Health effects of tobacco: Difference between revisions
| [pending revision] | [pending revision] |
Surv1v4l1st (talk | contribs) Undid revision 366838577 by 89.28.58.134 (talk) |
→Cognitive Function: citation needed |
||
| Line 212: | Line 212: | ||
A history of regular smoking was observed more frequently among individuals who had experienced a [[major depressive disorder]] at some time in their lives than among individuals who had never experienced major depression or among individuals with no psychiatric diagnosis.<ref>[http://jama.ama-assn.org/cgi/content/abstract/264/12/1546 Smoking, smoking cessation, and major depression]</ref> People with major depression are also much less likely to [[smoking cessation|quit]] due to the increased risk of experiencing mild to severe states of depression, including a major depressive episode.<ref>{{Cite doi|10.1300/J069v17n01_04 }}</ref> Depressed smokers appear to experience more withdrawal symptoms on quitting, are less likely to be successful at quitting, and are more likely to relapse.<ref>{{Cite doi|10.1037/0022-006X.61.5.761}}</ref> |
A history of regular smoking was observed more frequently among individuals who had experienced a [[major depressive disorder]] at some time in their lives than among individuals who had never experienced major depression or among individuals with no psychiatric diagnosis.<ref>[http://jama.ama-assn.org/cgi/content/abstract/264/12/1546 Smoking, smoking cessation, and major depression]</ref> People with major depression are also much less likely to [[smoking cessation|quit]] due to the increased risk of experiencing mild to severe states of depression, including a major depressive episode.<ref>{{Cite doi|10.1300/J069v17n01_04 }}</ref> Depressed smokers appear to experience more withdrawal symptoms on quitting, are less likely to be successful at quitting, and are more likely to relapse.<ref>{{Cite doi|10.1037/0022-006X.61.5.761}}</ref> |
||
Evidence suggests that non-smokers are up to twice as likely as smokers to develop [[Parkinson's disease]] or [[Alzheimer's disease]].<ref>{{Cite doi|10.1016/S0166-4328(00)00206-0}}</ref> A plausible explanation for these cases may be the effect of nicotine, a [[cholinergic]] [[stimulant]], decreasing the levels of [[acetylcholine]] in the smoker's brain; Parkinson's disease occurs when the effect of [[dopamine]] is less than that of acetylcholine. In addition, nicotine stimulates the mesolimbic dopamine pathway (as do other drugs of abuse), causing an effective increase in dopamine levels. Opponents counter by noting that consumption of pure nicotine may be as beneficial as smoking without the risks associated with smoking, although this is unlikely due to the importance of the MAO-B inhibitor compounds of tobacco in preventing neurodegenerative diseases. |
Evidence suggests that non-smokers are up to twice as likely as smokers to develop [[Parkinson's disease]] or [[Alzheimer's disease]].<ref>{{Cite doi|10.1016/S0166-4328(00)00206-0}}</ref> A plausible explanation for these cases may be the effect of nicotine, a [[cholinergic]] [[stimulant]], decreasing the levels of [[acetylcholine]] in the smoker's brain; Parkinson's disease occurs when the effect of [[dopamine]] is less than that of acetylcholine. In addition, nicotine stimulates the mesolimbic dopamine pathway (as do other drugs of abuse), causing an effective increase in dopamine levels. Opponents counter by noting that consumption of pure nicotine may be as beneficial as smoking without the risks associated with smoking, although this is unlikely due to the importance of the MAO-B inhibitor compounds of tobacco in preventing neurodegenerative diseases.{{cn}} |
||
===In pregnancy=== |
===In pregnancy=== |
||
Revision as of 22:28, 17 June 2010
| Part of a series on |
| Tobacco |
|---|
 |
The health effects of tobacco are the circumstances, mechanisms, and factors of tobacco consumption on human health. Epidemiological research have been focused primarily on tobacco smoking,[1] which has been studied more extensively than any other form of consumption.[2]
Tobacco is the single greatest cause of preventable death in the United States[3] and worldwide.[4] Tobacco use leads most commonly to diseases affecting the heart and lungs, with smoking being a major risk factor for heart attacks, strokes, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), emphysema, and cancer (particularly lung cancer, cancers of the larynx and mouth, and pancreatic cancer). It also causes peripheral vascular disease and hypertension, all developed due to the exposure time and the level of dosage of tobacco. Furthermore, the earlier and the higher level of tar content in the tobacco filled cigarettes causes the greater risk of these diseases. Cigarettes sold in developing nations tend to have higher tar content, and are less likely to be filtered, potentially increasing vulnerability to tobacco-related disease in these regions.[5]
The World Health Organization (WHO) estimate that tobacco caused 5.4 million deaths in 2004[6] and 100 million deaths over the course of the 20th century.[7] Similarly, the United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention describes tobacco use as "the single most important preventable risk to human health in developed countries and an important cause of premature death worldwide."[8]
Smoke contains several carcinogenic pyrolytic products that bind to DNA and cause many genetic mutations. There are over 19 known chemical carcinogens in cigarette smoke. Tobacco also contains nicotine, which is a highly addictive psychoactive chemical. When tobacco is smoked, nicotine causes physical and psychological dependency. Tobacco use is a significant factor in miscarriages among pregnant smokers, it contributes to a number of other threats to the health of the fetus such as premature births and low birth weight and increases by 1.4 to 3 times the chance for Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS).[9] The result of scientific studies done in neonatal rats seems to indicate that exposure to cigarette smoke in the womb may reduce the fetal brain's ability to recognize hypoxic conditions, thus increasing the chance of accidental asphyxiation.[10] Incidence of impotence is approximately 85 percent higher in male smokers compared to non-smokers,[11] and is a key factor causing erectile dysfunction (ED).[11][12][13]
Epidemiology
Prevalence
Although tobacco may be consumed by either smoking or other smokeless methods such as chewing, the World Health Organization (WHO) only collect data on smoked tobacco.[1] Smoking has therefore been studied more extensively than any other form of consumption.[2]
In 2000, smoking was practiced by 1.22 billion people, predicted to rise to 1.45 billion people in 2010 and 1.5 to 1.9 billion by 2025. If prevalence had decreased by 2% a year since 2000 this figure would have been 1.3 billion in 2010 and 2025.[15]
Smoking is generally five times more prevalent among males than females,[15] however the gender gap declines with younger age.[16][17] In developed countries smoking rates for men have peaked and have begun to decline, however for women they continue to climb.[18]
As of 2002, about twenty percent of young teens (13–15) smoke worldwide, with 80,000 to 100,000 children taking up the habit every day—roughly half of whom live in Asia. Half of those who begin smoking in adolescent years are projected to go on to smoke for 15 to 20 years.[19]
The WHO states that "Much of the disease burden and premature mortality attributable to tobacco use disproportionately affect the poor". Of the 1.22 billion smokers, 1 billion of them live in developing or transitional nations. Rates of smoking have leveled off or declined in the developed world.[20] In the developing world, however, tobacco consumption is rising by 3.4% per year as of 2002.[19]
The WHO in 2004 projected 58.8 million deaths to occur globally,[21] from which 5.4 million are tobacco-attributed,[22] and 4.9 million as of 2007.[23] As of 2002, 70% of the deaths are in developing countries.[23]
The shift in prevalence of tobacco smoking to a younger demographic, mainly in the developing world, can be attributed to several factors. The tobacco industry spends up to $12.5 billion dollars annually on advertising, which is increasingly geared towards adolescents in the third world because they are a very vulnerable audience for the marketing campaigns. Adolescents have more difficulty understanding the long term health risks that are associated with smoking and are also more easily influenced by “images of romance, success, sophistication, popularity, and adventure which advertising suggests they could achieve through the consumption of cigarettes”. This shift in marketing towards adolescents and even children in the tobacco industry is debilitating to organizations’ and countries’ efforts to improve child health and mortality in the developing world. It reverses or halts the effects of the work that has been done to improve health care in these countries, and although smoking is deemed as a “voluntary” health risk, the marketing of tobacco towards very impressionable adolescents in the developing world makes it less of a voluntary action and more of an inevitable shift.[24]
Studies
In 1938 a study by a John Hopkins University scientist suggested a strongly negative correlation between smoking and lifespan. In 1950 five studies were published in which "smoking was powerfully implicated in the causation of lung cancer".[25] These included the now classic paper "Smoking and Carcinoma of the Lung" which appeared in the British Medical Journal. This paper reported that "heavy smokers were fifty times as likely as non-smokers to contract lung cancer".[25][26]
A team of British scientists headed by Richard Doll carried out a longitudinal study of 34,439 medical specialists from 1951 to 2001, generally called the "British doctors study."[27] The study demonstrated that that about half of the persistent cigarette smokers born in 1900-1909 were eventually killed by their habit (calculated from the logarithms of the probabilities of surviving from 35-70, 70-80, and 80-90) and about two thirds of the persistent cigarette smokers born in the 1920s would eventually be killed by their habit. After a ban on smoking in all enclosed public places was introduced in Scotland in March 2006, there was a 17 percent reduction in hospital admissions for acute coronary syndrome. 67% of the decrease occurred in non-smokers.[28]
The health effects of tobacco have been significant for the development of the science of epidemiology. As the mechanism of carcinogenicity is radiomimetic or radiological, the effects are stochastic. Definite statements can be made only on the relative increased or decreased probabilities of contracting a given disease; Philosophically and theoretically speaking, it is impossible to definitively prove a direct causative link between exposure to a radiomimetic poison such as tobacco smoke and the cancer that follows. Tobacco companies have capitalized on this philosophical objection and exploited the doubts of clinicians, who consider only individual cases, on the causal link in the stochastic expression of the toxicity as actual disease.[29]
There have been multiple court cases on the issue that tobacco companies have researched the health effects of tobacco, but suppressed the findings or formatted them to imply lessened or no hazard.[29]
A study published in the journal Pediatrics[30] refers to the danger posed by what the authors call "third-hand smoke" — toxic substances that remain in areas where smoking has recently occurred. The study was reviewed in an story broadcast by the Voice of America.
