Black Mass: Difference between revisions
No, controversial claims cannot be anchored in a 100-year old text. These claims, if included at all, need to move down and be id'd as antique |
|||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
A '''Black Mass''' is a ritual performed as a [[sacrilege|sacrilegious]] parody of the [[Catholic Church|Roman Catholic]] [[mass (liturgy)|Mass]]. |
A '''Black Mass''' is a ritual performed as a [[sacrilege|sacrilegious]] parody of the [[Catholic Church|Roman Catholic]] [[mass (liturgy)|Mass]]. |
||
The history of such rituals is unclear before the modern era. The Black Mass was allegedly celebrated during the [[Witches' Sabbath]].<ref name="Rhodes">Rhodes, H.T.F. ''The Satanic Mass'', 1954.</ref> |
|||
The history of such rituals is unclear before the modern era. The Black Mass was allegedly celebrated during the [[Witches' Sabbath]].<ref name="Rhodes">Rhodes, H.T.F. ''The Satanic Mass'', 1954.</ref> Its main objective was the [[host desecration|profanation of the host]], although there is no agreement among authors on how [[Eucharist|hosts]] were obtained or profaned; the most common idea is that they were profaned by means of some ritual related to sexual practices.<ref name="Summers">Summers, Montague, ''The History of Witchcraft'', 1926, ch. IV, ''The Sabbat''</ref> Authors also disagree on which rites were performed during the ceremony.<ref name="Summers"/> Some medieval writers believed that the host was replaced by a [[toad]], a [[turnip]] or a piece of dry flesh, but most judges and authors believed that true hosts were given by [[Christianity|Christian]] [[priest]]s, who had made [[deal with the Devil|diabolical pacts]], to the attendants of the Sabbath to be profaned by them.<ref name="Summers"/> |
|||
It is not clear if the Black Mass was ever celebrated in medieval times; the works referring to them are lurid and unreliable manuals for witch-hunters written in Latin, such as the ''[[Malleus Maleficarum]]'' (1486) and the ''[[Compendium Maleficarum]]'' (1608), and it may have served solely as a shocking act with which to accuse enemies{{Citation needed|date=May 2014}}. |
It is not clear if the Black Mass was ever celebrated in medieval times; the works referring to them are lurid and unreliable manuals for witch-hunters written in Latin, such as the ''[[Malleus Maleficarum]]'' (1486) and the ''[[Compendium Maleficarum]]'' (1608), and it may have served solely as a shocking act with which to accuse enemies{{Citation needed|date=May 2014}}. |
||
Revision as of 20:07, 12 May 2014
This article contains weasel words: vague phrasing that often accompanies biased or unverifiable information. (February 2013) |
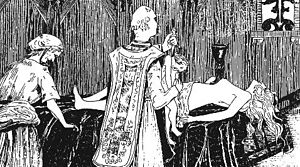
A Black Mass is a ritual performed as a sacrilegious parody of the Roman Catholic Mass.
The history of such rituals is unclear before the modern era. The Black Mass was allegedly celebrated during the Witches' Sabbath.[1]
It is not clear if the Black Mass was ever celebrated in medieval times; the works referring to them are lurid and unreliable manuals for witch-hunters written in Latin, such as the Malleus Maleficarum (1486) and the Compendium Maleficarum (1608), and it may have served solely as a shocking act with which to accuse enemies[citation needed].
Though the rite's history is uncertain, it seems largely a creation of 20th century Satanists and other occultists.
Origins and history of the Black Mass
One recent outline of the history of the Black Mass can be found in Richard Cavendish, The Black Arts[2] (1967) in the section on the Black Mass. Before that, an entire book was written about it, The Satanic Mass,[1] by H.T.F. Rhodes (1954). Additionally, a detailed study was published in German (and since translated into English) by Gerhard Zacharias, The Dark God: Satan Worship and Black Masses[3] (1964).
