Pompeii
| UNESCO World Heritage Site | |
|---|---|
 View into a narrow street of Pompeii | |
| Criteria | Cultural: iii, iv, v |
| Reference | 829 |
| Inscription | 1997 (21st Session) |
| Coordinates | 40°45′04″N 14°29′13″E / 40.751000°N 14.487000°E |
The city of Pompeii is a partially buried Roman town-city near modern Naples in the Italian region of Campania, in the territory of the comune of Pompei. Along with Herculaneum, Pompeii was partially destroyed and buried under 4 to 6 m (13 to 20 ft) of ash and pumice in the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in AD 79.
Pompeii was lost for nearly 1700 years before its rediscovery in 1748. Since then, its excavation has provided an extraordinarily detailed insight into the life of a city during the Pax Romana. Today, this UNESCO World Heritage Site is one of the most popular tourist attractions of Italy, with approximately 2,500,000 visitors every year.[1]
Name
Pompeii in Latin is a second declension plural (Pompeiī, -ōrum). According to Theodor Kraus, "The root of the word Pompeii would appear to be the Oscan word for the number five, pompe, which suggests that either the community consisted of five hamlets or, perhaps, it was settled by a family group (gens Pompeia)."[2]
Geography

The ruins of Pompeii are situated at coordinates 40°45′00″N 14°29′10″E / 40.75000°N 14.48611°E, near the modern suburban town of Pompei (nowadays written with one "i"). It stands on a spur formed by a lava flow to the north of the mouth of the Sarno River (known in ancient times as the Sarnus).
Today it is some distance inland, but in ancient times it would have been nearer to the coast. Pompeii is about 8 km (5.0 mi) away from Mount Vesuvius. It covered a total of 163 acres[citation needed] and would have been in the region of Campania.
History
Early history
The archaeological digs at the site extend to the street level of the 79 AD volcanic event; deeper digs in older parts of Pompeii and core samples of nearby drillings have exposed layers of jumbled sediment that suggest that the city had suffered from the volcano and other seismic events before then. Three sheets of sediment have been found on top of the lava that lies below the city and, mixed in with the sediment, archaeologists have found bits of animal bone, pottery shards and plants.
Carbon dating has relegated the oldest of these layers to the 8th–6th centuries BC, about the time that the city was founded. The other two strata are separated either by well-developed soil layers or Roman pavement, and were laid in the 4th century BC and 2nd century BC. It is theorized that the layers of jumbled sediment were created by large landslides, perhaps triggered by extended rainfall.[3]
The town was founded around the 7th–6th century BC by the Osci or Oscans, a people of central Italy, on what was an important crossroad between Cumae, Nola and Stabiae. It had already been used as a safe port by Greek and Phoenician sailors. According to Strabo, Pompeii was also captured by the Etruscans, and in fact recent[timeframe?] excavations have shown the presence of Etruscan inscriptions and a 6th century BC necropolis. Pompeii was captured for the first time by the Greek colony of Cumae, allied with Syracuse, between 525 and 474 BC.
In the 5th century BC, the Samnites conquered it (and all the other towns of Campania); the new rulers imposed their architecture and enlarged the town. After the Samnite Wars (4th century BC), Pompeii was forced to accept the status of socium of Rome, maintaining, however, linguistic and administrative autonomy. In the 4th century BC, it was fortified. Pompeii remained faithful to Rome during the Second Punic War.
Pompeii took part in the war that the towns of Campania initiated against Rome, but in 89 BC it was besieged by Sulla. Although the blunts of the Social League, headed by Lucius Cluentius, helped in resisting the Romans, in 80 BC Pompeii was forced to surrender after the conquest of Nola, culminating in many of Sulla's veterans being given land and property, while many of those who went against Rome were ousted from their homes. It became a Roman colony with the name of Colonia Cornelia Veneria Pompeianorum. The town became an important passage for goods that arrived by sea and had to be sent toward Rome or Southern Italy along the nearby Appian Way.
