2007–2008 financial crisis

| Part of a series on the |
| Great Recession |
|---|
| Timeline |
The financial crisis of 2007–2010 was triggered by a liquidity shortfall in the United States banking system.[1] It has resulted in the collapse of large financial institutions, the bailout of banks by national governments, and downturns in stock markets around the world. In many areas, the housing market has also suffered, resulting in numerous evictions, foreclosures and prolonged vacancies. It is considered by many economists to be the worst financial crisis since the Great Depression of the 1930s.[2] It contributed to the failure of key businesses, declines in consumer wealth estimated in the trillions of U.S. dollars, substantial financial commitments incurred by governments, and a significant decline in economic activity.[3] Many causes have been suggested, with varying weight assigned by experts.[4] Both market-based and regulatory solutions have been implemented or are under consideration,[5] while significant risks remain for the world economy over the 2010–2011 periods.[6]
Overview
The collapse of the housing bubble, which peaked in the U.S. in 2006, caused the values of securities tied to real estate pricing to plummet thereafter, damaging financial institutions globally.[7] Questions regarding bank solvency, declines in credit availability, and damaged investor confidence had an impact on global stock markets, where securities suffered large losses during late 2008 and early 2009. Economies worldwide slowed during this period as credit tightened and international trade declined.[8] Critics argued that credit rating agencies and investors failed to accurately price the risk involved with mortgage-related financial products, and that governments did not adjust their regulatory practices to address 21st century financial markets.[9] Governments and central banks responded with unprecedented fiscal stimulus, monetary policy expansion, and institutional bailouts.
Background
The immediate cause or trigger of the crisis was the bursting of the United States housing bubble which peaked in approximately 2005–2006.[10][11] Already-rising default rates on "subprime" and adjustable rate mortgages (ARM) began to increase quickly thereafter. As banks began to increasingly give out more loans to potential home owners, the housing price also began to rise. In the optimistic terms the banks would encourage the home owners to take on considerably high loans in the belief they would be able to pay it back more quickly overlooking the interest rates. Once the interest rates began to rise in mid 2007 the housing price started to drop significantly in 2006 leading into 2007. In many states like California refinancing became more difficult. As a result the number of foreclosed homes began to rise as well.
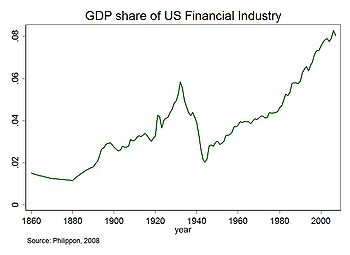
Steadily decreasing interest rates backed by the U.S Federal Reserve from 1982 onward and large inflows of foreign funds created easy credit conditions for a number of years prior to the crisis, fueling a housing construction boom and encouraging debt-financed consumption.[13] The combination of easy credit and money inflow contributed to the United States housing bubble. Loans of various types (e.g., mortgage, credit card, and auto) were easy to obtain and consumers assumed an unprecedented debt load.[14][15] As part of the housing and credit booms, the number of financial agreements called mortgage-backed securities (MBS) and collateralized debt obligations (CDO), which derived their value from mortgage payments and housing prices, greatly increased. Such financial innovation enabled institutions and investors around the world to invest in the U.S. housing market. As housing prices declined, major global financial institutions that had borrowed and invested heavily in subprime MBS reported significant losses. Falling prices also resulted in homes worth less than the mortgage loan, providing a financial incentive to enter foreclosure. The ongoing foreclosure epidemic that began in late 2006 in the U.S. continues to drain wealth from consumers and erodes the financial strength of banking institutions. Defaults and losses on other loan types also increased significantly as the crisis expanded from the housing market to other parts of the economy. Total losses are estimated in the trillions of U.S. dollars globally.[16]
While the housing and credit bubbles built, a series of factors caused the financial system to both expand and become increasingly fragile, a process called financialization. U. S. Government policy from the 1970s onward has emphasized deregulation to encourage business, which resulted in less oversight of activities and less disclosure of information about new activities undertaken by banks and other evolving financial institutions. Thus, policymakers did not immediately recognize the increasingly important role played by financial institutions such as investment banks and hedge funds, also known as the shadow banking system. Some experts believe these institutions had become as important as commercial (depository) banks in providing credit to the U.S. economy, but they were not subject to the same regulations.[17] These institutions, as well as certain regulated banks, had also assumed significant debt burdens while providing the loans described above and did not have a financial cushion sufficient to absorb large loan defaults or MBS losses.[18] These losses impacted the ability of financial institutions to lend, slowing economic activity. Concerns regarding the stability of key financial institutions drove central banks to provide funds to encourage lending and restore faith in the commercial paper markets, which are integral to funding business operations. Governments also bailed out key financial institutions and implemented economic stimulus programs, assuming significant additional financial commitments.
Growth of the housing bubble

Between 1997 and 2006, the price of the typical American house increased by 124%.[20] During the two decades ending in 2001, the national median home price ranged from 2.9 to 3.1 times median household income. This ratio rose to 4.0 in 2004, and 4.6 in 2006.[21] This housing bubble resulted in quite a few homeowners refinancing their homes at lower interest rates, or financing consumer spending by taking out second mortgages secured by the price appreciation.
In a Peabody Award winning program, NPR correspondents argued that a "Giant Pool of Money" (represented by $70 trillion in worldwide fixed income investments) sought higher yields than those offered by U.S. Treasury bonds early in the decade. This pool of money had roughly doubled in size from 2000 to 2007, yet the supply of relatively safe, income generating investments had not grown as fast. Investment banks on Wall Street answered this demand with the MBS and CDO, which were assigned safe ratings by the credit rating agencies. In effect, Wall Street connected this pool of money to the mortgage market in the U.S., with enormous fees accruing to those throughout the mortgage supply chain, from the mortgage broker selling the loans, to small banks that funded the brokers, to the giant investment banks behind them. By approximately 2003, the supply of mortgages originated at traditional lending standards had been exhausted. However, continued strong demand for MBS and CDO began to drive down lending standards, as long as mortgages could still be sold along the supply chain. Eventually, this speculative bubble proved unsustainable.[22]
The CDO in particular enabled financial institutions to obtain investor funds to finance subprime and other lending, extending or increasing the housing bubble and generating large fees. A CDO essentially places cash payments from multiple mortgages or other debt obligations into a single pool, from which the cash is allocated to specific securities in a priority sequence. Those securities obtaining cash first received investment-grade ratings from rating agencies. Lower priority securities received cash thereafter, with lower credit ratings but theoretically a higher rate of return on the amount invested.[23][24]
By September 2008, average U.S. housing prices had declined by over 20% from their mid-2006 peak.[25][26] As prices declined, borrowers with adjustable-rate mortgages could not refinance to avoid the higher payments associated with rising interest rates and began to default. During 2007, lenders began foreclosure proceedings on nearly 1.3 million properties, a 79% increase over 2006.[27] This increased to 2.3 million in 2008, an 81% increase vs. 2007.[28] By August 2008, 9.2% of all U.S. mortgages outstanding were either delinquent or in foreclosure.[29] By September 2009, this had risen to 14.4%.[30]
Easy credit conditions
Lower interest rates encourage borrowing. From 2000 to 2003, the Federal Reserve lowered the federal funds rate target from 6.5% to 1.0%.[31] This was done to soften the effects of the collapse of the dot-com bubble and of the September 2001 terrorist attacks, and to combat the perceived risk of deflation.[32]

Additional downward pressure on interest rates was created by the USA's high and rising current account (trade) deficit, which peaked along with the housing bubble in 2006. Ben Bernanke explained how trade deficits required the U.S. to borrow money from abroad, which bid up bond prices and lowered interest rates.[33]
Bernanke explained that between 1996 and 2004, the USA current account deficit increased by $650 billion, from 1.5% to 5.8% of GDP. Financing these deficits required the USA to borrow large sums from abroad, much of it from countries running trade surpluses, mainly the emerging economies in Asia and oil-exporting nations. The balance of payments identity requires that a country (such as the USA) running a current account deficit also have a capital account (investment) surplus of the same amount. Hence large and growing amounts of foreign funds (capital) flowed into the USA to finance its imports.
This created demand for various types of financial assets, raising the prices of those assets while lowering interest rates. Foreign investors had these funds to lend, either because they had very high personal savings rates (as high as 40% in China), or because of high oil prices. Bernanke referred to this as a "saving glut."[34]
A "flood" of funds (capital or liquidity) reached the USA financial markets. Foreign governments supplied funds by purchasing USA Treasury bonds and thus avoided much of the direct impact of the crisis. USA households, on the other hand, used funds borrowed from foreigners to finance consumption or to bid up the prices of housing and financial assets. Financial institutions invested foreign funds in mortgage-backed securities.
