Water: Difference between revisions
←Blanked the page |
m Reverted unexplained removal of content (HG) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{pp-move-indef}} |
|||
{{Redirect4|H2O|HOH}} |
|||
{{two other uses|general aspects of water|a detailed discussion of its properties|Properties of water}} |
|||
[[File:Iceberg with hole near sanderson hope 2007-07-28 2.jpg|300px|thumb|Water in three states: liquid, solid ([[ice]]), and (invisible) [[water vapor]] in the air. [[Clouds]] are accumulations of water droplets, [[condensation|condensed]] from vapor-saturated air.]] |
|||
'''Water''' is a [[chemical substance]] with the [[chemical formula]] {{chem|[[hydrogen|H]]|2|[[oxygen|O]]}}. A water [[molecule]] contains one [[oxygen]] and two [[hydrogen]] [[atoms]] connected by [[covalent]] bonds. Water is a [[liquid]] at [[Standard conditions for temperature and pressure|ambient conditions]], but it often co-exists on [[Earth]] with its [[solid]] state, [[ice]], and [[gaseous]] state ([[water vapor]] or [[steam]]). Water also exists in a [[liquid crystal]] state near [[Hydrophile|hydrophilic]] surfaces.<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Henniker |first=J. C. |title=The Depth of the Surface Zone of a Liquid |year=1949 |publisher=[[Reviews of Modern Physics]] |doi=10.1103/RevModPhys.21.322 |journal=Reviews of Modern Physics |volume=21 |issue=2 |pages=322–341}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://faculty.washington.edu/ghp/researcthemes/water-science |title=Water Science |author=Pollack, Gerald |publisher=[[University of Washington]], Pollack Laboratory |accessdate=2011-02-05 |quote=Water has three phases – gas, liquid, and solid; but recent findings from our laboratory imply the presence of a surprisingly extensive fourth phase that occurs at interfaces.}}</ref> Under nomenclature used to name [[chemical compounds]], ''dihydrogen monoxide'' is the scientific name for water, though it is almost never used.<ref>{{cite web|last=Bramer|first=Scott|title=Chemical Nomenclature|url=http://science.widener.edu/svb/pset/nomen_b.html|publisher=Widener University, Department of Chemistry|accessdate=20 September 2011}}</ref> |
|||
Water covers 70.9% of the [[Earth]]'s surface,<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/xx.html#Geo|title=CIA- The world fact book|publisher=[[Central Intelligence Agency]] |accessdate=2008-12-20}}</ref> and is vital for all known forms of [[Life#Range of tolerance|life]].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.un.org/waterforlifedecade/background.html |title=United Nations |publisher=Un.org |date=2005-03-22 |accessdate=2010-07-25}}</ref> On Earth, 96.5% of the planet's water is found in oceans, 1.7% in groundwater, 1.7% in glaciers and the ice caps of Antarctica and Greenland, a small fraction in other large water bodies, and 0.001% in the [[atmosphere|air]] as [[vapor]], [[cloud]]s (formed of solid and liquid water particles suspended in air), and [[precipitation (meteorology)|precipitation]].<ref name=b1>{{cite book| T|title = Water in Crisis: A Guide to the World's Freshwater Resources| editor = Gleick, P.H.| publisher = Oxford University Press|year = 1993| page = 13, Table 2.1 "Water reserves on the earth"}}</ref><ref> |
|||
[http://www.agu.org/sci_soc/mockler.html Water Vapor in the Climate System], Special Report, [AGU], December 1995 (linked 4/2007). [http://www.unep.org/dewa/assessments/ecosystems/water/vitalwater/ Vital Water] [[UNEP]].</ref> Only 2.5% of the Earth's water is freshwater, and 98.8% of that water is in ice and groundwater. Less than 0.3% of all freshwater is in rivers, lakes, and the atmosphere, and an even smaller amount of the Earth's freshwater (0.003%) is contained within biological bodies and manufactured products.<ref name=b1/> |
|||
Water on Earth moves continually through the [[hydrological cycle]] of [[evaporation]] and [[transpiration]] ([[evapotranspiration]]), [[condensation]], [[precipitation (meteorology)|precipitation]], and [[runoff (water)|runoff]], usually reaching the [[sea]]. Evaporation and transpiration contribute to the precipitation over land. |
|||
Safe [[drinking water]] is essential to [[humans]] and other lifeforms. Access to safe drinking water has improved over the last decades in almost every part of the world, but approximately one billion people still lack access to safe water and over 2.5 billion lack access to adequate sanitation.<ref name=UN /> There is a clear correlation between access to safe water and [[Gross domestic product|GDP]] per capita.<ref>[http://www.gapminder.org/videos/gapcasts/gapcast-9-public-services/ "Public Services"], Gapminder video</ref> However, some observers have estimated that by 2025 more than half of the [[world population]] will be facing water-based vulnerability.<ref>{{cite journal|author = Kulshreshtha, S.N|year = 1998|title = A Global Outlook for Water Resources to the Year 2025|journal = Water Resources Management|volume = 12|issue = 3|pages = 167–184|accessdate = 2008-06-09|doi = 10.1023/A:1007957229865}}</ref> A recent report (November 2009) suggests that by 2030, in some developing regions of the world, water demand will exceed supply by 50%.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.mckinsey.com/App_Media/Reports/Water/Charting_Our_Water_Future_Full_Report_001.pdf |title=Charting Our Water Future: Economic frameworks to inform decision-making |format=PDF |accessdate=2010-07-25}}</ref> Water plays an important role in the [[world economy]], as it functions as a [[solvent]] for a wide variety of chemical substances and facilitates industrial cooling and transportation. Approximately 70% of the [[fresh water]] used by humans goes to [[agriculture]].<ref name=Baroni2007>{{cite journal|author = Baroni, L.|coauthors = Cenci, L.; Tettamanti, M.; Berati, M.|year = 2007|title = Evaluating the environmental impact of various dietary patterns combined with different food production systems|journal = European Journal of Clinical Nutrition|volume = 61|pages = 279–286|doi = 10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602522|pmid = 17035955|issue = 2}}</ref> |
|||
==Chemical and physical properties== |
|||
{{Main|Water (properties)|Water (data page)|Water model}} |
|||
[[File:3D model hydrogen bonds in water.svg|left|thumb|Model of [[hydrogen bond]]s (1) between molecules of water]] |
|||
[[File:Water droplet blue bg05.jpg|right|thumb|Impact from a water drop causes an upward "rebound" jet surrounded by circular [[capillary wave]]s.]] |
|||
[[File:SnowflakesWilsonBentley.jpg|thumb|right|''[[Snowflake]]s'' by [[Wilson Bentley]], 1902]] |
|||
[[File:Spider web Luc Viatour.jpg|thumb|right|[[Dew]] drops adhering to a [[spider web]]]] |
|||
[[File:Capillarity.svg|right|thumb|[[Capillary action]] of water compared to [[Mercury (element)|mercury]]]] |
|||
Water is the [[chemical substance]] with [[chemical formula]] {{chem|H|2|O}}: one [[molecule]] of water has two [[hydrogen]] [[atom]]s [[covalent]]ly [[chemical bond|bonded]] to a single [[oxygen]] atom. |
|||
Water appears in nature in all three common states of matter and may take many different forms on Earth: water vapor and clouds in the sky; [[seawater]] in the oceans; [[iceberg]]s in the polar oceans; [[glacier]]s and [[river]]s in the [[mountain]]s; and the liquid in aquifers in the ground. |
|||
At high temperatures and pressures, such as in the interior of giant planets, it is argued that water exists as [[ionic water]] in which the molecules break down into a soup of hydrogen and oxygen ions, and at even higher pressures as [[superionic water]] in which the oxygen crystallises but the hydrogen ions float around freely within the oxygen lattice.<ref name="newscientist.com">[http://www.newscientist.com/article/mg20727764.500-weird-water-lurking-inside-giant-planets.html Weird water lurking inside giant planets], New Scientist,01 September 2010, Magazine issue 2776.</ref> |
|||
The major chemical and physical properties of water are: |
|||
*Water is a liquid at [[standard conditions|standard temperature and pressure]]. It is tasteless and odorless. The intrinsic [[colour of water]] and ice is a very slight blue hue, although both appear colorless in small quantities. Water vapour is essentially invisible as a gas.<ref>{{cite journal|last=Braun|first=Charles L.|coauthors=Sergei N. Smirnov|title=Why is water blue?|journal=J. Chem. Educ.|volume=70|issue=8|page=612|year=1993|url=http://www.dartmouth.edu/~etrnsfer/water.htm|doi=10.1021/ed070p612}}</ref> |
|||
*Water is [[transparency (optics)|transparent]] in the visible [[electromagnetic spectrum]]. Thus [[aquatic plant]]s can live in water because [[sunlight]] can reach them. Infrared light is strongly [[Absorption (electromagnetic radiation)|absorbed]] by the hydrogen-oxygen or OH bonds. |
|||
*Since the water molecule is not linear and the oxygen atom has a higher [[electronegativity]] than hydrogen atoms, it carries a slight negative charge, whereas the hydrogen atoms are slightly positive. As a result, water is a [[polar molecule]] with an [[electrical dipole moment]]. Water also can form an unusually large number of intermolecular [[hydrogen bonds]] (four) for a molecule of its size. These factors lead to strong attractive forces between molecules of water, giving rise to water's high [[surface tension]]<ref>{{cite book|last = Campbell|first = Neil A.|coauthors = Brad Williamson; Robin J. Heyden|title = Biology: Exploring Life|publisher = Pearson Prentice Hall|year = 2006|location = Boston, Massachusetts|url = http://www.phschool.com/el_marketing.html|isbn = 0-13-250882-6}}</ref> and capillary forces. The [[capillary action]] refers to the tendency of water to move up a narrow tube against the force of [[gravity]]. This property is relied upon by all [[vascular plant]]s, such as trees.<ref>[http://science.jrank.org/pages/1182/Capillary-Action.html Capillary Action – Liquid, Water, Force, and Surface – JRank Articles]. Science.jrank.org. Retrieved on 2011-11-03.</ref> |
|||
*Water is a good [[solvent]] and is often referred to as ''the universal [[solvent]]''. Substances that dissolve in water, e.g., [[Salt (chemistry)|salts]], [[sugar]]s, [[acid]]s, [[alkali]]s, and some [[gas]]es – especially oxygen, [[carbon dioxide]] ([[carbonation]]) are known as ''[[hydrophilic]]'' (water-loving) substances, while those that do not mix well with water (e.g., [[lipids|fats and oils]]), are known as ''[[hydrophobic]]'' (water-fearing) substances. |
|||
*All the major components in cells ([[protein]]s, [[DNA]] and [[polysaccharide]]s) are also dissolved in water. |
|||
*Pure water has a low [[electrical conductivity]], but this increases significantly with the [[dissolution]] of a small amount of ionic material such as [[sodium chloride]]. |
|||
*The boiling point of water (and all other liquids) is dependent on the [[barometric pressure]]. For example, on the top of [[Mt. Everest]] water boils at {{convert|68|°C}}, compared to {{convert|100|°C}} at [[sea level]]. Conversely, water deep in the ocean near geothermal vents can reach temperatures of hundreds of degrees and remain liquid. |
|||
*At 4181.3 J/(kg·K), water has a high [[specific heat capacity]], as well as a high [[heat of vaporization]] ({{nowrap|40.65 kJ·mol<sup>−1</sup>}}), both of which are a result of the extensive [[hydrogen bonding]] between its molecules. These two unusual properties allow water to moderate Earth's [[climate]] by buffering large fluctuations in temperature. |
|||
*The maximum [[density]] of water occurs at {{convert|3.98|°C}}.<ref>{{cite book| author = Kotz, J. C., Treichel, P., & Weaver, G. C.|year = 2005|title = Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity |publisher = Thomson Brooks/Cole| isbn = 053439597X}}</ref> It has the anomalous property of becoming less dense, not more, when it is cooled down to its solid form, ice. It expands to occupy 9% greater volume in this solid state, which accounts for the fact of ice floating on liquid water, as in [[icebergs]]. |
|||
*Its [[density]] is 1,000 kg/m<sup>3</sup> (62.428 lb/cu ft or 8.3454 lb/US gal) liquid (at 4 °C; ice has a density of 917 kg/m<sup>3</sup>).<ref>[http://www.kidsnewsroom.org/elmer/infocentral/conversions/density.htm Online Conversion – Density], Kidsnewsroom.org/elmer/infocentral/conversions</ref>[[File:Label for dangerous goods - class 4.3.svg|right|thumb|[[European Agreement concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Road|ADR]] [[Dangerous goods|label]] for transporting goods dangerously reactive with water]] |
|||
*Water is [[miscible]] with many liquids, such as [[ethanol]], in all proportions, forming a single [[Homogeneous (chemistry)|homogeneous]] liquid. On the other hand, water and most [[oil]]s are immiscible, usually forming layers according to increasing density from the top. As a gas, water vapor is completely [[miscible]] with air. |
|||
*Water forms an [[azeotrope]] with many other solvents. |
|||
*Water can be [[Electrolysis of water|split by electrolysis]] into hydrogen and oxygen. |
|||
*As an oxide of hydrogen, water is formed when hydrogen or hydrogen-containing compounds [[burn]] or [[Chemical reaction|react]] with oxygen or oxygen-containing compounds. Water is not a [[fuel]], it is an end-product of the combustion of hydrogen. The [[energy]] required to split water into hydrogen and oxygen by [[electrolysis]] or any other means is greater than the energy that can be collected when the hydrogen and oxygen recombine.<ref>{{cite web|last= Ball|first=Philip|authorlink = Philip Ball|title=Burning water and other myths|url= http://www.nature.com/news/2007/070910/full/070910-13.html|work= [[Nature (journal)|Nature]] News|date= 14 September 2007|accessdate= 2007-09-14}}</ref> |
|||
*[[Chemical element|Elements]] which are more [[Electropositivity|electropositive]] than hydrogen such as [[lithium]], [[sodium]], [[calcium]], [[potassium]] and [[caesium]] displace hydrogen from water, forming [[hydroxide]]s. Being a flammable gas, the hydrogen given off is dangerous and the reaction of water with the more electropositive of these elements may be violently explosive. |
|||
==Taste and odor== |
|||
Water can dissolve many different substances, giving it varying tastes and odors. [[Humans]] and other animals have developed senses that enable them to evaluate the [[drinking water|potability]] of water by avoiding water that is too salty or [[putrid]]. The taste of [[spring water]] and [[mineral water]], often advertised in marketing of consumer products, derives from the minerals dissolved in it. However, pure H<sub>2</sub>O is tasteless and odorless. The advertised purity of spring and mineral water refers to absence of [[toxin]]s, [[pollutant]]s and [[microorganism|microbes]], not the absence of naturally occurring minerals. |
|||
==Distribution in nature== |
|||
===In the universe=== |
|||
Much of the universe's water is produced as a byproduct of [[star formation]]. When stars are born, their birth is accompanied by a strong outward wind of gas and dust. When this outflow of material eventually impacts the surrounding gas, the shock waves that are created compress and heat the gas. The water observed is quickly produced in this warm dense gas.<ref>Melnick, Gary, [[Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics]] and Neufeld, David, [[Johns Hopkins University]] quoted in: |
|||
{{cite news| title=Discover of Water Vapor Near Orion Nebula Suggests Possible Origin of H20 in Solar System (sic)| publisher=The Harvard University Gazette| date=April 23, 1998| url=http://www.news.harvard.edu/gazette/1998/04.23/DiscoverofWater.html}} |
|||
{{cite news| title=Space Cloud Holds Enough Water to Fill Earth's Oceans 1 Million Times| publisher=Headlines@Hopkins, JHU| date= April 9, 1998| url=http://www.jhu.edu/news_info/news/home98/apr98/clouds.html}} |
|||
{{cite news| title=Water, Water Everywhere: Radio telescope finds water is common in universe| publisher=The Harvard University Gazette| date=February 25, 1999| url=http://news.harvard.edu/gazette/1999/02.25/telescope.html}}(linked 4/2007) |
|||
</ref> |
|||
On 22 July 2011, a report described the discovery of a gigantic cloud of water vapor, containing "140 trillion times more water than all of Earth's oceans combined," around a [[quasar]] located 12 billion light years from Earth. According to the researchers, the "discovery shows that water has been prevalent in the universe for nearly its entire existence."<ref name="Clavin">{{cite web |last1=Clavin |first1=Whitney |last2=Buis |first2=Alan |title=Astronomers Find Largest, Most Distant Reservoir of Water |url=http://www.nasa.gov/topics/universe/features/universe20110722.html |date=22 July 2011 |publisher=[[NASA]] |accessdate=2011-07-25}}</ref><ref name="water vapor cloud">{{cite web |author=Staff |title=Astronomers Find Largest, Oldest Mass of Water in Universe |url=http://www.space.com/12400-universe-biggest-oldest-cloud-water.html |date=22 July 2011 |publisher=[[Space.com]] |accessdate=2011-07-23}}</ref> |
|||
Water has been detected in [[interstellar cloud]]s within our [[galaxy]], the [[Milky Way]]. Water probably exists in abundance in other galaxies, too, because its components, hydrogen and oxygen, are among the most abundant elements in the universe. Interstellar clouds eventually condense into [[solar nebula]]e and [[solar system]]s such as ours. |
|||
Water vapor is present in |
|||
*[[Atmosphere of Mercury]]: 3.4%, and large amounts of water in Mercury's [[exosphere]]<ref name="planetary society">{{cite web |url=http://www.planetary.org/news/2008/0703_MESSENGER_Scientists_Astonished_to.html |title=MESSENGER Scientists 'Astonished' to Find Water in Mercury's Thin Atmosphere |accessdate=2008-07-05 |publisher=Planetary Society |date=2008-07-03}}</ref> |
|||
*[[Atmosphere of Venus]]: 0.002% |
|||
*[[Earth's atmosphere]]: ~0.40% over full atmosphere, typically 1–4% at surface |
|||
*[[Atmosphere of Mars]]: 0.03% |
|||
*[[Atmosphere of Jupiter]]: 0.0004% |
|||
*[[Atmosphere of Saturn]] – in [[volatiles|ices]] only |
|||
*[[Enceladus (moon)|Enceladus]] (moon of Saturn): 91% |
|||
*[[exoplanet]]s known as [[HD 189733 b]]<ref>[http://www.time.com/time/health/article/0,8599,1642811,00.html Water Found on Distant Planet] July 12, 2007 By Laura Blue, ''[[Time (magazine)|Time]]''</ref> and [[HD 209458 b]].<ref name="Space.com water">[http://www.space.com/scienceastronomy/070410_water_exoplanet.html Water Found in Extrasolar Planet's Atmosphere] – Space.com</ref> |
|||
Liquid water is present on |
|||
*Earth: 71% of surface |
|||
*[[Europa (moon)|Europa]]: 100 km deep subsurface ocean |
|||
Strong evidence suggests that liquid water is present just under the surface of Saturn's moon [[Enceladus (moon)|Enceladus]]. |
|||
Water ice is present on |
|||
*Earth – mainly as [[ice sheet]]s |
|||
*polar ice caps on [[Mars]] |
|||
*[[Lunar ice|Moon]] |
|||
*[[Titan (moon)|Titan]] |
|||
*[[Europa (moon)|Europa]] |
|||
*[[Rings of Saturn|Saturn's rings]]<ref name="Sparrow">{{cite book|last = Sparrow|first = Giles|title = The Solar System|publisher =Thunder Bay Press|year =2006|isbn =1592235794}}</ref> |
|||
*[[Enceladus (moon)|Enceladus]] |
|||
*[[Pluto]] and [[Charon (moon)|Charon]]<ref name="Sparrow"/> |
|||
*[[Comets]] and comet source populations ([[Kuiper belt]] and [[Oort cloud]] objects). |
|||
Water ice may be present on [[Ceres (dwarf planet)|Ceres]] and [[Tethys (moon)|Tethys]]. Water and other [[volatiles]] probably comprise much of the internal structures of [[Uranus]] and [[Neptune]] and the water in the deeper layers may be in the form of [[ionic water]] in which the molecules break down into a soup of hydrogen and oxygen ions, and deeper down as [[superionic water]] in which the oxygen crystallises but the hydrogen ions float around freely within the oxygen lattice.<ref name="newscientist.com"/> |
|||
Some of the Moon's minerals contain water molecules. For instance, in 2008 a laboratory device which ejects and identifies particles found small amounts of the compound in the inside of volcanic rock brought from Moon to Earth by the [[Apollo 15]] crew in 1971.<ref>[http://www.spiegel.de/wissenschaft/weltall/0,1518,564911,00.html Versteckt in Glasperlen: Auf dem Mond gibt es Wasser – Wissenschaft – [[Der Spiegel]] – Nachrichten]</ref> NASA reported the detection of water molecules by NASA's Moon Mineralogy Mapper aboard the Indian Space Research Organization's Chandrayaan-1 spacecraft in September 2009.<ref>[http://science.nasa.gov/headlines/y2009/24sep_moonwater.htm Water Molecules Found on the Moon], NASA, September 24, 2009</ref> |
|||
===Water and habitable zone=== |
|||
The existence of liquid water, and to a lesser extent its [[gas]]eous and solid forms, on Earth are vital to the existence of [[Organism|life on Earth]] as we know it. The Earth is located in the [[habitable zone]] of the [[solar system]]; if it were slightly closer to or farther from the [[Sun]] (about 5%, or about 8 million kilometers), the conditions which allow the three forms to be present simultaneously would be far less likely to exist.<ref>{{cite book| chapter = J. C. I. Dooge. "Integrated Management of Water Resources"| editor = Ehlers, E.; Krafft, T|title = Understanding the Earth System: compartments, processes, and interactions| publisher = Springer|year = 2001| page = 116}}</ref><ref>{{cite web| title =Habitable Zone|url =http://www.daviddarling.info/encyclopedia/H/habzone.html|publisher = The Encyclopedia of Astrobiology, Astronomy and Spaceflight}} |
|||
</ref> |
|||
Earth's [[gravity]] allows it to hold an [[Celestial body atmosphere|atmosphere]]. Water vapor and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere provide a temperature buffer ([[greenhouse effect]]) which helps maintain a relatively steady surface temperature. If Earth were smaller, a thinner atmosphere would allow temperature extremes, thus preventing the accumulation of water except in [[polar ice cap]]s (as on [[Mars]]). |
|||
The surface temperature of Earth has been relatively constant through [[geologic time]] despite varying levels of incoming solar radiation ([[insolation]]), indicating that a dynamic process governs Earth's temperature via a combination of greenhouse gases and surface or atmospheric [[albedo]]. This proposal is known as the ''[[Gaia hypothesis]]''. |
|||
The state of water on a planet depends on ambient pressure, which is determined by the planet's gravity. If a planet is sufficiently massive, the water on it may be solid even at high temperatures, because of the high pressure caused by gravity, as it was observed on exoplanets [[Gliese 436 b]]<ref>{{cite news| publisher=New Scientist| url=http://space.newscientist.com/article/dn11864-strange-alien-world-made-of-hot-ice-and-steam.html| title=Strange alien world made of "hot ice"| date=6 May 2007| first= David| last= Shiga| accessdate=2010-03-28}}</ref> and [[GJ 1214 b]].<ref> |
|||
{{cite web |url=http://www.cfa.harvard.edu/news/2009/pr200924.html |title=Astronomers Find Super-Earth Using Amateur, Off-the-Shelf Technology |author=Aguilar, David A. |date=16 December 2009 |publisher=Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics |accessdate=2010-03-28}}</ref> |
|||
There are various theories about [[origin of water on Earth]]. |
|||
==On Earth== |
|||
{{Main|Hydrology|Water distribution on Earth}} |
|||
[[File:Earth's water distribution.svg|thumb|400px|A graphical distribution of the locations of water on Earth.]] |
|||
[[File:The Earth seen from Apollo 17.jpg|thumb|left|Water covers 71% of the Earth's surface; the oceans contain 96.5% of the Earth's water. The [[Antarctic ice sheet]], which contains 61% of all fresh water on Earth, is visible at the bottom. Condensed atmospheric water can be seen as [[cloud]]s, contributing to the Earth's [[albedo]].]] |
|||
Hydrology is the study of the movement, distribution, and quality of water throughout the Earth. The study of the distribution of water is [[hydrography]]. The study of the distribution and movement of groundwater is [[hydrogeology]], of glaciers is [[glaciology]], of inland waters is [[limnology]] and distribution of oceans is [[oceanography]]. Ecological processes with hydrology are in focus of [[ecohydrology]]. |
|||
The collective mass of water found on, under, and over the surface of a planet is called the [[hydrosphere]]. Earth's approximate water volume (the total water supply of the world) is 1,338,000,000 km<sup>3</sup> (321,000,000 mi<sup>3</sup>).<ref name=b1/> |
|||
Liquid water is found in [[body of water|bodies of water]], such as an ocean, [[sea]], [[lake]], [[river]], [[stream]], [[canal]], [[pond]], or [[puddle]]. The majority of water on Earth is [[sea water]]. Water is also present in the atmosphere in solid, liquid, and vapor states. It also exists as groundwater in [[aquifer]]s. |
|||
Water is important in many geological processes. Groundwater is present in most [[rock (geology)|rocks]], and the pressure of this groundwater affects patterns of [[fault (geology)|faulting]]. Water in the [[Mantle (geology)|mantle]] is responsible for the melt that produces [[volcano]]es at [[subduction zone]]s. On the surface of the Earth, water is important in both chemical and physical [[weathering]] processes. Water and, to a lesser but still significant extent, ice, are also responsible for a large amount of [[sediment transport]] that occurs on the surface of the earth. [[Deposition (geology)|Deposition]] of transported sediment forms many types of [[sedimentary rock]]s, which make up the [[geologic record]] of [[History of the Earth|Earth history]]. |
|||
===Water cycle=== |
|||
{{Main|Water cycle}} |
|||
[[File:Water cycle.png|400px|thumb|[[Water cycle]]]] |
|||
The [[water cycle]] (known scientifically as the '''hydrologic cycle''') refers to the continuous exchange of water within the [[hydrosphere]], between the [[Earth atmosphere|atmosphere]], [[soil]] water, [[surface water]], [[groundwater]], and [[plant]]s. |
|||
Water moves perpetually through each of these regions in the ''[[water cycle]]'' consisting of following transfer processes: |
|||
*[[evaporation]] from oceans and other water bodies into the air and [[transpiration]] from land plants and animals into air. |
|||
*[[precipitation (meteorology)|precipitation]], from water vapor condensing from the air and falling to earth or ocean. |
|||
*[[runoff (water)|runoff]] from the land usually reaching the [[sea]]. |
|||
Most water vapor over the oceans returns to the oceans, but winds carry water vapor over land at the same rate as runoff into the sea, about 47 [[Metric tonne unit|Tt]] per year. Over land, evaporation and transpiration contribute another 72 Tt per year. Precipitation, at a rate of 119 Tt per year over land, has several forms: most commonly [[rain]], [[snow]], and [[hail]], with some contribution from [[fog]] and [[dew]].<ref>{{cite book| T|title = Water in Crisis: A Guide to the World's Freshwater Resources| editor = Gleick, P.H.| publisher = Oxford University Press|year = 1993| page = 15, Table 2.3}}</ref> Condensed water in the air may also [[refract]] [[sunlight]] to produce [[rainbow]]s. |
|||
Water runoff often collects over [[Drainage basin|watersheds]] flowing into rivers. A mathematical model used to simulate river or stream flow and calculate water quality parameters is [[hydrological transport model]]. Some of water is diverted to [[irrigation]] for agriculture. Rivers and seas offer opportunity for [[travel]] and [[commerce]]. Through [[erosion]], runoff shapes the environment creating river [[valley]]s and [[river delta|deltas]] which provide rich soil and level ground for the establishment of population centers. A [[flood]] occurs when an area of land, usually low-lying, is covered with water. It is when a river overflows its banks or flood from the sea. A [[drought]] is an extended period of months or years when a region notes a deficiency in its water supply. This occurs when a region receives consistently below average precipitation. |
|||
===Fresh water storage=== |
|||
{{imageframe |
|||
|width=400 |
|||
|content=[[File:Bay of Fundy High Tide.jpg|200px]][[File:Bay of Fundy Low Tide.jpg|200px]] |
|||
|caption=The [[Bay of Fundy]] at high tide (left) and low tide (right) |
|||
}} |
|||
{{Main|Water resources}} |
|||
Some runoff water is trapped for periods of time, for example in lakes. |
|||
At high altitude, during winter, and in the far north and south, snow collects in ice caps, snow pack and glaciers. |
|||
Water also infiltrates the ground and goes into aquifers. This groundwater later flows back to the surface in [[spring (hydrosphere)|springs]], or more spectacularly in [[hot spring]]s and [[geyser]]s. Groundwater is also extracted artificially in [[water well|wells]]. |
|||
This water storage is important, since clean, fresh water is essential to human and other land-based life. In many parts of the world, it is in short supply. |
|||
===Sea water=== |
|||
[[Seawater|Sea water]] contains about 3.5% [[sodium chloride|salt]] on average, plus smaller amounts of other substances. The physical properties of sea water differ from fresh water in some important respects. It freezes at a lower temperature (about −1.9 °C) and its density increases with decreasing temperature to the freezing point, instead of reaching maximum density at a temperature above freezing. The salinity of water in major seas varies from about 0.7% in the [[Baltic Sea]] to 4.0% in the [[Red Sea]]. |
|||
===Tides=== |
|||
[[Tide]]s are the cyclic rising and falling of local sea levels caused by the [[tidal force]]s of the Moon and the Sun acting on the oceans. Tides cause changes in the depth of the marine and [[estuary|estuarine]] water bodies and produce oscillating currents known as tidal streams. |
|||
The changing tide produced at a given location is the result of the changing positions of the Moon and Sun relative to the Earth coupled with the [[Coriolis effect|effects of Earth rotation]] and the local [[bathymetry]]. The strip of seashore that is submerged at high tide and exposed at low tide, the [[intertidal zone]], is an important ecological product of ocean tides. |
|||
==Effects on life== |
|||
[[File:Oasis in Lybia.JPG|thumb|left|An [[oasis]] is an isolated [[water source]] with [[vegetation]] in a [[desert]]]] |
|||
[[File:Auto-and heterotrophs.svg|thumb|right|Overview of [[photosynthesis|<span style="color:green;">photosynthesis</span>]] and [[cellular respiration|<span style="color:red;">respiration</span>]]. Water (at right), together with carbon dioxide (CO<sub>2</sub>), form oxygen and organic compounds (at left), which can be respired to water and (CO<sub>2</sub>).]] |
|||
From a [[biology|biological]] standpoint, water has many distinct properties that are critical for the proliferation of [[life]] that set it apart from other substances. It carries out this role by allowing [[organic compound]]s to react in ways that ultimately allow [[Self-replication|replication]]. All known forms of life depend on water. Water is vital both as a [[solvent]] in which many of the body's solutes dissolve and as an essential part of many [[metabolism|metabolic]] processes within the body. Metabolism is the sum total of anabolism and catabolism. In anabolism, water is removed from molecules (through energy requiring enzymatic chemical reactions) in order to grow larger molecules (e.g. starches, triglycerides and proteins for storage of fuels and information). In catabolism, water is used to break bonds in order to generate smaller molecules (e.g. glucose, fatty acids and amino acids to be used for fuels for energy use or other purposes). Without water, these particular metabolic processes could not exist. |
|||
Water is fundamental to photosynthesis and respiration. Photosynthetic cells use the sun's energy to split off water's hydrogen from oxygen. Hydrogen is combined with CO<sub>2</sub> (absorbed from air or water) to form glucose and release oxygen. All living cells use such fuels and oxidize the hydrogen and carbon to capture the sun's energy and reform water and CO<sub>2</sub> in the process (cellular respiration). |
|||
Water is also central to acid-base neutrality and enzyme function. An acid, a hydrogen ion (H<sup>+</sup>, that is, a proton) donor, can be neutralized by a base, a proton acceptor such as hydroxide ion (OH<sup>−</sup>) to form water. Water is considered to be neutral, with a [[pH]] (the negative log of the hydrogen ion concentration) of 7. [[Acids]] have pH values less than 7 while [[Base (chemistry)|bases]] have values greater than 7. |
|||
[[File:Blue Linckia Starfish.JPG|thumb|right|Some of the [[biodiversity]] of a [[coral reef]]]] |
|||
===Aquatic life forms=== |
|||
{{Main|Hydrobiology|Aquatic plant}} |
|||
[[File:Diatoms through the microscope.jpg|thumb|left|Some marine [[diatom]]s – a key [[phytoplankton]] group]] |
|||
Earth surface waters are filled with life. The earliest life forms appeared in water; nearly all [[fish]] live exclusively in water, and there are many types of marine mammals, such as [[dolphin]]s and [[whale]]s. Some kinds of animals, such as [[amphibian]]s, spend portions of their lives in water and portions on land. Plants such as [[kelp]] and [[algae]] grow in the water and are the basis for some underwater ecosystems. [[Plankton]] is generally the foundation of the ocean [[food chain]]. |
|||
Aquatic vertebrates must obtain oxygen to survive, and they do so in various ways. Fish have [[gills]] instead of [[lungs]], although some species of fish, such as the [[lungfish]], have both. [[Marine mammal]]s, such as dolphins, whales, [[otter]]s, and [[pinniped|seals]] need to surface periodically to breathe air. Some amphibians are able to absorb oxygen through their skin. Invertebrates exhibit a wide range of modifications to survive in poorly oxygenated waters including breathing tubes (see [[Siphon (insect)|insect]] and [[Siphon (mollusc)|mollusc siphons]]) and [[gills]] (''[[Carcinus]]''). However as invertebrate life evolved in an aquatic habitat most have little or no specialisation for respiration in water. |
|||
==Effects on human civilization== |
|||
[[File:Longwood Gardens-Italian Garden.jpg|thumb|right|Water [[fountain]]]] |
|||
Civilization has historically flourished around rivers and major waterways; [[Mesopotamia]], the so-called cradle of civilization, was situated between the major rivers [[Tigris]] and [[Euphrates]]; the ancient society of the [[Egyptians]] depended entirely upon the [[Nile]]. Large [[metropolis]]es like [[Rotterdam]], [[London]], [[Montreal]], [[Paris]], [[New York City]], [[Buenos Aires]], [[Shanghai]], [[Tokyo]], [[Chicago]], and [[Hong Kong]] owe their success in part to their easy accessibility via water and the resultant expansion of trade. Islands with safe water ports, like [[Singapore]], have flourished for the same reason. In places such as [[North Africa]] and the [[Middle East]], where water is more scarce, access to clean drinking water was and is a major factor in human development. |
|||
===Health and pollution=== |
|||
[[File:Field Trip- water sampling.jpg|thumb|left|Environmental Science Program, [[Iowa State University]] student sampling water.]] |
|||
Water fit for human consumption is called drinking water or [[potable water]]. Water that is not potable may be made potable by filtration or [[distillation]], or by a range of [[Water treatment|other methods]]. |
|||
Water that is not fit for drinking but is not harmful for humans when used for swimming or bathing is called by various names other than potable or drinking water, and is sometimes called [[safe water]], or "safe for bathing". Chlorine is a skin and mucous membrane irritant that is used to make water safe for bathing or drinking. Its use is highly technical and is usually monitored by government regulations (typically 1 part per million (ppm) for drinking water, and 1–2 ppm of chlorine not yet reacted with impurities for bathing water). Water for bathing may be maintained in satisfactory microbiological condition using chemical disinfectants such as [[chlorine]] or [[ozone]] or by the use of [[ultraviolet]] light. |
|||
In the USA, non-potable forms of [[wastewater]] generated by humans may be referred to as [[greywater]], which is treatable and thus easily able to be made potable again, and [[Blackwater (waste)|blackwater]], which generally contains [[sewage]] and other forms of waste which require [[Sewage treatment|further treatment]] in order to be made reusable. Greywater composes 50–80% of residential wastewater generated by a household's sanitation equipment ([[sink]]s, [[shower]]s and [[kitchen]] runoff, but not [[toilet]]s, which generate blackwater.) These terms may have different meanings in other countries and cultures. |
|||
This natural resource is becoming scarcer in certain places, and its availability is a major social and economic concern. Currently, about a billion people around the world routinely drink unhealthy water. Most countries accepted the goal of halving by 2015 the number of people worldwide who do not have access to safe water and [[sanitation]] during the [[29th G8 summit|2003 G8 Evian summit]].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.g8.fr/evian/english/navigation/2003_g8_summit/summit_documents/water_-_a_g8_action_plan.html |title=G8 "Action plan" decided upon at the 2003 Evian summit |publisher=G8.fr |date=2003-06-02 |accessdate=2010-07-25}}</ref> Even if this difficult goal is met, it will still leave more than an estimated half a billion people without access to safe drinking water and over a billion without access to adequate sanitation. Poor [[water quality]] and bad sanitation are deadly; some five million deaths a year are caused by polluted drinking water. The [[World Health Organization]] estimates that [[safe water]] could prevent 1.4 million child deaths from [[diarrhea]] each year.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.who.int/features/qa/70/en/ |title=World Health Organization. Safe Water and Global Health |publisher=Who.int |date=2008-06-25 |accessdate=2010-07-25}}</ref> Water, however, is not a finite resource, but rather re-circulated as potable water in precipitation in quantities many degrees of magnitude higher than human consumption. Therefore, it is the relatively small quantity of water in reserve in the earth (about 1% of our drinking [[water supply]], which is replenished in aquifers around every 1 to 10 years), that is a [[non-renewable resource]], and it is, rather, the distribution of potable and irrigation water which is scarce, rather than the actual amount of it that exists on the earth. Water-poor countries use importation of goods as the primary method of importing water (to leave enough for local human consumption), since the manufacturing process uses around 10 to 100 times products' masses in water. |
|||
In the developing world, 90% of all [[wastewater]] still goes untreated into local rivers and streams.<ref>{{cite book |title=Environmentally Sound Technology for Wastewater and Stormwater Management: An International Source Book |author=UNEP International Environment |year=2002 |publisher=IWA Publishing |isbn=1843390086 |oclc=49204666}}</ref> Some 50 countries, with roughly a third of the world’s population, also suffer from medium or high water stress, and 17 of these extract more water annually than is recharged through their natural water cycles.<ref>{{cite book |title=Climate Change and Developing Countries |last=Ravindranath |first=Nijavalli H. |coauthors=Jayant A. Sathaye |year=2002 |publisher=Springer |isbn=1402001045 |oclc=231965991}}</ref> The strain not only affects surface freshwater bodies like rivers and lakes, but it also degrades groundwater resources. |
|||
===Human uses=== |
|||
{{See|Water supply}} |
|||
====Agriculture==== |
|||
[[File:SiphonTubes.JPG|thumb|right|[[Irrigation]] of field crops]] |
|||
The most important use of water in [[agriculture]] is for [[irrigation]], which is a key component to produce enough food. Irrigation takes up to 90% of water withdrawn in some developing countries<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.wbcsd.org/includes/getTarget.asp?type=d&id=MTYyNTA |title=WBCSD Water Facts & Trends |accessdate=2010-07-25}}</ref> and significant proportions in more economically developed countries (United States, 30% of freshwater usage is for irrigation).<ref name="Water Use in the United States">[http://nationalatlas.gov/articles/water/a_wateruse.html Water Use in the United States], National Atlas.gov</ref> It takes around 3,000 litres of water, converted from liquid to vapour, to produce enough food to satisfy one person's daily dietary need. This is a considerable amount, when compared to that required for drinking, which is between two and five litres. To produce food for the 6.5 billion or so people who inhabit the planet today requires the water that would fill a canal ten metres deep, 100 metres wide and 7.1 million kilometres long – that's enough to circle the globe 180 times. |
|||
