Adrenocortical adenoma: Difference between revisions
m Grammar and links |
MehrAzin Z. (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Infobox medical condition (new) |
{{Infobox medical condition (new) |
||
| name = Adrenocortical |
| name = Adrenocortical Adenoma |
||
| image = Adrenal gland Conn syndrome4.jpg |
| image = Adrenal gland Conn syndrome4.jpg |
||
| caption = Adrenal adenoma in a patient with [[Conn syndrome]] |
| caption = Adrenal adenoma in a patient with [[Conn syndrome]] |
||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
| deaths = |
| deaths = |
||
|alt=}} |
|alt=}} |
||
An '''adrenocortical adenoma''' is a [[benign]] [[tumor]] of the [[adrenal cortex]]. It can present with [[Cushing's syndrome]] or [[primary aldosteronism]].<ref name="urlDefinition: adrenocortical adenoma from Online Medical Dictionary">{{cite web |url=http://cancerweb.ncl.ac.uk/cgi-bin/omd?adrenocortical+adenoma |title=Definition: adrenocortical adenoma from Online Medical Dictionary |format= |work= |accessdate=}}</ref> They may also secrete [[androgen]]s, causing [[hyperandrogenism]]. Also, they are often diagnosed incidentally as [[incidentaloma]]s. |
|||
'''Adrenocortical Adenoma''' [[ACA]] is commonly described as a [[benign]] [[neoplasm]] emerging from the cells that comprise the [[adrenal cortex]]. Like most [[adenomas]], the [[ACA]] is considered a [[benign tumor]] since the majority of them are non-functioning and [[asymptomatic]]. Adrenocortical Adenomas are classified as [[ACTH]]-independent disorders, and are commonly associated with conditions linked to [[Hyperadrenalism]] such as [[Cushing's syndrome]] ([[Hypercortisolism]]) or [[Conn's Syndrome]] ([[Hyperaldosteronism]]), which is also known as [[primary aldosteronism]]. <ref name="urlDefinition: adrenocortical adenoma from Online Medical Dictionary">{{cite web |url=http://cancerweb.ncl.ac.uk/cgi-bin/omd?adrenocortical+adenoma |title=Definition: adrenocortical adenoma from Online Medical Dictionary |format= |work= |accessdate=}}</ref> In addition, recent case reports further support the affiliation of adrenocortical adenomas with [[hyperandrogenism]] or [[Florid hyperandrogenism]] which can cause Hyperandrogenic [[Hirsutism]] in females. <ref>{{cite web |last1=LaVoie |first1=Melanie |last2=Constantinides |first2=Vasilis |last3=Robin |first3=Noel |last4=Kyriacou |first4=Angelos |title=Florid hyperandrogenism due to a benign adrenocortical adenoma |url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30061126 |website=BMJ case reports |doi=10.1136/bcr-2018-224804 |date=30 July 2018}}</ref> |
|||
It is a well circumscribed, yellow tumour in the adrenal cortex, which is usually 2–5 cm in diameter. The color of the tumour, as with adrenal cortex as a whole, is due to the stored [[lipid]] (mainly [[cholesterol]]), from which the cortical hormones are synthesized. These tumors are frequent incidental findings at post mortem examination and appear to have produced no significant metabolic disorder; only a very small percentage lead to Cushing's syndrome. Nevertheless, these apparently non-functioning adenomas are most often encountered in elder obese people. There is some debate that they may really represent nodules in diffuse nodular cortical hyperplasia. Very occasionally, a true adrenal cortical adenoma is associated with the clinical manifestations of Conn's syndrome, and can be shown to be excreting mineralocorticoids. |
|||
==Cause== |
|||
{{Infobox medical condition (new) |
|||
| name = Adrenal Glands Zonations |
|||
| image = Antinksčio sandara.png |
|||
| caption = |
|||
| |
|||
| pronounce = |
|||
| field = |
|||
| synonyms = |
|||
| symptoms = |
|||
| complications = |
|||
| onset = |
|||
| duration = |
|||
| types = |
|||
| causes = |
|||
| risks = |
|||
| diagnosis = |
|||
| differential = |
|||
| prevention = |
|||
| treatment = |
|||
| medication = |
|||
| prognosis = |
|||
| frequency = |
|||
| deaths = |
|||
|alt=}} |
|||
{{Infobox medical condition (new) |
|||
| name = Adrenal Glands Zonations |
|||
| image = 1818 The Adrenal Glands.jpg |
|||
| caption = |
|||
| |
|||
| pronounce = |
|||
| field = |
|||
| synonyms = |
|||
| symptoms = |
|||