The Fed then raised the Fed funds rate significantly between July 2004 and July 2006.[35] This contributed to an increase in 1-year and 5-year adjustable-rate mortgage (ARM) rates, making ARM interest rate resets more expensive for homeowners.[36] This may have also contributed to the deflating of the housing bubble, as asset prices generally move inversely to interest rates and it became riskier to speculate in housing.[37][38] USA housing and financial assets dramatically declined in value after the housing bubble burst.[39][40]
Weak and fraudulent underwriting practice
Testimony given to the Financial Crisis Inquiry Commission by Richard M. Bowen, III on events during his tenure as Citi's Business Chief Underwriter for Correspondent Lending in the Consumer Lending Group (where he was responsible for over 220 professional underwriters) suggests that by the final years of the US housing bubble (2006–2007), the collapse of mortgage underwriting standards was endemic. His testimony states that by 2006, 60% of mortgages purchased by Citi from some 1,600 mortgage companies were "defective" (were not underwritten to policy, or did not contain all policy-required documents). This, despite the fact that each of these 1,600 originators were contractually responsible (certified via representations and warrantees) that their mortgage originations met Citi's standards. Moreover, during 2007, "defective mortgages (from mortgage originators contractually bound to perform underwriting to Citi's standards) increased... to over 80% of production".[41]
In separate testimony to Financial Crisis Inquiry Commission, officers of Clayton Holdings—the largest residential loan due diligence and securitization surveillance company in the United States and Europe—testified that Clayton's review of over 900,000 mortgages issued from January 2006 to June 2007 revealed that scarcely 54% of the loans met their originators’ underwriting standards. The analysis (conducted on behalf of 23 investment and commercial banks, including 7 "Too Big To Fail" banks) additionally showed that 28% of the sampled loans did not meet the minimal standards of any issuer. Clayton's analysis further showed that 39% of these loans (i.e. those not meeting any issuer's minimal underwriting standards) were subsequently securitized and sold to investors.[42][43]
Sub-prime lending
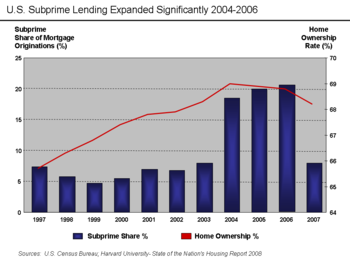
The term subprime refers to the credit quality of particular borrowers, who have weakened credit histories and a greater risk of loan default than prime borrowers.[44] The value of U.S. subprime mortgages was estimated at $1.3 trillion as of March 2007,[45] with over 7.5 million first-lien subprime mortgages outstanding.[46]
In addition to easy credit conditions, there is evidence that both government and competitive pressures contributed to an increase in the amount of subprime lending during the years preceding the crisis. Major U.S. investment banks and government sponsored enterprises like Fannie Mae played an important role in the expansion of higher-risk lending.[47][48]
Subprime mortgages remained below 10% of all mortgage originations until 2004, when they spiked to nearly 20% and remained there through the 2005-2006 peak of the United States housing bubble.[49] A proximate event to this increase was the April 2004 decision by the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) to relax the net capital rule, which permitted the largest five investment banks to dramatically increase their financial leverage and aggressively expand their issuance of mortgage-backed securities. This applied additional competitive pressure to Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac, which further expanded their riskier lending.[50] Subprime mortgage payment delinquency rates remained in the 10-15% range from 1998 to 2006,[51] then began to increase rapidly, rising to 25% by early 2008.[52][53]
Some, like American Enterprise Institute fellow Peter J. Wallison,[54] believe the roots of the crisis can be traced directly to sub-prime lending by Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac, which are government sponsored entities. On September 30, 1999, The New York Times reported that the Clinton Administration pushed for more lending to low and moderate income borrowers, while the mortgage industry sought guarantees for sub-prime loans:
Fannie Mae, the nation's biggest underwriter of home mortgages, has been under increasing pressure from the Clinton Administration to expand mortgage loans among low and moderate income people and felt pressure from stock holders to maintain its phenomenal growth in profits. In addition, banks, thrift institutions and mortgage companies have been pressing Fannie Mae to help them make more loans to so-called subprime borrowers... In moving, even tentatively, into this new area of lending, Fannie Mae is taking on significantly more risk, which may not pose any difficulties during flush economic times. But the government-subsidized corporation may run into trouble in an economic downturn, prompting a government rescue similar to that of the savings and loan industry in the 1980s.[55]
A 2000 United States Department of the Treasury study of lending trends for 305 cities from 1993 to 1998 showed that $467 billion of mortgage lending was made by Community Reinvestment Act (CRA)-covered lenders into low and mid level income (LMI) borrowers and neighborhoods, representing 10% of all US mortgage lending during the period. The majority of these were prime loans. Sub-prime loans made by CRA-covered institutions constituted a 3% market share of LMI loans in 1998. [56] Nevertheless, only 25% of all sub-prime lending occurred at CRA-covered institutions, and a full 50% of sub-prime loans originated at institutions exempt from CRA.[57] For at least one mortgage lender,CRA loans were the more "vulnerable during the downturn, to the detriment of both borrowers and lenders. For example, lending done under Community Reinvestment Act criteria, according to a quarterly report in October of 2008, constituted only 7% of the total mortgage lending by the Bank of America, but constituted 29% of its losses on mortgages."[58]
Others have pointed out that there were not enough of these loans made to cause a crisis of this magnitude. In an article in Portfolio Magazine, Michael Lewis spoke with one trader who noted that "There weren’t enough Americans with [bad] credit taking out [bad loans] to satisfy investors’ appetite for the end product." Essentially, investment banks and hedge funds used financial innovation to enable large wagers to be made, far beyond the actual value of the underlying mortgage loans, using derivatives called credit default swaps, CDO and synthetic CDO. As long as derivative buyers could be matched with sellers, the theoretical amount that could be wagered was infinite. "They were creating [synthetic loans] out of whole cloth. One hundred times over! That’s why the losses are so much greater than the loans."[59]
Economist Paul Krugman argued in January 2010 that the simultaneous growth of the residential and commercial real estate pricing bubbles undermines the case made by those who argue that Fannie Mae, Freddie Mac, CRA or predatory lending were primary causes of the crisis. In other words, bubbles in both markets developed even though only the residential market was affected by these potential causes.[60]
Predatory lending
Predatory lending refers to the practice of unscrupulous lenders, to enter into "unsafe" or "unsound" secured loans for inappropriate purposes.[61] A classic bait-and-switch method was used by Countrywide Financial, advertising low interest rates for home refinancing. Such loans were written into extensively detailed contracts, and swapped for more expensive loan products on the day of closing. Whereas the advertisement might state that 1% or 1.5% interest would be charged, the consumer would be put into an adjustable rate mortgage (ARM) in which the interest charged would be greater than the amount of interest paid. This created negative amortization, which the credit consumer might not notice until long after the loan transaction had been consummated.
Countrywide, sued by California Attorney General Jerry Brown for "unfair business practices" and "false advertising" was making high cost mortgages "to homeowners with weak credit, adjustable rate mortgages (ARMs) that allowed homeowners to make interest-only payments".[62] When housing prices decreased, homeowners in ARMs then had little incentive to pay their monthly payments, since their home equity had disappeared. This caused Countrywide's financial condition to deteriorate, ultimately resulting in a decision by the Office of Thrift Supervision to seize the lender.
Former employees from Ameriquest, which was United States's leading wholesale lender,[63] described a system in which they were pushed to falsify mortgage documents and then sell the mortgages to Wall Street banks eager to make fast profits.[63] There is growing evidence that such mortgage frauds may be a cause of the crisis.[63]
Deregulation
Critics[who?] have argued that the regulatory framework did not keep pace with financial innovation, such as the increasing importance of the shadow banking system, derivatives and off-balance sheet financing. In other cases, laws were changed or enforcement weakened in parts of the financial system. Key examples include:
- Jimmy Carter's Depository Institutions Deregulation and Monetary Control Act of 1980 (DIDMCA) phased out a number of restrictions on banks' financial practices, broadened their lending powers, and raised the deposit insurance limit from $40,000 to $100,000 (raising the problem of moral hazard).[64] Banks rushed into real estate lending, speculative lending, and other ventures just as the economy soured.[citation needed]
- In October 1982, U.S. President Ronald Reagan signed into Law the Garn–St. Germain Depository Institutions Act, which provided for adjustable-rate mortgage loans, began the process of banking deregulation,[citation needed] and contributed to the savings and loan crisis of the late 1980s/early 1990s.[65]
- In November 1999, U.S. President Bill Clinton signed into Law the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act, which repealed part of the Glass-Steagall Act of 1933. This repeal has been criticized for reducing the separation between commercial banks (which traditionally had a conservative culture) and investment banks (which had a more risk-taking culture).[66][67]
- In 2004, the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission relaxed the net capital rule, which enabled investment banks to substantially increase the level of debt they were taking on, fueling the growth in mortgage-backed securities supporting subprime mortgages. The SEC has conceded that self-regulation of investment banks contributed to the crisis.[68][69]
- Financial institutions in the shadow banking system are not subject to the same regulation as depository banks, allowing them to assume additional debt obligations relative to their financial cushion or capital base.[70] This was the case despite the Long-Term Capital Management debacle in 1998, where a highly-leveraged shadow institution failed with systemic implications.
