Dragon Quest (video game)
| Dragon Quest | |
|---|---|
 Box art of the original North American NES release, titled Dragon Warrior | |
| Developer(s) | Chunsoft |
| Director(s) | Koichi Nakamura |
| Producer(s) | Yukinobu Chida |
| Designer(s) | Yuji Horii |
| Programmer(s) | Koichi Nakamura |
| Artist(s) | Akira Toriyama |
| Composer(s) | Koichi Sugiyama |
| Series | Dragon Quest |
| Platform(s) | |
| Release | May 27, 1986
|
| Genre(s) | Role-playing |
| Mode(s) | Single-player |
Dragon Quest (Japanese: ドラゴンクエスト, Hepburn: Doragon Kuesuto), also released as Dragon Warrior, is the first role-playing video game (RPG) in the Dragon Quest media franchise. It was developed by Chunsoft for the Family Computer (or Famicom for short) and published by Enix in Japan in 1986 as Dragon Quest and by Nintendo in 1989 in North America for the Nintendo Entertainment System (or NES) as Dragon Warrior. Dragon Quest has been ported and remade for several video game platforms, including the MSX, PC-9801, X68000, Super Famicom, Game Boy Color, and mobile phones. In play, players control a hero character who is charged with saving the Kingdom of Alefgard and rescuing its princess from the evil Dragonlord. Dragon Warrior's story became the second part in a trilogy. Several more anime and manga games, which revolved around this overarching plot were created.
Dragon Quest was created by Yuji Horii, who took inspiration from previous role-playing games such as Wizardry, Ultima, and his own 1983 title The Portopia Serial Murder Case. Horii wanted to create an RPG which would appeal to a wide audience of people who were unfamiliar with the genre of video games in general. He tried to place a greater emphasis on storytelling and emotional involvement, as well as simplify the interface and expose the mostly Western computer genre to the Japanese console market. Manga artist and Dragon Ball creator Akira Toriyama produced the game's artwork and Koichi Sugiyama composed its music. The North American version featured numerous changes, including battery-backed RAM save games (rather than using a password save system), modified character sprites and pseudo-Elizabethan English style dialog.
Dragon Quest was commercially successful in Japan, with more than 2 million copies sold. Its release as Dragon Warrior in North America, and other Western countries, was less favorably received due to the more popular Final Fantasy series being released less than a year later. Later, Western critics noted the game's shortcomings but acknowledged its importance to the genre. Its original pseudo-Elizabethan English script has been praised in many of these reviews. Fan-made ROM hacks were released with substantial changes to the game. The game's sound effects have also been orchestrated, and its music has been performed at numerous concerts. As a whole, Dragon Warrior has been credited with establishing the basic template for the Japanese console RPGs that followed.
Gameplay
Dragon Warrior is a role-playing video game. Its gameplay mechanics have been described, years after its release, as simplistic and spartan.[3][4] Players control a young hero who sets out to defeat a being known as the Dragonlord.[5] Before starting the game, players are presented with a menu which allows them to begin a new quest (a game), continue a previous quest, or change the speed in which messages appear on the screen. In the Japanese version, continuing a quest requires players to enter a password; in the North American Nintendo Entertainment System (NES) English version, the quest is saved onto the game cartridge's battery-backup (known in the game as an "Adventure Log" in the "Imperial Scrolls of Honor").[3] The English version also has options to delete or duplicate a saved quest. If players choose to start a new quest, they may give the hero any name they wish in either Japanese kana or English letters depending on the version.[6][7] The hero's name has an effect on his initial ability scores and their statistical growth over the course of the game. Each stat falls into one of two categories, one with faster growth than the other, and the game determines which path each stat uses with a formula based on the kana or letters in the character's name.[8]
Dragon Warrior presents players with a clear objective from the start and uses a series of smaller scenarios to increase the hero's strength in order to achieve the objective.[9] The game begins in King Lorik's chamber in Tantegel Castle, where the hero receives information about the Dragonlord, whom he must defeat, and the stolen Balls of Light, which he must retrieve.[note 1] After receiving some items and gold, the hero sets out on his quest. Much of Dragon Warrior is spent talking to townspeople and gathering information from them that leads to additional places, events, and secrets. Players are advised to take notes of these hints for future reference. Towns contain shops that sell improved weapons and armor; general stores where the player may buy other goods; inns that allow the hero to recover his health and magic, and shops that offer keys for purchase. Players may sell items at half price to shops that provide weapons, armor, or general goods. The hero's status window is shown whenever he stops moving, displaying his current experience level (LV) and the amount of hit points (HP), magic points (MP), gold (G), and experience points (E).[10][11]
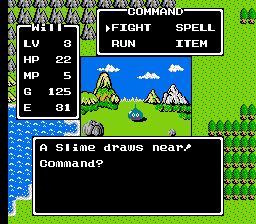
To safely progress to the next areas in the game, players need to accumulate experience points and gold by defeating enemies outside of towns – in the overworld and in dungeons.[12] Apart from the Dragonlord's castle, there are no physical restrictions on where players can roam.[13] Instead, monsters increase in difficulty as players venture further from Tantegel castle. As the hero's level increases, players can explore further afield with less risk.[14] Enemies appear in random encounters and the hero fights one opponent at a time.[3] The encounter rate is lowest on fields and increases in forests and hills.[15] Battles are turn-based and fought from a first-person perspective while the hero remains off-screen.[3] In combat, players must defeat the enemy by reducing its HP to zero. During combat, players have four commands: "fight", "run", "spell", and "item". The "fight" command causes the hero to attack the enemy with a weapon, or with his bare fists if no weapon is available, in an attempt to inflict damage. With the "run" command, the hero attempts to escape from a battle, which is recommended if his HP is low. The "spell" command casts magic that can, for example, heal the hero or damage the enemy. The "item" command uses herbs that replenish the hero's HP.[16]
During combat, the hero loses HP when he takes damage, and the display turns red when his HP is low. If his HP falls to zero, he dies and is taken back to King Lorik to be resurrected, and loses half his gold as punishment.[11] If the hero succeeds in defeating an enemy, he gains experience points and gold; if he gains enough experience points, his experience level increases, giving him greater strength, agility, speed, and the ability to use magic spells.[17] Every time a spell is used, the hero's MP decreases, with different spells costing different amounts of MP. Both HP and MP can be restored by resting at an inn. Additionally, a non-player character can replenish the hero's MP in Tantegel Castle.[16] As the hero earns more gold, he can purchase better weapons, armor, and items.[18] However, players have limited inventory space to hold items, so they must manage their item collection conservatively.[3] The caves which the hero explores are dark and require the use of a torch or the "RADIANT" spell to display a temporary field of vision around the character.[19] In the English version, players can return to King Lorik at any point to save the quest.[17][20] Because the Japanese version does not have a battery backup, players receive a password to return to a quest at a later time.[3]
The control pad may be used to move the hero in any direction and to move the flashing cursor in menu displays. Additional buttons confirm and cancel commands. In the English version, players use menu commands to talk to people, check their status, search beneath their feet, use items, take treasure chests, open doors, and go up or down stairs.[3][4][21] However, in some of the game's later remakes, certain commands were assigned to buttons, navigating stairs became automatic,[12][22] and the hero's speed was increased.[3] In the Japanese version, characters always face forward, so players must choose a command and then a direction in which to perform that action.[3] In the North American version, the hero turns to face the direction he is moving, making direction selection unnecessary.[3]
