Kuiper belt
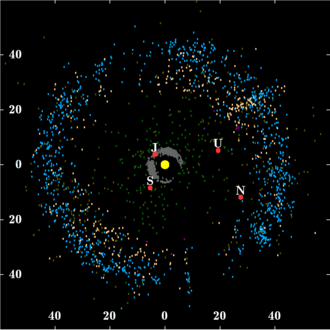
| Sun Jupiter trojans Giant planets: J · S · U · N | Kuiper belt Scattered disc Neptune trojans |
|
The Kuiper belt /ˈkaɪpər/ or /'køypǝr/[1] (as in Dutch), sometimes called the Edgeworth–Kuiper belt, is a region of the Solar System beyond the planets, extending from the orbit of Neptune (at 30 AU) to approximately 50 AU from the Sun.[2] It is similar to the asteroid belt, but it is far larger—20 times as wide and 20 to 200 times as massive.[3][4] Like the asteroid belt, it consists mainly of small bodies, or remnants from the Solar System's formation. Although many asteroids are composed primarily of rock and metal, most Kuiper belt objects are composed largely of frozen volatiles (termed "ices"), such as methane, ammonia and water. The Kuiper belt is home to three officially recognized dwarf planets: Pluto, Haumea, and Makemake. Some of the Solar System's moons, such as Neptune's Triton and Saturn's Phoebe, are also believed to have originated in the region.[5][6]
The Kuiper belt was named after Dutch-American astronomer Gerard Kuiper, though he did not actually predict its existence. In 1992, 1992 QB1 was discovered, the first Kuiper belt object (KBO) since Pluto.[7] Since its discovery, the number of known KBOs has increased to over a thousand, and more than 100,000 KBOs over 100 km (62 mi) in diameter are believed to exist.[8] The Kuiper belt was initially thought to be the main repository for periodic comets, those with orbits lasting less than 200 years. However, studies since the mid-1990s have shown that the belt is dynamically stable, and that comets' true place of origin is the scattered disc, a dynamically active zone created by the outward motion of Neptune 4.5 billion years ago;[9] scattered disc objects such as Eris have extremely eccentric orbits that take them as far as 100 AU from the Sun.[nb 1]
The Kuiper belt should not be confused with the hypothesized Oort cloud, which is a thousand times more distant and is not flat. The objects within the Kuiper belt, together with the members of the scattered disc and any potential Hills cloud or Oort cloud objects, are collectively referred to as trans-Neptunian objects (TNOs).[12]
Pluto is likely the largest and most-massive member of the Kuiper belt and the largest and the second-most-massive known TNO, surpassed only by Eris in the scattered disc.[nb 1] Originally considered a planet, Pluto's status as part of the Kuiper belt caused it to be reclassified as a dwarf planet in 2006. It is compositionally similar to many other objects of the Kuiper belt, and its orbital period is characteristic of a class of KBOs, known as "plutinos", that share the same 2:3 resonance with Neptune.
History
After the discovery of Pluto in 1930, many speculated that it might not be alone. The region now called the Kuiper belt was hypothesized in various forms for decades. It was only in 1992 that the first direct evidence for its existence was found. The number and variety of prior speculations on the nature of the Kuiper belt have led to continued uncertainty as to who deserves credit for first proposing it.
Hypotheses
The first astronomer to suggest the existence of a trans-Neptunian population was Frederick C. Leonard. Soon after Pluto's discovery by Clyde Tombaugh in 1930, Leonard pondered whether it was "not likely that in Pluto there has come to light the first of a series of ultra-Neptunian bodies, the remaining members of which still await discovery but which are destined eventually to be detected".[13] That same year, astronomer Armin O. Leuschner suggested that Pluto "may be one of many long-period planetary objects yet to be discovered."[14]

In 1943, in the Journal of the British Astronomical Association, Kenneth Edgeworth hypothesized that, in the region beyond Neptune, the material within the primordial solar nebula was too widely spaced to condense into planets, and so rather condensed into a myriad of smaller bodies. From this he concluded that "the outer region of the solar system, beyond the orbits of the planets, is occupied by a very large number of comparatively small bodies"[15] and that, from time to time, one of their number "wanders from its own sphere and appears as an occasional visitor to the inner solar system",[16] becoming a comet.
In 1951, in an article for the journal Astrophysics, Gerard Kuiper speculated on a similar disc having formed early in the Solar System's evolution; however, he did not believe that such a belt still existed today. Kuiper was operating on the assumption common in his time that Pluto was the size of Earth and had therefore scattered these bodies out toward the Oort cloud or out of the Solar System. Were Kuiper's hypothesis correct, there would not be a Kuiper belt today.[17]
The hypothesis took many other forms in the following decades. In 1962, physicist Al G.W. Cameron postulated the existence of "a tremendous mass of small material on the outskirts of the solar system".[18] In 1964, Fred Whipple, who popularised the famous "dirty snowball" hypothesis for cometary structure, thought that a "comet belt" might be massive enough to cause the purported discrepancies in the orbit of Uranus that had sparked the search for Planet X, or, at the very least, massive enough to affect the orbits of known comets.[19] Observation, however, ruled out this hypothesis.[18]
In 1977, Charles Kowal discovered 2060 Chiron, an icy planetoid with an orbit between Saturn and Uranus. He used a blink comparator, the same device that had allowed Clyde Tombaugh to discover Pluto nearly 50 years before.[20] In 1992, another object, 5145 Pholus, was discovered in a similar orbit.[21] Today, an entire population of comet-like bodies, called the centaurs, is known to exist in the region between Jupiter and Neptune. The centaurs' orbits are unstable and have dynamical lifetimes of a few million years.[22] From the time of Chiron's discovery in 1977, astronomers have speculated that the centaurs therefore must be frequently replenished by some outer reservoir.[23]
Further evidence for the existence of the Kuiper belt later emerged from the study of comets. That comets have finite lifespans has been known for some time. As they approach the Sun, its heat causes their volatile surfaces to sublimate into space, gradually dispersing them. In order for comets to continue to be visible over the age of the Solar System, they must be replenished frequently.[24] One such area of replenishment is the Oort cloud, a spherical swarm of comets extending beyond 50,000 AU from the Sun first hypothesised by Dutch astronomer Jan Oort in 1950.[25] The Oort cloud is believed to be the point of origin of long-period comets, which are those, like Hale–Bopp, with orbits lasting thousands of years.
