Pithole, Pennsylvania
Pithole
Pit Hole | |
|---|---|
 The site of Pithole in October 2009. The visitor center is visible at the top of the hill. | |
| Etymology: Pithole Creek | |
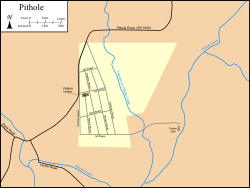 Map of Pithole and the surrounding area showing the city streets and Frazier Well, overlaid with modern roads and creeks | |
| Coordinates: 41°31′26″N 79°34′53″W / 41.52389°N 79.58139°W | |
| Country | United States |
| State | Pennsylvania |
| County | Venango |
| Founded | May 24, 1865 |
| Incorporated | November 30, 1865 |
| Unincorporated | August 1877 |
| Elevation | 1,316 ft (401 m) |
| Time zone | UTC-5 (Eastern (EST)) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-4 (EDT) |
| NRHP # | 73001667[2] |
Pithole, or Pithole City, is a ghost town in Cornplanter Township, Venango County, Pennsylvania, United States, about 6 miles (9.7 km) from Oil Creek State Park and the Drake Well Museum, the site of the first commercial oil well in the United States.[3] Pithole's sudden growth and equally rapid decline, as well as its status as a "proving ground" of sorts for the burgeoning petroleum industry, made it one of the most famous of oil boomtowns.[4][5]
Oil strikes at nearby wells in January 1865 prompted a large influx of people to the area that would become Pithole, most of whom were land speculators. The town was laid out in May 1865, and by December was incorporated with an approximate population of 20,000. At its peak, Pithole had at least 54 hotels, 3 churches, the third largest post office in Pennsylvania, a newspaper, a theater, a railroad, the world's first pipeline and a red-light district "the likes of Dodge City's."[6] By 1866, economic growth and oil production in Pithole had slowed. Oil strikes around other nearby communities and numerous fires drove residents away from Pithole and, by 1877, the borough was unincorporated.
The site was cleared of overgrowth and was donated to the Pennsylvania Historical and Museum Commission in 1961. A visitor center, containing exhibits pertaining to the history of Pithole, was built in 1972. Pithole was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1973.
Etymology
[edit]The city of Pithole derived its name from its proximity to Pithole Creek, which flows through Venango County to the Allegheny River.[7] The origin of the name "Pithole" itself, however, is a mystery. One origination theory is that early pioneers stumbled across strange fissures from which sulfurous fumes wafted.[6] Such "pit-holes" are found in the area where Pithole Creek empties into the Allegheny River, with some measuring 14 inches (36 cm) wide and 8 feet (2 m) long.
Another possible explanation involves the discovery of ancient pits dug by early settlers, some 8 feet (2 m) wide and 12 feet (4 m) deep, that were cribbed with oil-soaked timbers.[7] These "pit-holes", found along Oil Creek and in Cornplanter Township, supposedly predate the Senecas who inhabited the area from the mid-17th to the late 18th century.[8]
Geology
[edit]Most of the oil produced in northwestern Pennsylvania was formed in sandstone reservoir rocks at the boundary between the Mississippian and Devonian rock layers.[9] Over time, the oil migrated toward the surface, became trapped beneath an impervious layer of caprock, and formed a reservoir. The presence of upwards-curving folds in the caprock called anticlines, or sometimes an inversion of an anticline called a syncline, greatly varied the depth of the reservoirs, from around 4,000 feet (1,200 m) to just beneath the surface.[10]
The majority of the oil wells in the vicinity of Pithole and the Oil Creek valley tapped into a sandstone formation known as the Venango Third sand.[11] The Venango Third contained large volumes of oil under high pressure at only 450 to 550 feet (140 to 170 m) below ground level.[11] Other oil-producing formations in the area were "the Venango First and Second [sands], the latter often prevailing after the Third sand was lost."[11] At Pithole, the "first sandstone was reached at 115 feet [35 m], the second at 345 feet [105 m], the third at 480 feet [146 m], the fourth at 600 feet [183 m], and the oil itself at 615 feet [187 m]" by the Frazier Well, according to a report by the Oil City Register.[12] Inaccurate numbering of the layers by the drillers, however, put the Fourth sand above the real Third at 670 feet (200 m).[13]
Geography and climate
[edit]Pithole is located in northwestern Pennsylvania, 50 miles (80 km) southeast of Erie and 103 miles (166 km) north-northeast of Pittsburgh. The nearest cities to Pithole are Titusville, approximately 8 miles (13 km) to the northwest, and Oil City, 9 miles (14 km) to the southwest.[14][15] Pithole is located on Pithole Road (State Route 1006), almost 4 miles (6.4 km) southwest of Pennsylvania Route 36 and about 2 miles (3.2 km) east Pennsylvania Route 227.[16]
