Jeanne de Clisson
Jeanne Louise de Belleville, de Clisson, Dame de Montaigu | |
|---|---|
 Dual Coat of Arms of the de Belleville and de Clisson Families with the motto:"Pour ce que il me plest" (For what pleases me) | |
| Born | 1300 Belleville-sur-Vie, France |
| Died | 1359 Hennebont, Brittany |
| Nationality | Born French, married Breton |
| Other names | Jeanne de Belleville |
| Spouse(s) | Geoffrey de Châteaubriant VIII Guy de Penthièvre Olivier IV de Clisson Sir Walter Bentley |
| Children | Geoffrey IX de Châteaubriant, Louise de Châteaubriant, Isabeau de Clisson, Maurice de Clisson, Olivier V de Clisson, Guillaume de Clisson and Jeanne de Clisson |
| Piratical career | |
| Nickname | Lioness of Brittany |
| Type | Privateer |
| Allegiance | First allegiance: Party of Blois: |
| Years active | c. 1343 – c. 1356 |
| Commands | Black Fleet; My Revenge |
Jeanne de Clisson (1300–1359), also known as Jeanne de Belleville and the Lioness of Brittany, was a French / Breton former noblewoman who became a privateer to avenge her husband after he was executed for treason by the French king. She crossed the English Channel targeting French ships and often slaughtering their crew. It was her practice to leave at least one sailor alive to carry her message to the King of France.
Early life
Jeanne Louise de Belleville, de Clisson, Dame de Montaigu, was born in 1300 in Belleville-sur-Vie in the Vendée, a daughter of nobleman Maurice IV Montaigu of Belleville and Palluau (1263–1304) and Létice de Parthenay of Parthenay (1276–?) in the Gâtine Vendéenne.
Her father died when she was four years old and there are no known records that her mother remarried. It also appears she was born from her father's second marriage as some records suggest he was previously married to Sibille of Chateaubriant. This alliance had apparently produced a son, Maurice V Montaigu. In 1337, on the death of her half-brother, Maurice V, she inherited the seigneury of Montagu and that of Belleville as he had no heirs.[1]
As a seigneur family in the Bas-Poitou area, the de Montaigu family would have had direct or indirect business with wine making, salt farming and the merchant movements of these goods to and from markets as far as the Iberian Peninsula up towards England. This would have included contacts with merchant shipping.[2]
First marriage
In 1312, Jeanne married her first husband, 19-year-old Geoffrey de Châteaubriant VIII (died 1326), a Breton nobleman, who himself was already a widower to Alix de Thouars. They had two children:
- Geoffrey IX (1314–1347), inherited his father's estates as Baron, died in the Battle of La Roche-Derrien
- Louise (1316–1383), married Guy XII de Laval and subsequently inherited her brother's estate as Baroness.[3][4]
Second marriage
In 1328, Jeanne married Guy de Penthièvre of the House of Penthièvre, widower of Joan of Avaugour and son of the Duke of Brittany. Jeanne may have done this to protect her underage children.
The union was short-lived, as relatives of the Ducal family—in particular, from the de Blois faction—laid a complaint with the bishops of Vannes and Rennes to protect their heritage, and an investigation was conducted on February 10, 1330, resulting in the marriage being annulled by Pope John XXII.[5]
Guy then married into the de Blois faction to Marie de Blois, who was also a niece of Phillip VI of France. Guy, however, unexpectedly died on 26 March 1331, and his heritage passed to his daughter Jeanne of Penthièvre.
Marriage to Olivier IV de Clisson
In 1330, Jeanne married Olivier IV de Clisson, a wealthy Breton, holding a castle at Clisson, a manor house in Nantes and lands at Blain. Olivier was initially married to Blanche de Bouville (died 1329).