- Regulators and accounting standard-setters allowed depository banks such as Citigroup to move significant amounts of assets and liabilities off-balance sheet into complex legal entities called structured investment vehicles, masking the weakness of the capital base of the firm or degree of leverage or risk taken. One news agency estimated that the top four U.S. banks will have to return between $500 billion and $1 trillion to their balance sheets during 2009.[71] This increased uncertainty during the crisis regarding the financial position of the major banks.[72] Off-balance sheet entities were also used by Enron as part of the scandal that brought down that company in 2001.[73]
- As early as 1997, Federal Reserve Chairman Alan Greenspan fought to keep the derivatives market unregulated.[74] With the advice of the President's Working Group on Financial Markets,[75] the U.S. Congress and President allowed the self-regulation of the over-the-counter derivatives market when they enacted the Commodity Futures Modernization Act of 2000. Derivatives such as credit default swaps (CDS) can be used to hedge or speculate against particular credit risks. The volume of CDS outstanding increased 100-fold from 1998 to 2008, with estimates of the debt covered by CDS contracts, as of November 2008, ranging from US$33 to $47 trillion. Total over-the-counter (OTC) derivative notional value rose to $683 trillion by June 2008.[76] Warren Buffett famously referred to derivatives as "financial weapons of mass destruction" in early 2003.[77][78]
Increased debt burden or over-leveraging

U.S. households and financial institutions became increasingly indebted or overleveraged[citation needed] during the years preceding the crisis. This increased their vulnerability to the collapse of the housing bubble and worsened the ensuing economic downturn[citation needed]. Key statistics include:
- Free cash used by consumers from home equity extraction doubled from $627 billion in 2001 to $1,428 billion in 2005 as the housing bubble built, a total of nearly $5 trillion dollars over the period, contributing to economic growth worldwide.[79][80][81] U.S. home mortgage debt relative to GDP increased from an average of 46% during the 1990s to 73% during 2008, reaching $10.5 trillion.[82]
- USA household debt as a percentage of annual disposable personal income was 127% at the end of 2007, versus 77% in 1990.[83]
- In 1981, U.S. private debt was 123% of GDP; by the third quarter of 2008, it was 290%.[84]
- From 2004-07, the top five U.S. investment banks each significantly increased their financial leverage (see diagram), which increased their vulnerability to a financial shock. These five institutions reported over $4.1 trillion in debt for fiscal year 2007, about 30% of USA nominal GDP for 2007. Lehman Brothers was liquidated, Bear Stearns and Merrill Lynch were sold at fire-sale prices, and Goldman Sachs and Morgan Stanley became commercial banks, subjecting themselves to more stringent regulation. With the exception of Lehman, these companies required or received government support.[85]
- Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac, two U.S. Government sponsored enterprises, owned or guaranteed nearly $5 trillion in mortgage obligations at the time they were placed into conservatorship by the U.S. government in September 2008.[86][87]
These seven entities were highly leveraged and had $9 trillion in debt or guarantee obligations, an enormous concentration of risk[neutrality is disputed]; yet they were not subject to the same regulation as depository banks[citation needed].
Financial innovation and complexity
The term financial innovation refers to the ongoing development of financial products designed to achieve particular client objectives, such as offsetting a particular risk exposure (such as the default of a borrower) or to assist with obtaining financing. Examples pertinent to this crisis included: the adjustable-rate mortgage; the bundling of subprime mortgages into mortgage-backed securities (MBS) or collateralized debt obligations (CDO) for sale to investors, a type of securitization; and a form of credit insurance called credit default swaps (CDS). The usage of these products expanded dramatically in the years leading up to the crisis. These products vary in complexity and the ease with which they can be valued on the books of financial institutions.
As described in the section on subprime lending, the CDS and portfolio of CDS called synthetic CDO enabled a theoretically infinite amount to be wagered on the finite value of housing loans outstanding[citation needed], provided that buyers and sellers of the derivatives could be found. For example, selling a CDS to insure a CDO ended up giving the seller the same risk as if they owned the CDO, when those CDO's became worthless.
Certain financial innovation may also have the effect of circumventing regulations[citation needed], such as off-balance sheet financing that affects the leverage or capital cushion reported by major banks. For example, Martin Wolf wrote in June 2009: "...an enormous part of what banks did in the early part of this decade – the off-balance-sheet vehicles, the derivatives and the 'shadow banking system' itself – was to find a way round regulation."[88]
Incorrect pricing of risk

The pricing of risk refers to the incremental compensation required by investors for taking on additional risk, which may be measured by interest rates or fees. For a variety of reasons, market participants did not accurately measure the risk inherent with financial innovation such as MBS and CDO's or understand its impact on the overall stability of the financial system.[9] For example, the pricing model for CDOs clearly did not reflect the level of risk they introduced into the system. Banks estimated that $450bn of CDO were sold between "late 2005 to the middle of 2007"; among the $102bn of those that had been liquidated, JPMorgan estimated that the average recovery rate for "high quality" CDOs was approximately 32 cents on the dollar, while the recovery rate for mezzanine CDO was approximately five cents for every dollar.[89]
Another example relates to AIG, which insured obligations of various financial institutions through the usage of credit default swaps. The basic CDS transaction involved AIG receiving a premium in exchange for a promise to pay money to party A in the event party B defaulted. However, AIG did not have the financial strength to support its many CDS commitments as the crisis progressed and was taken over by the government in September 2008. U.S. taxpayers provided over $180 billion in government support to AIG during 2008 and early 2009, through which the money flowed to various counterparties to CDS transactions, including many large global financial institutions.[90][91]
The limitations of a widely-used financial model also were not properly understood.[92][93] This formula assumed that the price of CDS was correlated with and could predict the correct price of mortgage backed securities. Because it was highly tractable, it rapidly came to be used by a huge percentage of CDO and CDS investors, issuers, and rating agencies.[93] According to one wired.com article:
Then the model fell apart. Cracks started appearing early on, when financial markets began behaving in ways that users of Li's formula hadn't expected. The cracks became full-fledged canyons in 2008—when ruptures in the financial system's foundation swallowed up trillions of dollars and put the survival of the global banking system in serious peril... Li's Gaussian copula formula will go down in history as instrumental in causing the unfathomable losses that brought the world financial system to its knees.[93]
As financial assets became more and more complex, and harder and harder to value, investors were reassured by the fact that both the international bond rating agencies and bank regulators, who came to rely on them, accepted as valid some complex mathematical models which theoretically showed the risks were much smaller than they actually proved to be.[94] George Soros commented that "The super-boom got out of hand when the new products became so complicated that the authorities could no longer calculate the risks and started relying on the risk management methods of the banks themselves. Similarly, the rating agencies relied on the information provided by the originators of synthetic products. It was a shocking abdication of responsibility."[95]
Moreover, a conflict of interest between professional investment managers and their institutional clients, combined with a global glut in investment capital, led to bad investments by asset managers in over-priced credit assets. Professional investment managers generally are compensated based on the volume of client assets under management. There is, therefore, an incentive for asset managers to expand their assets under management in order to maximize their compensation. As the glut in global investment capital caused the yields on credit assets to decline, asset managers were faced with the choice of either investing in assets where returns did not reflect true credit risk or returning funds to clients. Many asset managers chose to continue to invest client funds in over-priced (under-yielding) investments, to the detriment of their clients, in order to maintain their assets under management. This choice was supported by a “plausible deniability” of the risks associated with subprime-based credit assets because the loss experience with early “vintages” of subprime loans was so low.[96]
Despite the dominance of the above formula, there are documented attempts of the financial industry, occurring before the crisis, to address the formula limitations, specifically the lack of dependence dynamics and the poor representation of extreme events.[97] The volume "Credit Correlation: Life After Copulas", published in 2007 by World Scientific, summarizes a 2006 conference held by Merrill Lynch in London where several practitioners attempted to propose models rectifying some of the copula limitations. See also the article by Donnelly and Embrechts [98] and the book by Brigo, Pallavicini and Torresetti, that reports relevant warnings and research on CDOs appeared in 2006. [99]
Boom and collapse of the shadow banking system
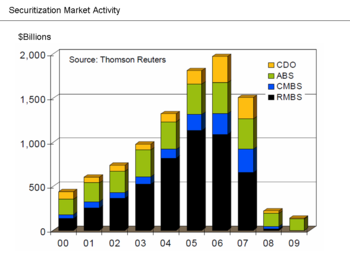