Fifty years ago, the common perception was that water was an infinite resource. At this time, there were fewer than half the current number of people on the planet. People were not as wealthy as today, consumed fewer calories and ate less meat, so less water was needed to produce their food. They required a third of the volume of water we presently take from rivers. Today, the competition for the fixed amount of water resources is much more intense, giving rise to the concept of [[peak water]].<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Gleick |first=P.H. |title=Peak Water |url=http://www.pacinst.org/press_center/press_releases/peak_water_pnas.pdf|accessdate=2011-10-11 |year=2010|publisher=[[National Academy of Science]]|doi=10.1073/pnas.1004812107 |journal=Proceedings National Academy of Science |volume=107 |issue=125 |pages=11155–11162}}</ref> This is because there are now nearly seven billion people on the planet, their consumption of water-thirsty meat and vegetables is rising, and there is increasing competition for water from [[industry]], [[urbanisation]] and biofuel crops. In future, even more water will be needed to produce food because the Earth's population is forecast to rise to 9 billion by 2050.<ref>United Nations Press Release POP/952, 13 March 2007. [http://www.un.org/News/Press/docs/2007/pop952.doc.htm World population will increase by 2.5 billion by 2050]</ref> An additional 2.5 or 3 billion people, choosing to eat fewer cereals and more meat and vegetables could add an additional five million kilometres to the virtual canal mentioned above. |
|||
An assessment of water management in agriculture was conducted in 2007 by the [[International Water Management Institute]] in [[Sri Lanka]] to see if the world had sufficient water to provide food for its growing population.<ref>Molden, D. (Ed). ''Water for food, Water for life: A Comprehensive Assessment of Water Management in Agriculture.'' Earthscan/IWMI, 2007.</ref> It assessed the current availability of water for agriculture on a global scale and mapped out locations suffering from water scarcity. It found that a fifth of the world's people, more than 1.2 billion, live in areas of [[physical water scarcity]], where there is not enough water to meet all demands. A further 1.6 billion people live in areas experiencing [[economic water scarcity]], where the lack of investment in water or insufficient human capacity make it impossible for authorities to satisfy the demand for water. The report found that it would be possible to produce the food required in future, but that continuation of today's food production and environmental trends would lead to crises in many parts of the world. To avoid a global water crisis, farmers will have to strive to increase productivity to meet growing demands for food, while industry and cities find ways to use water more efficiently.<ref>Chartres, C. and Varma, S. ''Out of water. From Abundance to Scarcity and How to Solve the World’s Water Problems'' FT Press (USA), 2010</ref> |
|||
====As a scientific standard==== |
|||
On 7 April 1795, the [[gram]] was defined in [[France]] to be equal to "the absolute weight of a volume of pure water equal to a cube of one hundredth of a meter, and to the temperature of the melting ice."<ref>[http://smdsi.quartier-rural.org/histoire/18germ_3.htm Décret relatif aux poids et aux mesures. 18 germinal an 3 (7 avril 1795)]. Decree relating to the weights and measurements (in French). quartier-rural.org</ref> For practical purposes though, a metallic reference standard was required, one thousand times more massive, the [[kilogram]]. Work was therefore commissioned to determine precisely the mass of one [[litre|liter]] of water. In spite of the fact that the decreed definition of the gram specified water at 0 °C — a highly reproducible ''temperature'' — the scientists chose to redefine the standard and to perform their measurements at the temperature of highest water ''density'', which was measured at the time as {{convert|4|C}}.<ref>[http://histoire.du.metre.free.fr/fr/index.htm here L'Histoire Du Mètre, La Détermination De L'Unité De Poids]. histoire.du.metre.free.fr</ref> |
|||
The [[Kelvin temperature scale]] of the SI system is based on the [[triple point]] of water, defined as exactly 273.16 K or 0.01 °C. The scale is an [[absolute temperature]] scale with the same increment as the Celsius temperature scale, which was originally defined according the [[boiling point]] (set to 100 °C) and [[melting point]] (set to 0 °C) of water. |
|||
Natural water consists mainly of the isotopes hydrogen-1 and oxygen-16, but there is also small quantity of heavier isotopes such as hydrogen-2 ([[deuterium]]). The amount of deuterium oxides or [[heavy water]] is very small, but it still affects the properties of water. Water from rivers and lakes tends to contain less deuterium than seawater. Therefore, standard water is defined in the [[Vienna Standard Mean Ocean Water]] specification. |
|||
====For drinking==== |
|||
{{Main|Drinking water}} |
|||
[[File:Humanitarian aid OCPA-2005-10-28-090517a.jpg|thumb|left|A young girl drinking [[bottled water]]]] |
|||
[[File:Water quality.jpg|thumb|right|Water quality: fraction of population using improved water sources by country]] |
|||
The human [[body]] contains from 55% to 78% water, depending on body size.<ref>[http://www.madsci.org/posts/archives/2000-05/958588306.An.r.html Re: What percentage of the human body is composed of water?] Jeffrey Utz, M.D., The MadSci Network</ref> To function properly, the body requires between one and seven liters of water per [[day]] to avoid [[dehydration]]; the precise amount depends on the level of activity, temperature, humidity, and other factors. Most of this is ingested through foods or beverages other than drinking straight water. It is not clear how much water intake is needed by healthy people, though most advocates agree that approximately 2 liters (6 to 7 glasses) of water daily is the minimum to maintain proper hydration.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.bbc.co.uk/health/healthy_living/nutrition/drinks_water.shtml |title=Healthy Water Living|publisher=BBC|accessdate=2007-02-01}}</ref> Medical literature favors a lower consumption, typically 1 liter of water for an average male, excluding extra requirements due to fluid loss from exercise or warm weather.<ref name=Rhoades_2003>{{cite book|author = Rhoades RA, Tanner GA|title = Medical Physiology|publisher = Lippincott Williams & Wilkins|edition = 2nd|location = Baltimore|year = 2003|isbn = 0781719364|oclc = 50554808}}</ref> For those who have healthy kidneys, it is rather difficult to drink too much water, but (especially in warm humid weather and while exercising) it is dangerous to drink too little. People can drink far more water than necessary while exercising, however, putting them at risk of [[water intoxication]] (hyperhydration), which can be fatal.<ref>{{cite journal |
|||
| author = Noakes TD, Goodwin N, Rayner BL, ''et al.'' |
|||
| title = Water intoxication: a possible complication during endurance exercise |
|||
| journal = Med Sci Sports Exerc |
|||
| year =1985 |
|||
| volume = 17 |
|||
| issue = 3 |
|||
| pages = 370–375 |
|||
| pmid = 4021781 |
|||
| url = http://journals.lww.com/acsm-msse/Abstract/1985/06000/Water_intoxication__a_possible_complication_during.12.aspx |
|||
}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |
|||
| author = Noakes TD, Goodwin N, Rayner BL, Branken T, Taylor RK |
|||
| title = Water intoxication: a possible complication during endurance exercise, 1985 |
|||
| journal = Wilderness Environ Med |
|||
| year = 2005 |
|||
| volume = 16 |
|||
| issue = 4 |
|||
| pages = 221–7 |
|||
| pmid = 16366205 |
|||
| doi=10.1580/1080-6032(2005)16[221:WIAPCD]2.0.CO;2 |
|||
}}</ref> The popular claim that "a person should consume eight glasses of water per day" seems to have no real basis in science.<ref>[http://ajpregu.physiology.org/cgi/content/full/283/5/R993 "Drink at least eight glasses of water a day." Really? Is there scientific evidence for "8 × 8"?] by Heinz Valdin, Department of Physiology, Dartmouth Medical School, Lebanon, [[New Hampshire]]</ref> Similar misconceptions concerning the effect of water on weight loss and constipation have also been dispelled.<ref>[http://www.factsmart.org/h2o/h2o.htm Drinking Water – How Much?], Factsmart.org web site and references within</ref> |
|||
[[File:D-P005 Kein Trinkwasser.svg|thumb|right|[[Hazard symbol]] for non-potable water]] |
|||
An original recommendation for water intake in 1945 by the Food and Nutrition Board of the [[United States National Research Council]] read: "An ordinary standard for diverse persons is 1 milliliter for each calorie of food. Most of this quantity is contained in prepared foods."<ref>{{cite book| title = Food and Nutrition Board, National Academy of Sciences. Recommended Dietary Allowances.| publisher = National Research Council, Reprint and Circular Series, No. 122| year = 1945|pages = 3–18}}</ref> The latest dietary reference intake report by the [[United States National Research Council]] in general recommended (including food sources): 3.7 liters for men and 2.7 liters of water total for women.<ref>[http://www.iom.edu/report.asp?id=18495 Dietary Reference Intakes: Water, Potassium, Sodium, Chloride, and Sulfate], Food and Nutrition Board</ref> Specifically, [[Pregnancy|pregnant]] and [[breastfeeding]] women need additional fluids to stay hydrated. The [[Institute of Medicine]] (U.S.) recommends that, on average, men consume 3.0 liters and women 2.2 liters; pregnant women should increase intake to 2.4 liters (10 cups) and breastfeeding women should get 3 liters (12 cups), since an especially large amount of fluid is lost during nursing.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/water/NU00283|title=Water: How much should you drink every day?|publisher=Mayoclinic.com|accessdate=2010-07-25}}</ref> Also noted is that normally, about 20% of water intake comes from food, while the rest comes from drinking water and beverages ([[Caffeine|caffeinated]] included). Water is excreted from the body in multiple forms; through [[urine]] and [[feces]], through [[sweat]]ing, and by exhalation of water vapor in the breath. With physical exertion and heat exposure, water loss will increase and daily fluid needs may increase as well. |
|||
Humans require water with few impurities. Common impurities include metal salts and oxides, including copper, iron, calcium and lead,<ref>"Conquering Chemistry" 4th Ed. Published 2008</ref> and/or harmful [[bacteria]], such as ''[[Vibrio]]''. Some [[Solution|solutes]] are acceptable and even desirable for taste enhancement and to provide needed [[electrolyte]]s.<ref>{{cite book |
|||
| last = Maton |
|||
| first = Anthea |
|||
| coauthors = Jean Hopkins, Charles William McLaughlin, Susan Johnson, Maryanna Quon Warner, David LaHart, Jill D. Wright |
|||
| title = Human Biology and Health |
|||
| publisher = Prentice Hall |
|||
| year = 1993 |
|||
| location = Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey, USA |
|||
| isbn = 0-13-981176-1 |
|||
| oclc = 32308337}}</ref> |
|||
The single largest (by volume) freshwater resource suitable for drinking is [[Lake Baikal]] in Siberia.<ref>{{cite book|url=http://books.google.com/?id=1cV8tziHZ5sC&pg=PA125|page=125|title=Water: a shared responsibility|author=Unesco|publisher=Berghahn Books|year=2006|isbn=1845451775}}</ref> |
|||
====Washing==== |
|||
The propensity of water to form [[Solvation|solutions]] and [[emulsion]]s is useful in various [[washing]] processes. Many industrial processes rely on reactions using chemicals dissolved in water, suspension of solids in water [[slurry|slurries]] or using water to dissolve and extract substances. Washing is also an important component of several aspects of personal [[body hygiene]]. |
|||
====Transportation==== |
|||
The use of water for transportation of materials through rivers and canals as well as the international shipping lanes is an important part of the world economy. |
|||
====Chemical uses==== |
|||
Water is widely used in chemical reactions as a [[solvent]] or [[reactant]] and less commonly as a [[solution|solute]] or [[catalyst]]. In inorganic reactions, water is a common solvent, dissolving many ionic compounds. In organic reactions, it is not usually used as a reaction solvent, because it does not dissolve the reactants well and is [[amphoteric]] (acidic ''and'' basic) and [[nucleophilic]]. Nevertheless, these properties are sometimes desirable. Also, acceleration of [[Diels-Alder reaction]]s by water has been observed. [[Supercritical water]] has recently been a topic of research. Oxygen-saturated supercritical water combusts organic pollutants efficiently. |
|||
====Heat exchange==== |
|||
Water and steam are used as heat transfer fluids in diverse heat exchange systems, due to its availability and high heat capacity, both as a coolant and for heating. Cool water may even be naturally available from a lake or the sea. Condensing [[steam]] is a particularly efficient heating fluid because of the large heat of vaporization. A disadvantage is that water and steam are somewhat corrosive. In almost all electric [[power station]]s, water is the coolant, which vaporizes and drives steam [[turbine]]s to drive generators. In the U.S., cooling power plants is the largest use of water.<ref name="Water Use in the United States"/> |
|||
In the [[nuclear power]] industry, water can also be used as a [[neutron moderator]]. In most [[nuclear reactor]]s, water is both a coolant and a moderator. This provides something of a passive safety measure, as removing the water from the reactor also [[Void coefficient|slows the nuclear reaction down]] – however other methods are favored for stopping a reaction and it is preferred to keep the nuclear core covered with water so as to ensure adequate cooling. |
|||
====Fire extinction==== |
|||
[[File:MH-60S Helicopter dumps water onto Fire.jpg|right|thumb|Water is used for [[fire fighting|fighting]] [[wildfire]]s.]] |
|||
Water has a high heat of vaporization and is relatively inert, which makes it a good [[Fire fighting#Use of water|fire extinguishing]] fluid. The evaporation of water carries heat away from the fire. It is dangerous to use water on fires involving oils and organic solvents, because many organic materials float on water and the water tends to spread the burning liquid. |
|||
Use of water in fire fighting should also take into account the hazards of a [[steam explosion]], which may occur when water is used on very hot fires in confined spaces, and of a hydrogen explosion, when substances which react with water, such as certain metals or hot carbon such as [[coal]], [[charcoal]], [[coke (fuel)|coke]] graphite, decompose the water, producing [[water gas]]. |
|||
The power of such explosions was seen in the [[Chernobyl disaster]], although the water involved did not come from fire-fighting at that time but the reactor's own water cooling system. A steam explosion occurred when the extreme overheating of the core caused water to flash into steam. A hydrogen explosion may have occurred as a result of reaction between steam and hot [[zirconium]]. |
|||
====Recreation==== |
|||
[[File:Grand Anse Beach Grenada.jpg|thumb|220p|right|Grand Anse Beach, St. George's, [[Grenada]], [[West Indies]], often reported as one of the top 10 beaches in the world.]] |
|||
{{Main|Water sport (recreation)}} |
|||
Humans use water for many recreational purposes, as well as for exercising and for sports. Some of these include [[swimming (sport)|swimming]], [[waterskiing]], [[boating]], [[surfing]] and [[diving]]. In addition, some sports, like [[ice hockey]] and [[ice skating]], are played on ice. Lakesides, beaches and [[water park]]s are popular places for people to go to relax and enjoy recreation. Many find the sound and appearance of flowing water to be calming, and fountains and other water features are popular decorations. Some keep fish and other life in [[aquarium]]s or [[pond]]s for show, fun, and companionship. Humans also use water for snow sports i.e. [[skiing]], [[sledding]], [[snowmobiling]] or [[snowboarding]], which requires the water to be frozen. |
|||
====Water industry==== |
|||
[[File:Water carrier.jpg|thumb|A water-carrier in [[India]], 1882. In many places where running water is not available, water has to be transported by people.]] |
|||
[[File:TapWater-china.JPG|thumb|left|A manual water [[pump]] in [[China]]]] |
|||
[[File:Usine Bret MG 1648.jpg|thumb|left|[[Water purification]] facility]] |
|||
The [[water industry]] provides drinking water and [[wastewater]] services (including [[sewage treatment]]) to [[household]]s and [[industry]]. [[Water supply]] facilities include [[water well]]s [[cistern]]s for [[rainwater harvesting]], [[water supply network]], [[water purification]] facilities, [[water tank]]s, [[water tower]]s, [[water pipe]]s including old [[aqueduct]]s. [[Atmospheric water generator]]s are in development. |
|||
Drinking water is often collected at [[spring (hydrosphere)|springs]], extracted from artificial [[Boring (earth)|borings]] (wells) in the ground, or pumped from lakes and rivers. Building more wells in adequate places is thus a possible way to produce more water, assuming the aquifers can supply an adequate flow. Other water sources include rainwater collection. Water may require purification for human consumption. This may involve removal of undissolved substances, dissolved substances and harmful [[microbe]]s. Popular methods are [[filter (water)|filtering]] with sand which only removes undissolved material, while [[chlorination]] and [[boiling]] kill harmful microbes. [[Distillation]] does all three functions. More advanced techniques exist, such as [[reverse osmosis]]. [[Desalination]] of abundant [[seawater]] is a more expensive solution used in coastal [[arid]] [[climate]]s. |
|||
The distribution of drinking water is done through [[municipal water system]]s, tanker delivery or as [[bottled water]]. Governments in many countries have programs to distribute water to the needy at no charge. |
|||
Reducing usage by using drinking (potable) water only for human consumption is another option. In some cities such as [[Hong Kong]], sea water is extensively used for flushing toilets citywide in order to [[Water conservation|conserve fresh water resources]]. |
|||
Polluting water may be the biggest single misuse of water; to the extent that a pollutant limits other uses of the water, it becomes a waste of the resource, regardless of benefits to the polluter. Like other types of pollution, this does not enter standard accounting of market costs, being conceived as [[externality|externalities]] for which the market cannot account. Thus other people pay the price of water pollution, while the private firms' profits are not redistributed to the local population victim of this pollution. [[Pharmaceuticals]] consumed by humans often end up in the waterways and can have detrimental effects on [[marine biology|aquatic]] life if they [[bioaccumulation|bioaccumulate]] and if they are not [[biodegradable]]. |
|||
Wastewater facilities are [[storm sewer]]s and [[Sewage treatment|wastewater treatment plants]]. Another way to remove pollution from [[surface runoff]] water is [[bioswale]]. |
|||
====Industrial applications==== |
|||
Water is used in [[power generation]]. [[Hydroelectricity]] is electricity obtained from [[hydropower]]. Hydroelectric power comes from water driving a water turbine connected to a generator. Hydroelectricity is a low-cost, non-polluting, renewable energy source. The energy is supplied by the motion of water. Typically a [[dam]] is constructed on a river, creating an artificial lake behind it. Water flowing out of the lake is forced through turbines that turn generators. |
|||
{{wide image|200407-sandouping-sanxiadaba-4.med.jpg|940px|[[Three Gorges Dam]] is the [[List of the largest hydroelectric power stations|largest hydro-electric power station]].}} |
|||
Pressurized water is used in [[Hydrodemolition|water blasting]] and [[water jet cutter]]s. Also, very high pressure water guns are used for precise cutting. It works very well, is relatively safe, and is not harmful to the environment. It is also used in the cooling of machinery to prevent overheating, or prevent saw blades from overheating. |
|||
Water is also used in many industrial processes and machines, such as the [[steam turbine]] and [[heat exchanger]], in addition to its use as a chemical [[solvent]]. Discharge of untreated water from industrial uses is [[pollution]]. Pollution includes discharged solutes ([[water pollution|chemical pollution]]) and discharged coolant water (thermal pollution). Industry requires pure water for many applications and utilizes a variety of purification techniques both in water supply and discharge. |
|||
====Food processing==== |
|||
[[File:Cuisson des pates.jpg|thumb|left|Water can be used to cook foods such as [[noodles]].]] |
|||
Water plays many critical roles within the field of [[food science]]. It is important for a food scientist to understand the roles that water plays within food processing to ensure the success of their products. |
|||
Solutes such as salts and sugars found in water affect the physical properties of water. The boiling and freezing points of water are affected by solutes, as well as [[air pressure]], which is in turn affected by [[altitude]]. Water boils at lower temperatures with the lower air pressure which occurs at higher elevations. One [[mole (unit)|mole]] of sucrose (sugar) per kilogram of water raises the boiling point of water by 0.51 °C, and one mole of salt per kg raises the boiling point by 1.02 °C; similarly, increasing the number of dissolved particles lowers water's freezing point.<ref name="vaclacik">{{cite book|title= Essentials of Food Science|url=http://books.google.com/?id=iCCsvwZrguUC&printsec=frontcover|year=2007|author= Vaclavik, Vickie A. and Christian, Elizabeth W|publisher=Springer|isbn=0387699392}}</ref> Solutes in water also affect water activity which affects many chemical reactions and the growth of microbes in food.<ref name="deman">{{cite book|url=http://books.google.com/?id=kDYJ7a1HbD0C&pg=PA434|title=Principles of Food Chemistry|year=1999|author=DeMan, John M|publisher=Springer|isbn=083421234X}}</ref> Water activity can be described as a ratio of the vapor pressure of water in a solution to the vapor pressure of pure water.<ref name="vaclacik"/> Solutes in water lower water activity. This is important to know because most bacterial growth ceases at low levels of water activity.<ref name="deman" /> Not only does microbial growth affect the safety of food but also the preservation and shelf life of food. |
|||
Water hardness is also a critical factor in food processing. It can |
|||
dramatically affect the quality of a product as well as playing a role |
|||
in sanitation. Water hardness is classified based on the amounts of |
|||
removable calcium carbonate salt it contains per gallon. Water |
|||
hardness is measured in grains; 0.064 g calcium carbonate is |
|||
equivalent to one grain of hardness.<ref name="vaclacik"/> Water is |
|||
classified as soft if it contains 1 to 4 grains, medium if it contains |
|||
5 to 10 grains and hard if it contains 11 to 20 grains. |
|||
{{Vague|please add totally metric definition too.|date=December 2008}} |
|||
<ref name="vaclacik"/> The hardness of water may be altered or treated by using a chemical ion exchange system. The hardness of water also affects its pH balance which plays a critical role in food processing. For example, hard water prevents successful production of clear beverages. Water hardness also affects sanitation; with increasing hardness, there is a loss of effectiveness for its use as a sanitizer.<ref name="vaclacik"/> |
|||
[[Boiling]], [[steaming]], and [[simmering]] are popular [[cooking]] methods that often require immersing food in water or its gaseous state, steam. Water is also used for [[dishwashing]]. |
|||
==Water law, water politics and water crisis== |
|||
[[File:Access to drinking water in third world.svg|thumb|310px|An estimate of the share of people in developing countries with access to [[potable water]] 1970–2000]] |
|||
{{Main|Water law|Water right|Water crisis}} |
|||
[[Water politics]] is [[politics]] affected by water and [[water resources]]. For this reason, water is a strategic resource in the globe and an important element in many political conflicts. It causes health impacts and damage to biodiversity. |
|||
1.6 billion people have gained access to a safe water source since 1990.<ref>[http://mdgs.un.org/unsd/mdg/Resources/Static/Products/Progress2008/MDG_Report_2008_En.pdf#page=44 The Millennium Development Goals Report], United Nations, 2008</ref> The proportion of people in developing countries with access to safe water is calculated to have improved from 30% in 1970<ref name=lomborg>{{cite book| author = Lomborg, Björn|year =2001|title =The Skeptical Environmentalist| publisher = [[Cambridge University Press]]| isbn = 0521010683| url =http://www.lomborg.com/dyn/files/basic_items/69-file/skeptenvironChap1.pdf|page =22}}</ref> to 71% in 1990, 79% in 2000 and 84% in 2004. This trend is projected to continue.<ref name=UN>{{cite web|url=http://mdgs.un.org/unsd/mdg/Resources/Static/Products/Progress2008/MDG_Report_2008_En.pdf#page=44 |title=MDG Report 2008 |accessdate=2010-07-25}}</ref> To halve, by 2015, the proportion of people without sustainable access to safe drinking water is one of the [[Millennium Development Goals]]. This goal is projected to be reached. |
|||
A 2006 [[United Nations]] report stated that "there is enough water for everyone", but that access to it is hampered by mismanagement and corruption.<ref>[[UNESCO]], (2006), [http://unesdoc.unesco.org/images/0014/001444/144409E.pdf Water, a shared responsibility. The United Nations World Water Development Report 2].</ref> In addition, global initiatives to improve the efficiency of aid delivery, such as the [[Paris Declaration on Aid Effectiveness]], have not been taken up by water sector donors as effectively as they have in education and health, potentially leaving multiple donors working on overlapping projects and recipient governments without empowerment to act.<ref>Welle, Katharina; Evans, Barbara; Tucker, Josephine and Nicol, Alan (2008) [http://www.odi.org.uk/resources/download/1894.pdf ''Is water lagging behind on Aid Effectiveness?'']</ref> |
|||
The authors of the 2007 [[Comprehensive Assessment of Water Management in Agriculture]] cited poor governance as one reason for some forms of water scarcity. Water governance is the set of formal and informal processes through which decisions related to water management are made. Good water governance is primarily about knowing what processes work best in a particular physical and socioeconomic context. Mistakes have sometimes been made by trying to apply 'blueprints' that work in the developed world to developing world locations and contexts. The Mekong river is one example; a review by the [[International Water Management Institute]] of policies in six countries that rely on the Mekong river for water found that thorough and transparent cost-benefit analyses and environmental impact assessments were rarely undertaken. They also discovered that Cambodia's draft water law was much more complex than it needed to be.<ref> [http://www.iwmi.cgiar.org/Publications/Water_Issue_Briefs/index.aspx ''Water governance''], Water Issue Brief, Issue 5, 2010, [[IWMI]]</ref> |
|||
The [[UN World Water Development Report]] (WWDR, 2003) from the [[World Water Assessment Program]] indicates that, in the next 20 years, the quantity of water available to everyone is predicted to decrease by 30%. 40% of the world's inhabitants currently have insufficient fresh water for minimal [[hygiene]]. More than 2.2 million people died in 2000 from [[waterborne diseases]] (related to the consumption of contaminated water) or [[drought]]. In 2004, the UK charity [[WaterAid]] reported that a child dies every 15 seconds from easily preventable water-related diseases; often this means lack of [[sewage]] disposal; see [[toilet]]. |
|||
Organizations concerned with water protection include [[International Water Association]] (IWA), [[WaterAid]], [[Water 1st]], [http://www.awra.org/ American Water Resources Association]. The [[International Water Management Institute]] undertakes projects with the aim of using effective water management to reduce poverty. Water related conventions are [[United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification]] (UNCCD), [[International Convention for the Prevention of Pollution from Ships]], [[United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea]] and [[Ramsar Convention]]. [[World Day for Water]] takes place on 22 March and [[World Ocean Day]] on 8 June. |
|||
Water used in the production of a good or service is [[virtual water]]. |
|||
==In culture== |
|||
===Religion=== |
|||
{{Main|Water and religion}} |
|||
Water is considered a purifier in most religions. Major faiths that incorporate ritual washing ([[Ritual purification|ablution]]) include [[Christianity]], [[Hinduism]], [[Islam]], [[Judaism]], [[Rastafari movement]], [[Shinto]], [[Taoism]], and [[Wicca]]. Immersion (or [[aspersion]] or [[affusion]]) of a person in water is a central [[sacrament]] of Christianity (where it is called [[baptism]]); it is also a part of the practice of other religions, including Islam (''[[Ghusl]]''), Judaism (''[[mikvah]]'') and [[Sikhism]] (''[[Amrit Sanskar]]''). In addition, a ritual bath in pure water is performed for the dead in many religions including Islam and Judaism. In Islam, the five daily prayers can be done in most cases after completing washing certain parts of the body using clean water (''[[wudu]]''), unless water is unavailable (see ''[[Tayammum]]''). In Shinto, water is used in almost all rituals to cleanse a person or an area (e.g., in the ritual of ''[[misogi]]''). Water is mentioned numerous times in the [[Bible]], for example: "The earth was formed out of water and by water" (NIV). In the Qur'an it is stated that "Living things are made of water" and it is often used to describe paradise. |
|||
===Philosophy=== |
|||
The Ancient Greek philosopher [[Empedocles]] held that water is one of the four [[classical elements]] along with [[fire]], earth and [[Air (classical element)|air]], and was regarded as the [[ylem]], or basic substance of the universe. Water was considered cold and moist. In the theory of the [[humorism|four bodily humors]], water was associated with [[phlegm]]. The [[Water (classical element)|classical element of Water]] was also one of the [[Five elements (Chinese philosophy)|five elements]] in traditional [[Chinese philosophy]], along with [[earth (classical element)|earth]], [[fire (classical element)|fire]], [[wood (classical element)|wood]], and [[metal (classical element)|metal]]. |
|||
Water is also taken as a role model in some parts of traditional and popular Asian philosophy. James Legge's 1891 translation of the Dao De Jing states "The highest excellence is like (that of) water. The excellence of water appears in its benefiting all things, and in its occupying, without striving (to the contrary), the low place which all men dislike. Hence (its way) is near to (that of) the Tao" and "There is nothing in the world more soft and weak than water, and yet for attacking things that are firm and strong there is nothing that can take precedence of it—for there is nothing (so effectual) for which it can be changed."<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.sacred-texts.com/tao/taote.htm |title=Internet Sacred Text Archive Home |publisher=Sacred-texts.com |accessdate=2010-07-25}}</ref> |
|||
===Literature=== |
|||
Water is used in literature as a symbol of purification. Examples include the critical importance of a river in ''[[As I Lay Dying (novel)|As I Lay Dying]]'' by [[William Faulkner]] and the drowning of [[Ophelia]] in ''[[Hamlet]]''. |
|||
[[Sherlock Holmes]] held that "From a drop of water, a logician could infer the possibility of an [[Atlantic Ocean|Atlantic]] or a [[Niagara Falls|Niagara]] without having seen or heard of one or the other."<ref>[[Arthur Conan Doyle]], ''[[A Study in Scarlet]]'', Chapter 2, "The Science of Deduction"</ref> |
|||
==See also== |
|||
{{Portal box|Water|Sustainable development}} |
|||
{{Main|List of water topics}} |
|||
*The [[water (data page)]] is a collection of the chemical and physical properties of water. |
|||
Water is described in many terms and contexts: |
|||
[[File:Liquid-water-and-ice.png|thumb|right|Liquid water and ice structures]] |
|||
*'''according to state''' |
|||
**solid – [[ice]] |
|||
**liquid – water |
|||
**gaseous – [[water vapor]] |
|||
**[[plasma (physics)|plasma]] |
|||
*'''according to [[meteorology]]''': |
|||
**[[hydrometeor]] |
|||
***[[Precipitation (meteorology)|precipitation]] |
|||
:{| border=0| |
|||
''' |
|||
|- |
|||
| ||precipitation according to movement|| ||precipitation according to state |
|||
|- |
|||
| |
|||
|valign=top | |
|||
*vertical (falling) precipitation |
|||
**[[rain]] |
|||
**[[freezing rain]] |
|||
**[[drizzle]] |
|||
**freezing drizzle |
|||
**[[snow]] |
|||
**[[snow pellets]] |
|||
**[[snow grains]] |
|||
**[[ice pellets]] |
|||
**frozen rain |
|||
**[[hail]] |
|||
**[[ice crystals]] |
|||
*horizontal (seated) precipitation |
|||
**[[dew]] |
|||
**[[hoarfrost]] |
|||
**[[atmospheric icing]] |
|||
**[[glaze ice]] |
|||
|| |
|||
|valign=top | |
|||
*liquid precipitation |
|||
**[[rain]] |
|||
**freezing rain |
|||
**[[drizzle]] |
|||
**freezing drizzle |
|||
**[[dew]] |
|||
*solid precipitation |
|||
**[[snow]] |
|||
**[[snow pellets]] |
|||
**[[snow grains]] |
|||
**[[ice pellets]] |
|||
**frozen rain |
|||
**[[hail]] |
|||
**[[ice crystals]] |
|||
**[[hoarfrost]] |
|||
**[[atmospheric icing]] |
|||
**[[glaze ice]] |
|||
*mixed precipitation |
|||
**in temperatures around 0 °C |
|||
|} |
|||
**levitating particles |
|||
***[[clouds]] |
|||
***[[fog]] |
|||
***[[mist]] |
|||
**ascending particles (drifted by wind) |
|||
***[[spindrift]] |
|||
***''stirred snow'' |
|||
*'''according to occurrence''' |
|||
**[[groundwater]] |
|||
**[[meltwater]] |
|||
**[[meteoric water]] |
|||
**[[connate fluids|connate water]] |
|||
**[[fresh water]] |
|||
**[[surface water]] |
|||
**[[mineral water]] – contains many minerals |
|||
**[[brackish water]] |
|||
**[[dead water]] – strange phenomenon which can occur when a layer of fresh or brackish water rests on top of denser salt water, without the two layers mixing. It is dangerous for ship traveling. |
|||
**[[seawater]] |
|||
**[[brine]] |
|||
*'''according to uses''' |
|||
**[[tap water]] |
|||
**[[bottled water]] |
|||
**[[drinking water]] or potable water – useful for everyday drinking, without fouling, it contains balanced minerals that are not harmful to health (see below) |
|||
**[[purified water]], laboratory-grade, analytical-grade or reagent-grade water – water which has been highly purified for specific uses in science or engineering. Often broadly classified as Type I, Type II, or Type III, this category of water includes, but is not limited to, the following: |
|||
***[[distilled water]] |
|||
***[[double distilled water]] |
|||
***[[deionized water]] |
|||
***[[reverse osmosis plant]] water |
|||
*'''according to other features''' |
|||
**[[soft water]] – contains fewer minerals |
|||
**[[hard water]] – from underground, contains more minerals |
|||
**[[distilled water]], [[double distilled water]], [[deionized water]] – contains no minerals |
|||
**[[water of crystallization]] — water incorporated into crystalline structures |
|||
**[[hydrates]] — water bound into other chemical substances |
|||
**[[heavy water]] – made from heavy atoms of hydrogen – [[deuterium]]. It is in nature in normal water in very low concentration. It was used in construction of first [[Nuclear reactor technology|nuclear reactors]]. |
|||
**[[tritiated water]] |
|||
*'''according to [[microbiology]]''' |
|||
**[[drinking water]] |
|||
**[[wastewater]] |
|||
**[[stormwater]] or [[surface water]] |
|||
*'''according to religion''' |
|||
**[[holy water]] |
|||
===Other topics=== |
|||
*[[Dihydrogen monoxide hoax]] |
|||
*[[Water Pasteurization Indicator]] |
|||
*[[Water intoxication]] |
|||
*[[Water pinch analysis]] |
|||
*[[Mpemba effect]] |
|||
==References== |
|||
{{Clear}} |
|||
{{Reflist|colwidth=30em}} |
|||
==Further reading== |
|||
*Jones, OA., JN Lester and N Voulvoulis, Pharmaceuticals: a threat to drinking water? ''TRENDS in Biotechnology'' 23(4): 163, 2005 |
|||
*Franks, F (Ed), Water, A comprehensive treatise, Plenum Press, New York, 1972–1982 |
|||
[http://www.oup.com/us/catalog/general/subject/EarthSciences/Oceanography/?view=usa&ci=9780195076288 Water in Crisis] |
|||
*Gleick,PH., (editor), ''The World's Water: The Biennial Report on Freshwater Resources''. Island Press, Washington, D.C. (published every two years, beginning in 1998.) [http://www.worldwater.org The World's Water, Island Press] |
|||
*Postel,S., ''Last Oasis: Facing Water Scarcity''. W.W. Norton and Company, New York. 1992 |
|||
*Reisner,M., ''Cadillac Desert: The American West and Its Disappearing Water''. Penguin Books, New York. 1986. |
|||
*Debenedetti,PG., and HE Stanley, "Supercooled and Glassy Water", ''Physics Today'' '''56''' (6), p. 40–46 (2003). [http://polymer.bu.edu/hes/articles/ds03.pdf Downloadable PDF (1.9 MB)] |
|||
*[http://ucowr.org/updates/index.html Journal of Contemporary Water Resources and Education] |
|||
*United Nations ''World Water Development Report''. Produced every three years. [http://www.unesco.org/water/wwap/wwdr/ UN World Water Development Report] |
|||
==External links== |
|||
{{Sisterlinks|water}} |
|||
*[http://stats.oecd.org/wbos/Index.aspx?DataSetCode=ENV_WAT OECD Water statistics] |
|||
*[http://www.worldwater.org The World's Water Data Page] |
|||
*[http://www.fao.org/nr/water/aquastat/main/index.stm FAO Comprehensive Water Database, AQUASTAT] |
|||
*[http://worldwater.org/conflict.html The Water Conflict Chronology: Water Conflict Database] |
|||
*[http://ga.water.usgs.gov/edu/ US Geological Survey Water for Schools information] |
|||
*[http://water.worldbank.org/water/ Portal to The World Bank's strategy, work and associated publications on water resources] |
|||
{{Food chemistry}} |
|||
[[Category:Articles containing video clips]] |
|||
[[Category:Hydrogen compounds]] |
|||
[[Category:Natural resources]] |
|||
[[Category:Oxides]] |
|||
[[Category:Inorganic solvents]] |
|||
[[Category:Water| ]] |
|||
[[Category:Liquids]] |
|||
{{Link FA|bjn}} |
|||
{{Link GA|eo}} |
|||
{{Link GA|es}} |
|||
{{Link GA|zh-classical}} |
|||
{{Link FA|eu}} |
|||
{{Link FA|he}} |
|||
{{Link FA|it}} |
|||
{{Link FA|mk}} |
|||
{{Link FA|vec}} |
|||
[[af:Water]] |
|||
[[als:Wasser]] |
|||
[[am:ውሃ]] |
|||
[[ang:Wæter]] |
|||
[[ar:ماء]] |
|||
[[an:Augua]] |
|||
[[arc:ܡܝܐ]] |
|||
[[ast:Agua]] |
|||
[[gn:Y]] |
|||
[[ay:Uma]] |
|||
[[az:Su]] |
|||
[[bm:Ji]] |
|||
[[bn:পানি]] |
|||
[[bjn:Banyu]] |
|||
[[zh-min-nan:Chúi]] |
|||
[[ba:Һыу]] |
|||
[[be:Вада]] |
|||
[[be-x-old:Вада]] |
|||
[[bh:पानी]] |
|||
[[bg:Вода]] |
|||
[[bar:Wossa]] |
|||
[[bo:ཆུ།]] |
|||
[[bs:Voda]] |
|||
[[br:Dour]] |
|||
[[ca:Aigua]] |
|||
[[cv:Шыв]] |
|||
[[ceb:Tubig]] |
|||
[[cs:Voda]] |
|||
[[ch:Hånom]] |
|||
[[sn:Mvura]] |
|||
[[co:Acqua]] |
|||
[[cy:Dŵr]] |
|||
[[da:Vand]] |
|||
[[pdc:Wasser]] |
|||
[[de:Wasser]] |
|||
[[dv:ފެން]] |
|||
[[nv:Tó]] |
|||
[[et:Vesi]] |
|||
[[el:Νερό]] |
|||
[[eml:Aqua]] |
|||
[[es:Agua]] |
|||
[[eo:Akvo]] |
|||
[[ext:Áugua]] |
|||
[[eu:Ur]] |
|||
[[fa:آب]] |
|||
[[hif:Paani]] |
|||
[[fr:Eau]] |
|||
[[fy:Wetter]] |
|||
[[fur:Aghe]] |
|||
[[ga:Uisce]] |
|||
[[gv:Ushtey]] |
|||
[[gd:Uisge]] |
|||
[[gl:Auga]] |
|||
[[gan:水]] |
|||
[[ki:Mai]] |
|||
[[gu:પાણી]] |
|||
[[hak:Súi]] |
|||
[[ko:물]] |
|||
[[hy:Ջուր]] |
|||
[[hi:जल (पानी)]] |
|||
[[hsb:Woda]] |
|||
[[hr:Voda]] |
|||
[[io:Aquo]] |
|||
[[ilo:Danúm]] |
|||
[[id:Air]] |
|||
[[ia:Aqua]] |
|||
[[ie:Aqua]] |
|||
[[os:Дон]] |
|||
[[xh:Amanzi]] |
|||
[[zu:Amanzi]] |
|||
[[is:Vatn]] |
|||
[[it:Acqua]] |
|||
[[he:מים]] |
|||
[[jv:Banyu]] |
|||
[[kn:ನೀರು]] |
|||
[[ka:წყალი]] |
|||
[[ks:پونۍ]] |
|||
[[kk:Су]] |
|||
[[sw:Maji]] |
|||
[[kg:Maza]] |
|||
[[ht:Dlo]] |
|||
[[ku:Av]] |
|||
[[lad:Agua]] |
|||
[[ltg:Iudiņs]] |
|||
[[la:Aqua]] |
|||
[[lv:Ūdens]] |
|||
[[lb:Waasser]] |
|||
[[lt:Vanduo]] |
|||
[[li:Water]] |
|||
[[ln:Mái]] |
|||
[[jbo:djacu]] |
|||
[[lmo:Aqua]] |
|||
[[hu:Víz]] |
|||
[[mk:Вода]] |
|||
[[mg:Rano]] |
|||
[[ml:ജലം]] |
|||
[[mr:पाणी]] |
|||
[[xmf:წყარი]] |
|||
[[mzn:ئو]] |
|||
[[ms:Air]] |
|||
[[cdo:Cūi]] |
|||
[[mwl:Auga]] |
|||
[[mdf:Ведь]] |
|||
[[mn:Ус]] |
|||
[[my:ရေ]] |
|||
[[nah:Ātl]] |
|||
[[na:Ebok]] |
|||
[[nl:Water]] |
|||
[[nds-nl:Woater]] |
|||
[[cr:ᓃᐲᔾ]] |
|||
[[ne:पानी]] |
|||
[[new:लः]] |
|||
[[ja:水]] |
|||
[[nap:Acqua]] |
|||
[[ce:Хи]] |
|||
[[no:Vann]] |
|||
[[nn:Vatn]] |
|||
[[nrm:Ieau]] |
|||
[[oc:Aiga]] |
|||
[[or:ଜଳ]] |
|||
[[om:Bishaan]] |
|||
[[uz:Suv]] |
|||
[[pa:ਪਾਣੀ]] |
|||
[[pnb:پانی]] |
|||
[[pap:Awa]] |
|||
[[ps:اوبه]] |
|||
[[nds:Water]] |
|||
[[pl:Woda]] |
|||
[[pt:Água]] |
|||
[[ksh:Wasser]] |
|||
[[ro:Apă]] |
|||
[[qu:Yaku]] |
|||
[[rue:Вода]] |
|||
[[ru:Вода]] |
|||
[[sah:Уу]] |
|||
[[sa:जलम्]] |
|||
[[sc:Aba]] |
|||
[[sco:Watter]] |
|||
[[sq:Uji]] |
|||
[[scn:Acqua (vìppita)]] |
|||
[[si:ජලය]] |
|||
[[simple:Water]] |
|||
[[sk:Voda]] |
|||
[[sl:Voda]] |
|||
[[szl:Woda]] |
|||
[[so:Biyo]] |
|||
[[ckb:ئاو]] |
|||
[[sr:Вода]] |
|||
[[sh:Voda]] |
|||
[[su:Cai]] |
|||
[[fi:Vesi]] |
|||
[[sv:Vatten]] |
|||
[[tl:Tubig]] |
|||
[[ta:நீர்]] |
|||
[[kab:Aman]] |
|||
[[tt:Су]] |
|||
[[te:నీరు]] |
|||
[[th:น้ำ]] |
|||
[[tg:Об]] |
|||
[[chr:ᎠᎹ]] |
|||
[[chy:Mahpe]] |
|||
[[tr:Su]] |
|||
[[uk:Вода]] |
|||
[[ur:پانی]] |
|||
[[za:Raemx]] |
|||
[[vec:Aqua]] |
|||
[[vep:Vezi]] |
|||
[[vi:Nước]] |
|||
[[vo:Vat]] |
|||
[[fiu-vro:Vesi]] |
|||
[[zh-classical:水]] |
|||
[[vls:Woater]] |
|||
[[war:Tubig]] |
|||
[[wo:Ndox]] |
|||
[[wuu:水]] |
|||
[[yi:וואסער]] |
|||
[[yo:Omi]] |
|||
[[zh-yue:水]] |
|||
[[bat-smg:Ondou]] |
|||
[[zh:水]] |
|||
Revision as of 11:41, 9 May 2012
Template:Redirect4 Template:Two other uses

Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H
2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state (water vapor or steam). Water also exists in a liquid crystal state near hydrophilic surfaces.[1][2] Under nomenclature used to name chemical compounds, dihydrogen monoxide is the scientific name for water, though it is almost never used.[3]
Water covers 70.9% of the Earth's surface,[4] and is vital for all known forms of life.[5] On Earth, 96.5% of the planet's water is found in oceans, 1.7% in groundwater, 1.7% in glaciers and the ice caps of Antarctica and Greenland, a small fraction in other large water bodies, and 0.001% in the air as vapor, clouds (formed of solid and liquid water particles suspended in air), and precipitation.[6][7] Only 2.5% of the Earth's water is freshwater, and 98.8% of that water is in ice and groundwater. Less than 0.3% of all freshwater is in rivers, lakes, and the atmosphere, and an even smaller amount of the Earth's freshwater (0.003%) is contained within biological bodies and manufactured products.[6]
Water on Earth moves continually through the hydrological cycle of evaporation and transpiration (evapotranspiration), condensation, precipitation, and runoff, usually reaching the sea. Evaporation and transpiration contribute to the precipitation over land.
Safe drinking water is essential to humans and other lifeforms. Access to safe drinking water has improved over the last decades in almost every part of the world, but approximately one billion people still lack access to safe water and over 2.5 billion lack access to adequate sanitation.[8] There is a clear correlation between access to safe water and GDP per capita.[9] However, some observers have estimated that by 2025 more than half of the world population will be facing water-based vulnerability.[10] A recent report (November 2009) suggests that by 2030, in some developing regions of the world, water demand will exceed supply by 50%.[11] Water plays an important role in the world economy, as it functions as a solvent for a wide variety of chemical substances and facilitates industrial cooling and transportation. Approximately 70% of the fresh water used by humans goes to agriculture.[12]
Chemical and physical properties
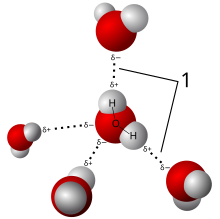



