Confederate States of America: Difference between revisions
→Bibliography: added 1999 Neely work and moved 1993 work to bibliography section |
|||
| Line 406: | Line 406: | ||
The Union government never declared war, but conducted its military efforts under a proclamation of [[Union blockade|blockade]] and rebellion. After the war, the U.S. Congress readmitted representation from the southern states. Mid-war negotiations between the two sides occurred without formal political recognition, though the [[laws of war]] governed military relationships. |
The Union government never declared war, but conducted its military efforts under a proclamation of [[Union blockade|blockade]] and rebellion. After the war, the U.S. Congress readmitted representation from the southern states. Mid-war negotiations between the two sides occurred without formal political recognition, though the [[laws of war]] governed military relationships. |
||
Four years after the war, in 1869, the [[Supreme Court of the United States|United States Supreme Court]] in ''[[Texas v. White]]'' |
Four years after the war, in 1869, the majority of the [[Supreme Court of the United States|United States Supreme Court]] in ''[[Texas v. White]]'' opined that Texas' secession was unconstitutional and [[Void (law)|legally null]]. The court's opinion was authored by Chief Justice [[Salmon P. Chase]]. However, since the actual issue of secession was not the original before the court, it has since been debated as to whether or not the final ruling on the matter meets the standards of [[stare decisis|stare decisis]] on the issue of secession. Some legal scholars have argued the majority opinion on the issue was [[obiter dictum|obiter dictum]], while others maintain it was [[ratio decidendi|ratio decidendi]]. |
||
The court did allow some possibility of separation from the Union "through revolution or through consent of the States."<ref>Aleksandar Pavković, Peter Radan, [http://books.google.com/books?id=-IjHbPvp1W0C Creating New States: Theory and Practice of Secession], p. 222, Ashgate Publishing, Ltd., 2007. |
|||
</ref><ref> |
</ref><ref> |
||
[http://www.law.cornell.edu/supct/html/historics/USSC_CR_0074_0700_ZO.html ''Texas v. White''], 74 U.S. 700 (1868) at [[Cornell University Law School]] Supreme Court collection. |
[http://www.law.cornell.edu/supct/html/historics/USSC_CR_0074_0700_ZO.html ''Texas v. White''], 74 U.S. 700 (1868) at [[Cornell University Law School]] Supreme Court collection. |
||
Revision as of 21:05, 26 July 2010
Confederate States of America | |
|---|---|
| 1861–1865 | |
| Motto: Deo Vindice (Latin) "With God our Vindicator" | |
| Anthem: (none official) "God Save the South" (unofficial) "The Bonnie Blue Flag" (popular) "Dixie" (traditional) | |
 | |
| Status | Unrecognized state |
| Capital | Montgomery, Alabama (until May 29, 1861) Richmond, Virginia (May 29, 1861–April 2, 1865) Danville, Virginia (from April 3, 1865) |
| Largest city | New Orleans (February 4, 1861–May 1, 1862) (captured) Richmond (May 1, 1862–surrender) |
| Common languages | English (de facto) |
| Government | Confederation |
| President | |
• 1861–1865 | Jefferson Davis |
| Vice President | |
• 1861–1865 | Alexander Stephens |
| Legislature | Congress of the Confederate States |
| Historical era | American Civil War |
• Confederacy formed | February 8 1861 |
| April 12, 1861 | |
• Military collapse[1] | April 9, 1865 |
| May 5 1865 | |
| Area | |
| 18601 | 1,995,392 km2 (770,425 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• 18601 | 9,103,332 |
• slaves2 | 3,521,110 |
| Currency | CSA dollar State Currencies |
1 Area and population values do not include Missouri and Kentucky nor the Confederate Territory of Arizona. Water area: 5.7%. 2 Slaves included in above population count 1860 Census | |
The Confederate States of America (also called the Confederacy, the Confederate States, and the CSA) was an unrecognized state set up from 1861 to 1865 by eleven southern slave states of the United States of America that had declared their secession from the U.S. The CSA's de facto control over its claimed territory varied during the course of the American Civil War, depending on the success of its military in battle.
Asserting that states had a right to secede, seven states declared their independence from the United States before the inauguration of Abraham Lincoln as President on March 4, 1861; four more did so after the Civil War began at the Battle of Fort Sumter (April 1861). The government of the United States of America (The Union) regarded secession as illegal and refused to recognize the Confederacy. Although British and French commercial interests sold warships and materials to the Confederacy, no European or other foreign nation officially recognized the CSA as an independent country.[2][3]
The CSA effectively collapsed when Ulysses S. Grant captured the CSA capital of Richmond, Virginia and Robert E. Lee's army in April 1865 and the remaining Confederate forces surrendered by the end of June, as the U.S. Army took control of the South.[4] Because Congress was not sure that white Southerners had really given up slavery or their dreams of Confederate nationalism, a decade-long process known as Reconstruction expelled ex-Confederate leaders from office, enacted civil rights legislation (including the right to vote) that included the freedmen (ex-slaves), and imposed conditions on the readmission of the states to Congress. The war and subsequent Reconstruction left the South economically prostrate and none of the states regained prosperity until after 1945.
History
Seceding states
- Northwest Ordinance
- Kentucky and Virginia Resolutions
- End of Atlantic slave trade
- Missouri Compromise
- Tariff of 1828
- Nat Turner's Rebellion
- Nullification crisis
- End of slavery in British colonies
- Texas Revolution
- United States v. Crandall
- Gag rule
- Commonwealth v. Aves
- Murder of Elijah Lovejoy
- Burning of Pennsylvania Hall
- American Slavery As It Is
- United States v. The Amistad
- Prigg v. Pennsylvania
- Texas annexation
- Mexican–American War
- Wilmot Proviso
- Nashville Convention
- Compromise of 1850
- Uncle Tom's Cabin
- Recapture of Anthony Burns
- Kansas–Nebraska Act
- Ostend Manifesto
- Bleeding Kansas
- Caning of Charles Sumner
- Dred Scott v. Sandford
- The Impending Crisis of the South
- Panic of 1857
- Lincoln–Douglas debates
- Oberlin–Wellington Rescue
- John Brown's raid on Harpers Ferry
- Virginia v. John Brown
- 1860 presidential election
- Crittenden Compromise
- Secession of Southern states
- Peace Conference of 1861
- Corwin Amendment
- Battle of Fort Sumter
 States in the CSA States and territories claimed by CSA without formal secession and/or control |
 |
|
Confederate States in the American Civil War |
|---|
|
|
| Dual governments |
| Territory |
|
Allied tribes in Indian Territory |
Seven states declared their secession from the United States before Lincoln took office on March 4, 1861:
- South Carolina (December 20, 1860)[5][6]
- Mississippi (January 9, 1861)[7]
- Florida (January 10, 1861)[8]
- Alabama (January 11, 1861)[9]
- Georgia (January 19, 1861)[10]
- Louisiana (January 26, 1861)[11]
- Texas (February 1, 1861)[12]
After the Confederate attack on Fort Sumter on April 12, 1861, and Lincoln's subsequent call for troops on April 15, four more states declared their secession:[13]
- Virginia (April 17, 1861; ratified by voters May 23, 1861)[14]
- Arkansas (May 6, 1861)[15]
- Tennessee (May 7, 1861; ratified by voters June 8, 1861)[16][17]
- North Carolina (May 20, 1861)[18]
The border states of Kentucky and Missouri declared neutrality very early in the war. In Kentucky, the state gradually came to side with the north; however, a second government (pro-Confederate) emerged in some southern counties (much like the situation in the counties that would become West Virginia) although its control in those regions did not last very long. A more complex situation surrounds the Missouri Secession. In Missouri a remnant of the General Assembly met on October 31, 1861 and, although lacking a quorum in either house, passed an ordinance of secession.[19][20] However, this occurred after a standing constitutional convention declared the legislature and governor void after Federal troops marched on and took over the capital. Missouri, since the Union already controlled most of it, was exempted from the Emancipation Proclamation that outlawed slavery elsewhere. However, the standing State constitutional convention repealed slavery in Missouri before Federal constitutional amendments passed. The Confederacy recognized the pro-Confederate claimants in both Kentucky and Missouri and laid claim to those states based on their authority, with representatives from both states seated in the Confederate Congress. Later versions of Confederate flags had thirteen stars, reflecting the Confederacy's claims to Kentucky and Missouri.
On April 27, 1861 President Lincoln, in response to the destruction of railroad bridges and telegraph lines by southern sympathizers in Maryland (the state which borders the U.S. capital, Washington, D.C., on three sides), authorized General Scott to suspend the writ of habeas corpus along the railroad line from Philadelphia to Baltimore to Washington.[21] Delaware, also a slave state, never considered secession, nor did Washington, D.C. Although the slave states of Maryland and Delaware did not secede, citizens from those states did exhibit divided loyalties. Only Delaware among the slave states did not produce a full regiment to fight for the Confederacy. Delaware achieved the distinction of providing more soldiers by percentage than any other state, and overwhelmingly they fought for the Union.