In a June 2008 speech, President and CEO of the New York Federal Reserve Bank Timothy Geithner—who in 2009 became Secretary of the United States Treasury—placed significant blame for the freezing of credit markets on a "run" on the entities in the "parallel" banking system, also called the shadow banking system. These entities became critical to the credit markets underpinning the financial system, but were not subject to the same regulatory controls. Further, these entities were vulnerable because of maturity mismatch, meaning that they borrowed short-term in liquid markets to purchase long-term, illiquid and risky assets. This meant that disruptions in credit markets would make them subject to rapid deleveraging, selling their long-term assets at depressed prices. He described the significance of these entities:
In early 2007, asset-backed commercial paper conduits, in structured investment vehicles, in auction-rate preferred securities, tender option bonds and variable rate demand notes, had a combined asset size of roughly $2.2 trillion. Assets financed overnight in triparty repo grew to $2.5 trillion. Assets held in hedge funds grew to roughly $1.8 trillion. The combined balance sheets of the then five major investment banks totaled $4 trillion. In comparison, the total assets of the top five bank holding companies in the United States at that point were just over $6 trillion, and total assets of the entire banking system were about $10 trillion. The combined effect of these factors was a financial system vulnerable to self-reinforcing asset price and credit cycles.[17]
Paul Krugman, laureate of the Nobel Prize in Economics, described the run on the shadow banking system as the "core of what happened" to cause the crisis. He referred to this lack of controls as "malign neglect" and argued that regulation should have been imposed on all banking-like activity.[70]
The securitization markets supported by the shadow banking system started to close down in the spring of 2007 and nearly shut-down in the fall of 2008. More than a third of the private credit markets thus became unavailable as a source of funds.[100] According to the Brookings Institution, the traditional banking system does not have the capital to close this gap as of June 2009: "It would take a number of years of strong profits to generate sufficient capital to support that additional lending volume." The authors also indicate that some forms of securitization are "likely to vanish forever, having been an artifact of excessively loose credit conditions."[101]
Economist Mark Zandi testified to the Financial Crisis Inquiry Commission in January 2010: "The securitization markets also remain impaired, as investors anticipate more loan losses. Investors are also uncertain about coming legal and accounting rule changes and regulatory reforms. Private bond issuance of residential and commercial mortgage-backed securities, asset-backed securities, and CDOs peaked in 2006 at close to $2 trillion...In 2009, private issuance was less than $150 billion, and almost all of it was asset-backed issuance supported by the Federal Reserve's TALF program to aid credit card, auto and small-business lenders. Issuance of residential and commercial mortgage-backed securities and CDOs remains dormant."[102]
Commodities boom
Rapid increases in a number of commodity prices followed the collapse in the housing bubble. The price of oil nearly tripled from $50 to $147 from early 2007 to 2008, before plunging as the financial crisis began to take hold in late 2008.[103] Experts debate the causes, with some attributing it to speculative flow of money from housing and other investments into commodities, some to monetary policy,[104] and some to the increasing feeling of raw materials scarcity in a fast growing world, leading to long positions taken on those markets, such as Chinese increasing presence in Africa. An increase in oil prices tends to divert a larger share of consumer spending into gasoline, which creates downward pressure on economic growth in oil importing countries, as wealth flows to oil-producing states.[105] A pattern of spiking instability in the price of oil over the decade leading up to the price high of 2008 has been recently identified. [106] The destabilizing effects of this price variance has been proposed as a contributory factor in the financial crisis.
In testimony before the Senate Committee on Commerce, Science, and Transportation on June 3, 2008, former director of the CFTC Division of Trading & Markets (responsible for enforcement) Michael Greenberger specifically named the Atlanta-based IntercontinentalExchange, founded by Goldman Sachs, Morgan Stanley and BP as playing a key role in speculative run-up of oil futures prices traded off the regulated futures exchanges in London and New York.[107] However, the IntercontinentalExchange (ICE) had been regulated by both European and US authorities since its purchase of the International Petroleum Exchange in 2001. Mr Greenberger was later corrected on this matter.[108]
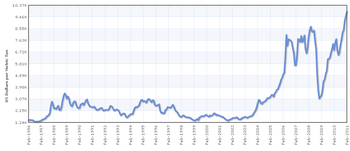
Copper prices increased at the same time as the oil prices. Copper traded at about $2,500 per tonne from 1990 until 1999, when it fell to about $1,600. The price slump lasted until 2004 which saw a price surge that had copper reaching $7,040 per tonne in 2008.[109]
Nickel prices boomed in the late 1990s, then the price of nickel imploded from around $51,000 /£36,700 per metric ton in May 2007 to about $11,550/£8,300 per metric ton in January 2009. Prices were only just starting to recover as of January 2010, but most of Australia's nickel mines had gone bankrupt by then.[110] As the price for high grade nickel sulphate ore recovered in 2010, so did the Australian nickel mining industry.[111]
Coincidentally with these price fluctuations, long-only commodity index funds became popular – by one estimate investment increased from $90 billion in 2006 to $200 billion at the end of 2007, while commodity prices increased 71% – which raised concern as to whether these index funds caused the commodity bubble.[112] The empirical research has been mixed.[112]
Systemic crisis
Another analysis, different from the mainstream explanation, is that the financial crisis is merely a symptom of another, deeper crisis, which is a systemic crisis of capitalism itself.[113] According to Samir Amin, an Egyptian Marxist economist, the constant decrease in GDP growth rates in Western countries since the early 1970s created a growing surplus of capital which did not have sufficient profitable investment outlets in the real economy. The alternative was to place this surplus into the financial market, which became more profitable than capital investment, especially with subsequent deregulation.[114] According to Samir Amin, this phenomenon has led to recurrent financial bubbles (such as the internet bubble) and is the deep cause of the financial crisis of 2007-2010.[115]
John Bellamy Foster, a political economy analyst and editor of the Monthly Review, believes that the decrease in GDP growth rates since the early 1970s is due to increasing market saturation.[116]
John C. Bogle wrote during 2005 that a series of unresolved challenges face capitalism that have contributed to past financial crises and have not been sufficiently addressed:
Corporate America went astray largely because the power of managers went virtually unchecked by our gatekeepers for far too long...They failed to 'keep an eye on these geniuses' to whom they had entrusted the responsibility of the management of America's great corporations.
He cites particular issues, including:[117][118]
- "Manager's capitalism" which he argues has replaced "owner's capitalism," meaning management runs the firm for its benefit rather than for the shareholders, a variation on the principal-agent problem;
- Burgeoning executive compensation;
- Managed earnings, mainly a focus on share price rather than the creation of genuine value; and
- The failure of gatekeepers, including auditors, boards of directors, Wall Street analysts, and career politicians.
Robert Reich has attributed the current economic downturn to the stagnation of wages in the United States, particularly those of the hourly workers who comprise 80% of the workforce. His claim is that this stagnation forced the population to borrow in order to meet the cost of living.[119]
Role of economic forecasting
The financial crisis was not widely predicted by mainstream economists, who instead spoke of The Great Moderation. A number of heterodox economists predicted the crisis, with varying arguments. Dirk Bezemer in his research[120] credits (with supporting argument and estimates of timing) 12 economists with predicting the crisis: Dean Baker (US), Wynne Godley (UK), Fred Harrison (UK), Michael Hudson (US), Eric Janszen (US), Steve Keen (Australia), Jakob Brøchner Madsen & Jens Kjaer Sørensen (Denmark), Kurt Richebächer (US), Nouriel Roubini (US), Peter Schiff (US), and Robert Shiller (US). Examples of other experts who gave indications of a financial crisis have also been given.[121][122][123]
A cover story in BusinessWeek magazine claims that economists mostly failed to predict the worst international economic crisis since the Great Depression of 1930s.[124] The Wharton School of the University of Pennsylvania's online business journal examines why economists failed to predict a major global financial crisis.[125] Popular articles published in the mass media have led the general public to believe that the majority of economists have failed in their obligation to predict the financial crisis. For example, an article in the New York Times informs that economist Nouriel Roubini warned of such crisis as early as September 2006, and the article goes on to state that the profession of economics is bad at predicting recessions.[126] According to The Guardian, Roubini was ridiculed for predicting a collapse of the housing market and worldwide recession, while The New York Times labelled him "Dr. Doom".[127]
Within mainstream financial economics, most believe that financial crises are simply unpredictable,[128] following Eugene Fama's efficient-market hypothesis and the related random-walk hypothesis, which state respectively that markets contain all information about possible future movements, and that the movement of financial prices are random and unpredictable.
