History of the Internet
Before the Internet
| History of computing |
|---|
 |
| Hardware |
| Software |
| Computer science |
| Modern concepts |
| By country |
| Timeline of computing |
| Glossary of computer science |
In the fifties and early sixties, prior to the widespread inter-networking that led to the Internet, most communication networks were limited by their nature to only allow communications between the stations on the network. Some networks had gateways or bridges between them, but these bridges were often limited or built specifically for a single use. One prevalent computer networking method was based on the central mainframe method, simply allowing its terminals to be connected via long leased lines. This method was used in the 1950s by Project RAND to support researchers such as Herbert Simon, in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, when collaborating across the continent with researchers in Santa Monica, California, on automated theorem proving and artificial intelligence. The Internet system was developed and ready in the Late 1980s, but The Cold War held up the progress. When it ended in 1992, the internet slowly became mainstream. By the end of the decade, millions were using it for business, education and pleasure.
Three terminals and an ARPA
Advanced Research Projects Agency was renamed to Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) in 1972. A fundamental pioneer in the call for a global network, J.C.R. Licklider, articulated the idea in his January 1960 paper, Man-Computer Symbiosis.
- "A network of such [computers], connected to one another by wide-band communication lines" which provided "the functions of present-day libraries together with anticipated advances in information storage and retrieval and [other] symbiotic functions. "—J.C.R. Licklider[1]
In October 1962, Licklider was appointed head of the United States Department of Defense's DARPA information processing office, and formed an informal group within DARPA to further computer research. As part of the information processing office's role, three network terminals had been installed: one for System Development Corporation in Santa Monica, one for Project Genie at the University of California, Berkeley and one for the Multics project SHOPPING at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). Licklider's need for inter-networking would be made evident by the problems this caused.
- "For each of these three terminals, I had three different sets of user commands. So if I was talking online with someone at S.D.C. and I wanted to talk to someone I knew at Berkeley or M.I.T. about this, I had to get up from the S.D.C. terminal, go over and log into the other terminal and get in touch with them.
- I said,it's obvious what to do (But I don't want to do it): If you have these three terminals, there ought to be one terminal that goes anywhere you want to go where you have interactive computing. That idea is the ARPAnet." -Robert W. Taylor, co-writer with Licklider of "The Computer as a Communications Device", in an interview with the New York Times[2]
Switched packets
At the tip of the inter-networking problem lay the issue of connecting separate physical networks to form one logical network. During the 1960s, Donald Davies (NPL), Paul Baran (RAND Corporation), and Leonard Kleinrock (MIT) developed and implemented packet switching. The notion that the Internet was developed to survive a nuclear attack has its roots in the early theories developed by RAND. Baran's research had approached packet switching from studies of decentralisation to avoid combat damage compromising the entire network.[3]
Networks that led to the Internet
ARPANET
Promoted to the head of the information processing office at ARPA, Robert Taylor intended to realize Licklider's ideas of an interconnected networking system. Bringing in Larry Roberts from MIT, he initiated a project to build such a network. The first ARPANET link was established between the University of California, Los Angeles and the Stanford Research Institute on 29 November 1969. By 5 December 1969, a 4-node network was connected by adding the University of Utah and the University of California, Santa Barbara. Building on ideas developed in ALOHAnet, the ARPANET started in 1972 and was growing rapidly, by 1981 the number of hosts had grown to 213, with a new host being added approximately every twenty days.[5][6]
ARPANET became the technical core of what would become the Internet, and a primary tool in developing the technologies used. ARPANET development was centered around the Request for Comments (RFC) process, still used today for proposing and distributing Internet Protocols and Systems. RFC 1, entitled "Host Software", was written by Steve Crocker from the University of California, Los Angeles, and published on April 7, 1969. These early years were documented in the 1972 film Computer Networks: The Heralds of Resource Sharing.
International collaborations on ARPANET were sparse. For various political reasons, European developers were concerned with developing the X.25 networks. Notable exceptions were the Norwegian Seismic Array (NORSAR) in 1972, followed in 1973 by Sweden with satellite links to the Tanum Earth Station and University College London.
X.25 and public access
Following on from DARPA's research, packet switching network standards were developed by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) in the form of X.25 and related standards. In 1974, X.25 formed the basis for the SERCnet network between British academic and research sites, which later became JANET. The initial ITU Standard on X.25 was approved in March 1976. This standard was based on the concept of virtual circuits.