In 1861, a Unionist legislature in Wheeling, Virginia seceded from Virginia, eventually claiming 50 counties for a new state. However, 24 of those counties had voted in favor of Virginia's secession, and control of these counties, as well as some counties that had voted against secession, remained contested until the end of the war.[22] West Virginia joined the United States in 1863 with a constitution that gradually abolished slavery. According to military historian Russell F. Weigley "Most of West Virginia went through the Civil War not as an asset to the Union but as a troublesome battleground..."[23]
Confederate declarations of martial law checked attempts to secede from the Confederate States of America by some counties in East Tennessee.[24][25]
Seceding territories
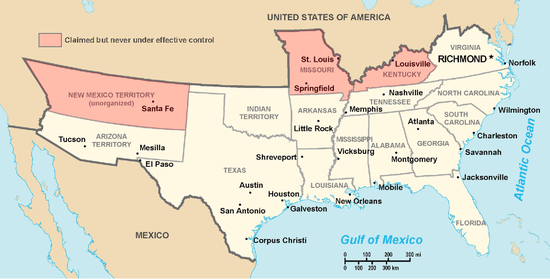
Citizens at Mesilla and Tucson in the southern part of New Mexico Territory (modern day New Mexico and Arizona) formed a secession convention, which voted to join the Confederacy on March 16, 1861 and appointed Lewis Owings as the new territorial governor. In July, the Mesilla government appealed to Confederate troops in El Paso, Texas, under Lieutenant Colonel John Baylor for help in removing the Union Army under Major Isaac Lynde that had taken up position nearby. The Confederates defeated Lynde's forces at the Battle of Mesilla on July 27, 1861. After the battle, Baylor established a territorial government for the Confederate Arizona Territory and named himself governor. The Confederacy proclaimed the portion of the New Mexico Territory south of the 34th parallel as the Confederate Arizona Territory on February 14, 1862,[26] with Mesilla serving as the territorial capital.[27] In 1862 the Confederate General Henry Hopkins Sibley led a New Mexico Campaign to take the northern half of New Mexico. Although Confederates briefly occupied the territorial capital of Santa Fe, they suffered defeat at Glorietta Pass in March and retreated, never to return. The Union regained military control of the area, and on February 24, 1863 set up the U.S. Arizona Territory with Fort Whipple as the capital.
Confederate supporters also claimed portions of modern-day Oklahoma as Confederate territory after the Union abandoned and evacuated the federal forts and installations in the territory. The five tribal governments of the Indian Territory — which became Oklahoma in 1907 — mainly supported the Confederacy, providing troops and one general officer. On July 12, 1861 the newly formed Confederate States government signed a treaty with both the Choctaw and Chickasaw Indian nations in the Indian Territory.[28][29] After 1863 the tribal governments sent representatives to the Confederate Congress: Elias Cornelius Boudinot representing the Cherokee and Samuel Benton Callahan representing the Seminole and Creek people. The Cherokee, in their declaration of causes, gave as reasons for aligning with the Confederacy the similar institutions and interests of the Cherokee nation and the Southern states, alleged violations of the Constitution by the North, claimed that the North waged war against Southern commercial and political freedom and for the abolition of slavery in general and in the Indian Territory in particular, and that the North intended to seize Indian lands as had happened in the past.[30]
Causes of secession
By 1860, sectional disagreements between North and South revolved primarily around the maintenance or expansion of slavery. Historian Drew Gilpin Faust observed that "leaders of the secession movement across the South cited slavery as the most compelling reason for southern independence."[31] Related and intertwined secondary issues also fueled the dispute; these secondary differences included tariffs, agrarianism vs. industrialization, and states' rights. The immediate spark for secession came from the victory of the Republican Party and the election of Abraham Lincoln in the 1860 elections. Civil War historian James M. McPherson wrote:
To southerners the election’s most ominous feature was the magnitude of Republican victory north of the 41st parallel. Lincoln won more than 60 percent of the vote in that region, losing scarcely two dozen counties. Three-quarters of the Republican congressmen and senators in the next Congress would represent this "Yankee" and antislavery portion of the free states. The New Orleans Crescent saw these facts as "full of portentous significance". "The idle canvas prattle about Northern conservatism may now be dismissed," agreed the Richmond Examiner. "A party founded on the single sentiment... of hatred of African slavery, is now the controlling power." No one could any longer "be deluded... that the Black Republican party is a moderate" party, pronounced the New Orleans Delta. "It is in fact, essentially, a revolutionary party."[32]
Four of the seceding states, the Deep South states of South Carolina,[33] Mississippi,[34] Georgia,[35] and Texas,[36] issued formal declarations of causes, each of which identified the threat to slaveholders’ rights as the cause of, or a major cause of, secession. Georgia also claimed a general Federal policy of favoring Northern over Southern economic interests. Texas mentioned slavery twenty-one times, but also listed the failure of the federal government to live up to its obligations, in the original annexation agreement, to protect settlers along the exposed western frontier. Texas further stated:
We hold as undeniable truths that the governments of the various States, and of the confederacy itself, were established exclusively by the white race, for themselves and their posterity; that the African race had no agency in their establishment; that they were rightfully held and regarded as an inferior and dependent race, and in that condition only could their existence in this country be rendered beneficial or tolerable.
In what later became known as the Cornerstone Speech, C.S. Vice President Alexander Stephens declared that the "cornerstone" of the new government "rest[ed] upon the great truth that the negro is not equal to the white man; that slavery—subordination to the superior race—is his natural and normal condition. This, our new government, is the first, in the history of the world, based upon this great physical, philosophical, and moral truth".[37]
Religion, slavery, and secession
As the nation divided over slavery, religion exacerbated the sectional differences. Methodists, Baptists, and Presbyterians in the first half of the nineteenth century expressed reservations about slavery,[38] but by 1850 John C. Calhoun would note that "already three great evangelical churches had been torn asunder" over slavery.[39] By the 1850s, as sectional tensions over slavery grew, more and more ministers in the South "who openly resisted southern evangelicals' accommodation with slavery found themselves silenced or driven out of the South".[40]
Rise and fall of the Confederacy
The American Civil War broke out in April 1861 with the Battle of Fort Sumter in Charleston, South Carolina. Federal troops of the U.S. had retreated to Fort Sumter soon after South Carolina declared its secession on 20 December 1860. U.S. President Buchanan had attempted to re-supply Sumter by sending the Star of the West, but Confederate forces led by cadets from The Citadel, fired upon the ship on Jan. 9, 1861, driving it away. U.S. President Abraham Lincoln also attempted to resupply Sumter. Lincoln notified South Carolina Governor Francis W. Pickens that "an attempt will be made to supply Fort Sumter with provisions only, and that if such attempt be not resisted, no effort to throw in men, arms, or ammunition will be made without further notice, [except] in case of an attack on the fort." However, suspecting just such an attempt to reinforce the fort, the Confederate cabinet decided at a meeting in Montgomery to capture Fort Sumter before the relief fleet arrived.
On April 12, 1861, Confederate troops, following orders from Davis and his Secretary of War, fired upon the federal troops occupying Fort Sumter, forcing their surrender. Nobody was killed in the battle, though two Union soldiers did die from an accidental explosion during the surrender ceremonies. After the war, Confederate Vice President Alexander H. Stephens maintained that Lincoln's attempt to resupply Sumter was a disguised reinforcement and had provoked the war.[41]

Following the Battle of Fort Sumter, Lincoln called for the states to send troops to recapture Sumter and all other federal property that had seized in the seven seceding states[42] Lincoln issued this call before Congress could convene on the matter, and the original request from the War Department called for volunteers for only three months of duty. Lincoln's call for troops resulted in four border states deciding to secede rather than provide troops that would be marching into neighboring Southern states. Virginia, Arkansas, Tennessee, and North Carolina joined the Confederacy, bringing the total to eleven states. Once Virginia had joined, the Confederate States moved their capital from Montgomery, Alabama, to Richmond, Virginia. All but two major battles (Antietam and Gettysburg) took place in Confederate territory.
By 1862, the Union had taken control of New Orleans, and had gained control of the contested northernmost slave states (Missouri, Kentucky, Maryland, Delaware and West Virginia). Two major Confederate incursions into Union territory, into Maryland in 1862 and into Pennsylvania in 1863, each lasted only a matter of days. By 1863 the Union held control of most of Tennessee; with the fall of Vicksburg, Mississippi on July 4 of that year, the Union gained complete control over the Mississippi River, cutting off the westernmost portions of the Confederacy (Arkansas, Louisiana, and Texas). In 1864, the Union took Mobile, Alabama, the last major port on the Gulf Coast, and by September 1864 Atlanta fell to Union troops, paving the way for the March to the Sea by William Tecumseh Sherman's forces; he reached Savannah by the end of the year, devastating the Confederate heartland. The Union took the Confederate capital, Richmond, Virginia, in April 1865. The surrender of the Army of Northern Virginia by General Lee at the Appomattox Court House on April 9, 1865 marked the end of the Confederacy. Some high officials escaped to Europe but Union patrols captured President Davis at Irwinville, Georgia, on May 10; all remaining Confederate forces surrendered by June 1865. The U.S. Army took control of the Confederate areas and there was no post-surrender insurgency or guerrilla warfare against the army, but there was a great deal of local violence, feuding and revenge killings.[43]
Government and politics
Constitution

President 1861–1865
The Southern leaders met in Montgomery, Alabama, to write their constitution. Much of the Confederate States Constitution replicated the United States Constitution verbatim, but it contained several explicit protections of the institution of slavery, though it maintained the existing ban on international slave-trading. In certain areas, the Confederate Constitution gave greater powers to the states (or curtailed the powers of the central government more) than the U.S. Constitution of the time did, but in other areas, the states actually lost rights they had under the U.S. Constitution. Although the Confederate Constitution, like the U.S. Constitution, contained a commerce clause, the Confederate version prohibited the central government from using revenues collected in one state for funding internal improvements in another state. The Confederate Constitution's equivalent to the U.S. Constitution's general welfare clause prohibited protective tariffs (but allowed tariffs for providing domestic revenue), and spoke of "carry[ing] on the Government of the Confederate States" rather than providing for the "general welfare". State legislatures had the power to impeach officials of the Confederate government in some cases. On the other hand, the Confederate Constitution contained a Necessary and Proper Clause and a Supremacy Clause that essentially duplicated the respective clauses of the U.S. Constitution. The Confederate Constitution also incorporated each of the twelve amendments to the U.S. Constitution that had been ratified up to that point.