Early Christianity
The Catholic Church regards the Eucharist as its most important sacrament, going back to apostolic times. In general its various liturgies followed the outline of Liturgy of the Word, Offertory, Liturgy of the Sacrament, and Benediction, which developed into what is known as the Mass. However, as early Christianity was becoming more established and growing in influence, the early Church fathers described a few heretical groups practicing their own versions of Masses, some of a bizarre sexual nature (such as among the Borborites).[4]
Middle Age Roman Catholic parodies and additions to the Mass
In the Middle Ages, beginning with the Latin writings of the Goliards, the Roman Catholic Mass was drawn from or elaborated upon to create parodies of it for certain Church festivities. Thus, there was a Mass parody called "The Feast of Asses", in which Balaam's Ass (from the Old Testament) would begin talking and saying parts of the Mass. A similar parody was the Feast of Fools. Other Middle Age parodies of the Mass, also written in ecclesiastical Latin, were "drinkers' masses" and "gamblers' Masses," which lamented the situation of drunk, gambling monks, and instead of calling to "Deus" (God), called to "Bacchus" (the God of Wine). Some of these Latin parody works are found in the medieval Latin collection of poetry, Carmina Burana, written around 1230. The Catholic Church, however, eventually reacted by condemning them as sacrilegious and blasphemous.[citation needed]
Additionally, the Rite of the Mass was not completely fixed, and there was a place at the end of the Offertory for the Secret prayers, when the priest could insert private prayers for various personal needs. These practices became especially prevalent in France (see Pre-Tridentine Mass). As these types of personal prayers within the Mass spread, the institution of the Low Mass became quite common, where priests would hire their services out to perform various Masses for the needs of their clients — such as blessing crops or cattle, achieving success in some enterprise, obtaining love, or cursing enemies (one way this latter was done was by inserting the enemy's name in a Mass for the dead, accompanied by burying an image of the enemy). However, such practices were condemned by the Church as sacrilegious.[citation needed]
A further source of late Medieval and Early Modern involvement with parodies and alterations of the Mass, were the writings of the European witch-hunt, which saw witches as being agents of the Devil, who were described as inverting the Christian Mass and employing the stolen Host for diabolical ends. The witch-hunter's manuals such as the Malleus Maleficarum and the Compendium Maleficarum give details relating to these supposed practices.[5]
Early modern France
Between the 16th and the 19th centuries, many examples of interest in the Black Mass come from France.
- 16th century: Catherine de' Medici, the Queen of France, was said by Jean Bodin to have performed a Black Mass, based on a story in his book on witchcraft, De la démonomanie des sorciers. In spite of its lurid details, there is little outside evidence to back up his story.
- 17th century: Catherine Monvoisin and the priest Étienne Guibourg performed "Black Masses" for Madame de Montespan, the mistress of King Louis XIV of France. Since a criminal investigation—L'affaire des poisons ("Affair of the Poisons")—was launched (resulting in the execution of Monvoisin and the imprisonment of Guibourg) many details of their Black Mass have come down to us.[6] It was a typical Roman Catholic Mass, but modified according to certain formulas (some reminiscent of the Latin Sworn Book of Honorius, or its French version, The Grimoire of Pope Honorius) and featuring the King's mistress (the Marquise de Montespan) as the central altar of worship, lying naked upon the altar with the chalice on her bare stomach, and holding two black candles in each of her outstretched arms. The Host was consecrated on her body, and then used in love potions designed to gain the love of the King (on account of the magical power believed to be in the consecrated Host). From these images of the Guibourg mass, further developments of the Black Mass derived.[7]
- 18th century: The Marquis de Sade, in many of his writings places the host and the Mass, monks, priests, and the Pope himself (Pope Pius VI in Juliette), in blasphemous sexual settings.
- 19th century: Joris-Karl Huysmans wrote the classic novel of French Satanism, Là-bas (1891). The characters in the novel have long discussions on the history of French Satanism up to their time, and eventually one of them is invited to participate in a Black Mass, the type of which Huysmans claimed was practised in Paris in those years. Although a work of fiction, Huysmans' description of the Black Mass remained influential simply because no other book went into as much detail. However, the actual text which Huysmans' satanic "priest" recites is nothing more than a long diatribe in French, praising Satan as the god of reason and the opponent of Christianity. In this way, it resembles the French poetry of Charles Baudelaire (in particular Les Litanies de Satan), more than it resembles an inversion of the Roman Catholic Mass.
Late 19th century and early 20th century scholarly interest in the Black Mass
Scholarly studies on the Black Mass relied almost completely on French and Latin sources (which also came from France):
- The French historian Jules Michelet was one of the first to analyze and attempt to understand the Black Mass, and wrote two chapters about it in his classic book, Satanism and Witchcraft (1862).
- J G Frazer included a description of The Mass of Saint-Secaire, an unusual French legend with similarities to the Black Mass, in The Golden Bough (1890). Frazer was recounting material already found in an 1883 French book entitled Quatorze superstitions populaires de la Gascogne[8] ("Fourteen Popular Superstitions of Gascony"), by Jean-François Bladé.
- Montague Summers discussed many classic portrayals of the Black Mass in a number of his works (especially in The History of Witchcraft and Demonology (1926), ch. IV, The Sabbat, with extensive quotations from the original French and Latin sources[9]).
20th century
- H. T. F. Rhodes' popular mass-market book, The Satanic Mass,[1] published in 1954, was a major inspiration for modern versions of the Black Mass, when they finally appeared. Rhodes claimed that, at the time of his writing, there did not exist a single first hand source which actually described the rites and ceremonies of a Black Mass.