There is, however, another comet population, known as short-period or periodic comets, consisting of those comets that, like Halley's Comet, have orbital periods of less than 200 years. By the 1970s, the rate at which short-period comets were being discovered was becoming increasingly inconsistent with their having emerged solely from the Oort cloud.[26] For an Oort cloud object to become a short-period comet, it would first have to be captured by the giant planets. In 1980, in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, Uruguayan astronomer Julio Fernández stated that for every short-period comet to be sent into the inner Solar System from the Oort cloud, 600 would have to be ejected into interstellar space. He speculated that a comet belt from between 35 and 50 AU would be required to account for the observed number of comets.[27] Following up on Fernández's work, in 1988 the Canadian team of Martin Duncan, Tom Quinn and Scott Tremaine ran a number of computer simulations to determine if all observed comets could have arrived from the Oort cloud. They found that the Oort cloud could not account for all short-period comets, particularly as short-period comets are clustered near the plane of the Solar System, whereas Oort-cloud comets tend to arrive from any point in the sky. With a "belt", as Fernández described it, added to the formulations, the simulations matched observations.[28] Reportedly because the words "Kuiper" and "comet belt" appeared in the opening sentence of Fernández's paper, Tremaine named this hypothetical region the "Kuiper belt".[29]
Discovery

In 1987, astronomer David Jewitt, then at MIT, became increasingly puzzled by "the apparent emptiness of the outer Solar System".[7] He encouraged then-graduate student Jane Luu to aid him in his endeavour to locate another object beyond Pluto's orbit, because, as he told her, "If we don't, nobody will."[30] Using telescopes at the Kitt Peak National Observatory in Arizona and the Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory in Chile, Jewitt and Luu conducted their search in much the same way as Clyde Tombaugh and Charles Kowal had, with a blink comparator.[30] Initially, examination of each pair of plates took about eight hours,[31] but the process was sped up with the arrival of electronic charge-coupled devices or CCDs, which, though their field of view was narrower, were not only more efficient at collecting light (they retained 90% of the light that hit them, rather than the 10% achieved by photographs) but allowed the blinking process to be done virtually, on a computer screen. Today, CCDs form the basis for most astronomical detectors.[32] In 1988, Jewitt moved to the Institute of Astronomy at the University of Hawaii. Luu later joined him to work at the University of Hawaii's 2.24 m telescope at Mauna Kea.[33] Eventually, the field of view for CCDs had increased to 1024 by 1024 pixels, which allowed searches to be conducted far more rapidly.[34] Finally, after five years of searching, on August 30, 1992, Jewitt and Luu announced the "Discovery of the candidate Kuiper belt object" (15760) 1992 QB1.[7] Six months later, they discovered a second object in the region, (181708) 1993 FW.[35]
Studies conducted since the trans-Neptunian region was first charted have shown that the region now called the Kuiper belt is not the point of origin of short-period comets, but that they instead derive from a linked population called the scattered disc. The scattered disc was created when Neptune migrated outward into the proto-Kuiper belt, which at the time was much closer to the Sun, and left in its wake a population of dynamically stable objects that could never be affected by its orbit (the Kuiper belt proper), and a population whose perihelia are close enough that Neptune can still disturb them as it travels around the Sun (the scattered disc). Because the scattered disc is dynamically active and the Kuiper belt relatively dynamically stable, the scattered disc is now seen as the most likely point of origin for periodic comets.[9]
Name
Astronomers sometimes use the alternative name Edgeworth–Kuiper belt to credit Edgeworth, and KBOs are occasionally referred to as EKOs. However, Brian G. Marsden claims that neither deserves true credit: "Neither Edgeworth nor Kuiper wrote about anything remotely like what we are now seeing, but Fred Whipple did".[36] David Jewitt comments: "If anything ... Fernández most nearly deserves the credit for predicting the Kuiper Belt."[17]
KBOs are sometimes called kuiperoids, a name suggested by Clyde Tombaugh.[37] The term trans-Neptunian object (TNO) is recommended for objects in the belt by several scientific groups because the term is less controversial than all others—it is not an exact synonym though, as TNOs include all objects orbiting the Sun past the orbit of Neptune, not just those in the Kuiper belt.
Origins

The precise origins of the Kuiper belt and its complex structure are still unclear, and astronomers are awaiting the completion of several wide-field survey telescopes such as Pan-STARRS and the future LSST, which should reveal many currently unknown KBOs. These surveys will provide data that will help determine answers to these questions.[3]
The Kuiper belt is believed to consist of planetesimals, fragments from the original protoplanetary disc around the Sun that failed to fully coalesce into planets and instead formed into smaller bodies, the largest less than 3,000 kilometres (1,900 mi) in diameter.
Modern computer simulations show the Kuiper belt to have been strongly influenced by Jupiter and Neptune, and also suggest that neither Uranus nor Neptune could have formed in their present positions, as too little primordial matter existed at that range to produce objects of such high mass. Instead, these planets are believed to have formed closer to Jupiter. Scattering of planetesimals early in the Solar System's history would have led to migration of the orbits of the giant planets: Saturn, Uranus and Neptune drifted outwards while Jupiter drifted inwards. Eventually, the orbits shifted to the point where Jupiter and Saturn reached an exact 2:1 resonance; Jupiter orbited the Sun twice for every one Saturn orbit. The gravitational repercussions of such a resonance ultimately disrupted the orbits of Uranus and Neptune, causing Neptune's orbit to become more eccentric and move outward into the primordial planetesimal disc, which sent the disc into temporary chaos.[38][39][40] As Neptune's orbit expanded, it excited and scattered many TNO planetesimals into higher and more eccentric orbits.[41] Many more were scattered inward, often to be scattered again and in some cases ejected by Jupiter. The process is thought to have reduced the primordial Kuiper belt population by 99% or more, and to have shifted the distribution of the surviving members outward.[40]
However, this currently most popular model, the "Nice model", still fails to account for some of the characteristics of the distribution and, quoting one of the scientific articles,[42] the problems "continue to challenge analytical techniques and the fastest numerical modeling hardware and software". The model predicts a higher average eccentricity in classical KBO orbits than is observed (0.10–0.13 versus 0.07).[40] The frequency of paired objects, many of which are far apart and loosely bound, also poses a problem for the model.[43]
Structure
At its fullest extent, including its outlying regions, the Kuiper belt stretches from roughly 30 to 55 AU. However, the main body of the belt is generally accepted to extend from the 2:3 resonance (see below) at 39.5 AU to the 1:2 resonance at roughly 48 AU.[44] The Kuiper belt is quite thick, with the main concentration extending as much as ten degrees outside the ecliptic plane and a more diffuse distribution of objects extending several times farther. Overall it more resembles a torus or doughnut than a belt.[45] Its mean position is inclined to the ecliptic by 1.86 degrees.[46]