Jeanne, a recent widow herself of the Lord of Chateaubriant, controlled areas in Poitou just south of the Breton border from Beauvoir-sur-Mer in the west to Châteaumur in the southeast of Clisson. Combining these assets made Jeanne and Olivier the seigneurial power (senior Lord of an area) in the border region of Brittany. Jeanne and Olivier eventually had five children:
- Isabeau, (1325–1343) born out of wedlock (5 years before the marriage to Olivier), she eventually married John I of Rieux and therefore was mother of Jean II de Rieux (died 1343)
- Maurice, (1333–1334, in Blain)
- Olivier V, (1336–1407), his father's successor, a future Constable of France, nicknamed "The Butcher"
- Guillaume, (1338–1345) died of exposure
- Jeanne, (1340–?) married Jean Harpedanne, Lord of Montendre IV's successor.

Breton War of Succession
During the Breton War of Succession, the de Clissons sided with the French choice for the empty Breton ducal crown, Charles de Blois, against the English preference, John de Montfort. The extended de Clisson family was not in full agreement in this matter, and Olivier IV's brother, Amaury de Clisson, embraced the de Montfort party. In January 1342, the de Clisson castle of Blain was chosen as headquarters by Robert Bertrand. The French King's Lieutenant sent to aid Charles de Blois.
In 1342, the English, after four attempts, captured the city of Vannes. Jeanne's husband Olivier and Hervé VII de Léon, the military commanders defending this city, were captured. Olivier was the only one released after an exchange for Ralph de Stafford, 1st Earl of Stafford (a prisoner of the French), and a surprisingly low sum was demanded. This led Olivier to be subsequently suspected of not having defended the city to his fullest and was alleged by Charles de Blois to be a traitor.
Tournament and trial
On 19 January 1343, the Truce of Malestroit was signed between England and France. Under the perceived safe conditions of this truce, Olivier and fifteen other Breton and Norman lords were invited to a tournament on French soil, where he was subsequently arrested, taken to Paris and tried by his peers.
Jeanne tried in vain to have him set free. She seems to have tried to bribe a King's sergeant.[6]
On the 2nd August 1343, Olivier IV was executed by beheading at Les Halles.
In the year of our Grace one thousand three hundred and forty-three, on Saturday, the second day of August, Olivier, Lord of Clisson, knight, prisoner in the Chatelet of Paris for several treasons and other crimes perpetrated by him against the king and the crown of France, and for alliances that he made with the king of England, enemy of the king and kingdom of France, as the said Olivier ... has confessed, was by judgement of the king given at Orleans drawn from the Chatelet of Paris to Les Halles ... and there on a scaffold had his head cut off. From there, his corpse was drawn to the gibbet of Paris and there hanged on the highest level, and his head was sent to Nantes in Brittany to be put on a lance over the Sauvetout gate as a warning to others.[7]
This execution shocked the nobility as the evidence of guilt was not publicly demonstrated, and the process of desecrating/exposing a body was reserved mainly for low-class criminals. This execution was judged harshly by Jean Froissart and his contemporaries.[8]
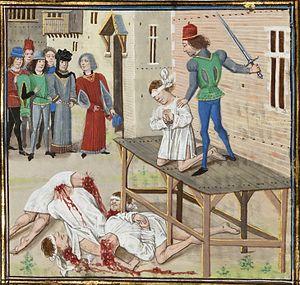
On 26 August 1343, for her attempted bribery of the king's sergeant, Jeanne was charged with the crime of Lèse-majesté, subsequently sentenced to banishment and confiscation of her property. She managed to evade arrest as she was being protected by Jean de Clisson, Olivier's eldest son; Guilaume Bérard, Jeanne's squire and valet; Guionnet de Fay; and Guillaume Denart.[9]

Jeanne took her two young sons, Olivier and Guillaume, from Clisson to Nantes, to show them the head of their father displayed at the Sauvetout gate.
