Sea of Azov
| Sea of Azov | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Coordinates | 46°N 37°E / 46°N 37°E |
| Primary inflows | Don and Kuban |
| Max. length | 360 km (220 mi)[1] |
| Max. width | 180 km (110 mi)[1] |
| Surface area | 39,000 km2 (15,000 sq mi)[1] |
| Average depth | 7 meters (23 ft)[1] |
| Max. depth | 14 m (46 ft)[1] |
| Water volume | 290 km3[1] |
The Sea of Azov (Russian: Азо́вское мо́ре – Azovskoye more; Ukrainian: Азо́вське мо́ре – Azovs'ke more, Crimean Tatar: Azaq deñizi) is a sea on the south of Eastern Europe. It is linked by the narrow (about 4 km) Strait of Kerch to the Black Sea to the south and is bounded on the north by Ukraine mainland, on the east by Russia, and on the west by the Crimean peninsula. The Don and Kuban are the major rivers that flow into it. The Sea of Azov is the shallowest sea in the world with the depth varying between 0.9 meters (2 ft 11 in) and 14 meters (46 ft).[1][2][3][4][5] There is a constant outflow of water from the Sea of Azov to the Black Sea.
The sea is largely affected by the inflow of numerous rivers, which bring sand, silt, and shells, forming numerous bays, limans, and narrow sandbanks called spits. Because of these deposits, the sea bottom is relatively smooth and flat with the depth gradually increasing toward the sea center. Also, due to the river inflow, water in the sea has low salinity and high content of biological matter, such as green algae that affects the water color. Abundant plankton results in unusually high fish productivity. The sea shores and spits are low; they are rich in vegetation and bird colonies.
Extent and juridical status
The International Hydrographic Organization defines the limit of the Sea of Azov in the Strait of Kerch [sic] as "The limit of the Black Sea", which is defined as "A line joining Cape Takil and Cape Panaghia (45°02'N)".[6] The sea is considered an internal sea of Russia and Ukraine, and its use is governed by an agreement between these countries ratified in 2003.[7]
Geology and bathymetry

The sea is 360 kilometers (220 mi) long and 180 kilometers (110 mi) wide and has an area of 39,000 square kilometers (15,000 sq mi); it is the smallest sea within the countries of the former Soviet Union.[8] The main rivers flowing into it are the Don and Kuban; they ensure that the waters of the sea have comparatively low salinity and are almost fresh in places, and also bring in huge volumes of silt and sand. Accumulation of sand and shells results in a smooth and low coastline, as well as in numerous spits and sandbanks.[9]
The Sea of Azov is the shallowest sea in the world with an average depth of 7 meters (23 ft) and maximum depth of 14 meters (46 ft);[1] in the bays, where silt has built up, the average depth is about 1 meter (3 ft). The sea bottom is also relatively flat with the depth gradually increasing from the coast to the center.[10] The Sea of Azov is an internal sea with the passage to the Atlantic Ocean going through the Black, Marmara, Aegean and Mediterranean seas. It is connected to the Black Sea with the Strait of Kerch, which has a smallest width of 4 kilometers (2.5 mi) and a maximum depth of 15 meters (49 ft).[1] The narrowness of the Kerch Strait limits the water exchange with the Black Sea. As a result, the salinity of the Sea of Azov is low; in the open sea it is 10–12 psu, that is about one third of the salinity the oceans, and is even lower (2–7 psu) in the Taganrog Bay. The long-term variations of salinity are within a few psu and are mostly caused by the changes in air humidity and precipitation.[11][12]
Whereas more than 20 rivers flow into the sea, mostly from the north,[10] two of them, the Don and Kuban rivers, account for more than 90% of water income. The contribution of Don is about twice larger than of Kuban.[10] The delta of Kuban is located southeast, to the right from the Kerch Strait. It is over 100 km long and covers vast flooded area with numerous channels. (Because of the spread, the delta has low contrast in satellite images and is hardly visible in the map.) Don flows from the north into the large Taganrog Bay. The depth there varies between 2 and 9 meters, and the maximum depth is observed in the middle of the sea.[13]