Pithole was laid out with four primary east–west streets: First, Second, Third and Fourth. Duncan, Mason, Prather, Brown and Holmden Streets traversed Pithole from north to south. Each street was 60 feet (18 m) wide, except for Duncan at 80 feet (24 m).[17] All five north–south streets terminated at First Street; Mason started at Third; Prather and Brown started at Fourth. Duncan and Holmden Streets both began at a Y-intersection with the road from Titusville. All four east–west streets began at Duncan and ended at Holmden Street except for First, which extended to the Frazier Well.[18]
July is the hottest month in Pithole, when the average high temperature is 81 °F (27 °C) and the average low is 57 °F (14 °C). January is the coldest month with an average high of 32 °F (0 °C) and an average low of 13 °F (−11 °C).[19] The average 44 inches (1,118 mm) of precipitation a year wreaked havoc on Pithole's many unpaved streets, especially the heavily traveled First and Holmden.[19][20] Portions of First Street were planked or corduroyed in response to the resulting quagmire of mud that would often trap wagons and draft animals.[21]
History
[edit]The area around Pithole, and modern-day Venango County, was formerly inhabited by Eries, who were eventually wiped out by the Iroquois in 1653.[22] On October 23, 1784, the Iroquois, which included the Seneca, ceded the land to Pennsylvania in the Treaty of Fort Stanwix.[23] Venango County was formed from portions of Allegheny and Lycoming counties on March 12, 1800.[24] Cornplanter Township was settled in 1795 and was incorporated on November 28, 1833.[24]

In 1859, Edwin Drake successfully drilled the first oil well along the banks of Oil Creek, outside of Titusville in Crawford County. Within a half year, over 500 wells were built along Oil Creek, in the 16-mile (26 km) corridor from Titusville to the creek's mouth at the Allegheny River in Oil City.[8] Other wells were drilled down the Allegheny towards Franklin and upriver to Tionesta in Forest County. Pithole Creek did not attract the same attention from speculators and investors, who preferred to risk their money on the tried-and-true method of drilling on flatter terrain near large rivers like the Allegheny and Oil Creek, rather than gamble on rougher terrain.[25] In January 1864, Isaiah Frazier leased two tracts of land, totaling 35 acres (14 ha), from Thomas Holmden, a farmer along Pithole Creek. Frazier, James Faulkner Jr., Frederick W. Jones and J. Nelson Tappan formed the United States Petroleum Company in April 1864 and started drilling what was dubbed the United States Well, or Frazier Well, in June. On January 7, 1865, the Frazier Well struck oil.[26]
Boom
[edit]Two weeks after the Frazier strike, the Twin Wells, just to the south of the Frazier Well, also struck oil. In May 1865, A. P. Duncan and George C. Prather purchased the Holmden Farm, including the portions still leased to United States Petroleum, for $25,000 and a bonus of $75,000. The wooded bluff overlooking the Frazier and Twin Wells was cleared and a town was laid out. The town was divided into 500 lots, which were put up for sale on May 24.[17] By July, the population was estimated to have been at least 2,000.[27] The population of Pithole rose to 15,000 people in September and 20,000 by Christmas.[28] Pithole was incorporated as a borough on November 30, 1865.[29]

As many residents were temporary, Pithole had a total of 54 hotels ranging from simple rooming houses to luxury hotels like the Chase and Danforth Houses, or the Bonta House located in Prather City on the bluff on the opposite side of Pithole Creek.[30] The Astor House, Pithole's first hotel, was built in one day. Construction of the hotel was especially poor; a lack of insulation and innumerable gaps in the walls made conditions in the hotel miserable during the winter.[31] At one point, the Pithole Post Office, located on the first-floor of the Chase House, was the third-busiest in the state of Pennsylvania, behind Philadelphia and Pittsburgh.[4] Three different churches—Catholic, Methodist and Presbyterian—were constructed by their respective congregations. Pithole's local newspaper, the Pithole Daily Record was started on September 5, 1865. The largest building in Pithole—the three-story, 1,100-seat Murphy's Theater—opened on September 17.[32] Among all the glamour, "every other building [in Pithole] was a bar".[6] Prostitution was rampant in Pithole, with most of the brothels built along First Street. Although the borough council passed ordinances banning the sex trade and carried out raids in an attempt to enforce them, they had little impact.[33]
