Appendicitis: Difference between revisions
added |
|||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
<!-- Treatment, history and epidemiology --> |
<!-- Treatment, history and epidemiology --> |
||
The standard treatment for acute appendicitis is [[Appendectomy|surgical removal of the appendix]].<ref name="Harrison's"/><ref name="Tintinalli"/> This may be done by an [[laparotomy|open incision in the abdomen]] or through a few [[laparoscopy|smaller incisions with the help of cameras]]. Surgery decreases the risk of side effects or death associated with rupture of the appendix.<ref name="hobbler">{{Cite journal|last=Hobler |first=K. |date=Spring 1998 |title=Acute and Suppurative Appendicitis: Disease Duration and its Implications for Quality Improvement |url=http://xnet.kp.org/permanentejournal/spring98pj/appendicitis.html |journal=Permanente Medical Journal |volume=2}}</ref> [[Antibiotic]]s may be equally effective in certain cases of non-ruptured appendicitis.<ref name=Antibiotics2012/> |
The standard treatment for acute appendicitis is [[Appendectomy|surgical removal of the appendix]].<ref name="Harrison's"/><ref name="Tintinalli"/> This may be done by an [[laparotomy|open incision in the abdomen]] or through a few [[laparoscopy|smaller incisions with the help of cameras]]. Surgery decreases the risk of side effects or death associated with rupture of the appendix.<ref name="hobbler">{{Cite journal|last=Hobler |first=K. |date=Spring 1998 |title=Acute and Suppurative Appendicitis: Disease Duration and its Implications for Quality Improvement |url=http://xnet.kp.org/permanentejournal/spring98pj/appendicitis.html |journal=Permanente Medical Journal |volume=2}}</ref> [[Antibiotic]]s may be equally effective in certain cases of non-ruptured appendicitis.<ref name=Antibiotics2012/> It is one of the most common and significant causes of severe abdominal [[pain]] [[Acute (medicine)|that comes on quickly]] worldwide. In 2013 it resulted in 72,000 deaths globally.<ref name=GBD204>{{cite journal|last1=GBD 2013 Mortality and Causes of Death|first1=Collaborators|title=Global, regional, and national age-sex specific all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013.|journal=Lancet|date=17 December 2014|pmid=25530442}}</ref> In the United States, appendicitis is the most common cause of acute abdominal pain requiring surgery.<ref name="Graffeo-1996"/> Each year in the United States, more than 300,000 persons with appendicitis have their appendix surgically removed.<ref>{{cite journal|last1=Mason|first1=RJ|title=Surgery for appendicitis: is it necessary?|journal=Surgical infections|date=August 2008|volume=9|issue=4|pages=481–8|pmid=18687030|doi=10.1089/sur.2007.079}}</ref> [[Reginald Heber Fitz|Reginald Fitz]] is credited with being the first person to describe the condition in a paper published in 1886.<ref>{{Cite journal|author=Fitz RH |title=Perforating inflammation of the vermiform appendix with special reference to its early diagnosis and treatment |journal=Am J Med Sci |volume= |issue=92 |pages=321–46 |year=1886}}</ref> |
||
{{TOC limit|3}} |
{{TOC limit|3}} |
||
Revision as of 07:08, 3 February 2015
| Appendicitis | |
|---|---|
| Specialty | General surgery |
Appendicitis (also called epityphlitis[1]) is inflammation of the appendix. Appendicitis commonly presents with right iliac fossa abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and decreased appetite.[2] However, one third to a half of persons do not have these typical signs and symptoms.[3] Severe complications of a ruptured appendix include wide spread, painful inflammation of the inner lining of the abdominal wall and sepsis.[4]
Appendicitis is caused by a blockage of the hollow portion of the appendix,[5][6] most commonly by a calcified "stone" made of feces. However inflamed lymphoid tissue from a viral infection, parasites, gallstone or tumors may also cause the blockage.[7] This blockage leads to increased pressures within the appendix, decreased blood flow to the tissues of the appendix, and bacterial growth inside the appendix causing inflammation.[7][8] The combination of inflammation, reduced blood flow to the appendix and distention of the appendix causes tissue injury and death.[9] If this process is left untreated, the appendix may burst releasing bacteria into the abdominal cavity, leading to severe abdominal pain, increased complications, longer hospital stays and the need for more antibiotics.[9][10]
The diagnosis of appendicitis is largely based on the persons signs and symptoms.[8] In cases where the diagnosis cannot be made based on the person's history and physical exam, close observation, radiographic imaging and laboratory tests can often be helpful.[11] The two most common imaging tests used are ultrasound and computer tomography (CT scan).[11] CT scan has been shown to be more accurate than ultrasound in detecting acute appendicitis.[12][13] However, ultrasound may be preferred as the first imaging test in children and pregnant women due to the risks associated with radiation exposure from CT scans.[11]
The standard treatment for acute appendicitis is surgical removal of the appendix.[7][8] This may be done by an open incision in the abdomen or through a few smaller incisions with the help of cameras. Surgery decreases the risk of side effects or death associated with rupture of the appendix.[4] Antibiotics may be equally effective in certain cases of non-ruptured appendicitis.[14] It is one of the most common and significant causes of severe abdominal pain that comes on quickly worldwide. In 2013 it resulted in 72,000 deaths globally.[15] In the United States, appendicitis is the most common cause of acute abdominal pain requiring surgery.[2] Each year in the United States, more than 300,000 persons with appendicitis have their appendix surgically removed.[16] Reginald Fitz is credited with being the first person to describe the condition in a paper published in 1886.[17]
