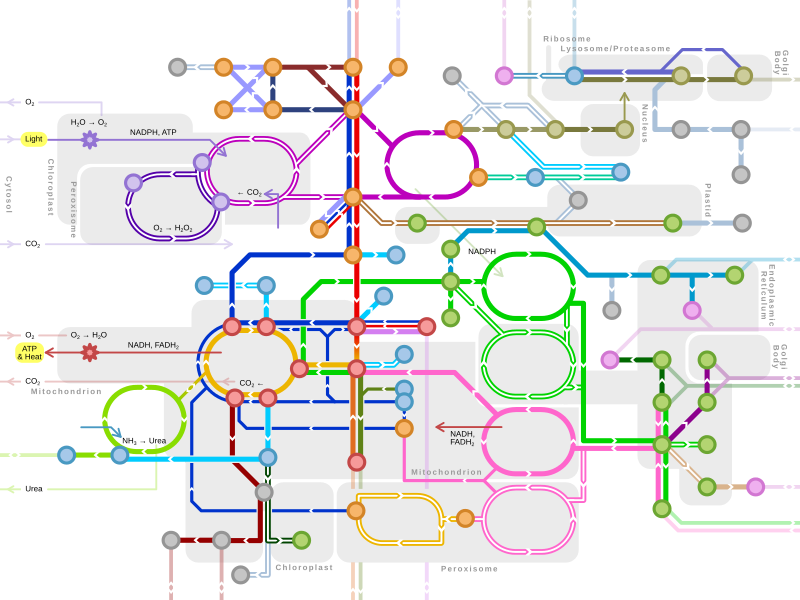
Metabolic pathway
| Part of a series on |
| Biochemistry |
|---|
 |
In biochemistry, a metabolic pathway is a linked series of chemical reactions occurring within a cell. The reactants, products, and intermediates of an enzymatic reaction are known as metabolites, which are modified by a sequence of chemical reactions catalyzed by enzymes.[1]: 26 In most cases of a metabolic pathway, the product of one enzyme acts as the substrate for the next. However, side products are considered waste and removed from the cell.[2] These enzymes often require dietary minerals, vitamins, and other cofactors to function.
Different metabolic pathways function based on the position within a eukaryotic cell and the significance of the pathway in the given compartment of the cell.[3] For instance, the, electron transport chain, and oxidative phosphorylation all take place in the mitochondrial membrane.[4]: 73, 74 & 109 In contrast, glycolysis, pentose phosphate pathway, and fatty acid biosynthesis all occur in the cytosol of a cell.[5]: 441–442
There are two types of metabolic pathways that are characterized by their ability to either synthesize molecules with the utilization of energy (anabolic pathway) or break down of complex molecules by releasing energy in the process (catabolic pathway).[6] The two pathways complement each other in that the energy released from one is used up by the other. The degradative process of a catabolic pathway provides the energy required to conduct a biosynthesis of an anabolic pathway.[6] In addition to the two distinct metabolic pathways is the amphibolic pathway, which can be either catabolic or anabolic based on the need for or the availability of energy.[7]
Pathways are required for the maintenance of homeostasis within an organism and the flux of metabolites through a pathway is regulated depending on the needs of the cell and the availability of the substrate. The end product of a pathway may be used immediately, initiate another metabolic pathway or be stored for later use. The metabolism of a cell consists of an elaborate network of interconnected pathways that enable the synthesis and breakdown of molecules (anabolism and catabolism).
Overview

Each metabolic pathway consists of a series of biochemical reactions that are connected by their intermediates: the products of one reaction are the substrates for subsequent reactions, and so on. Metabolic pathways are often considered to flow in one direction. Although all chemical reactions are technically reversible, conditions in the cell are often such that it is thermodynamically more favorable for flux to proceed in one direction of a reaction.[8] For example, one pathway may be responsible for the synthesis of a particular amino acid, but the breakdown of that amino acid may occur via a separate and distinct pathway. One example of an exception to this "rule" is the metabolism of glucose. Glycolysis results in the breakdown of glucose, but several reactions in the glycolysis pathway are reversible and participate in the re-synthesis of glucose (gluconeogenesis).
- Glycolysis was the first metabolic pathway discovered:
- As glucose enters a cell, it is immediately phosphorylated by ATP to glucose 6-phosphate in the irreversible first step.
- In times of excess lipid or protein energy sources, certain reactions in the glycolysis pathway may run in reverse to produce glucose 6-phosphate, which is then used for storage as glycogen or starch.
- Metabolic pathways are often regulated by feedback inhibition.
- Some metabolic pathways flow in a 'cycle' wherein each component of the cycle is a substrate for the subsequent reaction in the cycle, such as in the Krebs Cycle (see below).