Jeanne, enraged by her husband's execution, swore retribution against the French King, Philip VI, and Charles de Blois. She considered their actions a cowardly murder.[10]
Piracy and later life
After the execution of Olivier, Jeanne sold the de Clisson estates, raised a force of about 400 loyal men and started attacking French forces in Brittany.[10] Jeanne is said to have attacked:
- A castle at Touffou, near Bignon. The castle was built on the edge of a forest in the parish of Bignon, not far from the abbey of Villeneuve. The castle was under command of Galois de la Heuse, an officer of Charles de Blois, who apparently recognised Jeanne and let her in, whereopon her force massacred the entire garrison with the exception of one individual.
- A garrison at Château-Thébaud, about 20 km south east of Nantes, which had been a former post under control of her husband.
Black Fleet
With the English king's assistance and Breton sympathizers, Jeanne outfitted three warships.[11][12] These were painted black and their sails dyed red.[10][11] The flagship was named My Revenge.
The main sailing ships available in Brittany at that time were of the cog type (a flat-bottomed cargo ship with high sides and distinctive straight angled stem and stern post). The most visible give away that a ship was no longer just meant for cargo was if it had a forecastle or aft castle constructed on it. Not all of these were permanent in structure and were not integrated into the hull. [13][14]
The ships of this Black Fleet are said to initially attack shipping in the Bay of Biscay, but then moved into the English Channel hunting down French commerce ships, whereupon her force would kill entire crews, leaving only a few witnesses to transmit the news to the French King.[10] This earned Jeanne the moniker "The Lioness of Brittany".[10][12] The type of warfare is termed commerce raiding and is similar to guerilla warfare on land. Its main intent is to destroy or disrupt the logistics of an enemy on the open seas by attacking merchant shipping rather than engaging actual combatants. A few ships together would be used together in the employment of a swarming tactic. The crews would be equipped with grappling equipment for closing in and weapons such as crossbows, swords, and daggers. [15][16]
The Gironde estuary, the Breton coast near Saint Mathieu, the Charente estuary and the islands of Oléron, Re, and Aix were known to be especially dangerous since confined waters made it easier for ships to be outmaneuvered and surprised. The Pointe du Raz was an especially good spot to conduct piracy since these waters were dotted with numerous small often uninhabited islands which were ideal for ambushes.[17] Jeanne is also said to have attacked coastal villages in Normandy and have put several to sword and fire.
Jeanne is sometimes cited as a privateer of the English which would mean she would operate under certain protections and obligations. No letter patent or royal letter of protection is known to exist. In 1346, during the Crécy campaign in northern France, Jeanne used her ships to supply the English forces.
The French eventually managed to engage her fleet and sink her flagship. Jeanne and her two sons were adrift for five days; her son Guillaume died of exposure. Jeanne and Olivier were finally rescued and taken to Morlaix by Montfort supporters. Jeanne continued her piracy in the channel for another 13 years.[12] [18]
It must be noted that both sides employed pirates and operated with royal permission to prey on each other's shipping.[19][20]
Fourth marriage
In the 1350s, Jeanne married for a fourth time to Walter Bentley, one of King Edward III's military deputies during the campaign. Bentley had been appointed Edward's Lieutenant in Brittany in September 1350. In 1351, he had lifted the sieges of Ploërmel and Fougeres and on 4 August 1352, Bentley won the Battle of Mauron and was rewarded for his services with "the lands and castles" Beauvoir-sur-mer, of Ampant, of Barre, Blaye, Châteauneuf, Ville Maine, the island of Chauvet and from the islands of Noirmoutier and Bouin.[21]
Estate disputes
Raoul de Caours, Edward III's Lieutenant in the neighbouring province of Poitou, had wrested control of several of Jeanne's properties from the French. In 1349, Edward III ordered that the estates be returned to Bentley, but this changed when Edward III changed allegiances and started negotiating with the new Duke of Brittany, Charles.
As part of a treaty with Charles, Duke of Brittany, Edward III ordered Bentley to surrender Jeanne's remaining castles in Brittany.[22] Bentley refused and traveled to England to plead their case. He was imprisoned in the Tower of London while his case was heard. Eventually he was released and allowed to return. [23][24] At this point the war had come to a halt as both nations were exhausted, one of the main factors being the spread of the Black Plague which had decimated at least 20 percent of the population.