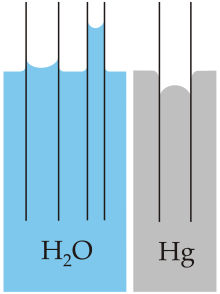
Water is the chemical substance with chemical formula H
2O: one molecule of water has two hydrogen atoms covalently bonded to a single oxygen atom.
Water appears in nature in all three common states of matter and may take many different forms on Earth: water vapor and clouds in the sky; seawater in the oceans; icebergs in the polar oceans; glaciers and rivers in the mountains; and the liquid in aquifers in the ground.
At high temperatures and pressures, such as in the interior of giant planets, it is argued that water exists as ionic water in which the molecules break down into a soup of hydrogen and oxygen ions, and at even higher pressures as superionic water in which the oxygen crystallises but the hydrogen ions float around freely within the oxygen lattice.[13]
The major chemical and physical properties of water are:
- Water is a liquid at standard temperature and pressure. It is tasteless and odorless. The intrinsic colour of water and ice is a very slight blue hue, although both appear colorless in small quantities. Water vapour is essentially invisible as a gas.[14]
- Water is transparent in the visible electromagnetic spectrum. Thus aquatic plants can live in water because sunlight can reach them. Infrared light is strongly absorbed by the hydrogen-oxygen or OH bonds.
- Since the water molecule is not linear and the oxygen atom has a higher electronegativity than hydrogen atoms, it carries a slight negative charge, whereas the hydrogen atoms are slightly positive. As a result, water is a polar molecule with an electrical dipole moment. Water also can form an unusually large number of intermolecular hydrogen bonds (four) for a molecule of its size. These factors lead to strong attractive forces between molecules of water, giving rise to water's high surface tension[15] and capillary forces. The capillary action refers to the tendency of water to move up a narrow tube against the force of gravity. This property is relied upon by all vascular plants, such as trees.[16]
- Water is a good solvent and is often referred to as the universal solvent. Substances that dissolve in water, e.g., salts, sugars, acids, alkalis, and some gases – especially oxygen, carbon dioxide (carbonation) are known as hydrophilic (water-loving) substances, while those that do not mix well with water (e.g., fats and oils), are known as hydrophobic (water-fearing) substances.
- All the major components in cells (proteins, DNA and polysaccharides) are also dissolved in water.
- Pure water has a low electrical conductivity, but this increases significantly with the dissolution of a small amount of ionic material such as sodium chloride.
- The boiling point of water (and all other liquids) is dependent on the barometric pressure. For example, on the top of Mt. Everest water boils at 68 °C (154 °F), compared to 100 °C (212 °F) at sea level. Conversely, water deep in the ocean near geothermal vents can reach temperatures of hundreds of degrees and remain liquid.
- At 4181.3 J/(kg·K), water has a high specific heat capacity, as well as a high heat of vaporization (40.65 kJ·mol−1), both of which are a result of the extensive hydrogen bonding between its molecules. These two unusual properties allow water to moderate Earth's climate by buffering large fluctuations in temperature.
- The maximum density of water occurs at 3.98 °C (39.16 °F).[17] It has the anomalous property of becoming less dense, not more, when it is cooled down to its solid form, ice. It expands to occupy 9% greater volume in this solid state, which accounts for the fact of ice floating on liquid water, as in icebergs.
- Its density is 1,000 kg/m3 (62.428 lb/cu ft or 8.3454 lb/US gal) liquid (at 4 °C; ice has a density of 917 kg/m3).[18]