It was fed with water by a spur from Aqua Augusta (Naples) built c. 20 BC by Agrippa; the main line supplied several other large towns, and finally the naval base at Misenum. The castellum in Pompeii is well preserved, and includes many details of the distribution network and its controls.
First century AD







The excavated town offers a snapshot of Roman life in the 1st century, frozen at the moment it was buried on 24 August AD 79.[5] The forum, the baths, many houses, and some out-of-town villas like the Villa of the Mysteries remain well preserved.
Details of everyday life are preserved. For example, on the floor of one of the houses (Sirico's), a famous inscription Salve, lucru (Welcome, money), perhaps humorously intended, indicates a trading company owned by two partners, Sirico and Nummianus (but this could be a nickname, since nummus means coin, money). Other houses provide details concerning professions and categories, such as for the "laundry" workers (Fullones). Wine jars have been found bearing what is apparently the world's earliest known marketing pun (technically a blend), Vesuvinum (combining Vesuvius and the Latin for wine, vinum). Graffiti carved on the walls provides information on street Latin (Vulgar Latin, a different dialect from the literary or classical Latin).
In 89 BC, after the final occupation of the city by Roman General Lucius Cornelius Sulla, Pompeii was finally annexed to the Roman Republic. During this period, Pompeii underwent a vast process of infrastructural development, most of which was built during the Augustan period. These include an amphitheatre, a palaestra with a central natatorium or swimming pool, and an aqueduct that provided water for more than 25 street fountains, at least four public baths, and a large number of private houses (domūs) and businesses. The amphitheatre has been cited by modern scholars as a model of sophisticated design, particularly in the area of crowd control.[6]
The aqueduct branched out through three main pipes from the Castellum Aquae, where the waters were collected before being distributed to the city; in case of extreme drought, the water supply would first fail to reach the public baths (the least vital service), then private houses and businesses, and when there would be no water flow at all, the system would fail to supply the public fountains (the most vital service) in the streets of Pompeii. The pools in Pompeii were used mostly for decoration.
The large number of well-preserved frescoes provide information on everyday life and have been a major advance in art history of the ancient world, with the innovation of the Pompeian Styles (First/Second/Third Style). Some aspects of the culture were distinctly erotic, including phallic worship. A large collection of erotic votive objects and frescoes were found at Pompeii. Many were removed and kept until recently in a secret collection at the University of Naples.
At the time of the eruption, the town may have had some 20,000 inhabitants, and was located in an area in which Romans had their holiday villas. Prof. William Abbott explains, "At the time of the eruption, Pompeii had reached its high point in society as many Romans frequently visited Pompeii on vacations." It is the only ancient town of which the whole topographic structure is known precisely as it was, with no later modifications or additions. Due to the difficult terrain it was not distributed on a regular plan as most Roman towns but its streets are straight and laid out in a grid in the Roman tradition; they are laid with polygonal stones, and have houses and shops on both sides of the street. It followed its decumanus and its cardo, centered on the forum.
Besides the forum, many other services were found: the Macellum (great food market), the Pistrinum (mill), the Thermopolium (sort of bar that served cold and hot beverages), and cauponae (small restaurants). An amphitheatre and two theatres have been found, along with a palaestra or gymnasium. A hotel (of 1,000 square metres) was found a short distance from the town; it is now nicknamed the "Grand Hotel Murecine".
In 2002, another discovery at the mouth of the Sarno River near Sarno revealed that the port also was populated and that people lived in palafittes, within a system of channels that suggested a likeness to Venice to some scientists.