The Confederate Constitution did not specifically include a provision allowing states to secede; the Preamble spoke of each state "acting in its sovereign and independent character" but also of the formation of a "permanent federal government". During the debates on drafting the Confederate Constitution, one proposal would have allowed states to secede from the Confederacy. The proposal was tabled with only the South Carolina delegates voting in favor of considering the motion.[44] The Confederate Constitution also explicitly denied States the power to bar slaveholders from other parts of the Confederacy from bringing their slaves into any state of the Confederacy or to interfere with the property rights of slave owners traveling between different parts of the Confederacy. In contrast with the secular 18th-century Enlightenment language of the United States Constitution, the Confederate Constitution overtly asked God's blessing ("...invoking the favor and guidance of Almighty God...").
The Constitution provided for a President of the Confederate States of America, elected to serve a six-year term but without the possibility of re-election. Unlike the Union Constitution, the Confederate Constitution gave the president the ability to subject a bill to a line item veto, a power also held by some state governors. The Confederate Congress could overturn either the general or the line item vetoes with the same two-thirds majorities that are required in the U.S. Congress. In addition, appropriations not specifically requested by the executive branch required passage by a two-thirds vote in both houses of Congress. The only person to serve as president was Jefferson Davis, due to the Confederacy being defeated before the completion of his term.
Executive

| Office | Name | Term |
| President | Jefferson Davis | 1861–1865 |
| Vice President | Alexander Stephens | 1861–1865 |
| Secretary of State | Robert Toombs | 1861 |
| Robert M.T. Hunter | 1861–1862 | |
| Judah P. Benjamin | 1862–1865 | |
| Secretary of the Treasury | Christopher Memminger | 1861–1864 |
| George Trenholm | 1864–1865 | |
| John H. Reagan | 1865 | |
| Secretary of War | Leroy Pope Walker | 1861 |
| Judah P. Benjamin | 1861–1862 | |
| George W. Randolph | 1862 | |
| James Seddon | 1862–1865 | |
| John C. Breckinridge | 1865 | |
| Secretary of the Navy | Stephen Mallory | 1861–1865 |
| Postmaster General | John H. Reagan | 1861–1865 |
| Attorney General | Judah P. Benjamin | 1861 |
| Thomas Bragg | 1861–1862 | |
| Thomas H. Watts | 1862–1863 | |
| George Davis | 1864–1865 | |
Legislative
As its legislative branch, the Confederate States of America instituted the Confederate Congress. Like the United States Congress, the Confederate Congress consisted of two houses:
- the Confederate Senate, whose membership included two senators from each state (and chosen by the state legislature)
- the Confederate House of Representatives, with members popularly elected by properly enfranchised residents of the individual states
Provisional Congress
For the first year, the unicameral Provisional Confederate Congress functioned as the Confederacy's legislative branch.
President of the Provisional Congress
- Howell Cobb, Sr. of Georgia — February 4, 1861-February 17, 1862
Presidents pro tempore of the Provisional Congress
- Robert Woodward Barnwell of South Carolina - February 4, 1861
- Thomas Stanhope Bocock of Virginia - December 10–21, 1861 and January 7–8, 1862
- Josiah Abigail Patterson Campbell of Mississippi - December 23–24, 1861 and January 6, 1862
Sessions of the Confederate Congress
Tribal Representatives to Confederate Congress
- Elias Cornelius Boudinot 1862-65 - Cherokee
- Samuel Benton Callahan Unknown years - Creek, Seminole
- Burton Allen Holder 1864-1865 - Chickasaw
- Robert McDonald Jones 1863-65 - Choctaw
Judicial
The Confederate Constitution outlined a judicial branch of the government, but the ongoing war and resistance from states-rights advocates, particularly on the question of whether it would have appellate jurisdiction over the state courts, prevented the creation or seating of the "Supreme Court of the Confederate States"; the state courts generally continued to operate as they had done, simply recognizing the CSA as the national government.[45] Confederate district courts were authorized by Article III, Section 1, of the CSA Constitution,[46] and President Davis appointed judges within the individual states of the Confederate States of America.[46] In many cases, the same US Federal District Judges were appointed as Confederate States District Judges. Confederate district courts began reopening in the spring of 1861 handling many of the same type cases as had been done before. Prize cases, in which Union ships were captured by the Confederate Navy or raiders and sold through court proceedings, were heard until the blockade of southern ports made this impossible. After a Sequestration Act was passed by the Confederate Congress, the Confederate district courts heard many cases in which enemy aliens (typically Northern absentee landlords owning property in the South) had their property sequestered (i.e., seized) by Confederate Receivers. When the matter came before the Confederate court, the property owner could not appear because he was unable to travel across the front lines between Union and Confederate forces. Thus, the CSA District Attorney won the case by default, the property was typically sold, and the money used to further the Southern war effort. Eventually, because there was no CSA Supreme Court, sharp attorneys like South Carolina's Edward McCrady began filing appeals. This prevented their clients' property from being sold until a supreme court could be constituted to hear the appeal, which never occurred.[46] Where Federal troops gained control over parts of the Confederacy and re-established civilian government, U.S. district courts sometimes resumed jurisdiction.[47]
Supreme Court - not established.
District Courts - judges
- Alabama William G. Jones 1861-1865
- Arkansas Daniel Ringo 1861-1865
- Florida Jesse J. Finley 1861-1862
- Georgia Henry R. Jackson 1861, Edward J. Harden 1861-1865
- Louisiana Edwin Warren Moise 1861-1865
- Mississippi Alexander Mosby Clayton 1861-1865
- North Carolina Asa Biggs 1861-1865
- South Carolina Andrew G. Magrath 1861-1864, Benjamin F. Perry 1865
- Tennessee West H. Humphreys 1861-1865
- Texas-East William Pinckney Hill 1861-1865
- Texas-West Thomas J. Devine 1861-1865
- Virginia-East James D. Halyburton 1861-1865
- Virginia-West John W. Brockenbrough 1861-1865
Civil liberties
The Confederacy actively used the military to arrest people suspected of loyalty to the United States. Historian Mark Neely found 4,108 names of men arrested and estimated a much larger total.[48] The CSA arrested suspects at about the same rate as the Union arrested Confederate loyalists. Neely concludes:
The Confederate citizen was not any freer than the Union citizen — and perhaps no less likely to be arrested by military authorities. In fact, the Confederate citizen may have been in some ways less free than his Northern counterpart. For example, freedom to travel within the Confederate states was severely limited by a domestic passport system.[49]
Capital

Montgomery, Alabama served as the capital of the Confederate States of America from February 4 until May 29, 1861. The naming of Richmond, Virginia as the new capital took place on May 30, 1861. Shortly before the end of the war, the Confederate government evacuated Richmond, planning to relocate farther south. Little came of these plans before Lee's surrender at Appomattox Court House on April 9, 1865. Danville, Virginia, served as the last capital of the Confederate States of America, from April 3 to April 10, 1865.
Financial instruments
Both the individual Confederate states and later the Confederate government printed Confederate States of America dollars as paper currency in various denominations, much of it signed by the Treasurer Edward C. Elmore. During the course of the war these severely depreciated and eventually became worthless. Many bills still exist, although in recent years copies have proliferated.
The Confederate government initially financed the war effort mostly through tariffs on imports, export taxes, and voluntary donations of coins and bullion. However, after the imposition of a self-embargo on cotton sales to Europe in 1861, these sources of revenue dried up and the Confederacy increasingly turned to issuing debt and printing money to pay for war expanses. As a result inflation increased and remained a problem for the southern states throughout the rest of the war.[50]

The Treasury also issued paper bonds in large numbers, and the Post Office produced a considerable number of postage stamps; both stamps and bonds (and especially bond coupons) remain readily available. The philatelic market regards as far more valuable the stamps placed on envelopes that were actually used during the war.
At the time of their secession, the states (and later the Confederate government) took over the national mints in their territories: the Charlotte Mint in North Carolina, the Dahlonega Mint in Georgia, and the New Orleans Mint in Louisiana. During 1861, the first two produced small amounts of gold coinage, the latter half dollars. Since the mints used the current dies on hand, these issues remain indistinguishable from those minted by the Union.
However the four half dollars with a CSA (rather than USA) reverse, mentioned below, used an obverse die that had a small crack. Thus "regular" 1861-O halves with this crack probably were among the 962,633 pieces struck under Confederate authority.[51]
In 1861 plans also originated to produce Confederate coins. The New Orleans Mint produced dies and four specimen half dollars, but a lack of bullion prevented any further minting. A jeweler in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, manufactured a dozen pennies under an agreement, but did not deliver them for fear of arrest. Over the years copies of both denominations have appeared. More details and pictures of the original issues appear in A Guide Book of United States Coins.
