Israeli pound
 IL 500 note (obverse and reverse) issued in 1975 | |
| ISO 4217 | |
| Code | ILP |
| Unit | |
| Plural | pounds (לירות lirot) |
| Symbol | ל"י (Hebrew), IL (Latin) |
| Denominations | |
| Subunit | |
| 1⁄1000 | mil (1951–1952) pruta (1952–1960) |
| 1⁄100 | agora (1960–1980) |
| Plural | |
| mil (1951–1952) pruta (1952–1960) | prutot (פרוטות) |
| agora (1960–1980) | agorot (אגורות) |
| Banknotes | IL 5, IL 10, IL 50, IL 100, IL 500 |
| Coins | 1, 5, 10, 25 agorot, IL 1⁄2, IL 1, IL 5 |
| Demographics | |
| Date of introduction | 9 June 1952 |
| Date of withdrawal | 23 February 1980 |
| Replaced by | First shekel |
| User(s) | |
| Issuance | |
| Central bank | Bank Leumi (1952–1955) Bank of Israel (1955–1980) |
| Valuation | |
| Pegged with | £1 stg at par (1952–1954) |
| This infobox shows the latest status before this currency was rendered obsolete. | |

The pound or lira (Hebrew: לירה ישראלית Lira Yisra'elit, Arabic: جنيه إسرائيلي Junayh ʾIsrāʾīlī; abbreviation: IL[1] in Latin, ל"י in Hebrew; code ILP) was the currency of the State of Israel from 9 June 1952 until 23 February 1980. The Israeli pound replaced the Palestine pound and was initially pegged at par to £1 sterling. It was replaced by the shekel on 24 February 1980, at the rate of IS 1 = IL 10, which was in turn replaced by the new shekel in 1985.
Before the new currency was brought in, the Anglo-Palestine Bank issued banknotes denominated in Palestine pounds. They were in Hebrew לירה א״י (lira E.Y. i.e. lira Eretz-Yisraelit) and Arabic junayh filisṭīnī (جنيه فلسطيني).[2]
On 1 May 1951, all the assets and liabilities of the Anglo Palestine Bank were transferred to a new company called Bank Leumi Le-Yisrael (Israel National Bank) and the currency name became: lira yisraelit (לירה ישראלית) in Hebrew, junayh ʾisrāʾīlī in Arabic, and Israeli pound in English.[3] The new currency was issued in 1952, and entered circulation on June 9. From 1955, after the Bank of Israel was established and took over the duty of issuing banknotes, only the Hebrew name was used.[4]
History
[edit]The British Mandate of Palestine was created in 1918. In 1927 the Palestine Currency Board, established by the British authorities, and subject to the British Secretary of State for the Colonies, issued the Palestine pound (£P) which was legal tender in Mandate Palestine and Transjordan. £P1 was fixed at exactly £1 sterling. It was divided into 1,000 mils.
The Mandate came to an end on 14 May 1948, but the Palestine pound continued in circulation until new currencies replaced it. In Israel, the Palestine pound continued in circulation until the Israeli pound was adopted in 1952. The Israeli pound was subdivided into 1,000 prutot. The Israeli pound retained the Palestine pound's sterling peg. In August 1948, new banknotes were issued by the London-based Anglo-Palestine Bank, owned by the Jewish Agency.
The new coins were the first to bear the new state's name, and the banknotes had "The Anglo-Palestine Bank Limited" written on them. While the first coins minted by Israel were still denominated in "mils", the next ones bore the Hebrew name prutah (Hebrew: פרוטה). A second series of banknotes was issued after the Anglo-Palestine Bank moved its headquarters to Tel Aviv and became the Bank Leumi (Hebrew: בנק לאומי "National Bank"). The peg to sterling was abolished on 1 January 1954, and in 1960, the subdivision of the pound was changed from 1,000 prutot to 100 agorot (singular agora, Hebrew: אגורה ,אגורות).
Because lira (Hebrew: לִירָה) was a loanword from Latin, a debate emerged in the 1960s over the name of the Israeli currency due to its non-Hebrew origins. This resulted in a law ordering the Minister of Finance to change the name from lira to the Hebrew name shekel (Hebrew: שקל). The law allowed the minister to decide on the date for the change. The law came into effect in February 1980, when the Israeli government introduced the 'Israeli shekel' (now called old Israeli shekel), at a rate of IL 10 = IS 1. On 1 January 1986, the old shekel was replaced by the Israeli new shekel at a ratio of IS 1,000 : ₪1.
Coins
[edit]Israel's first coins were aluminium 25 mil pieces, dated 1948 and 1949, which were issued in 1949 before the adoption of the pruta. Later in 1949, coins were issued in denominations of 1, 5, 10, 25, 50, 100 and 250 prutah. The coins were conceived, in part, by Israeli graphic designer Otte Wallish.
All coins and banknotes issued in Israel before June 1952 were part of the Palestine pound.
In 1960, coins were issued denominated in agora. There were 1, 5, 10 and 25 agorot pieces. In 1963, IL 1⁄2 and IL 1 coins were introduced, followed by IL 5 coins in 1978.
The IL 5 denomination had previously been used for non-circulating commemorative coins, including silver coins with a Hanukkah theme.[5]
Mil (1949)
[edit]| Image | Value | Diameter (mm) | Mass (g) | Composition | Obverse | Reverse | Date of issue | Date of withdrawal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
25 mils | 30 | 3.1—3.8 | aluminium 97%, magnesium 3% | Grape, "Israel" in Hebrew and Arabic | Value, olive ornament | 06.04.1949 | 06.09.1950 |
Pruta (1949–1960)
[edit]| Image | Value | Diameter (mm) | Mass (g) | Composition | Obverse | Reverse | Date of issue | Date of withdrawal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
1 pruta | 21 | 1.3 | aluminium 97%, magnesium 3% | Anchor, "Israel" in Hebrew and Arabic | Value, olive ornament | 25.10.1950 | 22.02.1960 |