| complications = |
|||
| onset = |
|||
| duration = |
|||
| types = |
|||
| causes = |
|||
| risks = |
|||
| diagnosis = |
|||
| differential = |
|||
| prevention = |
|||
| treatment = |
|||
| medication = |
|||
| prognosis = |
|||
| frequency = |
|||
| deaths = |
|||
|alt=}} |
|||
Study of the reported cases indicate that most adrenocortical adenomas occur due to neoplastic proliferation of adrenal cortical cells within the three distinct layers of adrenal cortex. In humans, the adrenal cortex comprises three concentric zones including the [[zona Glomerulosa]] (zG), [[zona Fasciculata]] (zF), and [[zona Reticularis]] (zR) that under normal conditions respond to body's physiological demands for steroid hormones. The adrenal cortex is considered a dynamic organ in which senescent cells are replaced by newly differentiated cells.This constant renewal facilitates organ remodeling which contributes to dynamic characteristics of the adrenal cortex. |
|||
<ref>{{cite web |last1=Pihlajoki |first1=Marjut |last2=Dörner |first2=Julia |last3=Cochran |first3=Rebecca S. |last4=Heikinheimo |first4=Markku |last5=Wilson |first5=David B. |title=Adrenocortical Zonation, Renewal, and Remodeling |url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4350438/ |website=Frontiers in Endocrinology |doi=10.3389/fendo.2015.00027 |date=5 March 2015}}</ref> correspondingly, the developmental physiology of the adrenal cortex is believed to play a pivotal role in formation of the adrenocortical tumors. Hence, the molecular mechanisms involved in normal development of the adrenal glands are like double edged swords that can lead to the formation of tumors within the adrenal cortex. Moreover, recent studies suggest that mutations affecting the molecular pathways of the adrenocortical region can stimulate abnormal proliferation and tumor formation. Through these studies, the [[cyclic AMP]]-dependent [[protein kinase]] A (PKA) signaling has been identified as a key mediator of cortisol secretion, and the mutations associated with the dysregulation of cAMP/ PKA pathways have been implicated in the adrenocortical pathophysiology.<ref>{{cite web |last1=Lodish |first1=Maya |title=Genetics of Adrenocortical Development and Tumors |url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5424622/ |website=Endocrinology and metabolism clinics of North America |pages=419–433 |doi=10.1016/j.ecl.2017.01.007 |date=NaN}}</ref> |
|||
==Clinical Features== |
|||
{{Infobox medical condition (new) |
|||
| name = Hypercortisolism |
|||
| image = Hypercortisolism.png |
|||
| caption = |
|||
| |
|||
| pronounce = |
|||
| field = |
|||
| synonyms = |
|||
| symptoms = Adrenal Lesion |
|||
| complications = |
|||
| onset = |
|||
| duration = |
|||
| types = |
|||
| causes = |
|||
| risks = |
|||
| diagnosis = |
|||
| differential = |
|||
| prevention = |
|||
| treatment = |
|||
| medication = |
|||
| prognosis = |
|||
| frequency = |
|||
| deaths = |
|||
|alt=}} |
|||
Adrenal Adenomas are often categorized as endocrine-inactive tumors considering that majority of them are non-functioning and [[asymptomatic]]. Functional Adrenocortical Adenomas demonstrate symptoms consistent with mixed endocrine syndromes. In most reported cases of Adrenocortical Adenoma (ACA), patients have presented with one or multiple endocrine syndromes such as [[Hyperaldosteronism]]/[[Conn's Syndrome]]<ref>{{cite web |last1=Wang |first1=Wei |last2=Wei |first2=Feng |last3=Li |first3=RanHao |last4=Tian |first4=JiaHui |title=A case report of idiopathic hyperaldosteronism characterized by bilateral adrenal adenoma |url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31651844 |website=Medicine |pages=e17418 |doi=10.1097/MD.0000000000017418 |date=October 2019}}</ref>, [[Hypercortisolism]]/[[Cushing's syndrome]]<ref>{{cite web |last1=Ren |first1=Kaiyun |last2=Wei |first2=Jia |last3=Liu |first3=Qilin |last4=Zhu |first4=Yuchun |last5=Wu |first5=Nianwei |last6=Tang |first6=Ying |last7=Li |first7=Qianrui |last8=Zhang |first8=Qianying |last9=Yu |first9=Yerong |last10=An |first10=Zhenmei |last11=Chen |first11=Jing |last12=Li |first12=Jianwei |title=Hypercortisolism and primary aldosteronism caused by bilateral