Typical values of the yearly inflow and outflow of water to the sea, averaged over the period from 1923 to 1985, are as follows: river inflow 38.6 km3, precipitation 15.5 km3, evaporation 34.6 km3, inflow from the Black Sea 36–38 km3, outflow 53–55 km3.[14] Thus, about 17 km3 of fresh water is outflowing from the Azov Sea to the Black Sea.[9] The depth of Azov Sea is decreasing, mostly due to the river-induced deposits.[8] Whereas the past hydrological expeditions recorded depths up to of 16 meters, more recent ones could not find places deeper than 13.5–14 meters.[8] This might explain the variation in the maximum depths among different sources. The water level fluctuates by some 20 cm over the year due to the snow melts in spring.[14]
The Taman Peninsula has about 25 mud volcanoes, most of which are active. Their eruptions are usually quiet, spilling out mud, and such gases as methane, carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide, but is sometimes violent and resembles regular volcanic eruptions. Some of those volcanoes are under water, near the shores of the peninsula. A major eruption on 6 September 1799, near stanitsa Golubitskaya, lasted about 2 hours and formed a mud island 100 meters in diameter and 2 meters in height; the island was then washed away by the sea. Similar eruptions occurred in 1862, 1906, 1924, 1950 and 1952.[8]
Coastal features and major population centers
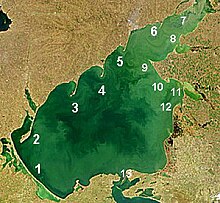
Many rivers flowing into the Sea of Azov form bays, lagoons and limans. The sand, silt and shells they bring are deposited in the areas of reduced flow, that is the sides of the bays, forming narrow sandbanks called spits. Typical maximum depth in the bays and limans is a few meters. Because of shallow waters and abundant rivers, the spits are remarkably long and numerous in the sea – the Arabatsk Spit stretches over 112 kilometers (70 mi) and is one of the world's longest spits; three other spits, Fedotov Spit, Achuevsk Spit and Obitochna Spit, are longer than 30 km. Most spits stretch from north to south and their shape can significantly change over just several years.[15][16]
A remarkable feature of the Sea of Azov is the large complex of shallow lagoons called Sivash. Their typical depth is only 0.5–1 meters with a maximum of 3 meters. They cover an area of 2,560 square kilometers (990 sq mi) in the northeastern Crimea which is separated from the sea by the Arabatsk Spit. North to the spit lies the city of Henichesk (population 22,500) and south to it is the Bay of Arabat.[17] Sivash accepts up to 1.5 km3 of Azov water per year. Because of the large and shallow geometry, the water rapidly evaporates there, resulting in the high salinity of 170 on the practical salinity scale (i.e. 170 psu). Therefore, Sivash has long had strong salt-producing industry.[13]

North to the Arabat Spit there is the Molochna Liman with the associated Fedotov Spit (45 km long) which are formed by the Molochna River. Farther north, between the Fedotov Spit and Obytochna Spit (30 km long), lies Obytochny Bay. More to the north, between Obytochna Spit and Berdyansk Spit (23 km long), there is Berdyansk Bay with two cities Berdyansk (population 112,000) and Primorsk (population 13,900). Further north lies Belosaraysk Bay with its Belosaraysk Spit which are formed by the river Kalmius. The major city in the area is Mariupol (population 491,600). Then, approaching the Taganrog Bay and very close to Taganrog, there are the Mius Liman and Krivaya Spit formed by the Mius River.[16]
With the area of about 5,600 square kilometers (2,200 sq mi), the Taganrog Bay is the largest bay of the Sea of Azov. It is located in its north-western part and is bound by the Belosaraysk and Dolgaya spits. The Don flows into it from the north-east. On its shores stand the two principal cities of the Sea of Azov, Taganrog (population 257,600) and Azov (population 83,200). South-east of the bay is Yeysk Liman. It lies entirely on the continent, entering the Taganrog Bay through the Yeysk and Glafirovsk Spits, and is the mouth of Yeya River. Yeysk Spit is part of Yeysk city which has a population of 87,500. It extends in the prominent Yeysk peninsula which is tipped on the north-west by the Dolgaya Spit. South of it, also enclosed by the continent, lies Beisug Liman, which is restricted by the Yasensk Spit and is fed by the Beysug River. South-west to the liman, the 31 km long Achuevsk Spit runs along the coastline. Between the Achuevsk spit and Beisug Liman stands Primorsko-Akhtarsk populated by 32,165 people.[15][16]

