/stories/200712310011.html "Kenya: Violence Erupts After Kibaki Sworn in"], The Nation (allafrica.com), 30 December 2007.</ref><ref>The Nation, [http://allafrica.com/stories/200712310456.html "Kenya: Death and Chaos After Kibaki Win"], The Nation (allafrica.com), 31 December 2007.</ref> Odinga alleged that "a clique of people around Kibaki" sought to rig the election, but said that democracy "is unstoppable like the flow of the Nile". The ODM announced its intention to hold a ceremony on 31 December in which Odinga would be declared the "people's president", but police said that this could incite violence and that Odinga could be arrested if the ceremony occurred.<ref name=Reject/> Odinga then delayed this, but called for a million-strong rally on 3 January 2008<ref>[http://web.archive.org/web/20080105055743/http://www.cbsnews.com/stories/2007/12/31/ap/world/main3658458.shtml "Kenya: Police Claim Shoot To Kill Orders"], Associated Press (CBS News), 31 December 2007.</ref> and for his supporters to wear black armbands as a show of mourning.<ref>Nick Wadhams, [http://www.time.com/time/world/article/0,8599,1699123,00.html "Will Kenya's Vote Lead to Tribal War?"], TIME.com, 31 December 2007.</ref> |
||
| Line 237: | Line 237: | ||
=== Results === |
=== Results === |
||
These are the official results as of 29 January 2008 as appears on the Electoral Commission of Kenya website. Alongside are figures put out by the Office of the Government Spokesman,<ref name=autogenerated2>{{cite web|url= |
These are the official results as of 29 January 2008 as appears on the Electoral Commission of Kenya website. Alongside are figures put out by the Office of the Government Spokesman,<ref name=autogenerated2>{{cite web|url=http://www.communication.go.ke/elections/default.asp |title=Office of the Government Spokesman |publisher=Communication.go.ke (Internet Archive) |date=30 December 2007 |accessdate=2013-03-30 |deadurl=yes |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/20130214220304/http://www.communication.go.ke:80/elections/default.asp |archivedate=14 February 2013 }}</ref> and also appeared at media websites soon after the results were announced.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://kenyaelections07.marsgroupkenya.org/data/results/ |title=released |publisher=Kenyaelections07.marsgroupkenya.org |date= |accessdate=2010-05-01}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/africa/7165406.stm |title=same figures in BBC-report |publisher=BBC News |date=31 December 2007 |accessdate=2010-05-01}}</ref> |
||
{| class="wikitable" |
{| class="wikitable" |
||
|- |
|- |
||
Revision as of 14:15, 18 January 2016
| ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
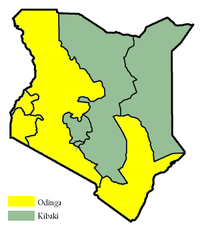 Presidential election results map. Green denotes provinces won by Kibaki, and Yellow denotes those won by Odinga. | ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
 |
|---|
|
|
A presidential election was held as part of the Kenyan general election on 27 December 2007; parliamentary elections were held on the same date.[1] Incumbent President Mwai Kibaki was declared the winner and sworn in at State House Nairobi on 30 December, despite opposition leader Raila Odinga's claims of victory.[2][3] There is agreement in the international community that the elections were at least partially manipulated.[4] In July 2008, an exit poll commissioned by the US was released, revealing that Odinga won the election by a comfortable margin of 6%, 46% to 40%, well outside of the exit poll's 1.3% margin of error.[5]
The election was strongly marked by tribalism, with Kibaki a member of the traditionally dominant Kikuyu ethnic group getting much support amongst people of Central Kenya i.e. Kikuyu and neighbouring groups like Embu and Meru. Odinga, as a member of the Luo ethnic group, succeeded in creating a wider base by building a coalition with regional leaders from the Luhya in Western Kenya, Kalenjin from the Rift Valley and Muslim leaders from the Coast Province. The third place candidate, Kalonzo Musyoka, had his base mainly amongst the Kamba. Following the announcement of Kibaki's victory, civil unrest broke out which was often directed against members of Kibaki's ethnic group residing outside their traditional settlement areas.[6][citation needed]