adrenocortical adenomas: a case report |url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6580498/ |website=BMC Endocrine Disorders |doi=10.1186/s12902-019-0395-y |date=17 June 2019}}</ref>, [[Hyperandrogenism]]/[[Feminization]]<ref>{{cite web |last1=LaVoie |first1=Melanie |last2=Constantinides |first2=Vasilis |last3=Robin |first3=Noel |last4=Kyriacou |first4=Angelos |title=Florid hyperandrogenism due to a benign adrenocortical adenoma |url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30061126?log$=activity |website=BMJ case reports |doi=10.1136/bcr-2018-224804 |date=30 July 2018}}</ref>, [[Virilization]]<ref>{{cite web |last1=Kobayashi |first1=Toshihiro |last2=Imachi |first2=Hitomi |last3=Sato |first3=Seisuke |last4=Ibata |first4=Tomohiro |last5=Fukunaga |first5=Kensaku |last6=Yoshimoto |first6=Takuo |last7=Kikuchi |first7=Fumi |last8=Yonezaki |first8=Kazuko |last9=Yamaji |first9=Nao |last10=Lyu |first10=Jingya |last11=Dong |first11=Tao |last12=Nagata |first12=Hiromi |last13=Kadota |first13=Kyuichi |last14=Kushida |first14=Yoshio |last15=Haba |first15=Reiji |last16=Murao |first16=Koji |title=Bilateral Adrenocortical Adenomas along with Virilization and Cushing's Syndrome |url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6395137/ |website=Internal Medicine |pages=405–409 |doi=10.2169/internalmedicine.0790-18 |date=1 February 2019}}</ref>, or [[Hirsutism]]<ref>{{cite web |last1=Rodríguez-Gutiérrez |first1=René |last2=Bautista-Medina |first2=Mario Arturo |last3=Teniente-Sanchez |first3=Ana Eugenia |last4=Zapata-Rivera |first4=Maria Azucena |last5=Montes-Villarreal |first5=Juan |title=Pure Androgen-Secreting Adrenal Adenoma Associated with Resistant Hypertension |url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3681270/ |website=Case Reports in Endocrinology |doi=10.1155/2013/356086 |date=2013}}</ref>. Some of the common symptoms associated with adrenocortical adenomas include: |
|||
'''Musculoskeletal''' |
|||
* [[Osteopenia]] |
|||
* [[Muscle weakness]]/ [[Muscle Atrophy]] |
|||
'''Cardiovascular''' |
|||
* [[Hypertension]] |
|||
'''Endocrine and Metabolic''' |
|||
* [[Obesity]] |
|||
→More prevalent Males |
|||
* [[virilization]] |
|||
→More prevalent in Females |
|||
* [[Hyperandrogenism]] |
|||
* Irregular [[menstrual cycles]] |
|||
'''Neuropsychological''' |
|||
* [[Sleep disorders]] |
|||
* [[Depression]] |
|||
'''Skin''' |
|||
* Easy bruising |
|||
* [[Stretch marks]] |
|||
* [[Hirsutism]] |
|||
* [[Acne]] |
|||
==Pathophysiology== |
|||
[[File:Adrenal Cortex Pathology.png|thumb]] |
|||
If functional, Adrenocortical Adenomas can affect the normal activities of the adrenal cortex. Located within the adrenal glands the three zones that are responsible for secretion of the three major classes of adrenal steroids. Hence, functional, adrenocortical adenomas can induce over secretion of adrenal steroids associated with pure or mixed endocrine syndromes, a condition commonly known as [[hyperadrenalism]]. |
|||
==Diagnosis== |
|||
Due to their asymptomatic nature, most reported cases of Adrenal Adenomas have been discerned fortuitously through [[autopsy]], or during medical imaging, particularly [[CT scan]] ([[Computed Tomography]]) and [[MRI]]. Hence, they have earned the title '''Incidentaloma''' referring to small adenoma discovered incidentally.<ref>{{cite web |last1=Lloyd |first1=Ricardo V. |title=Adrenal cortical tumors, pheochromocytomas and paragangliomas |url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21455202 |website=Modern Pathology: An Official Journal of the United States and Canadian Academy of Pathology, Inc |pages=S58–65 |doi=10.1038/modpathol.2010.126 |date=April 2011}}</ref> Though Adrenocortical Adenomas are considered challenging to differentiate from the normal adrenal cortex, they appear as well-circumscribed lesions once isolated. |
|||
'''Imaging Diagnostics''' |
|||
* [[Computed Tomography]] ([[CT scan]]) |
|||
* [[Magnetic Resonance Imaging]] ([[MRI]]) |
|||
<gallery> |
|||
Adrenal adenoma2 T1FS.jpg |
|||
</gallery> |
|||
'''Laboratory Tests''' |
|||
* [[CRH]] Stimulation Test |
|||
* High-dose-dexamethasone suppression test |
|||
==Gross Description== |
|||