Signs and symptoms
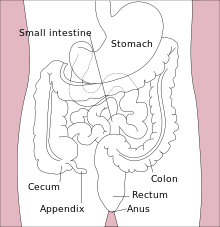
Pain first, nausea and vomiting next, and fever last has been described as the classic presentation of acute appendicitis. Because the innervation of the appendix enters the spinal cord at the same level as the umbilicus (belly button), the pain begins stomach-high. As the appendix becomes more swollen and inflamed, it begins to irritate the adjoining abdominal wall. This leads to the localization of the pain to the right lower quadrant. This classic migration of pain may not be seen in children under three years. This pain can be elicited through various signs and can be severe. Signs include localized findings in the right iliac fossa. The abdominal wall becomes very sensitive to gentle pressure (palpation). Also, there is severe pain on sudden release of deep pressure in the lower abdomen (rebound tenderness). If the appendix is retrocecal (localized behind the cecum), even deep pressure in the right lower quadrant may fail to elicit tenderness (silent appendix). This is because the cecum, distended with gas, protects the inflamed appendix from pressure. Similarly, if the appendix lies entirely within the pelvis, there is usually complete absence of abdominal rigidity. In such cases, a digital rectal examination elicits tenderness in the rectovesical pouch. Coughing causes point tenderness in this area (McBurney's point).
Causes
Based on experimental evidence, acute appendicitis seems to be the end result of a primary obstruction of the appendiceal lumen.[18][19] Once this obstruction occurs, the appendix becomes filled with mucus and swells. This continued production of intra-lumenal mucus leads to increased pressures within the lumen and the walls of the appendix. This increased pressure results in thrombosis and occlusion of the small vessels, and stasis of lymphatic flow. At this point spontaneous recovery rarely occurs. As the occlusion of blood vessels progresses, the appendix becomes ischemic and then necrotic. As bacteria begin to leak out through the dying walls, pus forms within and around the appendix (suppuration). The end result of this cascade is appendiceal rupture (a 'burst appendix') causing peritonitis, which may lead to sepsis and eventually death. This cascade of events is responsible for the slowly evolving abdominal pain and other commonly associated symptoms.[9]
The causative agents include bezoars, foreign bodies, trauma, intestinal worms, lymphadenitis, and, most commonly, calcified fecal deposits that are known as appendicoliths or fecaliths.[20] The occurrence of obstructing fecaliths has attracted attention since their presence in persons with appendicitis is higher in developed than in developing countries.[21] In addition an appendiceal fecalith is commonly associated with complicated appendicitis.[22] Also, fecal stasis and arrest may play a role, as demonstrated by persons with acute appendicitis having fewer bowel movements per week compared with healthy controls.[23][24] The occurrence of a fecalith in the appendix was thought to be attributed to a right-sided fecal retention reservoir in the colon and a prolonged transit time. However a prolonged transit time was not observed in subsequent studies.[25] From epidemiological data, it has been stated that diverticular disease and adenomatous polyps were unknown and colon cancer exceedingly rare in communities exempt from appendicitis.[26][27] Also, acute appendicitis has been shown to occur antecedent to cancer in the colon and rectum.[28] Several studies offer evidence that a low fiber intake is involved in the pathogenesis of appendicitis.[29][30][31] This low intake of dietary fiber is in accordance with the occurrence of a right-sided fecal reservoir and the fact that dietary fiber reduces transit time.[32]
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is based on a medical history (symptoms) and physical examination which can be supported by an elevation of neutrophilic white blood cells and imaging studies if needed. (Neutrophils are the primary white blood cells that respond to a bacterial infection.) Histories fall into two categories, typical and atypical. Typical appendicitis includes several hours of abdominal pain which begins in the region of the umbilicus with associated anorexia, nausea, or vomiting. The pain then "migrates" into the right lower quadrant (or the left lower quadrant in persons with situs inversus totalis), where tenderness develops. The combination of pain, anorexia, leukocytosis, and fever is classic. Atypical histories lack this typical progression and may include pain in the right lower quadrant as an initial symptom. Irritation of the peritoneum (inside lining of the abdominal wall) can lead to increased pain on movement, or jolting, for example going over speedbumps.[33] Atypical histories often require imaging with ultrasound and/or CT scanning.[34]
Clinical
- Aure-Rozanova sign: Increased pain on palpation with finger in right Petit triangle (can be a positive Shchetkin-Bloomberg's)
- Bartomier-Michelson's sign: Increased pain on palpation at the right iliac region as the person being examined lies on his/her left side compared to when he/she lies on his/her back.