|
5 prutot | 20 | 3.2 | copper 95%, tin 3%, zinc 2% | Lyre, "Israel" in Hebrew and Arabic | 28.12.1950 | 22.02.1960 | |
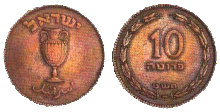
|
10 prutot | 27 | 6.1 | Amphora, "Israel" in Hebrew and Arabic | 04.01.1950 | 22.02.1960 | ||

|
10 prutot | 24.5 | 1.6 | aluminium 97%, magnesium 3% | Amphora, palms, "Israel" in Hebrew and Arabic | 18.09.1952 | 22.02.1960 | |

|
10 prutot | 24.5 | 1.6 | Amphora, palms, "Israel" in Hebrew and Arabic | 27.12.1956 | 22.02.1960 | ||

|
25 prutot | 19.5 | 2.8 | copper 75%, nickel 25% | Grape, "Israel" in Hebrew and Arabic | 04.01.1950 | 22.02.1960 | |

|
50 prutot | 23.5 | 5.6 | Grape, "Israel" in Hebrew and Arabic | 11.05.1949 | 22.02.1960 | ||
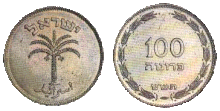
|
100 prutot | 28.5 | 11.3 | Palm, "Israel" in Hebrew and Arabic | 25.05.1949 | 22.02.1960 | ||

|
100 prutot | 25.6 | 7.3 | steel 90%, nickel 10% | Palm, "Israel" in Hebrew and Arabic | 21.04.1955 | 22.02.1960 | |

|
250 prutot | 32.2 | 14.1 | copper 75%, nickel 25% | Hordeum, "Israel" in Hebrew and Arabic | 11.10.1950 | 22.02.1960 | |

|
500 prutot | 37.1 | 25 | silver 50%, copper 37,5%, nickel 12,5% | Three pomegranates, "Israel" in Hebrew and Arabic | 22.05.1952 | 22.02.1960 |
Agora (1960–1978)
[edit]| Image | Value | Diameter (mm) | Mass (g) | Composition | Obverse | Reverse | Date of issue | Date of withdrawal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
1 agora | 21 | 1.3 | aluminium 97%, magnesium 3% | Barley, "Israel" in Hebrew and Arabic | Value, date | 12.05.1960 | 22.02.1980 |

|
5 agorot | 17,5 | 2.3 | 1960—1975: copper 92%, aluminium 6%, nickel 2%
1976—1979: aluminium 97%, magnesium 3% |
Three pomegranates, "Israel" in Hebrew and Arabic | 20.10.1960 | 22.02.1980 | |