The presence of Neptune has a profound effect on the Kuiper belt's structure due to orbital resonances. Over a timescale comparable to the age of the Solar System, Neptune's gravity destabilises the orbits of any objects that happen to lie in certain regions, and either sends them into the inner Solar System or out into the scattered disc or interstellar space. This causes the Kuiper belt to possess pronounced gaps in its current layout, similar to the Kirkwood gaps in the asteroid belt. In the region between 40 and 42 AU, for instance, no objects can retain a stable orbit over such times, and any observed in that region must have migrated there relatively recently.[47]
Classical belt
Between the 2:3 and 1:2 resonances with Neptune, at approximately 42–48 AU, the gravitational influence of Neptune is negligible, and objects can exist with their orbits essentially unaltered. This region is known as the classical Kuiper belt, and its members comprise roughly two thirds of KBOs observed to date.[48][49] Because the first modern KBO discovered, (15760) 1992 QB1, is considered the prototype of this group, classical KBOs are often referred to as cubewanos ("Q-B-1-os").[50][51] The guidelines established by the IAU demand that classical KBOs be given names of mythological beings associated with creation.[52]
The classical Kuiper belt appears to be a composite of two separate populations. The first, known as the "dynamically cold" population, has orbits much like the planets; nearly circular, with an orbital eccentricity of less than 0.1, and with relatively low inclinations up to about 10° (they lie close to the plane of the Solar System rather than at an angle). The second, the "dynamically hot" population, has orbits much more inclined to the ecliptic, by up to 30°. The two populations have been named this way not because of any major difference in temperature, but from analogy to particles in a gas, which increase their relative velocity as they become heated up.[53] The two populations not only possess different orbits, but different colors; the cold population is markedly redder than the hot. If this is a reflection of different compositions, it suggests they formed in different regions. The hot population is believed to have formed near Jupiter, and to have been ejected out by movements among the gas giants. The cold population, on the other hand, has been proposed to have formed more or less in its current position, although it might also have been later swept outwards by Neptune during its migration,[3][54] particularly if Neptune's eccentricity was transiently increased.[40] Although the Nice model appears to be able to at least partially explain a compositional difference, it has also been suggested the color difference may reflect differences in surface evolution.[40]
Resonances

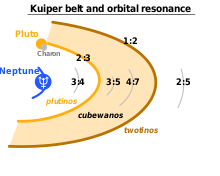
When an object's orbital period is an exact ratio of Neptune's (a situation called a mean-motion resonance), then it can become locked in a synchronised motion with Neptune and avoid being perturbed away if their relative alignments are appropriate. If, for instance, an object orbits the Sun twice for every three Neptune orbits, and if it reaches perihelion with Neptune a quarter of an orbit away from it, then whenever it returns to perihelion, Neptune will always be in about the same relative position as it began, because it will have completed 1+1⁄2 orbits in the same time. This is known as the 2:3 (or 3:2) resonance, and it corresponds to a characteristic semi-major axis of about 39.4 AU. This 2:3 resonance is populated by about 200 known objects,[55] including Pluto together with its moons. In recognition of this, the members of this family are known as plutinos. Many plutinos, including Pluto, have orbits that cross that of Neptune, though their resonance means they can never collide. Plutinos have high orbital eccentricities, suggesting that they are not native to their current positions but were instead thrown haphazardly into their orbits by the migrating Neptune.[56] IAU guidelines dictate that all plutinos must, like Pluto, be named for underworld deities.[52] The 1:2 resonance (whose objects complete half an orbit for each of Neptune's) corresponds to semi-major axes of ~47.7AU, and is sparsely populated.[57] Its residents are sometimes referred to as twotinos. Other resonances also exist at 3:4, 3:5, 4:7 and 2:5.[58] Neptune possesses a number of trojan objects, which occupy its L4 and L5 points; gravitationally stable regions leading and trailing it in its orbit. Neptune trojans are often described as being in a 1:1 resonance with Neptune. Neptune trojans typically have very stable orbits.
Additionally, there is a relative absence of objects with semi-major axes below 39 AU that cannot apparently be explained by the present resonances. The currently accepted hypothesis for the cause of this is that as Neptune migrated outward, unstable orbital resonances moved gradually through this region, and thus any objects within it were swept up, or gravitationally ejected from it.[59]
"Kuiper cliff"

The 1:2 resonance appears to be an edge beyond which few objects are known. It is not clear whether it is actually the outer edge of the classical belt or just the beginning of a broad gap. Objects have been detected at the 2:5 resonance at roughly 55 AU, well outside the classical belt; however, predictions of a large number of bodies in classical orbits between these resonances have not been verified through observation.[56]
Based on estimations of the primordial mass required to form Uranus and Neptune, as well as bodies as large as Pluto (see below), earlier models of the Kuiper belt had suggested that the number of large objects would increase by a factor of two beyond 50 AU,[60] so this sudden drastic falloff, known as the "Kuiper cliff", was completely unexpected, and its cause, to date, is unknown. In 2003, Bernstein and Trilling et al. found evidence that the rapid decline in objects of 100 km or more in radius beyond 50 AU is real, and not due to observational bias. Possible explanations include that material at that distance was too scarce or too scattered to accrete into large objects, or that subsequent processes removed or destroyed those that did.[61] Patryk Lykawka of Kobe University has claimed that the gravitational attraction of an unseen large planetary object, perhaps the size of Earth or Mars, might be responsible.[62][63]
Composition

Studies of the Kuiper belt since its discovery have generally indicated that its members are primarily composed of ices: a mixture of light hydrocarbons (such as methane), ammonia, and water ice,[64] a composition they share with comets.[65] The low densities observed in those KBOs whose diameter is known, (less than 1 g cm−3) is consistent with an icy makeup.[64] The temperature of the belt is only about 50 K,[66] so many compounds that would be gaseous closer to the Sun remain solid.
Due to their small size and extreme distance from Earth, the chemical makeup of KBOs is very difficult to determine. The principal method by which astronomers determine the composition of a celestial object is spectroscopy. When an object's light is broken into its component colors, an image akin to a rainbow is formed. This image is called a spectrum. Different substances absorb light at different wavelengths, and when the spectrum for a specific object is unravelled, dark lines (called absorption lines) appear where the substances within it have absorbed that particular wavelength of light. Every element or compound has its own unique spectroscopic signature, and by reading an object's full spectral "fingerprint", astronomers can determine what it is made of.
