BosWash: Difference between revisions
Wehttam1106 (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
repositioning the picture |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
The '''BosWash''' or '''Bosnywash''' or '''Boshington''' or simply '''Northeast''' [[megalopolis (term)|megalopolis]] is the name for a group of [[metropolitan area]]s in the [[Northeastern United States|northeastern]] [[United States]], extending from [[Boston, Massachusetts|Boston, MA]] to [[Washington, D.C.]], including [[Providence, Rhode Island|Providence, RI]], [[Hartford, Connecticut|Hartford, CT]], [[New Haven, Connecticut|New Haven, CT]], [[Stamford, Connecticut|Stamford, CT]], [[New York City|New York, NY]], [[Philadelphia, Pennsylvania|Philadelphia, PA]], [[Wilmington, Delaware|Wilmington, DE]] and [[Baltimore, Maryland|Baltimore, MD]]. The geographic trend was first identified in the [[1961]] book ''Megalopolis: The Urbanized Northeastern Seaboard of the United States'' by [[France|French]] [[geography|geographer]] [[Jean Gottmann]]. The cities are also linked economically, and by transportation and communications. |
The '''BosWash''' or '''Bosnywash''' or '''Boshington''' or simply '''Northeast''' [[megalopolis (term)|megalopolis]] is the name for a group of [[metropolitan area]]s in the [[Northeastern United States|northeastern]] [[United States]], extending from [[Boston, Massachusetts|Boston, MA]] to [[Washington, D.C.]], including [[Providence, Rhode Island|Providence, RI]], [[Hartford, Connecticut|Hartford, CT]], [[New Haven, Connecticut|New Haven, CT]], [[Stamford, Connecticut|Stamford, CT]], [[New York City|New York, NY]], [[Philadelphia, Pennsylvania|Philadelphia, PA]], [[Wilmington, Delaware|Wilmington, DE]] and [[Baltimore, Maryland|Baltimore, MD]]. The geographic trend was first identified in the [[1961]] book ''Megalopolis: The Urbanized Northeastern Seaboard of the United States'' by [[France|French]] [[geography|geographer]] [[Jean Gottmann]]. The cities are also linked economically, and by transportation and communications. |
||
| ⚫ | |||
According to Gottmann, BosWash "provides the whole of America with so many essential services, of the sort a community used to obtain in its 'downtown' section, that it may well deserve the nickname of [[Main Street]] of the nation." He also envisioned the development of two similar megalopoleis in the US: [[ChiPitts]] from [[Chicago]] to [[Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania|Pittsburgh]], and [[SanSan]] from [[San Francisco, California|San Francisco]] to [[San Diego, California|San Diego]]. However, a more accepted definition in California is [[Bajalta California]], comprising just the southern end of SanSan. |
According to Gottmann, BosWash "provides the whole of America with so many essential services, of the sort a community used to obtain in its 'downtown' section, that it may well deserve the nickname of [[Main Street]] of the nation." He also envisioned the development of two similar megalopoleis in the US: [[ChiPitts]] from [[Chicago]] to [[Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania|Pittsburgh]], and [[SanSan]] from [[San Francisco, California|San Francisco]] to [[San Diego, California|San Diego]]. However, a more accepted definition in California is [[Bajalta California]], comprising just the southern end of SanSan. |
||
[[Image:Bos-wash.png]] |
|||
==Extent== |
==Extent== |
||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
As large as Boswash is, internationally there are other larger megalopoleis, such as [[Taiheiyo Belt|Tokyo-Nagoya-Osaka-Hiroshima-Fukuoka]] containing 75 million people (being itself part of the larger Taiheiyo Belt of almost 83 million people), the very reason for the success of the bullet train ([[Shinkansen]]). The [[Pearl River Delta]] in China could also be considered a developing megalopolis as it is home to several cities with more than a million people in a small area. |
As large as Boswash is, internationally there are other larger megalopoleis, such as [[Taiheiyo Belt|Tokyo-Nagoya-Osaka-Hiroshima-Fukuoka]] containing 75 million people (being itself part of the larger Taiheiyo Belt of almost 83 million people), the very reason for the success of the bullet train ([[Shinkansen]]). The [[Pearl River Delta]] in China could also be considered a developing megalopolis as it is home to several cities with more than a million people in a small area. |
||
| ⚫ | |||
The major cities in the BosWash megalopolis include the following (north to south): |
The major cities in the BosWash megalopolis include the following (north to south): |
||
{| |
{| |
||
Revision as of 14:57, 25 January 2007
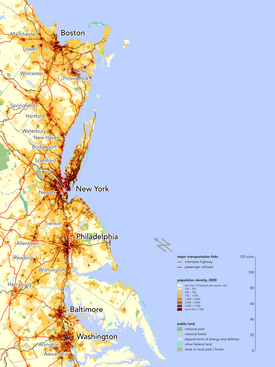
The BosWash or Bosnywash or Boshington or simply Northeast megalopolis is the name for a group of metropolitan areas in the northeastern United States, extending from Boston, MA to Washington, D.C., including Providence, RI, Hartford, CT, New Haven, CT, Stamford, CT, New York, NY, Philadelphia, PA, Wilmington, DE and Baltimore, MD. The geographic trend was first identified in the 1961 book Megalopolis: The Urbanized Northeastern Seaboard of the United States by French geographer Jean Gottmann. The cities are also linked economically, and by transportation and communications.