Lebanese-American trader and financial risk engineer Nassim Nicholas Taleb author of The Black Swan spent years warning against the breakdown of the banking system in particular and the economy in general owing to their use of bad risk models and reliance on forecasting, and their reliance on bad models, and framed the problem as part of "robustness and fragility".[129][130] He also reacted against the cold of the establishment by making a big financial bet on banking stocks and making a fortune from the crisis ("They didn't listen, so I took their money") .[131] According to David Brooks from the New York Times, "Taleb not only has an explanation for what’s happening, he saw it coming." .[132]
Financial markets impacts
Impacts on financial institutions

The International Monetary Fund estimated that large U.S. and European banks lost more than $1 trillion on toxic assets and from bad loans from January 2007 to September 2009. These losses are expected to top $2.8 trillion from 2007-10. U.S. banks losses were forecast to hit $1 trillion and European bank losses will reach $1.6 trillion. The IMF estimated that U.S. banks were about 60% through their losses, but British and eurozone banks only 40%.[133]
One of the first victims was Northern Rock, a medium-sized British bank.[134] The highly leveraged nature of its business led the bank to request security from the Bank of England. This in turn led to investor panic and a bank run in mid-September 2007. Calls by Liberal Democrat Treasury Spokesman Vince Cable to nationalise the institution were initially ignored; in February 2008, however, the British government (having failed to find a private sector buyer) relented, and the bank was taken into public hands. Northern Rock's problems proved to be an early indication of the troubles that would soon befall other banks and financial institutions.
Initially the companies affected were those directly involved in home construction and mortgage lending such as Northern Rock and Countrywide Financial, as they could no longer obtain financing through the credit markets. Over 100 mortgage lenders went bankrupt during 2007 and 2008. Concerns that investment bank Bear Stearns would collapse in March 2008 resulted in its fire-sale to JP Morgan Chase. The financial institution crisis hit its peak in September and October 2008. Several major institutions either failed, were acquired under duress, or were subject to government takeover. These included Lehman Brothers, Merrill Lynch, Fannie Mae, Freddie Mac, Washington Mutual, Wachovia, and AIG.[135]
Credit markets and the shadow banking system
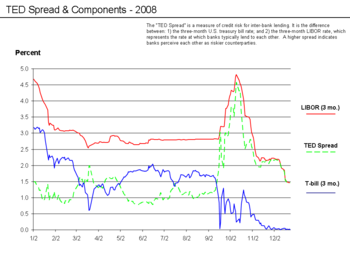
During September 2008, the crisis hit its most critical stage. There was the equivalent of a bank run on the money market mutual funds, which frequently invest in commercial paper issued by corporations to fund their operations and payrolls. Withdrawal from money markets were $144.5 billion during one week, versus $7.1 billion the week prior. This interrupted the ability of corporations to rollover (replace) their short-term debt. The U.S. government responded by extending insurance for money market accounts analogous to bank deposit insurance via a temporary guarantee[136] and with Federal Reserve programs to purchase commercial paper. The TED spread, an indicator of perceived credit risk in the general economy, spiked up in July 2007, remained volatile for a year, then spiked even higher in September 2008,[137] reaching a record 4.65% on October 10, 2008.
In a dramatic meeting on September 18, 2008, Treasury Secretary Henry Paulson and Fed Chairman Ben Bernanke met with key legislators to propose a $700 billion emergency bailout. Bernanke reportedly told them: "If we don't do this, we may not have an economy on Monday."[138] The Emergency Economic Stabilization Act, which implemented the Troubled Asset Relief Program (TARP), was signed into law on October 3, 2008.[139]
Economist Paul Krugman and U.S. Treasury Secretary Timothy Geithner explain the credit crisis via the implosion of the shadow banking system, which had grown to nearly equal the importance of the traditional commercial banking sector as described above. Without the ability to obtain investor funds in exchange for most types of mortgage-backed securities or asset-backed commercial paper, investment banks and other entities in the shadow banking system could not provide funds to mortgage firms and other corporations.[17][70]
This meant that nearly one-third of the U.S. lending mechanism was frozen and continued to be frozen into June 2009.[140] According to the Brookings Institution, the traditional banking system does not have the capital to close this gap as of June 2009: "It would take a number of years of strong profits to generate sufficient capital to support that additional lending volume." The authors also indicate that some forms of securitization are "likely to vanish forever, having been an artifact of excessively loose credit conditions." While traditional banks have raised their lending standards, it was the collapse of the shadow banking system that is the primary cause of the reduction in funds available for borrowing.[141]
Wealth effects

There is a direct relationship between declines in wealth, and declines in consumption and business investment, which along with government spending represent the economic engine. Between June 2007 and November 2008, Americans lost an estimated average of more than a quarter of their collective net worth[citation needed]. By early November 2008, a broad U.S. stock index the S&P 500, was down 45% from its 2007 high. Housing prices had dropped 20% from their 2006 peak, with futures markets signaling a 30-35% potential drop. Total home equity in the United States, which was valued at $13 trillion at its peak in 2006, had dropped to $8.8 trillion by mid-2008 and was still falling in late 2008. Total retirement assets, Americans' second-largest household asset, dropped by 22%, from $10.3 trillion in 2006 to $8 trillion in mid-2008. During the same period, savings and investment assets (apart from retirement savings) lost $1.2 trillion and pension assets lost $1.3 trillion. Taken together, these losses total a staggering $8.3 trillion.[142] Since peaking in the second quarter of 2007, household wealth is down $14 trillion.[143]
Further, U.S. homeowners had extracted significant equity in their homes in the years leading up to the crisis, which they could no longer do once housing prices collapsed. Free cash used by consumers from home equity extraction doubled from $627 billion in 2001 to $1,428 billion in 2005 as the housing bubble built, a total of nearly $5 trillion over the period.[79][80][81] U.S. home mortgage debt relative to GDP increased from an average of 46% during the 1990s to 73% during 2008, reaching $10.5 trillion.[82]
To offset this decline in consumption and lending capacity, the U.S. government and U.S. Federal Reserve have committed $13.9 trillion, of which $6.8 trillion has been invested or spent, as of June 2009.[144] In effect, the Fed has gone from being the "lender of last resort" to the "lender of only resort" for a significant portion of the economy. In some cases the Fed can now be considered the "buyer of last resort."
Economist Dean Baker explained the reduction in the availability of credit this way:
Yes, consumers and businesses can't get credit as easily as they could a year ago. There is a really good reason for tighter credit. Tens of millions of homeowners who had substantial equity in their homes two years ago have little or nothing today. Businesses are facing the worst downturn since the Great Depression. This matters for credit decisions. A homeowner with equity in her home is very unlikely to default on a car loan or credit card debt. They will draw on this equity rather than lose their car and/or have a default placed on their credit record. On the other hand, a homeowner who has no equity is a serious default risk. In the case of businesses, their creditworthiness depends on their future profits. Profit prospects look much worse in November 2008 than they did in November 2007 (of course, to clear-eyed analysts, they didn't look too good a year ago either). While many banks are obviously at the brink, consumers and businesses would be facing a much harder time getting credit right now even if the financial system were rock solid. The problem with the economy is the loss of close to $6 trillion in housing wealth and an even larger amount of stock wealth. Economists, economic policy makers and economic reporters virtually all missed the housing bubble on the way up. If they still can't notice its impact as the collapse of the bubble throws into the worst recession in the post-war era, then they are in the wrong profession.[145]
At the heart of the portfolios of many of these institutions were investments whose assets had been derived from bundled home mortgages. Exposure to these mortgage-backed securities, or to the credit derivatives used to insure them against failure, caused the collapse or takeover of several key firms such as Lehman Brothers, AIG, Merrill Lynch, and HBOS.[146][147][148]
European contagion
The crisis rapidly developed and spread into a global economic shock, resulting in a number of European bank failures, declines in various stock indexes, and large reductions in the market value of equities[149] and commodities.[150]
Both MBS and CDO were purchased by corporate and institutional investors globally. Derivatives such as credit default swaps also increased the linkage between large financial institutions. Moreover, the de-leveraging of financial institutions, as assets were sold to pay back obligations that could not be refinanced in frozen credit markets, further accelerated the solvency crisis and caused a decrease in international trade.