As oil production increased through the success of wells like the Frazier, Twin, Pool, Grant, and the two Homestead Wells, transportation of the oil to the outside world was still reliant on teamsters. The teamsters were notorious for mistreatment of their horses, most of which lost their hair due to a buildup of oil and only had a lifespan of a few months in Pithole. The high mortality rate caused a horse shortage, with more having to be brought in by rail from Ohio and New York.[34] Teamsters often refused to work on days when the roads were impassable or gouged the oil producers.[35]
Various investors, fed up with the teamsters, pooled resources and built a plank toll road from Pithole to Titusville.[36] Samuel Van Sykle, an oil buyer also frustrated with the teamsters, designed the world's first pipeline, which opened on October 9, 1865. [37] The 2-inch-diameter (51 mm), 5.5-mile-long (8.9 km) pipeline connected Pithole to the Oil Creek Railroad and was initially able to transport 81 barrels (13 m3) per hour operating with three steam engines, equivalent to 300 teams working a 10-hour shift.[38] A fourth engine brought the pipeline's maximum capacity to 2,500 barrels (397 m3) a day.
The Oil City and Pithole Branch Railroad (OC&P) was opened on December 18. It was renamed the Pithole Valley Railway in 1871, and was to be abandoned in 1874.[39] It ran from Oleopolis, and had passenger stops at Bennett, Woods Mill and Prather.[40] A second railroad was partly built but never finished -this was the Reno, Oil Creek and Pithole Railroad, which in 1865 was building from Reno west of Oil City to Pithole via Rouseville and Plumer. The intention was to boost Reno and bypass Oil City. It only laid track between Rouseville and Plumer, went bankrupt in 1866 and was scrapped.[41][42] Plans for other railroads never led to construction.[43]
Along with the pipeline, another innovation developed in Pithole was the railroad tank car, which was essentially two wooden tanks, each with a capacity of 80 barrels (13 m3), mounted onto a flatcar.[44]
Bust
[edit]
In March 1866, a chain of banks owned by Charles Vernon Culver, a financier and member of United States House of Representatives for Pennsylvania's 20th congressional district, collapsed. This triggered a financial panic throughout the oil region, bursting the oil bubble. Speculators and potential investors stopped coming to Pithole and life in Pithole settled down.
In the early morning of February 24, a house caught fire and the flames were spread to other buildings by the wind.[45] In two hours, most of Holmden Street, and parts of Brown and Second Streets, were reduced to smoldering ashes. The worst of multiple fires occurred on August 2, burning down several city blocks and destroying 27 wells.[46]
When many oil strikes occurred elsewhere in Venango County in 1867, people left Pithole, often taking their houses and places of business with them or abandoning their property.[47] By December 1866, the population had dropped to 2,000.[6] The newspaper was relocated to Petroleum Center in July 1868, becoming the Petroleum Center Daily Record.[48] Both the Chase House and Murphy's Theater were sold in August 1868 and moved to Pleasantville.[48] Prather and Duncan sold their interests in Pithole before the downturn; Prather split an estimated $3 million with his two brothers and moved to Meadville, while Duncan returned to Scotland with his fortune.[4]
The 1870 United States Census recorded the population of Pithole as only 237. The borough charter of Pithole was officially annulled in August 1877.[29] The remains of the city were sold, in 1879, back to Venango County for $4.37. The Catholic church was dismantled and moved to Tionesta in 1886; the Methodist church was kept in "usable condition" through private donations before being taken down in the 1930s.[49] A stone altar was erected and consecrated by the Methodist Episcopal Church on August 27, 1959, the centennial of the Drake Well strike.[50]
Visitor center
[edit]
The site was purchased in 1957 by James B. Stevenson, the publisher of the Titusville Herald, who later served as the chairman of the Pennsylvania Historical and Museum Commission from 1962 to 1971.[6] Stevenson cleared the brush from the site, and donated it to the Pennsylvania Historical and Museum Commission in 1961. Today, only a few foundations and mowed paths mark the buildings and former streets of Pithole. The site of Pithole was listed in the National Register of Historic Places on March 20, 1973. A walking tour of Pithole's 84.3 acres (34.1 ha) of streets can be completed in 42 minutes.[51][52] The visitor center was constructed in 1972.