Kenneth Matiba of Saba Saba Asili joined the race after a 10-year political hiatus. Other candidates were Joseph Ngacha Karani (Kenya Patriotic Trust), Nixon Jeremiah Kukubo (Republican Party of Kenya), Pius Muiru (Kenya Peoples’ Party), David Waweru Ng’ethe (Chama Cha Umma) and Nazlin Omar (Workers Congress Party).[6]
Timeline and preparations
Incumbent president Mwai Kibaki declared on 26 January 2007 his intentions of running for re-election, even though he had previously declared at the 2002 elections that he needed only one term as president.[7] At the time ODM-Kenya coalition was expected to field the strongest challenger for Kibaki. The main parties affiliated to ODM-Kenya were LDP and KANU.[8] At the time of the 2002 elections, LDP was part of the NARC movement backing Kibaki, but were dismissed from the cabinet after the 2005 constitutional referendum.[9] KANU, on the other hand is a former ruling party, but the former president Daniel arap Moi was among its faction opposing its involvement with the ODM-Kenya coalition.[10] KANU and LDP had originally teamed up for the 2005 referendum, under the banner Orange Democratic Movement.[11]
ODM-Kenya split in two in August 2007, with one faction (ODM-Kenya) led by Kalonzo Musyoka, while others joined the original ODM. KANU left the coalition. Former president Daniel arap Moi announced his support for the re-election of Kibaki, his former political enemy, in late August,[12] and Uhuru Kenyatta followed the suit and announced his support for Kibaki in mid-September. Kenyatta had earlier vied for presidential candidacy on the ODM ticket before he and his party KANU had ditched the coalition. KANU will field its own parliamentary candidates.[13]
Several ODM members vied for presidency, including Kalonzo Musyoka, Raila Odinga, Uhuru Kenyatta, William Ruto, Najib Balala, Musalia Mudavadi and Joseph Nyagah.[14] Following the August 2007 split, the ODM-K appointed Musyoka as its candidate on 31 August[15][16] and the ODM elected Odinga as its candidate on 1 September.[17]
On 16 September 2007, Kibaki announced that he would stand as the candidate of a new alliance called the Party of National Unity, which will include a number of parties, including KANU,[18][19] DP, Narc-Kenya, Ford-Kenya, Ford People, and Shirikisho among others.[19] He began his presidential campaign on 30 September at Nyayo Stadium in Nairobi.[20]
Odinga launched his campaign in Uhuru Park on 6 October 2007.[21][22] On the same day, three ODM supporters were shot (one of them fatally), allegedly by bodyguards of Stanley Livondo, who is running as the PNU candidate for Odinga's seat in parliament. Livondo was arrested, along with two of his bodyguards and released later.[22]
In October, Odinga led Kibaki in opinion polls. Two cabinet ministers, first Health Minister Charity Ngilu and then Regional Cooperation Minister John Koech, backed Odinga in October; Kibaki dismissed Ngilu from the cabinet.[23]
Pius Muiru, a bishop and the leader of Kenya Peoples Party (KPP), officially launched his bid for the presidency on 21 October 2007 at Kamukunji grounds.[24]
Parliament was dissolved on Tuesday 23 October, paving way for the Electoral Commission of Kenya (ECK) to announce the election date.[25] The date was officially announced on 26 October 2007 by the ECK, stating the elections would be held on Thursday 27 December 2007.[26]
Opinion polls in late October put Odinga at 50% support, Kibaki at 39%, and Musyoka at 8%.[27] The poll released in early November put Odinga at 45%, Kibaki at 41% and Musyoka at 11%, while on 23 November a poll placed Odinga and Kibaki at about the same level, with 43.6% and 43.3% support respectively.[28]