* Well-circumscribed lesion |
|||
* Size ≤ 5 cm |
|||
* Weight ≤ 50 grams |
|||
* often appear as golden-yellow color mass |
|||
(may have focal dark regions corresponding to [[hemorrhage]], lipid-depletion, and increased [[lipofuscin]])<ref>{{cite web |last1=Lloyd |first1=Ricardo V. |title=Adrenal cortical tumors, pheochromocytomas and paragangliomas |url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21455202 |website=Modern Pathology: An Official Journal of the United States and Canadian Academy of Pathology, Inc |pages=S58–65 |doi=10.1038/modpathol.2010.126 |date=April 2011}}</ref> |
|||
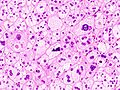
==Histopathology== |
|||
The microscopic [[histopathology]] analysis of the tissue samples obtained from the adrenal cortex of individuals presenting with adenoma-associated symptoms such as primary aldestronism (PA) indicates that adenoma cells are relatively larger with different cytoplasm, and increased variation in nuclear size. This indication is based on comparison between the healthy (normal) and affected (adenoma-associated) adrenal cortex tissue samples. |
|||
==Histopathology images== |
|||
<gallery> |
<gallery> |
||
Primary aldosteronism (1) adrenocortical adenoma.jpg |
Primary aldosteronism (1) adrenocortical adenoma.jpg |
||
| Line 33: | Line 182: | ||
Image:Primary aldosteronism (3) adrenocortical adenoma.jpg |
Image:Primary aldosteronism (3) adrenocortical adenoma.jpg |
||
</gallery> |
</gallery> |
||
==Treatment== |
|||
* Non-functioning cases of adrenocortical adenoma (ACA) can be managed through long-term followups and monitoring |
|||
* The treatment approach for the functioning cases of adrenocortical adenoma (ACA) depends on the type of disorders induced by ACA and their advancement. Surgical Excision of the ACA may be required if its presence is resulting in atrophy of the adrenal glands and the surrounding tissues. |
|||
In order to acquire better treatment strategies, it is important to further examine, study and discern the distinct molecular mechanisms involved in the formation of [[endogenous]] Adrenal Adenomas, [[hyperplasia]]s, and ACTH-independent Cushing's Syndrome to improve the available diagnostic and prognostic markers that can assist clinicians in the management and advance-treatment of such conditions.<ref>{{cite web |last1=Bourdeau |first1=Isabelle |last2=Lampron |first2=Antoine |last3=Costa |first3=Marcia Helena Soares |last4=Tadjine |first4=Mimi |last5=Lacroix |first5=André |title=Adrenocorticotropic hormone-independent Cushing's syndrome |url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17940443 |website=Current Opinion in Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Obesity |pages=219–225 |doi=10.1097/MED.0b013e32814db842 |date=June 2007}}</ref> |
|||
==Prognosis== |
|||
* The long-term outlook for individuals diagnosed with non-functional adrenocortical adenoma (ACA) is usually excellent. |
|||
* The long-term outlook for individuals diagnosed with functional adrenocortical adenoma (ACA) is good with early diagnosis and treatment. |
|||
==Epidemiology== |
|||
* Prevalence: Female > Male |
|||
* More common in adults |
|||
* Relatively earlier onset in Females (ages ≤ 20) than Males (ages ≤ 30) |
|||
* Most common cause of [[ACTH]]-independent [[Cushing's syndrome]] |
|||
==Notable Cases== |
|||
Female (Age:4) presented with [[Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome]] characterized by right adrenocortical adenoma. <ref>{{cite web |last1=Elnaw |first1=Eman Abdalla Ali |last2=Abdalla |first2=Awad Rhmattalla |last3=Abdullah |first3=Mohamed Ahmed |title=Adrenocortical adenoma in a Sudanese girl with Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome |url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31768183 |website=International Journal of Pediatric Endocrinology |pages=6 |doi=10.1186/s13633-019-0068-7 |date=2019}}</ref> |
|||