AD 62–79
The inhabitants of Pompeii had long been used to minor quaking (indeed, the writer Pliny the Younger wrote that earth tremors "were not particularly alarming because they are frequent in Campania"), but on 5 February 62,[7] there was a severe earthquake which did considerable damage around the bay and particularly to Pompeii. The earthquake, which took place on the afternoon of the 5th of February, is believed to have registered between about 5 and 6 on the Richter scale.[8]
On that day in Pompeii there were to be two sacrifices, as it was the anniversary of Augustus being named "Father of the Nation" and also a feast day to honour the guardian spirits of the city. Chaos followed the earthquake. Fires, caused by oil lamps that had fallen during the quake, added to the panic. Nearby cities of Herculaneum and Nuceria were also affected.[8]
Temples, houses, bridges, and roads were destroyed. It is believed that almost all buildings in the city of Pompeii were affected. In the days after the earthquake, anarchy ruled the city, where theft and starvation plagued the survivors. In the time between 62 and the eruption in 79, some rebuilding was done, but some of the damage had still not been repaired at the time of the eruption.[8] Although it is unknown how many, a considerable number of inhabitants moved to other cities within the Roman Empire while others remained and rebuilt.
An important field of current research concerns structures that were being restored at the time of the eruption (presumably damaged during the earthquake of 62). Some of the older, damaged, paintings could have been covered with newer ones, and modern instruments are being used to catch a glimpse of the long hidden frescoes. The probable reason why these structures were still being repaired around seventeen years after the earthquake was the increasing frequency of smaller quakes that led up to the eruption.
Eruption of Vesuvius
By the 1st century AD, Pompeii was one of a number of towns located near the base of the volcano, Mount Vesuvius. The area had a substantial population which grew prosperous from the region's renowned agricultural fertility. Many of Pompeii's neighboring communities, most famously Herculaneum, also suffered damage or destruction during the 79 eruption. The eruption occurred on August 24, just one day after Vulcanalia, the festival of the Roman god of fire, including that from volcanoes.[9]
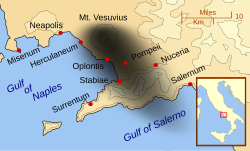
A multidisciplinary volcanological and bio-anthropological study of the eruption products and victims, merged with numerical simulations and experiments, indicate that at Vesuvius and surrounding towns heat was the main cause of death of people, previously believed to have died by ash suffocation. The results of the study, published in 2010, show that exposure to at least 250 °C hot surges at a distance of 10 kilometres from the vent was sufficient to cause instant death, even if people were sheltered within buildings.[10]
The people and buildings of Pompeii were covered in up to twelve different layers of tephra, in total 25 meters deep, which rained down for about 6 hours. Pliny the Younger provided a first-hand account of the eruption of Mount Vesuvius from his position across the Bay of Naples at Misenum, in a version which was written 25 years after the event. His uncle, Pliny the Elder, with whom he had a close relationship, died while attempting to rescue stranded victims. As Admiral of the fleet, Pliny the Elder had ordered the ships of the Imperial Navy stationed at Misenum to cross the bay to assist evacuation attempts. Volcanologists have recognised the importance of Pliny the Younger's account of the eruption by calling similar events "Plinian".