Plot
Dragon Warrior's plot is a simplistic medieval "rescue the princess, slay the dragonking, and get the orb of light" story.[4][12]
Backstory
Dragon Warrior, its sequel, Dragon Quest II, and its prequel, Dragon Quest III, comprise a trilogy with a shared timeline.[23][24] The story's background begins when the kingdom of Alefgard was shrouded in permanent darkness. The brave warrior Erdrick (known as "Loto" in the Game Boy Color (GBC) remake of the game) defeated an evil creature and restored light to the land. In Erdrick's possession was the Ball of Light,[note 1] which he used to drive away enemies who threatened the kingdom. Erdrick handed the Ball of Light to King Lorik, and Alefgard remained peaceful for a long time.[5] The Ball of Light kept winters short in Alefgard and helped maintain peace and prosperity for the region.[25]
However, there is one man who shunned the Ball of Light's radiance and secluded himself in a mountain cave. One day, while exploring the cave's extensive network of tunnels, the man encountered a sleeping dragon who awoke upon his entrance. He feared the dragon would incinerate him with its fiery breath, but the dragon instead knelt before him and obeyed his commands. This man, who is later discovered to be a dragon,[26] became known as the Dragonlord.[25] One day, after his soul became corrupted by learning magic,[26] the Dragonlord attacked Tantegel Castle and the nearby town of Breconnary with his fleet of dragons and set the town on fire. Riding a large red dragon, the Dragonlord descended upon Tantegel Castle and stole the Ball of Light. Soon, monsters began to appear throughout the entire land, destroying everything in their paths.[25] Much of the land became poisonous marshes, and at least one destroyed town (Hauksness, whose name is erroneously transposed with that of Rimuldar in the "Adventurer's Handbook" walkthrough) never recovered and remains in ruins even as of the time of gameplay.[5]
The following day, Erdrick arrived at Tantegel Castle to speak with King Lorik and offered his help to defeat the Dragonlord. After searching the land for clues to the Dragonlord's whereabouts, Erdrick found that the Dragonlord lived on an island that could be accessed only via a magical bridge that only a "Rainbow Drop" could generate. After venturing to the island, Erdrick was never heard from again.[25] Many years later, during King Lorik XVI's reign,[5] the Dragonlord attacked the kingdom again and captured Princess Gwaelin.[25] Many heroes tried to rescue the princess and recover the Ball of Light from the Dragonlord's castle, called Charlock, but none succeeded. The prophet Mahetta predicted that "One day, a descendant of the valiant Erdrick shall come forth to defeat the Dragonlord."[5] However, when the descendant (the game's hero) arrives, many of the people of Alefgard have forgotten the story of Erdrick, and those few who do remember consider it a myth and do not believe in Mahetta's prophecy. King Lorik starts to mourn the decline of his kingdom.[27]
Main story
The game begins when the player assumes the role of a stranger who arrives at Tantegel Castle. A castle guard tells him that a dragon has captured the princess and is holding her captive in a distant cave.[28] Determined to rescue the princess and defeat the Dragonlord, he discovers an ancient tablet hidden inside a desert cave; carved on the tablet is a message from Erdrick that outlines what the hero needs to do to follow in Erdrick's footsteps and defeat the Dragonlord.[25] The hero eventually rescues Princess Gwaelin, but realizes that in order to restore light to Alefgard, he must defeat the Dragonlord at Charlock Castle. After the hero collects a series of relics, he creates a bridge to reach Charlock and fights his way through the castle before finally confronting the Dragonlord. At this point the hero is given a dialogue choice – to side with the Dragonlord or to challenge him. If players choose the former, the game ends, the hero is put to sleep, and the game freezes (and, in the battery-operated North American NES version, deletes the player's saved game and possibly one or both others on the cartridge);[3] however, in the GBC remake, the hero instead wakes up from a bad dream. If players choose to fight, a final battle between the hero and the Dragonlord commences.[25][29]
Once the hero defeats the Dragonlord, he triumphantly returns to Tantegel Castle where King Lorik offers his kingdom as a reward. The hero turns down the offer and instead wishes to find his own kingdom. Accompanied by Princess Gwaelin, the hero then sets off in search of a new land; this sets the stage for the events in Dragon Warrior II, which take place many years later and tells the story of three of the hero's descendants.[25][30][31]
Characters
In Dragon Warrior the hero and the Dragonlord are the two main characters. Other major supporting characters are King Lorik (King Lars in the GBC remake); his daughter Princess Gwaelin (Lady Lora), and two sages the hero meets during his journey.[10]
The hero, who comes from a land beyond Alefgard,[32] is a descendant of the legendary Erdrick.[33][34] When the hero arrives, he does not appear to be a warrior – he arrives without weapons or armor – and is ignorant of the situation. The populace thinks his claim of the ability to defeat the Dragonlord are preposterous; however, King Lorik sees this ability, which give him hope and he aids the hero on his quest.[32]
The Dragonlord is a dragon who rules from Charlock Castle, which is visible from Tantegel Castle, the game's starting point.[9][10] His soul became evil by learning magic.[26] Rumors say that, through a spy network, he knows everything that happens in Alefgard.[32] He seeks "unlimited power and destruction",[26] which results in a rising tide of evil throughout Alefgard.[5] The Dragonlord wants to enslave the world with his army of monsters that he controls with his will.[10][32]
Development and release
Yuji Horii and his team at Chunsoft began developing Dragon Quest in 1985.[35] It was released in Japan in 1986 for the Famicom, the MSX,[36][37] and the PC-9801.[38] Dragon Quest has been released on multiple platforms since its initial release, including the X68000 in 1992 in Japan,[39] and for mobile phones in 2004 with updated graphics similar to those of Dragon Quest VI.[40]
Historical backdrop
When Eidansha Boshu Service Center was founded in 1975 it published tabloid magazines that advertised real estate. In 1982, after failing to establish a chain of stores, the company's founder Yasuhiro Fukushima transformed it into a software company devoted to gaming and renamed it Enix. To find talent for the company, Fukushima held the "Enix Game Hobby Program Contest". The competition was styled after manga competitions, was advertised in computer and manga magazines, and had a ¥1 million prize for the winners. The winners were Kazuro Morita (森田和郎), Koichi Nakamura, and manga magazine Shōnen Jump editor Yuji Horii, who was the top winner. Horii designed a tennis game, Love Match Tennis, which became Enix's first release. While he did not believe he would win, he was motivated by his editor, who enjoyed the games and published Horii's articles on them. Later, when Enix began creating games for the NES, Fukushima held another contest. This time, Nakamura won with his "cartoonish and creative contest entry" Door Door, which became Enix's first release for the NES.[41]
Horii's earliest inspiration for Dragon Quest is his own 1983 PC visual novel The Portopia Serial Murder Case[42] – a murder mystery adventure game that bears similarities to games such as Mystery House, Zork, King's Quest, and particularly Déjà Vu.[41][43] Horii wanted to advance the game's storyline by using dialogue. Portopia was originally released for Japan's NEC PC-6001 and was later ported to the NES in 1985.[43] The port is Enix's second release for the system and the first game which Horii and Nakamura worked on together.[41] Horii redesigned the interface for the port to accommodate the console's limited controls,[43] and added areas to the game in which the detective battles monsters.[41] While Portopia did not directly result in Dragon Quest's creation, it was, according to 1UP.com, "a proving ground" for the RPG. The menu-based command system of Portopia would later be used in Dragon Quest.[43]
At the time I first made Dragon Quest, computer and video game RPGs were still very much in the realm of hardcore fans and not very accessible to other players. So I decided to create a system that was easy to understand and emotionally involving, and then placed my story within that framework.