International diplomacy
Once the war with the United States began, the Confederacy pinned its hopes for survival on military intervention by Britain and France. The United States realized this as well and made it clear that diplomatic recognition of the Confederacy meant war with the United States — and the cutting off of food shipments into Britain. The Confederates who had believed that "cotton is king" — that is, Britain had to support the Confederacy to obtain cotton — proved mistaken. The British had ample stocks to last over a year and were not about to go to war with the U.S. to try to get more cotton.[52][53] By late 1862 the cotton shortages caused severe unemployment and hardship in textile-producing areas of England such as Lancashire. However, abolitionist sentiment among English workers ran counter to this economic interest in Confederate victory.[54]
The Confederate government sent repeated delegations to Europe; historians give them low marks for their poor diplomacy.[55] James M. Mason went to London and John Slidell traveled to Paris, but neither were officially received. Each did succeed in holding unofficial private meetings with high British and French officials but neither secured official recognition for the Confederacy. Britain and the United States came dangerously close to war during the Trent Affair (when the U.S. Navy seized two Confederate agents traveling on a British ship in late 1861), and it seemed possible that the Confederacy would see its much desired recognition. When Lincoln released the two, however, tensions cooled, and in the end the episode did not aid the Confederate cause.
Throughout the early years of the war, British foreign secretary Lord Russell, Napoleon III, and, to a lesser extent, British Prime Minister Lord Palmerston, showed interest in the idea of recognition of the Confederacy, or at least of offering a mediation. Recognition meant certain war with the United States, and war would have meant loss of American grain, loss of exports to the United States, loss of huge investments in American securities, invasion of Canada, much higher taxes, many lives lost and a threat to British trade. Recognition was considered following the Second Battle of Bull Run when the British government was preparing to mediate in the conflict, but the Union victory at the Battle of Antietam and Lincoln's Emancipation Proclamation, combined with internal opposition, caused the government to back away.
No country appointed any diplomat officially to the Confederacy, but several maintained their consuls in the South whom they had appointed before the outbreak of war.[56] In 1861, Ernst Raven applied for approval as the Saxe-Coburg-Gotha consul, but he held citizenship of Texas[citation needed] and officials in Saxe-Coburg and Gotha made clear that its request did not imply or extend diplomatic recognition,[57] that country remaining a strong friend of the United States. In 1863, the Confederacy expelled all foreign consuls (all of them European diplomats) for advising their subjects to refuse to serve in the Confederate army[58].
No nation ever sent an ambassador or an official delegation to Richmond. However, they applied principles of international law that recognized the Union and Confederate sides as belligerents. Both Confederate and Union agents were allowed to work openly in British North America. In Hamilton, Bermuda a Confederate agent openly worked to help blockade runners. Some state governments in northern Mexico negotiated local agreements to cover trade on the Texas border.[59]
"Died of states' rights"
Historian Frank Lawrence Owsley argued that the Confederacy "died of states' rights."[60] According to Owsley, strong-willed governors and state legislatures in the South refused to give the central government the soldiers and money it needed because they feared that Richmond would encroach on the rights of the states. Georgia's governor Joseph Brown warned that he saw the signs of a deep-laid conspiracy on the part of Jefferson Davis to destroy states' rights and individual liberty. Brown declaimed: "Almost every act of usurpation of power, or of bad faith, has been conceived, brought forth and nurtured in secret session." He saw granting the Confederate government the power to draft soldiers as the "essence of military despotism."[61] In 1863 governor Pendleton Murrah of Texas insisted that his State needed Texas troops for self-defense (against Native Americans or against a threatened Union advance), and refused to send them East.[62] Zebulon Vance, the governor of North Carolina, had a reputation for hostility to Davis and to his demands. North Carolina showed intense opposition to conscription, resulting in very poor results for recruiting. Governor Vance's faith in states' rights drove him into a stubborn opposition.[63]
Historian George Rable wrote:
For Alexander Stephens, any accommodation would only weaken the republic, and he therefore had no choice but to break publicly with the Confederate administration and the president. In an extraordinary three-hour speech to the legislature on the evening of March 16 [1864], the vice-president carefully outlined his position. Allowing Davis to make "arbitrary arrests" and to draft state officials conferred on him more power than the English Parliament had ever bestowed on the king. History proved the dangers of such unchecked authority.
....The Confederate government intended to suppress the peace meetings in North Carolina, he warned, and "put a muzzle upon certain presses" (i.e., the Raleigh Standard) in order to control elections in that state.[64]
Echoing Patrick Henry's "give me liberty or give me death" Stephens warned the Southerners they should never view liberty as "subordinate to independence" because the cry of "independence first and liberty second" was a "fatal delusion". As Rable concludes, "For Stephens, the essence of patriotism, the heart of the Confederate cause, rested on an unyielding commitment to traditional rights. In his idealist vision of politics, military necessity, pragmatism, and compromise meant nothing".[65]
Despite political differences within the Confederacy, no political parties were formed. Historian William C. Cooper Jr. wrote that "at the birth of their new nation, Confederates, in the language of the Founding Fathers, denounced the legitimacy of parties. Anti-partyism became an article of political faith. Almost nobody, even Davis’s most fervent antagonists, advocated parties."[66] This lack of a functioning two party system, according to historian David M. Potter, caused "real and direct damage" to the Confederate war effort since it prevented the formulation of any effective alternatives to the Davis administration's policies in conducting the war.[67]
The survival of the Confederacy depended on a strong base of civilians and soldiers devoted to victory. The soldiers performed well, though increasing numbers deserted in the last year of fighting, and the Confederacy never succeeded in replacing casualties as the Union could. The civilians, although enthusiastic in 1861-62 seem to have lost faith in the nation's future by 1864, and instead looked to protect their homes and communities. As Rable explains, "As the Confederacy shrank, citizens' sense of the cause more than ever narrowed to their own states and communities. This contraction of civic vision was more than a crabbed libertarianism; it represented an increasingly widespread disillusionment with the Confederate experiment."[68]
Relations with the United States
During the four years of its existence, the Confederate States of America asserted its independence and appointed dozens of diplomatic agents abroad. The United States government, by contrast, regarded the Southern states as states in rebellion and refused any formal recognition of their status. Thus, U.S. Secretary of State William H. Seward issued formal instructions to Charles Francis Adams, the newly-appointed minister to Great Britain:
You will indulge in no expressions of harshness or disrespect, or even impatience concerning the seceding States, their agents, or their people. But you will, on the contrary, all the while remember that those States are now, as they always heretofore have been, and, notwithstanding their temporary self-delusion, they must always continue to be, equal and honored members of this Federal Union, and that their citizens throughout all political misunderstandings and alienations, still are and always must be our kindred and countrymen.[69]
However, if the British seemed inclined to recognize the Confederacy, or even waver in that regard, they would receive a sharp warning, with a strong hint of war:
[if Britain is] tolerating the application of the so-called seceding States, or wavering about it, you will not leave them to suppose for a moment that they can grant that application and remain friends with the United States. You may even assure them promptly, in that case, that if they determine to recognize, they may at the same time prepare to enter into alliance with the enemies of this republic.[70]
The Confederate Congress responded to the Battle of Fort Sumter by formally declaring war on the United States in May 1861 — calling it "The War between the Confederate States of America and the United States of America".[71] The Union government never declared war, but conducted its military efforts under a proclamation of blockade and rebellion. After the war, the U.S. Congress readmitted representation from the southern states. Mid-war negotiations between the two sides occurred without formal political recognition, though the laws of war governed military relationships.
Four years after the war, in 1869, the majority of the United States Supreme Court in Texas v. White opined that Texas' secession was unconstitutional and legally null. The court's opinion was authored by Chief Justice Salmon P. Chase. However, since the actual issue of secession was not the original before the court, it has since been debated as to whether or not the final ruling on the matter meets the standards of stare decisis on the issue of secession. Some legal scholars have argued the majority opinion on the issue was obiter dictum, while others maintain it was ratio decidendi.
The court did allow some possibility of separation from the Union "through revolution or through consent of the States."[72][73] Jefferson Davis, former President of the Confederacy, and Alexander Stephens, its former Vice-President, both penned arguments in favor of secession's legality, most notably Davis' The Rise and Fall of the Confederate Government.
Confederate flags
 |
 |
 |

|
| 1st National Flag "Stars and Bars" |
2nd National Flag "Stainless Banner" |
3rd National Flag "Blood Stained Banner" |
CSA Naval Jack 1861–1863 |
 |
 |
 |

|
| CSA Naval Jack 1863–1865 |
Battle Flag "Southern Cross" |
"Bonnie Blue Flag" Unofficial Southern Flag |
"Confederate Flag" Rectangular Battle Flag Used by some Confederate Army units. |
The first official flag of the Confederate States of America, called the "Stars and Bars", originally had seven stars, representing the first seven states that initially formed the Confederacy, and as more states seceded, more stars were added. It sometimes proved difficult to distinguish the Stars and Bars from the Union flag under battle conditions, so the flag was changed to the "Stainless Banner". The Stainless Banner, known as the "Southern Cross", became the symbol more commonly used in military operations. The Southern Cross had 13 stars, adding the four states that joined the Confederacy after Fort Sumter, and the two divided states of Kentucky and Missouri. Due to similarities between the "Stainless Banner" and a white flag, a red stripe was appended vertically to the end of the flag, creating the third of the national flags.
Because of its depiction in 20th-century[citation needed] popular media, many people associate the rectangular battle flag used by military units such as the Army of Tennessee and the Fourth Florida Infantry Volunteer Regiment with the Confederacy, though most Confederate Battle Flags were square.