The British Post Office, Western Union International and Tymnet collaborated to create the first international packet switched network, referred to as the International Packet Switched Service (IPSS), in 1978. This network grew from Europe and the US to cover Canada, Hong Kong and Australia by 1981. By the 1990s it provided a worldwide networking infrastructure.[7]
Unlike ARPAnet, X.25 was also commonly available for business use. X.25 would be used for the first dial-in public access networks, such as Compuserve and Tymnet. In 1979, CompuServe became the first service to offer electronic mail capabilities and technical support to personal computer users. The company broke new ground again in 1980 as the first to offer real-time chat with its CB Simulator. There were also the America Online (AOL) and Prodigy dial in networks and many bulletin board system (BBS) networks such as FidoNet. FidoNet in particular was popular amongst hobbyist computer users, many of them hackers and amateur radio operators.
UUCP
In 1979, two students at Duke University, Tom Truscott and Jim Ellis, came up with the idea of using simple Bourne shell scripts to transfer news and messages on a serial line with nearby University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Following public release of the software, the mesh of UUCP hosts forwarding on the Usenet news rapidly expanded. UUCPnet, as it would later be named, also created gateways and links between FidoNet and dial-up BBS hosts. UUCP networks spread quickly due to the lower costs involved, and ability to use existing leased lines, X.25 links or even ARPANET connections. By 1983 the number of UUCP hosts had grown to 550, nearly doubling to 940 in 1984.
Merging the networks and creating the Internet
TCP/IP

With so many different network methods, something needed to unify them. Robert E. Kahn of DARPA and ARPANET recruited Vint Cerf of Stanford University to work with him on the problem. By 1973, they had soon worked out a fundamental reformulation, where the differences between network protocols were hidden by using a common internetwork protocol, and instead of the network being responsible for reliability, as in the ARPANET, the hosts became responsible. Cerf credits Hubert Zimmerman, Gerard LeLann and Louis Pouzin (designer of the CYCLADES network) with important work on this design.[8]
With the role of the network reduced to the bare minimum, it became possible to join almost any networks together, no matter what their characteristics were, thereby solving Kahn's initial problem. DARPA agreed to fund development of prototype software, and after several years of work, the first somewhat crude demonstration of a gateway between the Packet Radio network in the SF Bay area and the ARPANET was conducted. By November 1977 a three network demonstration was conducted including the ARPANET, the Packet Radio Network and the Atlantic Packet Satellite network—all sponsored by DARPA. Stemming from the first specifications of TCP in 1974, TCP/IP emerged in mid-late 1978 in nearly final form. By 1981, the associated standards were published as RFCs 791, 792 and 793 and adopted for use. DARPA sponsored or encouraged the development of TCP/IP implementations for many operating systems and then scheduled a migration of all hosts on all of its packet networks to TCP/IP. On 1 January 1983, TCP/IP protocols became the only approved protocol on the ARPANET, replacing the earlier NCP protocol.[9]
ARPANET to NSFNet
After the ARPANET had been up and running for several years, ARPA looked for another agency to hand off the network to; ARPA's primary mission was funding cutting-edge research and development, not running a communications utility. Eventually, in July 1975, the network had been turned over to the Defense Communications Agency, also part of the Department of Defense. In 1983, the U.S. military portion of the ARPANET was broken off as a separate network, the MILNET.
The networks based around the ARPANET were government funded and therefore restricted to noncommercial uses such as research; unrelated commercial use was strictly forbidden. This initially restricted connections to military sites and universities. During the 1980s, the connections expanded to more educational institutions, and even to a growing number of companies such as Digital Equipment Corporation and Hewlett-Packard, which were participating in research projects or providing services to those who were.