Yuji Horii on the design of the first Dragon Quest[44]
The original idea for Dragon Quest came during the development of Portopia. Horii and Nakamura came across the RPG Wizardry at a Macworld Conference & Expo. While it had some influence on Portopia's dungeon crawl segments, Horii liked the game's depth and visuals. He wanted to create a game similar to Wizardry, to expose the mainly Western-exclusive RPG genre to Japan and to expand the genre past computer enthusiasts.[41][43] Horii also cited Ultima as an inspiration for Dragon Quest's gameplay,[45][46] specifically the first-person random battles in Wizardry and the overhead perspective of Ultima.[3] While the RPG genre was predominantly Western and limited to PCs, Japanese gamers enjoyed home-grown games such as the The Black Onyx and the Dragon Slayer series alongside Western RPG ports. However, while Horii and Nakamura enjoyed the dungeon crawling and statistical nature of Wizardry, they realized most people would not. This had not originally been a concern, but the success of Super Mario Bros. greatly increased the potential audience of any new Famicom/NES game. To create Dragon Quest, the gameplay needed to be simplified.[41] According to Horii: "There was no keyboard, and the system was much simpler, using just a [game] controller. But I still thought that it would be really exciting for the player to play as their alter ego in the game. I personally was playing Wizardry and Ultima at the time, and I really enjoyed seeing my own self in the game."[43]
In order to create an RPG that would appeal to a wide audience unfamiliar with the genre, and video games in general, Horii wanted to create a new kind of RPG that did not rely on previous experience with the Dungeons & Dragons tabletop RPG, did not require hundreds of hours of rote fighting, and could appeal to any kind of gamer. To accomplish this he needed to simplify the system and have players associate themselves with the hero.[41][44] Thus as the game progressed, the hero would become stronger, in contrast to games like Super Mario Bros. where the character Mario did not become progressively more powerful during the game.[41] He wanted to build on Portopia and place a greater emphasis on storytelling and emotional involvement. He developed a coming-of-age tale that audiences could relate to and made use of RPG level-building gameplay as a way to represent this.[42]
Japanese development
Horii believed that the Famicom was the ideal platform for Dragon Quest, because unlike arcade games, players would not worry about spending money if they got a game over, and they could continue playing from where they left off.[9] Whenever the player loses a battle, they would immediately be restored to a previous save point rather than the game ending and returned to the main menu, making the game more accessible.[43] He also wanted to include multiple player characters but was forced to use only one due to memory constraints. Horii knew that RPGs had a steeper learning curve than other video games of the time, and to compensate for this he implemented quick level-ups at the start of the game and gave players a clear final goal that is visible from the world map's starting point: the Dragonlord's castle. He also provided a series of smaller scenarios in order to build up the player's strength to achieve the final objective.[9] He created an open world which is not blocked physically in any way except by monsters that can easily kill unprepared players; Gamasutra described this as one of the earliest examples of nonlinear gameplay. Horii used bridges to signify changes in difficulty and implemented a level progression with a high starting growth rate that decelerates over time, which contrasted to the random initial stats and constant growth rates of the early editions of Dungeons & Dragons.[47] To make the game appeal to a larger audience, manga artist and creator of Dragon Ball, Akira Toriyama, was hired to produce the artwork.[41][48] As with Dragon Ball, Toriyama's artwork features characters "whose strength and cunning transcend generations", but also includes humorous elements such as a chibi style.[49]
Koichi Sugiyama, the game's music composer, sought Enix out. Sugiyama sent a PC game's feedback questionnaire to Enix. He was already a well-known television composer, and, upon seeing Sugiyama's feedback, Fukushima contacted him to confirm that "he was the Sugiyama from television."[41] Upon confirmation, Fukushima asked Sugiyama to compose a score for Dragon Quest.[41] The game's classical score was Sugiyama's second video game composition after Wingman 2.[50] Sugiyama said it took him five minutes to compose the original opening theme, and noted the difficulty in adding a personal touch to the short jingles, but that his past experience with creating music for television commercials helped. According to Sugiyama, the composer has between three and five seconds to catch the audience's attention through music. The theme and his other jingles for Dragon Quest have remained relatively intact in its sequels.[50]
North American localization

Coverage of Dragon Quest's North American localization first appeared in Nintendo Fun Club News's winter 1988 issue – where the title changed to Dragon Warrior. The title was changed to avoid infringing on the trademark on wargame publisher Simulations Publications's pen-and-paper RPG DragonQuest.[46][51] The article about the game featured images from the game's Japanese version, Erdrick's original name ("Roto"), the Dragonlord's original name ("Dragon King"), and the original name of the game's starting location (Radatome Castle). It briefly explained the backstory and basic gameplay elements, comparing the game to The Legend of Zelda.[52] The game was later mentioned in Nintendo Power's "Pak Watch" preview section in March 1989, mentioning Dragon Quest III's Japanese release in the magazine's premiere July 1988 issue. It again mentioned the change of name from Dragon Quest to Dragon Warrior, its inspiration of two Japanese sequels, and that its release was still distant in time.[53]
Dragon Warrior was released in North America by Nintendo of America under the direction of Satoru Iwata with help from Horii in August 1989 – months before the Japanese release of Dragon Quest IV.[54][55] Because the game was released in North America nearly three years after the original release in Japan, the graphics were improved. Instead of lengthy passwords with kana characters, the North American version features a battery-backed RAM savegame.[3] Akira Toriyama's artwork in the instruction booklets was also changed to reflect more of a traditional tone as found in popular American based RPGs such as the Ultima series. The game's character sprites were changed so that they face their direction of travel; in the Japanese versions, the sprites are smaller and only face forwards, requiring players to choose a direction for actions from a menu. Spells were given self-explanatory one-word titles instead of the made-up words of the Japanese version. Locations were renamed, and dialogue was rewritten from its whimiscal style comparable to Dragon Ball to a style inspired by Elizabethan English,[3][56] with sentences such as "Thy hit points have decreased by 1."[54] Nintendo also removed salacious humor and religious connotations from the English-language version.[54] For example, in the Japanese version, in the town where the hero first buys keys, a woman offers to sell puff-puff – a Japanese onomatopoeia for a girl rubbing her breasts in someone's face, or juggling her own breasts. In the North American version, the same woman sells tomatoes.[46] The term has been included in the game's sequels as well as in Toriyama's Dragon Ball series.[57]
Katsuya Terada created some of the artwork for the early Dragon Warrior articles in Nintendo Power. Neither Terada nor those editing the artwork for the instruction booklet followed Toriyama's work; they instead used the settings and character poses to create alternate artwork in an American style.[58] While the Japanese hero was drawn in a super deformed manga style, the English version's appearance is based on "the West's template of a medieval hero".[58]
In June 1989, Electronic Gaming Monthly's "Quartermann" speculated that Dragon Warrior would be Nintendo's "big release" in North America that Christmas. He based this on the series's immense popularity in Japan especially after Dragon Quest III's sales.[59] Nintendo Power provided three feature articles on Dragon Warrior for issues between May and October 1989[17][26][34] and the November–December 1989 issue includes a strategy guide.[60] The March–April 1990 issue of Nintendo Power has a map of the game world, with a poster of Super Contra on the other side, and also features a Dragon Warrior text adventure.[61]
In late 1990, Nintendo Power gave free copies of Dragon Warrior to subscribers,[43] including a 64-page "Explorer's Handbook" that has a full walkthrough of the game and additional backstory not mentioned in the original instruction booklet.[62] Nintendo was reportedly interested in getting rid of unsold copies of the game, so it gave them away to subscribers.[63] At the time, the game cost approximately US$50 at retail and the magazine's subscription fee was only US$20 ($123 and $49 respectively, adjusted for inflation).[54] The giveaway attracted nearly 500,000 new magazine subscribers, and many more renewed their subscription just to get the game.[54][63][64] This ultimately led to the success of the series in the Western market.[63]
Re-releases and remakes

Enix remade Dragon Quest and Dragon Quest II for a one-cartridge compilation known as Dragon Quest I + II for the Super Famicom on December 18, 1993. The remake sold over 1.2 million copies in Japan.[65] In 1998, Enix released BS Dragon Quest for the Super Famicom Satellaview extension exclusively in Japan.[66] The latter consisted of four one-hour scenarios which players would download on a weekly schedule. Players were tasked with leveling their character, collecting medals and completing scenario-specific conditions with special events designed to occur under specific conditions in real-time.[67]
Dragon Warrior and Dragon Warrior II were re-released as part of a similar compilation for the GBC, titled Dragon Warrior I & II. It was developed by Tose and released by Enix on September 23, 1999 in Japan and September 27, 2000, in North America.[68][69] It uses an entirely new translation, discards the pseudo-Elizabethan English style and uses names closer to those in the Japanese version.[12][46] In this remake, "Dragonlord" is changed to "DracoLord", and "Erdrick" is changed to "Loto". Several additional features were added. For example, players can quicksave their game anytime outside a battle; the quicksave is deleted after it or a standard saved game is loaded.[4][22] Players can store some of their gold for future use in a bank in case they die.[12] The menu was streamlined and monsters yield more experience and gold to reduce the amount of time needed to increase levels and to make saving up for in-game purchases faster.[22]
In 2004, the game, along with its sequel, were remade for mobile phones in Japan. This version is graphically based on the Super Famicom remake of Dragon Quest III.[70]
Both the Famicom and Super Famicom versions of the game, together with Dragon Quest II and Dragon Quest III, were re-released on the Dragon Quest 25th Anniversary Collection compilation for the Wii in Japan on September 15, 2011. The compilation includes original copies of the games' strategy guides, original artwork and material on the games' development.[36] In October 2013, Square Enix announced that they were re-releasing Dragon Quest I–VIII for both Android and iOS.[71] In November 2013, the game was released for the iOS & Android mobile platforms in Japan. This release is based on the 2004 mobile remake of the game.[72] The United States and Europe mobile versions were released on September 11, 2014.[73]
Related media
Dragon Warrior has inspired related media in the form of a manga series, which has been adapted to anime, and a symphonic video game soundtrack.