- Dunphy's sign: Increased pain in the right lower quadrant with coughing.[35]
- Kocher's (Kosher's) sign: From the person's medical history, the start of pain in the umbilical region with a subsequent shift to the right iliac region.
- Massouh sign: Developed in and popular in southwest England, the examiner performs a firm swish with his/her index and middle finger across the abdomen from the Xiphoid process to the left and the right iliac fossa. A positive Massouh sign is a grimace of the person being examined upon a right sided (and not left) sweep.
- Obturator sign: The person being evaluated lies on her/his back with the hip and knee both flexed at ninety degrees. The examiner holds the person's ankle with one hand and knee with the other hand. The examiner rotates the hip by moving the person's ankle away from the his/her body while allowing the knee to move only inward. A positive test is pain with internal rotation of the hip.
- Psoas sign: Also known as the "Obraztsova's sign" is right lower-quadrant pain that is produced with either the passive extension of the right hip or by the active flexion of the person's right hip while supine. The pain that is elicited is due to inflammation of the peritoneum overlying the iliopsoas muscles and inflammation of the psoas muscles themselves. Straightening out the leg causes pain because it stretches these muscles, while flexing the hip activates the iliopsoas and therefore also causes pain.
- Rovsing's sign: Pain in the lower right abdominal quadrant with continuous deep palpation starting from the left iliac fossa upwards (counterclockwise along the colon). The thought is there will be increased pressure around the appendix by pushing bowel contents and air towards the ileocaecal valve provoking right sided abdominal pain.[36]
- Sitkovskiy (Rosenstein)'s sign: Increased pain in the right iliac region as the person is being examined lies on his/her left side.
Blood and urine test
While there is no laboratory test specific for appendicitis, a complete blood count (CBC) is done to check for signs of infection. Although 70-90 percent of people with appendicitis may have an elevated white blood cell (WBC) count, there are many other abdominal and pelvic conditions that can cause the WBC count to be elevated.[37]
A urinalysis generally does not show infection but it is important for determining pregnancy status, especially the possibility of an ectopic pregnancy in woman of childbearing age. The urinalysis is also important for ruling out a urinary tract infection as the cause of abdominal pain. The presence of more than 20 WBC per high-power field in the urine is more suggestive of a urinary tract disorder.[37]
Imaging
Appendicitis in children is common enough to merit special attention. Because of the health risks of exposing children to radiation, ultrasound is the preferred first choice with CT-scan being a legitimate follow-up if the ultrasound is inconclusive.[38][39][40] CT scan is more accurate than ultrasound for the diagnosis of appendicitis in adults and adolescents. CT scan has a sensitivity of 94%, specificity of 95%. Ultrasonography had an overall sensitivity of 86%, a specificity of 81%.[41]
Ultrasound

Ultrasonography and Doppler sonography provide useful means to detect appendicitis, especially in children. Ultrasound can also show free fluid collection in the right iliac fossa, along with a visible appendix without blood flow when using color Doppler. In some cases (15% approximately), however, ultrasonography of the iliac fossa does not reveal any abnormalities despite the presence of appendicitis. This false negative finding is especially true of early appendicitis before the appendix has become significantly distended. In addition false negative findings are more common in adults where larger amounts of fat and bowel gas make visualizing the appendix technically difficult. Despite these limitations, sonographic imaging in experienced hands can often distinguish between appendicitis and other diseases with similar symptoms. Some of these conditions include inflammation of lymph nodes near the appendix or pain originating from other pelvic organs such as the ovaries or fallopian tubes.
Computed tomography


Where it is readily available, computed tomography (CT scan) has become frequently used, especially in adults whose diagnosis is not obvious on history and physical examination. Concerns about radiation, however, tend to limit use of CT in pregnant women and children. A properly performed CT scan with modern equipment has a detection rate (sensitivity) of over 95%, and a similar specificity. Signs of appendicitis on CT scan include lack of oral contrast (oral dye) in the appendix, direct visualization of appendiceal enlargement (greater than 6 mm in cross-sectional diameter), and appendiceal wall enhancement with IV contrast (IV dye). The inflammation caused by appendicitis in the surrounding peritoneal fat (so called "fat stranding") can also be observed on CT, providing a mechanism to detect early appendicitis and a clue that appendicitis may be present even when the appendix is not well seen. This is the most reliable sign for appendicitis. Thus, diagnosis of appendicitis by CT is made more difficult in very thin persons and in children, both of whom tend to lack significant fat within the abdomen. The utility of CT scanning is made clear, however, by the impact it has had on negative appendectomy rates. For example, use of CT for diagnosis of appendicitis in Boston, MA has decreased the chance of finding a normal appendix at surgery from 20% in the pre-CT era to only 3% according to data from the Massachusetts General Hospital.