The eruption was documented by contemporary historians and is generally accepted as having started on 24 August 79, relying on one version of the text of Pliny's letter. However the archeological excavations of Pompeii suggest that the city was buried about three months later.[11] This is supported by another version of the letter[12] which gives the date of the eruption as November 23.[13]
People buried in the ash appear to be wearing warmer clothing than the light summer clothes that would be expected in August. The fresh fruit and vegetables in the shops are typical of October, and conversely the summer fruit that would have been typical of August was already being sold in dried, or conserved form. Wine fermenting jars had been sealed over, and this would have happened around the end of October. Coins found in the purse of a woman buried in the ash include one which features a fifteenth imperatorial acclamation among the emperor's titles. This cannot have been minted before the second week of September. So far there is no definitive theory as to why there should be such an apparent discrepancy.[14]
Rediscovery

After thick layers of ash covered the two towns, they were abandoned and eventually their names and locations were forgotten. The first time any part of them was unearthed was in 1599, when the digging of an underground channel to divert the river Sarno ran into ancient walls covered with paintings and inscriptions. The architect Domenico Fontana was called in and he unearthed a few more frescoes but then covered them over again, and nothing more came of the discovery. A wall inscription had mentioned a decurio Pompeii ("the town councillor of Pompeii") but that it indicated the name of an ancient Roman city hitherto unknown was missed.[15]
Fontana's act of covering over the paintings has been seen both as censorship – in view of the frequent sexual content of such paintings – and as a broad-minded act of preservation for later times as he would have known that paintings of the hedonistic kind later found in some Pompeian villas were not considered in good taste in the climate of the counter-reformation.[16]
Herculaneum was properly rediscovered in 1738 by workmen digging for the foundations of a summer palace for the King of Naples, Charles of Bourbon. Pompeii was rediscovered as the result of intentional excavations in 1748 by the Spanish military engineer Rocque Joaquin de Alcubierre.[17] These towns have since been excavated to reveal many intact buildings and wall paintings. Charles of Bourbon took great interest in the findings even after becoming king of Spain because the display of antiquities reinforced the political and cultural power of Naples.[18]
Karl Weber directed the first real excavations;[19] he was followed in 1764 by military engineer Franscisco la Vega. Franscisco la Vega was succeeded by his brother, Pietro, in 1804.[20] During the French occupation Pietro worked with Christophe Saliceti.[21]
Giuseppe Fiorelli took charge of the excavations in 1860. During early excavations of the site, occasional voids in the ash layer had been found that contained human remains. It was Fiorelli who realized these were spaces left by the decomposed bodies and so devised the technique of injecting plaster into them to recreate the forms of Vesuvius's victims. This technique is still in use today, with a clear resin now used instead of plaster because it is more durable, and does not destroy the bones, allowing further analysis.[22][23][24]
Some have theorized that Fontana found some of the famous erotic frescoes and, due to the strict modesty prevalent during his time, reburied them in an attempt at archaeological censorship. This view is bolstered by reports of later excavators who felt that sites they were working on had already been visited and reburied. Even many recovered household items had a sexual theme. The ubiquity of such imagery and items indicates that the sexual mores of the ancient Roman culture of the time were much more liberal than most present-day cultures, although much of what is described as erotic imagery (e.g. over-sized phalluses) was in fact fertility imagery.
This clash of cultures led to an unknown number of discoveries being hidden away again. A wall fresco which depicted Priapus, the ancient god of sex and fertility, with his extremely enlarged penis, was covered with plaster, even the older reproduction below was locked away "out of prudishness" and opened only on request and only rediscovered in 1998 due to rainfall.[25]
In 1819, when King Francis I of Naples visited the Pompeii exhibition at the National Museum with his wife and daughter, he was so embarrassed by the erotic artwork that he decided to have it locked away in a secret cabinet, accessible only to "people of mature age and respected morals". Re-opened, closed, re-opened again and then closed again for nearly 100 years, it was briefly made accessible again at the end of the 1960s (the time of the sexual revolution) and was finally re-opened for viewing in 2000. Minors are still allowed entry to the once secret cabinet only in the presence of a guardian or with written permission.[26]
Prior to or shortly after the destruction of Pompeii, one graffitist had scribbled "Sodom and Gomorrah" onto a wall near the city's central crossroads.[27] Some Christians have since invoked the destruction of Pompeii as divine retribution.[28][29][30]
A large number of artifacts from Pompeii are preserved in the Naples National Archaeological Museum.
Tourism
Pompeii has been a popular tourist destination for 250 years; it was on the Grand Tour. In 2008, it was attracting almost 2.6 million visitors per year, making it one of the most popular tourist sites in Italy.[31] It is part of a larger Vesuvius National Park and was declared a World Heritage Site by UNESCO in 1997. To combat problems associated with tourism, the governing body for Pompeii, the Soprintendenza Archaeological di Pompei have begun issuing new tickets that allow for tourists to also visit cities such as Herculaneum and Stabiae as well as the Villa Poppaea, to encourage visitors to see these sites and reduce pressure on Pompeii.