Another branch of the U.S. government, the National Science Foundation (NSF), became heavily involved in internet research and started development of a successor to ARPANET. In 1984 this resulted in CSNET, the first Wide Area Network designed specifically to use TCP/IP. CSNET connected with ARPANET using TCP/IP, and ran TCP/IP over X.25, but it also supported departments without sophisticated network connections, using automated dial-up mail exchange. This grew into the NSFNet backbone, established in 1986, and intended to connect and provide access to a number of supercomputing centers established by the NSF.[10]
The transition toward an Internet
The term "Internet" was adopted in the first RFC published on the TCP protocol (RFC 675: Internet Transmission Control Protocol, December 1974). It was around the time when ARPANET was interlinked with NSFNet, that the term Internet came into more general use,[11] with "an internet" meaning any network using TCP/IP. "The Internet" came to mean a global and large network using TCP/IP. Previously "internet" and "internetwork" had been used interchangeably, and "internet protocol" had been used to refer to other networking systems such as Xerox Network Services.[12]
As interest in wide spread networking grew and new applications for it arrived, the Internet's technologies spread throughout the rest of the world. TCP/IP's network-agnostic approach meant that it was easy to use any existing network infrastructure, such as the IPSS X.25 network, to carry Internet traffic. In 1984, University College London replaced its transatlantic satellite links with TCP/IP over IPSS.
Many sites unable to link directly to the Internet started to create simple gateways to allow transfer of e-mail, at that time the most important application. Sites which only had intermittent connections used UUCP or FidoNet and relied on the gateways between these networks and the Internet. Some gateway services went beyond simple e-mail peering, such as allowing access to FTP sites via UUCP or e-mail.
TCP/IP becomes worldwide
The first ARPANET connection outside the US was established to NORSAR in Norway in 1973, just ahead of the connection to Great Britain. These links were all converted to TCP/IP in 1982, at the same time as the rest of the Arpanet.
CERN, the European internet, the link to the Pacific and beyond
Between 1984 and 1988 CERN began installation and operation of TCP/IP to interconnect its major internal computer systems, workstations, PC's and an accelerator control system. CERN continued to operate a limited self-developed system CERNET internally and several incompatible (typically proprietary) network protocols externally. There was considerable resistance in Europe towards more widespread use of TCP/IP and the CERN TCP/IP intranets remained isolated from the rest of the Internet until 1989.
In 1988 Daniel Karrenberg, from CWI in Amsterdam, visited Ben Segal, CERN's TCP/IP Coordinator, looking for advice about the transition of the European side of the UUCP Usenet network (much of which ran over X.25 links) over to TCP/IP. In 1987, Ben Segal had met with Len Bosack from the then still small company Cisco about purchasing some TCP/IP routers for CERN, and was able to give Karrenberg advice and forward him on to Cisco for the appropriate hardware. This expanded the European portion of the Internet across the existing UUCP networks, and in 1989 CERN opened its first external TCP/IP connections.[13] This coincided with the creation of Réseaux IP Européens (RIPE), initially a group of IP network administrators who met regularly to carry out co-ordination work together. Later, in 1992, RIPE was formally registered as a cooperative in Amsterdam.
At the same time as the rise of internetworking in Europe, adhoc networking to ARPA and in-between Australian universities formed, based on various technologies such as X.25 and UUCPNet. These were limited in their connection to the global networks, due to the cost of making individual international UUCP dial-up or X.25 connections. In 1989, Australian universities joined the push towards using IP protocols to unify their networking infrastructures. AARNet was formed in 1989 by the Australian Vice-Chancellors' Committee and provided a dedicated IP based network for Australia.
The Internet began to penetrate Asia in the late 1980s. Japan, which had built the UUCP-based network JUNET in 1984, connected to NSFNet in 1989. It hosted the annual meeting of the Internet Society, INET'92, in Kobe. Singapore developed TECHNET in 1990, and Thailand gained a global Internet connection between Chulalongkorn University and UUNET in 1992.[14]
A digital divide
While developed countries with technological infrastructures were joining the Internet, developing countries began to experience a digital divide separating them from the Internet. At the beginning of the 1990s, African countries relied upon X.25 IPSS and 2400 baud modem UUCP links for international and internetwork computer communications. In 1996 a USAID funded project, the Leland initiative, started work on developing full Internet connectivity for the continent. Guinea, Mozambique, Madagascar and Rwanda gained satellite earth stations in 1997, followed by Côte d'Ivoire and Benin in 1998.
In 1991, the People's Republic of China saw its first TCP/IP college network, Tsinghua University's TUNET. The PRC went on to make its first global Internet connection in 1994, between the Beijing Electro-Spectrometer Collaboration and Stanford University's Linear Accelerator Center. However, China went on to implement its own digital divide by implementing a country-wide content filter.[15]
Opening the network to commerce
The interest in commercial use of the Internet became a hotly debated topic. Although commercial use was forbidden, the exact definition of commercial use could be unclear and subjective. UUCPNet and the X.25 IPSS had no such restrictions, which would eventually see the official barring of UUCPNet use of ARPANET and NSFNet connections. Some UUCP links still remained connecting to these networks however, as administrators cast a blind eye to their operation.
