Eurasian dotterel
| Eurasian dotterel | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Charadriiformes |
| Family: | Charadriidae |
| Genus: | Charadrius |
| Species: | C. morinellus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Charadrius morinellus | |
| |
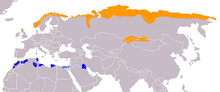
| Range of C. morinellus Breeding range Wintering range
| |
The Eurasian dotterel (Charadrius morinellus), also known in Europe as just dotterel, is a small wader in the plover family of birds.
The dotterel is a brown and black streaked bird with a broad white eye-stripe and an orange-red chest band when in breeding plumage. The female is more colourful than the male. The bird is tame and unsuspecting and the term "dotterel" has been applied contemptuously to mean an old fool.
The Eurasian dotterel is a migratory species, breeding in northern Europe and Asia and migrating south to north Africa and the Middle East in the winter. It nests in a bare scrape on the ground and lays two to four eggs. The male does the incubation and rears the chicks, the female having gone off to find another male and lay another clutch of eggs. It is a common bird with a wide range and the International Union for Conservation of Nature has rated it as being of "least concern".
Etymology
The English name dates from 1440 when it was used to refer to the bird and also as an insult for someone considered simple or a dotard. It is not clear which use is the oldest,[2] but the link is its tame and unsuspecting nature which made it easy to catch; its Scottish Gaelic name is amadan-mòintich, "fool of the moors."[3] King James VI and I went every year to Royston, Hertfordshire to shoot dotterels.[4] It was also easy prey for illegal poaching, which depleted its stocks.[citation needed] They were also prized as a delicacy: in 1534 Queen Anne Boleyn was presented with "a brace of dotterels".[citation needed]
The genus name Charadrius is a Late Latin word for a yellowish bird mentioned in the fourth-century Vulgate. It derives from Ancient Greek kharadrios a bird found in ravines and river valleys (kharadra, "ravine"). The specific morinellus is Ancient Greek derived from moros "foolish", due to the bird's trusting nature.[5]
Description
This plover is smaller and more compact than European golden plover (Pluvialis apricaria). It has a striking whitish supercilium in all plumages and has plain wings in flight. Adults in summer are unmistakable, with a chestnut breast bordered above with white, black belly and warm brown back. The legs are yellow, and the short bill is black. As with the phalaropes, the female is brighter than the male.
Winter birds lack the rich underpart colouration, apart from the white breast line, and are greyer above. Young birds are similar but have a scaly appearance to their backs.
Distribution and habitat
It breeds in the Arctic tundra of northern Eurasia, from Norway to eastern Siberia, and on suitable mountain plateaus such as the Scottish highlands and the Alps. This species is migratory, wintering in a narrow belt across north Africa from Morocco eastwards to Iran. Migration stopovers are traditional, and small parties (trips) of dotterels pass through each year at these usually inland arable or grassy sites. The winter habitat is semi-desert.
Behaviour and ecology
The dotterel's diet is made up of insects and other small invertebrates such as snails and worms and shellfish. These are obtained by a run-and-pause technique, rather than the steady probing used by other waders.
The flight call is a soft pyurr. The female's song is a simple repetitive whistle.
The male dotterel generally is responsible for incubation and looks after the chicks. In most cases the cock dotterel successfully prevents other males from getting his mate and fertilizing her eggs. He usually rears chicks that he has fathered and only 4.6% (2/44) of chicks were not the genetic offspring of the caring male, corresponding to 9.1% (2/22) broods affected.[6]
Status
It is a relatively common species with a wide range. Populations seem to be declining slowly but not alarmingly so, and the International Union for Conservation of Nature has rated it as a "least-concern species". A survey published in 2015 showed a fall in dotterel numbers in Scotland between 1987 and 2011, from 980 to 423 breeding males - representing a decline of 57%.[7] The Eurasian dotterel is one of the species to which the Agreement on the Conservation of African-Eurasian Migratory Waterbirds (AEWA) applies.
-
Male with chicks
-
Juvenile
-
Female with chick - only 4th record ever
-
Nest
-
ID composite
-
Egg – MHNT
References
- ^ Template:IUCN
- ^ "Dotterel". Oxford English Dictionary (Online ed.). Oxford University Press. (Subscription or participating institution membership required.)
- ^ https://books.google.ie/books?id=r4Bk4KKEjvMC&pg=PA20&lpg=PA20&dq=amadan-m%C3%B2intich&source=bl&ots=h9vIwxxLBb&sig=APNVokW1TrhLNf35b1AZCl3SIz8&hl=en&sa=X&ved=2ahUKEwiRzfH3vLDdAhUCI8AKHTkLAJAQ6AEwBXoECAUQAQ#v=onepage&q=amadan-m%C3%B2intich&f=false
- ^ Quinlan, Ray (2003). The Greater Ridgeway. Milnthorpe, Cumbria, UK: Cicerone Press Limited. p. 189. ISBN 978-1-85284-346-5.
- ^ Jobling, James A (2010). The Helm Dictionary of Scientific Bird Names. London: Christopher Helm. pp. 99, 260. ISBN 978-1-4081-2501-4.
- ^ Owens, Ian P.F.; Dixon, Andrew; Burke, Terry; Thompson, Des B.A. (1995). "Strategic paternity assurance in the sex-role reversed Eurasian dotterel (Charadrius morinellus): behavioral and genetic evidence". Behavioral Ecology. 6: 14. doi:10.1093/beheco/6.1.14.
- ^ "Changes in the abundance and distribution of a montane specialist bird". Bird Study. Retrieved 28 October 2015.
Further reading
- Hayman, Peter; Marchant, John; Prater, Tony (1991). Shorebirds: An Identification Guide to the Waders of the World. ISBN 0-7099-2034-2.
- Tsherbakov, B.V. "Breeding Dotterels Charadrius morinellus in the Altai mountains of Kazakhstan" (PDF). International Wader Studies. 10: 342–344.
It is not only the males which incubate clutches and rear the chicks: on 24 June 1971, a female was collected from a nest with eggs.
External links
- Ageing and sexing (PDF; 3.1 MB) by Javier Blasco-Zumeta & Gerd-Michael Heinze
- Charadrius morinellus in Field Guide: Birds of the World on Flickr
- BirdLife species factsheet for Charadrius morinellus
- "Charadrius morinellus". Avibase.
- "Eurasian dotterel media". Internet Bird Collection.
- Eurasian dotterel photo gallery at VIREO (Drexel University)
- Interactive range map of Charadrius morinellus at IUCN Red List maps
- Audio recordings of Eurasian dotterel on Xeno-canto.
- Eurasian dotterel media from ARKive