X–Ray
In general, plain abdominal radiography (PAR) is not useful in making the diagnosis of appendicitis and should not be routinely obtained in a person being evaluated for appendicitis.[42][43] Plain abdominal films may be useful for the detection of ureteral calculi, small bowel obstruction, or perforated ulcer, but these conditions are rarely confused with appendicitis.[44] An opaque fecalith can be identified in the right lower quadrant in less than 5% of persons being evaluated for appendicitis.[37] A barium enema has proven to be a poor diagnostic tool for appendicitis. While failure of the appendix to fill during a barium enema has been associated with appendicitis, up to 20% of normal appendices also do not fill.[44]
Scoring systems
Alvarado score
| Migratory right iliac fossa pain | 1 point |
| Anorexia | 1 point |
| Nausea and vomiting | 1 point |
| Right iliac fossa tenderness | 2 points |
| Rebound tenderness | 1 point |
| Fever | 1 point |
| Leukocytosis | 2 points |
| Shift to left (segmented neutrophils) | 1 point |
| Total score | 10 points |
|---|
A number of clinical and laboratory-based scoring systems have been devised to assist diagnosis. The most widely used is Alvarado score. A score below 5 is strongly against a diagnosis of appendicitis,[45] while a score of 7 or more is strongly predictive of acute appendicitis. In a person with an equivocal score of 5 or 6, a CT scan is used to reduce the rate of negative appendicectomy.
Tzanakis scoring
Tzanakis scoring: Tzanakis and colleagues, in 2005 published a simplified system, now called the Tzanakis scoring system for appendicitis, to aid the diagnosis of appendicitis. It incorporates the presence of four variables made up of specific signs and symptoms, laboratory findings, as well as ultrasound findings to compute a scoring to predict the presence of appendicitis. The maximum score is a total score of 15. When a person with suspected appendicitis scores 8 or more points, there is greater than 96% chance that appendicitis exists.
| Right lower abdominal tenderness | 4 points |
| Rebound tenderness | 3 points |
| White blood cells greater than 12,000 | 2 points |
| Positive ultrasound scan findings of appendicitis | 6 points |
| Total score | 15 points |
|---|
Pathology


The definitive diagnosis is based on pathology. The histologic finding of appendicitis is neutrophilic infiltrate of the muscularis propria.
Periappendicits, inflammation of tissues around the appendix, is often found in conjunction with other abdominal pathology.[46]
Differential diagnosis
Children: Gastroenteritis, mesenteric adenitis, Meckel's diverticulitis, intussusception, Henoch-Schönlein purpura, lobar pneumonia, urinary tract infection (abdominal pain in the absence of other symptoms can occur in children with UTI), new-onset Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis, pancreatitis, and abdominal trauma from child abuse; distal intestinal obstruction syndrome in children with cystic fibrosis; typhlitis in children with leukemia.
Women: A pregnancy test is important in all women of child bearing age, as ectopic pregnancies and appendicitis present similar symptoms. Other causes ovarian torsion, menarche, dysmenorrhea, pelvic inflammatory disease, endometriosis, Mittelschmerz (the passing of an egg in the ovaries approximately two weeks before an expected menstruation cycle).
Men: testicular torsion;
Adults: new-onset Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, regional enteritis, renal colic, perforated peptic ulcer, pancreatitis, rectus sheath hematoma;
Elderly: diverticulitis, intestinal obstruction, colonic carcinoma, mesenteric ischemia, leaking aortic aneurysm.
The term "pseudoappendicitis" is used to describe a condition mimicking appendicitis.[47] It can be associated with Yersinia enterocolitica.[48]
Management
Acute appendicitis is typically managed by surgery however in uncomplicated cases antibiotics are both effective and safe.[14] While antibiotics are effective for treating uncomplicated appendicitis 20% of people had a recurrence within a year and required eventual appendectomy.[14]
Pain
Pain medications (such as morphine) do not appear to affect the accuracy of the clinical diagnosis of appendicitis and therefore should be given early in the person's care.[49] Historically there were concerns among some general surgeons that analgesics would affect the clinical exam in children and thus some recommended that they not be given until the surgeon in question was able to examine the person for themselves.[49]
Surgery
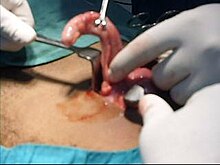

The surgical procedure for the removal of the appendix is called an appendicectomy. Laparoscopic removal (via three small incisions with a camera to visualize the area of interest in the abdomen) seem to have some advantages over an open procedures especially in young females and the obese.[50]
Laparotomy
Laparotomy is the traditional type of surgery used for treating appendicitis. This procedure consists in the removal of the infected appendix through a single larger incision in the lower right area of the abdomen.[51] The incision in a laparotomy is usually 2 to 3 inches (51 to 76 mm) long. This type of surgery is used also for visualizing and examining structures inside the abdominal cavity and it is called exploratory laparotomy.
During a traditional appendectomy procedure, the person with suspected appendicitis is placed under general anesthesia to keep the muscles completely relaxed and to keep the person unconscious. The incision is two to three inches (76 mm) long and it is made in the right lower abdomen, several inches above the hip bone.[52] Once the incision opens the abdomen cavity and the appendix is identified, the surgeon removes the infected tissue and cuts the appendix from the surrounding tissue. After careful and close inspection of the infected area, and ensuring there are no signs that surrounding tissues are damaged or infected, the surgeon will start closing the incision. This means sewing the muscles and using surgical staples or stitches to close the skin up. In order to prevent infections the incision is covered with a sterile bandage.