Presidential candidates presented their nomination papers on the 14 and 15 November to the ECK and 9 candidates were cleared to be on the ballot in December.[6]
Campaign issues
Some of the issues of the election being discussed by the 3 candidates were:
- Economy
- Infrastructure
- Corruption (see Wikileaks Kenya entry[29])
- Majimbo/Ugatuzi (federalism & devolution)
- Free High school Education
- Universal Health care
- Position of Muslims within Kenya
- Constitution (Odinga promised a new constitution within six months of taking office[30])
Opinion polls
*For a documentation of more opinion polls in the runup to the Kenyan election see Polls before the Kenyan elections 2007
| Poll date | Kibaki | Musyoka | Odinga | Mudavadi | Ruto | Kenyatta |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| October 2006[31] | 41% | 20% | 13% | 3% | 5% | |
| December 2006[32] | 42% | 20% | 14% | 3% | 5% | |
| March 2007[33] | 51% | 14% | 17% | 2% | 2% | 2% |
| April 2007[34] | 44.3% | 15.3% | 18.7% | 2.7% | 2.6% | 3.5% |
| June 2007[35] | 45% | 14% | 28% | 4% | 3% | 4% |
| July 2007[36] | 45% | 11% | 25% | 3% | 2% | 2% |
| August 2007[37] | 42% | 11% | 25% | 8% | 6% | 1% |
| August 2007[38] | 47% | 13% | 36% | 1% | 1% | |
| September 2007[39] | 38% | 8% | 47% | |||
| 13 October 2007[40] | 37% | 8% | 53% | |||
| 23 October 2007[41] | 39% | 8% | 50% | |||
| 9 November 2007[42] | 41% | 11% | 45% | |||
| 21 November 2007[43] | 41.4% | 14.7% | 40.7% | |||
| 17 November 2007[44] | 42% | 11% | 45% | |||
| 23 November 2007[45] | 43.3% | 11.4% | 43.6% | |||
| 7 December 2007[46] | 42% | 10% | 46% | |||
| 18 December 2007[47] | 43% | 10% | 45% |
The June 2007 poll also featured a section on a head-to-head poll with Kibaki against each of the ODM candidates. Both Musyoka and Odinga scored 45%, indicating a dead-tie with Kibaki. The rest of the candidates scored as follows against Kibaki: Najib Balala: 43%, William Ruto: 39%, Uhuru Kenyatta: 38%.[35]
Presidential election results

An exit poll conducted from 310 polling stations in 139 constituencies (out of 210) showed Kibaki getting 50.3% of the votes compared to 40.6% for Raila Odinga.[48] On the other hand, early results by Kenyan media gave Raila Odinga a narrow lead.[49]
Odinga held a strong lead in vote counting on 28 December,[50] and the ODM declared victory for Odinga on 29 December;[51] however, as more results were announced on the same day, the gap between the two candidates narrowed.[50][51] Early on 30 December, Odinga accused the government of fraud, urged Kibaki to concede defeat, and called for a recount.[52] The Electoral Commission declared Kibaki the winner later on 30 December, placing him ahead of Odinga by about 232,000 votes.[53][54] According to Odinga, at least 300,000 votes for Kibaki were falsely included in his total.[55] The Chairman of the Electoral Commission, Samuel Kivuitu, said that while irregularities did occur, they were a matter for the courts, not the Electoral Commission.[56] Following the Commission's declaration of his victory, Kibaki was sworn in for his second term later on the same day,[54][57] saying that he had been told by his people that he had won, calling for the "verdict of the people" to be respected and for "healing and reconciliation" to begin.[54]
Kivuitu said that there were some problems in the vote counting, noting that in one constituency voter turnout was reported as 115%,[58] this was later clarified by Kivuitu appearing in an interview by Nation Television due to a double entry of one polling station in Maragua Constituency on the parliamentary tally and not the presidential tally. According to the European Union's head observer in the election, Alexander Graf Lambsdorff, the election was "flawed"[50] and the Electoral Commission failed to establish "the credibility of the tallying process to the satisfaction of all parties and candidates."[59] The United Kingdom's Foreign Secretary, David Miliband, said that his country had "real concerns" about the election. While the United States initially congratulated Kibaki and called for the results to be respected,[60] it also expressed concern,[61] and on 2 January 2008 a spokesman for the US State Department declined to confirm US recognition of Kibaki's victory.[62] Kivuitu said on 2 January that he had been pressured by PNU and ODM-K (Kibaki's and Kalonzo Musyoka's parties) into announcing the results without delay, declaring Kibaki as elected winner; claiming that he did not personally know who really won.[63]