Anime and manga
The manga series, Dragon Quest Retsuden: Roto no Monshō (ドラゴンクエスト列伝 ロトの紋章, Dragon Quest Saga: Emblem of Roto), was written by Chiaki Kawamata and Junji Koyanagi, with artwork by Kamui Fujiwara, and was published between 1991 and 1997 by Monthly Shōnen Gangan.[74] Enix compiled the series into 21 volumes,[75] which were later released on compact disc in 1994. It was released on December 11, 2009 for the PlayStation Store as part of the initial launch of Sony's digital comic distribution.[76] In 1996, an anime movie based on the manga was released on videocassette.[77] Square Enix started publishing a sequel series, Dragon Quest Retsuden: Roto no Monshō ~Monshō o Tsugumono-tachi e~ (ドラゴンクエスト列伝 ロトの紋章 ~紋章を継ぐ者達へ~, Dragon Quest Retsuden: Emblem of Roto – To the Children Who Inherit the Emblem), in 2005.[78] ja wrote the first four volumes, and Takashi Umemura wrote the last five; Yuji Horii supervised the manga, while Kamui Fujiwara contributed the artwork.[79]
Dragon Quest Saga: Emblem of Roto takes place between Dragon Warrior III and Dragon Warrior. After monsters possessed Carmen's king for seven years, the kingdom fell to the hordes of evil. The only survivors were Prince Arus and an army General's daughter, Lunafrea. Meanwhile, in the Kingdom of Loran, a child is born and is named Jagan in accordance with the demon lord Imagine's orders. Arus and Lunafrea set out to defeat the monsters and restore peace to the world.[80] The sequel, To the Children Who Inherit the Emblem, takes place five years after the events in Dragon Quest Saga: Emblem of Roto. The world is again in chaos and a young boy, Arosu (アロス), sets out to gather companions to help him save the world from evil.[79]
Soundtrack
Koichi Sugiyama composed and directed the music for Dragon Warrior.[45] The soundtrack included eight tracks, which RPGFan said was "the foundation for Sugiyama's career".[81] The pieces were arranged and incorporated into later Dragon Warrior games' soundtracks.[81] The music has been released in a variety of formats. The first is as a Drama CD, released by Enix on July 19, 1991, which incorporated a narrated story.[82][83] Super Famicom Edition Symphonic Suite Dragon Quest I, published by Sony Records on January 12, 1994, followed; the soundtrack featured orchestral versions of the tracks played by the London Philharmonic Orchestra and the original versions of the tunes.[84] The game's classical score was considered revolutionary for console game music.[85] The soundtrack's "eight melodies" approach set the template for most RPG soundtracks released since then, hundreds of which have been organized in a similar manner.[86]
The orchestral albums for Dragon Warrior I and II were combined in Symphonic Suite Dragon Quest I•II, released by SME Visual Works on August 23, 2000, King Records reprinted it on October 7, 2009.[87] The orchestral tracks were again released in the Symphonic Suite Dragon Quest I album, including orchestral versions of the game's sound effects.[81] Numerous live concerts have featured performances of the game's music; many performances were later released as albums such as Dragon Quest in Concert and Suite Dragon Quest I•II.[88][89]
Reception and sales
NES version
| Aggregator | Score | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| GBC | NES | SNES | |
| GameRankings | 84.36% | ||
| Publication | Score | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| GBC | NES | SNES | |
| Famitsu | 30 / 40[90] | 35 / 40 | |
| GameSpot | 8.0 / 10 | ||
| IGN | 9.6 / 10 | 7.8 / 10 | |
| Nintendo Power | 8 / 10 | 3 / 5 | |
Initial sales of the game were so low, Enix was going to lose money, but several Shonen Jump articles by Horii helped increase its sales substantially. People liked Toriyama's artwork and Sugiyama's music, which the book Power-Up: How Japanese Video Games Gave the World an Extra Life said "was richer and more exciting than any game music had ever sounded".[41] The game was extremely popular in Japan and became the first in a series that, as of 2012[update], includes ten games with several spin-off series and stand-alone titles. More than 2 million copies were sold of the Japanese version.[41] The Dragon Quest I & II remake for the SNES yielded 1.2 million copies sold in Japan.[65][91] The 1989 "All Soft Catalog" issue of Famicom Tsūshin (now Famitsu) included Dragon Quest in its list of the best games of all time, receiving the Best RPG and Best Character Design awards, but losing to Dragon Quest III for the overall Grand Prize for best game of all time.[92]
Several years after its Japanese release, the first English-language version of Dragon Warrior garnered average reviews overall. Nintendo Power ranked it as third out of five upon its original release.[26] It debuted at No. 7 on the magazine's bimonthly "Top 30" top NES games list in November 1989.[93] It climbed to No. 5 in January 1990 and remained there for 4 months;[94][95] it then dropped to No. 11 in May,[96] No. 14 in July,[97] and No. 16 in September 1990 before it dropped off the list.[98] In the "Nintendo Power Awards 1989", the game was nominated for "Best Theme, Fun" and "Best Overall";[99] it failed to win in either category.[100] In response to Japanese youths' arrests while waiting for Dragon Quest III's release, Electronic Gaming Monthly's Quartermann said that the game was not "that special at all", compared it to the NES version of Ultima III: Exodus and recommended that others play that game instead.[101] While the English version has been seen as a commercial failure,[63] according to Chris Kohler, the Nintendo Power subscription was a success and allowed Enix to bring the next three games over. He said Nintendo profited immensely from the Dragon Warrior subscription giveaway because "Nintendo Power was essentially a hundred-page monthly ad for Nintendo products", and it was now in thousands of households.[54]
The game's release has been regarded as important in the history of the console RPG.[35][51] Kohler noted that Toriyama's and Sugiyama's contributions to the game "made Dragon Quest as visually and aurally exciting as the game play was unique and sophisticated."[41] GameSpot named it as one of the fifteen most influential titles in video game history.[102] IGN listed it as the eighth best all-time NES game.[103] In 2005, it listed it as the 92nd-best all-time video game,[104] and in 2007 it listed the game as the 29th best.[105] Nintendo Power rated Dragon Warrior as the 140th-best game made for the Nintendo System in its Top 200 Games list in 2006.[106] IGN reviewed the game years later and gave it a 7.8 out of 10,[107] and RPGamer's Bill Johnson gave it a 4 out of 5 overall score.[4][108] The NES' localization received considerable praise for adding extra characters and depth to the story.[3][4] The removal of the stylized dialogue in the GBC remake has similarly been lamented.[12]
Seemingly primitive by today's standards, Dragon Warrior features one-on-one combat, a limited item and equipment array, ten spells, five towns, and five dungeons.[3][4][8][34] While noting its importance to the development of the RPG genre, Allgame reviewer Kyle Knight states that "taken on its own merits, it's just not an enjoyable game to play."[109] 1UP.com explained why the series was not immensely popular at first in North America; American console gamers were not used to the idea of RPGs, and they said that it would take a decade for the genre to be "flashy enough to distract from all of those words they made you read".[63] GameCritics' Chi Kong Lui wrote that the game added realism to video games, and added, "If a player perished in Dragon Warrior, he or she had to suffer the dire consequences of losing progress and precious gold. That element of death evoked a sense of instinctive fear and tension for survival."[110] This, he said, allowed players to identify with the main character on a much larger scale. IGN writer Mark Nix compared the game's seemingly archaic plot to more modern RPGs; he said: "Noble blood means nothing when the society is capitalist, aristocratic, or militaristic. Damsels don't need rescuing – they need a battle axe and some magic tutoring in the field."[12] While reviewing Dragon Quest VIII: Journey of the Cursed King, GameSpy staff wrote that, for many gamers, Dragon Warrior is their first exposure to the console RPG. Recalling their past, a staff member commented:
It opened my eyes to a fun new type of gameplay. Suddenly strategy (or at least pressing the "A" button) was more important than reflex, and the story was slightly (slightly!) more complex than the 'rescue the princess' stuff I'd seen up 'till then. After all, Dragon Warrior was only half-over when you rescued its princess.[111]