Geography
The Confederate States of America claimed a total of 2,919 miles (4,698 km) of coastline, thus a large part of its territory lay on the seacoast with level and often sandy or marshy ground. Most of the interior portion consisted of arable farmland, though much was also hilly and mountainous, and the far western territories were deserts. The lower reaches of the Mississippi River bisected the country, with the western half often referred to as the Trans-Mississippi. The highest point (excluding Arizona and New Mexico) was Guadalupe Peak in Texas at 8,750 feet (2,667 m).
Climate
Much of the area claimed by the Confederate States of America had a humid subtropical climate with mild winters and long, hot, humid summers. The climate and terrain varied from vast swamps (such as those in Florida and Louisiana) to semi-arid steppes and arid deserts west of longitude 96 degrees west. The subtropical climate made winters mild but allowed infectious diseases to flourish. Consequently, on both sides more soldiers died from disease than were killed in combat.[74]
River system
In peacetime, the vast system of navigable rivers allowed for cheap and easy transportation of farm products. The railroad system, built as a supplement, tied plantation areas to the nearest river or seaport. The vast geography of the Confederacy made logistics difficult for the Union, and the Union armies assigned many of their soldiers to garrison captured areas and to protect rail lines. Nevertheless, the Union Navy had seized most of the navigable rivers by 1862, making its own logistics easy and Confederate movements difficult. After the fall of Vicksburg in July 1863, it became impossible for Confederate units to cross the Mississippi: Union gunboats constantly patrolled the river. The South thus lost the use of its western regions.
Railroad system
The outbreak of war had a depressing effect on the economic fortunes of the railroad system in Confederate territory. The hoarding of the cotton crop in an attempt to entice European intervention left railroads bereft of their main source of income.[75] Many had to lay off employees, and in particular, let go skilled technicians and engineers.[76] For the early years of the war, the Confederate government had a hands-off approach to the railroads. Only in mid-1863 did the Confederate government initiate an overall policy, and it was confined solely to aiding the war effort.[77] With the legislation of impressment the same year, railroads and their rolling stock came under the de facto control of the military.
In the last year before the end of the war, the Confederate railroad system stood permanently on the verge of collapse. There was no new equipment and raids on both sides systematically destroyed key bridges, as well as locomotives and freight cars. Spare parts were cannibalized; feeder lines were torn up to get replacement rails for trunk lines, and the heavy use of rolling stock wore them out.[78]
Rural/urban configuration
The area claimed by the Confederate States of America consisted overwhelmingly of rural land. Few urban areas had populations of more than 1,000 — the typical county seat had a population of fewer than 500 people. Cities were rare. Of the twenty largest U.S. cities in the 1860 census, only New Orleans lay in Confederate territory[79] — and the Union captured New Orleans in 1862. Only 13 Confederate-controlled cities ranked among the top 100 U.S. cities in 1860, most of them ports whose economic activities vanished or suffered severely in the Union blockade. The population of Richmond swelled after it became the national capital, reaching an estimated 128,000 in 1864[80]. Other large Southern cities (Baltimore, St. Louis, Louisville, and Washington, D.C as well as Wheeling, West Virginia, and Alexandria, Virginia) never came under the control of the Confederate government.
The cities of the Confederacy included most prominently in order of size of population:
| # | City | 1860 population | 1860 U.S. rank | Return to U.S. control |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | New Orleans, Louisiana | 168,675 | 6 | 1862 |
| 2. | Charleston, South Carolina | 40,522 | 22 | 1865 |
| 3. | Richmond, Virginia | 37,910 | 25 | 1865 |
| 4. | Mobile, Alabama | 29,258 | 27 | 1865 |
| 5. | Memphis, Tennessee | 22,623 | 38 | 1862 |
| 6. | Savannah, Georgia | 22,292 | 41 | 1864 |
| 7. | Petersburg, Virginia | 18,266 | 50 | 1865 |
| 8. | Nashville, Tennessee | 16,988 | 54 | 1862 |
| 9. | Norfolk, Virginia | 14,620 | 61 | 1862 |
| 10. | Augusta, Georgia | 12,493 | 77 | 1865 |
| 11. | Columbus, Georgia | 9,621 | 97 | 1865 |
| 12. | Atlanta, Georgia | 9,554 | 99 | 1864 |
| 13. | Wilmington, North Carolina | 9,553 | 100 | 1865 |
(See also Atlanta in the Civil War, Charleston, South Carolina, in the Civil War, Nashville in the Civil War, New Orleans in the Civil War, Wilmington, North Carolina, in the American Civil War, and Richmond in the Civil War).
Economy
The Confederacy started its existence as an agrarian economy with exports, to a world market, of cotton, and, to a lesser extent, tobacco and sugarcane. Local food production included grains, hogs, cattle, and gardens. The 11 states produced $155 million in manufactured goods in 1860, chiefly from local grist-mills, and lumber, processed tobacco, cotton goods and naval stores such as turpentine. By the 1830s, the 11 states produced more cotton than all of the other countries in the world combined.
The CSA adopted a low tariff of 15 per cent, but imposed it on all imports from other countries, including the Union states.[81] The tariff mattered little; the Union blockade minimized commercial traffic through the Confederacy's ports, and very few people paid taxes on goods smuggled from the Union states. The government collected about $3.5 million in tariff revenue from the start of their war against the Union to late 1864. The lack of adequate financial resources led the Confederacy to finance the war through printing money, which led to high inflation. The requirements of its military encouraged the Confederate government to take a dirigiste-style approach to industrialization.[82] But such efforts faced setbacks: Union raids and in particular Sherman's scorched-earth campaigning destroyed much economic infrastructure.[83]
Demographics
The United States Census of 1860[84] gives a picture of the overall 1860 population of the areas that joined the Confederacy. Note that population-numbers exclude non-assimilated Indian tribes.
| State |
Total Population |
Total # of Slaves |
Total # of Households |
Total Free Population |
Total #[85] Slaveholders |
% of Free Population Owning Slaves[86] |
Slaves as % of Population |
Total free colored |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alabama | 964,201 | 435,080 | 96,603 | 529,121 | 33,730 | 6% | 45% | 2,690 |
| Arkansas | 435,450 | 111,115 | 57,244 | 324,335 | 11,481 | 4% | 26% | 144 |
| Florida | 140,424 | 61,745 | 15,090 | 78,679 | 5,152 | 7% | 44% | 932 |
| Georgia | 1,057,286 | 462,198 | 109,919 | 595,088 | 41,084 | 7% | 44% | 3,500 |
| Louisiana | 708,002 | 331,726 | 74,725 | 376,276 | 22,033 | 6% | 47% | 18,647 |
| Mississippi | 791,305 | 436,631 | 63,015 | 354,674 | 30,943 | 9% | 55% | 773 |
| North Carolina | 992,622 | 331,059 | 125,090 | 661,563 | 34,658 | 5% | 33% | 30,463 |
| South Carolina | 703,708 | 402,406 | 58,642 | 301,302 | 26,701 | 9% | 57% | 9,914 |
| Tennessee | 1,109,801 | 275,719 | 149,335 | 834,082 | 36,844 | 4% | 25% | 7,300 |
| Texas | 604,215 | 182,566 | 76,781 | 421,649 | 21,878 | 5% | 30% | 355 |
| Virginia | 1,596,318 | 490,865 | 201,523 | 1,105,453 | 52,128 | 5% | 31% | 58,042 |
| Total | 9,103,332 | 3,521,110 | 1,027,967 | 5,582,222 | 316,632 | 6% | 39% | 132,760 |
(Figures for Virginia include the future West Virginia.)
| Age structure | 0–14 years | 15–59 years | 60 years and over | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| White males | 43% | 52% | 4% | |
| White females | 44% | 52% | 4% | |
| Male slaves | 44% | 51% | 4% | |
| Female slaves | 45% | 51% | 3% | |
| Free black males | 45% | 50% | 5% | |
| Free black females | 40% | 54% | 6% | |
| Total population | 44% | 52% | 4% |
(Rows may not total to 100% due to rounding)
In 1860 the areas that later formed the eleven Confederate States (and including the future West Virginia) had 132,760 (1.46%) free blacks. Males made up 49.2% of the total population and females 50.8% (whites: 48.60% male, 51.40% female; slaves: 50.15% male, 49.85% female; free blacks: 47.43% male, 52.57% female).[87]
Armed forces

The military armed forces of the Confederacy comprised three branches:
The Confederate military leadership included many veterans from the United States Army and United States Navy who had resigned their Federal commissions and had won appointment to senior positions in the Confederate armed forces. Many had served in the Mexican-American War (including Robert E. Lee and Jefferson Davis), but some such as Leonidas Polk (who had attended West Point but did not graduate) had little or no experience. The Confederate officer corps consisted of men from both slave-owning and non-slave-owning families. The Confederacy appointed junior and field grade officers by election from the enlisted ranks. Although no Army service academy was established for the Confederacy, many colleges of the South (such as The Citadel and Virginia Military Institute) maintained cadet corps that were seen as a training ground for Confederate military leadership. A naval academy was established at Drewry’s Bluff, Virginia[88] in 1863, but no midshipmen graduated before the Confederacy's end.