Within minutes of the Commission's declaration of Kibaki's victory, tribe-based rioting and violence, primarily directed against Kikuyus, broke out across Kenya,[50] and the government suspended live television coverage for some days.[50][60][64][65] Odinga alleged that "a clique of people around Kibaki" sought to rig the election, but said that democracy "is unstoppable like the flow of the Nile". The ODM announced its intention to hold a ceremony on 31 December in which Odinga would be declared the "people's president", but police said that this could incite violence and that Odinga could be arrested if the ceremony occurred.[60] Odinga then delayed this, but called for a million-strong rally on 3 January 2008[66] and for his supporters to wear black armbands as a show of mourning.[67]
Odinga said that the ODM would not negotiate with Kibaki unless he resigned, because to do so would, according to Odinga, mean acknowledging Kibaki's legitimacy; he also said that, unless stopped, the "ruling clique" could rig the next election in five years as well, and that he was not afraid of being arrested, having been jailed many times in the past.[68] For his part, Kibaki emphasised the importance of peace, stability, and tolerance in his 2008 New Year's message, speaking of the election as a concluded event and warning that law-breakers would be punished.[69]
Results
These are the official results as of 29 January 2008 as appears on the Electoral Commission of Kenya website. Alongside are figures put out by the Office of the Government Spokesman,[70] and also appeared at media websites soon after the results were announced.[71][72]
| Party | Candidate | Votes (ECK) 29 Jan | Votes (Kibaki Gov't)[70] | ||
| PNU | Mwai Kibaki | 4,578,034 | 4,584,721 | 47% | |
| ODM | Raila Odinga | 4,352,860 | 4,352,993 | 44% | |
| ODM-K | Kalonzo Musyoka | 879,899 | 879,903 | 9% | |
| KPTP | Joseph Karani | 21,168 | 21,171 | 0.2% | |
| KPP | Pius Muiru | 9,665 | 9,667 | 0.09% | |
| WCPK | Nazlin Omar | 8,624 | 8,624 | 0.087% | |
| SSA | Kenneth Matiba | 8,049 | 8,046 | 0.081% | |
| CCUP | David Ng'ethe | 5,976 | 5,976 | 0.06% | |
| RPK | Nixon Kukubo | 5,926 | 5,927 | 0.06% | |
Provincial results
| Province | Kibaki | % | Odinga | % | Kalonzo | % | Others | % | Votes Cast | Registered Voters | Turnout |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAIROBI | 313,478 | 47.7% | 288,922 | 44.0% | 52,974 | 8.1% | 1,845 | 0.3% | 657,219 | 1,275,021 | 51.5% |
| COAST | 197,354 | 33.1% | 353,773 | 59.4% | 38,881 | 6.5% | 5,909 | 1.0% | 595,917 | 1,045,629 | 57.0% |
| NORTH EASTERN | 97,263 | 50.3% | 91,440 | 47.2% | 4,498 | 2.3% | 333 | 0.2% | 193,534 | 315,664 | 61.3% |
| EASTERN | 835,481 | 50.4% | 83,575 | 5.0% | 726,782 | 43.8% | 13,229 | 0.8% | 1,659,067 | 2,516,998 | 65.9% |
| CENTRAL | 1,741,086 | 97.0% | 34,046 | 1.9% | 11,702 | 0.7% | 7,215 | 0.4% | 1,794,049 | 2,186,315 | 82.1% |
| RIFT VALLEY | 818,445 | 33.5% | 1,580,880 | 64.6% | 33,863 | 1.4% | 12,300 | 0.5% | 2,445,488 | 3,358,285 | 72.8% |
| WESTERN | 312,300 | 32.2% | 639,246 | 65.9% | 6,729 | 0.7% | 11,417 | 1.2% | 969,692 | 1,564,854 | 62.0% |
| NYANZA | 262,627 | 16.9% | 1,280,978 | 82.4% | 4,476 | 0.3% | 7,160 | 0.5% | 1,555,235 | 2,041,686 | 76.2% |
| Totals | 4,578,034 | 46.4% | 4,352,860 | 44.1% | 879,899 | 8.9% | 59,408 | 0.6% | 9,870,201 | 14,304,452 | 69.0% |
NB – In addition to receiving the largest number of votes in absolute terms, a successful presidential candidate must also win 25% or more of the vote in at least five of Kenya's eight provinces to avoid a runoff.