On the south, the Sea of Azov is connected to the Black Sea via the Strait of Kerch, which is bordered to the west by the Kerch peninsula on the Crimea, belonging to the Ukraine and to the east by the Russian Taman peninsula in Krasnodar Kraj. The city of Kerch (population 151,300) is located on the Kerch peninsula, and the Taman peninsula contains the delta of the Kuban, a major Russian river. The strait is 41 kilometers long and 4 to 15 kilometers wide. Its narrowest part lies on the Sea of Azov side, restricted by the Chushka Spit which faces southwards in consequence of the outflow from the Azov to the Black Sea.[18]
Climate
The sea is relatively small and practically completely surrounded by land. Therefore, its climate is continental, with cold winters and hot and dry summers. In autumn-winter, the weather is affected by the Siberian Anticyclone which brings cold and dry air from Siberia with winds of 4–7 m/s, sometimes up to 15 m/s. Those winds may lower the winter temperatures from the usual −1 to −5 °C to below −30 °C. The mean mid-summer temperatures are 23–25 °C with a maximum of about 40 °C.[13] Winds are weaker in summer, typically 3–5 m/s.[10] Precipitation varies between 312 and 528 mm/year and is 1.5–2 times larger in summer than in winter.[9]
Average water temperatures are 0–1 °C in winter (2–3 °C in the Kerch Strait) and 24–25 °C in summer, with a maximum of about 28 °C in the open sea and above 30 °C near the shores. During the summer, the sea surface is usually slightly warmer than the air.[10] Because of the shallow character of the sea, the temperature usually lowers by only about 1 °C with depth, but in cold winters, the difference can reach 5–7 °C.[10][19]
The winds cause frequent storms, with the waves reaching 6 meters in the Taganrog Bay, 2–4 meters near the southern shores, and 1 meter in the Kerch Strait. In the open sea, their hight is usually 1–2 meters, sometimes up to 3 meters. Winds also induce frequent seiches – freestanding oscillations of the sea bottom with the spatial period of 20–50 cm which last from minutes to hours. Another consequence of the winds is water currents. The prevailing current is a counter-clockwise swirl due to the westerly and south-westerly winds. Their speed is typically less than 10 cm/s, but can reach 60–70 cm/s for 15–20 m/s winds. In the bays, the flow is largely controlled by the inflow of the rivers and is directed away from the shore.[14] In the Kerch Strait, the flow is normally toward the Black Sea due to the predominance of northern winds and the water inflow from the rivers; its average speed is 10–20 cm/s, reaching 30–40 cm in the narrowest parts.[20] Tides are variable but can peak at 5.5 meters.[21]

The shallowness and low salinity of the sea make it vulnerable to freezing during the winter. Fast ice bands ranging from 7 km in the north to 1.5 km in the south can occur temporarily at any time from late December to mid-March. Under the present climate the sea no longer freezes over, although during the 18th and 19th centuries, and as recently as in the late 1970s, it was normally frozen over every year by early February. The ice thickness reaches 30–40 cm in most parts of the sea and 60–80 cm in the Taganrog Bay.[20] The ice is often unstable and piles up to the height of several meters. Before introduction of icebreakers, navigation was halted in the winter.[19]
Hydrology and hydrochemistry
The current vertical profile of the Sea of Azov exhibits oxygenated surface waters and anoxic bottom waters, with the anoxic waters forming in a layer 0.5 to 4 meters (1.6–13.1 ft) in thickness. The occurrence of the anoxic layer is attributed to seasonal eutrophication events associated with increased sedimentary input from the Don and Kuban Rivers. This sedimentary input stimulates biotic activity in the surfaces layers, which photosynthesize under aerobic conditions. Once expired, the dead organic matter sinks to the bottom of the sea where bacteria and microorganisms, using all available oxygen, consume the organic matter, leading to anoxic conditions. Studies have shown that in the Sea of Azov, the exact vertical structure is dependent on wind strength and sea surface temperature, but typically a 'stagnation zone' lies between the oxic and anoxic layers.[22]
Flora and fauna