Initially, such detailed analysis of KBOs was impossible, and so astronomers were only able to determine the most basic facts about their makeup, primarily their color.[67] These first data showed a broad range of colors among KBOs, ranging from neutral grey to deep red.[68] This suggested that their surfaces were composed of a wide range of compounds, from dirty ices to hydrocarbons.[68] This diversity was startling, as astronomers had expected KBOs to be uniformly dark, having lost most of the volatile ices from their surfaces to the effects of cosmic rays.[69] Various solutions were suggested for this discrepancy, including resurfacing by impacts or outgassing.[67] However, Jewitt and Luu's spectral analysis of the known Kuiper belt objects in 2001 found that the variation in color was too extreme to be easily explained by random impacts.[70]
Although to date most KBOs still appear spectrally featureless due to their faintness, there have been a number of successes in determining their composition.[66] In 1996, Robert H. Brown et al. obtained spectroscopic data on the KBO 1993 SC, revealing its surface composition to be markedly similar to that of Pluto, as well as Neptune's moon Triton, possessing large amounts of methane ice.[71]
Water ice has been detected in several KBOs, including 1996 TO66,[72] 38628 Huya and 20000 Varuna.[73] In 2004, Mike Brown et al. determined the existence of crystalline water ice and ammonia hydrate on one of the largest known KBOs, 50000 Quaoar. Both of these substances would have been destroyed over the age of the Solar System, suggesting that Quaoar had been recently resurfaced, either by internal tectonic activity or by meteorite impacts.[66]
Mass and size distribution
Despite its vast extent, the collective mass of the Kuiper belt is relatively low. The total mass is estimated to range between 1/25th and 1/10th the mass of the Earth,[74] with some estimates placing it at one thirtieth of an Earth mass.[75] Conversely, models of the Solar System's formation predict a collective mass for the Kuiper belt of 30 Earth masses.[3] This missing >99% of the mass can hardly be dismissed, because it is required for the accretion of any KBOs larger than 100 km (62 mi) in diameter. If the Kuiper belt had always had its current low density these large objects simply could not have formed.[3] Moreover, the eccentricity and inclination of current orbits makes the encounters quite "violent" resulting in destruction rather than accretion. It appears that either the current residents of the Kuiper belt have been created closer to the Sun or some mechanism dispersed the original mass. Neptune's current influence is too weak to explain such a massive "vacuuming", though the Nice model proposes that it could have been the cause of mass removal in the past. Although the question remains open, the conjectures vary from a passing star scenario to grinding of smaller objects, via collisions, into dust small enough to be affected by solar radiation.[54]
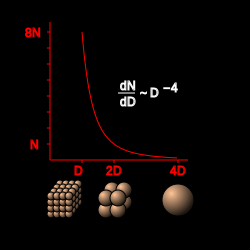
Bright objects are rare compared with the dominant dim population, as expected from accretion models of origin, given that only some objects of a given size would have grown further. This relationship between N(D) (the number of objects of diameter greater than D) and D, referred to as brightness slope, has been confirmed by observations. The slope is inversely proportional to some power of the diameter D:
- where the current measures[76] give q = 4 ±0.5.
This implies (assuming q is not 1) that
(The constant may be non-zero only if the power law doesn't apply at high values of D.)
Less formally, if q is 4, for example, there are 8 (=23) times more objects in the 100–200 km range than in the 200–400 km range, and for every object with a diameter between 1000 and 1010 km there should be around 1000 (=103) objects with diameter of 100 to 101 km.
If q is 1 or less, the law implies an infinite number and mass of large objects in the Kuiper belt. If 1<q≤4 there will be a finite number of objects greater than a given size, but the expected value of their combined mass would be infinite. If q is 4 or more, the law would imply an infinite mass of small objects. More accurate models find that the "slope" parameter q is in effect greater at large diameters and lesser at small diameters.[76] It seems that Pluto is somewhat unexpectedly large, having several percent of the total mass of the Kuiper belt. It is not expected that anything larger than Pluto exists in the Kuiper belt, and in fact most of the brightest (largest) objects at inclinations less than 5° have probably been found.[76]
Of course, only the absolute magnitude is actually known, the size is inferred assuming a given albedo (not a safe assumption for larger objects).
As of December 2009, the smallest Kuiper belt object detected is 980 m across. It is too dim (magnitude 35) to be seen by Hubble directly, but it was detected by Hubble's star tracking system when it occulted a star.[77]
Scattered objects

The scattered disc is a sparsely populated region, overlapping with the Kuiper belt but extending to beyond 100 AU. Scattered disc objects (SDOs) have very elliptical orbits, often also very inclined to the ecliptic. Most models of Solar System formation show both KBOs and SDOs first forming in a primordial belt, with later gravitational interactions, particularly with Neptune, sending the objects outward, some into stable orbits (the KBOs) and some into unstable orbits, the scattered disc.[9] Due to its unstable nature, the scattered disc is believed to be the point of origin of many of the Solar System's short-period comets. Their dynamic orbits occasionally force them into the inner Solar System, first becoming centaurs, and then short-period comets.[9]
According to the Minor Planet Center, which officially catalogues all trans-Neptunian objects, a KBO, strictly speaking, is any object that orbits exclusively within the defined Kuiper belt region regardless of origin or composition. Objects found outside the belt are classed as scattered objects.[78] However, in some scientific circles the term "Kuiper belt object" has become synonymous with any icy minor planet native to the outer Solar System believed to have been part of that initial class, even if its orbit during the bulk of Solar System history has been beyond the Kuiper belt (e.g. in the scattered-disc region). They often describe scattered disc objects as "scattered Kuiper belt objects".[79] Eris, which is known to be more massive than Pluto, is often referred to as a KBO, but is technically an SDO.[78] A consensus among astronomers as to the precise definition of the Kuiper belt has yet to be reached, and this issue remains unresolved.