Election observers statement
The following account is drawn from the statements of four of the five domestic election observers allowed into the verification process the Electoral Commission of Kenya (ECK) afforded political party representatives the night before the announcement of the results for the Presidency. Kenyans for Peace with Truth and Justice (KPTJ)
- Count Down to Deception: 30 Hours that Destroyed Kenya
- Kenyan Elections Observers’ Log: December 29–30, 2007
- Kenyan Elections Observers' Log: the cost of anomalies, malpractices and illegalities noted to voters and their votes (spreadsheet)
- Kenya 2007 General Election: Comparison of Total Parliamentary vs. Total Presidential Votes Cast ECK Figures*(spreadsheet)
Aftermath
Riots erupted in Kenya after Kibaki was declared re-elected as President. Certain opposition supporters, angered by alleged electoral manipulation by President Kibaki, allegedly incited civil unrest. The unrest involved ethnic violence between members of different tribes, particularly between the Kikuyu and the Kalenjin.[73] Eventually, a power-sharing agreement, according to which Kibaki would remain President and Odinga would gain the new post of Prime Minister, was reached in late February 2008, and a coalition government, with an equal number of ministers for the PNU and the ODM, was named in April.
Also see The Truth, Justice and Reconciliation Commission of Kenya.
In August 2012, the Nakuru County Peace Accord was signed, a treaty designed to address sources of ethnic conflict and violence in the rift valley region of Kenya.
January 2008 Government
After being sworn in as President, Kibaki named a partial Cabinet on 8 January 2008, composed of 17 members of parliament from his party PNU and ODM-Kenya which entered into a coalition agreement, along with KANU. A number of further cabinet slots were left temporarily open, presumably to give space for negotiations with the opposition ODM which, however, immediately challenged the constitutionality of this government.
This cabinet consisted of:
- (1) Vice-President and Minister for Home Affairs: Stephen Kalonzo Musyoka
- (2) Minister of State for Provincial Administration and Internal Security, Office of the President: Yusuf Haji
- (3) Minister of State for Defence, Office of the President: Yussuf Mohamed Haji
- (4) Minister of State for Special Programmes, Office of the President: Dr. Naomi Namsi Shaban
- (5) Minister for Public Service, Office of the President : Asman Abongotum Kamama
- (6) Minister for Finance : Amos Muhinga Kimunya
- (7) Minister for Education : Professor Sam Ongeri
- (8) Minister for Foreign Affairs : Moses Wetangula
- (9) Minister for Local Government : Uhuru Kenyatta
- (10) Minister for Information and Communications : Samuel Lesuron Poghisio
- (11) Minister for Water and Irrigation : John Munyes
- (12) Minister for Energy : Kiraitu Murungi
- (13) Minister for Roads and Public Works : John Njoroge Michuki
- (14) Minister for Science and Technology : Noah M. Wekesa
- (15) Minister for Justice and Constitutional Affairs : Martha Karua
- (16) Minister for East African Community : Dr. Wilfred Machage
- (17) Minister for Transport: Chirau Ali Mwakwere
US Exit Poll
While few reports mentioned it, the US, acting through USAID commissioned the International Republican Institute, to conduct an exit poll during the election. IRI initially did not have confidence in the integrity of the poll data. It therefore believed the poll to be invalid and decided not to release the poll. However, after an audit of the poll data file, IRI reversed its earlier position and released the poll in July 2008.[74][75]
The poll indicated that Odinga won the election by a margin of 6%, 46% to 40%, well outside of the exit poll's 1.3% margin of error.[5][76]
See also
References
- ^ ECK sets poll date as Raila maintains lead The Standard, 26 October 2007
- ^ "Dozens dead in Kenya poll clashes", BBC news(BBC), 31 December 2007.
- ^ "Protests as Kenya's president begins 2nd term after allegations of rigging, deadly violence", Associated Press (International Herald Tribune), 31 December 2007.
- ^ "Kenya election was rigged, U.S. envoy says". CTV.ca. 7 January 2008. Retrieved 1 May 2010.