Occasional Smoking
The term "smoker" is used to mean a person who habitually smokes tobacco on a daily basis. This category has been the focus of the vast majority of tobacco studies. However, the health effects of less-than-daily smoking are far less well understood. Studies have often taken the data of "occasional smokers" (those who have never smoked daily) and grouped them with those who have never smoked.[31]
A recent European study on occasional smoking published findings that the risk of the major smoking-related cancers was 1.24 times higher for occasional smokers than for those who have never smoked at all. (For a confidence interval of 95%, this data showed an incidence rate ratio of 0.80 to 1.94.)[31] This compares to studies showing that habitual heavy smokers have greater than 50 times the incidence of smoking-related cancers.
Mechanism
Chemical carcinogens
Smoke, or any partially burnt organic matter, contains carcinogens (cancer-causing agents). The potential effects of smoking, such as lung cancer, can take up to 20 years to manifest themselves. Historically, women began smoking en masse later than men, so an increased death rate caused by smoking amongst women did not appear until later. The male lung cancer death rate decreased in 1975 — roughly 20 years after the initial decline in cigarette consumption in men. A fall in consumption in women also began in 1975 but by 1991 had not manifested in a decrease in lung cancer related mortalities amongst women.[33]
Smoke contains several carcinogenic pyrolytic products that bind to DNA and cause genetic mutations. Particularly potent carcinogens are polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH), which are toxicated to mutagenic epoxides. The first PAH to be identified as a carcinogen in tobacco smoke was benzopyrene, which has been shown to toxicate into an epoxide that irreversibly attaches to a cell's nuclear DNA, which may either kill the cell or cause a genetic mutation. If the mutation inhibits programmed cell death, the cell can survive to become a cancer cell. Similarly, acrolein, which is abundant in tobacco smoke, also irreversibly binds to DNA, causes mutations and thus also cancer. However, it needs no activation to become carcinogenic.[34]
There are over 19 known carcinogens in cigarette smoke.[35] The following are some of the most potent carcinogens:
- Polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons are tar components produced by pyrolysis in smoldering organic matter and emitted into smoke. Many of them are highly carcinogenic and mutagenic, because they are toxicated to mutagenic epoxides, which are electrophilic alkylating agents. The first PAH to be identified as a carcinogen in tobacco smoke was benzopyrene, which been shown to toxicate into a diol epoxide and then permanently attach to nuclear DNA, which may either kill the cell or cause a genetic mutation. The DNA contains the information on how the cell function; in practice, it contains the recipes for protein synthesis. If the mutation inhibits programmed cell death, the cell can survive to become a cancer cell, a cell that does not function like a normal cell. The carcinogenity is radiomimetic, i.e. similar to that produced by ionizing nuclear radiation. Tobacco manufacturers have experimented with combustionless vaporizer technology to allow cigarettes to be consumed without the formation of carcinogenic benzopyrenes.[36] However, such products have not become popular.
- Acrolein is a pyrolysis product that is abundant in cigarette smoke. It gives smoke an acrid smell and an irritating, lachromatory effect and is a major contributor to its carcinogenity. Like PAH metabolites, acrolein is also an electrophilic alkylating agent and permanently binds to the DNA base guanine, by a conjugate addition followed by cyclization into a hemiaminal. The acrolein-guanine adduct induces mutations during DNA copying and thus causes cancers in a manner similar to PAHs. However, acrolein is 1000 times more abundant than PAHs in cigarette smoke, and is able to react as is, without metabolic activation. Acrolein has been shown to be a mutagen and carcinogen in human cells. The carcinogenity of acrolein has been difficult to study by animal experimentation, because it has such a toxicity that it tends to kill the animals before they develop cancer.[34] Generally, compounds able to react by conjugate addition as electrophiles (so-called Michael acceptors after Michael reaction) are toxic and carcinogenic, because they can permanently alkylate DNA, similarly to mustard gas or aflatoxin. Acrolein is only one of them present in cigarette smoke; for example, crotonaldehyde has been found in cigarette smoke.[37] Michael acceptors also contribute to the chronic inflammation present in tobacco disease.[38]
- Nitrosamines are a group of carcinogenic compounds found in cigarette smoke but not in uncured tobacco leaves. Nitrosamines form on flue-cured tobacco leaves during the curing process through a chemical reaction between nicotine and other compounds contained in the uncured leaf and various oxides of nitrogen found in all combustion gases. Switching to Indirect fire curing has been shown to reduce nitrosamine levels to less than 0.1 parts per million.[39][40]
Radioactive carcinogens
In addition to chemical, nonradioactive carcinogens, tobacco and tobacco smoke contain small amounts of lead-210 (210Pb) and polonium-210 (210Po) both of which are radioactive carcinogens. The presence of polonium-210 in mainstream cigarette smoke has been experimentally measured at levels of 0.0263–0.036 pCi (0.97–1.33 mBq),[41] which is equivalent to about 0.1 pCi per milligram of smoke (4 mBq/mg); or about 0.81 pCi of lead 210 per gram of dry condensed smoke (30 Bq/kg).
Research by NCAR radiochemist Ed Martell determined that radioactive compounds in cigarette smoke are deposited in "hot spots" where bronchial tubes branch. Since tar from cigarette smoke is resistant to dissolving in lung fluid, the radioactive compounds have a great deal of time to undergo radioactive decay before being cleared by natural processes. Indoors, these radioactive compounds linger in secondhand smoke, and therefore greater exposure occurs when these radioactive compounds are inhaled during normal breathing, which is deeper and longer than when inhaling cigarettes. Damage to the protective epithelial tissue from smoking only increases the prolonged retention of insoluble polonium 210 compounds produced from burning tobacco. Martell estimated that a carcinogenic radiation dose of 80-100 rads is delivered to the lung tissue of most smokers who die of lung cancer.[42]
The view that polonium 210 is responsible for many cases of cancer in tobacco smokers is disputed by at least one researcher.[43][44]
Nicotine

Nicotine that is contained in cigarettes and other smoked tobacco products is a stimulant and is one of the main factors leading to continued tobacco smoking. Although the amount of nicotine inhaled with tobacco smoke is quite small (most of the substance is destroyed by the heat) it is still sufficient to cause physical and/or psychological dependence. The amount of nicotine absorbed by the body from smoking depends on many factors, including the type of tobacco, whether the smoke is inhaled, and whether a filter is used. Despite the design of various cigarettes advertised and even tested on machines to deliver less of the toxic tar, studies show that when smoked by humans instead of machines, they deliver the same net amount of smoke. Ingesting a compound by smoking is one of the most rapid and efficient methods of introducing it into the bloodstream, second only to injection, which allows for the rapid feedback which supports the smokers' ability to titrate their dosage. On average it takes about ten seconds for the substance to reach the brain. As a result of the efficiency of this delivery system, many smokers feel as though they are unable to cease. Of those who attempt cessation and last three months without succumbing to nicotine, most are able to remain smoke free for the rest of their lives.[45] There exists a possibility of depression in some who attempt cessation, as with other psychoactive substances. Depression is also common in teenage smokers; teens who smoke are four times as likely to develop depressive symptoms as their nonsmoking peers.[46]
Although nicotine does play a role in acute episodes of some diseases (including stroke, impotence, and heart disease) by its stimulation of adrenaline release, which raises blood pressure,[47] heart rate, and free fatty acids, the most serious longer term effects are more the result of the products of the smouldering combustion process. This has enabled development of various nicotine delivery systems, such as the nicotine patch or nicotine gum, that can satisfy the addictive craving by delivering nicotine without the harmful combustion by-products. This can help the heavily dependent smoker to quit gradually, while discontinuing further damage to health.