Bill Johnson compared Dragon Warrior to modern RPGs and noted the game's complete lack of replay value, which is due as much to the requirement that almost everything in the game must be done to beat it as to its difficulty. Johnson noted the game's historical importance; he said: "[Playing Dragon Warrior is] a tough road to walk, but reaching its end will instill a new appreciation of what today's RPG's are all about."[4] The 2009 book Vintage Games contrasted Dragon Warrior to the 1986 NES title The Legend of Zelda; it said, while both titles share common RPG elements, Zelda features a fantasy setting and magic but no level or turn-based combat system, and Dragon Warrior features both.[112] Nintendo Power said the game's historical significance is its greatest aspect, and noted that "playing Dragon Warrior these days can be a bit of a chore".[46] GamePro wrote that their favorite aspect of the game was the Elizabethan-English dialogue, and that they were disappointed by its removal in the GBC remake.[56]
Remakes
Famitsu gave the SNES compilation remake Dragon Quest I + II a rating of 35 out of 40.[113] The Satellaview remake was given a mixed, but overall positive review by Microgroup. The touches such as the real-time event and voicing were appreciated, but their implementation left much to be desired. However, the medal collection is a nice way to compete with friends and the reviewer enjoyed the game.[67] Dragon Warrior's English remake, as part of the dual GBC cartridge Dragon Warrior I & II, received better reviews than the original, garnering praise. IGN and Nintendo Power gave it an 8 out of 10. IGN's Marc Nix noted that while "it's one of the only interesting RPGs on the Game Boy Color to actually make American shores", players will feel frustrated; those who played the original will lament the changes, while new players will feel that the game is too linear and simple.[114][115] GameSpot gave it a 9.6 out of 10, citing the great improvements to sound quality and the appeal of playing both games in succession,[116] and GameRankings reports an 83.46% overall score.[115] It received RPGamer's Game Boy Color Award of the Year for 2000.[117] Comparing it to its NES counterpart, RPGamer's Derek Cavin awarded it 3 out of 5, and wrote that the game is above average in all aspects, and particularly praised the visual elements. He criticized the game's repetitiveness, and said that it is short enough that most players should finish the game before repetition becomes an issue.[108] Combined, both the SNES and GBC remakes saw more than 1.94 million copies sold worldwide.[118] With the remakes' good sales performances, Enix released Dragon Warrior III for the GBC in 2001, which was based on a previously unreleased SNES update of Dragon Quest III' English version.[119]
Related media
Square Enix Music Online's Juan2Darien reviewed the game's symphonic scores: Dragon Quest Suite; Dragon Quest I Remix Symphonic Suite (London Philharmonic Orchestra); Dragon Quest I & II Symphonic Suite (London Philharmonic Orchestra Remastered); and Dragon Quest I Symphonic Suite (Tokyo Metropolitan Symphony Orchestra). Comparing each of the suites, he gave all ratings ranging 7 through 9 out of 10, and found the Tokyo Strings Ensemble recording superior to the aforementioned symphonic suites. While the music is somewhat flat, Juan2Darien acknowledged this is due to the source material and praised Koichi Sugiyama's and the orchestras' efforts to compose an above-average piece despite the limitation.[120] Gamasutra's Kurt Kalata also praised the symphonies' melody, commenting that "the overworld theme ... is pretty simplistic and grating, but actually sounds pretty beautiful when played by a live orchestra".[3]
Dragon Quest Retsuden: Roto no Monshō – To the Children Who Inherit the Emblem sold well in Japan. For the week of August 26 to September 1, 2008, volume 7 was ranked 9th in Japan, selling 59,540 copies.[121] For the week of February 24 to March 2, 2009, volume 8 was ranked 19th in Japan, selling 76,801 copies.[122] For the week of October 26 to November 1, 2009, volume 9 was ranked 16th in Japan, selling 40,492 copies for a total of 60,467.[78]
Legacy
Bits and pieces of Dragon Warrior had been seen in video games before, but never all sewn up together so neatly. DW's incredible combination of gameplay elements established it as THE template for console RPGs to follow.
William Cassidy, The GameSpy Hall of Fame: Dragon Warrior[123]
Dragon Warrior's release has been noted as a notable turning point in video game history.[35] The game has been listed as a genre builder for RPGs.[35][51][124] Its popularity in Japan is synonymous with RPGs.[41] While the game's elements had been present in previous RPG titles, Dragon Warrior set the template for others; almost all of its elements became the foundation for nearly every later game of the genre, from gameplay to narrative,[51][110][123][124][125] replacing D&D as the model to follow. According to Shigeru Miyamoto, the success of Dragon Warrior changed the nature of video game development by making scenario writers far more important.[41]
When Dragon Warrior was released, many of the development techniques used were intended to compensate for hardware limitations, but contemporary RPG developers continue to use these techniques despite technological advances that made them unnecessary.[110] Dragon Warrior introduced the damsel-in-distress storyline that many RPGs follow,[102] and a fresh plot twist to the "saving the princess" formula, where the game's true objective is not revealed until the princess is rescued.[126] The game also introduced an element of romance, where the player character is given a dialogue choice to respond to the princess's question of whether he loves her; romance has since become a commonplace feature the genre.[127] The game's 2D graphic style was used by most RPGs until the advent of 3D graphics.[102] Dragon Warrior's top-down perspective has become "a dead giveaway to an RPG".[102] The game featured elements still found in most RPGs, such as the ability to obtain better equipment, major quests that intertwine with minor subquests, an incremental spell system, use of hit points and experience points, and a medieval theme.[128] Reviewers said that, while Final Fantasy has been considered more important due to its popularity and attention in North America, Dragon Warrior laid the fundamentals on which Final Fantasy was based.[102][123][124] Dragon Quest is also credited with affecting Dungeons & Dragons' leveling system to even out its randomness by giving more bonuses early on and giving players maximum hit points on the first level.[47]
In the Nintendo Power's November 2010 issue, in celebration of the NES' 25th anniversary in North America, Horii recalled the making of Dragon Warrior. Horiii was a fan of basic RPG mechanics, and wanted to simplify the interfaces; he said that many other RPGs' interfaces at the time "were so complicated that they intimidated new users". He said that Dragon Warrior's simplified gameplay made the game appealing to people and made the franchise successful. he had been told that the NES lacked sufficient capacity for RPGs, which further motivated him to make one.[129]
Dragon Quest became a national phenomenon in Japan, inspiring spinoff media and figurines.[123] The video game industry has called it as Japan's national game.[130] Horii, who was linked through his Shonen Jump articles, increased in celebrity status, and become a household name in Japan, as well known in Japan as Steven Spielberg is in the US; in contrast Miyamoto, creator of Super Mario Bros. and The Legend of Zelda, is not nearly as well-known.[41] In a Famitsu poll, the Japanese public voted Dragon Quest as the seventh favorite game for the NES.[131] Several clones such as Glory of Heracles, Legend of the Ghost Lion and Mother were inspired by the Japanese version's success.[132] For Mother, Shigesato Itoi, a fan of Dragon Warrior, and Miyamoto, a detractor of RPGs, created an RPG that would subvert the Dragon Warrior RPG template by changing the setting and themes from the Middle Ages to the US.[41] Dragon Warrior, along with other NES titles, has spawned many ROM hacks in recent years. One notable hack includes Super Mario Remix II, which features a new plot and revised character sprites to reflect the Mario series, while the gameplay and layout remain the same.[133] Dragon Warrior became so popular in Japan that, if asked to draw 'slime', a Japanese person is likely to draw a shape similar to that of the game's interpretation of slime.[41]
Many aspects of pop culture still reference Dragon Warrior. The video game music band Descendants of Erdrick, based in Austin, Texas, is named after the game's main character.[134] On April Fools Day 2012, Google added a Dragon Warrior-inspired 8-bit option to Google Maps.[135][136][137]
See also
References
- Notes
- Citations
- ^ Spencer. "Dragon Quest Anniversary Collection Brings First Three Games To Wii". Retrieved 13 May 2011.
