Hazarajat
34°49′00″N 67°49′00″E / 34.8167°N 67.8167°E
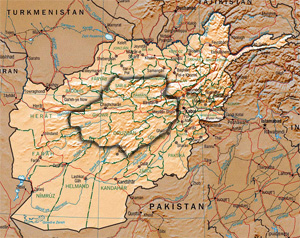 Hazaristan region shown within Afghanistan | |
| Area | Approx: 80,000 sq mi (207,199 km2) |
|---|---|
| Population | circa 8,000,000 |
| Density | 50/km2 (130/sq mi) |
| Provinces within Hazāristān | Bamyan, Daykundi, Ghor and parts of northern Ghazni, Uruzgan, Parwan and Maidan Wardak provinces[1] |
| Ethnicity | Hazaras |
| Languages spoken | Dari language (Hazaragi dialect) |
| Part of a series on |
| Hazaras |
|---|
 |
|
|
|
Hazāristān (Template:Lang-prs)[2] or Hazārajāt (هزاره جات) is a mountainous region in the central highlands of Afghanistan, among the Koh-i-Baba mountains in the western extremities of the Hindu Kush. It is the homeland of the Hazara people who make up the majority of its population. "Hazārajāt denotes an ethnic and religious zone."[3] Hazarajat is primarily made up of the provinces of Bamyan, Daykundi, Ghor and parts of northern Ghazni, Urozgan, Parwan and Maidan Wardak. The most populous towns in Hazarajat are Bamyan, Yakawlang (Bamyan), Nili (Daykundi), Lal wa Sarjangal (Ghor), Sang-e-Masha (Ghazni), Gizab (Urozgan) and Behsud (Maidan Wardak). The Kabul, Farah, Hari, Murghab, Balkh and Kunduz rivers originate from Hazarajat.
The name "Hazarajat" first appears in the 16th-century book Baburnama, written by Mughal Emperor Babur (died 1530). When the famous geographer Ibn Battuta arrived in Khurasan in 1333, he traveled across the country but did not record any place by the name of Hazarajat.[4]
Etymology and usage
The Hazara people[5] and surrounding peoples use the names Hazarajat or Hazaristan to identify the historic Hazara lands. Hazarajat is a compound of Hazara and the Dari suffix jat,[6] which is used to make words associated with land in south, central and west Asia.[7][need quotation to verify]
The Arab geographer Maqdesi (c. 945/946 – 991) named Hazarajat as Gharjistan or Gharj Al-Shar (Gharj meaning "mountain") area ruled by chiefs.[8][9] The name Hazarajat first appears in the 16th-century in Baburnama, written by Mughal Emperor Babur (r. 1526–1530).
Geography

Topography

The Hazarajat lies in the central highlands of Afghanistan, among the Koh-i Baba mountains and the western extremities of the Hindu Kush. Its boundaries have historically been inexact and shifting. Its physical boundaries, however, are roughly marked by the Bā-miān Basin (see BĀMIĀN ii.) to the north, the headwaters of the Helmand River (q.v.) to the south, Firuzkuh to the west, and the Unai Pass to the east. The regional terrain is very mountainous and extends to the Safid Kuh and the Siāh Kuh mountains, where the highest peaks are between 15,000 to 17,000 feet. Both sides of the Kuh-e Bābā range contain a succession of valleys. The north face of the range descends steeply, merging into low foothills and short semi-arid plains, while the south face stretches towards the Helmand Valley and the mountainous district of Behsud.[3][10]
The northeastern part of the Hazarajat, is the site of ancient Bamyan, a center of Buddhism and a key caravanserai on the Silk Road. The town is situated at a height of 7,500 feet and surrounded by the Hindu Kush to the north and Koh-i Baba to the south.[3]
Climate
Hazarajat is mountainous,[11] and a series of mountain passes extend along its eastern edge. One of them, Salang Pass, is blocked by snow six months out of the year. Another, Shibar Pass, at a lower elevation, is blocked by snow only two months out of the year.[12] Bamyan is the colder part of the region; winters there are severe.[13]
Hazarajat is the source of the rivers that run through Kabul, Arghandab, Helmand, Hari, Murghab, Balkh, and Kunduz, and during the spring and summer months, it has some of the greenest pastures in Afghanistan.[14] Natural lakes, green valleys and caves are found in Bamyan.[15]
History

| History of Afghanistan |
|---|
 |
| Timeline |