Nicotine is a highly addictive psychoactive chemical. When tobacco is smoked, most of the nicotine is pyrolyzed; a dose sufficient to cause mild somatic dependency and mild to strong psychological dependency remains. There is also a formation of harmane (a MAO inhibitor) from the acetaldehyde in cigarette smoke, which seems to play an important role in nicotine addiction[48] probably by facilitating dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens in response to nicotine stimuli. According to studies by Henningfield and Benowitz, nicotine is more addictive than cannabis, caffeine, ethanol, cocaine, and heroin when considering both somatic and psychological dependence. However, due to the stronger withdrawal effects of ethanol, cocaine and heroin, nicotine may have a lower potential for somatic dependence than these substances.[49][50] About half of Canadians who currently smoke have tried to quit.[51] McGill University health professor Jennifer O'Loughlin stated that nicotine addiction can occur as soon as five months after the start of smoking.[52]
Recent evidence has shown that smoking tobacco increases the release of dopamine in the brain, specifically in the mesolimbic pathway, the same neuro-reward circuit activated by drugs of abuse such as heroin and cocaine. This suggests nicotine use has a pleasurable effect that triggers positive reinforcement.[53] One study found that smokers exhibit better reaction-time and memory performance compared to non-smokers, which is consistent with increased activation of dopamine receptors.[54] Neurologically, rodent studies have found that nicotine self-administration causes lowering of reward thresholds—a finding opposite that of most other drugs of abuse (e.g. cocaine and heroin). This increase in reward circuit sensitivity persisted months after the self-administration ended, suggesting that nicotine's alteration of brain reward function is either long lasting or permanent.[citation needed] Furthermore, it has been found that nicotine can activate long term potentiation in vivo and in vitro.[citation needed] These studies suggest nicotine’s "trace memory" may contribute to difficulties in nicotine abstinence.[original research?]
The carcinogenity of tobacco smoke is not explained by nicotine per se, which is not carcinogenic or mutagenic. However, it inhibits apoptosis, therefore accelerating existing cancers.[55] Also, NNK, a nicotine derivative converted from nicotine, can be carcinogenic.
It is worth noting that nicotine, although frequently implicated in producing tobacco addiction, is not significantly addictive when administered alone.[56] The addictive potential manifests itself after co-administration of an MAOI, which specifically causes sensitization of the locomotor response in rats, a measure of addictive potential.[57]
Genetic
According to three separate studies commissioned by governments in the US and Europe, scientists have identified a genetic link that makes people more likely to become addicted to tobacco. This genetic variation causes individuals to smoke more cigarettes, makes it harder for them to quit and increases their likelihood of developing lung cancer by up to 80%.[58]
Genetic markers of more than 35,000 people (mostly smokers and ex-smokers) were surveyed by scientists in three separate studies, and all three found lung cancer to be associated with similar sets of genetic differences. The genetic variations of note encode nicotine receptors on cells and were identified on a region of chromosome 15.[59] Possessing a single copy of the mutation raises an individual's risk of lung cancer by approximately 30%; for two copies the increase is about 80%. The gene was found to be attributable to 14% of lung cancer cases, and it was found to confer similar lung cancer risks irrespective of smoking status or quantity smoked.[60]
Another study related to genetic changes in smokers was conducted by Wan L Lam and Stephen Lam from the BC Cancer Agency, in 2007. The study revealed that cigarette smoke can turn on or off some of the genes, which otherwise would remain inactive. Some changes on genetic level could be reversed after the smoking was quit, yet others could not. Examples of reversible genes involved the so-called xenofobic functions, nucleotide metabolism and mucus secretion. Smoking turns off some DNA repair genes that cannot be reversed. It also switches off some genes responsible from protection from cancer growth in the body.[61]
Health effects
This article may require copy editing for grammar, style, cohesion, tone, or spelling. (December 2008) |
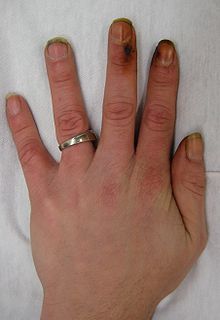

A person's increased risk of contracting disease is directly proportional to the length of time that a person continues to smoke as well as the amount smoked. However, if someone stops smoking, then these chances gradually decrease as the damage to their body is repaired. A year after quitting, the risk of contracting heart disease is half that of a continuing smoker.[62] The health risks of smoking are not uniform across all smokers. Risks vary according to amount of tobacco smoked, with those who smoke more at greater risk. Light smoking is still a health risk. Likewise, smoking "light" cigarettes does not reduce the risks.
Tobacco use most commonly leads to diseases affecting the heart and lungs, with smoking being a major risk factor for heart attacks, Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD), emphysema, and cancer, particularly lung cancer, cancers of the larynx and mouth, and pancreatic cancer. Overall life expectancy is also reduced in regular smokers, with estimates ranging from 10[27] to 17.9 [63] years fewer than nonsmokers.[64] About two thirds of male smokers will die of illness due to smoking.[65] The association of smoking with lung cancer is strongest, both in the public perception and etiologically. People who have smoked tobacco at some point have about a one in ten chance of developing lung cancer during their lifetime.[66] If one looks at men who continue to smoke tobacco, the risk increases to one in six.[67] Historically, lung cancer was considered to be a rare disease prior to World War I and was perceived as something most physicians would never see during their career. With the postwar rise in popularity of cigarette smoking came a virtual epidemic of lung cancer.[68][69]
Mortality
Male and female smokers lose an average of 13.2 and 14.5 years of life, respectively.[70]
According to the results of a 50 year study of 34,439 male British doctors, at least half of all lifelong smokers die earlier as a result of smoking.[27]
Smokers are three times as likely to die before the age of 60 or 70 as nonsmokers.[71][72][73]
In the United States alone, cigarette smoking and exposure to tobacco smoke results in at least 443,000 premature deaths annually.[74]
In the United States alone, tobacco kills the equivalent of three jumbo jets full of people crashing every day, with no survivors, 365 days of the year. -ABC's Peter Jennings[75] On a worldwide basis, it's 1 jumbo jet per hour, 24 hours a day, 365 days of the year. -WHO [76]
Cancer
The primary risks of tobacco usage include many forms of cancer, particularly lung cancer,[77] cancer of the kidney,[78] cancer of the larynx and head and neck, breast cancer,[79][80] bladder,[81] esophagus, pancreas,[82] and stomach.[83] There is some evidence suggesting an increased risk of myeloid leukemia, squamous cell sinonasal cancer, liver cancer, cervical cancer, colorectal cancer after an extended latency, childhood cancers and cancers of the gall bladder, adrenal gland and small intestine.
Lung Cancer
The risk of dying from lung cancer before age 85 is 22.1% for a male smoker and 11.9% for a female current smoker, in the absence of competing causes of death. The corresponding estimates for lifelong nonsmokers are a 1.1% probability of dying from lung cancer before age 85 for a man of European descent, and a 0.8% probability for a woman.[84]
Pulmonary

In smoking, long term exposure to compounds found in the smoke such as carbon monoxide, cyanide, and so forth—, are believed to be responsible for pulmonary damage and for loss of elasticity in the alveoli, leading to emphysema and COPD. The carcinogen acrolein and its derivatives also contribute to the chronic inflammation present in COPD.[38]
Secondhand smoke is a mixture of smoke from the burning end of a cigarette, pipe or cigar and the smoke exhaled from the lungs of smokers. It is involuntarily inhaled, lingers in the air hours after cigarettes have been extinguished, and can cause a wide range of adverse health effects, including cancer, respiratory infections, and asthma.[85] Nonsmokers who are exposed to secondhand smoke at home or work increase their heart disease risk by 25–30% and their lung cancer risk by 20–30%. Secondhand smoke has been estimated to cause 38,000 deaths per year, of which 3,400 are deaths from lung cancer in non-smokers.[86]
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) caused by smoking, known as tobacco disease, is a permanent, incurable reduction of pulmonary capacity characterized by shortness of breath, wheezing, persistent cough with sputum, and damage to the lungs, including emphysema and chronic bronchitis.[87]
Influenza
A study of an outbreak of A(H1N1) influenza in an Israeli military unit of 336 healthy young men to determine the relation of cigarette smoking to the incidence of clinically apparent influenza, revealed that, of 168 smokers, 68.5 percent had influenza, as compared with 47.2 percent of nonsmokers. Influenza was also more severe in the smokers; 50.6 percent of the smokers lost work days or required bed rest, or both, as compared with 30.1 percent of the nonsmokers[88].
According to a study of 1,900 male cadets after the 1968 Hong Kong A2 influenza epidemic at a South Carolina military academy, compared with nonsmokers heavy smokers (more than 20 cigarettes per day), had 21% more illnesses and 20% more bed rest, light smokers (less than 20 cigarettes per day) had 10% more illnesses and 7% more bed rest[89].