By January 1357, Walter and Jeanne were granted the barony of La Roche-Moisan as compensation. [22]
Death
Jeanne finally settled at the Castle of Hennebont, a port town on the Brittany coast, which had been in the territory of her de Montfort allies. Walter died in December 1359 and Jeanne a few weeks later.
Historical evidence
Verifiable references relating to Jeanne's exploits exist. These include:
- Papal records of the annulment of her second marriage.
- A French judgement from 1343 convicting Jeanne as a traitor and confirming the confiscation of the de Clisson lands.
- Records from the English court from 1343, indicating King Edward granting Jeanne an income from lands controlled in Brittany by the English.
- Jeanne is mentioned in the truce between France and England in 1347 as an English ally. (Truce of Calais, 28 September 1347)[25]
- A 15th-century manuscript, known as the Chronographia Regum Francorum, confirms some of the details of her life.[26]
- Amaury de Clisson, the brother of Olivier, is used as an emissary from Joanna of Flanders (Jehanne de Montfort) to ask King Edward III for aid to relieve Hennebont. The de Clisson family was at that stage definitely on the de Montfort side.
- Records exist where shortly after Olivier de Clisson's execution, several other knights were accused of similar crimes. The Lord of Malestroit and his son, the Lord of Avaugour, Sir Tibaut de Morillon, Alain de Quédillac, Guillaume, Jean and Olivier de Brieux, Denis du Plessis, Jean Malart, Jean de Senadavy, Thibaut de Morillon, Denis de Callac, and other lords of Brittany, to the number of ten knights and squires, were beheaded at Paris. Four other knights of Normandy: Sir William Baron, Sir Henry de Malestroit, the Lord of Rochetesson, and Sir Richard de Persy were put to death upon reports.
- The name of Jeanne de Belleville is also attached to the Breviary of Belleville, a book of prayers that follow the liturgical year. This manuscript in Latin and in French and in two volumes dated around 1323–1326 with illuminations by Jean Pucelle. Jeanne de Belleville would have received it as a gift for her wedding with Olivier. Around 1379–1380, an inventory was made of King Charles V's property, and the breviary was described herein.

Detail of the Belleville Breviary, 1323-26 kept at the Bibliotheque Nationale, Paris. (MS. Lat. 10484, folio 37 recto) - The Treaty of Westminster of 1353, although the original document is lost, some details are known, such as a very particular clause stating that "The titles of property in Brittany are to be restored as they were before the war. If Englishmen are married to Breton Heiresses they must not be disturbed in their rights, and an amnesty is to be granted to all adherents of Montfort."
- Great Chronicles of France, t.5, of John (II) the Good to Charles (V) the Wise (1350/1380);
- Latin chronicle of Guillaume de Nangis and his continuations, (1317/1368);
- Chronicles of the first four Valois, (1327/1393)
- Chronicon, (1328/1364)
- Chronicles of the reigns of John II and Charles V, t1 (1350/1364)
- Norman Chronicle of the 14th Century
- Chronicles of Mont-Saint-Michel, t.1 (1343/1432)
Legacy
In 1868, French-Breton writer Émile Pehant's novel Jeanne de Belleville was published in France. Written at the height of the French romantic movement, Pehant's novel shares many details with the legend attached to Jeanne.[citation needed]
On 24 September 1999, the City Council of Nantes named a street in honour of Jeanne: "A route beginning in the Embellie street is to be named: Rue Jeanne la Corsaire, wife of Olivier de Clisson, 1300 -1359."[citation needed]
See also
- Belleville Breviary, a book of prayers.
- Cog (ship), prevalent merchant ship type of the era sometimes converted for warfare.
- John Crabbe (died 1352), a contemporary pirate also in the employ of the English.
- John Hawley (died 1408), a contemporary pirate also in the employ of the English.