Pompeii is also a driving force behind the economy of the nearby town of Pompei. Many residents are employed in the tourism and hospitality business, serving as taxi or bus drivers, waiters or hotel operators. The ruins can be easily reached on foot from the Circumvesuviana train stop called Pompei Scavi, directly at the ancient site. There are also car parks nearby.
Excavations in the site have generally ceased due to the moratorium imposed by the superintendent of the site, Professor Pietro Giovanni Guzzo. Additionally, the site is generally less accessible to tourists, with less than a third of all buildings open in the 1960s being available for public viewing today. Nevertheless, the sections of the ancient city open to the public are extensive, and tourists can spend several days exploring the whole site.
In popular culture
Pompeii has been in popular culture significantly since rediscovery. Book I of the Cambridge Latin Course teaches Latin while telling the story of a Pompeii resident, Lucius Caecilius Iucundus, from the reign of Nero to that of Vespasian. The book ends when Mount Vesuvius erupts, and Caecilius and his household are killed. The books have a cult following and students have been known to attempt to track down Caecilius's house during visits to Pompeii.[32]
Pompeii was the setting for the British comedy television series Up Pompeii! and the movie of the series. Pompeii also featured in the second episode of the fourth season of revived BBC drama series Doctor Who, named "The Fires of Pompeii".[33]
In 1971, the rock band Pink Floyd recorded the live concert film Pink Floyd: Live at Pompeii, performing six songs in the ancient Roman amphitheatre in the city. The audience consisted only of the film's production crew and some local children.
Conservation

The objects buried beneath Pompeii were well-preserved for almost two thousand years. The lack of air and moisture allowed for the objects to remain underground with little to no deterioration, which meant that, once excavated, the site had a wealth of sources and evidence for analysis, giving detail into the lives of the Pompeiians. However, once exposed, Pompeii has been subject to both natural and man-made forces which have rapidly increased their rate of deterioration.
Weathering, erosion, light exposure, water damage, poor methods of excavation and reconstruction, introduced plants and animals, tourism, vandalism and theft have all damaged the site in some way. Two-thirds of the city has been excavated, but the remnants of the city are rapidly deteriorating.[34]
The concern for conservation has continually troubled archaeologists. The ancient city was included in the 1996 World Monuments Watch by the World Monuments Fund, and again in 1998 and in 2000. In 1996 the organization claimed that Pompeii "desperately need[ed] repair" and called for the drafting of a general plan of restoration and interpretation.[35] The organization supported conservation at Pompeii with funding from American Express and the Samuel H. Kress Foundation.[36]
Today, funding is mostly directed into conservation of the site; however, due to the expanse of Pompeii and the scale of the problems, this is inadequate in halting the slow decay of the materials. An estimated $335 million is needed for all necessary work on Pompeii.[citation needed]
House of the Gladiators collapse
The 2,000-year-old Schola Armatorum (House of the Gladiators) collapsed on 6 November 2010. The structure was not open to visitors, but the outside was visible to tourists. There was no immediate determination as to what caused the building to collapse, although reports suggested water infiltration following heavy rains might have been responsible. There has been fierce controversy after the collapse, with accusations of neglect.[37][38]
Gallery
-
The Circumvesuviana stop at Pompeii.
-
Theatre at Pompeii
-
Small theatre. 80 BC.
-
Cast of a dog that archaeologists believe was chained outside the House of Vesonius Primus, a Pompeiian fuller.
-
Karl Briullov, The Last Day of Pompeii (1830–33).
See also
- Erotic art in Pompeii and Herculaneum
- Eumachia
- House of Julia Felix
- House of Loreius Tiburtinus
- House of Menander
- House of Sallust
- House of the Tragic Poet
- House of the Vettii
- Lupanar (Pompeii)
- Macellum of Pompeii
- Robert Rive, 1850s photographer of Pompeii
- Suburban Baths (Pompeii)
- Temple of Isis (Pompeii)
- Volcanic destruction
- Armero tragedy; a city in Colombia that suffered a similar fate
- Mount Pelée/Saint-Pierre, Martinique (similar destructive eruption at Martinique in 1902)
- Plymouth, Montserrat, a city buried by volcanic ash from the Soufrière Hills volcano in the 1990s
- Joya de Cerén, known as the "Pompeii of the Americas"
Notes
- ^ "Dossier Musei 2008" (in Italian). Touring Club Italiano.