The Pennsylvania Historical and Museum Commission operates the visitor center as part of the nearby Drake Well Museum, adjacent to Oil Creek State Park, outside of Titusville.[53] The visitor center contains several exhibits, including a scale model of the city at its peak, an oil-transport wagon that is stuck in mud, and a small, informational theater.[52] The visitor center is usually open, annually, from the Memorial Day weekend, at end of May, through Labor Day in September.[6] The season is kicked off with the annual Wildcatter Day celebration featuring music, tours, demonstrations and other activities.[54]
See also
[edit]- List of ghost towns in Pennsylvania
- National Register of Historic Places listings in Venango County, Pennsylvania
- Oil Region
- Pennsylvanian oil rush
References
[edit]- ^ "Pithole City". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey. Retrieved April 6, 2011.
- ^ "NPS Focus". National Register of Historic Places. National Park Service. Archived from the original on July 25, 2008. Retrieved February 12, 2010.
- ^ "Oil Creek State Park". Pennsylvania Department of Conservation and Natural Resources. Archived from the original on August 14, 2009. Retrieved February 27, 2010.
- ^ a b c "Pithole's Rise and Fall" (PDF). The New York Times. December 26, 1879. p. 2. Retrieved February 16, 2010.
- ^ Darrah 1972, p. 240.
- ^ a b c d e f Hirschl, Beatrice Paul (August 12, 1996). "A peak [sic] at Pithole's past". Pittsburgh Post-Gazette. p. D1.
- ^ a b Darrah 1972, p. 1.
- ^ a b Darrah 1972, p. 2.
- ^ Caplinger 1997, p. 6.
- ^ Caplinger 1997, pp. 4, 6.
- ^ a b c Pees 1998, p. 15.
- ^ Darrah 1972, pp. 11–12.
- ^ Carll 1880, pp. 140, 176.
- ^ Oil City, Pennsylvania (Map). 1 : 100,000. 30 × 60 Minute Series (Topographic). United States Geological Survey. 1983.
- ^ Warren, Pennsylvania – New York (Map). 1 : 100,000. 30 × 60 Minute Series (Topographic). United States Geological Survey. 1983.
- ^ General Highway Map Venango County, Pennsylvania (PDF) (Map). 1:65,000. Type 10. Pennsylvania Department of Transportation. 2017. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 1, 2017. Retrieved September 30, 2017.
- ^ a b Darrah 1972, p. 29.
- ^ Map showing the subdivisions of the Holmden, Hyner, Morey, McKinney, Dawson, Rooker, Blackmer, Ball, Walter, Holmden, Reynolds, Luther Wood & Copeland Farms on Pithole Creek (Map). 1 = 5 chains. Murdock and Hanning. October 1865.
- ^ a b "Monthly Averages for Historic Pithole City". The Weather Channel. Retrieved February 17, 2010.
- ^ Darrah 1972, p. 63.
- ^ Darrah 1972, pp. 27, 63.
- ^ Bell 1890, pp. 25–26.
- ^ Bell 1890, p. 71.
- ^ a b Hottenstein & Welch 1965, p. 125.
- ^ Darrah 1972, pp. 3–4.
- ^ Darrah 1972, p. 10.
- ^ Darrah 1972, p. 32.
- ^ "Tappan's Mushroom City" (PDF). The New York Times. September 8, 1884. p. 8. Retrieved February 16, 2010.
- ^ a b Bell 1890, p. 121.
- ^ Darrah 1972, p. 83.
- ^ Tassin 2007, p. 5.
- ^ Darrah 1972, p. 140.
- ^ Darrah 1972, pp. 148–149.
- ^ Darrah 1972, p. 23.