Historically, the sea has had rich marine life, both in variety, with over 80 fish and 300 invertebrate species identified, and in their numbers. Consequently, fishery has long been a major activity in the area. The annual catchment of recent years was 300,000 tonnes, about half of which are valuable species (sturgeons, pike-perches, breams, sea-roaches, etc.).[23] This was partly due to extremely high biological productivity of the sea, which was stimulated by the strong supply of nutrients from numerous rivers feeding the sea, low water salinity, ample heating due to shallow waters and long vegetation period. However, diversity and numbers have been reduced by artificial reduction of river flow (construction of dams), over-fishing and water-intense large-scale cultivation of cotton, causing increasing levels of pollution. The fish hauls have rapidly decreased and in particular anchovy fisheries have collapsed.[1][23][24][25]
Plankton and benthos
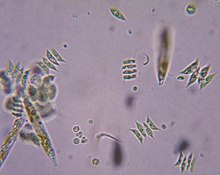
Because of shallow waters, the development of aquatic life in the Sea of Azov is more characteristic of a lagoon, and the plankton patterns are rather similar in the open sea and near the shores. However, despite shallowness, water has low transparency. Therefore, the bottom plants are poorly developed and most algae are of planktonic type. The sea is characterized by high concentration of organic matter and long blooming periods. Another specific feature of the sea is variable salinity – low in the large bays and higher in the open sea, especially near the Kerch Strait. Therefore, the plankton species are distributed inhomogeneously in the Sea of Azov. Although many additional species are brought from the salty Black Sea, most of them can not adjust to the variable salinity of the Sea of Azov, except for the euryhaline species.[26] About 600 species of planktonic algae are known in the Sea of Azov.[23] The number of species is dominated by diatoms and green algae; blue-green algae and pyrophites are significant, and euglena and yellow-green algae form only 5% of the species. Green algae are mostly responsible for the color of the sea in the satellite images (see photos above).[26]
Regarding zooplankton, freshwaters of the Tanganrog Bay are inhabited by cladocera, copepoda and rotifers, such as Brachionus plicatilis, Keratella curdata and Asplanchna. Western part of the sea, which is more saline, hosts three forms of Acartia clausi, as well as Centropages ponticus, meroplankton and larvae of gastropoda, bivalvia and polychaete.[27]
Benthos species reside mostly at the sea bottom and include worms, crustaceans, bottom protists, coelenterata and mollusks. Mollusks account for 60–98% of the invertebrate biomass at the Sea of Azov bottom.[27]

Fish
There are 183 ichthyofauna species from 112 genera and 55 families in the Sea of Azov region. Among them, there are 50 rare and 19 endangered species, and the sturgeon Acipenser nudiventris is probably extinct in the region.[28]
The fauna of the freshwater Taganrog Bay is much poorer – it consists of 55 species from 36 general and 16 families; among them, three species are rare and 6 are endangered.[29]
Flora

The shores of the Sea of Azov contain numerous limans, estuaries and marshes and are dominated by reeds, sedges, Typha and Sparganium. Typical submerged plants are Charales, pond weed, hornworts and water lilies. Also common is lotus which was brought to the area from Africa.[8] The number of species is large; for example, the Belosaraysk and Berdyansk spits alone contain more than 200 each. Some spits are declared national nature reserves, such as Beglitsk,[30] Belosaraysk,[31] Krivaya[31] and Berdyansk Spits.[16][32][33]
Fauna

Limans, estuaries and spits of the sea are rich in birds, mostly waterfowl, such as wild geese, ducks and seagulls. Colonies of cormorants and pelicans are common. Also frequently observed are swans, herons, sandpipers and many birds of prey. Mammals include foxes, wild cats, hare, hedgehogs, weasels, martens and wild boars.[33] Muskrats were introduced to the area in the early 20th century and are hunted for their fur.[8]
Migrating and invading species

Some ichthyofauna species, such as anchovy, garfish, Black Sea whiting and pickerel, visit the Sea of Azov from the Black Sea for spawning. This was especially frequent in 1975–77 when the salinity of the southern Sea of Azov was unusually high, and additional species were seen such as bluefish, turbot, chuco, spurdog, Black Sea salmon, mackerel and even corkwing wrasse, rock hopper, bullhead and eelpout. Contrary to the Black Sea plankton which does not adapt well to the low salinity of the Sea of Azov and concentrate near the Kerch Strait, fishes and vertebrae of Black Sea adjust well. They are often stronger than the native species, are used to the relatively low temperatures of the Black Sea and survive well the winter of the Sea of Azov.[34]
