Shenzhou 14
 Roll out of Shenzhou 14 | |
| Mission type | Tiangong Space Station crew transport |
|---|---|
| COSPAR ID | 2022-060A |
| SATCAT no. | 52797 |
| Mission duration | 182 days, 9 hours and 25 minutes |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Spacecraft | Shenzhou 14 |
| Spacecraft type | Shenzhou |
| Manufacturer | China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation |
| Crew | |
| Crew size | 3 |
| Members | Chen Dong Liu Yang Cai Xuzhe |
| EVAs | 3 |
| EVA duration | 15 hours 53 minutes |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | 5 June 2022, 02:44:10 UTC[1] |
| Rocket | Long March 2F |
| Launch site | Jiuquan, LA-4/SLS |
| Contractor | China Academy of Launch Vehicle Technology |
| End of mission | |
| Landing date | 4 December 2022, 12:09 UTC[2] |
| Landing site | Inner Mongolia, China |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | Geocentric orbit |
| Regime | Low Earth orbit |
| Inclination | 41.5° |
| Docking with Tiangong Space Station | |
| Docking port | Tianhe Nadir |
| Docking date | 5 June 2022, 09:42 UTC |
| Undocking date | 4 December 2022, 03:01 UTC |
| Time docked | 181 days, 17 hours and 19 minutes |
 Shenzhou 14 mission patch  Cai Xuzhe, Chen Dong and Liu Yang | |
Shenzhou 14 (Chinese: 神舟十四号; pinyin: Shénzhōu Shísì-hào; lit. 'Divine Boat Number 14') was a Chinese spaceflight that launched on 5 June 2022 at 02:44 UTC. The flight marked the ninth crewed Chinese spaceflight and the fourteenth flight of the Shenzhou program. The spacecraft carried three People's Liberation Army Astronaut Corps (PLAAC) taikonauts on the third flight to the Tianhe core module, the first module of the Tiangong space station.[3] The launch of the three-person crew with a Long March 2F launch vehicle took place from the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center.
Shenzhou 14 successfully undocked from the Tianhe core module on 4 December 2022 at 03:01 UTC and subsequently performed a series of fast return de-orbit procedures which would enable the spacecraft to touchdown in nine hours. The reentry module returned to Earth on the same day at 12:09 UTC.
Background
The spaceflight was the second Chinese mission set to last six months (180 days).[4] After that, the six-month stay aboard the space station will become the normal duration of the astronaut crew in orbit.[5] The flight marked the third of four crewed missions scheduled to dock with the Tiangong space station by the end of construction in 2022.[6]
Mission

The mission visited the Tianhe core module following the launch and docking of Tianzhou 4, the third resupply mission to the station. The crew assisted with the assembly of the Wentian and Mengtian laboratories, which arrived at Tiangong in July and October respectively.[7] The Shenzhou 15 crew is scheduled to arrive 10 days before Shenzhou 14 departs, which means that the Shenzhou 14 mission marks the beginning of keeping the station permanently inhabited.[8]
The crew saluted while entering the Tianhe core module later on 5 June 2022, at 12:50 UTC as the third expedition to the Tiangong space station. On 24 July, Wentian was launched and successfully docked with Tianhe expanding the space station. On 25 July 2022 at 02:03 UTC, the crew of Shenzhou 14 opened the hatch and entered the Wentian module for the first time. On 31 October, Mengtian was launched and successfully docked with Tianhe forming the 'T-shape' structure of the space station. On 3 November 2022 at 07:12 UTC, the crew opened the hatch and entered the Mengtian module for the first time.
Three spacewalks took place during the crew's six-month stay in orbit. Shenzhou 15 was on standby for any possible rescue mission.[9]
Spacewalks
On 1 September 2022, the first planned spacewalk was carried out by Chen Dong and Liu Yang as they left the airlock of the Wentian lab module to conduct extravehicular activities. Liu became the second Chinese woman to carry out a spacewalk. They completed a series of tasks including installing an additional pump on the exterior, raising panoramic camera B, installing a workbench, demonstrating emergency return, etc. The spacewalk lasted for 6 hours and 7 minutes.[10][11]
On 17 September 2022, the second scheduled spacewalk was carried out by Chen Dong and Cai Xuzhe through the airlock of the Wentian lab module, with Liu Yang assisting the pair from inside the Tianhe core module. Chen and Cai completed a series of tasks, including the completion of the installation of foot restraints and extravehicular workbenches, and will follow up with the support of the small robotic arm, and cooperate with each other to carry out the installation of the outboard booster handle, the installation of the load circuit expansion pump set, and the verification of the extravehicular rescue capability. The spacewalk lasted for 4 hours and 12 minutes.[12]
On 17 November 2022, the third spacewalk was carried out by Chen Dong and Cai Xuzhe through the airlock of the Wentian lab module, with Liu Yang assisting the pair from inside the Tianhe core module. Chen and Cai completed a series of tasks, including the installation of a connection device between the Tianhe core module and Wentian lab module, the installation of an inter-chamber connection device between the Tianhe core module and Mengtian lab module, the raising of panoramic camera A of the Wentian lab module and the installation of a small mechanical arm power-assisted handle. The spacewalk lasted for 5 hours and 34 minutes.[13][14]
Spacecraft
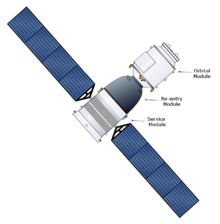
Shenzhou 14 spacecraft is based on Soyuz MS design concept. Shenzhou was approved in 1992 as part of the Chinese space program Project 921, and has a design similar to the Russian Soyuz spacecraft.[15]
In the front of the spacecraft, there is the orbital module which contains an androgynous docking ring based on APAS technology, which is used to dock to the Tianhe core module. In the middle is the reentry module containing the crew which is a scaled-up version of the Soyuz descent module. The rear of the spacecraft is the service module which is equipped with engines, fuel tanks, and solar panels.[16]
Crew
The crew was publicly announced in a press conference on 4 June 2022. Each crew member saluted when introduced, as is required by all taikonauts.[17]
Senior Colonel Chen Dong is a veteran of Shenzhou 11. Senior Colonel Liu Yang previously flew on Shenzhou 9, becoming the first Chinese woman in space. Senior Colonel Cai Xuzhe makes his first flight to space. By the time Shenzhou 14 completes the 180-day mission, Chen will have spent about 213 days in space, setting a new record for a Chinese astronaut.