The effect of cigarette smoking upon epidemic influenza was studied prospectively among 1,811 male college students. Clinical influenza incidence among those who daily smoked 21 or more cigarettes was 21% higher than that of non-smokers. Influenza incidence among smokers of 1 to 20 cigarettes daily was intermediate between non-smokers and heavy cigarette smokers[90].
Surveillance of a 1979 influenza out-break at a military base for women in Israel revealed that, Influenza symptoms developed in 60.0% of the current smokers vs. 41.6% of the nonsmokers[91].
Smoking seems to cause a higher relative influenza-risk in older populations than in younger populations. In a prospective study of community-dwelling people 60–90 years of age, during 1993, of unimmunized people 23% of smokers had clinical influenza as compared with 6% of non-smokers[92].
Smoking may substantially contribute to the growth of influenza epidemics affecting the entire population[88]. However the proportion of influenza cases in the general non-smoking population attributable to smokers has not yet been calculated.
Cardiovascular
Inhalation of tobacco smoke causes several immediate responses within the heart and blood vessels. Within one minute the heart rate begins to rise, increasing by as much as 30 percent during the first 10 minutes of smoking. Carbon monoxide in tobacco smoke exerts its negative effects by reducing the blood’s ability to carry oxygen.[93]
Smoking also increases the chance of heart disease, stroke, atherosclerosis, and peripheral vascular disease. Several ingredients of tobacco lead to the narrowing of blood vessels, increasing the likelihood of a blockage, and thus a heart attack or stroke. According to a study by an international team of researchers, people under 40 are five times more likely to have a heart attack if they smoke.[94]
Latest research of the American biologists have determined that cigarette smoke also influences the process of cell division in the cardiac muscle and changes heart's shape.[95]
The usage of tobacco has also been linked to Buerger's disease (thromboangiitis obliterans) the acute inflammation and thrombosis (clotting) of arteries and veins of the hands and feet.[citation needed]
The current Surgeon General’s Report concluded that there is no risk-free level of exposure to secondhand smoke. Even short exposures to secondhand smoke can cause blood platelets to become stickier, damage the lining of blood vessels, decrease coronary flow velocity reserves, and reduce heart rate variability, potentially increasing the risk of heart attack. New research indicates that private research conducted by cigarette company Philip Morris in the 1980s showed that secondhand smoke was toxic, yet the company suppressed the finding during the next two decades.[85]
Although cigarette smoking causes a greater increase of the risk of cancer than cigar smoking, cigar smokers still have an increased risk for many health problems, including cancer, when compared to non-smokers.[96][97] As for Environmental Tobacco Smoke (ETS, or "Second-hand Smoking"), the NIH study points to the large amount of smoke generated by one cigar, saying "cigars can contribute substantial amounts of tobacco smoke to the indoor environment; and, when large numbers of cigar smokers congregate together in a cigar smoking event, the amount of ETS produced is sufficient to be a health concern for those regularly required to work in those environments."[98]
Smoking tends to increase blood cholesterol levels. Furthermore, the ratio of high-density lipoprotein (the "good" cholesterol) to low-density lipoprotein (the "bad" cholesterol) tends to be lower in smokers compared to non-smokers. Smoking also raises the levels of fibrinogen and increases platelet production (both involved in blood clotting) which makes the blood viscous. Carbon monoxide binds to haemoglobin (the oxygen-carrying component in red blood cells), resulting in a much stabler complex than haemoglobin bound with oxygen or carbon dioxide—the result is permanent loss of blood cell functionality. Blood cells are naturally recycled after a certain period of time, allowing for the creation of new, functional erythrocytes. However, if carbon monoxide exposure reaches a certain point before they can be recycled, hypoxia (and later death) occurs. All these factors make smokers more at risk of developing various forms of arteriosclerosis. As the arteriosclerosis progresses, blood flows less easily through rigid and narrowed blood vessels, making the blood more likely to form a thrombosis (clot). Sudden blockage of a blood vessel may lead to an infarction (stroke). However, it is also worth noting that the effects of smoking on the heart may be more subtle. These conditions may develop gradually given the smoking-healing cycle (the human body heals itself between periods of smoking), and therefore a smoker may develop less significant disorders such as worsening or maintenance of unpleasant dermatological conditions, e.g. eczema, due to reduced blood supply. Smoking also increases blood pressure and weakens blood vessels.[47]
Oral
Perhaps the most serious oral condition that can arise is that of oral cancer. However, smoking also increases the risk for various other oral diseases, some almost completely exclusive to tobacco users. The National Institutes of Health, through the National Cancer Institute, determined in 1998 that "cigar smoking causes a variety of cancers including cancers of the oral cavity (lip, tongue, mouth, throat), esophagus, larynx, and lung."[98] Pipe smoking involves significant health risks,[99][100] particularly oral cancer.[101][102] Roughly half of periodontitis or inflammation around the teeth cases attributed to current or former smoking. Smokeless tobacco causes gingival recession and white mucosal lesions. Up to 90% of periodontitis patients who are not helped by common modes of treatment are smokers. Smokers have significantly greater loss of bone height than nonsmokers, and the trend can be extended to pipe smokers to have more bone loss than nonsmokers.[103] Smoking has been proven to be an important factor in the staining of teeth.[104][105] Halitosis or bad breath is common among tobacco smokers[106]. Tooth loss has been shown to be 2[107] to 3 times[108] higher in smokers than in non-smokers.[109] In addition, complications may further include leukoplakia, the adherent white plaques or patches on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, including the tongue, and a loss of taste sensation or salivary changes.[citation needed]
Infection
Tobacco is also linked to susceptibility to infectious diseases, particularly in the lungs. Smoking more than 20 cigarettes a day increases the risk of tuberculosis by two to four times,[110][111] and being a current smoker has been linked to a fourfold increase in the risk of invasive pneumococcal disease.[112] It is believed that smoking increases the risk of these and other pulmonary and respiratory tract infections both through structural damage and through effects on the immune system. The effects on the immune system include an increase in CD4+ cell production attributable to nicotine, which has tentatively been linked to increased HIV susceptibility.[113] The usage of tobacco also increases rates of infection: common cold and bronchitis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, emphysema and chronic bronchitis in particular.[citation needed]
Smoking reduces the risk of Kaposi's sarcoma in people without HIV infection.[114] One study found this only with the male population and could not draw any conclusions for the female participants in the study.[115]
Impotence
In a study of men ages 24 to 36 seeking treatment for infertility, Panayiotis Zavos, Ph.D., confirmed the results of earlier studies demonstrating that smoking harms sperm quality in every way, from longevity to motility. But Zavos also found that smoking affected sexual behavior. The smokers had sex an average of 5.7 times per month, while the nonsmokers reported an average of 11.6 encounters. And on a scale of 1 to 10, the smokers rated the quality of sex at a lackluster 5.2, compared to 8.7 for nonsmokers."[116]
Psychological
Immediate Effects
Smokers report a variety of physical and psychological effects from smoking tobacco. Those new to smoking may experience nausea, dizziness, and rapid heart beat. The unpleasant symptoms will eventually vanish over time, with repeated use, as the body builds a tolerance to the chemicals in the cigarettes, such as nicotine.