Balanus improvisus is the first benthos species which spread from the Black Sea in the early 20th century and settled in the Sea of Azov. Its current density is 7 kg/m2. From 1956, Rapana venosa is observed in the Sea of Azov, but it could not adjust to low salinity and therefore is limited to the neighborhood of the Kerch Strait. Several Sea of Azov mollusks, such as shipworm (Teredo navalis), soft-shell clam (Mya arernaria), Mediterranean mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis) and Anadara inaequivalvis, originate from the Black Sea. Another example of invading species is the Dutch crab Rhithropanopeus harrisii which is observed both in saline and freshwater parts.[34]
Three types of dolphins, short-beaked common dolphin, common bottlenose dolphin and harbour porpoise, regularly visited the Sea of Azov from the Black Sea. One type of harbour porpoise, Phocoena phocoena relicta, used to stay in the Sea of Azov and therefore was called "Azov dolphin" (Russian: азовка) in Soviet Union. Nowadays, dolphins are rarely observed in the Sea of Azov. This is attributed to shallowing of the sea, increasing navigation activities, pollution and reduction in the fish population.[35][36]
Economy and ecology
For centuries, the Sea of Azov has been an important waterway for transportation of goods and passengers. Especially important was transport of iron ores from the mines of Kerch peninsula to the major processing plant Azovstal in Zhdanov, Ukraine; this activity has stopped due to the closure of the mines in the 1990s.[37] The navigation has surged after construction in 1952 of the Volga–Don Canal which connected the Sea of Azov with the Volga River – the most important riverine transport route in the central Russia – and thus with such major cities as Moscow, Volgograd and Astrakhan.[8] Currently, the major ports are in Taganrog, Zhdanov, Yeysk and Berdyansk.[9][21]
Increasing navigation rates result in more pollution and even in ecological disasters. On 11 November 2007, strong storm resulted in the sinking of four ships in the Strait of Kerch, in the Russian Port Kavkaz. The ships were Russian bulk carriers Volnogorsk, Nakhichevan, Kovel and Georgian Haji Izmail with Turkish crew. Six other ships were driven from their anchors and stranded, and two tankers damaged (Volgoneft-139 and Volgoneft-123). As a result, about 1300 tons of fuel oil and about 6800 tons of sulfur fell into the sea.[38][39]
Another traditional activity in the sea is fishing. The Sea of Azov used to be the most productive fishing area in the Soviet Union: typical annual fish catchments of 300,000 tonnes converted to 80 kg per hectare of surface. The corresponding numbers are 2 kg in the Black Sea and 0.5 kg in the Mediterranean Sea.[40] The catchment has decreased in the 21 century, but more accent is put on fish farming, especially of sturgeons. Most of the Sea of Azov coastline is also a traditional zone of health resorts.[10]
The irrigation system of Taman Peninsula, supplied by the extended delta of Kuban River is favorable for agriculture and the region is famous for its grape. The area of Sivash lagoons and Arabat Spit had traditional salt producing industry. The Arabat Spit alone produced about 24,000 tonnes/year in 19th century.[8][17]
History and etymology
The Black Sea deluge theory dates the genesis of the Sea of Azov to 5600 BC, and there are traces of Neolithic settlement in the area now covered by it. In antiquity, it was known as Lake Mæotis,[41][42] the Maeotian Lake or the Maeotian Sea (Greek ἡ Μαιῶτις λίμνη and Latin Palus Maeotis), after the tribe of Maeotae which inhabited the Maeotian marshes to the east from the sea. In the antique epoch, locals called the sea Temerinds. In medieval times, Russians named it Surozh Sea, after the Crimean city of Surozh (now Sudak).[1][9]
The current name is popularly said to come from a Polovtsian prince named Azum or Asuf, who was killed defending a town in this region in 1067. Alternatively, it may originate from Turkish "asak" which means "low" and may refer to the location of the sea.[43] The sea is called "The Sea of Azof" in the 1898 Henry James' novel The Turn of the Screw.