- Zacharias[3] and Cavendish,[2] both writing in the middle of the 1960s, while presenting detailed studies of source material, offer no new sources for a Black Mass, relying solely on material that was already known to Rhodes.
| Part of a series on |
| LaVeyan Satanism |
|---|
 |
| Organizations |
| Notable people |
| Texts |
| Media |
| Related Topics |
- When Anton Szandor LaVey published his Satanic Bible in 1969, he wrote that:
He went on in the Satanic Rituals (1972) to present it as the most representatively satanic ritual in the book.[11]The usual assumption is that the Satanic ceremony or service is always called a Black Mass. A Black Mass is not the magical ceremony practiced by Satanists. The Satanist would only employ the use of a Black Mass as a form of psychodrama. Furthermore, a Black Mass does not necessarily imply that the performers of such are Satanists. A Black Mass is essentially a parody on the religious service of the Roman Catholic Church, but can be loosely applied to a satire on any religious ceremony.[10]
The Modern Black Mass
In spite of the huge amount of French literature discussing the Black Mass (Messe Noire) at the end of the 19th century and early 20th century, no set of written instructions for performing one, from any purported group of Satanists, turned up in writing until the 1960s, and appeared not in France, but in the United States. As can be seen from these first Black Masses and Satanic Masses appearing in the U.S., the creators drew heavily from occult novelists such as Dennis Wheatley and Joris-Karl Huysmans, and from non-fiction occult writers popular in the 1960s, such as H. T. F. Rhodes (who provided a title in his 1954 book The Satanic Mass), and Grillot de Givry (author of the popular illustrated book Witchcraft, Magic and Alchemy).
A growing interest in witchcraft and satanism in the 1960s inspired the creation of two recordings, both made in 1968, and both called "Satanic Mass":
- The first was a 13 minute recording of a full-length "Satanic Mass" made by the U.S. band Coven. Coven's Satanic Mass, part of their stage show in 1968, was included on their 1969 record album "Witchcraft Destroys Minds & Reaps Souls",[12] together with the full published text. On the album cover, it is stated that they spent a long time researching the material, and to their knowledge it was the first Black Mass published in any language. The result was eclectic, drawing chants and material from numerous sources, including two medieval French miracle plays, Le Miracle de Théophile and Jeu de Saint Nicolas, which both contain invocations to the Devil in an unknown language.[13] These chants, along with other material on the album, could be found in books on witchcraft popular in the 60s, notably Grillot de Givry's Witchcraft, Magic and Alchemy (originally published in France in 1929).[14] A large portion of the English dialogue was taken verbatim from Dennis Wheatley's 1960 occult novel, The Satanist, in which the female protagonist is initiated into a Satanic cult. Additionally, the recording, while using a couple of the Latin phrases the Church of Satan was already making popular, also added a substantial amount of church Latin, in the form of Gregorian chants sung by the band, to create the genuine effect of the Catholic Latin Mass being inverted and sung to Satan.
- The second was a record album of readings in Satanic ritual and philosophy by the Church of Satan, called "The Satanic Mass",[15] which contained material later to appear in their Satanic Bible (published in 1969). In spite of the title and a few phrases in Latin, this album did not deal with the Black Mass.
Soon after Coven created their Satanic Mass recording, the Church of Satan began creating their own Black Masses, two of which are available to the public. The first, created for the Church of Satan by Wayne West in 1970, was entitled "Missa Solemnis" (originally published only in pamphlet form, later published in Michael Aquino's history of The Church of Satan[16]), and the second, created by an unknown author, was entitled "Le Messe Noir" (published in Anton LaVey's 1972 book The Satanic Rituals).
All three of these Satanic Masses (the one by Coven and the two by the Church of Satan) contain the Latin phrase "In nomine Dei nostri Satanas Luciferi Excelsi", as well as the phrases "Rege Satanas" and "Ave Satanas" (which, incidentally, are also the only three Latin phrases which appeared in the Church of Satan's 1968 recording, "The Satanic Mass"). Additionally, all three modify other Latin parts of the Roman Catholic Missal to make them into Satanic versions. The Church of Satan's two Black Masses also use the French text of the Black Mass in Huysmans' Là-Bas to a great extent. (West only uses the English translation, LaVey publishes also the original French). Thus, the Black Mass found in The Satanic Rituals is a combination of English, French, and Latin.
A writer using the pseudonym "Aubrey Melech" published, in 1986, a Black Mass entirely in Latin, entitled "Missa Niger". (This Black Mass is available on the Internet). Aubrey Melech's Black Mass contains almost exactly the same original Latin phrases as the Black Mass published by LaVey in The Satanic Rituals. The difference is that the amount of Latin has now more than doubled, so that the entire Black Mass is in Latin.