ADR label for transporting goods dangerously reactive with water - Water is miscible with many liquids, such as ethanol, in all proportions, forming a single homogeneous liquid. On the other hand, water and most oils are immiscible, usually forming layers according to increasing density from the top. As a gas, water vapor is completely miscible with air.
- Water forms an azeotrope with many other solvents.
- Water can be split by electrolysis into hydrogen and oxygen.
- As an oxide of hydrogen, water is formed when hydrogen or hydrogen-containing compounds burn or react with oxygen or oxygen-containing compounds. Water is not a fuel, it is an end-product of the combustion of hydrogen. The energy required to split water into hydrogen and oxygen by electrolysis or any other means is greater than the energy that can be collected when the hydrogen and oxygen recombine.[19]
- Elements which are more electropositive than hydrogen such as lithium, sodium, calcium, potassium and caesium displace hydrogen from water, forming hydroxides. Being a flammable gas, the hydrogen given off is dangerous and the reaction of water with the more electropositive of these elements may be violently explosive.
Taste and odor
Water can dissolve many different substances, giving it varying tastes and odors. Humans and other animals have developed senses that enable them to evaluate the potability of water by avoiding water that is too salty or putrid. The taste of spring water and mineral water, often advertised in marketing of consumer products, derives from the minerals dissolved in it. However, pure H2O is tasteless and odorless. The advertised purity of spring and mineral water refers to absence of toxins, pollutants and microbes, not the absence of naturally occurring minerals.
Distribution in nature
In the universe
Much of the universe's water is produced as a byproduct of star formation. When stars are born, their birth is accompanied by a strong outward wind of gas and dust. When this outflow of material eventually impacts the surrounding gas, the shock waves that are created compress and heat the gas. The water observed is quickly produced in this warm dense gas.[20]
On 22 July 2011, a report described the discovery of a gigantic cloud of water vapor, containing "140 trillion times more water than all of Earth's oceans combined," around a quasar located 12 billion light years from Earth. According to the researchers, the "discovery shows that water has been prevalent in the universe for nearly its entire existence."[21][22]
Water has been detected in interstellar clouds within our galaxy, the Milky Way. Water probably exists in abundance in other galaxies, too, because its components, hydrogen and oxygen, are among the most abundant elements in the universe. Interstellar clouds eventually condense into solar nebulae and solar systems such as ours.
Water vapor is present in
- Atmosphere of Mercury: 3.4%, and large amounts of water in Mercury's exosphere[23]
- Atmosphere of Venus: 0.002%
- Earth's atmosphere: ~0.40% over full atmosphere, typically 1–4% at surface
- Atmosphere of Mars: 0.03%
- Atmosphere of Jupiter: 0.0004%
- Atmosphere of Saturn – in ices only
- Enceladus (moon of Saturn): 91%
- exoplanets known as HD 189733 b[24] and HD 209458 b.[25]
Liquid water is present on
- Earth: 71% of surface
- Europa: 100 km deep subsurface ocean
Strong evidence suggests that liquid water is present just under the surface of Saturn's moon Enceladus.
Water ice is present on
- Earth – mainly as ice sheets
- polar ice caps on Mars
- Moon
- Titan
- Europa
- Saturn's rings[26]
- Enceladus
- Pluto and Charon[26]
- Comets and comet source populations (Kuiper belt and Oort cloud objects).
Water ice may be present on Ceres and Tethys. Water and other volatiles probably comprise much of the internal structures of Uranus and Neptune and the water in the deeper layers may be in the form of ionic water in which the molecules break down into a soup of hydrogen and oxygen ions, and deeper down as superionic water in which the oxygen crystallises but the hydrogen ions float around freely within the oxygen lattice.[13]
Some of the Moon's minerals contain water molecules. For instance, in 2008 a laboratory device which ejects and identifies particles found small amounts of the compound in the inside of volcanic rock brought from Moon to Earth by the Apollo 15 crew in 1971.[27] NASA reported the detection of water molecules by NASA's Moon Mineralogy Mapper aboard the Indian Space Research Organization's Chandrayaan-1 spacecraft in September 2009.[28]
Water and habitable zone
The existence of liquid water, and to a lesser extent its gaseous and solid forms, on Earth are vital to the existence of life on Earth as we know it. The Earth is located in the habitable zone of the solar system; if it were slightly closer to or farther from the Sun (about 5%, or about 8 million kilometers), the conditions which allow the three forms to be present simultaneously would be far less likely to exist.[29][30]
Earth's gravity allows it to hold an atmosphere. Water vapor and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere provide a temperature buffer (greenhouse effect) which helps maintain a relatively steady surface temperature. If Earth were smaller, a thinner atmosphere would allow temperature extremes, thus preventing the accumulation of water except in polar ice caps (as on Mars).
The surface temperature of Earth has been relatively constant through geologic time despite varying levels of incoming solar radiation (insolation), indicating that a dynamic process governs Earth's temperature via a combination of greenhouse gases and surface or atmospheric albedo. This proposal is known as the Gaia hypothesis.
The state of water on a planet depends on ambient pressure, which is determined by the planet's gravity. If a planet is sufficiently massive, the water on it may be solid even at high temperatures, because of the high pressure caused by gravity, as it was observed on exoplanets Gliese 436 b[31] and GJ 1214 b.[32]
There are various theories about origin of water on Earth.
On Earth
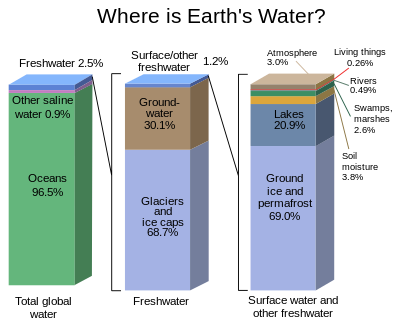