The entire procedure does not last longer than an hour if complications do not occur.
Laparoscopic
The newer method to treat appendicitis is the laparoscopic surgery. This surgical procedure consists of making three to four incisions in the abdomen, each 0.25 to 0.5 inches (6.4 to 12.7 mm) long. This type of appendectomy is made by inserting a special surgical tool called laparoscope into one of the incisions. The laparoscope is connected to a monitor outside the person's body and it is designed to help the surgeon to inspect the infected area in the abdomen. The other two incisions are made for the specific removal of the appendix by using surgical instruments. Laparoscopic surgery also requires general anesthesia and it can last up to two hours. The latest methods are NOTES appendectomy pioneered in Coimbatore, India where there is no incision on the external skin[53] and SILS (Single incision laparoscopic Surgery) where a single 2.5 cm incision is made to perform the surgery. .
Pre surgery
The treatment begins by keeping the person who will be having surgery from eating or drinking for a given period of time, usually overnight. An intravenous drip is used to hydrate the person who will be having surgery. Antibiotics given intravenously such as cefuroxime and metronidazole may be administered early to help kill bacteria and thus reduce the spread of infection in the abdomen and postoperative complications in the abdomen or wound. Equivocal cases may become more difficult to assess with antibiotic treatment and benefit from serial examinations. If the stomach is empty (no food in the past six hours) general anaesthesia is usually used. Otherwise, spinal anaesthesia may be used.
Once the decision to perform an appendectomy has been made, the preparation procedure takes approximately one to two hours. Meanwhile, the surgeon will explain the surgery procedure and will present the risks that must be considered when performing an appendectomy. With all surgeries there are certain risks that must be evaluated before performing the procedures. However, the risks are different depending on the state of the appendix. If the appendix has not ruptured, the complication rate is only about 3% but if the appendix has ruptured, the complication rate rises to almost 59%.[54] The most usual complications that can occur are pneumonia, hernia of the incision, thrombophlebitis, bleeding or adhesions. Recent evidence indicates that a delay in obtaining surgery after admission results in no measurable difference in outcomes to the person with appendicitis.[55]
The surgeon will also explain how long the recovery process should take. Abdomen hair is usually removed in order to avoid complications that may appear regarding the incision. In most of the cases persons going in for surgery experience nausea or vomiting which requires specific medication before surgery. Antibiotics along with pain medication may also be administrated prior to appendectomies.
After surgery
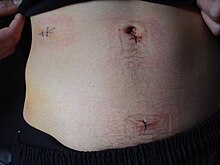
Hospital lengths of stay typically range from a few hours to a few days, but can be a few weeks if complications occur. The recovery process may vary depending on the severity of the condition, if the appendix had ruptured or not before surgery. Appendix surgery recovery is generally a lot faster if the appendix did not rupture.[56] It is important that persons undergoing surgery respect their doctor's advice and limit their physical activity so the tissues can heal faster. Recovery after an appendectomy may not require diet changes or a lifestyle change.
After surgery occurs, the patient will be transferred to a postanesthesia care unit so his or her vital signs can be closely monitored to detect anesthesia- and/or surgery-related complications. Pain medication may also be administered if necessary. After patients are completely awake, they are moved into a hospital room to recover. Most individuals will be offered clear liquids the day after the surgery, then progress to a regular diet when the intestines start to function properly. Patients are recommended to sit up on the edge of the bed and walk short distances for several times a day. Moving is mandatory and pain medication may be given if necessary. Full recovery from appendectomies takes about four to six weeks, but can be prolonged to up to eight weeks if the appendix had ruptured.
Prognosis
Most persons with appendicitis recover easily after surgical treatment, but complications can occur if treatment is delayed or if peritonitis occurs. Recovery time depends on age, condition, complications, and other circumstances, including the amount of alcohol consumption, but usually is between 10 and 28 days. For young children (around 10 years old), the recovery takes three weeks.
The real possibility of life-threatening peritonitis is the reason why acute appendicitis warrants speedy evaluation and treatment. Persons with suspected appendicitis may have to undergo a medical evacuation. Appendectomies have occasionally been performed in emergency conditions (i.e., not in a proper hospital), when a timely medical evaluation was impossible.
Typical acute appendicitis responds quickly to appendectomy and occasionally will resolve spontaneously. If appendicitis resolves spontaneously, it remains controversial whether an elective interval appendectomy should be performed to prevent a recurrent episode of appendicitis. Atypical appendicitis (associated with suppurative appendicitis) is more difficult to diagnose and is more apt to be complicated even when operated early. In either condition, prompt diagnosis and appendectomy yield the best results with full recovery in two to four weeks usually. Mortality and severe complications are unusual but do occur, especially if peritonitis persists and is untreated. Another entity known as appendicular lump is talked about quite often. It happens when the appendix is not removed early during infection and omentum and intestine adhere to it, forming a palpable lump. During this period, surgery is risky unless there is pus formation evident by fever and toxicity or by USG. Medical management treats the condition.