- ^ "DRAGON QUEST Portal App for iOS and Android will be available in Japan. DRAGON QUEST I will be available for free for the first one million download (For Japan)" (in Japanese). Square Enix. 2013-11-28. Retrieved 2013-11-28.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q Kalata, Kurt (February 4, 2008). "The History of Dragon Quest". Gamasutra. Retrieved March 26, 2011.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Johnson, Bill. "Dragon Quest – Review". RPGamer. Retrieved March 26, 2011.
- ^ a b c d e f g Dragon Warrior: Instruction Booklet. Redmond, WA: Nintendo of America. 1989. pp. 5–6. NES-DQ-USA.
- ^ "Welcome to the Realm of "Dragon Warrior"". Dragon Warrior: Instruction Booklet. Redmond, WA: Nintendo of America. 1989. pp. 7–8. NES-DQ-USA.
- ^ Chunsoft (1986). Dragon Quest (NES). Enix.
- ^ a b Dragon Warrior I & II Official Strategy Guide. New York, NY: Prima Publishing. 2000. pp. 6, 105. ISBN 978-0-7615-3157-9.
- ^ a b c d "Dragon Quest: Sentinel of the Starry Skies". Iwata Asks. Square Enix. The History of Dragon Quest. Retrieved December 5, 2010.
- ^ a b c d Chunsoft (1989). Dragon Warrior (Nintendo Entertainment System). Nintendo.
- ^ a b "How to Start Off on the Right Foot (What you must do at the beginning of the game)". Dragon Warrior: Instruction Booklet. Redmond, WA: Nintendo of America. 1989. pp. 20–21, 29–32. NES-DQ-USA.
- ^ a b c d e f g Nix, Mark (October 4, 2000). "Dragon Warrior I & II Review". IGN. Retrieved October 6, 2009.
- ^ "Dragon Quest and the Art of Efficient Exploration". 1UP.com. Retrieved September 1, 2011.
- ^ "As your level rises, travel further afield". Dragon Warrior Explorer's Handbook. Redmond, WA: Nintendo. 1989. p. 27.
- ^ "Getting to know your terrain". Dragon Warrior Explorer's Handbook. Redmond, WA: Nintendo. 1989. pp. 18–19.
- ^ a b "Entering Commands during Fighting Mode/More About Your Character". Dragon Warrior: Instruction Booklet. Redmond, WA: Nintendo of America. 1989. pp. 13–14. NES-DQ-USA.
- ^ a b c "Dragon Warrior". Nintendo Power (8). Redmond, WA: Tokuma Shoten: 20–27. September–October 1989. ISSN 1041-9551. OCLC 18893582.
- ^ Dragon Warrior I & II Official Strategy Guide. New York, NY: Prima Publishing. 2000. pp. 3, 5. ISBN 978-0-7615-3157-9.
- ^ Kalata, Kurt. "The History of Dragon Quest". Features. Gamasutra. Retrieved February 22, 2011.
- ^ "Visit the King And Have Your Deeds Recorded on the Imperial Scrolls of Honor (to save your game)". Dragon Warrior: Instruction Booklet. Redmond, WA: Nintendo of America. 1989. p. 28. NES-DQ-USA.
- ^ "How to use the Controller and Displays". Dragon Warrior: Instruction Booklet. Redmond, WA: Nintendo of America. 1989. pp. 9–12. NES-DQ-USA.
- ^ a b c TOSE (2000). Dragon Warrior I & II (Game Boy Color). Enix.
- ^ Fukushima, Yasuhiro (1990). Unveiled Secrets of Dragon Warrior II. Redmond, WA: Enix. p. 3.
- ^ Shoemaker, Brad (August 1, 2001). "Dragon Warrior III Review". GameSpot. Retrieved February 12, 2011.
- ^ a b c d e f g h "Dragon Warrior – The Saga". Dragon Warrior Explorer's Handbook. pp. 58–60.
- ^ a b c d e f "Previews – Dragon Warrior". Nintendo Power (6). Redmond, WA: Tokuma Shoten: 52–53. May–June 1989. ISSN 1041-9551. OCLC 18893582.
- ^ Otsuka, Tsutomu (1989). Orimo, Ani; Yazawa, Tomy (eds.). Dragon Warrior: Strategy Guide. Terado, Katsuya; Imai, Shuji. illustrators. Redmond, WA: Nintendo of America. p. 4. OCLC 30018721.
- ^ "Tantegel Castle – Before You Leave the Castle". Dragon Warrior Explorer's Handbook. Redmond, WA: Nintendo of America. 1989. p. 7. NES-DQA-USA.
- ^ Dragon Warrior I & II Official Strategy Guide. New York, NY: Prima Publishing. 2000. p. 30. ISBN 978-0-7615-3157-9.
- ^ Dragon Warrior I & II Official Strategy Guide. New York, NY: Prima Publishing. 2000. p. 6. ISBN 978-0-7615-3157-9.
- ^ "The Story of Dragon Warrior". Dragon Warrior II: Instruction Booklet. Redmond, WA: Enix. 1990. p. 5. NES-D2-USA.
- ^ a b c d Otsuka, Tsutomu (1989). Orimo, Ani; Yazawa, Tomy (eds.). Dragon Warrior: Strategy Guide. Terado, Katsuya; Imai, Shuji. illustrators. Redmond, WA: Nintendo of America. p. 5. OCLC 30018721.
- ^ Dragon Warrior I & II Official Strategy Guide. New York, NY: Prima Publishing. 2000. p. 5. ISBN 978-0-7615-3157-9.
- ^ a b c "Nintendo Power". Nintendo Power (7). Redmond, WA: Tokuma Shoten: 39–50. July–August 1989. ISSN 1041-9551. OCLC 18893582.
- ^ a b c d Gifford, Kevin. "20. Dragon Warrior: Though Art a Hero". The Essential 50 Archives: The Most Important Games Ever Made. 1UP.com. Retrieved March 26, 2011.
- ^ a b Ramos, Cassandra (June 30, 2011). "Dragon Quest Collection to Come With Bonus Dragon Quest X Video". RPGamer. Retrieved July 14, 2011.
- ^ Chunsoft (1986). Dragon Quest (MSX). Enix. Scene: Title screen.
- ^ "Dragon Quest (PC98)". GameSpot. Retrieved July 30, 2011.
- ^ "Dragon Quest (X68)". GameSpot. Retrieved July 30, 2011.
- ^ "Dragon Quest for Mobile Phones". GameSpot. 2004. Retrieved October 14, 2007.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s Kohler, Chris (2004). "4 – Quests and Fantasies: The Japanese RPG". Power-Up: How Japanese Video Games Gave the World an Extra Life. Indianapolis, IN: BradyGames. pp. 84–89. ISBN 978-0-7440-0424-3.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|titlelink=ignored (|title-link=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Gotemba, Goro (2006). Japan on the Upswing: Why the Bubble Burst and Japan's Economic Renewal. Algora. p. 201. ISBN 0-87586-462-7.
- ^ a b c d e f g h "East and West, Warrior and Quest: A Dragon Quest Retrospective". 1UP.com. Retrieved July 5, 2011.