Stress
Smokers report high levels of everyday stress.[117] Several studies have monitored feelings of stress over time, and they find reduced stress after quitting.[118][119]
The deleterious mood effects of abstinence explain why smokers suffer more daily stress than non-smokers, and become less stressed when they quit smoking. Deprivation reversal also explains much of the arousal data, with deprived smokers being less vigilant and less alert than non-deprived smokers or non-smokers.[120]
Social and Behavioral
Medical researchers have found that smoking is a predictor of divorce[121]. Smokers have 53% more divorce than nonsmokers.[122]
Cognitive Function
The usage of tobacco also creates cognitive dysfunction, which include: increased risk[123] of Alzheimer's disease and decline in cognitive abilities,[124] reduced memory and cognitive abilities in adolescent smokers,[125] brain shrinkage (cerebral atrophy).[126][127]
In many respects, nicotine acts on the nervous system in a similar way to caffeine. Some writings have stated that smoking can also increase mental concentration; one study documents a significantly better performance on the normed Advanced Raven Progressive Matrices test after smoking.[128]
Most smokers, when denied access to nicotine, exhibit symptoms such as irritability, jitteriness, dry mouth, and rapid heart beat.[129] The onset of these symptoms is very fast, nicotine's half-life being only 2 hours. Withdrawal symptoms can appear even if the smoker's consumption is very limited or irregular, appearing after only 4-5 cigarettes in most adolescents. An ex-smoker's chemical dependence to nicotine will cease after approximately ten to twenty days, although the brain's number of nicotine receptors is permanently altered,[130] and the psychological dependence may linger for months or even many years. Unlike some recreational drugs, nicotine does not measurably alter a smoker's motor skills, judgement, or language abilities while under the influence of the drug. Tobacco withdrawal has been shown to cause clinically significant distress.[131]
Most notably, some studies have found that patients with Alzheimer's disease are more likely not to have smoked than the general population, which has been interpreted to suggest that smoking offers some protection against Alzheimer's. However, the research in this area is limited and the results are conflicting; some studies show that smoking increases the risk of Alzheimer's disease. A recent review of the available scientific literature concluded that the apparent decrease in Alzheimer risk may be simply due to the fact that smokers tend to die before reaching the age at which Alzheimer normally occurs. "Differential mortality is always likely to be a problem where there is a need to investigate the effects of smoking in a disorder with very low incidence rates before age 75 years, which is the case of Alzheimer's disease," it stated, noting that smokers are only half as likely as non-smokers to survive to the age of 80.[123]
Former and current smokers have a lower incidence of Parkinson's disease compared to people who have never smoked,[132][133] although the authors stated that it was more likely that the movement disorders which are part of Parkinson's disease prevented people from being able to smoke than that smoking itself was protective. Another study considered a possible role of nicotine in reducing Parkinson's risk: nicotine stimulates the dopaminergic system of the brain, which is damaged in Parkinson's disease, while other compounds in tobacco smoke inhibit MAO-B, an enzyme which produces oxidative radicals by breaking down dopamine.[134]
A very large percentage of schizophrenics smoke tobacco as a form of self medication.[135][136][137][138] The high rate of tobacco use by the mentally ill is a major factor in their decreased life expectancy, which is about 25 years shorter than the general population.[139] Following the observation that smoking improves condition of people with schizophrenia, in particular working memory deficit, nicotine patches had been proposed as a way to treat schizophrenia.[140] Some studies suggest that a link exists between smoking and mental illness, citing the high incidence of smoking amongst those suffering from schizophrenia[141] and the possibility that smoking may alleviate some of the symptoms of mental illness,[142] but these have not been conclusive.
Recent studies have linked smoking to anxiety disorders, suggesting the correlation (and possibly mechanism) may be related to the broad class of anxiety disorders, and not limited to just depression. Current and ongoing research attempt to explore the addiction-anxiety relationship.
Data from multiple studies suggest that anxiety disorders and depression play a role in cigarette smoking.[143] A history of regular smoking was observed more frequently among individuals who had experienced a major depressive disorder at some time in their lives than among individuals who had never experienced major depression or among individuals with no psychiatric diagnosis.[144] People with major depression are also much less likely to quit due to the increased risk of experiencing mild to severe states of depression, including a major depressive episode.[145] Depressed smokers appear to experience more withdrawal symptoms on quitting, are less likely to be successful at quitting, and are more likely to relapse.[146]
Evidence suggests that non-smokers are up to twice as likely as smokers to develop Parkinson's disease or Alzheimer's disease.[147] A plausible explanation for these cases may be the effect of nicotine, a cholinergic stimulant, decreasing the levels of acetylcholine in the smoker's brain; Parkinson's disease occurs when the effect of dopamine is less than that of acetylcholine. In addition, nicotine stimulates the mesolimbic dopamine pathway (as do other drugs of abuse), causing an effective increase in dopamine levels. Opponents counter by noting that consumption of pure nicotine may be as beneficial as smoking without the risks associated with smoking, although this is unlikely due to the importance of the MAO-B inhibitor compounds of tobacco in preventing neurodegenerative diseases.[citation needed]
In pregnancy
A number of studies have shown that tobacco use is a significant factor in miscarriages among pregnant smokers, and that it contributes to a number of other threats to the health of the fetus.[148][149] Second-hand smoke appears to present an equal danger to the fetus, as one study noted that "heavy paternal smoking increased the risk of early pregnancy loss."[150]
Other harm
Studies suggest that smoking decreases appetite, but did not conclude that overweight people should smoke or that their health would improve by smoking. This is also a cause of heart diseases.However due to some new processes of treating tobacco, especially in the case of cigarette, heavy smokers tend to become overweight as the processing involves large quantities of starch.This effect is not seen in occasional smokers. [151][152] Smoking also decreases weight by overexpressing the gene AZGP1 which stimulates lipolysis.[153]
Preliminary reports suggest that smoking can decrease the incidence of acne prophylactically. This was seen by a decreased percentage ratio of patients needing acne medication versus the percentage of entire population of smokers. (A smaller percentage of patients who smoked needed medication than found in the population as a whole).[154]
A protective effect of current smoking against ulcerative colitis, although smoking increases the risk of Crohn's disease, the other form of inflammatory bowel disease.[155] There is some evidence for decreased rates of endometriosis in infertile smoking women,[156] although other studies have found that smoking increases the risk in infertile women.[157] There is little or no evidence of a protective effect in fertile women. Some preliminary data from 1996 suggested a reduced incidence of uterine fibroids,[158] but overall the evidence is unconvincing.[159]
A new research has found that women who smoke are at significantly increased risk of developing an abdominal aortic aneurysm, a condition in which a weak area of the abdominal aorta expands or bulges.[160]
Benefits
Several types of "Smoker’s Paradoxes",[161] (cases where smoking appears to have specific beneficial effects), have been observed; often the actual mechanism remains undetermined.
- Risk of ulcerative colitis has been frequently shown to be reduced by smokers on a dose-dependent basis; the effect is eliminated if the individual stops smoking.[162][163]
- Smoking appears to interfere with development of:
- Kaposi's sarcoma[164]
- breast cancer among women carrying the very high risk BRCA gene[165]
- preeclampsia[166]
- atopic disorders such as allergic asthma[167]
A plausible mechanism of action in these cases may be the nicotine in tobacco smoke acting as an anti-inflammatory agent and interfering with the disease process.[168]
Smoking can also reduce rates of uterine fibroids.[169][170] This may be due to estrogen inhibition, as opposed to general inhibition of inflammation.
Particular forms of tobacco use
Chewing tobacco
Chewing tobacco has been known to cause cancer, particularly of the mouth and throat.[171] According to the International Agency for Research on Cancer, "Some health scientists have suggested that smokeless tobacco should be used in smoking cessation programmes and have made implicit or explicit claims that its use would partly reduce the exposure of smokers to carcinogens and the risk for cancer. These claims, however, are not supported by the available evidence."[171] Oral and spit tobacco increase the risk for leukoplakia a precursor to oral cancer.[172]
Cigars
Like other forms of tobacco use, cigar smoking poses a significant health risk depending on dosage: risks are greater for those who inhale more when they smoke, smoke more cigars, or smoke them longer.[97] The risk of dying from any cause is significantly greater for cigar smokers, with the risk particularly higher for smokers less than 65 years old, and with risk for moderate and deep inhalers reaching levels similar to cigarette smokers.[173] Little cigars are commonly inhaled and likely pose the same health risks as cigarettes.[174] The increased risk for those smoking 1–2 cigars per day is too small to be statistically significant,[173] and the health risks of the 3/4 of cigar smokers who smoke less than daily are not known[175] and are hard to measure; although it has been claimed that people who smoke few cigars have no increased risk, a more accurate statement is that their risks are proportionate to their exposure.[176] Health risks are similar to cigarette smoking in nicotine addiction, periodontal health, tooth loss, and many types of cancer, including cancers of the mouth, throat, and esophagus. Cigar smoking also can cause cancers of the lung and larynx, where the increased risk is less than that of cigarettes. Many of these cancers have extremely low cure rates. Cigar smoking also increases the risk of lung and heart diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.[97]
Hookahs
A common belief among users is that the smoke is significantly less dangerous than that from cigarettes.[177] The water moisture induced by the hookah makes the smoke less irritating and may give a false sense of security and reduce concerns about true health effects.[178] Doctors at institutions including the Mayo Clinic have stated that use of hookah can be as detrimental to a person's health as smoking cigarettes,[179][180] and a study by the World Health Organization also confirmed these findings.[181]
Each hookah session typically lasts more than 40 minutes, and consists of 50 to 200 inhalations that each range from 0.15 to 0.50 liters of smoke.[182][183] Reports by the World Health Organization and the American Cancer Society have shown that, in a one-hour hookah session, users consume about 100 to 200 times the smoke and about 70 times the nicotine as they do in one cigarette.[184]
A study in the Journal of Periodontology found that water pipes smokers were five times more likely than non-smokers to show signs of gum disease. People who smoked water pipes had five times the risk of lung cancer as non-smokers.[185]
The water used to filter the chemicals does not work efficiently to remove all the harmful chemicals.[186]
A study on hookah smoking and cancer in Pakistan was published in 2008.[187] Its objective was "to find serum CEA levels in ever/exclusive hookah smokers, i.e. those who smoked only hookah (no cigarettes, bidis, etc.), prepared between 1 and 4 times a day with a quantity of up to 120 g of a tobacco-molasses mixture each (i.e. the tobacco weight equivalent of up to 60 cigarettes of 1 g each) and consumed in 1 to 8 sessions". Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) is a marker found in several forms of cancer. Levels in exclusive hookah smokers were lower compared to cigarette smokers although the difference was not statistically significant between a hookah smoker and a non-smoker. Also the study concluded that heavy hookah smoking (2–4 daily preparations; 3–8 sessions a day ; >2 hrs to ≤ 6 hours) substantially raises CEA levels.