- Luis de la Cerda, Franco-Castillian Admiral of France involved in several contemporary engagements around the coast of Brittany.
- Walter Manny, 1st Baron Manny, English Admiral that relieved Hennebont, involved in several contemporary engagements around the coast of Brittany.
References
- ^ vendeens-archives.vendee.fr
- ^ Heebøll-Holm, Thomas, K. Ports, piracy, and maritime war: piracy in the English Channel and the Atlantic, c. 1280– c. 1330 / by Thomas K. Heebøll-Holm. ISBN 978-90-04-23570-0
- ^ Buffé, Marcel (1983). Châteaubriant, une cité dans l'histoire - De la préhistoire à nos jours. Éditions Cid. p. 15.
- ^ Ville de Châteaubriant (ed.). "Castelbus". Archived from the original on 2012-12-28. Retrieved 2013-02-18.
- ^ On February 10, 1330, in Avignon, at the request of Guy de Bretagne, Pope Jean XXII appointed the bishops of Rennes and Vannes to investigate the alleged marriage which was allegedly contracted in 1328 by Jeanne de Belleville, widow of the Lord of Chateaubriant, and Guy de Bretagne, seigneur de Penthievre (Mollat, G ,. op cit, pj, no II pg 49-50. See also Jean XXII (1316-1334) Lettres secretes et curiales relating to France, by Coulon, A. and Clemencet, S.) If Jeanne could not deny Guy's words. Guy could remarry (Mollat, G. op. Cit., Pg. 47) A little later, on April 30, 1330, Jeanne de Belleville, widow of Geoffroy de Chateaubriant, asked the Holy See for a dispensation to marry Olivier de Clisson (Mollat, G. op cit, pg 47 after Vatican Register, no 95, Lettres commune 81. See John XXII (1316-1334). Joint letters analyzed according to the so-called Avignon or Vatican registers, by Mollat, G. 1921-1947)
- ^ On March 12, 1343, it was decided that Pierre Nicolas, the King's sergeant, detained at the Chatelet in Paris for having at the request of the Lady of Bellville, the Sire de Clisson hampered the execution, would be extended until further notice. His statement was made in front of Robert Mulet and were in the hands of master Guillaume de Dol. He was only, for the moment, suspended from his office. (Arche. Nat. X2A4, no 4097 G. Journa: Acts of the Parliament of Paris, Criminal Parliament. Reign of Philippe 6 de Valois. Analytical inventory of registers X2A to 5, by Brigitte Labat-Poussin, Monique Langlois and Yvonne Lanhers, Paris , 1987, pg 177)
- ^ The Law of Treason and Treason Trials in Later Medieval France (Cambridge Studies in Medieval Life and Thought: Third Series). 18 December 2003
- ^ "The Online Froissart". www.hrionline.ac.uk.
- ^ Cazelles, R. Political society and the crisis of royalty under Philippe VI Valois, Paris, 1958
- ^ a b c d e Duncombe, Laura (1 April 2017). Pirate Women: The Princesses, Prostitutes, and Privateers Who Ruled the Seven Seas. Chicago Review Press. ISBN 9781613736043 – via Google Books.
- ^ a b Vencel, Wendy (1 January 2018). "Women at the Helm: Rewriting Maritime History through Female Pirate Identity and Agency". Undergraduate Honors Thesis Collection.
- ^ a b c Vázquez, Germán (2004). Mujeres Piratas. EDAF. ISBN 9788496107267 – via Google Books.