The centaurs, which are not normally considered part of the Kuiper belt, are also believed to be scattered objects, the only difference being that they were scattered inward, rather than outward. The Minor Planet Center groups the centaurs and the SDOs together as scattered objects.[78]
Triton

During its period of migration, Neptune is thought to have captured one of the larger KBOs: This is its moon Triton, which is the only large moon in the Solar System to have a retrograde orbit; it orbits opposite to Neptune's rotation. This suggests that, unlike the large moons of Jupiter, Saturn, and Uranus, which are thought to have coalesced from spinning discs of material encircling their young parent planets, Triton was a fully formed body that was captured from surrounding space. Gravitational capture of an object is not easy; it requires some mechanism to slow down the object enough to be caught by the larger object's gravity. Triton may have encountered Neptune as part of a binary (many KBOs are members of binaries; see below); ejection of the other member of the binary by Neptune could then explain Triton's capture.[80] Triton is only slightly larger than Pluto, and spectral analysis of both worlds shows that they are largely composed of similar materials, such as methane and carbon monoxide. All this points to the conclusion that Triton was once a KBO that was captured by Neptune during its outward migration.[81]
Largest KBOs

Since 2000, a number of KBOs with diameters of between 500 and 1,500 km (932 mi), more than half that of Pluto (diameter 2370 km), have been discovered. 50000 Quaoar, a classical KBO discovered in 2002, is over 1,200 km across. Makemake and Haumea, both announced on July 29, 2005, are larger still. Other objects, such as 28978 Ixion (discovered in 2001) and 20000 Varuna (discovered in 2000) measure roughly 500 km (311 mi) across.[3]
Pluto
The discovery of these large KBOs in similar orbits to Pluto led many to conclude that, bar its relative size, Pluto was not particularly different from other members of the Kuiper belt. Not only did these objects approach Pluto in size, but many also possessed satellites, and were of similar composition (methane and carbon monoxide have been found both on Pluto and on the largest KBOs).[3] Thus, just as Ceres was considered a planet before the discovery of its fellow asteroids, some began to suggest that Pluto might also be reclassified.
The issue was brought to a head by the discovery of Eris, an object in the scattered disc far beyond the Kuiper belt, that is now known to be 27% more massive than Pluto.[82] (Eris was originally thought to be larger than Pluto by volume, but the New Horizons mission found this not to be the case.) In response, the International Astronomical Union (IAU), was forced to define what a planet is for the first time, and in so doing included in their definition that a planet must have "cleared the neighbourhood around its orbit".[83] As Pluto shared its orbit with so many KBOs, it was deemed not to have cleared its orbit, and was thus reclassified from a planet to a member of the Kuiper belt.
Although Pluto is currently the largest known KBO, there is at least one known larger object currently outside the Kuiper belt that probably originated in it: Neptune's moon Triton (which, as explained above, is probably a captured KBO).
As of 2008, only five objects in the Solar System (Ceres, Eris, and the KBOs Pluto, Makemake and Haumea) are listed as dwarf planets by the IAU. However, 90482 Orcus, 28978 Ixion and many other Kuiper-belt objects are large enough to be in hydrostatic equilibrium; most of them will probably qualify when more is known about them.[84][85][86]
Satellites
Of the four largest TNOs, three (Eris, Pluto, and Haumea) have satellites, and two have more than one. A higher percentage of the larger KBOs possess satellites than the smaller objects in the Kuiper belt, suggesting that a different formation mechanism was responsible.[87] There are also a high number of binaries (two objects close enough in mass to be orbiting "each other") in the Kuiper belt. The most notable example is the Pluto–Charon binary, but it is estimated that around 11% of KBOs exist in binaries.[88]
Exploration

On January 19, 2006, the first spacecraft mission to explore the Kuiper belt, New Horizons, was launched. The mission, headed by Alan Stern of the Southwest Research Institute, flew by Pluto on July 14, 2015, and, circumstances permitting, will continue on to study another as-yet-undetermined KBO. Any KBO chosen will be between 40 and 90 km (25 to 55 miles) in diameter and, ideally, white or grey, to contrast with Pluto's reddish color.[90] John Spencer, an astronomer on the New Horizons mission team, says that no target for a post-Pluto Kuiper belt encounter has yet been selected, as they are awaiting data from the Pan-STARRS survey project to ensure as wide a field of options as possible.[91] The Pan-STARRS project, partially operational since May 2010,[92] will, when fully online, survey the entire sky with four 1.4 gigapixel digital cameras to detect any moving objects, from near-Earth objects to KBOs.[93] To speed up the detection process, the New Horizons team established Ice Hunters, a citizen science project that allowed members of the public to participate in the search for suitable KBO targets;[94][95][96] the project has subsequently been transferred to another site, Ice Investigators,[97] produced by CosmoQuest.[98]
On October 15, 2014, NASA announced finding several KBOs that may be targeted by New Horizons.[89]
Extrasolar Kuiper belts

By 2006, astronomers had resolved dust discs believed to be Kuiper belt-like structures around nine stars other than the Sun. They appear to fall into two categories: wide belts, with radii of over 50 AU, and narrow belts (tentatively like that of the Solar System) with radii of between 20 and 30 AU and relatively sharp boundaries.[99] Beyond this, 15–20% of solar-type stars have an observed infrared excess that is believed to indicate massive Kuiper-belt-like structures.[100] Most known debris discs around other stars are fairly young, but the two images on the right, taken by the Hubble Space Telescope in January 2006, are old enough (roughly 300 million years) to have settled into stable configurations. The left image is a "top view" of a wide belt, and the right image is an "edge view" of a narrow belt.[99][101] Computer simulations of dust in the Kuiper belt suggest that when it was younger, it may have resembled the narrow rings seen around younger stars.[102]
See also
Notes
- ^ a b The literature is inconsistent in the usage of the terms scattered disc and Kuiper belt. For some, they are distinct populations; for others, the scattered disc is part of the Kuiper belt. Authors may even switch between these two uses in a single publication.[10] Because the International Astronomical Union's Minor Planet Center, the body responsible for cataloguing minor planets in the Solar System, makes the distinction,[11] the current editorial choice for Wikipedia articles on the trans-Neptunian region is to make this distinction as well. This choice means that, on Wikipedia, Eris, the most-massive known trans-Neptunian object, is not part of the Kuiper belt, and this makes Pluto the most-massive Kuiper belt object.
References
- ^ Kuiper belt - oxforddictionaries.com
- ^ Alan Stern; Colwell, Joshua E. (1997). "Collisional Erosion in the Primordial Edgeworth-Kuiper Belt and the Generation of the 30–50 AU Kuiper Gap". The Astrophysical Journal. 490 (2): 879–882. Bibcode:1997ApJ...490..879S. doi:10.1086/304912.
- ^ a b c d e f g Audrey Delsanti; David Jewitt. "The Solar System Beyond The Planets" (PDF). Institute for Astronomy, University of Hawaii. Archived from the original (PDF) on September 25, 2007. Retrieved March 9, 2007.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|last-author-amp=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ Krasinsky, G. A.; Pitjeva, E. V.; Vasilyev, M. V.; Yagudina, E. I. (July 2002). "Hidden Mass in the Asteroid Belt". Icarus. 158 (1): 98–105. Bibcode:2002Icar..158...98K. doi:10.1006/icar.2002.6837.