Female (Age:18) presented with Pure Androgen-Secreting Adrenal Adenoma Associated with Resistant [[Hypertension]].<ref>{{cite web |last1=Rodríguez-Gutiérrez |first1=René |last2=Bautista-Medina |first2=Mario Arturo |last3=Teniente-Sanchez |first3=Ana Eugenia |last4=Zapata-Rivera |first4=Maria Azucena |last5=Montes-Villarreal |first5=Juan |title=Pure Androgen-Secreting Adrenal Adenoma Associated with Resistant Hypertension |url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3681270/ |website=Case Reports in Endocrinology |doi=10.1155/2013/356086 |date=2013}}</ref> |
|||
Female (Age:26) presented with Florid [[hyperandrogenism]] due to a benign Adrenocortical Adenoma (ACA). <ref>{{cite web |last1=LaVoie |first1=Melanie |last2=Constantinides |first2=Vasilis |last3=Robin |first3=Noel |last4=Kyriacou |first4=Angelos |title=Florid hyperandrogenism due to a benign adrenocortical adenoma |url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30061126?log$=activity |website=BMJ case reports |doi=10.1136/bcr-2018-224804 |date=30 July 2018}}</ref> |
|||
Female (Age:27) presented with [[Virilization]] and [[Cushing's Syndrome]] associated with Bilateral Adrenocortical Adenomas.<ref>{{cite web |last1=Kobayashi |first1=Toshihiro |last2=Imachi |first2=Hitomi |last3=Sato |first3=Seisuke |last4=Ibata |first4=Tomohiro |last5=Fukunaga |first5=Kensaku |last6=Yoshimoto |first6=Takuo |last7=Kikuchi |first7=Fumi |last8=Yonezaki |first8=Kazuko |last9=Yamaji |first9=Nao |last10=Lyu |first10=Jingya |last11=Dong |first11=Tao |last12=Nagata |first12=Hiromi |last13=Kadota |first13=Kyuichi |last14=Kushida |first14=Yoshio |last15=Haba |first15=Reiji |last16=Murao |first16=Koji |title=Bilateral Adrenocortical Adenomas along with Virilization and Cushing's Syndrome |url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6395137/ |website=Internal Medicine |pages=405–409 |doi=10.2169/internalmedicine.0790-18 |date=1 February 2019}}</ref> |
|||
Female (Age:46) presented with [[idiopathic]] [[hyperaldosteronism]] characterized by [[bilateral]] [[adrenal adenoma]] <ref>{{cite web |last1=Wang |first1=Wei |last2=Wei |first2=Feng |last3=Li |first3=RanHao |last4=Tian |first4=JiaHui |title=A case report of idiopathic hyperaldosteronism characterized by bilateral adrenal adenoma |url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31651844 |website=Medicine |pages=e17418 |doi=10.1097/MD.0000000000017418 |date=October 2019}}</ref> |
|||
Male (Age:30) presented with co-existing [[Cushing’s syndrome]] and [[primary aldosteronism]] caused by [[bilateral]] adrenocortical adenomas.<ref>{{cite web |last1=Ren |first1=Kaiyun |last2=Wei |first2=Jia |last3=Liu |first3=Qilin |last4=Zhu |first4=Yuchun |last5=Wu |first5=Nianwei |last6=Tang |first6=Ying |last7=Li |first7=Qianrui |last8=Zhang |first8=Qianying |last9=Yu |first9=Yerong |last10=An |first10=Zhenmei |last11=Chen |first11=Jing |last12=Li |first12=Jianwei |title=Hypercortisolism and primary aldosteronism caused by bilateral adrenocortical adenomas: a case report |url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6580498/ |website=BMC Endocrine Disorders |doi=10.1186/s12902-019-0395-y |date=17 June 2019}}</ref> |
|||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
* [[Hyperplasia]] |
|||
* [[Adrenal tumor]] |
* [[Adrenal tumor]] |
||
* [[Cushing's syndrome]] |
|||
* [[Conn's syndrome]] |
|||
* [[Hypercortisolism]] |
|||
* [[Hyperaldosteronism]] |
|||
* [[Hyperandrogenism]] |
|||
* [[Adrenal gland]] |
|||
* Adrenal [[paraganglioma]] |
|||
* Adrenal [[Pheochromocytoma]] |
|||
* Adrenal [[ganglioneuroma]] |
|||
* [[Primary Cushing's syndrome]] |
|||
* [[Endogenous Cushing's syndrome]] |
|||
==References== |
==References== |
||
{{reflist}} |
{{reflist}} |
||
== External links == |
== External links == |
||
{{Medical resources |
{{Medical resources |
||
| Line 54: | Line 250: | ||
{{Endocrine gland neoplasia}} |
{{Endocrine gland neoplasia}} |
||
[[Category:Endocrine neoplasia]] |
[[:Category:Endocrine neoplasia]] |
||
[[Category:Adrenal gland disorders]] |
[[:Category:Adrenal gland disorders]] |
||
Revision as of 06:38, 14 December 2019
| Adrenocortical Adenoma | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Adrenal cortical adenoma, adrenal adenoma |
 | |
| Adrenal adenoma in a patient with Conn syndrome | |
| Specialty | Endocrinology, oncology |