Hydrology is the study of the movement, distribution, and quality of water throughout the Earth. The study of the distribution of water is hydrography. The study of the distribution and movement of groundwater is hydrogeology, of glaciers is glaciology, of inland waters is limnology and distribution of oceans is oceanography. Ecological processes with hydrology are in focus of ecohydrology.
The collective mass of water found on, under, and over the surface of a planet is called the hydrosphere. Earth's approximate water volume (the total water supply of the world) is 1,338,000,000 km3 (321,000,000 mi3).[6]
Liquid water is found in bodies of water, such as an ocean, sea, lake, river, stream, canal, pond, or puddle. The majority of water on Earth is sea water. Water is also present in the atmosphere in solid, liquid, and vapor states. It also exists as groundwater in aquifers.
Water is important in many geological processes. Groundwater is present in most rocks, and the pressure of this groundwater affects patterns of faulting. Water in the mantle is responsible for the melt that produces volcanoes at subduction zones. On the surface of the Earth, water is important in both chemical and physical weathering processes. Water and, to a lesser but still significant extent, ice, are also responsible for a large amount of sediment transport that occurs on the surface of the earth. Deposition of transported sediment forms many types of sedimentary rocks, which make up the geologic record of Earth history.
Water cycle

The water cycle (known scientifically as the hydrologic cycle) refers to the continuous exchange of water within the hydrosphere, between the atmosphere, soil water, surface water, groundwater, and plants.
Water moves perpetually through each of these regions in the water cycle consisting of following transfer processes:
- evaporation from oceans and other water bodies into the air and transpiration from land plants and animals into air.
- precipitation, from water vapor condensing from the air and falling to earth or ocean.
- runoff from the land usually reaching the sea.
Most water vapor over the oceans returns to the oceans, but winds carry water vapor over land at the same rate as runoff into the sea, about 47 Tt per year. Over land, evaporation and transpiration contribute another 72 Tt per year. Precipitation, at a rate of 119 Tt per year over land, has several forms: most commonly rain, snow, and hail, with some contribution from fog and dew.[33] Condensed water in the air may also refract sunlight to produce rainbows.
Water runoff often collects over watersheds flowing into rivers. A mathematical model used to simulate river or stream flow and calculate water quality parameters is hydrological transport model. Some of water is diverted to irrigation for agriculture. Rivers and seas offer opportunity for travel and commerce. Through erosion, runoff shapes the environment creating river valleys and deltas which provide rich soil and level ground for the establishment of population centers. A flood occurs when an area of land, usually low-lying, is covered with water. It is when a river overflows its banks or flood from the sea. A drought is an extended period of months or years when a region notes a deficiency in its water supply. This occurs when a region receives consistently below average precipitation.
Fresh water storage
Some runoff water is trapped for periods of time, for example in lakes. At high altitude, during winter, and in the far north and south, snow collects in ice caps, snow pack and glaciers. Water also infiltrates the ground and goes into aquifers. This groundwater later flows back to the surface in springs, or more spectacularly in hot springs and geysers. Groundwater is also extracted artificially in wells. This water storage is important, since clean, fresh water is essential to human and other land-based life. In many parts of the world, it is in short supply.
Sea water
Sea water contains about 3.5% salt on average, plus smaller amounts of other substances. The physical properties of sea water differ from fresh water in some important respects. It freezes at a lower temperature (about −1.9 °C) and its density increases with decreasing temperature to the freezing point, instead of reaching maximum density at a temperature above freezing. The salinity of water in major seas varies from about 0.7% in the Baltic Sea to 4.0% in the Red Sea.
Tides
Tides are the cyclic rising and falling of local sea levels caused by the tidal forces of the Moon and the Sun acting on the oceans. Tides cause changes in the depth of the marine and estuarine water bodies and produce oscillating currents known as tidal streams. The changing tide produced at a given location is the result of the changing positions of the Moon and Sun relative to the Earth coupled with the effects of Earth rotation and the local bathymetry. The strip of seashore that is submerged at high tide and exposed at low tide, the intertidal zone, is an important ecological product of ocean tides.
Effects on life


From a biological standpoint, water has many distinct properties that are critical for the proliferation of life that set it apart from other substances. It carries out this role by allowing organic compounds to react in ways that ultimately allow replication. All known forms of life depend on water. Water is vital both as a solvent in which many of the body's solutes dissolve and as an essential part of many metabolic processes within the body. Metabolism is the sum total of anabolism and catabolism. In anabolism, water is removed from molecules (through energy requiring enzymatic chemical reactions) in order to grow larger molecules (e.g. starches, triglycerides and proteins for storage of fuels and information). In catabolism, water is used to break bonds in order to generate smaller molecules (e.g. glucose, fatty acids and amino acids to be used for fuels for energy use or other purposes). Without water, these particular metabolic processes could not exist.
Water is fundamental to photosynthesis and respiration. Photosynthetic cells use the sun's energy to split off water's hydrogen from oxygen. Hydrogen is combined with CO2 (absorbed from air or water) to form glucose and release oxygen. All living cells use such fuels and oxidize the hydrogen and carbon to capture the sun's energy and reform water and CO2 in the process (cellular respiration).
Water is also central to acid-base neutrality and enzyme function. An acid, a hydrogen ion (H+, that is, a proton) donor, can be neutralized by a base, a proton acceptor such as hydroxide ion (OH−) to form water. Water is considered to be neutral, with a pH (the negative log of the hydrogen ion concentration) of 7. Acids have pH values less than 7 while bases have values greater than 7.