- ^ Darrah 1972, p. 100.
- ^ Darrah 1972, pp. 100–101.
- ^ Darrah 1972, pp. 104–105.
- ^ Darrah 1972, p. 105.
- ^ Connelly, E: Railroad Operations Vol. 4 2002 p. 46.
- ^ Walker, M: SPV's Comprehensive Railroad Atlas of North America, Northeast 2007 p. 56
- ^ Venango County, Pennsylvania: her Pioneers and People 1919 p. 562
- ^ Christopher T. Baer: A GENERAL CHRONOLOGY OF THE PENNSYLVANIA RAILROAD COMPANY 1865 2015 p. 78
- ^ Darrah 1972, p. 115.
- ^ Darrah 1972, p. 114.
- ^ Darrah 1972, p. 223.
- ^ Darrah 1972, p. 171.
- ^ Darrah 1972, pp. 167, 222.
- ^ a b Darrah 1972, p. 224.
- ^ Darrah 1972, p. 233.
- ^ Darrah 1972, pp. 240–239.
- ^ Pennsylvania Register of Historic Sites and Landmarks 1972, § 10.
- ^ a b Love, Gilbert (June 22, 1975). "Once-booming Pithole revisited in 'world's 1st oil town' museum". The Pittsburgh Press. p. C1. Retrieved February 17, 2010.
- ^ Hahn, Tim (June 6, 2010). "Budget constraints, construction cut Pithole visitor opportunities". Erie Times-News. Archived from the original on June 6, 2011. Retrieved June 6, 2010.
- ^ "Experience oil boomtown with Wildcatter Day". Titusville Herald. May 24, 2014. Archived from the original on June 1, 2014. Retrieved June 1, 2014.
Sources
[edit]- Bell, Herbert C, ed. (1890). History of Venango County, Pennsylvania. Chicago: Brown, Runk & Co.
- Caplinger, Michael W (1997). "Allegheny National Forest Oil Heritage". Historic American Engineering Record. National Park Service. Retrieved May 24, 2010.
- Carll, John F (1880). The geology of the oil regions of Warren, Venango, Clarion, and Butler counties. Harrisburg: Second Geological Survey of Pennsylvania. OCLC 5966119.
- Darrah, William Culp (1972). Pithole, the vanished city. Gettysburg: William Culp Darrah. ISBN 0-913116-03-3. LCCN 72078194.
- Hottenstein, JoAnne; Welch, Sibyl (1965). "Venango County". Incorporation dates of Pennsylvania municipalities (PDF). Harrisburg: Bureau of Municipal Affairs, Pennsylvania Department of Internal Affairs. Retrieved June 1, 2010.
- Pees, Samuel T (Spring 1998). "Oil Creek's Riparian Wells" (PDF). Pennsylvania Geology. 29 (1). Pennsylvania Department of Conservation and Natural Resources: 14–18. Archived from the original (PDF) on April 20, 2004. Retrieved February 21, 2010.
- Pennsylvania Register of Historic Sites and Landmarks (February 24, 1972). "Pithole City" (PDF). National Register of Historic Places Inventory—Nomination Form. Harrisburg: Pennsylvania Historical and Museum Commission. Retrieved February 15, 2010.
- Tassin, Susan (2007). Pennsylvania ghost towns. Mechanicsburg: Stackpole Books. ISBN 978-0-8117-3411-0.
Further reading
[edit]- Leonard, Charles C (1867). History of Pithole. Pithole City: Morton, Longwell & Co.
External links
[edit]- Official site of Pithole City and the Drake Well Museum
- Online archive of the Pithole Daily Record
- "Pit-Hole City" (1960), folk song about Pithole from a record at YouTube
- 1877 disestablishments in Pennsylvania
- Former municipalities in Pennsylvania
- Ghost towns in Pennsylvania
- History museums in Pennsylvania
- History of the petroleum industry in the United States
- Museums in Venango County, Pennsylvania
- Industrial buildings and structures on the National Register of Historic Places in Pennsylvania
- National Register of Historic Places in Venango County, Pennsylvania
- Populated places established in 1865
- Geography of Venango County, Pennsylvania
- 1865 establishments in Pennsylvania
- Populated places on the National Register of Historic Places in Pennsylvania