The area was ruled successively by the Achaemenids, Seleucids, Mauryas, Kushans, and Hephthalites before the Saffarids Islamized it and made it part of their empire. It was taken over by the Samanids, followed by the Ghaznavids and Ghurids before falling to the Delhi Sultanate. In the 13th century, it was invaded by Genghis Khan and his Mongols. In the following decades the Qarlughids emerged to create a local dynasty that offered a few decades of self-rule. Later, the area became part of the Timurid dynasty, the Mughal Empire and the Durrani Empire. The subjugation of the Hazarajat, particularly the mountain fortresses of Bamyan, proved difficult for the invaders at their conquest of the region. "adopted the language of the vanquished".[16][17][18]
19th century
In the 18th and 19th centuries developed among the Hazara tribes and the Pashtun tribes, began to coalesce.[19] It has been suggested that in the 19th century there was an emerging awareness of ethnic and religious differences among the population of Kabul. This brought about divisions along "confessional lines" that became reflected in new "spatial boundaries".[20] During the reign of Dost Mohammad Khan, Mir Yazdanbakhsh, a diligent chief of the Behsud Hazaras, consolidated many of the districts they controlled. Mir Yazdanbakhsh collected revenues and safeguarded caravans traveling on the Hajigak route through Bamyan to Kabul through Shekh Ali and Behsud areas. The consolidation of the Hazarajat thus increasingly made the region and its inhabitants a threat to the Durrani state.[21]

Until the late 19th century, the Hazarajat remained as a small part of Afghanistan and local chieftains obeyed from central government.[22] Joseph Pierre Ferrier, a French author who supposedly traveled through the region in the mid-19th century, described the inhabitants settled in the mountains near the rivers Balkh and Kholm "The Hazara population is very less but ungovernable, and has no occupation but pillage; they will pillage and pillage only, and plunder from camp to camp".[23] Only Pashtun rulers would control the area as they controlled it for centuries.[24]
Later in the early 1890s, the tribes of the Hazara were more noticed.[citation needed] Their population was about hundred thousand and were living in the central Afghanistan areas.[25]
During the Second Anglo-Afghan War, Colonel T. H. Holdich of the Indian Survey Department referred to the Hazarajat as "great unknown highlands".[26] And for the next few years, neither the Survey nor the Indian Intelligence Department succeeded in obtaining any trustworthy information on the routes between Herat and Kabul through the Hazarajat.[27]
Various members of the Afghan Boundary Commission were able to gather information that brought the geography of remote regions such as the Hazarajat further under state surveillance. In November 1884, the Commission crossed over the Koh-i Baba mountains by the Chashma Sabz Pass. General Peter Lumsden and Major C. E. Yate, who surveyed the tracts between Herat and the Oxus, visited the Qala-e Naw Pashtuns in the Paropamisus mountain range, to the east of the Jamshidis of Kushk. Noting surviving evidence of terraced cultivation in times past, both described the northern Pashtuns as semi-nomadic with large flocks of sheep and black cattle. They possessed an "inexhaustible supply of grass, the hills around being covered knee-deep with a luxuriant crop of pure rye".[28] Yate noted clusters of kebetkas, or the summer dwellings of the Qala-e Naw Pashtuns on the hillsides, and described "flocks and herds grazing in all directions".[29][30]
The geographical reach of the authority of the Afghan state was extended into the Hazarajat during the reign of Abdul Rahman Khan. Caught between the strategic interests of foreign powers and disappointed by the demarcation of the Durand Line in southern Afghanistan, which cut into Pashtun territory, he set out to bring the northern peripheries of the country more firmly under his control. This policy had disastrous consequences for the Hazarajat, whose inhabitants were singled out by Abdur Rahman Khan's regime.[31]
20th and 21st century
In the 1920s the ancient Shibar Pass road which leads through Bamyan and east to the Panjshir Valley was paved for lorries, and it remained the busiest road across the Hindu Kush until the building of the Salang tunnel in 1964 and the opening of a winter route. Hazaras migrated to cities and to surrounding countries, where they became laborers and undertook the hardest and lowest-paid work.[3]