{{cite web}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help);|archive-url=requires|url=(help); Missing or empty|url=(help) - ^ Kraus 1975, p. [page needed]
- ^ Senatore, Stanley & Pescatore 2004, p. [page needed]
- ^ Clarke 2006, pp. 262–264
- ^ De Carolis & Patricelli 2003, p. 83
- ^ Berinato, Scott (May 18, 2007). "Crowd Control in Ancient Pompeii". CSO. Retrieved September 30, 2012.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ "Patterns of Reconstruction at Pompeii". University of Virginia. Retrieved September 30, 2012.
- ^ a b c "Visiting Pompeii". Current Archaeology. p. 3.
{{cite web}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help);|archive-url=requires|url=(help); Missing or empty|url=(help) - ^ "The Destruction of Pompeii, 79 AD". EyeWitness to History. 1999. Retrieved September 30, 2012.
- ^ Mastrolorenzo et al. 2010, p. e11127
- ^ Gabi Laske. "The A.D. 79 Eruption at Mt. Vesuvius". Lecture notes for UCSD-ERTH15: "Natural Disasters". Retrieved 2008-07-28.
- ^ Stefani 2006, pp. 10–14
- ^ Grant 2001, p. 223
- ^ Stefani 2006, pp. 10–14
- ^ Grant 2001, p. 215
- ^ Ozgenel 2008, p. 13
- ^ Ozgenel, Lalo, A Tale of Two Cities: In Search of Ancient Pompeii and Herculaneum, METU JFA 2008/1 (25:1), p1-25
- ^ Ozgenel 2008, p. 19
- ^ Parslow 1995, p. [page needed]
- ^ Pagano 1997, p. [page needed]
- ^ POMPEIA d'Ernest Breton (3eme éd. 1870) "Introduction – La résurrection de la ville" in French
- ^ "Orto dei Fuggiaschi". Marketplace.it. Retrieved 2010-02-01.
- ^ "Orto dei Fuggiaschi (2)". Marketplace.it. Retrieved 2010-02-01.
- ^ "Orto dei Fuggiaschi (3)". Marketplace.it. Retrieved 2010-02-01.
- ^ As reported by the Evangelist pressedienst press agency in March, 1998.
- ^ Karl Schefold (2003), Die Dichtung als Führerin zur Klassischen Kunst. Erinnerungen eines Archäologen (Lebenserinnerungen Band 58), edd. M. Rohde-Liegle et al., Hamburg. p. 134 ISBN 3-8300-1017-6.
- ^ Butterworth & Laurence 2005, p. 284
- ^ Fletcher 1835, p. 328
- ^ Alexander John Scott, Discourses, p. 41
- ^ "C. H. SpurgeonVoices From Pompeii". Spurgeon.org. Retrieved 2010-10-16.
- ^ Nadeau, Barbie Selling Pompeii, Newsweek, April 14, 2008
- ^ "The Italian Job". Classics at RGSW. Retrieved 2010-10-16.
- ^ "Doctor Who – News – Rome Sweet Rome". BBC. Retrieved 2010-10-16.
- ^ "Ashes to ashes: the latter-day ruin of Pompeii". Prospectmagazine.co.uk. 2010-04-29. Retrieved 2010-10-16.
- ^ "World Monuments Fund, ''List of 100 Most Endangered Sites – 1996,'' New York, NY: 1996, p. 31" (PDF). Retrieved 2012-07-07.
- ^ "World Monuments Fund – Ancient Pompeii". Wmf.org. 2010-12-13. Retrieved 2012-07-07.
- ^ "Pompeii collapse prompts charges of official neglect".