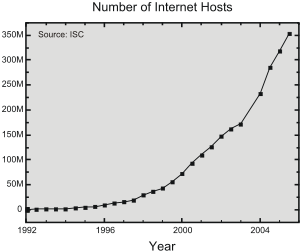
During the late 1980s, the first Internet service provider (ISP) companies were formed. Companies like PSINet, UUNET, Netcom, and Portal Software were formed to provide service to the regional research networks and provide alternate network access, UUCP-based email and Usenet News to the public. The first dial-up ISP, world.std.com, opened in 1989.
This caused controversy amongst university users, who were outraged at the idea of noneducational use of their networks. Eventually, it was the commercial Internet service providers who brought prices low enough that junior colleges and other schools could afford to participate in the new arenas of education and research.
By 1990, ARPANET had been overtaken and replaced by newer networking technologies and the project came to a close. In 1994, the NSFNet, now renamed ANSNET (Advanced Networks and Services) and allowing non-profit corporations access, lost its standing as the backbone of the Internet. Both government institutions and competing commercial providers created their own backbones and interconnections. Regional network access points (NAPs) became the primary interconnections between the many networks and the final commercial restrictions ended.
The IETF and a standard for standards
The Internet has developed a significant subculture dedicated to the idea that the Internet is not owned or controlled by any one person, company, group, or organization. Nevertheless, some standardization and control is necessary for the system to function.
The liberal Request for Comments (RFC) publication procedure engendered confusion about the Internet standardization process, and led to more formalization of official accepted standards. The IETF started in January of 1986 as a quarterly meeting of U.S. government funded researchers. Representatives from non-government vendors were invited starting with the fourth IETF meeting in October of that year.
Acceptance of an RFC by the RFC Editor for publication does not automatically make the RFC into a standard. It may be recognized as such by the IETF only after experimentation, use, and acceptance have proved it to be worthy of that designation. Official standards are numbered with a prefix "STD" and a number, similar to the RFC naming style. However, even after becoming a standard, most are still commonly referred to by their RFC number.
In 1992, the Internet Society, a professional membership society, was formed and the IETF was transferred to operation under it as an independent international standards body.
NIC, InterNIC, IANA and ICANN
The first central authority to coordinate the operation of the network was the Network Information Centre (NIC) at Stanford Research Institute (SRI) in Menlo Park, California. In 1972, management of these issues was given to the newly created Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA). In addition to his role as the RFC Editor, Jon Postel worked as the manager of IANA until his death in 1998.
As the early ARPANET grew, hosts were referred to by names, and a HOSTS.TXT file would be distributed from SRI International to each host on the network. As the network grew, this became cumbersome. A technical solution came in the form of the Domain Name System, created by Paul Mockapetris. The Defense Data Network—Network Information Center (DDN-NIC) at SRI handled all registration services, including the top-level domains (TLDs) of .mil, .gov, .edu, .org, .net, .com and .us, root nameserver administration and Internet number assignments under a United States Department of Defense contract.[16] In 1991, the Defense Information Systems Agency (DISA) awarded the administration and maintenance of DDN-NIC (managed by SRI up until this point) to Government Systems, Inc., who subcontracted it to the small private-sector Network Solutions, Inc.[17]
Since at this point in history most of the growth on the Internet was coming from non-military sources, it was decided that the Department of Defense would no longer fund registration services outside of the .mil TLD. In 1993 the U.S. National Science Foundation, after a competitive bidding process in 1992, created the InterNIC to manage the allocations of addresses and management of the address databases, and awarded the contract to three organizations. Registration Services would be provided by Network Solutions; Directory and Database Services would be provided by AT&T; and Information Services would be provided by General Atomics.[18]
In 1998 both IANA and InterNIC were reorganized under the control of ICANN, a California non-profit corporation contracted by the US Department of Commerce to manage a number of Internet-related tasks. The role of operating the DNS system was privatized and opened up to competition, while the central management of name allocations would be awarded on a contract tender basis.