World political leaders, national ministers of finance and central bank directors coordinated their efforts[151] to reduce fears, but the crisis continued. At the end of October 2008 a currency crisis developed, with investors transferring vast capital resources into stronger currencies such as the yen, the dollar and the Swiss franc, leading many emergent economies to seek aid from the International Monetary Fund.[152][153]
Effects on the global economy
Global effects
A number of commentators have suggested that if the liquidity crisis continues, there could be an extended recession or worse.[154] The continuing development of the crisis has prompted in some quarters fears of a global economic collapse although there are now many cautiously optimistic forecasters in addition to some prominent sources who remain negative.[155] The financial crisis is likely to yield the biggest banking shakeout since the savings-and-loan meltdown.[156] Investment bank UBS stated on October 6 that 2008 would see a clear global recession, with recovery unlikely for at least two years.[157] Three days later UBS economists announced that the "beginning of the end" of the crisis had begun, with the world starting to make the necessary actions to fix the crisis: capital injection by governments; injection made systemically; interest rate cuts to help borrowers. The United Kingdom had started systemic injection, and the world's central banks were now cutting interest rates. UBS emphasized the United States needed to implement systemic injection. UBS further emphasized that this fixes only the financial crisis, but that in economic terms "the worst is still to come".[158] UBS quantified their expected recession durations on October 16: the Eurozone's would last two quarters, the United States' would last three quarters, and the United Kingdom's would last four quarters.[159] The economic crisis in Iceland involved all three of the country's major banks. Relative to the size of its economy, Iceland’s banking collapse is the largest suffered by any country in economic history.[160]
At the end of October UBS revised its outlook downwards: the forthcoming recession would be the worst since the early 1980s recession with negative 2009 growth for the U.S., Eurozone, UK; very limited recovery in 2010; but not as bad as the Great Depression.[161]
The Brookings Institution reported in June 2009 that U.S. consumption accounted for more than a third of the growth in global consumption between 2000 and 2007. "The US economy has been spending too much and borrowing too much for years and the rest of the world depended on the U.S. consumer as a source of global demand." With a recession in the U.S. and the increased savings rate of U.S. consumers, declines in growth elsewhere have been dramatic. For the first quarter of 2009, the annualized rate of decline in GDP was 14.4% in Germany, 15.2% in Japan, 7.4% in the UK, 18% in Latvia,[162] 9.8% in the Euro area and 21.5% for Mexico.[163]
Some developing countries that had seen strong economic growth saw significant slowdowns. For example, growth forecasts in Cambodia show a fall from more than 10% in 2007 to close to zero in 2009, and Kenya may achieve only 3-4% growth in 2009, down from 7% in 2007. According to the research by the Overseas Development Institute, reductions in growth can be attributed to falls in trade, commodity prices, investment and remittances sent from migrant workers (which reached a record $251 billion in 2007, but have fallen in many countries since).[164] This has stark implications and has led to a dramatic rise in the number of households living below the poverty line, be it 300,000 in Bangladesh or 230,000 in Ghana.[164]
The World Bank reported in February 2009 that in the Arab World, was far less severely affected by the credit crunch. With generally good balance of payments positions coming into the crisis or with alternative sources of financing for their large current account deficits, such as remittances, Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) or foreign aid, Arab countries were able to avoid going to the market in the latter part of 2008. This group is in the best position to absorb the economic shocks. They entered the crisis in exceptionally strong positions. This gives them a significant cushion against the global downturn. The greatest impact of the global economic crisis will come in the form of lower oil prices, which remains the single most important determinant of economic performance. Steadily declining oil prices would force them to draw down reserves and cut down on investments. Significantly lower oil prices could cause a reversal of economic performance as has been the case in past oil shocks. Initial impact will be seen on public finances and employment for foreign workers.[165]
U.S. economic effects
Real gross domestic product — the output of goods and services produced by labor and property located in the United States—decreased at an annual rate of approximately 6% in the fourth quarter of 2008 and first quarter of 2009, versus activity in the year-ago periods.[166] The U.S. unemployment rate increased to 10.1% by October 2009, the highest rate since 1983 and roughly twice the pre-crisis rate. The average hours per work week declined to 33, the lowest level since the government began collecting the data in 1964.[167][168]
Distribution of wealth - The very rich lost relatively less in the crisis than the remainder of the population, widening the divide between the economic classes. Thus the top 1% who had a share of 34.6% of the nation's wealth in 2007 increased their share to 37.1% by 2009.[169]
Official economic projections
On November 3, 2008, the European Commission at Brussels predicted for 2009 an extremely weak growth of GDP, by 0.1%, for the countries of the Eurozone (France, Germany, Italy, Belgium etc.) and even negative number for the UK (-1.0%), Ireland and Spain. On November 6, the IMF at Washington, D.C., launched numbers predicting a worldwide recession by -0.3% for 2009, averaged over the developed economies. On the same day, the Bank of England and the European Central Bank, respectively, reduced their interest rates from 4.5% down to 3%, and from 3.75% down to 3.25%. As a consequence, starting from November 2008, several countries launched large "help packages" for their economies.
The U.S. Federal Reserve Open Market Committee release in June 2009 stated:
...the pace of economic contraction is slowing. Conditions in financial markets have generally improved in recent months. Household spending has shown further signs of stabilizing but remains constrained by ongoing job losses, lower housing wealth, and tight credit. Businesses are cutting back on fixed investment and staffing but appear to be making progress in bringing inventory stocks into better alignment with sales. Although economic activity is likely to remain weak for a time, the Committee continues to anticipate that policy actions to stabilize financial markets and institutions, fiscal and monetary stimulus, and market forces will contribute to a gradual resumption of sustainable economic growth in a context of price stability.[170] Economic projections from the Federal Reserve and Reserve Bank Presidents include a return to typical growth levels (GDP) of 2-3% in 2010; an unemployment plateau in 2009 and 2010 around 10% with moderation in 2011; and inflation that remains at typical levels around 1-2%.[171]
2010 European sovereign debt crisis
One of the long-term worldwide consequences of the economic breakdown is the 2010 European sovereign debt crisis. This crisis primarily impacted five countries: Greece, Ireland, Portugal, Italy, and Spain. The governments of these nations habitually run large government budget deficits. Other Eurozone countries include: France, Belgium, The Netherlands, Luxembourg, Germany, Finland, Slovenia and Austria. Greece, which at the time of the crisis also suffered from bad governing with widespread corruption and tax evasion, was hit the hardest and was thus targeted by credit rating agencies as the weak link of the Eurozone. Fear that Greece's debt problems would cause lenders to stop lending to it, with the result that Greece would default on its sovereign debt, sparked speculation that such a default would cause lenders to stop loaning money to the other PIGS (Portugal, Ireland/Italy, Greece and Spain) as well, with the result that they would also eventually default on their sovereign debt. A sovereign default by Spain, Portugal, Italy and Greece would result in bank losses so large that almost every bank in Europe would become insolvent due to the now uncollectible outstanding loans to those four countries.
On Friday, May 7, 2010 a long-desired financial aid package for Greece was constructed; however, it was obvious that other states, because of their extremely large debts, would have - or already had - financial difficulties. Therefore, the following Sunday a large group of ministers of Eurozone gathered in Brussels, decided on a mutual financial aid package of €750 billion; and the European Central Bank announced that in the future it would support by explicit monetary help, if necessary, government bonds of the Eurozone countries (which was not allowed before, because of fears of inflation).
Already on May 21, 2010 the German parliament, only with a slight majority, was the first one to accept the new rules.
While this aid package has so far averted a financial panic, the PIGS continue to have difficulties.[172]
Responses to financial crisis
Emergency and short-term responses
The U.S. Federal Reserve and central banks around the world have taken steps to expand money supplies to avoid the risk of a deflationary spiral, in which lower wages and higher unemployment lead to a self-reinforcing decline in global consumption. In addition, governments have enacted large fiscal stimulus packages, by borrowing and spending to offset the reduction in private sector demand caused by the crisis. The U.S. executed two stimulus packages, totaling nearly $1 trillion during 2008 and 2009.[173]
This credit freeze brought the global financial system to the brink of collapse. The response of the U.S. Federal Reserve, the European Central Bank, and other central banks was immediate and dramatic. During the last quarter of 2008, these central banks purchased US$2.5 trillion of government debt and troubled private assets from banks. This was the largest liquidity injection into the credit market, and the largest monetary policy action, in world history. The governments of European nations and the USA also raised the capital of their national banking systems by $1.5 trillion, by purchasing newly issued preferred stock in their major banks.[135] In October 2010, Nobel laureate Joseph Stiglitz explained how the U.S. Federal Reserve was implementing another monetary policy —creating currency— as a method to combat the liquidity trap.[174] By creating $600,000,000,000 and inserting this directly into banks the Federal Reserve intended to spur banks to finance more domestic loans and refinance mortgages. However, banks instead were spending the money in more profitable areas by investing internationally in emerging markets. Banks were also investing in foreign currencies which Stiglitz and others point out may lead to currency wars while China redirects its currency holdings away from the United States.[175]
Governments have also bailed out a variety of firms as discussed above, incurring large financial obligations. To date, various U.S. government agencies have committed or spent trillions of dollars in loans, asset purchases, guarantees, and direct spending. For a summary of U.S. government financial commitments and investments related to the crisis, see CNN - Bailout Scorecard. Significant controversy has accompanied the bailout, leading to the development of a variety of "decision making frameworks", to help balance competing policy interests during times of financial crisis. [176]
Regulatory proposals and long-term responses
United States President Barack Obama and key advisers introduced a series of regulatory proposals in June 2009. The proposals address consumer protection, executive pay, bank financial cushions or capital requirements, expanded regulation of the shadow banking system and derivatives, and enhanced authority for the Federal Reserve to safely wind-down systemically important institutions, among others.[177][178][179] In January 2010, Obama proposed additional regulations limiting the ability of banks to engage in proprietary trading. The proposals were dubbed "The Volcker Rule", in recognition of Paul Volcker, who has publicly argued for the proposed changes.[180][181]
The U.S. Senate passed a regulatory reform bill in May 2010, following the House which passed a bill in December 2009. These bills must now be reconciled. The New York Times provided a comparative summary of the features of the two bills, which address to varying extent the principles enumerated by the Obama administration.[182] For instance, the Volcker Rule against proprietary trading is not part of the legislation, though in the Senate bill regulators have the discretion but not the obligation to prohibit these trades.