- ^ "Pompeii Gladiator Training Centre Collapses".
References
- Beard, Mary (2008). Pompeii: The Life of a Roman Town. Profile Books. ISBN 978-1-86197-596-6.
- Butterworth, Alex; Laurence, Ray (2005). Pompeii: The Living City. St. Martin's Press. ISBN 978-0-312-35585-2.
- Cioni, Rafaello; Gurioli, L; Lanza, R; Zanella, E (2004). "Temperatures of the A.D. 79 pyroclastic density current deposits (Vesuvius, Italy)". Journal of Geophysical Research. 109. doi:10.1029/2002JB002251.
- Clarke, John (2006). Visual Representation and Non-Elite Viewers in Italy, 100 BC – AD 315. University of California. ISBN 978-0-520-24815-1.
- De Carolis, Ernesto; Patricelli, Giovanni (2003). Vesuvius, A.D. 79: the destruction of Pompeii and Herculaneum. L'erma Di Bretschneider. ISBN 978-88-8265-199-2.
- Fletcher, John (1835). The whole works of ... John Flecter. Oxford University.
- Grant, Michael (2001). Cities of Vesuvius: Pompeii and Herculaneum. Phoenix. ISBN 9781842122198.
- Hodge, Trevor (2001). Roman Aqueducts & Water Supply. Duckworth. ISBN 9780715631713.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|rev=ignored (help) - Kraus, Theodor (1975). Pompeii and Herculaneum: The Living Cities of the Dead. H. N. Abrams. ISBN 9780810904187.
- Maiuri, Amedeo (1994). "Pompeii". Scientific American.
- Mastrolorenzo, Giuseppe; Petrone, Pierpaolo; Pappalardo, Lucia; Guarino, Fabio (2010). "Lethal Thermal Impact at Periphery of Pyroclastic Surges: Evidences at Pompeii". PLOS One. 5 (6). doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0011127.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - Pagano, Mario (1997). I Diari di Scavo di Pompeii, Ercolano e Stabiae di Francesco e Pietro la Vega (1764–1810) (in Italian). L'Erma di Bretschneidein. ISBN 88-7062-967-8.
- Parslow, Christopher (1995). Rediscovering antiquity: Karl Weber and the excavation of Herculaneum, Pompeii, and Stabiae. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-47150-8.
- Senatore, Maria; Stanley, Jean-Daniel; Pescatore, Tullio (November 7–10, 2004). "Avalanche-associated mass flows damaged Pompeii several times before the Vesuvius catastrophic eruption in the 79 CE". 2004 Denver Annual Meeting.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - Stefani, Grete (October 2006). La vera data dell'eruzione. Archeo.
- Steven, Ellis (2004). "The distribution of bars at Pompeii: Archaeological, spatial and viewshed analyses". Journal of Roman Archaeology. 17 (1). ISSN 1047-7594.
- Zarmati, Louise (2005). Heinemann ancient and medieval history: Pompeii and Herculaneum. Heinemann. ISBN 1-74081-195-X.
External links
- Official website
- Data on new excavations from the International Association for Classical Archaeology (AIAC)
- Template:Dmoz
- Forum of Pompeii Digital Media Archive (creative commons-licensed photos, laser scans, panoramas), data from a University of Ferrara/CyArk research partnership
- Romano-Campanian Wall-Painting (English, Italian, Spanish and French introduction) mainly focusing on wall-paintings from Pompeian houses and villas
- Purcell, N., R. Talbert, T. Elliott, S. Gillies. "Places: 433032 (Pompeii)". Pleiades. Retrieved March 8, 2012.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link GA Template:Link GA
- Ancient cities
- Archaeological sites in Italy
- Destroyed cities
- Former populated places in Italy
- Osci
- Pompeii (ancient city)
- Populated places established in the 1st millennium BC
- Roman Empire paintings
- Roman sites of Campania
- Visitor attractions in Campania
- Museums in Campania
- Museums of Ancient Rome
- Archaeological museums in Italy