- Anabolic and catabolic pathways in eukaryotes often occur independently of each other, separated either physically by compartmentalization within organelles or separated biochemically by the requirement of different enzymes and co-factors.
Major metabolic pathways
- See also: External links section for additional infographics of major metabolic pathways
Single lines: pathways common to most lifeforms. Double lines: pathways not in humans (occurs in e.g. plants, fungi, prokaryotes). |
Catabolic pathway (catabolism)
A catabolic pathway is a series of reactions that bring about a net release of energy in the form of a high energy phosphate bond formed with the energy carriers adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and guanosine diphosphate (GDP) to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and guanosine triphosphate (GTP), respectively.[4]: 91–93 The net reaction is, therefore, thermodynamically favorable, for it results in a lower free energy for the final products.[9]: 578–579 A catabolic pathway is an exergonic system that produces chemical energy in the form of ATP, GTP, NADH, NADPH, FADH2, etc. from energy containing sources such as carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. The end products are often carbon dioxide, water, and ammonia. Coupled with an endergonic reaction of anabolism, the cell can synthesize new macromolecules using the original precursors of the anabolic pathway.[10] An example of a coupled reaction is the phosphorylation of fructose-6-phosphate to form the intermediate fructose-1,6-bisphosphate by the enzyme phosphofructokinase accompanied by the hydrolysis of ATP in the pathway of glycolysis. The resulting chemical reaction within the metabolic pathway is highly thermodynamically favorable and, as a result, irreversible in the cell.[5]: 74–478
Cellular respiration
A core set of energy-producing catabolic pathways occur within all living organisms in some form. These pathways transfer the energy released by breakdown of nutrients into ATP and other small molecules used for energy (e.g. GTP, NADPH, FADH). All cells can perform anaerobic respiration by glycolysis. Additionally, most organisms can perform more efficient aerobic respiration through the citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation. Additionally plants, algae and cyanobacteria are able to use sunlight to anabolically synthesize compounds from non-living matter by photosynthesis.

Anabolic pathway (anabolism)
In contrast to catabolic pathways, anabolic pathways require an energy input to construct macromolecules such as polypeptides, nucleic acids, proteins, polysaccharides, and lipids. The isolated reaction of anabolism is unfavorable in a cell due to a positive Gibbs Free Energy (+ΔG). Thus, an input of chemical energy through a coupling with an exergonic reaction is necessary.[1]: 25–27 The coupled reaction of the catabolic pathway affects the thermodynamics of the reaction by lowering the overall activation energy of an anabolic pathway and allowing the reaction to take place.[1]: 25 Otherwise, an endergonic reaction is non-spontaneous.
An anabolic pathway is a biosynthetic pathway, meaning that it combines smaller molecules to form larger and more complex ones.[9]: 570 An example is the reversed pathway of glycolysis, otherwise known as gluconeogenesis, which occurs in the liver and sometimes in the kidney to maintain proper glucose concentration in the blood and supply the brain and muscle tissues with adequate amount of glucose. Although gluconeogenesis is similar to the reverse pathway of glycolysis, it contains three distinct enzymes from glycolysis that allow the pathway to occur spontaneously.[11] An example of the pathway for gluconeogenesis is illustrated in the image titled "Gluconeogenesis Mechanism".
Amphibolic pathway

An amphibolic pathway is one that can be either catabolic or anabolic based on the availability of or the need for energy.[9]: 570 The currency of energy in a biological cell is adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which stores its energy in the phosphoanhydride bonds. The energy is utilized to conduct biosynthesis, facilitate movement, and regulate active transport inside of the cell.[9]: 571 Examples of amphibolic pathways are the citric acid cycle and the glyoxylate cycle. These sets of chemical reactions contain both energy producing and utilizing pathways.[5]: 572 To the right is an illustration of the amphibolic properties of the TCA cycle.
The glyoxylate shunt pathway is an alternative to the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, for it redirects the pathway of TCA to prevent full oxidation of carbon compounds, and to preserve high energy carbon sources as future energy sources. This pathway occurs only in plants and bacteria and transpires in the absence of glucose molecules.[12]
Regulation
The flux of the entire pathway is regulated by the rate-determining steps.[1]: 577–578 These are the slowest steps in a network of reactions. The rate-limiting step occurs near the beginning of the pathway and is regulated by feedback inhibition, which ultimately controls the overall rate of the pathway.[13] The metabolic pathway in the cell is regulated by covalent or non-covalent modifications. A covalent modification involves an addition or removal of a chemical bond, whereas a non-covalent modification (also known as allosteric regulation) is the binding of the regulator to the enzyme via hydrogen bonds, electrostatic interactions, and Van Der Waals forces.[14]
The rate of turnover in a metabolic pathway, also known as the metabolic flux, is regulated based on the stoichiometric reaction model, the utilization rate of metabolites, and the translocation pace of molecules across the lipid bilayer.[15] The regulation methods are based on experiments involving 13C-labeling, which is then analyzed by Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) or gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS)-derived mass compositions. The aforementioned techniques synthesize a statistical interpretation of mass distribution in proteinogenic amino acids to the catalytic activities of enzymes in a cell.[15]: 178
See also
References
- ^ a b c d David L. Nelson; Cox, Michael M. (2008). Lehninger principles of biochemistry (5th ed.). New York: W.H. Freeman. ISBN 978-0-7167-7108-1.