| Position[18] | Crew member | |
|---|---|---|
| Commander | Second spaceflight | |
| Operator | Second spaceflight | |
| System and Science Operator | First spaceflight | |
Space lecture
On 12 October 2022 at 4:01 p.m. Beijing time (8:01 a.m. UTC), the three crew members held a lesson and conducted the scientific experiments from space station. The "main classroom" was in Beijing, and "branch classrooms" were in Zhengzhou, Henan province, Heze, Shandong province and Dali, Yunnan province. Chen Dong and Liu Yang introduced the functions of the Wentian module and conducted the scientific experiments and taught a science lesson to Chinese students by live television broadcast while Cai Xuzhe filmed the entire lecture. After a brief presentation of the taikonauts it was followed by the opportunity to answer schoolchildren's questions from the classrooms.[19]
See also
References
- ^ China Spaceflight [@CNSpaceflight] (6 April 2022). "Shenzhou 14 to be launched by Long March 2F Y14 on June.05 2022" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- ^ "长征二号F • 神舟十四号载人飞船(2022年待定) | 航天爱好者网". Archived from the original on 2021-08-04. Retrieved 2021-10-18.
- ^ Barbosa, Rui C. (1 March 2021). "China preparing to build Tiangong station in 2021, complete by 2022". NASASpaceFlight.com. Retrieved 1 March 2021.
- ^ "中国航天进入空间站建造关键时期——访中国载人航天工程办公室主任郝淳". xinhuanet.com. Retrieved 29 April 2021.
- ^ "空间站建造后续有四次载人飞行,航天员每次在轨驻留3至6个月". thepaper.cn. Retrieved 29 April 2021.
- ^ Barbosa, Rui C. (1 March 2021). "China preparing to build Tiangong station in 2021, complete by 2022". NASASpaceFlight.com. Retrieved 1 March 2021.
- ^ "www.spaceflightfans.cn/event/cz-5b_mt". spaceflightfans.cn. Archived from the original on 2021-04-26. Retrieved 2021-10-18.
- ^ "China reveals missions of Shenzhou-14, Shenzhou-15 space crews". 19 April 2022.
- ^ "China's next crewed spacecraft is ready for potential space station rescue mission". Space.com. Retrieved 8 June 2022.
- ^ Tong, Zhang. "China's spacewalkers take 2 steps towards faster Tiangong space station construction". South China Morning Post. Retrieved 2 September 2022.
- ^ Jones, Andrew. "China's Shenzhou 14 astronauts perform 1st spacewalk out of new module (video)". Space.com. Retrieved 4 September 2022.
- ^ Howell, Elizabeth (17 September 2022). "Chinese astronauts take 4-hour spacewalk outside new lab at Tiangong space station". Space.com. Retrieved 17 September 2022.
- ^ "Shenzhou-14 taikonauts perform third spacewalk". The Star. Retrieved 18 November 2022.
- ^ Jones, Andrew (18 November 2022). "China's Shenzhou 14 astronauts complete their 3rd and final spacewalk (video)". Space.com. Retrieved 28 November 2022.
- ^ William J. Broad (October 14, 2003). "China's Long March Into Orbit". The New York Times. Retrieved March 19, 2023.
- ^ "China's Shenzhou 13 crew docks with space station for 6-month stay". South China Morning Post. Retrieved 16 October 2021.
- ^ "Nation's latest space launch set for Sunday". RTHK. Reuters. 4 June 2022. Retrieved 4 June 2022.
- ^ "Shenzhou 14".
- ^ "中国空间站第三次太空授课活动取得圆满成功". 新华网. Retrieved 2022-10-12.