Aquatic life forms

Earth surface waters are filled with life. The earliest life forms appeared in water; nearly all fish live exclusively in water, and there are many types of marine mammals, such as dolphins and whales. Some kinds of animals, such as amphibians, spend portions of their lives in water and portions on land. Plants such as kelp and algae grow in the water and are the basis for some underwater ecosystems. Plankton is generally the foundation of the ocean food chain.
Aquatic vertebrates must obtain oxygen to survive, and they do so in various ways. Fish have gills instead of lungs, although some species of fish, such as the lungfish, have both. Marine mammals, such as dolphins, whales, otters, and seals need to surface periodically to breathe air. Some amphibians are able to absorb oxygen through their skin. Invertebrates exhibit a wide range of modifications to survive in poorly oxygenated waters including breathing tubes (see insect and mollusc siphons) and gills (Carcinus). However as invertebrate life evolved in an aquatic habitat most have little or no specialisation for respiration in water.
Effects on human civilization

Civilization has historically flourished around rivers and major waterways; Mesopotamia, the so-called cradle of civilization, was situated between the major rivers Tigris and Euphrates; the ancient society of the Egyptians depended entirely upon the Nile. Large metropolises like Rotterdam, London, Montreal, Paris, New York City, Buenos Aires, Shanghai, Tokyo, Chicago, and Hong Kong owe their success in part to their easy accessibility via water and the resultant expansion of trade. Islands with safe water ports, like Singapore, have flourished for the same reason. In places such as North Africa and the Middle East, where water is more scarce, access to clean drinking water was and is a major factor in human development.
Health and pollution

Water fit for human consumption is called drinking water or potable water. Water that is not potable may be made potable by filtration or distillation, or by a range of other methods.
Water that is not fit for drinking but is not harmful for humans when used for swimming or bathing is called by various names other than potable or drinking water, and is sometimes called safe water, or "safe for bathing". Chlorine is a skin and mucous membrane irritant that is used to make water safe for bathing or drinking. Its use is highly technical and is usually monitored by government regulations (typically 1 part per million (ppm) for drinking water, and 1–2 ppm of chlorine not yet reacted with impurities for bathing water). Water for bathing may be maintained in satisfactory microbiological condition using chemical disinfectants such as chlorine or ozone or by the use of ultraviolet light.
In the USA, non-potable forms of wastewater generated by humans may be referred to as greywater, which is treatable and thus easily able to be made potable again, and blackwater, which generally contains sewage and other forms of waste which require further treatment in order to be made reusable. Greywater composes 50–80% of residential wastewater generated by a household's sanitation equipment (sinks, showers and kitchen runoff, but not toilets, which generate blackwater.) These terms may have different meanings in other countries and cultures.
This natural resource is becoming scarcer in certain places, and its availability is a major social and economic concern. Currently, about a billion people around the world routinely drink unhealthy water. Most countries accepted the goal of halving by 2015 the number of people worldwide who do not have access to safe water and sanitation during the 2003 G8 Evian summit.[34] Even if this difficult goal is met, it will still leave more than an estimated half a billion people without access to safe drinking water and over a billion without access to adequate sanitation. Poor water quality and bad sanitation are deadly; some five million deaths a year are caused by polluted drinking water. The World Health Organization estimates that safe water could prevent 1.4 million child deaths from diarrhea each year.[35] Water, however, is not a finite resource, but rather re-circulated as potable water in precipitation in quantities many degrees of magnitude higher than human consumption. Therefore, it is the relatively small quantity of water in reserve in the earth (about 1% of our drinking water supply, which is replenished in aquifers around every 1 to 10 years), that is a non-renewable resource, and it is, rather, the distribution of potable and irrigation water which is scarce, rather than the actual amount of it that exists on the earth. Water-poor countries use importation of goods as the primary method of importing water (to leave enough for local human consumption), since the manufacturing process uses around 10 to 100 times products' masses in water.
In the developing world, 90% of all wastewater still goes untreated into local rivers and streams.[36] Some 50 countries, with roughly a third of the world’s population, also suffer from medium or high water stress, and 17 of these extract more water annually than is recharged through their natural water cycles.[37] The strain not only affects surface freshwater bodies like rivers and lakes, but it also degrades groundwater resources.
Human uses
Agriculture

The most important use of water in agriculture is for irrigation, which is a key component to produce enough food. Irrigation takes up to 90% of water withdrawn in some developing countries[38] and significant proportions in more economically developed countries (United States, 30% of freshwater usage is for irrigation).[39] It takes around 3,000 litres of water, converted from liquid to vapour, to produce enough food to satisfy one person's daily dietary need. This is a considerable amount, when compared to that required for drinking, which is between two and five litres. To produce food for the 6.5 billion or so people who inhabit the planet today requires the water that would fill a canal ten metres deep, 100 metres wide and 7.1 million kilometres long – that's enough to circle the globe 180 times.
Fifty years ago, the common perception was that water was an infinite resource. At this time, there were fewer than half the current number of people on the planet. People were not as wealthy as today, consumed fewer calories and ate less meat, so less water was needed to produce their food. They required a third of the volume of water we presently take from rivers. Today, the competition for the fixed amount of water resources is much more intense, giving rise to the concept of peak water.[40] This is because there are now nearly seven billion people on the planet, their consumption of water-thirsty meat and vegetables is rising, and there is increasing competition for water from industry, urbanisation and biofuel crops. In future, even more water will be needed to produce food because the Earth's population is forecast to rise to 9 billion by 2050.[41] An additional 2.5 or 3 billion people, choosing to eat fewer cereals and more meat and vegetables could add an additional five million kilometres to the virtual canal mentioned above.
An assessment of water management in agriculture was conducted in 2007 by the International Water Management Institute in Sri Lanka to see if the world had sufficient water to provide food for its growing population.[42] It assessed the current availability of water for agriculture on a global scale and mapped out locations suffering from water scarcity. It found that a fifth of the world's people, more than 1.2 billion, live in areas of physical water scarcity, where there is not enough water to meet all demands. A further 1.6 billion people live in areas experiencing economic water scarcity, where the lack of investment in water or insufficient human capacity make it impossible for authorities to satisfy the demand for water. The report found that it would be possible to produce the food required in future, but that continuation of today's food production and environmental trends would lead to crises in many parts of the world. To avoid a global water crisis, farmers will have to strive to increase productivity to meet growing demands for food, while industry and cities find ways to use water more efficiently.[43]
As a scientific standard
On 7 April 1795, the gram was defined in France to be equal to "the absolute weight of a volume of pure water equal to a cube of one hundredth of a meter, and to the temperature of the melting ice."[44] For practical purposes though, a metallic reference standard was required, one thousand times more massive, the kilogram. Work was therefore commissioned to determine precisely the mass of one liter of water. In spite of the fact that the decreed definition of the gram specified water at 0 °C — a highly reproducible temperature — the scientists chose to redefine the standard and to perform their measurements at the temperature of highest water density, which was measured at the time as 4 °C (39 °F).[45]
The Kelvin temperature scale of the SI system is based on the triple point of water, defined as exactly 273.16 K or 0.01 °C. The scale is an absolute temperature scale with the same increment as the Celsius temperature scale, which was originally defined according the boiling point (set to 100 °C) and melting point (set to 0 °C) of water.
Natural water consists mainly of the isotopes hydrogen-1 and oxygen-16, but there is also small quantity of heavier isotopes such as hydrogen-2 (deuterium). The amount of deuterium oxides or heavy water is very small, but it still affects the properties of water. Water from rivers and lakes tends to contain less deuterium than seawater. Therefore, standard water is defined in the Vienna Standard Mean Ocean Water specification.
For drinking


The human body contains from 55% to 78% water, depending on body size.[46] To function properly, the body requires between one and seven liters of water per day to avoid dehydration; the precise amount depends on the level of activity, temperature, humidity, and other factors. Most of this is ingested through foods or beverages other than drinking straight water. It is not clear how much water intake is needed by healthy people, though most advocates agree that approximately 2 liters (6 to 7 glasses) of water daily is the minimum to maintain proper hydration.[47] Medical literature favors a lower consumption, typically 1 liter of water for an average male, excluding extra requirements due to fluid loss from exercise or warm weather.[48] For those who have healthy kidneys, it is rather difficult to drink too much water, but (especially in warm humid weather and while exercising) it is dangerous to drink too little. People can drink far more water than necessary while exercising, however, putting them at risk of water intoxication (hyperhydration), which can be fatal.[49][50] The popular claim that "a person should consume eight glasses of water per day" seems to have no real basis in science.[51] Similar misconceptions concerning the effect of water on weight loss and constipation have also been dispelled.[52]

An original recommendation for water intake in 1945 by the Food and Nutrition Board of the United States National Research Council read: "An ordinary standard for diverse persons is 1 milliliter for each calorie of food. Most of this quantity is contained in prepared foods."[53] The latest dietary reference intake report by the United States National Research Council in general recommended (including food sources): 3.7 liters for men and 2.7 liters of water total for women.[54] Specifically, pregnant and breastfeeding women need additional fluids to stay hydrated. The Institute of Medicine (U.S.) recommends that, on average, men consume 3.0 liters and women 2.2 liters; pregnant women should increase intake to 2.4 liters (10 cups) and breastfeeding women should get 3 liters (12 cups), since an especially large amount of fluid is lost during nursing.[55] Also noted is that normally, about 20% of water intake comes from food, while the rest comes from drinking water and beverages (caffeinated included). Water is excreted from the body in multiple forms; through urine and feces, through sweating, and by exhalation of water vapor in the breath. With physical exertion and heat exposure, water loss will increase and daily fluid needs may increase as well.
Humans require water with few impurities. Common impurities include metal salts and oxides, including copper, iron, calcium and lead,[56] and/or harmful bacteria, such as Vibrio. Some solutes are acceptable and even desirable for taste enhancement and to provide needed electrolytes.[57]
The single largest (by volume) freshwater resource suitable for drinking is Lake Baikal in Siberia.[58]
Washing
The propensity of water to form solutions and emulsions is useful in various washing processes. Many industrial processes rely on reactions using chemicals dissolved in water, suspension of solids in water slurries or using water to dissolve and extract substances. Washing is also an important component of several aspects of personal body hygiene.
Transportation
The use of water for transportation of materials through rivers and canals as well as the international shipping lanes is an important part of the world economy.
Chemical uses
Water is widely used in chemical reactions as a solvent or reactant and less commonly as a solute or catalyst. In inorganic reactions, water is a common solvent, dissolving many ionic compounds. In organic reactions, it is not usually used as a reaction solvent, because it does not dissolve the reactants well and is amphoteric (acidic and basic) and nucleophilic. Nevertheless, these properties are sometimes desirable. Also, acceleration of Diels-Alder reactions by water has been observed. Supercritical water has recently been a topic of research. Oxygen-saturated supercritical water combusts organic pollutants efficiently.
Heat exchange
Water and steam are used as heat transfer fluids in diverse heat exchange systems, due to its availability and high heat capacity, both as a coolant and for heating. Cool water may even be naturally available from a lake or the sea. Condensing steam is a particularly efficient heating fluid because of the large heat of vaporization. A disadvantage is that water and steam are somewhat corrosive. In almost all electric power stations, water is the coolant, which vaporizes and drives steam turbines to drive generators. In the U.S., cooling power plants is the largest use of water.[39]
In the nuclear power industry, water can also be used as a neutron moderator. In most nuclear reactors, water is both a coolant and a moderator. This provides something of a passive safety measure, as removing the water from the reactor also slows the nuclear reaction down – however other methods are favored for stopping a reaction and it is preferred to keep the nuclear core covered with water so as to ensure adequate cooling.
Fire extinction

Water has a high heat of vaporization and is relatively inert, which makes it a good fire extinguishing fluid. The evaporation of water carries heat away from the fire. It is dangerous to use water on fires involving oils and organic solvents, because many organic materials float on water and the water tends to spread the burning liquid.
Use of water in fire fighting should also take into account the hazards of a steam explosion, which may occur when water is used on very hot fires in confined spaces, and of a hydrogen explosion, when substances which react with water, such as certain metals or hot carbon such as coal, charcoal, coke graphite, decompose the water, producing water gas.
The power of such explosions was seen in the Chernobyl disaster, although the water involved did not come from fire-fighting at that time but the reactor's own water cooling system. A steam explosion occurred when the extreme overheating of the core caused water to flash into steam. A hydrogen explosion may have occurred as a result of reaction between steam and hot zirconium.
Recreation

Humans use water for many recreational purposes, as well as for exercising and for sports. Some of these include swimming, waterskiing, boating, surfing and diving. In addition, some sports, like ice hockey and ice skating, are played on ice. Lakesides, beaches and water parks are popular places for people to go to relax and enjoy recreation. Many find the sound and appearance of flowing water to be calming, and fountains and other water features are popular decorations. Some keep fish and other life in aquariums or ponds for show, fun, and companionship. Humans also use water for snow sports i.e. skiing, sledding, snowmobiling or snowboarding, which requires the water to be frozen.
Water industry



The water industry provides drinking water and wastewater services (including sewage treatment) to households and industry. Water supply facilities include water wells cisterns for rainwater harvesting, water supply network, water purification facilities, water tanks, water towers, water pipes including old aqueducts. Atmospheric water generators are in development.
Drinking water is often collected at springs, extracted from artificial borings (wells) in the ground, or pumped from lakes and rivers. Building more wells in adequate places is thus a possible way to produce more water, assuming the aquifers can supply an adequate flow. Other water sources include rainwater collection. Water may require purification for human consumption. This may involve removal of undissolved substances, dissolved substances and harmful microbes. Popular methods are filtering with sand which only removes undissolved material, while chlorination and boiling kill harmful microbes. Distillation does all three functions. More advanced techniques exist, such as reverse osmosis. Desalination of abundant seawater is a more expensive solution used in coastal arid climates.
The distribution of drinking water is done through municipal water systems, tanker delivery or as bottled water. Governments in many countries have programs to distribute water to the needy at no charge.
Reducing usage by using drinking (potable) water only for human consumption is another option. In some cities such as Hong Kong, sea water is extensively used for flushing toilets citywide in order to conserve fresh water resources.
Polluting water may be the biggest single misuse of water; to the extent that a pollutant limits other uses of the water, it becomes a waste of the resource, regardless of benefits to the polluter. Like other types of pollution, this does not enter standard accounting of market costs, being conceived as externalities for which the market cannot account. Thus other people pay the price of water pollution, while the private firms' profits are not redistributed to the local population victim of this pollution. Pharmaceuticals consumed by humans often end up in the waterways and can have detrimental effects on aquatic life if they bioaccumulate and if they are not biodegradable.
Wastewater facilities are storm sewers and wastewater treatment plants. Another way to remove pollution from surface runoff water is bioswale.
Industrial applications
Water is used in power generation. Hydroelectricity is electricity obtained from hydropower. Hydroelectric power comes from water driving a water turbine connected to a generator. Hydroelectricity is a low-cost, non-polluting, renewable energy source. The energy is supplied by the motion of water. Typically a dam is constructed on a river, creating an artificial lake behind it. Water flowing out of the lake is forced through turbines that turn generators.
Pressurized water is used in water blasting and water jet cutters. Also, very high pressure water guns are used for precise cutting. It works very well, is relatively safe, and is not harmful to the environment. It is also used in the cooling of machinery to prevent overheating, or prevent saw blades from overheating.
Water is also used in many industrial processes and machines, such as the steam turbine and heat exchanger, in addition to its use as a chemical solvent. Discharge of untreated water from industrial uses is pollution. Pollution includes discharged solutes (chemical pollution) and discharged coolant water (thermal pollution). Industry requires pure water for many applications and utilizes a variety of purification techniques both in water supply and discharge.
Food processing

Water plays many critical roles within the field of food science. It is important for a food scientist to understand the roles that water plays within food processing to ensure the success of their products.
Solutes such as salts and sugars found in water affect the physical properties of water. The boiling and freezing points of water are affected by solutes, as well as air pressure, which is in turn affected by altitude. Water boils at lower temperatures with the lower air pressure which occurs at higher elevations. One mole of sucrose (sugar) per kilogram of water raises the boiling point of water by 0.51 °C, and one mole of salt per kg raises the boiling point by 1.02 °C; similarly, increasing the number of dissolved particles lowers water's freezing point.[59] Solutes in water also affect water activity which affects many chemical reactions and the growth of microbes in food.[60] Water activity can be described as a ratio of the vapor pressure of water in a solution to the vapor pressure of pure water.[59] Solutes in water lower water activity. This is important to know because most bacterial growth ceases at low levels of water activity.[60] Not only does microbial growth affect the safety of food but also the preservation and shelf life of food.
Water hardness is also a critical factor in food processing. It can dramatically affect the quality of a product as well as playing a role in sanitation. Water hardness is classified based on the amounts of removable calcium carbonate salt it contains per gallon. Water hardness is measured in grains; 0.064 g calcium carbonate is equivalent to one grain of hardness.[59] Water is classified as soft if it contains 1 to 4 grains, medium if it contains 5 to 10 grains and hard if it contains 11 to 20 grains.[vague] [59] The hardness of water may be altered or treated by using a chemical ion exchange system. The hardness of water also affects its pH balance which plays a critical role in food processing. For example, hard water prevents successful production of clear beverages. Water hardness also affects sanitation; with increasing hardness, there is a loss of effectiveness for its use as a sanitizer.[59]
Boiling, steaming, and simmering are popular cooking methods that often require immersing food in water or its gaseous state, steam. Water is also used for dishwashing.
Water law, water politics and water crisis