|
10 agorot | 21,5 | 5 | 1960—1977: copper 92%, aluminium 6%, nickel 2%
1978—1979: aluminium 97%, magnesium 3% |
Date palm, "Israel" in Hebrew and Arabic | 06.05.1960 | 31.03.1984 | |

|
25 agorot | 25,5 | 6.5 | copper 92%, aluminium 6%, nickel 2% | Lyre, "Israel" in Hebrew and Arabic | 17.03.1960 | 22.02.1980 | |

|
IL 1⁄2 | 24,5 | 6.8 | copper 75%, nickel 25% | The state emblem, "Israel" in Hebrew, Arabic and English | 12.09.1963 | 31.03.1984 | |

|
IL 1 | 27,5 | 9 | |||||

|
IL 1 | 27,5 | 9 | Three pomegranates, the state emblem, "Israel" in Hebrew, Arabic and English | Value, date, two stars | 1967 | ||

|
IL 5 | 30 | 11,2 | Lion, the state emblem, "Israel" in Hebrew, Arabic and English | 21.09.1978 |
Banknotes
[edit]In 1948, the government issued fractional notes for 50 and 100 mils. The Anglo-Palestine Bank issued banknotes for 500 mils, 1, 5, 10 and 50 pounds between 1948 and 1951. In 1952, the government issued a second series of fractional notes for 50 and 100 prutah with 250 prutah notes added in 1953. Also in 1952, the "Bank Leumi Le-Israel" took over paper money production and issued the same denominations as the Anglo-Palestine Bank except that the 500 mils was replaced by a 500 prutah note.
The Bank of Israel began note production in 1955, also issuing notes for 500 prutah, IL 1, IL 5, IL 10 and IL 50. In 1968, IL 100 notes were introduced, followed by IL 500 notes in 1975.
Bank Leumi series (1952)
[edit]| Image | Value | Dimensions | Main Colour | Description | Date of | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Obverse | Reverse | issue | ceased to be legal tender | ||||

|
500 prutah (IL1⁄2) | 148 × 72 mm | Olive-green on light-blue | The denomination in centre and above "Bank Leumi le-Israel B.M." all in Hebrew; all surrounded by guilloches. | The denomination and "Bank Leumi le-Israel B.M." all in Arabic and English; all surrounded by guilloches. | 9 June 1952 | 7 February 1961 |

|
IL 1 | 150 × 75 mm | Green-pink | ||||

|
IL 5 | 155 × 80 mm | Red-brown | ||||

|
IL 10 | 155 × 80 mm | Gray-pink | ||||

|
IL 50 | 160 × 85 mm | Brown-green | ||||
First series (1955)
[edit]| Image | Value | Dimensions | Main Colour | Description | Date of | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Obverse | Reverse | Watermark | issue | ceased to be legal tender | ||||

|
500 pruta (IL 1⁄2) | 130 × 72 mm | Red | Ruins of an ancient synagogue at Bir'am in the Upper Galilee. | An abstract design. | Menorah with an imprint of cyclamen. | 4 August 1955 | 31 March 1984 |

|
IL 1 | 135 × 72 mm | Blue | View of the Upper Galilee. | Menorah with an imprint of anemones. | 27 October 1955 | ||

|
IL 5 | 140 × 78 mm | Brown | Negev landscape with a settlement and farm equipment. | Menorah with an imprint of irises. | |||

|
IL 10 | 150 × 82 mm | Green | View of the Jezreel Valley depicting settlements and cultivated fields. | Menorah with an imprint of tulips. | 4 August 1955 | ||

|
IL 50 | 160 × 87 mm | Blue | The road to Jerusalem. | Menorah with an imprint of oleander. | 19 September 1957 | ||
Second series (1959)
[edit]| Image | Value | Dimensions | Main Colour | Description | Date of | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Obverse | Reverse | Watermark | issue | ceased to be legal tender | ||||

|
IL 1⁄2 | 130 × 70 mm | Green | Pioneer-woman soldier holding a basket of oranges against a background of fields. | Tomb of the Sanhedrin in Jerusalem. | The profile of the woman. | 15 October 1959 | 31 March 1984 |

|
IL 1 | 135 × 75 mm | Blue | Fisherman carrying fishing gear against a background of a bay. | Mosaic from the floor of an ancient synagogue at lssafiya on Mt. Carmel. | The profile of the fisherman. | ||