In 1979, there were reportedly less than half million Hazaras in the Hazarajat and Kabul, although a reliable census has never been taken in Afghanistan.[32] As the Afghan state weakened, uprisings broke out in the Hazarajat, freeing the region from state rule by the summer of 1979 for the first time since the death of Amir Abdur Rahman Khan some Hazara resistance groups were formed in Iran, including Nasr and Sipah-i Pasdaran, with some being "committed to the idea of a separate Hazara national identity".[33] During the war with the Democratic Republic of Afghanistan, most of the Hazarajat was unoccupied and free of Soviet or state presence. The region became ruled once again by local leaders, or mirs, and a new stratum of young radical Shiʿi commanders. Economic conditions are reported to have decreased in the Hazarajat during the war.[34]
The group ruling Hazarajat was the Revolutionary Council of Islamic Unity of Afghanistan or Shura-i Ettefaq, led by Sayyid Ali Beheshti. The region's geographic nature and un-strategic location meant that the government and Soviets ignored it as they fought rebels elsewhere. This effectively allowed the Shura-i Ettefaq administration to rule over the region and give autonomy to the Hazaras. Their politically opposing groups were the pro-Iran Nasr and the Khans, who were mostly educated, secular and left-wing.[35][36] The Shura wanted a return to the 19th century status quo whereas the Nasr wanted an Iranian-style government of clerics. Between 1982 and 1984, an internal civil war caused the Shura to be overthrown by the Sazman-i Nasr and Sepah-i Pasdaran groups. However inter-factional rivalry continued thereafter. Most of the Hazara groups united in 1987 and in 1989 formed the Hizb-i-Wahdat.[36]
During the rule of Taliban, once again violence struck Hazarajat. In 1997, a revolt broke out among Hazara people in Mazar-i-Sharif when they refused to be disarmed by Taliban; 600 Taliban were killed in subsequent fighting.[37] In retaliation, the genocidal policies of Amir Abdur Rahman Khan's era was adopted by Taliban. In 1998, six hundred Hazaras were killed in the north; the intention was ethnic cleansing of Hazara.[38] At that stage, Hazarajat does not exist as an official region; the area comprises of the administrative provinces of Bamyan, Ghor, Wardak, Ghazni, Oruzgan, Juzjan, and Samangan.[34]
Demographics
Ethnic groups
The Hazaras constitute the majority of the Hazarajat population, with small Tajiks and Pashtuns minorities.[citation needed]
Language
Dari language is the official language in Hazarajat.
Health

Leprosy has been reported in the Hazarajat region of Afghanistan. The vast majority (60%) of the leprosy victims are Hazara.[39] In 1999, Leprosy Control stated that they were the only NGO providing anti-leprosy aid in the Hazarajat, and had been doing so since 1984.
A 1989 report noted that common diseases in the Hazarajat included gastrointestinal infections, typhoid, whooping cough, measles, leprosy, tuberculosis, rheumatoid arthritis and malaria.[40]
See also
References
- ^ "Bamyan Province". Naval Postgraduate School. 2011-11-15. Retrieved 2012-12-05.
- ^ – Some Hazara prefer to call the area Hazaristan, using the more modern "istan" ending.
- ^ a b c d Khazeni, Arash. "HAZĀRA i. Historical geography of Hazārajāt". Encyclopedia Iranica. Retrieved September 15, 2011.
- ^ Battuta, Ibn (2004). Travels in Asia and Africa, 1325–1354 (reprint, illustrated ed.). Routledge. p. 179. ISBN 978-0-415-34473-9. Retrieved 2010-09-10.
- ^ Bellew, H.W. (1880). The Races of Afghanistan: Being a Brief Account of the Principal Nations Inhabiting that Country. Calcutta: Thacker, Spink & Co. p. 114.
- ^
Mousavi, S. A. (1998). "1: Who are the Hazaras?". The Hazaras of Afghanistan: an historical, sultural, economic and political study. Abingdon: Routledge (published 2018). ISBN 9781136800160. Retrieved 26 January 2020.
Hazarajat is a composite name made up of Hazara and the Farsi-Arabic plural suffix, jat [...].
- ^ Mousavi, S.A. (1998). The Hazaras of Afghanistan: An Historical, Cultural, Economic and Political Study. Richmond, Surrey UK: Curzon Press. p. 34. ISBN 0-7007-0630-5.
- ^ Ḥamd-Allah Mostawfi, Nozhat al-qolub, tr. Guy Le Strange, London 1919. pp 415–16
- ^ S. A. Mousavi, The Hazaras of Afghanistan, London, 1998, p. 39.