According to Gottmann, BosWash "provides the whole of America with so many essential services, of the sort a community used to obtain in its 'downtown' section, that it may well deserve the nickname of Main Street of the nation." He also envisioned the development of two similar megalopoleis in the US: ChiPitts from Chicago to Pittsburgh, and SanSan from San Francisco to San Diego. However, a more accepted definition in California is Bajalta California, comprising just the southern end of SanSan.
Extent
BosWash theoretically extends from extreme southern Maine and New Hampshire all the way south to Virginia, where recently, with the explosion of population in the Hampton Roads area, the megalopolis now includes the three largest cities in southeastern Virginia: Virginia Beach, Norfolk, and Chesapeake. The megalopolis contains a reported population of 44 million, or 16 percent of the population of the United States (about 0.7 percent of the world population), three world cities (New York, Washington, and Boston), and four of the world's 70 largest metropolitan areas (New York, Philadelphia, Boston, and Baltimore-Washington), as well as the New York Stock Exchange and NASDAQ, the White House and United States Capitol, the UN Headquarters, the headquarters of ABC, NBC, CBS, and the New York Times Company as well as the Washington Post, and six of the eight Ivy League schools. Amtrak's fastest train, the Acela Express, runs on the Northeast Corridor, an electrified rail line extending the length of the BosWash area. Interstate 95, arguably one of the most vital highways in the country, is also a major transportation route for the BosWash area.
As large as Boswash is, internationally there are other larger megalopoleis, such as Tokyo-Nagoya-Osaka-Hiroshima-Fukuoka containing 75 million people (being itself part of the larger Taiheiyo Belt of almost 83 million people), the very reason for the success of the bullet train (Shinkansen). The Pearl River Delta in China could also be considered a developing megalopolis as it is home to several cities with more than a million people in a small area.
The major cities in the BosWash megalopolis include the following (north to south):
Several small and medium-sized metropolitan areas near the southwestern end of the corridor, including Lancaster, Pennsylvania, Harrisburg, Pennsylvania, York, Pennsylvania, Hagerstown, Maryland, and Frederick, Maryland, are also sometimes considered part of the region, though opinions vary from geographer to geographer as to which cities are included or excluded.
Population statistics
| Rank | Combined Statistical Area | State(s) | 2004 Estimate | 2000 Population | 1990 Population | Percent Change (1990-2000) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | New York-Newark-Bridgeport | NY-NJ-CT-PA | 21,858,830 | 21,361,797 | 19,710,239 | 8.4 |
| 4 | Washington-Baltimore-Northern Virginia | DC-MD-VA-WV | 8,026,807 | 7,538,385 | 6,665,228 | 13.1 |
| 6 | Philadelphia-Camden-Vineland | PA-NJ-DE-MD | 5,951,797 | 5,833,585 | 5,573,521 | 4.7 |
| 8 | Boston-Worcester-Manchester | MA-NH | 5,809,111 | 5,715,698 | 5,348,894 | 6.9 |
| Combined | 41,646,545 | 40,449,465 | 37,297,882 | 8.4 |
Included or neighboring MSAs not in a CSA
| Rank | Metropolitan Statistical Area | State(s) and/or Territory | 1 July 2004 Population Estimate |
|---|---|---|---|
| 33 | Virginia Beach-Norfolk-Newport News | VA-NC | 1,644,250 |
| 34 | Providence-New Bedford-Fall River | RI-MA | 1,628,808 |
| 44 | Hartford-West Hartford-East Hartford | CT | 1,184,564 |
| 46 | Richmond | VA | 1,154,317 |
| 59 | Albany-Schenectady-Troy | NY | 845,269 |
| 63 | Allentown - Bethlehem - Easton | PA-NJ | 779,816 |
| 70 | Springfield | MA | 687,973 |
| 86 | Scranton--Wilkes-Barre | PA | 551,531 |
| 91 | Harrisburg-Carlisle | PA | 519,331 |
| 96 | Portland-South Portland-Biddeford | ME | 510,791 |
| 99 | Lancaster | PA | 487,332 |
| 117 | York-Hanover | PA | 401,613 |
| 121 | Reading | PA | 391,640 |
| 164 | Atlantic City | NJ | 268,693 |
| 183 | Barnstable | MA | 228,683 |
| 216 | Charlottesville | VA | 180,901 |
| 254 | Bangor | ME | 148,196 |
| 268 | Dover | DE | 138,752 |
| 275 | Pittsfield | MA | 132,486 |
| 288 | Lebanon | PA | 124,489 |
| 311 | Harrisonburg | VA | 111,284 |
| 327 | Lewiston-Auburn | ME | 107,022 |
| Combined non-CSA MSAs | 12,224,733 | ||
| Combined CSAs and MSAs | 53,871,278 |
References
- Gottmann, Jean (1961), Megalopolis: the Urbanized Northeastern Seaboard of the United States. ISBN 0-527-02819-3
- Gottmann, Jean (1987), Megalopolis Revisted—25 Years Later. ISBN 0-913749-04-4
- Swatridge, L.A. (1971), The Bosnywash megalopolis: A region of great cities. ISBN 0-07-092795-2
See also
- List of U.S. multistate regions
- Highways along the BosWash corridor
- Megacity
- Mega-City One, another science fiction megalopolis based on BosWash from the Judge Dredd series
- Northeast Corridor, the railroad line that runs through the region.
- Overpopulation
- Quebec City-Windsor Corridor, the Canadian equivalent of the Northeast Corridor/BosWash
- The Sprawl, a science fiction extension of BosWash which extends from Boston to Atlanta from the books of William Gibson
- Urban sprawl