- ^ a b Horii, Yuji (November 2007). "Nintendo Power". Nintendo Power (221). South San Francisco, CA: Future US: 78–80. ISSN 1041-9551.
At the time I first made Dragon Quest, computer and video game RPGs were still very much in the realm of hardcore fans and not very accessible to other players. So I decided to create a system that was easy to understand and emotionally involving, and then placed my story within that framework.
- ^ a b Johnston, Chris; Ricciardi, John; Ohbuchi, Yotaka (December 1, 2001). "Role-Playing 101: Dragon Warrior". Electronic Gaming Monthly. Lombard, IL: Sendai Publications: 48–51. ISSN 1058-918X. OCLC 23857173.
- ^ a b c d e "Nintendo Power". Nintendo Power (238). South San Francisco, CA: Future US: 84. February 2008. ISSN 1041-9551.
{{cite journal}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|1=(help) - ^ a b Harris, John (September 26, 2007). "Game Design Essentials: 20 Open World Games". Gamasutra. p. 8. Retrieved January 31, 2011.
- ^ "Top 100 Game Creators of All Time – 74. Akira Toriyama". IGN. Retrieved July 7, 2011.
- ^ Oxford, Nadia (May 26, 2010). "Getting to Know Dragon Warrior Again (and Again)". 1up. Retrieved July 7, 2011.
- ^ a b Gifford, Kevin (February 24, 2010). "Dragon Quest Composer Reflects on 24 Years of Games: Kouichi Sugiyama on Japan's most recognized game music". 1UP.com. Retrieved April 18, 2011.
- ^ a b c d "The GameSpy Hall of Fame: Dragon Warrior". GameSpy. February 1, 2002. p. 1. Archived from the original on 2004-06-16. Retrieved October 9, 2009.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Sneak Peeks – Dragon Warrior". Nintendo Fun Club News (4): 14. Winter 1988.
- ^ "Pak Watch". Nintendo Power (5). Redmond, WA: Tokuma Shoten: 103. March–April 1989. ISSN 1041-9551. OCLC 18893582.
- ^ a b c d e f Kohler, Chris (2004). "8 – Lost in Translation: This Game are Sick". Power-Up: How Japanese Video Games Gave the World an Extra Life. Indianapolis, IN: BradyGames. pp. 222–223. ISBN 978-0-7440-0424-3.
- ^ "社長が訊く『ドラゴンクエストIX 星空の守り人』". Nintendo. Retrieved September 28, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Kat Bailey, Justin Haywald, Ray Barnholt and Tim Rogers (2011-05-25). "Dragon Quest 25th Anniversary Edition". GamePro. Archived from the original (mp3) on 2011-12-05.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Kauz, Andrew (August 21, 2010). "The rubbing of breasts on faces in Dragon Quest IX". Destructoid. Retrieved July 14, 2011.
- ^ a b Oxford, Nadia (2011-05-25). "The Art of Dragon Quest". GamePro. Archived from the original on 2011-11-30. Retrieved 2011-08-03.
- ^ Quartermann (June 1989). "Gaming Gossip". Electronic Gaming Monthly (2). Lombard, IL: Sendai Publications: 26. ISSN 1058-918X. OCLC 23857173.
- ^ "Table of Contents". Nintendo Power (9). Redmond, WA: Tokuma Shoten: 5. November–December 1989. ISSN 1041-9551. OCLC 18893582.
- ^ "Dragon Warrior Text Adventure". Nintendo Power (11). Redmond, WA: Tokuma Shoten: 51–54. March–April 1990. ISSN 1041-9551. OCLC 18893582.
- ^ Dragon Warrior Explorer's Handbook. Redmond, WA: Nintendo of America. 1989. NES-DQA-USA.
- ^ a b c d e Mackey, Bob (February 5, 2007). "Smart Bombs: Celebrating Gaming's Most Beloved Flops". 1UP.com. p. 2. Retrieved July 11, 2011.
- ^ "50 Issues of Nintendo Power: A View from Inside Out". Nintendo Power (50). Redmond, WA: Tokuma Shoten: 39. July 1993. ISSN 1041-9551. OCLC 18893582.
- ^ a b Hitmitsu, Suppai (April 8, 2004). "Dragon Quest V Breaks Record". IGN. Retrieved July 24, 2011.
- ^ "BS Dragon Quest". GameSpot. Retrieved July 24, 2011.
- ^ a b Hayashi Mura Wataru. BSドラゴンクエスト リアルタイムを考慮した巧みな演出を (in Japanese). Micro Group. Archived from the original on August 27, 2006. Retrieved October 25, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help) - ^ "International Outlook". Electronic Gaming Monthly (149). Lombard, IL: Sendai Publications: 51. December 2001. ISSN 1058-918X. OCLC 23857173.
- ^ Provo, Frank (September 29, 2000). "Dragon Warrior I & II Review". GameSpot. Retrieved August 13, 2011.
- ^ "Dragon's Den > Dragon Quest 1 Mobile > Screenshots". Retrieved November 21, 2015.
- ^ Seppala, Timothy J. (October 9, 2013). "Dragon Quest Series Coming to Android and iOS this Winter". Engadget. Retrieved October 18, 2013.
- ^ "ドラゴンクエストポータルアプリ - Android Apps on Google Play". SQUARE ENIX Co.,Ltd. Retrieved November 21, 2015.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|1=(help) - ^ Yin-Poole, Wesley (September 11, 2014). "The first Dragon Quest launches on iOS and Android". Eurogamer. Retrieved 2014-09-11.
- ^ ドラゴンクエスト列伝 ロトの紋章 完全版 (in Japanese). Square Enix. Retrieved November 9, 2009.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help) - ^ ロトの紋章―ドラゴンクエスト列伝 (21) (ガンガンコミックス) (コミック) (in Japanese). Amazon. ASIN 4870252058.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help) - ^ "Japan's Sony PSP Manga Distribution Service Detailed". News. Anime News Network. September 24, 2009. Retrieved November 9, 2009.
- ^ "ドラゴンクエスト列伝・ロトの紋章 [VHS]" (in Japanese). Amazon. Retrieved November 9, 2009.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help) - ^ a b "Japanese Comic Ranking, October 26 – November 1". News. Anime News Network. November 4, 2009. Retrieved November 9, 2009.
- ^ a b ドラゴンクエスト列伝 ロトの紋章 ~紋章を継ぐ者達へ~ (in Japanese). Square Enix. Retrieved November 9, 2009.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help) - ^ "Emblem of Roto". The Dragon Quest Dragon Warrior Shrine. Retrieved April 10, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ a b c Gann, Patrick (May 15, 2008). "Symphonic Suite Dragon Quest I". RPGFan. Retrieved December 1, 2009.
- ^ Gann, Patrick (September 13, 2001). "CD Theater Dragon Quest I". RPGFan. Retrieved December 1, 2009.
- ^ "Dragon Quest I CD Theater". Square Enix Music Online. Retrieved April 10, 2011.
- ^ Gann, Patrick (November 18, 2008). "Super Famicom Edition Symphonic Suite Dragon Quest I". RPGFan. Retrieved December 1, 2009.
- ^ Gifford, Kevin. "The Essential 50 Part 20 - Dragon Warrior". 1UP.com. Retrieved May 15, 2011.
- ^ Gann, Patrick. "The "Eight Melodies" Template: How Sugiyama Shaped RPG Soundtracks". RPGFan. Retrieved September 4, 2011.
- ^ Prievert, Alexander (February 7, 2006). "Super Famicom Edition Symphonic Suite Dragon Quest I". RPGFan. Retrieved December 1, 2009.
- ^ Patrick Gann (2007). "Dragon Quest in Concert". RPGfan. Retrieved August 31, 2007.
- ^ Gann, Patrick (October 27, 2009). "Suite Dragon Quest I•II". RPGFan. Retrieved December 1, 2009.
- ^ ゲームボーイ - ゲームボーイ ドラゴンクエストI・II. Weekly Famitsu. No.915 Pt.2. Pg.111. 30 June 2006.