- ^ Wilfred Thesiger "The Hazaras of Central Afghanistan," The Geographical Journal 71/3, 1955, pp. 313
- ^ Anonymous, Ḥodud al-ʿālam, tr. Minorsky, London, 1937; reprinted, 1982, p. 105
- ^ Johannes Humlum, La geographie de l’Afghanistan, Copenhagen, 1959, p. 64
- ^ Ebn Ḥawqal, Ke-tāb ṣurat al-arż, trs. J. H. Kramers and G. Wiet as Configuration de la terre, II, Paris, 1964, p. 227
- ^ Ḥamd-Allah Mostawfi, Nozhat al-qolub, tr. Guy Le Strange, London 1919, p. 212
- ^ S. A. Mousavi, The Hazaras of Afghanistan, London, 1998, p. 71
- ^ W. Barthold, An Historical Geography of Iran, Princeton, 1984, p. 82
- ^ J. P. Ferrier, Caravan Journeys and Wanderings in Persia, Afghanistan, Turkestan, and Beloochistan, London, 1856, p. 221
- ^ Johannes Humlum, La geographie de l’Afghanistan, Copenhagen, 1959, p. 87
- ^ Robert L. Canfield, Hazara Integration into the Afghan Nation, New York, 1973, p. 3
- ^ Christine Noelle, State and Tribe in Nineteenth-Century Afghanistan, Richmond, 1997, p. 22
- ^ C. Masson, Narrative of Various Journeys in Baloochistan, Afghanistan, and the Punjab. London, 1842, II, p. 296
- ^ W. Barthold, An Historical Geography of Iran, Princeton, 1984, pp. 82–83
- ^ J. P. Ferrier, Caravan Journeys and Wanderings in Persia, Afghanistan, Turkestan, and Beloochistan, London, 1856, pp. 219–20
- ^ Klaus Ferdinand, Preliminary Notes on Hazāra Culture, Copenhagen, 1959,p. 18
- ^ S. A. Mousavi, The Hazaras of Afghanistan, London, 1998, p. 95
- ^ T. H. Holdich, The Indian Borderland, 1880–1900, London, 1901, p. 41
- ^ A. C. Yate, Travels with the Afghan Boundary Commission, Edinburgh, 1887 pp. 147–48
- ^ C. E. Yate, Northern Afghanistan, Edinburgh, 1888, p. 9
- ^ C. E. Yate, Northern Afghanistan, Edinburgh, 1888, pp. 7–8
- ^ Peter Lumsden, "Countries and Tribes bordering on the Koh-e Baba Range," Proceedings of the Royal Geographical Society 7, 1885, pp. 562–63
- ^ Mir Munshi, ed., The Life of Abdur Rahman, Amir of Afghanistan, II, London, 1900, p. 276
- ^ Barnett Rubin, The Fragmentation of Afghanistan, New Haven, 2002, p. 26
- ^ Barnett Rubin, The Fragmentation of Afghanistan, New Haven, 2002. pp. 186, 191, 223
- ^ a b Barnett Rubin, The Fragmentation of Afghanistan, New Haven, 2002, p. 246
- ^ Ibrahimi, Niamatullah (September 2006). "THE FAILURE OF A CLERICAL PROTO-STATE: HAZARAJAT, 1979 - 1984" (Document). Crisis States Research Centre.
{{cite document}}: Unknown parameter|citeseerx=ignored (help) - ^ a b Nation, Ethnicity and the Conflict in Afghanistan: Political Islam and the rise of ethno-politics 1992–1996 by Raghav Sharma, 2016.
- ^ Ahmed Rashid, Taliban: Militant Islam, Oil, and Fundamentalism in Central Asia, London and New Haven, 2000, p. 58
- ^ Ahmed Rashid, Taliban: Militant Islam, Oil, and Fundamentalism in Central Asia, London and New Haven, 2000, pp. 67–74
- ^ Dr. Mohammad Salim Rasooli. Leprosy Situation in Afghanistan in 2001–2006 Archived 2011-07-25 at the Wayback Machine. Ministry of Public Health (MoPH) National Leprosy Control Program. 7–9 July 2008.
- ^ Poladi, Hassan (February 1989). The Hazāras. Mughal Pub. Co. ISBN 978-0-929824-00-0. Retrieved 7 March 2011.