- ^ Thomas K. Heebøll-Holm, Ports, Piracy and Maritime War: Piracy in the English Channel and the Atlantic, c. 1280-c. 1330, Medieval Law and its Practice volume 15, Brill Publishers, 2013
- ^ Hutchinson, G. Pivotal points in the transmission of medieval shipbuilding technology, Archaeonautica, 1998, pp.185-190
- ^ Thomas K. Heebøll-Holm, Ports, Piracy and Maritime War: Piracy in the English Channel and the Atlantic, c. 1280-c. 1330, Medieval Law and its Practice volume 15, Brill Publishers, 2013
- ^ Cassard, Jean-Christophe, Les Bretons et la mer as Moyen Age (Rennes, 1998) pg 152
- ^ Thomas K. Heebøll-Holm, Ports, Piracy and Maritime War: Piracy in the English Channel and the Atlantic, c. 1280-c. 1330, Medieval Law and its Practice volume 15, Brill Publishers, 2013
- ^ Cassard, Jean-Christophe, Les marins Bretons a Bordeaux au debut du XIV siècle, Annales de Bretagne et des Pays del’Ouest, vol 86 (1979), 379-397
- ^ Alvarez, S. Ships and Fleets in Anglo-French Warfare, 1337-1360 deremilitari.org,2014
- ^ Runyan, T.J. Naval Power and Maritime Technology during the Hundred Years War, Cambridge University Press, Edited by Hattendorf, J.B., Unger, R.W.2013
- ^ "Battle of Mauron, 14 August 1352 (Brittany)". www.historyofwar.org.
- ^ a b Wagner 2006, p. 51.
- ^ Some New Documents illustrating the early Years of the Hundred Years War (1353-1356) By Dr Freiedrich Bock, John Rylands Library escholar.manchester.ac.uk
- ^ Arthur de La Borderie, Le Quémenet-Héboi and the seigneuries of La Roche-Moisan, Fiefs-de-Léon and Pontcallec. Revue de Bretagne et de Vendée, Tome X, 1861, pg.372-387
- ^ Wagner, J. A. (2006). Encyclopedia of the Hundred Years War. Westport, Conn.: Greenwood Press. ISBN 0-313-32736-X. OCLC 65205034.
- ^ Régis Rech. "Chronographia regum Francorum". Encyclopedia of the Medieval Chronicle. Edited by Graeme Dunphy. Brill Online, 2014. 30 October 2014
Further reading
- d'Eaubonne, Françoise (1998), Les grandes aventurieres (in French), Saint-Amard-Montrond: Vernal and Philippe Lebaud, pp. 17–27, ISBN 2865940381
- Hearst, Michael (2015), Extraordinary People, San Francisco: Chronicle, pp. 28–29, ISBN 978-1-4521-2709-5
- Froissart, Jean; Scheler, Auguste (1875), Oeuvres de Froissart: publiées avec les variantes des divers manuscrits, vol. 21, p. 12
- Henneman, John Bell (June 1996), Olivier de Clisson and political society in France under Charles V and Charles VI, Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press
- Jaeger, Gérard A. (1984), Les femmes d'abordage: Chroniques historiques et legendaires des aventurières de la mer, Paris: Clancier-Guénaud, pp. 31–39
- Lapouge, Gilles (1987), Les Pirates, forbans, flibustiers, boucaniers et autres gueux de mer
- Gicquel, Yvonig (1981), Olivier de Clisson, connétable de France ou chef de parti breton?, París: Jean Picollec, pp. 39–41, ISBN 2-86477-025-3
- Richard, Philippe (2007), Olivier de Clisson, connétable de France, grand seigneur breton, Haute-Goulaine: Ediciones Opéra, pp. 39–43, ISBN 978-2-35370-030-1
- Robbins, Trina (2004), Wild Irish Roses: Tales of Brigits, Kathleens, and Warrior Queens, Conari Press, pp. 115–116, ISBN 1-57324-952-1
- de Tourville, Anne (1958), Femmes de la mer, Paris: Le Livre Contemporain, pp. 37–47
- Vázquez Chamorro, Germán (October 2004), "Jeanne de Classon. La leona sangrienta", Mujeres Piratas (in Spanish), Algaba, pp. 107–115, ISBN 84-96107-26-4
- Sténuit, Marie-Ève (2015), pirates Women: the foamy sea (in French), ISBN 979-1-09-153415-4


