Shu'fat Camp
Shu'fat, or more commonly Shuafat (Arabic: شعفاط Šuʿafāṭ), is a Palestinian refugee camp in Jerusalem jurisdiction located next to Shuafat, a Palestinian Arab neighborhood of East Jerusalem. The camp is located outside the Israeli West Bank barrier (unlike most other Jerusalem's neighborhoods), but technically the Shuafat refugee camp is the only Palestinian UNRWA-run refugee camp, located inside what is officially Israeli territory.
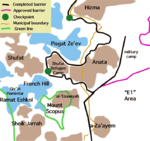
Often, the entire area within the municipal boundaries of Jerusalem that is located beyond the Shu'fat refugee camp checkpoint, is referred to as "Shu'fat Refugee Camp." However, in reality, the area of the refugee camp (under UNRWA responsibility) constitutes only a small part of this territory, characterized by low-rise construction. To the west of the refugee camp, still within the area beyond the separation barrier, lies Ras Khamis; to the south of the refugee camp is Ras Shehadeh; and to the east of the camp is Dahiyat al-Salam, extending eastward to the municipal boundary of the city, beyond which lies the village of Anata (located outside the municipal area). The neighborhoods surrounding the camp are characterized by dense high-rise construction. To the north, the refugee camp extends to the separation barrier, just a few hundred meters from the Pisgat Ze'ev neighborhood.
Shuafat refugee camp
[edit]In the wake of the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, the Red Cross accommodated Palestinian refugees in the depopulated and partly destroyed Jewish Quarter of Jerusalem.[1] This grew into the Muaskar refugee camp managed by UNRWA, which housed refugees from 48 locations now in Israel.[2] Over time many poor non-refugees also settled in the camp.[2] Conditions became unsafe for habitation due to lack of maintenance and sanitation, but neither UNRWA nor the Jordanian government wanted the negative international response that would result if they demolished the old Jewish houses.[2]




In 1964, a decision was made to move the refugees to a new camp constructed on mostly Jewish land near Shuafat.[2] Most of the refugees refused to move, since it would mean losing their livelihood, the market and the tourists, as well as reducing their access to the holy sites.[2] In the end, many of the refugees were moved to Shuafat by force during 1965 and 1966.[1][2]
History
[edit]After the 1967 Six-Day War, East Jerusalem, including the town and refugee camp, was occupied and later annexed by Israel, in a move not internationally recognized, and were incorporated into the Jerusalem municipal district.[3][4] The residents were offered Israeli citizenship, but most refused it as they considered the area to be illegally occupied. Many accepted permanent residency status instead.[4]
The Shuafat refugee camp is the only Palestinian refugee camp located inside Jerusalem or any other Israeli-administered area. While its residents carry Jerusalem identity cards, which grants them the same privileges and rights as regular Israelis, the camp itself is largely serviced by UNRWA, even though 40-50% of the camp's population are not registered refugees. The Israeli West Bank barrier was partially constructed between the camp and the rest of Shuafat and Jerusalem. Some health services are provided by Israeli clinics in the camp. The Israeli presence is limited to checkpoints controlling entry and exit. According to Ir Amim, the camp suffers from high crime because Israeli Police rarely enter due to security concerns, while the Palestinian Civil Police Force does not operate in Israeli-administered municipalities. Unlike other UN-run refugee camps, residents of Shuafat camp pay taxes to the Israeli authorities.[5][6]
In a survey conducted as part of the research for the book Negotiating Jerusalem (2000), it was reported that 59% of Israeli Jews supported redefining the borders of the city of Jerusalem so as to exclude Arab settlements such as Shuafat, in order to ensure a "Jewish majority" in Jerusalem.[7]
In July 2001, the Israeli authorities destroyed 14 homes under construction in Shuafat on the orders of then mayor Ehud Olmert, who said the structures were built without permits. No one was yet living in them.[8] The families acknowledged they do not own the land they built on, but believed they had permission to build there from Islamic Trust religious authorities and argue that obtaining permits to build legally is nearly impossible. Olmert said the houses were being constructed on public land in a "green area" and posed a security threat to the Jews of Pisgat Ze'ev.[9] According to Isabel Kershner of the New York Times, Shuafat suffered from an absence of municipal planning, overcrowding, and potholed roads in 2007.[4]
As prime minister, Ehud Olmert questioned whether the annexation of areas like Shuafat into the Jerusalem area was necessary.[10] The Israeli initiative to transfer control of the area to the Palestinian National Authority led to a split in the community: a camp official favored being under Palestinian sovereignty, while the neighborhood's mukhtar rejected the plan, citing his residents' participation in Israeli elections as well as the danger of Palestinian rocket attacks on Israel[11]
Urban development
[edit]In 2012, Sorbonne scholar professor Sylvaine Bulle cited the Shuafat refugee camp for its urban renewal dynamic, seeing it as an example of a creative adaptation to the fragmented space of the camps towards creating a bricolage city, with businesses relocating from east Jerusalem there and new investment in commercial projects.[12]
Gallery
[edit]-
Dahiyat al-Salam
References
[edit]- ^ a b Meron Benvenisti (1976). Jerusalem: The Torn City. Isratypeset. p. 70.
- ^ a b c d e f Avi Plascov (1981). The Palestinian Refugees in Jordan 1948–1957. Frank Cass. p. 171.
- ^ Noah Browning, 'In bleak Arab hinterland, hints of Jerusalem's partition,' Reuters December 20, 2013.
- ^ a b c Isabel Kershner (June 5, 2007). "Under a Divided City, Evidence of a Once United One". The New York Times. Retrieved 2008-01-29.
- ^ "New checkpoint opened at entrance to Shuafat". The Jerusalem Post. December 2011. Retrieved 2012-02-20.
- ^ "Jerusalem Neighborhood Profile: Shuafat Refugee Camp". Ir Amim. August 2006. Archived from the original (DOC) on 2011-08-22. Retrieved 2008-02-01.
- ^ Jerome M. Segal (2000). Negotiating Jerusalem. SUNY Press. p. 127. ISBN 0-7914-4537-2.
- ^ "Violence flares in Jerusalem as Israeli bulldozers destroy dozen 'illegal' homes". Independent.co.uk.
- ^ Tracy Wilkinson (July 10, 2001). "Israel Razes 14 Arab Homes at Refugee Camp". Los Angeles Times. p. in print edition A-4. Retrieved 2008-09-07.
- ^ Meranda, Amnon (October 15, 2007). "Olmert hints at possible concessions in Jerusalem". Ynetnews. Ynet. Retrieved 2008-02-01.
- ^ "Shuafat area residents split over plan to divide Jerusalem in two". The Jerusalem Post. October 2007. Retrieved 2012-02-20.
- ^ Esther Zandberg (2008-10-23). "Their Shoafat outshines her Paris". HAARETZ. Retrieved 2012-12-04.
External links
[edit]- Welcome To Shu'fat R.C.
- Camp profile on UNWRA website
- Shuafat Camp Website Archived 2018-04-20 at the Wayback Machine