- ^ a b The Nation, 11 July 2008 http://web.archive.org/web/20080724031125/http://www.nationmedia.com/dailynation/nmgcontententry.asp?category_id=2&newsid=127059 US-funded exit poll says Raila won elections
- ^ a b c Nine to fight it out as Kibaki clearedThe Standard, 16 November 2007 Cite error: The named reference "cleared" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ^ Kibaki declares he is ready for a second presidential term The Standard
- ^ ODM’s long and bumpy journey The Standard, 7 October 2007
- ^ Raila to President: Spare me the blame, I was in your Cabinet for only three years Daily Nation, 20 October 2007
- ^ No Let-Up in Kanu Row Over ODM Daily Nation, 17 November 2006
- ^ Q&A: Kenya political crisis BBC News, 8 December 2007
- ^ "Moi throws weight behind Kibaki", BBC News, 28 August 2007.
- ^ "Ex-rival backs Kibaki re-election", BBC News, 14 September 2007.
- ^ "It's make or break as ODM leaders start forum to decide on candidate", Daily Nation, 11 January 2007.
- ^ Malcolm Webb, "Kenya's Opposition Chooses Presidential Candidate", VOA News, 31 August 2007.
- ^ Eric Shimoli and Dave Opiyo, "Kenya: Kalonzo Picked to Hoist ODM-K Flag", The Nation (allAfrica.com), 1 September 2007.
- ^ "Kenya: It's Raila for President", East Africa Standard (allAfrica.com), 1 September 2007.
- ^ "Kenyan president announces new party affiliation for re-election bid", Associated Press (International Herald Tribune), 16 September 2007.
- ^ a b "Kenya president eyes re-election", BBC News, 16 September 2007.
- ^ "Kibaki: I deserve another term", AFP (News24.com), 30 September 2007.
- ^ Anthony Kaikai, "ODM party launches its Presidential campaigns", Kenya Broadcasting Corporation, 6 October 2007.
- ^ a b "Kenya opposition kicks off campaign, says 3 supporters shot", Associated Press (International Herald Tribune), 6 October 2007.
- ^ "Kenyan presidential hopeful gains favour", AFP (IOL), 12 October 2007.
- ^ Bishop tells voters to send off Kibaki and his team The Standard, 22 October 2007
- ^ Martin Mutua and Edith Fortunate, "Curtain falls on Ninth Parliament", The Standard, 23 October 2007.
- ^ Kenya Elections set for Dec 27 Nationmedia.com, 26 October 2007
- ^ "Kenya: Could the president be ousted?", The Economist, 1 November 2007
- ^ "Kibaki neck-and-neck with challenger", Reuters (IOL), 23 November 2007.
- ^ [1] Archived 2007-12-18 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Noel Mwakugu (14 November 2007). "Africa | Kenyans ready for December poll". BBC News. Retrieved 1 May 2010.
- ^ Survey shows Kibaki’s popularity on the rise The Standard (Poll by Steadman International)
- ^ Kibaki leads again in poll The Standard (Poll by Steadman International)
- ^ Raila finally Hummers Kalonzo The Standard (Poll by Steadman International)
- ^ It’s Kibaki-Raila battle The Standard (Poll by International Republican Institute)
- ^ a b Why Kibaki will win polls The Standard (Poll by Research and Marketing Services (RMS))
- ^ Kalonzo drops, Raila shoots up, Kibaki holds on The Standard (Poll by Steadman International)
- ^ Raila preferred ODM flagbearer, poll shows The Standard, 8 August 2007 (Poll by Infotrak Research and Consulting and Harris Interactive Global)
- ^ Kibaki, Raila ahead of pack in new opinion poll The Standard, 30 August 2007 (Poll by Steadman International)
- ^ Raila tops table The Daily Nation, 29 September 2007 (Poll by Steadman International)
- ^ Raila widens gap The Standard (Online edition), 13 October 2007 (Poll by Steadman International)
- ^ Raila’s third win The Standard (Online edition), 23 October 2007 (Poll by Steadman International)
- ^ Raila drops in new ratings Daily Nation, 9 November 2007 (Poll by Steadman International)
- ^ Latest surveys forecast tight race for State House Daily Nation (Poll by Consumer Insight), 17 November 2007
- ^ New poll predicts close race Daily Nation (Poll by Gallup), 21 November 2007
- ^ Raila, Kibaki in nip and tuck race Capital FM (Poll by Steadman International), 23 November 2007
- ^ Raila maintains lead in latest poll Capital FM (Poll by Steadman International), 7 December 2007
- ^ Last poll, last push The Standard (Poll by Steadman International), 18 December 2007
- ^ "General Elections 2007: Presidential Exit Polls". IED Africa. Retrieved 1 May 2010.