- ^ Alison, Snape (2014). Biochemistry and molecular biology. Papachristodoulou, Despo K., Elliott, William H., Elliott, Daphne C. (Fifth ed.). Oxford. ISBN 9780199609499. OCLC 862091499.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Nicholson, Donald E. (March 1971). An Introduction to Metabolic Pathways by S. DAGLEY (Vol. 59, No. 2 ed.). Sigma Xi, The Scientific Research Society. p. 266.
- ^ a b Harvey, Richard A (2011). Biochemistry (5th ed.). Baltimore, MD 21201: Wolters Kluwer. ISBN 978-1-60831-412-6.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - ^ a b c Voet, Donald; Judith G. Voet; Charlotte W. Pratt (2013). Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecular Level (4th ed.). Hoboken, NJ: Wiley. ISBN 978-0470-54784-7.
- ^ a b Reece, Jane B. (2011). Campbell biology / Jane B. Reece ... [et al.] (9th ed.). Boston: Benjamin Cummings. pp. 143. ISBN 978-0-321-55823-7.
- ^ Berg, Jeremy M.; Tymoczko, John L.; Stryer, Lubert; Gatto, Gregory J. (2012). Biochemistry (7th ed.). New York: W.H. Freeman. p. 429. ISBN 978-1429229364.
- ^ Cornish-Bowden, A; Cárdenas, ML (2000). "10 Irreversible reactions in metabolic simulations: how reversible is irreversible?" (PDF). Animating the Cellular Map: 65–71.
- ^ a b c d Clarke, Jeremy M. Berg; John L. Tymoczko; Lubert Stryer. Web content by Neil D. (2002). Biochemistry (5. ed., 4. print. ed.). New York, NY [u.a.]: W. H. Freeman. ISBN 0716730510.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Peter H. Raven; Ray F. Evert; Susan E. Eichhorn (2011). Biology of plants (8. ed.). New York, NY: Freeman. pp. 100–106. ISBN 978-1-4292-1961-7.
- ^ Berg, Jeremy M.; Tymoczko, John L.; Stryer, Lubert; Gatto, Gregory J. (2012). Biochemistry (7th ed.). New York: W.H. Freeman. pp. 480–482. ISBN 9781429229364.
- ^ Choffnes, Eileen R.; Relman, David A.; Leslie Pray (2011). The science and applications of synthetic and systems biology workshop summary. Washington, D.C.: National Academies Press. p. 135. ISBN 978-0-309-21939-6.
- ^ Hill, Steve A.; Ratcliffe, R. George (1999). Kruger, Nicholas J. (ed.). Regulation of primary metabolic pathways in plants : [proceedings of an international conference held on 9 - 11 January 1997 at St Hugh's College, Oxford under the auspices of the Phytochemical Society of Europe]. Dordrecht [u.a.]: Kluwer. p. 258. ISBN 079235494X.
- ^ White, David (1995). The physiology and biochemistry of prokaryotes. New York [u.a.]: Oxford Univ. Press. p. 133. ISBN 0-19-508439-X.
- ^ a b Weckwerth, Wolfram, ed. (2006). Metabolomics methods and protocols. Totowa, N.J.: Humana Press. p. 177. ISBN 1597452440.
External links
- Full map of metabolic pathways
- Overview Map from BRENDA
- BioCyc: Metabolic network models for thousands of sequenced organisms
- KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes
- Reactome, a database of reactions, pathways and biological processes
- MetaCyc: A database of experimentally elucidated metabolic pathways (2,200+ pathways from more than 2,500 organisms).
- MetaboMAPS: A platform for pathway sharing and data visualization on metabolic pathways
- The Pathway Localization database (PathLocdb)
- Metabolism, Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis - The Virtual Library of Biochemistry, Molecular Biology and Cell Biology
- DAVID: Visualize genes on pathway maps
- Wikipathways: pathways for the people
- ConsensusPathDB
- metpath: Integrated interactive metabolic chart