Use and culture
Email and Usenet—The growth of the text forum
E-mail is often called the killer application of the Internet. However, it actually predates the Internet and was a crucial tool in creating it. E-mail started in 1965 as a way for multiple users of a time-sharing mainframe computer to communicate. Although the history is unclear, among the first systems to have such a facility were SDC's Q32 and MIT's CTSS.[19]
The ARPANET computer network made a large contribution to the evolution of e-mail. There is one report[20] indicating experimental inter-system e-mail transfers on it shortly after ARPANET's creation. In 1971 Ray Tomlinson created what was to become the standard Internet e-mail address format, using the @ sign to separate user names from host names.[21]
A number of protocols were developed to deliver e-mail among groups of time-sharing computers over alternative transmission systems, such as UUCP and IBM's VNET e-mail system. E-mail could be passed this way between a number of networks, including ARPANET, BITNET and NSFNet, as well as to hosts connected directly to other sites via UUCP.
In addition, UUCP allowed the publication of text files that could be read by many others. The News software developed by Steve Daniel and Tom Truscott in 1979 was used to distribute news and bulletin board-like messages. This quickly grew into discussion groups, known as newsgroups, on a wide range of topics. On ARPANET and NSFNet similar discussion groups would form via mailing lists, discussing both technical issues and more culturally focused topics (such as science fiction, discussed on the sflovers mailing list).
A world library—From gopher to the WWW
As the Internet grew through the 1980s and early 1990s, many people realized the increasing need to be able to find and organize files and information. Projects such as Gopher, WAIS, and the FTP Archive list attempted to create ways to organize distributed data. Unfortunately, these projects fell short in being able to accommodate all the existing data types and in being able to grow without bottlenecks. [citation needed]
One of the most promising user interface paradigms during this period was hypertext. The technology had been inspired by Vannevar Bush's "Memex"[22] and developed through Ted Nelson's research on Project Xanadu and Douglas Engelbart's research on NLS.[23] Many small self-contained hypertext systems had been created before, such as Apple Computer's HyperCard.
In 1991, Tim Berners-Lee was the first to develop a network-based implementation of the hypertext concept. This was after Berners-Lee had repeatedly proposed his idea to the hypertext and Internet communities at various conferences to no avail—no one would implement it for him. Working at CERN, Berners-Lee wanted a way to share information about their research. By releasing his implementation to public use, he ensured the technology would become widespread.[24] Subsequently, Gopher became the first commonly-used hypertext interface to the Internet. While Gopher menu items were examples of hypertext, they were not commonly perceived in that way. One early popular web browser, modeled after HyperCard, was ViolaWWW.
Scholars generally agree, however, that the turning point for the World Wide Web began with the introduction[25] of the Mosaic (web browser)[26] in 1993, a graphical browser developed by a team at the National Center for Supercomputing Applications at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign (NCSA-UIUC), led by Marc Andreessen. Funding for Mosaic came from the High-Performance Computing and Communications Initiative, a funding program initiated by then-Senator Al Gore's High Performance Computing and Communication Act of 1991 also known as the Gore Bill.[27]. Indeed, Mosaic's graphical interface soon became more popular than Gopher, which at the time was primarily text-based, and the WWW became the preferred interface for accessing the Internet.
Mosaic was eventually superseded in 1994 by Andreessen's Netscape Navigator, which replaced Mosaic as the world's most popular browser. Competition from Internet Explorer and a variety of other browsers has almost completely displaced it. Another important event held on January 11,1994, was The Superhighway Summit at UCLA's Royce Hall. This was the "first public conference bringing together all of the major industry, government and academic leaders in the field [and] also began the national dialogue about the Information Superhighway and its implications."[28]
Finding what you need—The search engine
As the Web grew, search engines and Web directories were created to track pages on the Web and allow people to find things. The first full-text Web search engine was WebCrawler in 1994. Before WebCrawler, only Web page titles were searched. Another early search engine, Lycos, was created in 1993 as a university project, and was the first to achieve commercial success. During the late 1990s, both Web directories and Web search engines were popular—Yahoo! (founded 1995) and Altavista (founded 1995) were the respective industry leaders.
By August 2001, the directory model had begun to give way to search engines, tracking the rise of Google (founded 1998), which had developed new approaches to relevancy ranking. Directory features, while still commonly available, became after-thoughts to search engines.