|
IL 5 | 140 × 78 mm | Brown | Labourer holding a sledge-hammer against a background of an industrial plant. | Roaring lion depicted on an ancient Hebrew seal found at Megiddo. | The profile of the labourer. | ||

|
IL 10 | 150 × 82 mm | Purple | Scientist in a laboratory. | Passage from the Book of Isaiah and the Dead Sea Scrolls. | The profile of the scientist. | ||

|
IL 50 | 178 × 93 mm | Brown | Two young pioneers against a background of an agricultural settlement in the Negev. | Menorah from the ancient synagogue of Nirim in the Negev. | The profile of the pioneers. | 9 December 1960 | |
Third series (1970)
[edit]| Image | Value | Dimensions | Main Colour | Description | Date of | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Obverse | Reverse | Watermark | issue | ceased to be legal tender | ||||

|
IL 5 | 150 × 75 mm | Light blue | Portrait of Albert Einstein. | The Atomic reactor at Nahal Sorek. | Profile of Albert Einstein. | 13 January 1972 | 31 March 1984 |

|
IL 10 | 160 × 82 mm | Yellow-ivory | Portrait of Chaim Nachman Bialik. | Bialik's home in Tel-Aviv. | Profile of Chaim Nachman Bialik. | 6 August 1970 | |

|
IL 50 | 170 × 84 mm | Brown-red | Portrait of Chaim Weizmann. | The Knesset Building in Jerusalem. | Profile of Chaim Weizmann. | 13 January 1972 | |

|
IL 100 | 180 × 90 mm | Blue | Portrait of Theodor Herzl. | The Emblem of the State of Israel surrounded by the emblems of the twelve tribes. | Profile of Theodor Herzl. | 27 February 1969 | |
Fourth series (1975)
[edit]| Image | Value | Dimensions | Main Colour | Description | Date of | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Obverse | Reverse | Watermark | issue | ceased to be legal tender | ||||

|
IL 5 | 128 × 76 mm | Brown | Portrait of Henrietta Szold; Hadassah Hospital on Mt. Scopus in Jerusalem. | Lion's Gate in the Old City of Jerusalem. | Profile of Henrietta Szold. | 11 March 1976 | 31 March 1984 |

|
IL 10 | 135 × 76 mm | Pink-purple | Portrait of Moshe Montefiori; the Mishkanot Shaananim quarter in Jerusalem with the windmill. | Jaffa Gate in the Old City of Jerusalem. | Profile of Moshe Montefiori. | 30 January 1975 | |

|
IL 50 | 141 × 76 mm | Green | Portrait of Chaim Weizmann; the Wix Library at the Weizmann Institute of Science. | Damascus gate in the Old City of Jerusalem. | Profile of Chaim Weizmann. | 26 January 1978 | |

|
IL 100 | 147 × 76 mm | Blue | Portrait of Theodor Herzl; the entrance gate to Mt. Herzl in Jerusalem. | Zion Gate in the Old City of Jerusalem. | Profile of Theodor Herzl. | 14 March 1975 | |

|
IL 500 | 153 × 76 mm | Ivory-brown | Portrait of David Ben-Gurion; the library at kibbutz Sde Boker. | Golden Gate in the Old City of Jerusalem. | Profile of David Ben-Gurion. | 26 May 1977 | |
See also
[edit]Citations
[edit]- ^ "Bank of Israel Law, 5714–1954*" (PDF). 3 September 1954.
- ^ One Palestine Pound, IL: Bank of Israel, archived from the original on April 27, 2006
- ^ One Israeli Pound, IL: Bank of Israel, archived from the original on 2007-09-27
- ^ First Series of the Pound, IL: Bank Le-Israel, archived from the original on 2007-09-27
- ^ Thomas V. Haney (November 5, 1972). "Israel Series Marks 25th Anniversary". New York Times. Retrieved January 8, 2024.
General and cited references
[edit]- Krause, Chester L.; Clifford Mishler (1991). Standard Catalog of World Coins: 1801–1991 (18th ed.). Krause Publications. ISBN 0873411501.
- Pick, Albert (1994). Standard Catalog of World Paper Money: General Issues. Colin R. Bruce II and Neil Shafer (editors) (7th ed.). Krause Publications. ISBN 0-87341-207-9.
External links
[edit]- Past Notes & Coins Series. Bank of Israel