Adrenocortical Adenoma ACA is commonly described as a benign neoplasm emerging from the cells that comprise the adrenal cortex. Like most adenomas, the ACA is considered a benign tumor since the majority of them are non-functioning and asymptomatic. Adrenocortical Adenomas are classified as ACTH-independent disorders, and are commonly associated with conditions linked to Hyperadrenalism such as Cushing's syndrome (Hypercortisolism) or Conn's Syndrome (Hyperaldosteronism), which is also known as primary aldosteronism. [1] In addition, recent case reports further support the affiliation of adrenocortical adenomas with hyperandrogenism or Florid hyperandrogenism which can cause Hyperandrogenic Hirsutism in females. [2]
Cause
| Adrenal Glands Zonations | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Specialty | Endocrinology, oncology |
| Adrenal Glands Zonations | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Specialty | Endocrinology, oncology |
Study of the reported cases indicate that most adrenocortical adenomas occur due to neoplastic proliferation of adrenal cortical cells within the three distinct layers of adrenal cortex. In humans, the adrenal cortex comprises three concentric zones including the zona Glomerulosa (zG), zona Fasciculata (zF), and zona Reticularis (zR) that under normal conditions respond to body's physiological demands for steroid hormones. The adrenal cortex is considered a dynamic organ in which senescent cells are replaced by newly differentiated cells.This constant renewal facilitates organ remodeling which contributes to dynamic characteristics of the adrenal cortex. [3] correspondingly, the developmental physiology of the adrenal cortex is believed to play a pivotal role in formation of the adrenocortical tumors. Hence, the molecular mechanisms involved in normal development of the adrenal glands are like double edged swords that can lead to the formation of tumors within the adrenal cortex. Moreover, recent studies suggest that mutations affecting the molecular pathways of the adrenocortical region can stimulate abnormal proliferation and tumor formation. Through these studies, the cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase A (PKA) signaling has been identified as a key mediator of cortisol secretion, and the mutations associated with the dysregulation of cAMP/ PKA pathways have been implicated in the adrenocortical pathophysiology.[4]
Clinical Features
| Hypercortisolism | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Specialty | Endocrinology, oncology |
| Symptoms | Adrenal Lesion |
Adrenal Adenomas are often categorized as endocrine-inactive tumors considering that majority of them are non-functioning and asymptomatic. Functional Adrenocortical Adenomas demonstrate symptoms consistent with mixed endocrine syndromes. In most reported cases of Adrenocortical Adenoma (ACA), patients have presented with one or multiple endocrine syndromes such as Hyperaldosteronism/Conn's Syndrome[5], Hypercortisolism/Cushing's syndrome[6], Hyperandrogenism/Feminization[7], Virilization[8], or Hirsutism[9]. Some of the common symptoms associated with adrenocortical adenomas include:
Musculoskeletal
Cardiovascular
Endocrine and Metabolic
→More prevalent Males
→More prevalent in Females
- Hyperandrogenism
- Irregular menstrual cycles
Neuropsychological
Skin
- Easy bruising
- Stretch marks
- Hirsutism
- Acne
Pathophysiology

If functional, Adrenocortical Adenomas can affect the normal activities of the adrenal cortex. Located within the adrenal glands the three zones that are responsible for secretion of the three major classes of adrenal steroids. Hence, functional, adrenocortical adenomas can induce over secretion of adrenal steroids associated with pure or mixed endocrine syndromes, a condition commonly known as hyperadrenalism.
Diagnosis
Due to their asymptomatic nature, most reported cases of Adrenal Adenomas have been discerned fortuitously through autopsy, or during medical imaging, particularly CT scan (Computed Tomography) and MRI. Hence, they have earned the title Incidentaloma referring to small adenoma discovered incidentally.[10] Though Adrenocortical Adenomas are considered challenging to differentiate from the normal adrenal cortex, they appear as well-circumscribed lesions once isolated.