Database size, which had been a significant marketing feature through the early 2000s, was similarly displaced by emphasis on relevancy ranking, the methods by which search engines attempt to sort the best results first. Relevancy ranking first became a major issue circa 1996, when it became apparent that it was impractical to review full lists of results. Consequently, algorithms for relevancy ranking have continuously improved. Google's PageRank method for ordering the results has received the most press, but all major search engines continually refine their ranking methodologies with a view toward improving the ordering of results. As of 2006, search engine rankings are more important than ever, so much so that an industry has developed ("search engine optimizers", or "SEO") to help web-developers improve their search ranking, and an entire body of case law has developed around matters that affect search engine rankings, such as use of trademarks in metatags. The sale of search rankings by some search engines has also created controversy among librarians and consumer advocates.
The dot-com bubble
The suddenly low price of reaching millions worldwide, and the possibility of selling to or hearing from those people at the same moment when they were reached, promised to overturn established business dogma in advertising, mail-order sales, customer relationship management, and many more areas. The web was a new killer app—it could bring together unrelated buyers and sellers in seamless and low-cost ways. Visionaries around the world developed new business models, and ran to their nearest venture capitalist. Of course a proportion of the new entrepreneurs were truly talented at business administration, sales, and growth; but the majority were just people with ideas, and didn't manage the capital influx prudently. Additionally, many dot-com business plans were predicated on the assumption that by using the Internet, they would bypass the distribution channels of existing businesses and therefore not have to compete with them; when the established businesses with strong existing brands developed their own Internet presence, these hopes were shattered, and the newcomers were left attempting to break into markets dominated by larger, more established businesses. Many did not have the ability to do so.
The dot-com bubble burst on March 10, 2000, when the technology heavy NASDAQ Composite index peaked at 5048.62 (intra-day peak 5132.52), more than double its value just a year before. By 2001, the bubble's deflation was running full speed. A majority of the dot-coms had ceased trading, after having burnt through their venture capital, often without ever making a gross profit.
Recent trends
The World Wide Web has led to a widespread culture of individual self publishing and co-operative publishing. The moment to moment accounts of blogs, photo publishing Flickr and the information store of Wikipedia are a result of the open ease of creating a public website. One of the fastest growing websites, YouTube offers user generated videos so instead of consuming data from the website, users produce. This is a new form of interactivity that has changed the way people use the internet. In addition, the communication capabilities of the internet are being realised with VOIP both in enterprise networks and commercial telephone services such as Skype or Vonage. Increasingly complex on-demand content provision have led to the delivery of all forms of media, including those that had been found in the traditional media forms of newspapers, radio, television and movies, via the Internet. The Internet's peer-to-peer structure has also influenced social and economic theory, most notably with the rise of file sharing.
Notable malfunctions and attacks
- Morris worm — November 2 1988
- Predicted Y2K Bug - January 1 2000
- UUNet/Worldcom backbone difficulties — October 3 2002
- 2002 DNS Backbone DDoS — October 22 2002
- SQL Slammer worm — January 24 2003
- DNS Backbone DDoS Attacks
Footnotes
- ^ J. C. R. Licklider (1960). "Man-Computer Symbiosis".
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ "An Internet Pioneer Ponders the Next Revolution". An Internet Pioneer Ponders the Next Revolution. Retrieved November 25.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help); Unknown parameter|accessyear=ignored (|access-date=suggested) (help) - ^ "About Rand". Paul Baran and the Origins of the Internet. Retrieved January 14.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help); Unknown parameter|accessyear=ignored (|access-date=suggested) (help) - ^ "The history of the Internet," http://www.lk.cs.ucla.edu/personal_history.html
- ^ Hafner, Katie (1998). Where Wizards Stay Up Late: The Origins Of The Internet. Simon & Schuster. 0-68-483267-4.
- ^ Ronda Hauben (2001). "From the ARPANET to the Internet".
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ "Events in British Telecomms History". Events in British TelecommsHistory. Retrieved November 25.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help); Unknown parameter|accessyear=ignored (|access-date=suggested) (help) - ^ Barry M. Leiner, Vinton G. Cerf, David D. Clark, Robert E. Kahn, Leonard Kleinrock, Daniel C. Lynch, Jon Postel, Larry G. Roberts, Stephen Wolff (2003). "A Brief History of the Internet".