The soldiers of the Confederate armed forces consisted mainly of white males aged between sixteen and twenty-eight.[citation needed] The Confederacy adopted conscription in 1862. Many thousands of slaves served as laborers, cooks, and pioneers. Some freed blacks and men of color served in local state militia units of the Confederacy, primarily in Louisiana and South Carolina, but their officers deployed them for "local defense, not combat."[89] Depleted by casualties and desertions, the military suffered chronic manpower shortages. In the spring of 1865, the Confederate Congress, influenced by the public support by General Lee, approved the recruitment of black infantry units. Contrary to Lee’s and Davis’s recommendations, the Congress refused “to guarantee the freedom of black volunteers.” No more than two hundred black troops were ever raised.[90]
Military leaders
Military leaders of the Confederacy (with their state or country of birth and highest rank)[91] included:

- Robert E. Lee (Virginia) - General and General-in-Chief (1865)
- Albert Sidney Johnston (Kentucky) - General
- Joseph E. Johnston (Virginia) - General
- Braxton Bragg (North Carolina) - General
- P.G.T. Beauregard (Louisiana) - General
- Richard S. Ewell (Virginia) - Lieutenant General
- Samuel Cooper (New York) - General (Adjutant General and highest ranking general in the Army); not in combat
- James Longstreet (South Carolina) - Lieutenant General
- Thomas J. "Stonewall" Jackson (Virginia now West Virginia)- Lieutenant General
- John Hunt Morgan (Kentucky) - Brigadier General
- A.P. Hill (Virginia) - Lieutenant General
- John Bell Hood (Kentucky) - Lieutenant General (temporary General)
- Wade Hampton III (South Carolina) - Lieutenant General
- Nathan Bedford Forrest (Tennessee) - Lieutenant General
- John Singleton Mosby, the "Grey Ghost of the Confederacy" (Virginia) - Colonel
- J.E.B. Stuart (Virginia) - Major General
- Edward Porter Alexander (Georgia) - Brigadier General
- Franklin Buchanan (Maryland) - Admiral
- Raphael Semmes (Maryland) - Rear Admiral
- Stand Watie (Georgia) - Brigadier General (last to surrender)
- Leonidas Polk (North Carolina) - Lieutenant General
- Sterling Price (Virginia) - Major General
- Jubal Anderson Early (Virginia) - Lieutenant General
- Richard Taylor (Kentucky) - Lieutenant General (Son of U.S. President Zachary Taylor)
- Lloyd J. Beall (South Carolina) - Colonel - Commandant of the Confederate States Marine Corps
- Stephen Dodson Ramseur (North Carolina) Major General
- Camille Armand Jules Marie, Prince de Polignac (France) Major General
- John Austin Wharton (Tennessee) Major General
- Thomas L. Rosser (Virginia) Major General
- Patrick Cleburne (Ireland) Major General
- William N. Pendleton (Virginia) Brigadier General
Member States of the Confederate States
| Member State | Flag | Ordinance of Secession | Date of Admission | Under predominant Union control |
Readmitted to representation in Congress |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| South Carolina | Dec. 20, 1860 | Feb. 8, 1861 | 1865 | July 9, 1868 | |
| Mississippi | Jan. 9, 1861 | Feb. 8, 1861 | 1863 | Feb. 23, 1870 | |
| Florida | Jan. 10, 1861 | Feb. 8, 1861 | 1865 | June 25, 1868 | |
| Alabama | Jan. 11, 1861 | Feb. 8, 1861 | 1865 | July 13, 1868 | |
| Georgia | Jan. 19, 1861 | Feb. 8, 1861 | 1865 | 1st Date July 21, 1868; 2nd Date July 15, 1870 | |
| Louisiana | Jan. 26, 1861 | Feb. 8, 1861 | 1863 | July 9, 1868 | |
| Texas | Feb. 1, 1861 | March 2, 1861 | 1865 | March 30, 1870 | |
| Virginia | April 17, 1861 | May 7, 1861 | 1865; (1862/63 for West Virginia) |
Jan. 26, 1870 | |
| Arkansas | May 6, 1861 | May 18, 1861 | 1864 | June 22, 1868 | |
| North Carolina | May 20, 1861 | May 21, 1861 | 1865 | July 4, 1868 | |
| Tennessee | June 8, 1861 | July 2, 1861 | 1863 | July 24, 1866 | |
| Missouri (exiled government) | Oct. 31, 1861 | Nov. 28, 1861 | 1861 | Unionist govt. appointed by Missouri Constitutional Convention 1861 | |
| Kentucky (Russellville Convention) | Nov. 20, 1861 | Dec. 10, 1861 | 1861 | Elected Union and unelected rump Confederate governments from 1861 |
Member Territories of the Confederate States
See also
- Conclusion of the American Civil War
- Confederados
- Confederate colonies
- Confederate war finance
- Confederate Patent Office
- Confederate States of America dollar
- Flags of the Confederate States of America
- Golden Circle (Slavery)
- History of the Southern United States
- Military of the Confederate States of America
- Origins of the American Civil War
- Seal of the Confederate States of America
- Southern United States
- Stamps and postal history of the Confederate States
References
- Bowman, John S. (ed), The Civil War Almanac, New York: Bison Books, 1983
- Eicher, John H., & Eicher, David J., Civil War High Commands, Stanford University Press, 2001, ISBN 0-8047-3641-3
- Wilentz, Sean, The Rise of American Democracy, W.W. Norton & Co., ISBN 0-393-32921-6
Bibliography
- Bonner, Robert E., “Proslavery Extremism Goes to War: The Counterrevolutionary Confederacy and Reactionary Militarism,” Modern Intellectual History, 6 (Aug. 2009), 261–85.
- Cooper, William J. Jr. Jefferson Davis, American. (2000)
- Coulter, E. Merton The Confederate States of America, 1861-1865, 1950
- Crofts, Daniel W. Reluctant Confederates: Upper South Unionists in the Secession Crisis. (1989) ISBN 0-8078-1809-7.
- Current, Richard N., ed. Encyclopedia of the Confederacy (4 vol), 1993. 1900 pages, articles by scholars.
- William C. Davis (2003). Look Away! A History of the Confederate States of America. New York: Free Press. ISBN 0-684-86585-8.
- Davis, William C. A Government of Our Own. (1994) ISBN 0-8071-2177-0
- Eaton, Clement A History of the Southern Confederacy, 1954
- Eckenrode, H. J., Jefferson Davis: President of the South, 1923
- Gallgher, Gary W., The Confederate War, 1999
- Faust, Patricia L. ed, Historical Times Illustrated Encyclopedia of the Civil War, 1986
- Gallagher, Gary W., “Disaffection, Persistence, and Nation: Some Directions in Recent Scholarship on the Confederacy,” Civil War History, 55 (Sept. 2009), 329–53. Historiography
- Gallagher, Gary W. The Confederate War (1997) ISBN 0-674-16055-X
- Heidler, David S., et al. Encyclopedia of the American Civil War: A Political, Social, and Military History, 2002 2400 pages (ISBN 0-393-04758-X)
- Levine, Bruce Confederate Emancipation. (2006)
- McPherson, James M. Battle Cry of Freedom. (1988), standard military history of te war; Pulitzer Prize
- Neely, Mark E., Jr., Confederate Bastille: Jefferson Davis and Civil Liberties (1993)
- Neely, Mark E. Jr. Southern Rights: Political Prisoners and the Myth of Confederate Constitutionalism. (1999) ISBN 0-8139-1894-4
- Rable, George C., The Confederate Republic: A Revolution against Politics, 1994
- Riggs, David F. "Robert Young Conrad and the Ordeal of Secession."The Virginia Magazine of History and Biography, Vol. 86, No. 3 (July 1978), pp. 259-274.
- Roland, Charles P. The Confederacy, (1960) brief survey
- Rubin, Sarah Anne A Shattered Nation: The Rise & Fall of the Confederacy 1861-1868 (2005)
- Thomas, Emory M. Confederate Nation: 1861-1865, 1979 Standard political-economic-social history
- Wakelyn, Jon L. Biographical Dictionary of the Confederacy Greenwood Press ISBN 0-8371-6124-X
- Weigley, Russell F. A Great Civil War: A Military and Political History, 1861-1865. (2000) ISBN 0-253-33738-0
- Woodworth, Steven E. ed. The American Civil War: A Handbook of Literature and Research, 1996 750 pages of historiography and bibliography
State studies
- Smith, Timothy B. Mississippi in the Civil War: The Home Front (University Press of Mississippi, 2010) 265 pages; Examines the declining morale of Mississippians as they witnessed extensive destruction and came to see victory as increasingly improbable
Economic and social history
see Economy of the Confederate States of America
- Black, Robert C., III. The Railroads of the Confederacy, 1988.
- Clinton, Catherine, and Silber, Nina, eds. Divided Houses: Gender and the Civil War, 1992
- Dabney, Virginius Richmond: The Story of a City. Charlottesville: The University of Virginia Press, 1990 ISBN 0-8139-1274-1
- Faust, Drew Gilpin Mothers of Invention: Women of the Slaveholding South in the American Civil War, 1996
- Grimsley, Mark The Hard Hand of War: Union Military Policy toward Southern Civilians, 1861-1865, 1995
- Lentz, Perry Carlton Our Missing Epic: A Study in the Novels about the American Civil War, 1970
- Massey, Mary Elizabeth Bonnet Brigades: American Women and the Civil War, 1966
- Massey, Mary Elizabeth Refugee Life in the Confederacy, 1964
- Rable, George C. Civil Wars: Women and the Crisis of Southern Nationalism, 1989
- Ramsdell, Charles. Behind the Lines in the Southern Confederacy, 1994.
