Flag of the United Kingdom: Difference between revisions
m Reverted edits by 129.241.214.20 to last version by ClueBot |
|||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
Placing the flag upside down is considered to be [[lèse majesté]] and is offensive to some,<ref>[http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/uk/politics/29213.stm Defence Secretary apologises for flag blunder] ''[[BBC News Online]]'', [[November 13]], [[1997]]</ref>. However, it can be deliberately flown upside down by the military as a distress signal.{{Fact|date=November 2007}} While this is currently rarely done, it was used by groups under siege during the [[Boer War]] and during campaigns in India in the late 18th century. |
Placing the flag upside down is considered to be [[lèse majesté]] and is offensive to some,<ref>[http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/uk/politics/29213.stm Defence Secretary apologises for flag blunder] ''[[BBC News Online]]'', [[November 13]], [[1997]]</ref>. However, it can be deliberately flown upside down by the military as a distress signal.{{Fact|date=November 2007}} While this is currently rarely done, it was used by groups under siege during the [[Boer War]] and during campaigns in India in the late 18th century. |
||
===Campaign for a new Union Flag=== |
|||
Wrexham’s Labour MP Ian Lucas said, on [[27 November]] [[2007]] in a House of Commons debate that the Union Jack should be combined with the Welsh flag to reflect Wales’ status within the UK, and that the Red Dragon should be added to the Union Jack’s red, white and blue pattern <ref>[http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/uk/7114248.stm Welsh dragon call for Union flag] ''[[BBC News Online]]'' [[November 27]] [[2007]]</ref>. He said the Union Jack currently only represented the other three UK nations, and Culture Minister Margaret Hodge conceded that Mr Lucas had raised a valid point for debate. She said the government is: "keen to make the Union Jack a positive symbol of Britishness reflecting the diversity of our country today and encouraging people to take pride in our flag". |
|||
===Flag Days (United Kingdom Government)=== |
===Flag Days (United Kingdom Government)=== |
||
Revision as of 18:08, 26 February 2008
It has been suggested that Union Flag and Talk:Flag of the United Kingdom#Merger proposal be merged into this article. (Discuss) Proposed since December 2007. |
 | |
| Union Flag or Union Jack | |
| Use | Civil and state flag |
|---|---|
| Proportion | 1:2 |
| Adopted | 1 January 1801 |
| Design | A white-fimbriated symmetric red cross on a blue field with a white-fimbriated counterchanged saltire of red and white. |
 | |
| Use | War flag |
| Proportion | 3:5 |
| Design | Same as above. |
 | |
| Use | Civil ensign |
| Proportion | 1:2 |
| Design | A red field with the Union Flag in the canton. See Red ensign. |
 | |
| Use | State ensign |
| Proportion | 1:2 |
| Design | A blue field with the Union Flag in the canton. See Blue ensign. |
 | |
| Use | Naval ensign |
| Proportion | 1:2 |
| Design | A symmetric red cross on a white field with the Union Flag in the canton. See White ensign. |
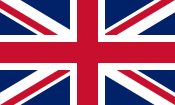
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland uses as its national flag the royal banner locally known as the Union Flag or, popularly, Union Jack [1] (although this name is the only one that is correct when the flag is flown on a jackstaff at sea)[2]. The current design of the Union Flag dates from the union of Ireland and Great Britain in 1801. It consists of the red cross of Saint George (patron saint of England), edged in white, superimposed on the diagonal red cross of Saint Patrick (patron saint of Ireland), which are superimposed on the Saltire of Saint Andrew (patron saint of Scotland).
Its correct proportions are 1:2. However, the version officially used by the British Army modifies the proportions to 3:5.
Flying the flag
The Union Flag can be flown by any individual or organisation in England, Scotland or Wales on any day of their choice. Legal regulations restrict the use of the Union Flag on Government buildings in Northern Ireland. Long-standing restrictions on Government use of the flag elsewhere were abolished in July 2007.[3][4]
Upside-down

While the flag appears, superficially, to be symmetric, closer inspection shows that the white lines above and below the diagonal red lines are of slightly different widths. On the side closest to the flagpole (or on the left when depicted on paper), the white lines above the diagonals are wider than the ones below; on the side furthest from the flagpole (or on the right when depicted on paper), the converse is true. Thus, rotating the flag by 180 degrees will have no change, but if mirrored the flag will be upside-down.
Placing the flag upside down is considered to be lèse majesté and is offensive to some,[5]. However, it can be deliberately flown upside down by the military as a distress signal.[citation needed] While this is currently rarely done, it was used by groups under siege during the Boer War and during campaigns in India in the late 18th century.
Flag Days (United Kingdom Government)
Until July 2007, the Union Flag was only flown on Government buildings on a limited number of special days each year. The choice of days was managed by the Department for Culture, Media and Sport (DCMS).[3] Government buildings are those used by civil servants, the Crown, or the armed forces. They were not applicable to private citizens, corporations, or local authorities.[3]
On 3 July 2007, the Justice Secretary Jack Straw laid a green paper before Parliament entitled The Governance of Britain.[4] Alongside a range of proposed changes to the constitutional arrangements of the UK was a specific announcement that there would be consultation on whether the rules on flag-flying on Government buildings should be relaxed.
Two days later, Prime Minister Gordon Brown announced that with immediate effect that the Union Flag would fly from the flag pole above the front entrance of 10 Downing Street on every day of the year. The intention was to increase feelings of 'Britishness'. Other Government departments were asked to follow this lead, and all Government buildings in Whitehall did so.[6][7][8][9][10][11][12]
Scotland Yard however stated that they would follow the previous rules until they are formally abolished by DCMS.[13]
James Purnell, the Culture Secretary has since concurred with the abolition of the restrictions – pending consultation on longer term arrangements.