A variety of other regulatory changes have been proposed by economists, politicians, journalists, and business leaders to minimize the impact of the current crisis and prevent recurrence. None of the proposed solutions have yet been implemented. These include:
- Ben Bernanke: Establish resolution procedures for closing troubled financial institutions in the shadow banking system, such as investment banks and hedge funds.[183]
- Nassim Nicholas Taleb: "Black Swan Robustness" i.e. Robustness against High Impact Rare Events("Fat Tails").
- Joseph Stiglitz: Restrict the leverage that financial institutions can assume. Require executive compensation to be more related to long-term performance.[184] Re-instate the separation of commercial (depository) and investment banking established by the Glass-Steagall Act in 1933 and repealed in 1999 by the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act.[185]
- Simon Johnson: Break-up institutions that are "too big to fail" to limit systemic risk.[186]
- Paul Krugman: Regulate institutions that "act like banks" similarly to banks.[70]
- Alan Greenspan: Banks should have a stronger capital cushion, with graduated regulatory capital requirements (i.e., capital ratios that increase with bank size), to "discourage them from becoming too big and to offset their competitive advantage."[187]
- Warren Buffett: Require minimum down payments for home mortgages of at least 10% and income verification.[188]
- Eric Dinallo: Ensure any financial institution has the necessary capital to support its financial commitments. Regulate credit derivatives and ensure they are traded on well-capitalized exchanges to limit counterparty risk.[189]
- Raghuram Rajan: Require financial institutions to maintain sufficient "contingent capital" (i.e., pay insurance premiums to the government during boom periods, in exchange for payments during a downturn.).[190]
- HM Treasury: Contingent capital or capital insurance held by the private sector could supplement common equity in times of crisis. There are a variety of proposals (e.g. Raviv 2004, Flannery 2009) under which banks would issue fixed income debt that would convert into capital according to a predetermined mechanism, either bank-specific (related to levels of regulatory capital) or a more general measure of crisis. Alternatively, under capital insurance, an insurer would receive a premium for agreeing to provide an amount of capital to the bank in case of systemic crisis. Following Raviv (2004) proposal, on November 3 Lloyds Banking Group (LBG), Britain’s biggest retail bank, said it would convert existing debt into about £7.5 billion ($12.3 billion) of “contingent core Tier-1 capital” (dubbed CoCos). This is a kind of debt that will automatically convert into shares if the bank’s cushion of equity capital falls below 5%.[191][192]
- A. Michael Spence and Gordon Brown: Establish an early-warning system to help detect systemic risk.[193]
- Niall Ferguson and Jeffrey Sachs: Impose haircuts on bondholders and counterparties prior to using taxpayer money in bailouts. In other words, bondholders with a claim of $100 would have their claim reduced to $80, creating $20 in equity. This is also called a debt for equity swap. This is frequently done in bankruptcies, where the current shareholders are wiped out and the bondholders become the new stockholders, agreeing to reduce the company's debt burden in the process. This is being done with General Motors, for example.[194][195]
- Nouriel Roubini: Nationalize insolvent banks.[196] Reduce mortgage balances to assist homeowners, giving the lender a share in any future home appreciation.[197]
- Adair Turner: In August 2009 in a roundtable interview in Prospect Adair Turner supported the idea of new global taxes on financial transactions, warning that a “swollen” financial sector paying excessive salaries has grown too big for society.[198] Lord Turner’s suggestion that a “Tobin tax” – named after the economist James Tobin – should be considered for financial transactions reverberated around the world.[199][200]
- Let Wall Street Pay for the Restoration of Main Street Bill - in the US only (not international) - Proposed legislation introduced December 3, 2009 - Contained in the US House of Representatives bill entitled "H.R. 4191: Let Wall Street Pay for the Restoration of Main Street Act of 2009"[201][202] It is a proposed piece of legislation that was introduced into the United States House of Representatives to assess a minuscule tax on US Financial market ("Wall Street") securities transactions. If passed, the money it generates will be used to rebuild "Main Street." On the day it was introduced, it had the support of 22 representatives.[203]
- Volcker Rule - (in US) - Endorsed by President Barack Obama on January 21, 2010. At its heart, it is a proposal by US economist Paul Volcker to restrict banks from making speculative investments that do not benefit their customers.[181] Volcker has argued that such speculative activity played a key role in the financial crisis of 2007–2010.
- The Financial Crisis Responsibility Fee is a proposed tax by U.S. President Barack Obama on certain financial firms that would be imposed until the financial firm had paid off all money provided to it under the Troubled Assets Relief Program.[204] It was proposed in January 2010.[205]
- On April 16, 2010, the IMF proposed two types of global taxes on banks: The "Financial Activities Tax" comes in two varieties. The simple version is a straight tax on a bank's gross profits—before deducting compensation. A "financial stability contribution", would initially be at a flat rate, this would eventually be refined so that riskier businesses paid more.[206] The second, more complex tax aims directly at excess bank profit and pay.[207][208] (See also Bank tax)
- Maximum wage is an idea which has been enacted in early 2009 in the United States, where they capped executive pay at $500,000 per year for companies receiving extraordinary financial assistance from the US Taxpayers. [209]
United States Congress response
- On December 11, 2009 - House cleared bill H.R.4173 - Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act of 2009[210]
- On April 15, 2010 - Senate introduced bill S.3217 - Restoring American Financial Stability Act of 2010[211]
- On July 21, 2010.[212] - the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act was enacted.[213]
Media on the crisis
The financial crises have generated many articles and books outside of the scholarly and financial press. Most notable have been articles and books by author William Greider, economist Michael Hudson, author and former bond salesman Michael Lewis, Congressman Ron Paul, author Kevin Phillips, and Rolling Stone national correspondent Matt Taibbi.
In May 2010 premiered Overdose: A Film about the Next Financial Crisis[214], a documentary about how the financial crisis came about and how the solutions that have been applied by many Governments are setting the stage for the next crisis. The film is based on the book Financial Fiasco by Johan Norberg.
In October 2010, a new documentary film about the crisis, Inside Job directed by Charles Ferguson, was released by Sony Pictures Classics.
In addition, a number of blogs experienced phenomenal growth, including The Baseline Scenario by James Kwak and Simon Johnson, Calculated Risk by Bill McBride, and Zero Hedge by "Tyler Durden".
Second wave of the crisis?
The analysis of log-linear oscillations in the gold price dynamics for 2003–2010 conducted by Askar Akayev's research group in 2010 allowed them to forecast a possible start of the second wave of the global crisis in April – June 2011.[215]
See also
- 1929 stock market crash
- 2009 G-20 London summit protests
- 2008 Greek riots
- 2009 Icelandic financial crisis protests
- 2009 May Day protests
- 2009 Moldova civil unrest
- 2009 Riga riot
- 2008–2010 bank failures in the United States
- Causes of the financial crisis of 2007-2010
- Crisis (Marxian)
- Dot-com bubble
- Financial Crisis Responsibility Fee
- Europeans for Financial Reform
- Keynesian resurgence of 2008
- List of acquired or bankrupt banks in the late 2000s financial crisis
- List of acquired or bankrupt United States banks in the late 2000s financial crisis
- List of economic crises
- List of entities involved in 2007–2008 financial crises
- List of largest U.S. bank failures
- Low-Income Countries Under Stress (LICUS) (World Bank program)
- Mark-to-market accounting
- Private equity in the 2000s
- Subprime crisis impact timeline
- Foreclosure crisis
- Late-2000s recession
References
- ^ Ivry, Bob (September 24, 2008). "(quoting Joshua Rosner as stating "It's not a liquidity problem, it's a valuation problem.''". Bloomberg. Retrieved June 27, 2010.
- ^ Three top economists agree 2009 worst financial crisis since great depression; risks increase if right steps are not taken. (February 29, 2009). Reuters. Retrieved 2009-09-30, from Business Wire News database.
- ^ "Brookings-Financial Crisis" (PDF). Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ "Bernanke-Four Questions". Federalreserve.gov. April 14, 2009. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ "Obama-Regulatory Reform Speech June 17, 2009". Whitehouse.gov. June 18, 2009. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ "Roubini-10 Risks to Global Growth". Forbes. May 27, 2009. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ This American Life. "NPR-The Giant Pool of Money-April 2009". Pri.org. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ "World Economic Outlook: Crisis and Recovery, April 2009" (PDF). Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ a b "Declaration of G20". Whitehouse.gov. Retrieved February 27, 2009.