Snuff
Users of snuff are believed to face less cancer risk than smokers, but are still at greater risk than people who do not use any tobacco products.[188] They also have an equal risk of other health problems directly linked to nicotine such as increased rate of atherosclerosis.
History
The late-19th century invention of automated cigarette-making machinery in the American South made possible mass production of cigarettes at low cost, and cigarettes became elegant and fashionable among society men as the Victorian era gave way to the Edwardian. In 1912, American Dr. Isaac Adler was the first to strongly suggest that lung cancer is related to smoking.[189] In 1929, Fritz Lickint of Dresden, Germany, published a formal statistical evidence of a lung cancer–tobacco link, based on a study showing that lung cancer sufferers were likely to be smokers.[190] Lickint also argued that tobacco use was the best way to explain the fact that lung cancer struck men four or five times more often than women (since women smoked much less).[190]
Prior to World War I, lung cancer was considered to be a rare disease, which most physicians would never see during their career.[68][191] With the postwar rise in popularity of cigarette smoking, however, came an epidemic of lung cancer.
In 1950, Richard Doll published research in the British Medical Journal showing a close link between smoking and lung cancer.[26] Four years later, in 1954 the British Doctors Study, a study of some 40 thousand doctors over 20 years, confirmed the suggestion, based on which the government issued advice that smoking and lung cancer rates were related.[192] The British Doctors Study lasted till 2001, with results published every ten years and final results published in 2004 by Doll and Richard Peto.[72] Much early research was also done by Alton Ochsner. Reader's Digest magazine for many years published frequent anti-smoking articles. In 1964 the United States Surgeon General's Report on Smoking and Health, led millions of American smokers to quit, the banning of certain advertising, and the requirement of warning labels on tobacco products.
The Canadian province of British Columbia has the Tobacco Damages and Health Care Costs Recovery Act.
References
- ^ a b "Prevalence of current tobacco use among adults aged=15 years (percentage)". World Health Organization. Retrieved 2009-01-02.
- ^ a b "Mayo report on addressing the worldwide tobacco epidemic through effective, evidence-based treatment". World Health Organization. p. 2. Retrieved 2009-01-02.
- ^ Actual Causes of Death in the United States, 2000, JAMA. 2004;291:1238-1245
- ^ www.who.int/tobacco/mpower/mpower_report_full_2008.pdf
- ^ Nichter, M., and E. Cartwright. 1991. Saving the children for the tobacco industry. Medical Anthropology Quarterly 5 (3):236-256.
- ^ WHO global burden of like ftw!disease report 2008
- ^ WHO Report on the Global Tobacco Epidemic, 2008
- ^ "Nicotine: A Powerful Addiction." Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
- ^ "The health consequences of involuntary exposure to tobacco smoke: a report of the Surgeon General" (PDF). Atlanta, U.S., page 93: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, Office on Smoking and Health. 2006. Retrieved 2009-02-15.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1164/rccm.200711-1739OC, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1164/rccm.200711-1739OCinstead. - ^ a b "The Tobacco Reference Guide". Retrieved 2006-07-15.
- ^ Attention: This template ({{cite pmid}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by PMID 15924009, please use {{cite journal}} with
|pmid=15924009instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1385/ENDO:23:2-3:087, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1385/ENDO:23:2-3:087instead. - ^ WHO REPORT on the global TOBACCO epidemic 2008, pp. 267–288
- ^ a b Guindon, G. Emmanuel; Boisclair, David (2003). Past, current and future trends in tobacco use (PDF). Washington DC: The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development / The World Bank. pp. 13–16. Retrieved 2009-03-22.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|doi_brokendate=(help) - ^ The World Health Organization, and the Institute for Global Tobacco Control, Johns Hopkins School of Public Health (2001). "Women and the Tobacco Epidemic: Challenges for the 21st Century" (PDF). World Health Organization. pp. 5–6. Retrieved 2009-01-02.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Surgeon General's Report—Women and Smoking". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2001. p. 47. Retrieved 2009-01-03.
- ^ Peto, Richard; Lopez, Alan D; Boreham, Jillian; Thun, Michael (2006). Mortality from Smoking in Developed Countries 1950-2000: indirect estimates from national vital statistics (PDF). Oxford University Press. p. 9. Retrieved 2009-03-22.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|doi_brokendate=(help) - ^ a b "WHO/WPRO-Smoking Statistics". World Health Organization Regional Office for the Western Pacific. 2002-05-28. Retrieved 2009-01-01.
- ^ VJ Rock, MPH, A Malarcher, PhD, JW Kahende, PhD, K Asman, MSPH, C Husten, MD, R Caraballo, PhD (2007-11-09). "Cigarette Smoking Among Adults --- United States, 2006". United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved 2009-01-01.
[...]In 2006, an estimated 20.8% (45.3 million) of U.S. adults[...]
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ The Global Burden of Disease 2004 Update 2008, p. 8
- ^ The Global Burden of Disease 2004 Update 2008, p. 23
- ^ a b "WHO/WPRO-Tobacco Fact sheet". World Health Organization Regional Office for the Western Pacific. 2007-05-29. Retrieved 2009-01-01.
- ^ Nichter, M., and E. Cartwright. 1991. Saving the children for the tobacco industry. Medical Anthropology Quarterly 5 (3):236-256.
- ^ a b David Michaels (2008). Doubt is Their Product, Oxford University Press, pp. 4-5.
- ^ a b Attention: This template ({{cite pmid}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by PMID 14772469, please use {{cite journal}} with
|pmid=14772469instead. - ^ a b c Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1136/bmj.38142.554479.AE, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1136/bmj.38142.554479.AEinstead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1056/NEJMsa0706740, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1056/NEJMsa0706740instead. - ^ a b Review (Helsingin Sanomat 30.3.2008, [1]) on Allan M. Brandt: The Cigarette Century. Basic Books. ISBN 978-0465070473. http://www.cigarettecentury.com/
- ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1542/peds.2008-2184, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1542/peds.2008-2184instead. - ^ a b The effect of occasional smoking on smoking-related cancers: in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17111263 Cite error: The named reference "Bjerregaard, et al" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ^ Created from PDB 1JDG
- ^ Jones Mary, Fosbery Richard, Taylor Dennis (2000). "Answers to self-assessment questions". Biology 1. Cambridge Advanced Sciences. p. 250. ISBN 0-521-78719-X.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1073/pnas.0607031103, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1073/pnas.0607031103instead. - ^ Dr. C. Everett Koop. "Smoking and smokeless tobacco". Retrieved July 15, 2006.
- ^ "DNA interaction with Benzopyrene". DNA. Retrieved March 5, 2005.
- ^ Kataoka, H. et al. Chromatographia, Volume 44, Numbers 9-10 / May, Pages 491-496, 1997. DOI: 10.1007/BF02466742
- ^ a b Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1165/rcmb.2007-0130OC, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1165/rcmb.2007-0130OCinstead. - ^ Sumner; et al. "Retrofitting Tobacco Curing Barns". Retrieved June 9, 2006.
{{cite web}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help) - ^ NOVA. "Search for a Safer Cigarette".
- ^ U.S. Army Center for Health Promotion and Preventive Medicine. "Radiological Sources of Potential Exposure and/or Contamination" (PDF).
- ^ E. A. Martell (1983). "Radiation Dose at Bronchial Bifurcations of Smokers from Indoor Exposure to Radon Progeny". Retrieved June 9, 2006.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|year=(help) - ^ Hecht, Stephen S. (1997). "Approaches to Chemoprevention of Lung Cancer Based on Carcinogens in Tobacco Smoke". Environmental Health Perspectives. 105 (S4). Retrieved 2006-12-06.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite pmid}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by PMID 10413421 , please use {{cite journal}} with
|pmid=10413421instead. - ^ Quitting Smoking: Why To Quit and How To Get Help - National Cancer Institute
- ^ Smoking increases teen depression
- ^ a b Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1080/08037050510034202, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1080/08037050510034202instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1016/j.euroneuro.2007.02.013, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1016/j.euroneuro.2007.02.013instead. - ^ Relative Addictiveness of Drugs
- ^ The Henningfield-Benowitz substance comparison charts
- ^ AADAC|Truth About Tobacco - Addiction
- ^ Cigarette addiction faster than expected. The London Free Press (August 2, 2006).