- ^ "Japan Platinum Game Chart (Games sold over Million Copies)". The Magicbox. Enix. Retrieved April 18, 2011.
- ^ "Famitsu", Famicom Tsūshin, no. All Soft Catalog '89, 1989
- ^ "Top 30". Nintendo Power (9). Redmond, WA: Tokuma Shoten: 81. November–December 1989. ISSN 1041-9551. OCLC 18893582.
- ^ "Top 30". Nintendo Power (10). Redmond, WA: Tokuma Shoten: 49. January–February 1990. ISSN 1041-9551. OCLC 18893582.
- ^ "Top 30". Nintendo Power (11). Redmond, WA: Tokuma Shoten: 41. March–April 1990. ISSN 1041-9551. OCLC 18893582.
- ^ "Top 30". Nintendo Power (12). Redmond, WA: Tokuma Shoten: 43. May–June 1990. ISSN 1041-9551. OCLC 18893582.
- ^ "Top 30". Nintendo Power (14). Redmond, WA: Tokuma Shoten: 67. July–August 1990. ISSN 1041-9551. OCLC 18893582.
- ^ "Top 30". Nintendo Power (16). Redmond, WA: Tokuma Shoten: 23. September–October 1990. ISSN 1041-9551. OCLC 18893582.
- ^ "Nintendo Power Awards '89". Nintendo Power (11). Redmond, WA: Tokuma Shoten: 98–99. March–April 1990. ISSN 1041-9551. OCLC 18893582.
- ^ "Nintendo Power Awards '89". Nintendo Power (12). Redmond, WA: Tokuma Shoten: 26–29. May–June 1990. ISSN 1041-9551. OCLC 18893582.
- ^ Quartermann (September 1989). "Gaming Gossip". Electronic Gaming Monthly (3). Lombard, IL: Sendai Publications: 28. ISSN 1058-918X. OCLC 23857173.
- ^ a b c d e "15 Most Influential Games". GameSpot. 2005. Archived from the original on June 10, 2009. Retrieved September 1, 2009.
- ^ Moriarty, Colin. "Top 100 NES Games of all Time". IGN. Archived from the original on October 28, 2009. Retrieved October 16, 2009.
- ^ "Top 100 Games of all Time: 091-100". IGN. July 29, 2005. Retrieved October 27, 2009.
- ^ "Top 100 Games of all Time: Dragon Warrior". IGN. December 3, 2007. Retrieved October 27, 2009.
- ^ "Nintendo Power's Top 200 All-Time Games". Nintendo Power (200). Redmond, WA: Tokuma Shoten: 58–66. February 2006. ISSN 1041-9551. OCLC 18893582.
- ^ "Dragon Warrior". IGN. Retrieved December 5, 2009.
- ^ a b Calvin, Derek "Roku". "Here's a Stick, Go Save the World". RPGamer. Retrieved April 14, 2011.
- ^ Knight, Kyle. "Dragon Warrior". allgame. Retrieved 2011-12-04.
- ^ a b c Chi Kong Lui (March 2, 2001). "Dragon Warrior I & II". GameCritics. Retrieved October 6, 2009.
- ^ "The Annual E3 Awards 2005". GameSpy. IGN. Archived from the original on May 31, 2005. Retrieved November 29, 2015.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|1=(help); Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Loguidice, Bill; Barton, Matt (2009). "21 – The Legend of Zelda (1986)". Vintage Games. Burlington, MA: Focal Press. p. 305. ISBN 978-0-240-81146-8.
- ^ 週刊ファミ通クロスレビュープラチナ殿堂入りソフト一覧 (in Japanese). Geimen. No 294. Retrieved April 20, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help) - ^ Nix, Marc (October 4, 2000). "Dragon Warrior I & II Return to the days of yore with Enix's Game Boy Color RPG revival". IGN. Retrieved April 10, 2008.
- ^ a b "Dragon Warrior I & II". GameRankings. 2000. Retrieved January 31, 2011.
- ^ Provo, Frank (September 29, 2000). "Dragon Warrior I & II for Game Boy Color Review". GameSpot. Retrieved April 10, 2008.
- ^ "RPGamer's Awards 2000: Game Boy Color RPG of the Year". RPGamer. 2000. Retrieved April 10, 2008.
- ^ "February 2, 2004 – February 4, 2004" (PDF). Square Enix. Retrieved December 13, 2008.
- ^ Sellers, Peter (July 20, 2001). "Dragon Warrior III". IGN. Retrieved July 22, 2011.
- ^ Juan2Darien. "Dragon Quest I Symphonic Suite". Square Enix Music Online. Retrieved February 13, 2011.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ "Japanese Comic Ranking, August 26 – September 1". News. Anime News Network. September 3, 2009. Retrieved November 9, 2009.
- ^ "Japanese Comic Ranking, February 24 – March 2". News. Anime News Network. September 3, 2009. Retrieved November 9, 2009.
- ^ a b c d "The GameSpy Hall of Fame: Dragon Warrior". GameSpy. p. 2. Retrieved October 9, 2009.
- ^ a b c Reeves, Ben (February 14, 2011). "A Warrior's Quest: A Retrospective of Square-Enix's Classic RPG Series". Game Informer. Retrieved September 2, 2011.
- ^ Andrew Vestal (November 2, 1998). "Other Game Boy RPGs". GameSpot. Retrieved November 18, 2011.
- ^ "East and West, Warrior and Quest: A Dragon Quest Retrospective - An anniversary look back at the most influential console RPG ever made". 1UP.com. May 2011. Archived from the original on 21 December 2011. Retrieved 28 December 2011.
- ^ Bailey, Kat (February 2010). "The Uncanny Valley of Love: The challenges and rewards of crafting a video game romance". 1UP.com. Retrieved September 12, 2011.
- ^ Vestal, Andrew (November 2, 1998). "The History of Console RPGs – Dragon Quest". GameSpot. Retrieved July 11, 2011.
- ^ Horii, Yuji (November 2010). "25 Years of the NES". Nintendo Power (260). South San Francisco, CA: Future US: 50. ISSN 1041-9551.
- ^ "【CEDEC 2009】『ドラクエ』は藤子さんになれたらいい――堀井氏が基調講演" (in Japanese). Famitsu. September 1, 2009. Retrieved February 14, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help); Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help) - ^ "Feature: Hardware – The Family Computer". Retro Gamer (16). Bournemouth: Imagine Publishing: 33. May 2005. ISSN 1742-3155. OCLC 489477015.
- ^ "Clone Warriors: RPGs Inspired by Dragon Quest". The 25th Anniversary of Dragon Quest. 1up. Retrieved September 1, 2011.
- ^ "The Best ROM Hacks". Retro Gamer (13). Bournemouth: Imagine Publishing: 72. February 2005. ISSN 1742-3155. OCLC 489477015.
- ^ Sonntag, Lawrence (October 14, 2010). "The Descendants of Erdrick Rock the Gaming Music Scene". Inside Gaming Daily. Retrieved March 11, 2012.
- ^ Robertson, Adi (March 31, 2012). "Google Maps coming soon to the NES". The Verge. Retrieved March 31, 2012.
- ^ Ponce, Tony (March 31, 2012). "Google Maps: Dragon Quest Edition!". Destructoid. Retrieved October 18, 2013.
- ^ Molina, Brett (April 1, 2012). "Google Maps Gets 8-bit NES Treatment". USA Today. Retrieved October 18, 2013.
External links
- Official Dragon Quest for smartphone site
- Official Dragon Quest site Template:Ja icon
- Official Dragon Quest for smartphone site Template:Ja icon
- Dragon Warrior at MobyGames
- Dragon Quest for mobiles at MobyGames
- Role-playing video games introduced in 1986
- Android (operating system) games
- Chunsoft games
- Dragon Quest video games
- Game Boy games
- Game Boy Color games
- IOS games
- MSX games
- MSX2 games
- NEC PC-9801 games
- Nintendo Entertainment System games
- Satellaview games
- Sharp X68000 games
- Super Nintendo Entertainment System games
- 1986 video games
