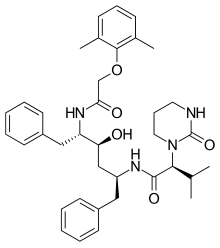
Lopinavir
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | ABT-378 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| MedlinePlus | a602015 |
| License data | |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Unknown |
| Protein binding | 98-99% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Elimination half-life | 5 to 6 hours |
| Excretion | Mostly fecal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.281.362 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C37H48N4O5 |
| Molar mass | 628.814 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Lopinavir is an antiretroviral of the protease inhibitor class. It is used against HIV infections as a fixed-dose combination with another protease inhibitor, ritonavir (lopinavir/ritonavir).[1]
It was patented in 1995 and approved for medical use in 2000.[2]
Side effects
Side effects, interactions, and contraindications have only been evaluated in the drug combination lopinavir/ritonavir.
Pharmacology
Lopinavir is highly bound to plasma proteins (98–99%).[3]
Reports are contradictory regarding lopinavir penetration into the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Anecdotal reports state that lopinavir cannot be detected in the CSF; however, a study of paired CSF-plasma samples from 26 patients receiving lopinavir/ritonavir found lopinavir CSF levels above the IC50 in 77% of samples.[4]
Research
A 2014 study indicates that lopinavir is effective against the human papilloma virus (HPV). The study used the equivalent of one tablet twice a day applied topically to the cervices of women with high-grade and low-grade precancerous conditions. After three months of treatment, 82.6% of the women who had high-grade disease had normal cervical conditions, confirmed by smears and biopsies.[5] In 2020 lopinavir/ritonavir was found not to work in severe COVID-19. In this trial the medication was started typically around 13 days after the start of symptoms.[6]
Lopinavir is found to inhibit MERS-CoV replication in the low-micromolar range in cell cultures.[7]
References
- ^ "FDA Approved Drug Products: Kaletra". Retrieved 30 April 2004.
- ^ Fischer, Jnos; Ganellin, C. Robin (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 510. ISBN 9783527607495.
- ^ KALETRA (lopinavir/ritonavir) capsules; (lopinavir/ritonavir) oral solution. Prescribing information. April 2009
- ^ Capparelli E, Holland D, Okamoto C, et al. (2005). "Lopinavir concentrations in cerebrospinal fluid exceed the 50% inhibitory concentration for HIV". AIDS. 19 (9).
- ^ HIV drug used to reverse effects of virus that causes cervical cancer University of Manchester, 17 February 2014.
- ^ Cao, Bin; Wang, Yeming; Wen, Danning; Liu, Wen; Wang, Jingli; Fan, Guohui; Ruan, Lianguo; Song, Bin; Cai, Yanping; Wei, Ming; Li, Xingwang; Xia, Jiaan; Chen, Nanshan; Xiang, Jie; Yu, Ting; Bai, Tao; Xie, Xuelei; Zhang, Li; Li, Caihong; Yuan, Ye; Chen, Hua; Li, Huadong; Huang, Hanping; Tu, Shengjing; Gong, Fengyun; Liu, Ying; Wei, Yuan; Dong, Chongya; Zhou, Fei; Gu, Xiaoying; Xu, Jiuyang; Liu, Zhibo; Zhang, Yi; Li, Hui; Shang, Lianhan; Wang, Ke; Li, Kunxia; Zhou, Xia; Dong, Xuan; Qu, Zhaohui; Lu, Sixia; Hu, Xujuan; Ruan, Shunan; Luo, Shanshan; Wu, Jing; Peng, Lu; Cheng, Fang; Pan, Lihong; Zou, Jun; Jia, Chunmin; Wang, Juan; Liu, Xia; Wang, Shuzhen; Wu, Xudong; Ge, Qin; He, Jing; Zhan, Haiyan; Qiu, Fang; Guo, Li; Huang, Chaolin; Jaki, Thomas; Hayden, Frederick G.; Horby, Peter W.; Zhang, Dingyu; Wang, Chen (18 March 2020). "A Trial of Lopinavir–Ritonavir in Adults Hospitalized with Severe Covid-19". New England Journal of Medicine. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2001282.
- ^ de Wilde, Adriaan H.; Jochmans, Dirk; Posthuma, Clara C.; Zevenhoven-Dobbe, Jessika C.; van Nieuwkoop, Stefan; Bestebroer, Theo M.; van den Hoogen, Bernadette G.; Neyts, Johan; Snijder, Eric J. (August 2014). "Screening of an FDA-Approved Compound Library Identifies Four Small-Molecule Inhibitors of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Replication in Cell Culture". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 58 (8): 4875–4884. doi:10.1128/AAC.03011-14.
External links