- ^ Nicotine and the Brain
- ^ The effects of cigarette smoking on overnight performance
- ^ Attention: This template ({{cite pmid}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by PMID 7848904, please use {{cite journal}} with
|pmid=7848904instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2139-05.2005, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2139-05.2005instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite pmid}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by PMID 14592678, please use {{cite journal}} with
|pmid=14592678instead. - ^ [2]
- ^ Access : Genetic link for lung cancer identified : Nature News
- ^ Attention: This template ({{cite pmid}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by PMID 18385738, please use {{cite journal}} with
|pmid=18385738instead. - ^ "Genes Permanently Turned On by Smoking". InfoNIAC.com. Retrieved 2009-01-14.
- ^ "Smoking Cessation Guidelines" American Heart Foundation
- ^ Contingencies May-June 1990. http://tobaccodocuments.org/ti/TIMN0020615-0620.html
- ^ Attention: This template ({{cite pmid}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by PMID 10192312, please use {{cite journal}} with
|pmid=10192312instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite pmid}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by PMID 7755693, please use {{cite journal}} with
|pmid=7755693instead. - ^ David C. Christiani. "Lung Cancer Suscepitibility and Outcomes study". Harvard School of Public Health. Retrieved 2009-01-03.
- ^ Attention: This template ({{cite pmid}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by PMID 7895211, please use {{cite journal}} with
|pmid=7895211instead. - ^ a b Attention: This template ({{cite pmid}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by PMID 11606795, please use {{cite journal}} with
|pmid=11606795instead. - ^ Adler I. Primary malignant growths of the lungs and bronchi. New York: Longmans, Green, and Company; 1912., cited in Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1164/rccm.200504-531OE, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1164/rccm.200504-531OEinstead. - ^ MMWR April 12, 2002 / 51(14);300-3
- ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1016/j.ehj.2003.12.015, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1016/j.ehj.2003.12.015instead. - ^ a b Attention: This template ({{cite pmid}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by PMID 15213107, please use {{cite journal}} with
|pmid=15213107instead. - ^ American Journal of Public Health p.1223
- ^ Adhikari B, Kahende J, Malarcher A, Pechacek T, Tong V (2008). "Smoking-attributable mortality, years of potential life lost, and productivity losses—United States, 2000–2004". MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 57 (45): 1226–8. PMID 19008791.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Never Say Die, an ABC News special by Peter Jennings 6/27/1996
- ^ http://ws.missouristate.edu/breatheeasymo/upload/Newsletters/Newsletter62.pdf
- ^ American Legacy Foundation factsheet on lung cancer; their cited source is: CDC (Centers for Disease Control) The Health Consequences of Smoking: A Report of the Surgeon General. 2004.
- ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1016/j.juro.2006.07.130, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1016/j.juro.2006.07.130instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1007/s10549-006-9255-3, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1007/s10549-006-9255-3instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite pmid}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by PMID 8178779, please use {{cite journal}} with
|pmid=8178779instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1080/03008880802283664, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1080/03008880802283664instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1007/s00423-007-0266-2, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1007/s00423-007-0266-2instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite pmid}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by PMID 12270001, please use {{cite journal}} with
|pmid=12270001instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.0050185, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1371/journal.pmed.0050185instead. - ^ a b "Secondhand Smoke Fact Sheet", American Lung Association June 2007.
- ^ "Tobacco-Free Florida", Centers for Disease Control & Prevention Fact Sheets
- ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1136/bmj.332.7550.1142, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1136/bmj.332.7550.1142instead. - ^ a b http://content.nejm.org/content/vol307/issue17/index.dtl
- ^ Finklea et al. 1969
- ^ Finklea, J. F., S. H. Sandifer and D. D. Smith. Cigarette smoking and epidemic influenza. Amer. J. Epid., 90: 390–399.—
- ^ Kark and Lebiush American Journal of Public Health, Vol. 71, Issue 5 530-532 1981
- ^ Epidemiology and Infection (1999), 123:1:103-108 Cambridge University Press
- ^ Haldane J (1895). "The action of carbonic oxide on man". J Physiol. 18 (5–6): 430–462. PMC 1514663. PMID 16992272.
- ^ "Health : Young smokers' heart attack risk". BBC. 2004-08-24. Retrieved 2005-12-18.
- ^ "Cigarette Smoke Changes Heart's Shape". InfoNIAC.com. Retrieved 2009-01-10.
- ^ David M. Burns, M.D. (February 1998). "Cigars: Health Effects and Trends".
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ a b c Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1007/s10935-005-5389-z, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1007/s10935-005-5389-zinstead. Cite error: The named reference "Symm" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page). - ^ a b National Institutes of Health (1998-04-10). "Background on Cigar Monograph: Cigars: Health Effects and Trends". Retrieved 2008-01-04.
- ^ American Cancer Society. "Questions About Smoking, Tobacco, and Health". Retrieved 2008-01-04.
- ^ Attention: This template ({{cite pmid}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by PMID 15173269, please use {{cite journal}} with
|pmid=15173269instead. - ^ Loren Stein. "Pipe Smoking". A Healthy Me!. Retrieved 2008-01-04.
- ^ Commission on Life Sciences. "Environmental Tobacco Smoke: Measuring Exposures and Assessing Health Effects (1986)". Retrieved 2008-01-04.
- ^ Attention: This template ({{cite pmid}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by PMID 11336116, please use {{cite journal}} with
|pmid=11336116instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1159/000069845, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1159/000069845instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite pmid}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by PMID 264419, please use {{cite journal}} with
|pmid=264419instead. - ^ "Helping you to Stop Smoking!". Retrieved 2008-01-04.
- ^ Attention: This template ({{cite pmid}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by PMID 1156044, please use {{cite journal}} with
|pmid=1156044instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite pmid}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by PMID 17384035, please use {{cite journal}} with
|pmid=17384035instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1111/j.1600-0765.2007.00988.x, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1111/j.1600-0765.2007.00988.xinstead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1016/j.trstmh.2005.06.034, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1016/j.trstmh.2005.06.034instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1056/NEJMsa0707719, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1056/NEJMsa0707719instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1056/NEJM200003093421002, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1056/NEJM200003093421002instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1001/archinte.164.20.2206 , please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1001/archinte.164.20.2206instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite pmid}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by PMID 12441327, please use {{cite journal}} with
|pmid=12441327instead. - ^ http://www.data-yard.net/10b/kaposi.htm
- ^ Men's Journal, March 2000, p. 69
- ^ Nesbitt’s Paradox resolved? Stress and arousal modulation during cigarette smoking. Addiction (1998) 93 (1), 27-39
- ^ HUGHES, J. R. (1992) Tobacco withdrawal in selfquitters, Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 60, 689-697
- ^ COHEN, S. & LICHTENSTEIN, E. (1990) Perceived stress, quitting smoking, and smoking relapse, Health Psychology, 9, 466-478
- ^ Nesbitt’s Paradox resolved? Stress and arousal modulation during cigarette smoking. Addiction (1998) 93 (1), 27-39
- ^ Bachman, et al., Smoking, Drinking, and Drug Use in Young Adulthood (Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Assoc, Pub, 1997), p 70
- ^ See Doherty, et al., Cigarette Smoking and Divorce, 16 Families, Systems & Health 393-400 (1998)
- ^ a b Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1046/j.1360-0443.2002.00016.x, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1046/j.1360-0443.2002.00016.xinstead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1093/aje/kwm116, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1093/aje/kwm116instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2004.10.022, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1016/j.biopsych.2004.10.022instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite pmid}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by PMID 14706428, please use {{cite journal}} with
|pmid=14706428instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite pmid}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by PMID 9395125, please use {{cite journal}} with
|pmid=9395125instead. - ^ Con Stough, Gordon Mangan, Tim Bates, O. Pellett (1994) Smoking and Raven IQ. Psycho-pharmacology 116:382-384
- ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1136/bmj.328.7434.277, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1136/bmj.328.7434.277instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite pmid}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by PMID 7965705, please use {{cite journal}} with
|pmid=7965705instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1080/14622200500494856, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1080/14622200500494856instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1002/mds.20029, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1002/mds.20029instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite pmid}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by PMID 15706049, please use {{cite journal}} with
|pmid=15706049instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1016/j.tins.2004.06.008, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1016/j.tins.2004.06.008instead. - ^ McNeill, Ann (2001). "Smoking and mental health - a review of the literature" (PDF). SmokeFree London Programme. Retrieved 2008-10-05.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Meltzer, H., Gill, B., Petticrew, M., Hinds. K. (1995). "OPCS Surveys of Psychiatric Morbidity Report 3: Economic Activity and Social Functioning of Adults With Psychiatric Disorders". London, Her Majesty’s Stationery Office.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite pmid}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by PMID 10553739, please use {{cite journal}} with
|pmid=10553739instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite pmid}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by PMID 3487983, please use {{cite journal}} with
|pmid=3487983instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1056/NEJMsa073350, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1056/NEJMsa073350instead. - ^ Health Report - 22 July 2002 - Schizophrenia and Smoking
- ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1177/0269881104047273, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1177/0269881104047273instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2005.02.006, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1016/j.neubiorev.2005.02.006instead. - ^ Depression and the dynamics of smoking. A national perspective
- ^ Smoking, smoking cessation, and major depression
- ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1300/J069v17n01_04 , please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1300/J069v17n01_04instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1037/0022-006X.61.5.761, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1037/0022-006X.61.5.761instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1016/S0166-4328(00)00206-0, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1016/S0166-4328(00)00206-0instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite pmid}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by PMID 9929522, please use {{cite journal}} with
|pmid=9929522instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite pmid}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by PMID 11978283, please use {{cite journal}} with
|pmid=11978283instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite pmid}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by PMID 15128612, please use {{cite journal}} with
|pmid=15128612instead. - ^ News-Medical.Net, [3], accessed on Jan 3, 2008
- ^ mytelus.com, [4], accessed on Jan 3, 2008
- ^ Attention: This template ({{cite pmid}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by PMID 19188554, please use {{cite journal}} with
|pmid=19188554instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1186/1471-5945-5-2, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1186/1471-5945-5-2instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite pmid}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by PMID 17120402, please use {{cite journal}} with
|pmid=17120402instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1093/aje/kwh275, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1093/aje/kwh275instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1093/humrep/deh374, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1093/humrep/deh374instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite pmid}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by PMID 8746297, please use {{cite journal}} with
|pmid=8746297instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite pmid}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by PMID 11035989, please use {{cite journal}} with
|pmid=11035989instead. - ^ Smoking may perk up women's risk of developing deadly AAA|TheMedGuru
- ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1161/hc3201.094225, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1161/hc3201.094225instead. - ^ Longmore, M., Wilkinson, I., Torok, E. Oxford Handbook of Clinical Medicine (Fifth Edition) p. 232
- ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1046/j.1365-2036.2000.00847.x, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1046/j.1365-2036.2000.00847.xinstead. - ^ "Smoking Cuts Risk of Rare Cancer". UPI. March 29, 2001.