- ^ Johnson, Torrence V.; and Lunine, Jonathan I.; Saturn's moon Phoebe as a captured body from the outer Solar System, Nature, Vol. 435, pp. 69–71
- ^ Craig B. Agnor; Douglas P. Hamilton (2006). "Neptune's capture of its moon Triton in a binary-planet gravitational encounter" (PDF). Nature. Archived from the original (PDF) on June 21, 2007. Retrieved June 20, 2006.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|last-author-amp=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c Jewitt, David; Luu, Jane (1993). "Discovery of the candidate Kuiper belt object 1992 QB1". Nature. 362 (6422): 730. Bibcode:1993Natur.362..730J. doi:10.1038/362730a0.
- ^ NEW HORIZONS The PI's Perspective
- ^ a b c d Harold F. Levison; Luke Donnes (2007). "Comet Populations and Cometary Dynamics". In Lucy Ann Adams McFadden; Paul Robert Weissman; Torrence V. Johnson (eds.). Encyclopedia of the Solar System (2nd ed.). Amsterdam; Boston: Academic Press. pp. 575–588. ISBN 0-12-088589-1.
- ^ Weissman and Johnson, 2007, Encyclopedia of the solar system, footnote p. 584
- ^ IAU: Minor Planet Center (January 3, 2011). "List Of Centaurs and Scattered-Disk Objects". Central Bureau for Astronomical Telegrams, Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics. Retrieved January 3, 2011.
- ^ Gérard FAURE (2004). "Description of the System of Asteroids as of May 20, 2004". Archived from the original on May 29, 2007. Retrieved June 1, 2007.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "What is improper about the term "Kuiper belt"? (or, Why name a thing after a man who didn't believe its existence?)". International Comet Quarterly. Retrieved October 24, 2010.
- ^ J. K. Davies; J. McFarland; M. E. Bailey; B. G. Marsden; W. I. Ip (2008). "The Early Development of Ideas Concerning the Transneptunian Region". In M. Antonietta Baracci; Hermann Boenhardt; Dale Cruikchank; Alissandro Morbidelli (eds.). The Solar System Beyond Neptune (PDF). University of Arizona Press. pp. 11–23.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|display-editors=4(help) - ^ John Davies (2001). Beyond Pluto: Exploring the outer limits of the solar system. Cambridge University Press. xii.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|nopp=ignored (|no-pp=suggested) (help) - ^ Davies, p. 2
- ^ a b David Jewitt. "WHY "KUIPER" BELT?". University of Hawaii. Retrieved June 14, 2007.
- ^ a b Davies, p. 14
- ^ Rao, M. M. (1964). "Decomposition of Vector Measures" (PDF). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 51 (5): 771. Bibcode:1964PNAS...51..771R. doi:10.1073/pnas.51.5.771.
- ^ CT Kowal; W Liller; BG Marsden (1977). "The discovery and orbit of /2060/ Chiron". In: Dynamics of the solar system; Proceedings of the Symposium. 81. Hale Observatories, Harvard–Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics: 245. Bibcode:1979IAUS...81..245K.
- ^ JV Scotti; DL Rabinowitz; CS Shoemaker; EM Shoemaker; DH Levy; TM King; EF Helin; J Alu; K Lawrence; RH McNaught; L Frederick; D Tholen; BEA Mueller (1992). "1992 AD". IAU Circ. 5434: 1. Bibcode:1992IAUC.5434....1S.
- ^ Horner, J.; Evans, N.W.; Bailey, M. E. (2004). "Simulations of the Population of Centaurs I: The Bulk Statistics". MNRAS. 354 (3): 798–810. arXiv:astro-ph/0407400. Bibcode:2004MNRAS.354..798H. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2004.08240.x.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Davies p. 38
- ^ David Jewitt (2002). "From Kuiper Belt Object to Cometary Nucleus: The Missing Ultrared Matter". The Astronomical Journal. 123 (2): 1039–1049. Bibcode:2002AJ....123.1039J. doi:10.1086/338692.
- ^ Oort, J. H. (1950). "The structure of the cloud of comets surrounding the Solar System and a hypothesis concerning its origin". Bull. Astron. Inst. Neth. 11: 91. Bibcode:1950BAN....11...91O.
- ^ Davies p. 39
- ^ JA Fernández (1980). "On the existence of a comet belt beyond Neptune". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 192: 481. Bibcode:1980MNRAS.192..481F. doi:10.1093/mnras/192.3.481.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ M. Duncan; T. Quinn; S. Tremaine (1988). "The origin of short-period comets". Astrophysical Journal. 328: L69. Bibcode:1988ApJ...328L..69D. doi:10.1086/185162.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|last-author-amp=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ Davies p. 191
- ^ a b Davies p. 50
- ^ Davies p. 51
- ^ Davies pp. 52, 54, 56
- ^ Davies pp. 57, 62
- ^ Davies p. 65
- ^ BS Marsden; Jewitt, D.; Marsden, B. G. (1993). "1993 FW". IAU Circ. 5730. Minor Planet Center: 1. Bibcode:1993IAUC.5730....1L.
- ^ Davies p. 199
- ^ Clyde Tombaugh, "The Last Word", Letters to the Editor, Sky & Telescope, December, 1994, p. 8
- ^ Hansen, K. (June 7, 2005). "Orbital shuffle for early solar system". Geotimes. Retrieved August 26, 2007.
- ^ Tsiganis, K.; Gomes, R.; Morbidelli, A.; Levison, H. F. (2005). "Origin of the orbital architecture of the giant planets of the Solar System". Nature. 435 (7041): 459–461. Bibcode:2005Natur.435..459T. doi:10.1038/nature03539. PMID 15917800.
- ^ a b c d e Levison, H. F.; Morbidelli, A.; Van Laerhoven, C.; Gomes, R. (2008). "Origin of the structure of the Kuiper belt during a dynamical instability in the orbits of Uranus and Neptune". Icarus. 196 (1): 258–273. arXiv:0712.0553. Bibcode:2008Icar..196..258L. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2007.11.035.
- ^ Thommes, E. W.; Duncan, M. J.; Levison, H. F. (2002). "The Formation of Uranus and Neptune among Jupiter and Saturn". The Astronomical Journal. 123 (5): 2862. arXiv:astro-ph/0111290. Bibcode:2002AJ....123.2862T. doi:10.1086/339975.
- ^ Malhotra, R. (1994). "Nonlinear Resonances in the Solar System". Physica D. 77: 289. arXiv:chao-dyn/9406004. Bibcode:1994PhyD...77..289M. doi:10.1016/0167-2789(94)90141-4.