- Riggs, David F. "Robert Young Conrad and the Ordeal of Secession."The Virginia Magazine of History and Biography, Vol. 86, No. 3 (July 1978), pp. 259-274.
- Roark, James L. Masters without Slaves: Southern Planters in the Civil War and Reconstruction, 1977.
- Rubin, Anne Sarah. A Shattered Nation: The Rise and Fall of the Confederacy, 1861-1868, 2005 A cultural study of Confederates' self images
- Thomas, Emory M. The Confederacy as a Revolutionary Experience, 1992
- Wallenstein, Peter, and Bertram Wyatt-Brown, eds. Virginia's Civil War (2008) excerpt and text search
- Wiley, Bell Irwin Confederate Women, 1975
- Wiley, Bell Irwin The Plain People of the Confederacy, 1944
- Woods, James M. Rebellion and Realignment:Arkansas's Road to Secession. (1987)
- Woodward, C. Vann, ed. Mary Chesnut's Civil War, 1981
Politics
- Alexander, Thomas B., and Beringer, Richard E. The Anatomy of the Confederate Congress: A Study of the Influences of Member Characteristics on Legislative Voting Behavior, 1861-1865, (1972)
- Boritt, Gabor S., et al., Why the Confederacy Lost, (1992)
- Cooper, William J, Jefferson Davis, American (2000), standard biography
- Downing, David C. A South Divided: Portraits of Dissent in the Confederacy. (2007). ISBN 978-1-58182-587-9
- Faust, Drew Gilpin. The Creation of Confederate Nationalism: Ideology and Identity in the Civil War South. (1988)
- Rembert, W. Patrick Jefferson Davis and His Cabinet (1944).
- Williams, William M. Justice in Grey: A History of the Judicial System of the Confederate States of America (1941)
- Yearns, Wilfred Buck The Confederate Congress (1960)
Diplomacy
- Blumenthal, Henry. "Confederate Diplomacy: Popular Notions and International Realities," Journal of Southern History, Vol. 32, No. 2 (May, 1966), pp. 151–171 in JSTOR
- Daddysman, James W. The Matamoros Trade: Confederate Commerce, Diplomacy, and Intrigue. (1984).
- Hubbard, Charles M. The Burden of Confederate Diplomacy (1998)
- Jones, Howard. Blue and Gray Diplomacy: A History of Union and Confederate Foreign Relations (2009) excerpt and text search
- Merli, Frank J. The Alabama, British Neutrality, and the American Civil War (2004). 225 pp.
- Owsley, Frank. King Cotton Diplomacy: Foreign Relations of the Confederate States of America (2nd ed. 1959)
Primary sources
- Carter, Susan B., ed. The Historical Statistics of the United States: Millennial Edition (5 vols), 2006
- Davis, Jefferson, The Rise and Fall of the Confederate Government (2 vols), 1881.
- Harwell, Richard B., The Confederate Reader (1957)
- Jones, John B. A Rebel War Clerk's Diary at the Confederate States Capital, edited by Howard Swiggert, [1935] 1993. 2 vols.
- Richardson, James D., ed. A Compilation of the Messages and Papers of the Confederacy, Including the Diplomatic Correspondence 1861-1865, 2 volumes, 1906.
- Yearns, W. Buck and Barret, John G.,eds. North Carolina Civil War Documentary, 1980.
- Confederate official government documents major online collection of complete texts in HTML format, from University of North Carolina
- Journal of the Congress of the Confederate States of America, 1861-1865 (7 vols), 1904. Available online at the Library of Congress[92]
Notes
- ^ Gallagher p. 157. Gallagher notes, "The Confederacy capitulated in the spring of 1865 because northern armies had demonstrated their ability to crush organized southern military resistance. Soldiers laid down their arms at Appomattox and Durham Station when brought to bay by imposing Federal forces under the resolute command of U. S. Grant and William Tecumseh Sherman. Civilians who had maintained faith in their defenders despite material hardship and social disruption similarly recognized that the end had come.... [M]ost Confederates knew that as a people they had expended blood and treasure in profusion before ultimately collapsing in the face of northern power sternly applied."
- ^ "Preventing Diplomatic Recognition of the Confederacy, 1861-1865". U.S. Department of State.
- ^
McPherson, James M. (2007). This mighty scourge: perspectives on the Civil War. Oxford University Press US. p. 65. ISBN 0195313666.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|isbn13=ignored (help) - ^ The very last Confederate surrender came on November 6, 1865, aboard the CSS Shenandoah
- ^ The text of South Carolina's Ordinance of Secession.
- ^ South Carolina documents including signatories
- ^ The text of Mississippi's Ordinance of Secession.
- ^ The text of Florida's Ordinance of Secession.
- ^ The text of Alabama's Ordinance of Secession.
- ^ The text of Georgia's Ordinance of Secession.
- ^ The text of Louisiana's Ordinance of Secession.
- ^ The text of Texas' Ordinance of Secession.
- ^ Some southern unionists blamed Lincoln's call for troops as the precipitating event for the second wave of secessions. Historian James McPherson argues that such claims have "a self-serving quality" and regards them as misleading. He wrote:
As the telegraph chattered reports of the attack on Sumter April 12 and its surrender next day, huge crowds poured into the streets of Richmond, Raleigh, Nashville, and other upper South cities to celebrate this victory over the Yankees. These crowds waved Confederate flags and cheered the glorious cause of southern independence. They demanded that their own states join the cause. Scores of demonstrations took place from April 12 to 14, before Lincoln issued his call for troops. Many conditional unionists were swept along by this powerful tide of southern nationalism; others were cowed into silence.
— McPherson p. 278Historian Daniel W. Crofts disagrees with McPherson. Crofts wrote:
Crofts further noted that,The bombardment of Fort Sumter, by itself, did not destroy Unionist majorities in the upper South. Because only three days elapsed before Lincoln issued the proclamation, the two events viewed retrospectively, appear almost simultaneous. Nevertheless, close examination of contemporary evidence ... shows that the proclamation had a far more decisive impact.
— Crofts p. 336Many concluded ... that Lincoln had deliberately chosen 'to drive off all the Slave states, in order to make war on them and annihilate slavery.'
— Crofts pp. 337-338, quoting the North Carolina politician Jonathan Worth (1802-1869). - ^ The text of Virginia's Ordinance of Secession. Virginia seceded in two steps, first by secession convention vote on April 17, 1861, and then by ratification of this by a popular vote conducted on May 23, 1861. A Unionist Restored government of Virginia also operated. Virginia did not turn over its military to the Confederate States until June 8, 1861. The Commonwealth of Virginia ratified the Constitution of the Confederate States on June 19, 1861.
- ^ The text of Arkansas' Ordinance of Secession.
- ^ The text of Tennessee's Ordinance of Secession.
- ^ The Tennessee legislature ratified an agreement to enter a military league with the Confederate States on May 7, 1861. Tennessee voters approved the agreement on June 8, 1861.
- ^ The text of North Carolina's Ordinance of Secession.
- ^ Weigley (2000) p. 43
- ^ Missouri's Ordinance of Secession.
- ^ White (2009) p. 416
- ^ R. Curry, "A House Divided".
- ^ Weigley, Russell Frank, A Great Civil War, W.W. Norton, 2003, pg. 55
- ^ ""Marx and Engels on the American Civil War", Army of the Cumberland and George H. Thomas source page.
- ^ "Background of the Confederate States Constitution", The American Civil War Home Page.
- ^ History of Arizona vol. 2 by Thomas Edwin Farish (1915) [1].
- ^ Bowman, p. 48.
- ^ University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Documenting the American South collection, Confederate States of America War Department, Communication From the Secretary of War, February 4th, 1863.
- ^ This Day in History, July 12, 1861 Confederacy signs treaties with Choctaw and Chickasaw Tribes.
- ^ Declaration by the People of the Cherokee Nation of the Causes Which Have Impelled Them to Unite Their Fortunes With Those of the Confederate States of America.
- ^ Faust, Drew Gilpin (1988). The creation of Confederate nationalism : ideology and identity in the Civil War South. Baton Rouge: Louisiana State University Press. p. 59. ISBN 0807115096.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameters:|origmonth=,|chapterurl=,|origdate=, and|month=(help) - ^ McPherson pp. 232-233.
- ^ The text of the Declaration of the Immediate Causes Which Induce and Justify the Secession of South Carolina from the Federal Union.
- ^ The text of A Declaration of the Immediate Causes which Induce and Justify the Secession of the State of Mississippi from the Federal Union.
- ^ The text of Georgia's secession declaration.
- ^ The text of A Declaration of the Causes which Impel the State of Texas to Secede from the Federal Union.
- ^ McPherson pg. 244. The text of Alexander Stephens' "Cornerstone Speech".
- ^ Levine (1992) p. 109. Stampp (1956) p. 157.
- ^ Levine (1992) p. 113.
- ^ Levine (1992) p. 112.
- ^ Stephens, Alexander H. (1870). A Constitutional View of the Late War Between the States (PDF). Vol. 2. p. 36.
I maintain that it was inaugurated and begun, though no blow had been struck, when the hostile fleet, styled the 'Relief Squadron,' with eleven ships, carrying two hundred and eighty-five guns and two thousand four hundred men, was sent out from New York and Norfolk, with orders from the authorities at Washington, to reinforce Fort Sumter peaceably, if permitted 'but forcibly if they must'...
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameters:|laydate=,|coauthors=,|nopp=,|separator=,|laysummary=,|chapterurl=,|month=, and|lastauthoramp=(help) - ^ Lincoln's proclamation calling for troops from the remaining states (bottom of page); Department of War details to States (top).