Water politics is politics affected by water and water resources. For this reason, water is a strategic resource in the globe and an important element in many political conflicts. It causes health impacts and damage to biodiversity.
1.6 billion people have gained access to a safe water source since 1990.[61] The proportion of people in developing countries with access to safe water is calculated to have improved from 30% in 1970[62] to 71% in 1990, 79% in 2000 and 84% in 2004. This trend is projected to continue.[8] To halve, by 2015, the proportion of people without sustainable access to safe drinking water is one of the Millennium Development Goals. This goal is projected to be reached.
A 2006 United Nations report stated that "there is enough water for everyone", but that access to it is hampered by mismanagement and corruption.[63] In addition, global initiatives to improve the efficiency of aid delivery, such as the Paris Declaration on Aid Effectiveness, have not been taken up by water sector donors as effectively as they have in education and health, potentially leaving multiple donors working on overlapping projects and recipient governments without empowerment to act.[64]
The authors of the 2007 Comprehensive Assessment of Water Management in Agriculture cited poor governance as one reason for some forms of water scarcity. Water governance is the set of formal and informal processes through which decisions related to water management are made. Good water governance is primarily about knowing what processes work best in a particular physical and socioeconomic context. Mistakes have sometimes been made by trying to apply 'blueprints' that work in the developed world to developing world locations and contexts. The Mekong river is one example; a review by the International Water Management Institute of policies in six countries that rely on the Mekong river for water found that thorough and transparent cost-benefit analyses and environmental impact assessments were rarely undertaken. They also discovered that Cambodia's draft water law was much more complex than it needed to be.[65]
The UN World Water Development Report (WWDR, 2003) from the World Water Assessment Program indicates that, in the next 20 years, the quantity of water available to everyone is predicted to decrease by 30%. 40% of the world's inhabitants currently have insufficient fresh water for minimal hygiene. More than 2.2 million people died in 2000 from waterborne diseases (related to the consumption of contaminated water) or drought. In 2004, the UK charity WaterAid reported that a child dies every 15 seconds from easily preventable water-related diseases; often this means lack of sewage disposal; see toilet.
Organizations concerned with water protection include International Water Association (IWA), WaterAid, Water 1st, American Water Resources Association. The International Water Management Institute undertakes projects with the aim of using effective water management to reduce poverty. Water related conventions are United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD), International Convention for the Prevention of Pollution from Ships, United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea and Ramsar Convention. World Day for Water takes place on 22 March and World Ocean Day on 8 June.
Water used in the production of a good or service is virtual water.
In culture
Religion
Water is considered a purifier in most religions. Major faiths that incorporate ritual washing (ablution) include Christianity, Hinduism, Islam, Judaism, Rastafari movement, Shinto, Taoism, and Wicca. Immersion (or aspersion or affusion) of a person in water is a central sacrament of Christianity (where it is called baptism); it is also a part of the practice of other religions, including Islam (Ghusl), Judaism (mikvah) and Sikhism (Amrit Sanskar). In addition, a ritual bath in pure water is performed for the dead in many religions including Islam and Judaism. In Islam, the five daily prayers can be done in most cases after completing washing certain parts of the body using clean water (wudu), unless water is unavailable (see Tayammum). In Shinto, water is used in almost all rituals to cleanse a person or an area (e.g., in the ritual of misogi). Water is mentioned numerous times in the Bible, for example: "The earth was formed out of water and by water" (NIV). In the Qur'an it is stated that "Living things are made of water" and it is often used to describe paradise.
Philosophy
The Ancient Greek philosopher Empedocles held that water is one of the four classical elements along with fire, earth and air, and was regarded as the ylem, or basic substance of the universe. Water was considered cold and moist. In the theory of the four bodily humors, water was associated with phlegm. The classical element of Water was also one of the five elements in traditional Chinese philosophy, along with earth, fire, wood, and metal.
Water is also taken as a role model in some parts of traditional and popular Asian philosophy. James Legge's 1891 translation of the Dao De Jing states "The highest excellence is like (that of) water. The excellence of water appears in its benefiting all things, and in its occupying, without striving (to the contrary), the low place which all men dislike. Hence (its way) is near to (that of) the Tao" and "There is nothing in the world more soft and weak than water, and yet for attacking things that are firm and strong there is nothing that can take precedence of it—for there is nothing (so effectual) for which it can be changed."[66]
Literature
Water is used in literature as a symbol of purification. Examples include the critical importance of a river in As I Lay Dying by William Faulkner and the drowning of Ophelia in Hamlet.
Sherlock Holmes held that "From a drop of water, a logician could infer the possibility of an Atlantic or a Niagara without having seen or heard of one or the other."[67]
See also
- The water (data page) is a collection of the chemical and physical properties of water.
Water is described in many terms and contexts:

- according to state
- solid – ice
- liquid – water
- gaseous – water vapor
- plasma
- according to meteorology:
precipitation according to movement precipitation according to state - vertical (falling) precipitation
- rain
- freezing rain
- drizzle
- freezing drizzle
- snow
- snow pellets
- snow grains
- ice pellets
- frozen rain
- hail
- ice crystals
- horizontal (seated) precipitation
- liquid precipitation
- solid precipitation
- mixed precipitation
- in temperatures around 0 °C
- vertical (falling) precipitation
- according to occurrence
- groundwater
- meltwater
- meteoric water
- connate water
- fresh water
- surface water
- mineral water – contains many minerals
- brackish water
- dead water – strange phenomenon which can occur when a layer of fresh or brackish water rests on top of denser salt water, without the two layers mixing. It is dangerous for ship traveling.
- seawater
- brine
- according to uses
- tap water
- bottled water
- drinking water or potable water – useful for everyday drinking, without fouling, it contains balanced minerals that are not harmful to health (see below)
- purified water, laboratory-grade, analytical-grade or reagent-grade water – water which has been highly purified for specific uses in science or engineering. Often broadly classified as Type I, Type II, or Type III, this category of water includes, but is not limited to, the following:
- according to other features
- soft water – contains fewer minerals
- hard water – from underground, contains more minerals
- distilled water, double distilled water, deionized water – contains no minerals
- water of crystallization — water incorporated into crystalline structures
- hydrates — water bound into other chemical substances
- heavy water – made from heavy atoms of hydrogen – deuterium. It is in nature in normal water in very low concentration. It was used in construction of first nuclear reactors.
- tritiated water
- according to microbiology
- according to religion
Other topics
- Dihydrogen monoxide hoax
- Water Pasteurization Indicator
- Water intoxication
- Water pinch analysis
- Mpemba effect
References
- ^ Henniker, J. C. (1949). "The Depth of the Surface Zone of a Liquid". Reviews of Modern Physics. 21 (2). Reviews of Modern Physics: 322–341. doi:10.1103/RevModPhys.21.322.
- ^ Pollack, Gerald. "Water Science". University of Washington, Pollack Laboratory. Retrieved 2011-02-05.
Water has three phases – gas, liquid, and solid; but recent findings from our laboratory imply the presence of a surprisingly extensive fourth phase that occurs at interfaces.
- ^ Bramer, Scott. "Chemical Nomenclature". Widener University, Department of Chemistry. Retrieved 20 September 2011.
- ^ "CIA- The world fact book". Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 2008-12-20.
- ^ "United Nations". Un.org. 2005-03-22. Retrieved 2010-07-25.
- ^ a b c Gleick, P.H., ed. (1993). Water in Crisis: A Guide to the World's Freshwater Resources. Oxford University Press. p. 13, Table 2.1 "Water reserves on the earth".
{{cite book}}: Text "T" ignored (help) - ^ Water Vapor in the Climate System, Special Report, [AGU], December 1995 (linked 4/2007). Vital Water UNEP.
- ^ a b "MDG Report 2008" (PDF). Retrieved 2010-07-25.
- ^ "Public Services", Gapminder video
- ^ Kulshreshtha, S.N (1998). "A Global Outlook for Water Resources to the Year 2025". Water Resources Management. 12 (3): 167–184. doi:10.1023/A:1007957229865.
{{cite journal}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help) - ^ "Charting Our Water Future: Economic frameworks to inform decision-making" (PDF). Retrieved 2010-07-25.
- ^ Baroni, L. (2007). "Evaluating the environmental impact of various dietary patterns combined with different food production systems". European Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 61 (2): 279–286. doi:10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602522. PMID 17035955.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Weird water lurking inside giant planets, New Scientist,01 September 2010, Magazine issue 2776.
- ^ Braun, Charles L. (1993). "Why is water blue?". J. Chem. Educ. 70 (8): 612. doi:10.1021/ed070p612.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Campbell, Neil A. (2006). Biology: Exploring Life. Boston, Massachusetts: Pearson Prentice Hall. ISBN 0-13-250882-6.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Capillary Action – Liquid, Water, Force, and Surface – JRank Articles. Science.jrank.org. Retrieved on 2011-11-03.
- ^ Kotz, J. C., Treichel, P., & Weaver, G. C. (2005). Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity. Thomson Brooks/Cole. ISBN 053439597X.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Online Conversion – Density, Kidsnewsroom.org/elmer/infocentral/conversions
- ^ Ball, Philip (14 September 2007). "Burning water and other myths". Nature News. Retrieved 2007-09-14.
- ^ Melnick, Gary, Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics and Neufeld, David, Johns Hopkins University quoted in: "Discover of Water Vapor Near Orion Nebula Suggests Possible Origin of H20 in Solar System (sic)". The Harvard University Gazette. April 23, 1998. "Space Cloud Holds Enough Water to Fill Earth's Oceans 1 Million Times". Headlines@Hopkins, JHU. April 9, 1998. "Water, Water Everywhere: Radio telescope finds water is common in universe". The Harvard University Gazette. February 25, 1999.(linked 4/2007)
- ^ Clavin, Whitney; Buis, Alan (22 July 2011). "Astronomers Find Largest, Most Distant Reservoir of Water". NASA. Retrieved 2011-07-25.
- ^ Staff (22 July 2011). "Astronomers Find Largest, Oldest Mass of Water in Universe". Space.com. Retrieved 2011-07-23.
- ^ "MESSENGER Scientists 'Astonished' to Find Water in Mercury's Thin Atmosphere". Planetary Society. 2008-07-03. Retrieved 2008-07-05.
- ^ Water Found on Distant Planet July 12, 2007 By Laura Blue, Time
- ^ Water Found in Extrasolar Planet's Atmosphere – Space.com
- ^ a b Sparrow, Giles (2006). The Solar System. Thunder Bay Press. ISBN 1592235794.
- ^ Versteckt in Glasperlen: Auf dem Mond gibt es Wasser – Wissenschaft – Der Spiegel – Nachrichten
- ^ Water Molecules Found on the Moon, NASA, September 24, 2009
- ^ Ehlers, E.; Krafft, T, ed. (2001). "J. C. I. Dooge. "Integrated Management of Water Resources"". Understanding the Earth System: compartments, processes, and interactions. Springer. p. 116.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: editors list (link) - ^ "Habitable Zone". The Encyclopedia of Astrobiology, Astronomy and Spaceflight.
- ^ Shiga, David (6 May 2007). "Strange alien world made of "hot ice"". New Scientist. Retrieved 2010-03-28.
- ^ Aguilar, David A. (16 December 2009). "Astronomers Find Super-Earth Using Amateur, Off-the-Shelf Technology". Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics. Retrieved 2010-03-28.
- ^ Gleick, P.H., ed. (1993). Water in Crisis: A Guide to the World's Freshwater Resources. Oxford University Press. p. 15, Table 2.3.
{{cite book}}: Text "T" ignored (help) - ^ "G8 "Action plan" decided upon at the 2003 Evian summit". G8.fr. 2003-06-02. Retrieved 2010-07-25.
- ^ "World Health Organization. Safe Water and Global Health". Who.int. 2008-06-25. Retrieved 2010-07-25.
- ^ UNEP International Environment (2002). Environmentally Sound Technology for Wastewater and Stormwater Management: An International Source Book. IWA Publishing. ISBN 1843390086. OCLC 49204666.
- ^ Ravindranath, Nijavalli H. (2002). Climate Change and Developing Countries. Springer. ISBN 1402001045. OCLC 231965991.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ "WBCSD Water Facts & Trends". Retrieved 2010-07-25.
- ^ a b Water Use in the United States, National Atlas.gov
- ^ Gleick, P.H. (2010). "Peak Water" (PDF). Proceedings National Academy of Science. 107 (125). National Academy of Science: 11155–11162. doi:10.1073/pnas.1004812107. Retrieved 2011-10-11.
- ^ United Nations Press Release POP/952, 13 March 2007. World population will increase by 2.5 billion by 2050
- ^ Molden, D. (Ed). Water for food, Water for life: A Comprehensive Assessment of Water Management in Agriculture. Earthscan/IWMI, 2007.
- ^ Chartres, C. and Varma, S. Out of water. From Abundance to Scarcity and How to Solve the World’s Water Problems FT Press (USA), 2010
- ^ Décret relatif aux poids et aux mesures. 18 germinal an 3 (7 avril 1795). Decree relating to the weights and measurements (in French). quartier-rural.org
- ^ here L'Histoire Du Mètre, La Détermination De L'Unité De Poids. histoire.du.metre.free.fr
- ^ Re: What percentage of the human body is composed of water? Jeffrey Utz, M.D., The MadSci Network
- ^ "Healthy Water Living". BBC. Retrieved 2007-02-01.
- ^ Rhoades RA, Tanner GA (2003). Medical Physiology (2nd ed.). Baltimore: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 0781719364. OCLC 50554808.
- ^ Noakes TD, Goodwin N, Rayner BL; et al. (1985). "Water intoxication: a possible complication during endurance exercise". Med Sci Sports Exerc. 17 (3): 370–375. PMID 4021781.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Noakes TD, Goodwin N, Rayner BL, Branken T, Taylor RK (2005). "Water intoxication: a possible complication during endurance exercise, 1985". Wilderness Environ Med. 16 (4): 221–7. doi:10.1580/1080-6032(2005)16[221:WIAPCD]2.0.CO;2. PMID 16366205.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Drink at least eight glasses of water a day." Really? Is there scientific evidence for "8 × 8"? by Heinz Valdin, Department of Physiology, Dartmouth Medical School, Lebanon, New Hampshire
- ^ Drinking Water – How Much?, Factsmart.org web site and references within
- ^ Food and Nutrition Board, National Academy of Sciences. Recommended Dietary Allowances. National Research Council, Reprint and Circular Series, No. 122. 1945. pp. 3–18.
- ^ Dietary Reference Intakes: Water, Potassium, Sodium, Chloride, and Sulfate, Food and Nutrition Board
- ^ "Water: How much should you drink every day?". Mayoclinic.com. Retrieved 2010-07-25.
- ^ "Conquering Chemistry" 4th Ed. Published 2008
- ^ Maton, Anthea (1993). Human Biology and Health. Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey, USA: Prentice Hall. ISBN 0-13-981176-1. OCLC 32308337.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Unesco (2006). Water: a shared responsibility. Berghahn Books. p. 125. ISBN 1845451775.
- ^ a b c d e Vaclavik, Vickie A. and Christian, Elizabeth W (2007). Essentials of Food Science. Springer. ISBN 0387699392.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b DeMan, John M (1999). Principles of Food Chemistry. Springer. ISBN 083421234X.
- ^ The Millennium Development Goals Report, United Nations, 2008
- ^ Lomborg, Björn (2001). The Skeptical Environmentalist (PDF). Cambridge University Press. p. 22. ISBN 0521010683.
- ^ UNESCO, (2006), Water, a shared responsibility. The United Nations World Water Development Report 2.
- ^ Welle, Katharina; Evans, Barbara; Tucker, Josephine and Nicol, Alan (2008) Is water lagging behind on Aid Effectiveness?
- ^ Water governance, Water Issue Brief, Issue 5, 2010, IWMI
- ^ "Internet Sacred Text Archive Home". Sacred-texts.com. Retrieved 2010-07-25.
- ^ Arthur Conan Doyle, A Study in Scarlet, Chapter 2, "The Science of Deduction"
Further reading
- Jones, OA., JN Lester and N Voulvoulis, Pharmaceuticals: a threat to drinking water? TRENDS in Biotechnology 23(4): 163, 2005
- Franks, F (Ed), Water, A comprehensive treatise, Plenum Press, New York, 1972–1982
- Gleick,PH., (editor), The World's Water: The Biennial Report on Freshwater Resources. Island Press, Washington, D.C. (published every two years, beginning in 1998.) The World's Water, Island Press
- Postel,S., Last Oasis: Facing Water Scarcity. W.W. Norton and Company, New York. 1992
- Reisner,M., Cadillac Desert: The American West and Its Disappearing Water. Penguin Books, New York. 1986.
- Debenedetti,PG., and HE Stanley, "Supercooled and Glassy Water", Physics Today 56 (6), p. 40–46 (2003). Downloadable PDF (1.9 MB)
- Journal of Contemporary Water Resources and Education
- United Nations World Water Development Report. Produced every three years. UN World Water Development Report
External links
- OECD Water statistics
- The World's Water Data Page
- FAO Comprehensive Water Database, AQUASTAT
- The Water Conflict Chronology: Water Conflict Database
- US Geological Survey Water for Schools information
- Portal to The World Bank's strategy, work and associated publications on water resources
Template:Link FA Template:Link GA Template:Link GA Template:Link GA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA




