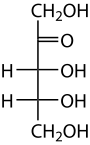
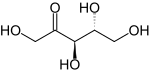
Ribulose
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(3R,4R)-1,3,4,5-Tetrahydroxypentan-2-one
| |||
| Other names
d-erythro-2-Pentulose
Adonose Arabinulose Araboketose Ribosone | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
| ||
| ChEBI |
| ||
| ChemSpider | |||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII |
| ||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C5H10O5 | |||
| Molar mass | 150.130 g·mol−1 | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Ribulose is a ketopentose — a monosaccharide containing five carbon atoms, and including a ketone functional group. It has chemical formula Template:Carbon5Template:Hydrogen10Template:Oxygen5. Two enantiomers are possible, d-ribulose (d-erythro-pentulose) and l-ribulose (l-erythro-pentulose). d-Ribulose is the diastereomer of d-xylulose.
Ribulose sugars are composed in the pentose phosphate pathway. They are important in the formation of many bioactive substances. For example, d-ribulose is an intermediate in the fungal pathway for d-arabitol production. Also, as the 1,5-bisphosphate, d-ribulose combines with carbon dioxide at the start of the photosynthesis process in green plants (carbon dioxide trap).