Deluge theory
In 1997, William Ryan and Walter Pitman from Columbia University published a theory that a massive flood through the Bosporus occurred in ancient times. They claim that the Black and Caspian Seas were vast freshwater lakes, but then about 5600 BC, the Mediterranean spilled over a rocky sill at the Bosporus, creating the current communication between the Black and Mediterranean Seas. Subsequent work has been done both to support and to discredit this theory, and archaeologists still debate it. This has led some to associate this catastrophe with prehistoric flood myths.[44]
Azov campaigns of 1695–96 and 1736–37

The Sea of Azov had long been a matter of military conflicts between Russia, pursuing naval expansion to the south, and the major power in the region, Turkey. During the Russo-Turkish War (1686–1700), there were two campaigns in 1695–96 to capture the then Turkish fortress of Azov defended by a garrison of 7,000. The campaigns were headed by Peter I and aimed to gain Russian access to the Azov and Black seas. First campaign began in the spring of 1695. The Russian army consisted of 31 thousand people and 170 cannons and included selected trained regimens and Cossacks. It reached Azov on June 27–28 and besieged it by land by 5 July. After two unsuccessful assaults on 5 August and 25 September, the siege was lifted.[45]
The second campaign involved both ground forces and the Azov fleet, which was built in Moscow Oblast, Voronezh, Bryansk and other regions between winter of 1695 and spring of 1696. In April 1696, the army of 75,000 headed by Aleksei Shein moved to Azov on the ground and by ships via Don River to Taganrog. In early May, they were joined by another fleet led by Peter I. On 27 May, the Russian fleet blocked Azov by sea. On 14 June, Turkish fleet tried to break the blockade, but after losing two ships retreated to the sea. After intensive bombardment of the fortress from the ground and sea, on 17 July the Russian army broke the defense lines and occupied parts of the wall. After heavy fighting, the garrison surrendered on 17 July. After the war, the Russian fleet base was moved to Taganrog and Azov, and 215 ships were built there between 1696 and 1711. In 1711, as a result of the Russo-Turkish War (1710–1711) and the Treaty of the Pruth, Azov was returned to Turkey and the Russian Azov fleet was destroyed.[45][46] The city was captured back by Russians in 1737 during the Russo-Austrian-Turkish War (1735–1739). However, as a result of the consequent Treaty of Niš, they were not allowed to keep the fortress and military fleet.[47]
Crimean War 1853–56

Another major military campaign on the Sea of Azov took place during the Crimean War of 1853–56. A naval and ground campaign pitting the Allied navies of Britain and France against Russia took place between May and November 1855. The British and French forces besieged Taganrog, aiming to disrupt Russian supplies to Crimea. Capturing Taganrog would also result in an attack on Rostov, which was a strategic city for Russian support of their Caucasian operations. On 12 May 1855, the allied forces easily captured Kerch and gained access to Azov sea, and on 22 May they attacked Taganrog. The attack failed and was followed by a siege. Despite the vast superiority of the allied forces (about 16,000 soldiers against fewer than 2,000), the city withstood all attempts to capture it, which ended around August 1855 with the retreat of the allied army. Individual coastal attacks continued but without success and were ceased in October 1855.[48]
References
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k Kostianoy, p. 65
- ^ The New Encyclopaedia Britannica, Volume 1. 2005. p. 758. ISBN 1593392362.
With a maximum depth of only about 46 feet (14 m), the Azov is the world's shallowest sea
- ^ Incorporated, Grolier (1996). Academic American encyclopedia, Volume 1. Grolier. ISBN 0717220648.
The Azov is the world's shallowest sea, with depths ranging from 0.9 to 14 m (3 to 46 ft)
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|unused_data=ignored (help) - ^ "National geographic". 185. National Geographic Society. 1994: 138.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Earth from space, NASA
- ^ "Limits of Oceans and Seas, 3rd edition" (PDF). International Hydrographic Organization. 1953. Retrieved 7 February 2010.
- ^ Treaty between the Russian Federation and Ukraine on cooperation in the use of the Sea of Azov and Kerch Strait, December 24, 2003, kremlin.ru (in Russian)
- ^ a b c d e f g h V. I. Borisov and E. I. Kapitonov (1973). Sea of Azov (in Russian). KKI.