- ^ Lovett, R. (2010). "Kuiper Belt may be born of collisions". Nature. doi:10.1038/news.2010.522.
- ^ M. C. De Sanctis; M. T. Capria; A. Coradini (2001). "Thermal Evolution and Differentiation of Edgeworth-Kuiper Belt Objects". The Astronomical Journal. 121 (5): 2792–2799. Bibcode:2001AJ....121.2792D. doi:10.1086/320385.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|last-author-amp=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ "Discovering the Edge of the Solar System". American Scientists.org. 2003. Archived from the original on March 5, 2008. Retrieved June 23, 2007.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Michael E. Brown; Margaret Pan (2004). "The Plane of the Kuiper Belt". The Astronomical Journal. 127 (4): 2418–2423. Bibcode:2004AJ....127.2418B. doi:10.1086/382515.
- ^ Jean-Marc Petit; Alessandro Morbidelli; Giovanni B. Valsecchi (1998). "Large Scattered Planetesimals and the Excitation of the Small Body Belts" (PDF). Retrieved June 23, 2007.
- ^ Lunine, J. (2003). "The Kuiper Belt" (PDF). Retrieved June 23, 2007.
- ^ Jewitt, D. (February 2000). "Classical Kuiper Belt Objects (CKBOs)". Archived from the original on June 9, 2007. Retrieved June 23, 2007.
- ^ Murdin, P. (2000). "Cubewano". The Encyclopedia of Astronomy and Astrophysics. Bibcode:2000eaa..bookE5403.. doi:10.1888/0333750888/5403. ISBN 0-333-75088-8.
- ^ Elliot, J. L.; et al. (2005). "The Deep Ecliptic Survey: A Search for Kuiper Belt Objects and Centaurs. II. Dynamical Classification, the Kuiper Belt Plane, and the Core Population" (PDF). The Astronomical Journal. 129: 1117–1162. Bibcode:2005AJ....129.1117E. doi:10.1086/427395.
- ^ a b "Naming of Astronomical Objects: Minor Planets". International Astronomical Union. Retrieved November 17, 2008.
- ^ Levison, H. F; Morbidelli, A. (2003). "The formation of the Kuiper belt by the outward transport of bodies during Neptune's migration". Nature. 426 (6965): 419–421. Bibcode:2003Natur.426..419L. doi:10.1038/nature02120. PMID 14647375.
- ^ a b Morbidelli, A. (2005). "Origin and Dynamical Evolution of Comets and their Reservoirs". arXiv:astro-ph/0512256.
{{cite arXiv}}:|class=ignored (help) - ^ "List Of Transneptunian Objects". Minor Planet Center. Retrieved June 23, 2007.
- ^ a b Chiang; et al. (2003). "Resonance Occupation in the Kuiper Belt: Case Examples of the 5:2 and Trojan Resonances". The Astronomical Journal. 126 (1): 430–443. arXiv:astro-ph/0301458. Bibcode:2003AJ....126..430C. doi:10.1086/375207.
- ^ Wm. Robert Johnston (2007). "Trans-Neptunian Objects". Retrieved June 23, 2007.
- ^ Davies p. 104
- ^ Davies p. 107
- ^ E. I. Chiang; M. E. Brown (1999). "Keck Pencil-Beam Survey For Faint Kuiper Belt Objects" (PDF). Retrieved July 1, 2007.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|last-author-amp=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ G.M. Bernstein; D.E. Trilling; R.L. Allen; M.E. Brown; M. Holman; R. Malhotra (2004). "The Size Distribution of Trans-Neptunian Bodies" (PDF). The Astrophysical Journal. 128 (3): 1364. arXiv:astro-ph/0308467. Bibcode:2004AJ....128.1364B. doi:10.1086/422919.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|last-author-amp=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ Michael Brooks (2007). "13 Things that do not make sense". NewScientistSpace.com. Retrieved June 23, 2007.
- ^ Govert Schilling (2008). "The mystery of Planet X". New Scientist. Retrieved February 8, 2008.
- ^ a b Stephen C. Tegler (2007). "Kuiper Belt Objects: Physical Studies". In Lucy-Ann McFadden; et al. (eds.). Encyclopedia of the Solar System. pp. 605–620.
- ^ Altwegg, K.; Balsiger, H.; Geiss, J. (1999). "Composition of the Volatile Material in Halley's Coma from In Situ Measurements". Space Science Reviews. 90: 3–18. Bibcode:1999SSRv...90....3A. doi:10.1023/A:1005256607402.
- ^ a b c David C. Jewitt; Jane Luu (2004). "Crystalline water ice on the Kuiper belt object (50000) Quaoar" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on June 21, 2007. Retrieved June 21, 2007.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|last-author-amp=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Dave Jewitt (2004). "Surfaces of Kuiper Belt Objects". University of Hawaii. Archived from the original on June 9, 2007. Retrieved June 21, 2007.
- ^ a b Jewitt, David; Luu, Jane (1998). "Optical-Infrared Spectral Diversity in the Kuiper Belt". The Astronomical Journal. 115 (4): 1667. Bibcode:1998AJ....115.1667J. doi:10.1086/300299.
- ^ Davies p. 118
- ^ Jewitt, David C.; Luu, Jane X. (2001). "Colors and Spectra of Kuiper Belt Objects". The Astronomical Journal. 122 (4): 2099. arXiv:astro-ph/0107277. Bibcode:2001AJ....122.2099J. doi:10.1086/323304.
- ^ Brown, R. H.; Cruikshank, DP; Pendleton, Y; Veeder, GJ (1997). "Surface Composition of Kuiper Belt Object 1993SC". Science. 276 (5314): 937–9. Bibcode:1997Sci...276..937B. doi:10.1126/science.276.5314.937. PMID 9163038.
- ^ Brown, Michael E.; Blake, Geoffrey A.; Kessler, Jacqueline E. (2000). "Near-Infrared Spectroscopy of the Bright Kuiper Belt Object 2000 EB173". The Astrophysical Journal. 543 (2): L163. Bibcode:2000ApJ...543L.163B. doi:10.1086/317277.
- ^ Licandro; Oliva; Di MArtino (2001). "NICS-TNG infrared spectroscopy of trans-neptunian objects 2000 EB173 and 2000 WR106". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 373 (3): L29. arXiv:astro-ph/0105434. Bibcode:2001A&A...373L..29L. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20010758.
- ^ Gladman, Brett; et al. (August 2001). "The structure of the Kuiper belt". Astronomical Journal. 122 (2): 1051–1066. Bibcode:2001AJ....122.1051G. doi:10.1086/322080.