Flag days
Until July 2007, the Union Flag was only flown on days marking the birthdays of members of the Royal Family, the wedding anniversary of the Monarch, Commonwealth Day, Accession Day, Coronation Day, The Queen's official birthday, Remembrance Sunday and on the days of the State Opening and prorogation of Parliament. The flag days when the Union Flag should be flown from government buildings all over the UK were:
- 20 January: birthday of Sophie, The Countess of Wessex
- 6 February: anniversary of the accession of Queen Elizabeth II
- 19 February: birthday of Prince Andrew, Duke of York
- Second Sunday in March: Commonwealth Day
- 10 March: birthday of Prince Edward, Earl of Wessex
- 21 April: birthday of Queen Elizabeth II
- 9 May: Europe Day
- 2 June: anniversary of the coronation of Queen Elizabeth II
- 10 June: birthday of Prince Philip, Duke of Edinburgh
- A Saturday in June: Official Birthday of Queen Elizabeth II
- 17 July: birthday of Camilla, The Duchess of Cornwall
- 15 August: birthday of Anne, Princess Royal
- Second Sunday in November: Remembrance Sunday
- 14 November: birthday of Charles, Prince of Wales
- 20 November: anniversary of the wedding of Queen Elizabeth II and Prince Philip
In addition, the flag should be flown in the following areas on the specified days:
- Wales – 1 March: Saint David's Day
- Northern Ireland – 17 March: Saint Patrick's Day
- England – 23 April: Saint George's Day
- Scotland – 30 November: Saint Andrew's Day
- Greater London: The day of the opening or proroguing of Parliament
On the national days of England, Scotland and Wales, their respective flags may also be flown if there is a second flagpole available, however the Union Flag should not be lowered if only one is present.
Flag Days (Scottish Government)

In Scotland, the Scottish Government has decreed that the Flag of Scotland ("the Saltire") will fly on all its buildings everyday from 8am until sunset, but there is no specific policy on flying the Union Flag and as such it is sometimes flown alongside the saltire and sometimes omitted. An exception is made for "national days". On these days, the Saltire shall be lowered and replaced with the Union Flag. These are the same as the flag days noted above with the exception of:
- 3 September: Merchant Navy Day
Another difference is that on Saint Andrew's Day, the Union Flag can only be flown if the building has more than one flagpole – the Saltire will not be lowered to makeway for the Union Flag if there is only one flagpole.[14]
Flag Days (Northern Ireland)
In Northern Ireland, the Union Flag is flown from buildings of the Northern Ireland Office as decreed by Regulations published in 2000.[15] The Regulations were amended in 2002 to remove the requirement to fly the flag on the birthdays of Queen Elizabeth, the Queen Mother and Princess Margaret, Countess of Snowdon who both died that year.[16] The current flag days are now the same as the United Kingdom government days noted above with the exception of the Duchess of Cornwall's birthday, which was only added to the UK flag days after her wedding to the Prince of Wales in 2005, and has not yet been extended to Northern Ireland.
The Police Service of Northern Ireland is the only body in the United Kingdom that is not permitted to fly the Union Flag, and is only permitted to fly its service flag or the Royal Standard in the event of a visit by the Sovereign.[17]
Half-mast
The Union Flag is flown from Government buildings at half-mast in the following situations:[18]
- from the announcement of the death of the Sovereign (an exception is made for Proclamation Day – the day the new Sovereign is proclaimed, when the Flag is flown at full staff from 11 am to sunset)
- the day of the funeral of a member of the British Royal Family
- the funeral of a foreign ruler
- the funeral of a current or former Prime Minister
The Sovereign sometimes declares other days when the Union Flag is to fly at half-mast. Half-mast means the flag is flown two-thirds up between the top and bottom of the flagstaff.[19]
Other bodies
Individuals, companies, local authorities, hospitals, and schools are free to fly the flag whenever they choose. Planning permission is not required to fly the Union Flag from a flagpole.
See also
- Union Flag
- List of British flags - a list of flags used within the United Kingdom, the Crown Dependencies and the British overseas territories.
- List of English flags - a list of flags used within England
- List of Scottish flags - a list of flags used within Scotland
- List of Welsh flags - a list of flags used within Wales
- List of Irish flags - a list of flags used within the Republic of Ireland
- Flag Institute
- National colours of the United Kingdom
References
- ^ Hansard Fourth Series Volume CXCII (192) pages 579-580 - formal announcement by the House of Lords
- ^ Royal Navy: Ship's Badges and Flags, see Union Flag
- ^ a b c Department for Culture, Media and Sport: Flag Flying
- ^ a b The Governance of Britain, for flying the Union Flag, see pp. 57–58
- ^ Defence Secretary apologises for flag blunder BBC News Online, November 13, 1997
- ^ We're all proud to fly the flag The Sun, 5 July 2007
- ^ Morning Press Briefing by Prime Minister's Spokesman, 6 July 2007
- ^ Union flag already flying all year round The Daily Telegraph 7 July 2007
- ^ Brown lifts ban on national flag BBC News Online 6 July 2007
- ^ Brown flies flag for Britain The Guardian 6 July 2007
- ^ Union Jack will fly over No 10 permanently 'to show values' The Times July 6, 2007
- ^ Gordon orders Whitehall to fly the flag in boost for Britishness Evening Standard 6 July 2007
- ^ Scotland Yard in flag cop out The Sun, 5 July 2007
- ^ Royal and ceremonial Scottish Government
- ^ The Flags Regulations (Northern Ireland) 2000
- ^ The Flags Regulations (Northern Ireland) (Amendment) 2002
- ^ Police Emblems and Flags Regulations (Northern Ireland) 2002
- ^ FAQ Department for Culture, Media and Sport
- ^ Rules Department for Culture, Media and Sport