The language of the Black Mass
The French sections that LaVey published were quotations from Huysmans's La Bas. The Latin of Melech and LaVey is based on the Roman Catholic Latin Missal, reworded so as to give it a Satanic meaning (e.g. the Roman Mass starts "In nomine Patris, et Filii, et Spiritus Sancti, introibo ad altare Dei", while LaVey's version, printed in the Satanic Rituals, starts "In nomine magni dei nostri Satanas, introibo ad altare Domini Inferi"). There are a small amount of copyist and grammatical errors. For example, "dignum" from the Mass, is once incorrectly spelled "clignum", in the printed Satanic Rituals. Another example, also appearing once, is "laefificat" instead of "laetificat". One of the more obvious grammatical errors is "ego vos benedictio", "I bless you", which should have been "ego vos benedico". Another grammatical peculiarity, is that throughout his version of the Mass, LaVey does not decline the name Satanas, as is typically done in Latin if the endings are used, but uses only the one form of the word regardless of the case.[17] Melech uses Satanus. "Satanas" as a name for Satan appears in some examples of Latin texts popularly associated with satanism and witchcraft, such as the middle age pact with the Devil supposedly written by Urbain Grandier. Both Black Masses end with the Latin expression "Ave, Satanas!" - "Welcome, Satan!" (expressing the opposite sentiments of the similar statement made by Jesus to Satan in the Latin Vulgate Bible (Latin Vulgate, Matthew 4:10),[18] "Vade, Satanas!" - "Go away, Satan!").
See also
- Ave Satani
- Black magic
- Host desecration
- The Mass of Saint-Secaire
- Parody mass
- Requiem mass ("Mass for the Dead", sometimes called a "Black Mass" due to the black vestments the priest wears)
- Gnostic mass
- The All-Joking, All-Drunken Synod of Fools and Jesters
References
- ^ a b c Rhodes, H.T.F. The Satanic Mass, 1954.
- ^ a b Cavendish, Richard. The Black Arts, 1967.
- ^ a b Zacharias, Gerhard. Der dunkle Gott: Satanskult und Schwarze Messe, München, 1964.
- ^ Zacharias discusses some of these in the first part of his book.
- ^ Summers, Montague, translator, The Malleus Maleficarum of Kramer and Sprenger, 1948. (Originally published in Germany, in Latin, 1487.)
- ^ Ravaisson, François Archives de la Bastille (Paris, 1866-1884, volumes IV, V, VI, VII)
- ^ Geography of Witchcraft by Montague Summers (1927; reprint Kessinger Publishing, 2003)
- ^ Bladé, Jean-François. Quatorze superstitions populaires de la Gascogne, 1883.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Summerswas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ LaVey, Anton. The Satanic Bible, 1969.
- ^ "The Original Psychodrama — Le Messe Noir", in LaVey, Anton. The Satanic Rituals, 1972.
- ^ Coven, Witchcraft Destroys Minds & Reaps Souls, LP (Dunwich Productions/Mercury Records, 1969)
- ^ discussed in: Grillot de Givry, Witchcraft, magic & alchemy, Courier Dover Publications, 1971, p. 109.
- ^ English translation: Grillot de Givry, Witchcraft, magic & alchemy, Courier Dover Publications, 1971.
- ^ LaVey, Anton, The Satanic Mass, LP (Murgenstrumm Records, 1968)
- ^ Aquino, Michael (2002). The Church of Satan (PDF)., Appendix 7.
- ^ LaVey, Anton. The Satanic Rituals, 1972
- ^ Biblia Sacra Vulgata (Deutsche Bibelgesellschaft, Stuttgart, 1994), Matt. 4:10: Tunc dicit ei Iesus, "Vade Satanas! Scriptum est Dominum Deum tuum adorabis et illi soli servies."
Studies of the Black Mass
- Rhodes, H.T.F. (1954). The Satanic Mass. ISBN 978-0-09-086730-1.
- Zacharias, Gerhard (1964). Der dunkle Gott: Satanskult und Schwarze Messe. ISBN 978-3-8090-2187-2.
- Cavendish, Richard (1967). The Black Arts. ISBN 978-0-399-50035-0. (See especially, Chapter 7, "The Worship of the Devil", section 3, "The Black Mass")
- Zacharias, Gerhard (1980). The Dark God: Satan Worship and Black Masses. ISBN 978-0-04-133008-3. (Translated from the German by Christine Trollope)
Sources
- Huysmans, Joris-Karl (1891). Là-Bas.
- LaVey, Anton (1972). The Satanic Rituals. pp. 100–101.
- Melech, Aubrey (1986). Missa Niger: La Messe Noire: a True and Factual Account of the Principal Ritual of Satanic Worship.
External links
- Black Mass, The - article at the Mystica
- Black Mass Gallery, historical depictions of the Black Mass