An unusual complication of an appendectomy is "stump appendicitis": inflammation occurs in the remnant appendiceal stump left after a prior incomplete appendectomy.[57]
Epidemiology

Appendicitis is most common between the ages of 5 and 40;[59] the median age is 28. It tends to affect males, those in lower income groups, and, for unknown reasons, people living in rural areas.[60]
In the United States, there were nearly 293,000 hospitalizations involving appendicitis in 2010.[10] Appendicitis is one of the most frequent diagnoses for emergency department visits resulting in hospitalization among children aged 5–17 years in the United States.[61]
Globally, as of 2010 (during one year or during decades[clarification needed]), it resulted in about 35,000 deaths.[62]
Society and culture
Length of stay
Length of hospital stays for appendicitis varies on the severity of the condition. A study from the United States found that in 2010, the average appendicitis hospital stay was 1.8 days. For stays where the person's appendix had ruptured, the average length of stay was 5.2 days.[10]
References
- ^ MerriamWebster definition
- ^ a b Graffeo, CS; Counselman, FL (1996). "Appendicitis". Emergency medicine clinics of North America. 14 (4): 653–71. doi:10.1016/s0733-8627(05)70273-x. PMID 8921763.
- ^ Graffeo, CS; Counselman, FL (November 1996). "Appendicitis". Emergency medicine clinics of North America. 14 (4): 653–71. doi:10.1016/s0733-8627(05)70273-x. PMID 8921763.
- ^ a b Hobler, K. (Spring 1998). "Acute and Suppurative Appendicitis: Disease Duration and its Implications for Quality Improvement". Permanente Medical Journal. 2.
- ^ Wangensteen OH, Bowers WF (1937). "Significance of the obstructive factor in the genesis of acute appendicitis". Arch Surg. 34 (3): 496–526. doi:10.1001/archsurg.1937.01190090121006.
- ^ Pieper R, Kager L, Tidefeldt U (1982). "Obstruction of appendix vermiformis causing acute appendicitis. One of the most common causes of this is an acute viral infection which causes lymphoid hyperplasia and therefore obstruction. An experimental study in the rabbit". Acta Chir Scand. 148 (1): 63–72. PMID 7136413.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b c al.], ed. Dan L. Longo ... [et (2012). Harrison's principles of internal medicine (18th ed. ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill. p. Chapter 300. ISBN 978-0-07174889-6. Retrieved 6 November 2014.
{{cite book}}:|edition=has extra text (help);|first1=has generic name (help) - ^ a b c Tintinalli, editor-in-chief Judith E. (2011). Emergency medicine : a comprehensive study guide (7. ed. ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill. p. Chapter 84. ISBN 978-0-07-174467-6. Retrieved 6 November 2014.
{{cite book}}:|edition=has extra text (help);|first1=has generic name (help) - ^ a b c al.], editor-in-chief, F. Charles Brunicardi ; associate editors, Dana K. Andersen ... [et (2010). Schwartz's principles of surgery (9th ed. ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill, Medical Pub. Division. p. Chapter 30. ISBN 978-0-07-1547703. Retrieved 6 November 2014.
{{cite book}}:|edition=has extra text (help);|first1=has generic name (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b c Barrett ML, Hines AL, Andrews RM. Trends in Rates of Perforated Appendix, 2001–2010. HCUP Statistical Brief #159. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, Rockville, MD. July 2013. [1]
- ^ a b c Paulson, EK; Kalady, MF; Pappas, TN (16 January 2003). "Clinical practice. Suspected appendicitis". The New England journal of medicine. 348 (3): 236–42. doi:10.1056/nejmcp013351. PMID 12529465.
- ^ Pickuth, D; Heywang-Köbrunner, SH; Spielmann, RP (April 2000). "Suspected acute appendicitis: is ultrasonography or computed tomography the preferred imaging technique?". The European journal of surgery = Acta chirurgica. 166 (4): 315–9. doi:10.1080/110241500750009177. PMID 10817330.
- ^ Balthazar, EJ; Birnbaum, BA; Yee, J; Megibow, AJ; Roshkow, J; Gray, C (January 1994). "Acute appendicitis: CT and US correlation in 100 patients". Radiology. 190 (1): 31–5. doi:10.1148/radiology.190.1.8259423. PMID 8259423.
- ^ a b c Varadhan KK, Neal KR, Lobo DN (2012). "Safety and efficacy of antibiotics compared with appendicectomy for treatment of uncomplicated acute appendicitis: meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials". BMJ. 344: e2156. doi:10.1136/bmj.e2156. PMC 3320713. PMID 22491789.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ GBD 2013 Mortality and Causes of Death, Collaborators (17 December 2014). "Global, regional, and national age-sex specific all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013". Lancet. PMID 25530442.
{{cite journal}}:|first1=has generic name (help)CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ Mason, RJ (August 2008). "Surgery for appendicitis: is it necessary?". Surgical infections. 9 (4): 481–8. doi:10.1089/sur.2007.079. PMID 18687030.
- ^ Fitz RH (1886). "Perforating inflammation of the vermiform appendix with special reference to its early diagnosis and treatment". Am J Med Sci (92): 321–46.
- ^ Wangensteen OH, Bowers WF (1937). "Significance of the obstructive factor in the genesis of acute appendicitis". Arch Surg. 34 (3): 496–526. doi:10.1001/archsurg.1937.01190090121006.
- ^ Pieper R, Kager L, Tidefeldt U (1982). "Obstruction of appendix vermiformis causing acute appendicitis. One of the most common causes of this is an acute viral infection which causes lymphoid hyperplasia and therefore obstruction. An experimental study in the rabbit". Acta Chir Scand. 148 (1): 63–72. PMID 7136413.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Hollerman J.; et al. (1988). "Acute recurrent appendicitis with appendicolith". Am J Emerg Med. 6 (6): 614–7. doi:10.1016/0735-6757(88)90105-2.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help) - ^ Jones BA, Demetriades D, Segal I, Burkitt DP (1985). "The prevalence of appendiceal fecaliths in patients with and without appendicitis. A comparative study from Canada and South Africa". Ann. Surg. 202 (1): 80–2. doi:10.1097/00000658-198507000-00013. PMC 1250841. PMID 2990360.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Nitecki S, Karmeli R, Sarr MG (1990). "Appendiceal calculi and fecaliths as indications for appendectomy". Surg Gynecol Obstet. 171 (3): 185–8. PMID 2385810.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Arnbjörnsson E (1985). "Acute appendicitis related to faecal stasis". Annales Chirurgiae Et Gynaecologiae. 74 (2): 90–3. PMID 2992354.
- ^ Dehghan A, Moaddab AH, Mozafarpour S (June 2011). "An unusual localization of trichobezoar in the appendix". The Turkish Journal of Gastroenterology. 22 (3): 357–8. PMID 21805435.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Raahave D, Christensen E, Moeller H, Kirkeby LT, Loud FB, Knudsen LL (2007). "Origin of acute appendicitis: fecal retention in colonic reservoirs: a case control study". Surg Infect (Larchmt). 8 (1): 55–62. doi:10.1089/sur.2005.04250. PMID 17381397.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Burkitt DP (1971). "The aetiology of appendicitis". Br J Surg. 58 (9): 695–9. doi:10.1002/bjs.1800580916. PMID 4937032.
- ^ Segal I, Walker AR (1982). "Diverticular disease in urban Africans in South Africa". Digestion. 24 (1): 42–6. doi:10.1159/000198773. PMID 6813167.
- ^ Arnbjörnsson E (1982). "Acute appendicitis as a sign of a colorectal carcinoma". J Surg Oncol. 20 (1): 17–20. doi:10.1002/jso.2930200105. PMID 7078180.
- ^ Burkitt DP, Walker AR, Painter NS (1972). "Effect of dietary fibre on stools and the transit-times, and its role in the causation of disease". Lancet. 2 (7792): 1408–12. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(72)92974-1. PMID 4118696.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Adamis D, Roma-Giannikou E, Karamolegou K (2000). "Fiber intake and childhood appendicitis". Int J Food Sci Nutr. 51 (3): 153–7. doi:10.1080/09637480050029647. PMID 10945110.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Hugh TB, Hugh TJ (2001). "Appendicectomy--becoming a rare event?". Med. J. Aust. 175 (1): 7–8. PMID 11476215.
- ^ Gear JS, Brodribb AJ, Ware A, Mann JI (January 1981). "Fibre and bowel transit times". The British Journal of Nutrition. 45 (1): 77–82. doi:10.1079/BJN19810078. PMID 6258626.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Ashdown, H. F.; D'Souza, N.; Karim, D.; Stevens, R. J.; Huang, A.; Harnden, A. (17 December 2012). "Pain over speed bumps in diagnosis of acute appendicitis: diagnostic accuracy study". BMJ. 345 (dec14 14): e8012–e8012. doi:10.1136/bmj.e8012.
- ^ Hobler, K. (Spring 1998). "Acute and Suppurative Appendicitis: Disease Duration and its Implications for Quality Improvement" (PDF). Permanente Medical Journal. 2 (2).
- ^ Small V (2008) Surgical emergencies. In Dolan B and Holt L (eds) Accident and Emergency: Theory into Practice, 2nd edition. Elsevier.[page needed]
- ^ N. T. Rovsing, "Indirektes Hervorrufen des typischen Schmerzes an McBurney's Punkt. Ein Beitrag zur diagnostik der Appendicitis und Typhlitis". Zentralblatt für Chirurgie, Leipzig, 1907, 34: 1257-1259 Template:De icon
- ^ a b c CDEM Curriculum
- ^ American College of Radiology, "Five Things Physicians and Patients Should Question" (PDF), Choosing Wisely: an initiative of the ABIM Foundation, American College of Radiology, retrieved August 17, 2012
- ^ Template:Cite PMID
- ^ Template:Cite PMID
- ^ Terasawa T, Blackmore CC, Bent S, Kohlwes RJ (October 2004). "Systematic review: computed tomography and ultrasonography to detect acute appendicitis in adults and adolescents". Annals of Internal Medicine. 141 (7): 537–46. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-141-7-200410050-00011. PMID 15466771.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Rao PM, Rhea JT, Rao JA, Conn AK (July 1999). "Plain abdominal radiography in clinically suspected appendicitis: diagnostic yield, resource use, and comparison with CT". The American Journal of Emergency Medicine. 17 (4): 325–8. doi:10.1016/S0735-6757(99)90077-3. PMID 10452424.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Boleslawski E, Panis Y, Benoist S, Denet C, Mariani P, Valleur P (March 1999). "Plain abdominal radiography as a routine procedure for acute abdominal pain of the right lower quadrant: prospective evaluation". World Journal of Surgery. 23 (3): 262–4. doi:10.1007/pl00013181. PMID 9933697.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b APPENDICITIS from Townsend: Sabiston Textbook of Surgery on MD Consult
- ^ "BestBets: The Alvarado Scoring System is an accurate diagnostic tool for appendicitis".
- ^ Fink AS, Kosakowski CA, Hiatt JR, Cochran AJ (June 1990). "Periappendicitis is a significant clinical finding". American Journal of Surgery. 159 (6): 564–8. doi:10.1016/S0002-9610(06)80067-X. PMID 2349982.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Cunha BA, Pherez FM, Durie N (July 2010). "Swine influenza (H1N1) and acute appendicitis". Heart Lung. 39 (6): 544–6. doi:10.1016/j.hrtlng.2010.04.004. PMID 20633930.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Zheng H, Sun Y, Lin S, Mao Z, Jiang B (August 2008). "Yersinia enterocolitica infection in diarrheal patients". Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 27 (8): 741–52. doi:10.1007/s10096-008-0562-y. ISBN 0-9600805-6-2. PMID 18575909.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Anderson, M; Collins, E (November 2008). "Analgesia for children with acute abdominal pain and diagnostic accuracy". Archives of Disease in Childhood. 93 (11): 995–7. doi:10.1136/adc.2008.137174. PMID 18305071.
- ^ Sauerland, S; Jaschinski, T; Neugebauer, EA (Oct 6, 2010). "Laparoscopic versus open surgery for suspected appendicitis". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (10): CD001546. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001546.pub3. PMID 20927725.
- ^ Appendicitis procedures explained National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse. Retrieved on 2010-02-01
- ^ Laparotomy abdominal surgery About surgeries online portal. Retrieved on 2010-02-01
- ^ 28
- ^ Appendicitis surgery procedures Encyclopedia of surgery Portal. Retrieved on 2010-02-01
- ^ "'Emergency' appendix surgery can wait: MDs". CBC News. 2010-09-21.
- ^ Appendicitis surgery, removal and recovery Retrieved on 2010-02-01
- ^ Liang MK, Lo HG, Marks JL (2006). "Stump appendicitis: a comprehensive review of literature". The American surgeon. 72 (2): 162–6. PMID 16536249.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "WHO Disease and injury country estimates". World Health Organization. 2009. Archived from the original on 11 November 2009. Retrieved Nov 11, 2009.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Ellis, H (March 2012). "Acute appendicitis". British journal of hospital medicine (London, England : 2005). 73 (3): C46-8. PMID 22411604.
- ^ Appendicitis epidemiological data VoxHealth medical information based on CDC medical records. Retrieved on 12-24-2012.
- ^ Wier LM, Hao Y, Owens P, Washington R. Overview of Children in the Emergency Department, 2010. HCUP Statistical Brief #157. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, Rockville, MD. May 2013. [2]
- ^ Lozano R, Naghavi M, Foreman K; et al. (December 2012). "Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010". Lancet. 380 (9859): 2095–128. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61728-0. PMID 23245604.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
External links
- CT of the abdomen showing acute appendicitis
- Anatomy of Appendix and Appendicits | Medchrome
- Podcast on the management of appendicitis
- Appendicitis and Appendectomy author Dennis Lee, M.D. editor Jay Marks, M.D. - MedicineNet.com, Doctor Produced information plus Patient Discussions provided by MedicineNet.com
- Appendicitis - MayoClinic.com, from the Web site of the Mayo Clinic
- Appendicitis, history, diagnosis and treatment by Surgeons Net Education
- Appendicitis Research Latest research from the literature on appendicitis
- Acute and Suppurative Appendicitis from the Spring 1998 issue of The Permanente Medical Journal
- Appendicitis Update Complete information including laparoscopic appendectomy
- History of Appendicitis Vermiformis: Its diseases and treatment. By Arthur C. McCarty, M.D.
- How to Recognize the Symptoms of Appendicitis, a how-to article from wikiHow
- Appendicitis: Acute Abdomen and Surgical Gastroenterology from the Merck Manual Professional (Content last modified September 2007)
- Abdominal Emergencies, 'Surgical Abdomen'.By DR David Bednarczyk; Pediatric Surgery