- ^ Reuters, 28 December 2007: [2] Early results show Kibaki trailing in Kenya vote
- ^ a b c d e Jeffrey Gettleman, "Disputed Vote Plunges Kenya Into Bloodshed", The New York Times, 31 December 2007.
- ^ a b "Kenya opposition declares victory", AFP (IOL), 29 December 2007.
- ^ Stephen Ndegwa, "Kenya: Raila Calls for Vote Recount", The East African Standard (allAfrica.com), 30 December 2007.
- ^ Barney Jopson, "Kenyan police try to block opposition rally", Reuters (Financial Times), 3 January 2008.
- ^ a b c "Kibaki named victor in Kenya vote", BBC News, 20 December 2007.
- ^ "Kenyans riot after 'rigged' election", AFP (theage.com.au), 31 December 2007.
- ^ Jeffrey Gettleman, "Tribal violence breaks out in Kenya over disputed election result", International Herald Tribune, 30 December 2007.
- ^ Stephanie McCrummen, "Incumbent Declared Winner in Kenya's Disputed Election", The Washington Post, 31 December 2007, page A11.
- ^ "Kenya election results expected today", SABC News, 30 December 2007.
- ^ "Kibaki re-elected as president of Kenya", Reuters (Financial Times), 30 December 2008.
- ^ a b c "Odinga rejects Kenya poll result", BBC News, 31 December 2007.
- ^ Mike Pflanz, "Kenya election riots leave more than 120 dead", Telegraph.co.uk, 31 December 2007.
- ^ David Gollust, "US in Diplomatic Push to End Kenya Violence", VOA News, 2 January 2007.
- ^ "The Standard | Online Edition | I acted under a pressure, says Kivuitu". Eastandard.net (Internet Archive). 2 January 2008. Archived from the original on 29 May 2013. Retrieved 30 March 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ The Nation, "Kenya: Violence Erupts After Kibaki Sworn in", The Nation (allafrica.com), 30 December 2007.
- ^ The Nation, "Kenya: Death and Chaos After Kibaki Win", The Nation (allafrica.com), 31 December 2007.
- ^ "Kenya: Police Claim Shoot To Kill Orders", Associated Press (CBS News), 31 December 2007.
- ^ Nick Wadhams, "Will Kenya's Vote Lead to Tribal War?", TIME.com, 31 December 2007.
- ^ "Raila’s terms for talks with Kibaki on crisis", Daily Nation (Kenya), 1 January 2008.
- ^ Fred Mukinda and Samwel Kumba, "Kibaki warns law breakers of stern action", Daily Nation (Kenya), 1 January 2008.
- ^ a b "Office of the Government Spokesman". Communication.go.ke (Internet Archive). 30 December 2007. Archived from the original on 14 February 2013. Retrieved 30 March 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "released". Kenyaelections07.marsgroupkenya.org. Retrieved 1 May 2010.
- ^ "same figures in BBC-report". BBC News. 31 December 2007. Retrieved 1 May 2010.
- ^ "Scores Dead in Kenya Poll Clashes". BBC. 31 December 2007. Retrieved 31 December 2007.
- ^ IRI Statement on Kenya Election Day Poll <http://www.iri.org/africa/kenya/2008-08-14-kenya.asp>
- ^ Memo from Bob Carpenter, American Viewpoint to IRI "Subject: Kenya Exit Poll", 7 July 2008
- ^ International Republican Institute (IRI) Strategic Public Relations and Research, "Kenya Election day Poll", www.iri.org, 27 December 2007.
External links
- Election results – Government Website
- BBC summary (08-01-2008): "Kenya's dubious election"
- Electoral Commission of Kenya -slow in updating-
- Electionkenya.com -preelection page, shows no results-
- Daily Nation – Kenya Elections 2007 – results are no more visible
- The Standard – Election Platform – results not updated
- How Kenya polls were messed up – by Tabu Butagira & Jeff Otieno, Monitor, Uganda 3 January 2008
- Count Down to Deception: 30 Hours that Destroyed Kenya – KPTJ Pambazuka News – check pdfs at bottom