- ^ Lorenzo Iorio (2007). "Dynamical determination of the mass of the Kuiper Belt from motions of the inner planets of the Solar system". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 375 (4): 1311–1314. Bibcode:2007MNRAS.tmp...24I. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2006.11384.x.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: bibcode (link) CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ a b c Bernstein, G. M.; Trilling, D. E.; Allen, R. L.; Brown, K. E.; Holman, M.; Malhotra, R. (2004). "The size distribution of transneptunian bodies". The Astronomical Journal. 128 (3): 1364–1390. arXiv:astro-ph/0308467. Bibcode:2004AJ....128.1364B. doi:10.1086/422919.
- ^ "Hubble Finds Smallest Kuiper Belt Object Ever Seen". HubbleSite. December 2009. Retrieved June 29, 2015.
- ^ a b c "List Of Centaurs and Scattered-Disk Objects". IAU: Minor Planet Center. Retrieved October 27, 2010.
- ^ David Jewitt (2005). "The 1000 km Scale KBOs". University of Hawaii. Retrieved July 16, 2006.
- ^ Craig B. Agnor; Douglas P. Hamilton (2006). "Neptune's capture of its moon Triton in a binary-planet gravitational encounter" (PDF). Nature. Archived from the original (PDF) on June 21, 2007. Retrieved October 29, 2007.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|last-author-amp=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ Encrenaz, Thérèse; Kallenbach, R.; Owen, T.; Sotin, C. (2004). TRITON, PLUTO, CENTAURS, AND TRANS-NEPTUNIAN BODIES. Springer. ISBN 978-1-4020-3362-9. Retrieved June 23, 2007.
{{cite book}}:|work=ignored (help) - ^ Mike Brown (2007). "Dysnomia, the moon of Eris". CalTech. Retrieved June 14, 2007.
- ^ "Resolution B5 and B6" (PDF). International Astronomical Union. 2006.
- ^ "Ixion". eightplanets.net. Retrieved June 23, 2007.
- ^ John Stansberry; Will Grundy; Mike Brown; Dale Cruikshank; John Spencer; David Trilling; Jean-Luc Margot (2007). "Physical Properties of Kuiper Belt and Centaur Objects: Constraints from Spitzer Space Telescope". arXiv:astro-ph/0702538.
- ^ "IAU Draft Definition of Planet". IAU. 2006. Retrieved October 26, 2007.
- ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1086/501524 , please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1086/501524instead. - ^ Agnor, C.B.; Hamilton, D.P. (2006). "Neptune's capture of its moon Triton in a binary-planet gravitational encounter" (PDF). Nature. 441 (7090): 192–4. Bibcode:2006Natur.441..192A. doi:10.1038/nature04792. PMID 16688170.
- ^ a b Brown, Dwayne; Villard, Ray (October 15, 2014). "RELEASE 14-281 NASA's Hubble Telescope Finds Potential Kuiper Belt Targets for New Horizons Pluto Mission". NASA. Retrieved October 16, 2014.
- ^ "New Horizons mission timeline". NASA. Retrieved March 19, 2011.
- ^ Cal Fussman (2006). "The Man Who Finds Planets". Discover magazine. Retrieved August 13, 2007.
- ^ Institute for Astronomy, University of Hawai (2010). "PS1 goes Operational and begins Science Mission, May 2010". Retrieved August 30, 2010.
- ^ "Pan-Starrs: University of Hawaii". 2005. Retrieved August 13, 2007.
- ^ "Ice Hunters web site". Zooniverse.Org. Retrieved July 8, 2011.
- ^ "Citizen Scientists: Discover a New Horizons Flyby Target". NASA. June 21, 2011. Retrieved August 23, 2011.
- ^ Lakdawalla, Emily (June 21, 2011). "The most exciting citizen science project ever (to me, anyway)". The Planetary Society. Retrieved August 31, 2011.
- ^ "Ice Investigators". web site. CosmoQuest. 2012. Retrieved May 23, 2012.
- ^ "Finding Ice". CosmoQuest web site. CosmoQuest. May 20, 2012. Retrieved May 23, 2012.
{{cite web}}: External link in|work= - ^ a b Kalas, Paul; Graham, James R.; Clampin, Mark C.; Fitzgerald, Michael P. (2006). "First Scattered Light Images of Debris Disks around HD 53143 and HD 139664". The Astrophysical Journal. 637: L57. arXiv:astro-ph/0601488. Bibcode:2006ApJ...637L..57K. doi:10.1086/500305.
- ^ Trilling, D. E.; Bryden, G.; Beichman, C. A.; Rieke, G. H.; Su, K. Y. L.; Stansberry, J. A.; Blaylock, M.; Stapelfeldt, K. R.; Beeman, J. W.; Haller, E. E. (February 2008). "Debris Disks around Sun-like Stars". The Astrophysical Journal. 674 (2): 1086–1105. arXiv:0710.5498. Bibcode:2008ApJ...674.1086T. doi:10.1086/525514.
- ^ "Dusty Planetary Disks Around Two Nearby Stars Resemble Our Kuiper Belt". 2006. Retrieved July 1, 2007.
- ^ Kuchner, M. J.; Stark, C. C. (2010). "Collisional Grooming Models of the Kuiper Belt Dust Cloud". The Astronomical Journal. 140 (4): 1007–1019. arXiv:1008.0904. Bibcode:2010AJ....140.1007K. doi:10.1088/0004-6256/140/4/1007.
External links and data sources
- Dave Jewitt's page @ UCLA
- List of short period comets by family
- Kuiper Belt Profile by NASA's Solar System Exploration
- The Kuiper Belt Electronic Newsletter
- Wm. Robert Johnston's TNO page
- Minor Planet Center: Plot of the Outer Solar System, illustrating Kuiper gap
- Website of the International Astronomical Union (debating the status of TNOs)
- XXVIth General Assembly 2006
- nature.com article: diagram displaying inner solar system, Kuiper Belt, and Oort Cloud, taken from Alan Stern, S. (2003). "The evolution of comets in the Oort cloud and Kuiper belt". Nature. 424 (6949): 639–42. doi:10.1038/nature01725. PMID 12904784.
- SPACE.com: Discovery Hints at a Quadrillion Space Rocks Beyond Neptune (Sara Goudarzi) August 15, 2006 06:13 am ET
- The Outer Solar System Astronomy Cast episode No. 64, includes full transcript.
- The Kuiper belt at 365daysofastronomy.org
- Nine Planets' webpage on the Edgeworth-Kuiper Belt and Oort Cloud
- List of TNOS