- ^ Recer Paul (May 19, 1998). "Cigarettes May Have an Up Side". Associated Press. Retrieved November 6, 2006.
- ^ Attention: This template ({{cite pmid}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by PMID 11422156, please use {{cite journal}} with
|pmid=11422156instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1046/j.1365-2222.2001.01096.x, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1046/j.1365-2222.2001.01096.xinstead. - ^ Melton Lisa (2006). "Body Blazes". Scientific American: 24.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Ross RK, Pike MC, Vessey MP, Bull D, Yeates D, Casagrande JT (1986). "Risk factors for uterine fibroids: reduced risk associated with oral contraceptives". Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 293 (6543): 359–62. PMC 1341047. PMID 3730804.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Templeman C, Marshall SF, Clarke CA; et al. (2009). "Risk factors for surgically removed fibroids in a large cohort of teachers". Fertil. Steril. 92 (4): 1436–46. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2008.08.074. PMC 2765807. PMID 19019355.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b "Smokeless Tobacco and Some Tobacco-specific N-Nitrosamines" (PDF). IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. 87. 2007.
- ^ Detailed Guide: Cancer (General Information) Signs and Symptoms of Cancer http://www.cancer.org/docroot/CRI/content/CRI_2_4_3X_What_are_the_signs_and_symptoms_of_cancer.asp
- ^ a b Shanks TG, Burns DM (1998). "Disease consequences of cigar smoking". In Shopland DR, Burns DM, Hoffman D, Cummings KM, Amacher RH (eds.) (ed.). Cigars: Health Effects and Trends. Smoking and Tobacco Control Monograph No. 9. National Cancer Institute. pp. 105–160.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help);|editor=has generic name (help);|format=requires|url=(help); External link in|chapterurl=|chapterurl=ignored (|chapter-url=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: editors list (link) - ^ Dollar KM, Mix JM, Kozlowski LT (2008). "Little cigars, big cigars: omissions and commissions of harm and harm reduction information on the Internet". Nicotine Tob Res. 10 (5): 819–26. doi:10.1080/14622200802027214. PMID 18569755.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Questions and answers about cigar smoking and cancer". National Cancer Institute. 2000-03-07. Retrieved 2008-10-21.
- ^ Burns DM (1998). "Cigar smoking: overview and current state of the science". In Shopland DR, Burns DM, Hoffman D, Cummings KM, Amacher RH (eds.) (ed.). Cigars: Health Effects and Trends. Smoking and Tobacco Control Monograph No. 9. National Cancer Institute. pp. 1–20.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help);|editor=has generic name (help);|format=requires|url=(help); External link in|chapterurl=|chapterurl=ignored (|chapter-url=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: editors list (link) - ^ JARED MISNER (November 18, 2009). "UF study finds more teens smoke hookah". The Independent Florida Alligator.
- ^ Barry Knishkowy and Yona Amitai (2005). "Water-Pipe (Narghile) Smoking: An Emerging Health Risk Behaviour". Pediatrics; journal of the American Academy of Pediatrics.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Hookah smoking: Is it safer than cigarettes? - MayoClinic.com
- ^ Water pipe smoking a significant TB risk - IRIN News, March 2008
- ^ Egyptians warned on pipe smoking | The Australian
- ^ Alan Shihadeh, Sima Azar, Charbel Antonios, Antoine Haddad (September, 2004). "Towards a topographical model of narghile water-pipe café smoking: a pilot study in a high socioeconomic status neighbourhood of Beirut, Lebanon". Elsevier Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior, Volume 79, Issue 1. doi:10.1016/j.pbb.2004.06.005.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Cite journal requires|journal=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Mirjana V. Djordjevic, Steven D. Stellman, Edith Zang (January 19, 2000). "Doses of Nicotine and Lung Carcinogens Delivered to Cigarette Smokers". Journal of the National Cancer Institute, Vol. 92, No. 2. doi:10.1093/jnci/92.2.106.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Hookah smoking poses health risks". Rocky Mountain Collegian. November 20, 2008.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Koch, Wendy (December 28, 2005). "Hookah trend is puffing along". USA Today. Retrieved 2010-05-04.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ "WHO warns the hookah may pose same risk as cigarettes". USA Today. May 29, 2007.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ "Hookah smoking and cancer: carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) levels in exclusive/ever hookah smokers". Harm Reduction Journal. May 24, 2008.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Boffetta P, Hecht S, Gray N, Gupta P, Straif K (2008). "Smokeless tobacco and cancer". Lancet Oncol. 9 (7): 667–75. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(08)70173-6. PMID 18598931.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Isaac Adler. "Primary Malignant Growth of the Lung and Bronchi". (1912) New York, Longmans, Green. pp. 3-12. Reprinted (1980) by A Cancer Journal for Clinicians
- ^ a b Commentary: Schairer and Schoniger's forgotten tobacco epidemiology and the Nazi quest for racial purity - Proctor 30 (1): 31 - International Journal of Epidemiology
- ^ Adler I. Primary malignant growths of the lungs and bronchi. New York: Longmans, Green; 1912., cited in Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1164/rccm.200504-531OE, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1164/rccm.200504-531OEinstead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1136/bmj.328.7455.1529, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1136/bmj.328.7455.1529instead.
Bibliography
- "WHO REPORT on the global TOBACCO epidemic" (PDF). World Health Organization. 2008. Retrieved 2008-01-01.
- "The Global Burden of Disease 2004 Update" (PDF). World Health Organization. 2008. Retrieved 2008-01-01.
- "Chapter 1: Introduction and Approach to Causal Inference". 2004 Surgeon General's Report—The Health Consequences of Smoking (PDF). Washington DC: Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, Office on Smoking and Health. 2004. Retrieved 2009-05-24.
{{cite book}}: External link in|chapterurl=|chapterurl=ignored (|chapter-url=suggested) (help) - "The health consequences of involuntary exposure to tobacco smoke: a report of the Surgeon General" (PDF). Atlanta, U.S.: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, Office on Smoking and Health. 2006. Retrieved 2009-02-15.
- "Cancer Facts and Figures 2004: Basic Cancer Facts". American Cancer Society. Retrieved 2009-01-21.
- Environmental and Heritable Factors in the Causation of Cancer — Analyses of Cohorts of Twins from Sweden, Denmark, and Finland. Vol. 343. New England Journal of Medicine. 2000. Retrieved 2009-01-21.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Montesano, R., and Hall, J. (2001). "Environmental causes of human cancers". European Journal of Cancer. Retrieved 2009-01-21.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