- ^ a b c d e "Sea of Azov" (in Russian). Great Soviet Encyclopedia.
- ^ a b c d e f g A. D. Dobrovolsky and B. S. Zalogin (1982). Seas of USSR (in Russian). Moscow University.
- ^ Kostianoy, pp. 69–73
- ^ "Climatological Atlas of the Sea of Azov". National Oceanographic Data Centre. Retrieved 2008-01-06.
- ^ a b c Kostianoy, p. 66
- ^ a b c Kostianoy, p. 67
- ^ a b Complex characteristics of the present condition of the Sea of Azov shore within the Krasnodar Krai (in Russian)
- ^ a b c d Lotysh, I.P. (2006). Geography of Kuban. Collegiate Dictionary. Maikop.
- ^ a b Semenov, Petr Petrovich (1862). Geografichesko-statisticheskìĭ slovar' Rossìĭskoĭ imperìi (Geographical-statistical disctionary of Russian Empire) (in Russian). Oxford University. p. 111.
- ^ "Kerch Strait" (in Russian). Great Soviet Encyclopedia.
- ^ a b Kostianoy, p. 69
- ^ a b Kostianoy, p. 68
- ^ a b Sea of Azov, Britannica
- ^ Debolskaya, E. I.; et al. (2008). "Analysis of the hydrophysical structure of the Sea of Azov in the period of the bottom anoxia development". Journal of Marine Systems. 70: 300. doi:10.1016/j.jmarsys.2007.02.027.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help) - ^ a b c d Kostianoy, p. 76
- ^ Kostianoy, p. 86
- ^ Alien invaders in our seas Jessica Lindström Battle, WWF, Gland, Switzerland, 02-14-2004
- ^ a b Kostianoy, p. 77
- ^ a b Kostianoy, p. 78
- ^ Kostianoy, p. 79
- ^ ostianoy, p. 81
- ^ Основные положения о территориальном планировании, содержащиеся в "Схеме территориального планирования рекреационного комплекса прибрежных территорий Азовского моря и Нижнего Дона" (in Russian)
- ^ a b List of nature reserves (in Russian)
- ^ Basics of ecology (in Russian). Ministry of Education and Science of Ukraine. 2005.
- ^ a b Berdyansk Spit, web site of Berdyansk (in Russian)
- ^ a b Kostianoy, pp. 83–85
- ^ "Dolphins are leaving the polluted Sea of Azov" (in Russian). Novosti.dn.ua. 19 February 2010.
- ^ M. Klinowska (1991). Dolphins, porpoises and whales of the world: the IUCN red data book. IUCN. p. 89. ISBN 2880329361.
- ^ Hirnycyj encyklopedycnyj slovnyk, Volume 3 (in Ukrainian). Schidnyj Vydavnyčyj Dim. 2004. ISBN 966780478X.
- ^ EU experts to assess ecological situation in Kerch Strait, 18 March 2008, kmu.gov.ua
- ^ Oil Spill Near Black Sea Causes 'Ecological Catastrophe', Associated Press, 13 November 2007
- ^ Fauna of the Sea of Azov (in Russian)
- ^ Lordkipanidze, Otar (2000) Phasis: The River and City in Colchis Franz Steiner Verlag, Stuttgart, p. 25, ISBN 3-515-07271-3
- ^ Vasiliev, Alexander Alexandrovich (1936) The Goths in the Crimea Mediaeval Academy of America, Cambridge, Mass., p.17, OCLC 1043381
- ^ Adrian Room (2006). Placenames of the world. McFarland. p. 42. ISBN 0786422483.
- ^ Ryan, W (1997). "An abrupt drowning of the Black Sea shelf" (PDF). Marine Geology. 138: 119. doi:10.1016/S0025-3227(97)00007-8.
- ^ a b "Azov campaign 1695–96" (in Russian). Great Soviet Encyclopedia.
- ^ "Azov fleet" (in Russian). Great Soviet Encyclopedia.
- ^ B. V. Sokolov Russo-Turkish wars of 18–19 centuries (in Russian)
- ^ Pavel Filevsky "History of Taganrog", Moscow, 1898
Bibliography
- Andrey G. Kostianoy, Aleksey N. Kosarev (2007). The Black Sea Environment. Springer. ISBN 3540742913.
