Capricornus
| Constellation | |
 | |
| Abbreviation | Cap |
|---|---|
| Genitive | Capricorni |
| Right ascension | 21 |
| Declination | −20 |
| Area | 414 sq. deg. (40th) |
| Meteor showers | |
| Bordering constellations | |
| Visible at latitudes between +60° and −90°. Best visible at 21:00 (9 p.m.) during the month of September. | |
- For the astrological sign see Capricorn.
Capricornus (![]() or
or ![]() , Unicode: ♑), a name meaning "Horned Goat" or "That which has horns like a goat's" in Latin, is one of the constellations of the zodiac. It is commonly called Capricorn, especially in astrology. It is commonly called the sea-goat, as it is in an area of the sky known as the Sea. Capricornus is one of the 88 modern constellations, and was also one of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy. Under its modern boundaries it is bordered by Aquila, Sagittarius, Microscopium, Piscis Austrinus and Aquarius.
, Unicode: ♑), a name meaning "Horned Goat" or "That which has horns like a goat's" in Latin, is one of the constellations of the zodiac. It is commonly called Capricorn, especially in astrology. It is commonly called the sea-goat, as it is in an area of the sky known as the Sea. Capricornus is one of the 88 modern constellations, and was also one of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy. Under its modern boundaries it is bordered by Aquila, Sagittarius, Microscopium, Piscis Austrinus and Aquarius.
Notable features
This constellation is the dimmest in the zodiac besides Cancer. Its brighter stars are found on a triangle whose vertices are α Cap (Giedi), δ Cap (Deneb Algiedi), and ω Cap.
History
This constellation is one of the oldest to have been identified, possibly the oldest, despite its dimness. Since it falls in an area of the sky known as the sea, it became considered a sea-goat (in the same sense as a sea-maiden). Depictions of a goat or goat-fish have been found on Babylonian tablets dating back three thousand years. The constellation may owe its antiquity to the fact that at that time, the northern hemisphere's Winter Solstice occurred while the sun was in Capricorn. The concern for the sun's rebirth might have rendered astronomical and astrological observation of this region of space very important.
For the same reason, the sun's most southerly position, which is attained at the northern hemisphere's winter solstice, is now called the Tropic of Capricorn, a term which also applies to the line on earth where the sun is directly overhead at noon on that solstice.
Due to early Greek beliefs that sin accumulated throughout the year, causing the darkness to increase, together with the sun's descent and pause at the Solstice, the ancient Greeks referred to this area of sky as the Augean Stable, where they considered the sun stabled during the year. The cause of the association with the location or name of Augeas is not currently known. However, during the classical period of Greek history, this name gradually fell out of use.
Due to the precession of the equinoxes, the December solstice no longer takes place while the sun is in Capricorn, but the astrological period called Capricorn begins at approximately the same time as the solstice.
The planet Neptune was discovered in this constellation by German astronomer Johann Galle, near Deneb Algedi (δ Capricorni) on September 23, 1846, which is reasonable as Capricornus can be seen best at 9:00 in September.
Mythology
This constellation is sometimes identified as Amalthea, the goat that suckled the infant Zeus after his mother Rhea saved him from being devoured by his father Cronos in Greek mythology. The goat's broken horn was transformed into the cornucopia or horn of plenty. Some ancient sources claim that this derives from the sun "taking nourishment" while in the constellation, in preparation for its climb back northward.
However, the constellation is often depicted as a sea-goat, a goat with a fish's tail. One myth that deals with this says that when the goat-god Pan was attacked by the monster Typhon, he dove into the Nile; the parts above the water remained a goat, but those under the water transformed into a fish.
In Sumeria, the constellation was associated with the god Ea or Enki, who brought culture out of the sea to humankind.
The constellation, together with its early Greek name, associated ideas about sin, and the constellation of Aquarius, who was said to have poured out a river, may represent the origin of the myth of the Augean Stable, which forms one of The Twelve Labours of Herakles.
The constellation is located in an area of sky called the Sea or Water, consisting of many watery constellations such as Aquarius, Pisces, and Eridanus.
Astrology
The Western astrological sign Capricorn of the tropical zodiac (December 22 - January 19) differs from the astronomical constellation and the Hindu astrological sign of the sidereal zodiac (January 19 - February 15).
In some cosmologies, Capricorn is associated with the classical element Earth, and thus called an Earth Sign (with Taurus and Virgo). It is also one of the four Cardinal signs (along with Aries, Cancer, and Libra). It is the domicile of Saturn and the exaltation of Mars. Its polar opposite is Cancer. Each astrological sign is assigned a part of the body, viewed as the seat of its power. Capricorn rules the knees, bones, and skin. The ancient symbol of this sign is the sea monster, which harks back to the time in antiquity when Capricorn was considered a water sign and not an earth sign. The symbol for this eventually changed to that of a seagoat, which is a mythological creature that has the head and upper body of a goat and the lower body of a fish, and this was an attempt to meld the watery qualities that this sign originally possessed with the earthly qualities that astrologers wanted it to acquire. In modern times the symbolism for this sign has evolved once again, with astrologers doing away with the figure of the seagoat altogether in favour of the mountain goat, which has almost eradicated the watery themes that once encompassed this sign.