Imaging Diagnostics
Laboratory Tests
- CRH Stimulation Test
- High-dose-dexamethasone suppression test
Gross Description
- Well-circumscribed lesion
- Size ≤ 5 cm
- Weight ≤ 50 grams
- often appear as golden-yellow color mass
(may have focal dark regions corresponding to hemorrhage, lipid-depletion, and increased lipofuscin)[11]
Histopathology
The microscopic histopathology analysis of the tissue samples obtained from the adrenal cortex of individuals presenting with adenoma-associated symptoms such as primary aldestronism (PA) indicates that adenoma cells are relatively larger with different cytoplasm, and increased variation in nuclear size. This indication is based on comparison between the healthy (normal) and affected (adenoma-associated) adrenal cortex tissue samples.
Treatment
- Non-functioning cases of adrenocortical adenoma (ACA) can be managed through long-term followups and monitoring
- The treatment approach for the functioning cases of adrenocortical adenoma (ACA) depends on the type of disorders induced by ACA and their advancement. Surgical Excision of the ACA may be required if its presence is resulting in atrophy of the adrenal glands and the surrounding tissues.
In order to acquire better treatment strategies, it is important to further examine, study and discern the distinct molecular mechanisms involved in the formation of endogenous Adrenal Adenomas, hyperplasias, and ACTH-independent Cushing's Syndrome to improve the available diagnostic and prognostic markers that can assist clinicians in the management and advance-treatment of such conditions.[12]
Prognosis
- The long-term outlook for individuals diagnosed with non-functional adrenocortical adenoma (ACA) is usually excellent.
- The long-term outlook for individuals diagnosed with functional adrenocortical adenoma (ACA) is good with early diagnosis and treatment.
Epidemiology
- Prevalence: Female > Male
- More common in adults
- Relatively earlier onset in Females (ages ≤ 20) than Males (ages ≤ 30)
- Most common cause of ACTH-independent Cushing's syndrome
Notable Cases
Female (Age:4) presented with Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome characterized by right adrenocortical adenoma. [13]
Female (Age:18) presented with Pure Androgen-Secreting Adrenal Adenoma Associated with Resistant Hypertension.[14]
Female (Age:26) presented with Florid hyperandrogenism due to a benign Adrenocortical Adenoma (ACA). [15]
Female (Age:27) presented with Virilization and Cushing's Syndrome associated with Bilateral Adrenocortical Adenomas.[16]
Female (Age:46) presented with idiopathic hyperaldosteronism characterized by bilateral adrenal adenoma [17]
Male (Age:30) presented with co-existing Cushing’s syndrome and primary aldosteronism caused by bilateral adrenocortical adenomas.[18]
See also
- Hyperplasia
- Adrenal tumor
- Cushing's syndrome
- Conn's syndrome
- Hypercortisolism
- Hyperaldosteronism
- Hyperandrogenism
- Adrenal gland
- Adrenal paraganglioma
- Adrenal Pheochromocytoma
- Adrenal ganglioneuroma
- Primary Cushing's syndrome
- Endogenous Cushing's syndrome
References
- ^ "Definition: adrenocortical adenoma from Online Medical Dictionary".
- ^ LaVoie, Melanie; Constantinides, Vasilis; Robin, Noel; Kyriacou, Angelos (30 July 2018). "Florid hyperandrogenism due to a benign adrenocortical adenoma". BMJ case reports. doi:10.1136/bcr-2018-224804.
- ^ Pihlajoki, Marjut; Dörner, Julia; Cochran, Rebecca S.; Heikinheimo, Markku; Wilson, David B. (5 March 2015). "Adrenocortical Zonation, Renewal, and Remodeling". Frontiers in Endocrinology. doi:10.3389/fendo.2015.00027.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Lodish, Maya (NaN). "Genetics of Adrenocortical Development and Tumors". Endocrinology and metabolism clinics of North America. pp. 419–433. doi:10.1016/j.ecl.2017.01.007.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Wang, Wei; Wei, Feng; Li, RanHao; Tian, JiaHui (October 2019). "A case report of idiopathic hyperaldosteronism characterized by bilateral adrenal adenoma". Medicine. pp. e17418. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000017418.
- ^ Ren, Kaiyun; Wei, Jia; Liu, Qilin; Zhu, Yuchun; Wu, Nianwei; Tang, Ying; Li, Qianrui; Zhang, Qianying; Yu, Yerong; An, Zhenmei; Chen, Jing; Li, Jianwei (17 June 2019). "Hypercortisolism and primary aldosteronism caused by bilateral adrenocortical adenomas: a case report". BMC Endocrine Disorders. doi:10.1186/s12902-019-0395-y.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ LaVoie, Melanie; Constantinides, Vasilis; Robin, Noel; Kyriacou, Angelos (30 July 2018). "Florid hyperandrogenism due to a benign adrenocortical adenoma". BMJ case reports. doi:10.1136/bcr-2018-224804.