- ^ The crew of the CSS Shenandoah hauled down the last Confederate flag at Liverpool in the UK on November 6, 1865. John Baldwin (Author), Ron Powers (Author). Last Flag Down: The Epic Journey of the Last Confederate Warship (May 6, 2008 ed.). Three Rivers Press. p. 368. ISBN 0307236560.
{{cite book}}:|last=has generic name (help) - ^ Davis p. 248.
- ^ "Legal Materials on the Confederate States of America in the Schaffer Law Library", Albany Law School.
- ^ a b c [Moise, E. Warren, Rebellion in the Temple of Justice (iUniverse 2003)]
- ^ Records of District Courts of the United States, National Archives.
- ^ Neely (1999) p.1
- ^ Neely (1993) pp. 11, 16.
- ^ Richard Burdekin and Farrokh Langdana, "War Finance in the Southern Confederacy, 1861-1865", Explorations in Economic History, Vol 30, No 3, July 1993
- ^ The SS Republic Shipwreck Project: the Coin Collection, p.23
- ^ Blumenthal (1966)
- ^ Stanley Lebergott Why the South Lost: Commercial Purpose in the Confederacy, 1861-1865 The Journal of American History, Vol. 70, No. 1. (June, 1983), p. 61.
- ^ See the text of the inscription on the Abraham Lincoln statue in Manchester.
- ^ Blumenthal (1966); Jones (2009); Owsley (1959)
- ^ In November 1863, Confederate diplomat A. Dudley Mann met Pope Pius IX and received a letter addressed "to the Illustrious and Honorable Jefferson Davis, President of the Confederate States of America". Mann, in his dispatch to Richmond, interpreted the letter as "a positive recognition of our Government". Confederate Secretary of State Judah P. Benjamin, however, interpreted it as "a mere inferential recognition, unconnected with political action or the regular establishment of diplomatic relations" and thus did not assign it the weight of formal recognition. See Official Records of the Union and Confederate Navies in the War of the Rebellion, p. 1015.
- ^ Berwanger, Eugene H (1994). The British Foreign Service and the American Civil War. U of Kentucky Press. p. 111.
- ^ Alexander DeConde, ed. Encyclopedia of American foreign policy (2001) vol 1 p 202
- ^ Wise, Stephen R., Lifeline of the Confederacy: Blockade Running During the Civil War, University of South Carolina Press, 1991, ISBN 0872497992, 9780872497993, p. 86.
- ^ Frank L. Owsley, State Rights in the Confederacy (Chicago, 1925).
- ^ Rable (1994) 257; however Wallace Hettle in The Peculiar Democracy: Southern Democrats in Peace and Civil War (2001) p. 158 says Owsley's "famous thesis... is overstated."
- ^ John Moretta; "Pendleton Murrah and States Rights in Civil War Texas," Civil War History, Vol. 45, 1999.
- ^ Albert Burton Moore, Conscription and Conflict in the Confederacy. (1924) p. 295.
- ^ Rable (1994) p. 258
- ^ Rable (1994) p. 259.
- ^ Cooper (2000) p. 462. Rable (1994) pp. 2-3. Rable wrote, "But despite heated arguments and no little friction between the competing political cultures of unity and liberty, antiparty and broader fears about politics in general shaped civic life. These beliefs could obviously not eliminate partisanship or prevent Confederates from holding on to and exploiting old political prejudices. Indeed, some states, notably Georgia and North Carolina, remained political tinderboxes throughout the war. Even the most bitter foes of the Confederate government, however, refused to form an opposition party, and the Georgia dissidents, to cite the most prominent example, avoided many traditional political activities. Only in North Carolina did there develop anything resembling a party system, and there the central values of the Confederacy's two political cultures had a far more powerful influence on political debate than did organizational maneuvering."
- ^ David Herbert Donald, , ed. Why the North Won the Civil War. (1996) p.112-113. Potter wrote in his contribution to this book, "Where parties do not exist, criticism of the administration is likely to remain purely an individual matter; therefore the tone of the criticism is likely to be negative, carping, and petty, as it certainly was in the Confederacy. But where there are parties, the opposition group is strongly impelled to formulate real alternative policies and to press for the adoption of these policies on a constructive basis. ... But the absence of a two-party system meant the absence of any available alternative leadership, and the protest votes which were cast in the [1863 Confederate mid-term] election became more expressions of futile and frustrated dissatisfaction rather than implements of a decision to adopt new and different policies for the Confederacy."
- ^ Rable (1994) p. 265.
- ^ William Seward to Charles Francis Adams, April 10, 1861 in Marion Mills Miller, Ed. Life And Works Of Abraham Lincoln (1907) Vol 6.
- ^ William Seward to Charles Francis Adams, April 10, 1861, in Marion Mills Miller (ed): Life And Works Of Abraham Lincoln (1907) Vol 6.
- ^ Moore, Frank, The Rebellion Record, Volume I, G.P. Putnam, 1861, Doc. 140, pp. 195-197.
- ^ Aleksandar Pavković, Peter Radan, Creating New States: Theory and Practice of Secession, p. 222, Ashgate Publishing, Ltd., 2007.
- ^ Texas v. White, 74 U.S. 700 (1868) at Cornell University Law School Supreme Court collection.
- ^ Two-thirds of soldiers' deaths occurred due to disease. Nofi, Al (2001-06-13). "Statistics on the War's Costs". Louisiana State University. Retrieved 2008-09-08.
- ^ Charles W. Ramsdell, "The Confederate Government and the Railroads, American Historical Review, Vol. 22, No. 4 (July, 1917), p. 795.
- ^ Charles W. Ramsdell The Confederate Government and the Railroads The American Historical Review, Vol. 22, No. 4 (July, 1917), p. 795.
- ^ Mary Elizabeth Massey. Ersatz in the Confederacy (1952) p. 128.
- ^ Ramsdell, "The Confederate Government and the Railroads," pp. 809-810.
- ^ U.S. Bureau of the Census, Population of the 100 Largest Urban Places: 1860, Internet Release date: June 15, 1998
- ^ Dabney 1990 p. 182
- ^ Tariff of the Confederate States of America, May 21, 1861.
- ^
Ian Drury, ed. (2003) [2000]. "American Civil War: Naval & Economic Warfare". History of war. London: Times Books. p. 138. ISBN 0-00-716458 0.
The Confederacy underwent a government-led industrial revolution during the war, but its economy was slowly strangled.
{{cite book}}:|first1=missing|last1=(help); Cite has empty unknown parameters:|laydate=,|coauthors=,|nopp=,|separator=,|chapterurl=,|laysummary=,|month=, and|lastauthoramp=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^
Ian Drury, ed. (2003) [2000]. "American Civil War: Naval & Economic Warfare". History of war. London: Times Books. p. 138. ISBN 0-00-716458 0.
Like other belligerents unable to occupy enemy territory effectively, the US army resorted to raids. The most spectacular was Sherman's march through Georgia to the sea. This not only inflicted economic damage on the areas traversed, but disrupted the railways that supplied Confederate armies.
{{cite book}}:|first1=missing|last1=(help); Cite has empty unknown parameters:|laydate=,|coauthors=,|nopp=,|separator=,|chapterurl=,|laysummary=,|month=, and|lastauthoramp=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ http://www.census.gov/prod/www/abs/decennial/1860.htm
- ^ Form available for viewing at http://c.ancestry.com/pdf/trees/charts/1860Slave.pdf shows how data on slave ownership was collected.
- ^ Calculated by dividing the number of owners (obtained via the census) by the number of free persons.
- ^ All data for this section taken from the University of Virginia Library, Historical Census Browser, Census Data for Year 1860.
- ^ 1862blackCSN.
- ^ Rubin p. 104.
- ^ Levine pp. 146-147.
- ^ Eicher, Civil War High Commands.
- ^ Journal of the Confederate Congress Home Page: U.S. Congressional Documents.
External links
- The McGavock Confederate Cemetery at Franklin, TN
- Confederate offices Index of Politicians by Office Held or Sought
- Civil War Research & Discussion Group -*Confederate States of Am. Army and Navy Uniforms, 1861
- The Countryman, 1862-1866, published weekly by Turnwold, Ga., edited by J.A. Turner
- The Federal and the Confederate Constitution Compared
- The Making of the Confederate Constitution, by A. L. Hull, 1905.
- Confederate Currency
- Photographs of the original Confederate Constitution and other Civil War documents owned by the Hargrett Rare Book and Manuscript Library at the University of Georgia Libraries.
- Photographic History of the Civil War, 10 vols., 1912.
- DocSouth: Documenting the American South - numerous online text, image, and audio collections.
- Confederate States of America: A Register of Its Records in the Library of Congress
- Abbeville's Confederate Colonels Historical Marker
- Burt Stark House / Jefferson Davis's Flight
- The First Organized Meeting Advocating the Right of a State to Secede from the Union Historical Marker
- Thus Secession Had its Birth Historical Marker
- "Original Confederate Soldier Records"
- Last Cabinet Meeting Historical Marker
- Secession Hill Historical Marker
- Images of Georgia's Ordinance of Secession, Confederate Pension Records, and Muster Rolls from the collection of the Georgia Archives.
- "Original Confederate Soldier Service Records From NARA"
| Member Territory | Flag | Ordinance of Secession | Date of Admission | Under predominant Union control |
Date of Admission to the United States |
|---|