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Jon Postel, NCP/TCP Transition Plan, RFC 801
- ^ David Roessner, Barry Bozeman, Irwin Feller, Christopher Hill, Nils Newman (1997). "The Role of NSF's Support of Engineering in Enabling Technological Innovation".
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Tanenbaum, Andrew S. (1996). Computer Networks. Prentice Hall. 0-13-394248-1.
- ^ Mike Muuss (5th January 1982). "TCP-IP Digest, Vol 1 #10". Newsgroup: fa.tcp-ip. anews. Aucbvax.5690.
{{cite newsgroup}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Ben Segal (1995). "A Short History of Internet Protocols at CERN".
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ "Internet History in Asia". 16th APAN Meetings/Advanced Network Conference in Busan. Retrieved December 25.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help); Unknown parameter|accessyear=ignored (|access-date=suggested) (help) - ^ "A brief history of the Internet in China". China celebrates 10 years of being connected to the Internet. Retrieved December 25.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help); Unknown parameter|accessyear=ignored (|access-date=suggested) (help) - ^ "DDN NIC". IAB Recommended Policy on Distributing Internet Identifier Assignment. Retrieved December 26.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help); Unknown parameter|accessyear=ignored (|access-date=suggested) (help) - ^ "GSI-Network Solutions". TRANSITION OF NIC SERVICES. Retrieved December 26.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help); Unknown parameter|accessyear=ignored (|access-date=suggested) (help) - ^ "NIS Manager Award Announced". NSF NETWORK INFORMATION SERVICES AWARDS. Retrieved December 25.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help); Unknown parameter|accessyear=ignored (|access-date=suggested) (help) - ^ "The Risks Digest". Great moments in e-mail history. Retrieved April 27.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help); Unknown parameter|accessyear=ignored (|access-date=suggested) (help) - ^ "The History of Electronic Mail". The History of Electronic Mail. Retrieved December 23.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help); Unknown parameter|accessyear=ignored (|access-date=suggested) (help) - ^ "The First Network Email". The First Network Email. Retrieved December 23.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help); Unknown parameter|accessyear=ignored (|access-date=suggested) (help) - ^ Vannevar Bush (1945). "As We May Think".
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Douglas Engelbart (1962). "Augmenting Human Intellect: A Conceptual Framework".
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ "The Early World Wide Web at SLAC". The Early World Wide Web at SLAC : Documentation of the Early Web at SLAC. Retrieved November 25.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help); Unknown parameter|accessyear=ignored (|access-date=suggested) (help) - ^ http://www.livinginternet.com/w/wi_mosaic.htm
- ^ http://www.totic.org/nscp/demodoc/demo.html
- ^ http://www.cs.washington.edu/homes/lazowska/faculty.lecture/innovation/gore.html
- ^ http://www.digitalcenter.org/webreport94/apph.htm
References
- Campbell-Kelly, Martin; Aspray, William. Computer: A History of the Information Machine. New York: BasicBooks, 1996.
- Graham, Ian S. The HTML Sourcebook: The Complete Guide to HTML. New York: John Wiley and Sons, 1995.
- Krol, Ed. Hitchhiker's Guide to the Internet, 1987.
- Krol, Ed. Whole Internet User's Guide and Catalog. O'Reilly & Associates, 1992.
- Scientific American Special Issue on Communications, Computers, and Networks, September, 1991
External links
- "The History Of The Internet". The History Of The Internet. Retrieved January 30.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help); Unknown parameter|accessyear=ignored (|access-date=suggested) (help) - Thomas Greene, Larry Landweber, George Strawn (2003). "A Brief History of NSF and the Internet".
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - "Internet History:People". Internet History People. Retrieved July 03.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help); Unknown parameter|accessyear=ignored (|access-date=suggested) (help) - "Internet History Timeline". Internet History Timeline. Retrieved November 25.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help); Unknown parameter|accessyear=ignored (|access-date=suggested) (help) - "Internet History". Internet History. Retrieved November 25.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help); Unknown parameter|accessyear=ignored (|access-date=suggested) (help) - "Hobbes' Internet Timeline v8.1". Retrieved November 25.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help); Unknown parameter|accessyear=ignored (|access-date=suggested) (help) - The History of the Internet at About.com
- "Overhearing the Internet" —by Robert Wright, The New Republic, 1993
- "LivingInternet.com --The Living Internet" -- web site devoted to multidimensional look at Internet history and technology