Graphic visualization
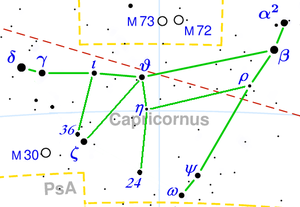
The stars of the constellation Capricorn can be connected in an alternative way, which graphically shows a goat.
The goat's head is formed by the triangle of stars ι Capricorni, θ Capricorni, and ζ Capricorni. The goat's horn sticks out with stars γ Capricorni and δ Capricorni. Star δ Capricorni, at the tip of the horn, is of the third magnitude.
The goat's tail consists of stars β Capricorni and α Capricorni: star β Capricorni being of the third magnitude.
The goat's hind foot consists of stars ψ Capricorni and ω Capricorni. Both of these stars are of the fourth magnitude.
Reference
- H. A. Rey, The Stars — A New Way To See Them. Enlarged World-Wide Edition. Houghton Mifflin, Boston, 1997. ISBN 0-395-24830-2.
Notable and named stars
| BD | F | Names and other designations | Mag. | Ly away | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δ | 49 | Delta Capricorni, Deneb Algiedi, Scheddi | 2.87 | 38.6 |
|
| β1,2 | 9 | Beta Capricorni, Dabih | 2.99 | 328 |
|
| α² | 6 | Alpha2 Capricorni, Algedi Secunda, Secunda Giedi | 3.56 | 109 |
|
| γ | 40 | Gamma Capricorni, Nashira | 3.68 | 139 |
|
| ζ | 34 | Zeta Capricorni | 3.77 | 398 |
|
| θ | 23 | Theta Capricorni | 4.08 | 158 | |
| ω | 18 | Omega Capricorni | 4.12 | 630 | |
| ψ | 16 | Psi Capricorni | 4.13 | 47.9 | |
| α¹ | 5 | Alpha1 Capricorni, Algedi Prima, Prima Giedi | 4.24 | 690 |
|
| ι | 32 | Iota Capricorni | 4.28 | 216 | |
| A | 24 | 24 Capricorni | 4.49 | 523 | |
| b | 36 | 36 Capricorni | 4.50 | 179 | |
| ε | 39 | Epsilon Capricorni, Kastra | 4.51 | 660 | |
| κ | 43 | Kappa Capricorni | 4.72 | 291 | |
| ν | 8 | Nu Capricorni, Alshat | 4.75 | 272 |
|
| ρ | 11 | Rho Capricorni | 4.77 | 98.7 | |
| η | 22 | Eta Capricorni, Arm | 4.82 | 158 | |
| μ | 51 | Mu Capricorni | 5.08 | 90.2 | |
| π | 10 | Pi Capricorni, Okul | 5.08 | 670 | |
| c | 46 | 46 Capricorni | 5.10 | 800 | |
| υ | 15 | Upsilon Capricorni | 5.15 | 760 | |
| 42 | 42 Capricorni, BY Capricorni | 5.16 | 106 | ||
| φ | 28 | Phi Capricorni | 5.17 | 690 | |
| τ² | 14 | Tau2 Capricorni | 5.24 | 1750 | |
| 41 | 41 Capricorni | 5.24 | 247 | ||
| σ | 7 | Sigma Capricorni | 5.28 | 700 | |
| χ | 25 | Chi Capricorni | 5.30 | 191 | |
| 29 | 29 Capricorni | 5.31 | |||
| 33 | 33 Capricorni | 5.38 | |||
| 30 | 30 Capricorni | 5.40 | |||
| ο | 12 | Omicron Capricorni | 5.57 | 137 |
double star, component magnitudes 5.94, 6.74 |
| λ | 48 | Lambda Capricorni | 5.57 | 294 | |
| 37 | 37 Capricorni | 5.70 | |||
| 19 | 19 Capricorni | 5.78 | |||
| 35 | 35 Capricorni | 5.78 | |||
| ξ² | 2 | Xi2 Capricorni | 5.84 | 91.5 | |
| 4 | 4 Capricorni | 5.86 | |||
| 44 | 44 Capricorni | 5.88 | |||
| 17 | 17 Capricorni | 5.91 | |||
| 45 | 45 Capricorni | 5.96 | |||
| 47 | 47 Capricorni | 6.00 | |||
| 27 | 27 Capricorni | 6.25 | |||
| 20 | 20 Capricorni | 6.26 | |||
| 3 | 3 Capricorni | 6.30 | |||
| ξ¹ | 1 | Xi1 Capricorni | 6.34 | 483 | |
| τ¹ | 13 | Tau1 Capricorni | 6.76 | 880 | |
| 31 | 31 Capricorni | 7.18 | |||
| HD 202206 | 8.08 |
Source: The Bright Star Catalogue, 5th Revised Ed., The Hipparcos Catalogue, ESA SP-1200
Stars with planets
| Star | Planet | Distance (ly) |
Discovered |
|---|---|---|---|
| HD 202206 | HD 202206 b | 151.14 | 2000 |
| HD 202206 c | 151.14 | 2004 |