- ^ Kobayashi, Toshihiro; Imachi, Hitomi; Sato, Seisuke; Ibata, Tomohiro; Fukunaga, Kensaku; Yoshimoto, Takuo; Kikuchi, Fumi; Yonezaki, Kazuko; Yamaji, Nao; Lyu, Jingya; Dong, Tao; Nagata, Hiromi; Kadota, Kyuichi; Kushida, Yoshio; Haba, Reiji; Murao, Koji (1 February 2019). "Bilateral Adrenocortical Adenomas along with Virilization and Cushing's Syndrome". Internal Medicine. pp. 405–409. doi:10.2169/internalmedicine.0790-18.
- ^ Rodríguez-Gutiérrez, René; Bautista-Medina, Mario Arturo; Teniente-Sanchez, Ana Eugenia; Zapata-Rivera, Maria Azucena; Montes-Villarreal, Juan (2013). "Pure Androgen-Secreting Adrenal Adenoma Associated with Resistant Hypertension". Case Reports in Endocrinology. doi:10.1155/2013/356086.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Lloyd, Ricardo V. (April 2011). "Adrenal cortical tumors, pheochromocytomas and paragangliomas". Modern Pathology: An Official Journal of the United States and Canadian Academy of Pathology, Inc. pp. S58–65. doi:10.1038/modpathol.2010.126.
- ^ Lloyd, Ricardo V. (April 2011). "Adrenal cortical tumors, pheochromocytomas and paragangliomas". Modern Pathology: An Official Journal of the United States and Canadian Academy of Pathology, Inc. pp. S58–65. doi:10.1038/modpathol.2010.126.
- ^ Bourdeau, Isabelle; Lampron, Antoine; Costa, Marcia Helena Soares; Tadjine, Mimi; Lacroix, André (June 2007). "Adrenocorticotropic hormone-independent Cushing's syndrome". Current Opinion in Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Obesity. pp. 219–225. doi:10.1097/MED.0b013e32814db842.
- ^ Elnaw, Eman Abdalla Ali; Abdalla, Awad Rhmattalla; Abdullah, Mohamed Ahmed (2019). "Adrenocortical adenoma in a Sudanese girl with Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome". International Journal of Pediatric Endocrinology. p. 6. doi:10.1186/s13633-019-0068-7.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Rodríguez-Gutiérrez, René; Bautista-Medina, Mario Arturo; Teniente-Sanchez, Ana Eugenia; Zapata-Rivera, Maria Azucena; Montes-Villarreal, Juan (2013). "Pure Androgen-Secreting Adrenal Adenoma Associated with Resistant Hypertension". Case Reports in Endocrinology. doi:10.1155/2013/356086.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ LaVoie, Melanie; Constantinides, Vasilis; Robin, Noel; Kyriacou, Angelos (30 July 2018). "Florid hyperandrogenism due to a benign adrenocortical adenoma". BMJ case reports. doi:10.1136/bcr-2018-224804.
- ^ Kobayashi, Toshihiro; Imachi, Hitomi; Sato, Seisuke; Ibata, Tomohiro; Fukunaga, Kensaku; Yoshimoto, Takuo; Kikuchi, Fumi; Yonezaki, Kazuko; Yamaji, Nao; Lyu, Jingya; Dong, Tao; Nagata, Hiromi; Kadota, Kyuichi; Kushida, Yoshio; Haba, Reiji; Murao, Koji (1 February 2019). "Bilateral Adrenocortical Adenomas along with Virilization and Cushing's Syndrome". Internal Medicine. pp. 405–409. doi:10.2169/internalmedicine.0790-18.
- ^ Wang, Wei; Wei, Feng; Li, RanHao; Tian, JiaHui (October 2019). "A case report of idiopathic hyperaldosteronism characterized by bilateral adrenal adenoma". Medicine. pp. e17418. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000017418.
- ^ Ren, Kaiyun; Wei, Jia; Liu, Qilin; Zhu, Yuchun; Wu, Nianwei; Tang, Ying; Li, Qianrui; Zhang, Qianying; Yu, Yerong; An, Zhenmei; Chen, Jing; Li, Jianwei (17 June 2019). "Hypercortisolism and primary aldosteronism caused by bilateral adrenocortical adenomas: a case report". BMC Endocrine Disorders. doi:10.1186/s12902-019-0395-y.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link)
External links
Category:Endocrine neoplasia Category:Adrenal gland disorders