- ^ "Episode 06292007". Bill Moyers Journal. June 29, 2007. PBS.
{{cite episode}}: External link in|transcripturl=|transcripturl=ignored (|transcript-url=suggested) (help) - ^ Lahart, Justin (December 24, 2007). "Egg Cracks Differ In Housing, Finance Shells". The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved July 13, 2008.
- ^ Confer Thomas Philippon: "The future of the financial industry", Finance Department of the New York University Stern School of Business at New York University, link to blog [1]
- ^ "President Bush's Address to Nation". The New York Times. September 24, 2008. Retrieved May 2, 2010.
- ^ "Bernanke-Four Questions About the Financial Crisis". Federalreserve.gov. April 14, 2009. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ Krugman, Paul (March 2, 2009). "Revenge of the Glut". The New York Times.
- ^ "IMF Loss Estimates" (PDF). Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ a b c "Geithner-Speech Reducing Systemic Risk in a Dynamic Financial System". Newyorkfed.org. June 9, 2008. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ "Greenspan-We Need a Better Cushion Against Risk". Financial Times. March 26, 2009. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ http://www.census.gov/const/uspriceann.pdf
- ^ "CSI: credit crunch". The Economist. October 18, 2007. Retrieved May 19, 2008.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|year=/|date=mismatch (help) - ^ Ben Steverman and David Bogoslaw (October 18, 2008). "The Financial Crisis Blame Game - BusinessWeek". BusinessWeek. Retrieved October 24, 2008.
- ^ This American Life. "NPR-The Giant Pool of Money". Pri.org. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ Eavis, Peter (November 25, 2007). "CDO Explained". CNN. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ "Portfolio-CDO Explained". Portfolio.com. September 11, 2008. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ http://www2.standardandpoors.com/spf/pdf/index/CSHomePrice_Release_112555.pdf
- ^ "Economist-A Helping Hand to Homeowners". The Economist. October 23, 2008. Retrieved February 27, 2009.
- ^ "U.S. FORECLOSURE ACTIVITY INCREASES 75 PERCENT IN 2007". RealtyTrac. January 29, 2008. Retrieved June 6, 2008.
- ^ "RealtyTrac Press Release 2008FY". Realtytrac.com. January 15, 2009. Retrieved February 27, 2009.
- ^ "MBA Survey".
- ^ "MBA Survey-Q3 2009". Mbaa.org. November 19, 2009. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ "Federal Reserve Board: Monetary Policy and Open Market Operations". Retrieved May 19, 2008.
- ^ "The Wall Street Journal Online - Featured Article". 2008. Retrieved May 19, 2008.
- ^ "Bernanke-The Global Saving Glut and U.S. Current Account Deficit". Federalreserve.gov. Retrieved February 27, 2009.
- ^ "Chairman Ben S. Bernanke, At the Bundesbank Lecture, Berlin, Germany September 11, 2007: Global Imbalances: Recent Developments and Prospects". Federalreserve.gov. Retrieved May 3, 2009.
- ^ "Fed Historical Data-Fed Funds Rate". Federalreserve.gov. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ John Mastrobattista. "Mastrobattista". National Review. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ Max, Sarah (July 27, 2004). "CNN-The Bubble Question". CNN. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ "Business Week-Is a Housing Bubble About to Burst?". BusinessWeek. July 19, 2004. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ "Economist-When a Flow Becomes a Flood". The Economist. January 22, 2009. Retrieved February 27, 2009.
- ^ Roger C. Altman. "Altman-Foreign Affairs-The Great Crash of 2008". Foreignaffairs.org. Retrieved February 27, 2009.
- ^ "Hearing on Subprime Lending And Securitization And Government Sponsored Enterprises, April 7, 2010" (PDF). 2010. Retrieved October 29, 2010.
- ^ Morgenson, Gretchen (September 26, 2010). "Raters Ignored Proof of Unsafe Loans, Panel Is Told". The New York Times. Retrieved October 28, 2010.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link) - ^ "All Clayton Trending Reports 1st Quarter 2006 - 2nd Quarter 2007" (PDF). 2010. Retrieved October 28, 2010.
- ^ "FDIC-Guidance for Subprime Lending". Fdic.gov. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ "How severe is subprime mess?". msnbc.com. Associated Press. March 13, 2007. Retrieved July 13, 2008.
- ^ Ben S. Bernanke (May 17, 2007). The Subprime Mortgage Market (Speech). Chicago, Illinois. Retrieved July 13, 2008.
- ^ NY Times-The Reckoning-Agency 04 Rule Lets Banks Pile on Debt
- ^ NYT-The Reckoning-Pressured to Take More Risk, Fannie Reached Tipping Point
- ^ "Harvard Report-State of the Nation's Housing 2008 Report" (PDF). Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ The Reckoning - Agency 04 Rule Lets Banks Pile on Debt, New York Times
- ^ Chicago Federal Reserve Letter August 2007[dead link]
- ^ "Bernanke-Mortgage Delinquencies and Foreclosures May 2008". Federalreserve.gov. May 5, 2008. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ "Mortgage Bankers Association - National Delinquency Survey". Mortgagebankers.org. May 28, 2009. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ Wallison, Peter J. (December 9, 2008). "''What Got Us Here?'', December 2008". Aei.org. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ Holmes, Steven A. (September 30, 1999). "Fannie Mae Eases Credit To Aid Mortgage Lending". The New York Times. pp. section C page 2. Retrieved March 8, 2009.
- ^ "''The Community Reinvestment Act After Financial Modernization'', April 2000". Ustreas.gov. April 15, 2000. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ Robert Gordon, (April 7, 2008). "'Did Liberals Cause the Sub-Prime Crisis?'". American Prospect. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: extra punctuation (link) - ^ Sowell, Thomas. "The Housing Boom & Bust". (New York: Best Books, 2009). Page 66, 2nd paragraph. Retrieved on May 18, 2010.
- ^ "Portfolio-Michael Lewis-"The End"-December 2008". Portfolio.com. September 11, 2008. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ Krugman, Paul (January 7, 2010). "CRE-ative destruction". New York Times. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ "Letter from the Comptroller of the Currency Regarding Predatory Lending". Banking.senate.gov. Retrieved November 11, 2009.
- ^ "BofA Modifies 64,000 Home Loans as Part of Predatory Lending Settlement | Debt Relief Blog". Thinkdebtrelief.com. May 25, 2009. Retrieved November 11, 2009.
- ^ a b c Road to Ruin: Mortgage Fraud Scandal Brewing May 13, 2009 by American News Project hosted by The Real News
- ^ Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation, History of the Eighties - Lessons for the Future, Vol. 1. December 1997.
- ^ Leibold, Arthur. "Some Hope for the Future After a Failed National Policy for Thrifts". In Barth, James R.; Trimbath, Susanne; Yago, Glenn (eds.). The Savings and Loan Crisis: Lessons from a Regulatory Failure. Milken Institute. pp. 58–59. ISBN 1402078714. (further references: Strunk; Case (1988). Where Deregulation Went Wrong: A Look at the Causes Behind the Savings and Loan Failures in the 1980s. U.S. League of Savings Institutions. pp. 14–16. ISBN 9780929097329.)
- ^ Stiglitz, Joseph E. (October 20, 2009). "Stiglitz-Capitalist Fools". Vanityfair.com. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ Ekelund, Robert (September 4, 2008). "More Awful Truths About Republicans". Ludwig von Mises Institute. Retrieved September 7, 2008.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Labaton, Stephen (September 27, 2008). "SEC Concedes Oversight Flaws". The New York Times. Retrieved May 2, 2010.
- ^ Labaton, Stephen (October 3, 2008). "The Reckoning". The New York Times. Retrieved May 2, 2010.
- ^ a b c d Krugman, Paul (2009). The Return of Depression Economics and the Crisis of 2008. W.W. Norton Company Limited. ISBN 978-0-393-07101-6.
- ^ "Bloomberg-Bank Hidden Junk Menaces $1 Trillion Purge". Bloomberg. March 25, 2009. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ "Bloomberg-Citigroup SIV Accounting Tough to Defend". Bloomberg. October 24, 2007. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ Healy, Paul M. & Palepu, Krishna G.: "The Fall of Enron" - Journal of Economics Perspectives, Volume 17, Number 2. (Spring 2003), p.13
- ^ Greenspan, Alan (February 21, 1997). Government regulation and derivative contracts (Speech). Coral Gables, FL. Retrieved October 22, 2009.
{{cite speech}}: More than one of|author=and|last=specified (help)[dead link] - ^ Summers, Lawrence (1999-11). "Over-the-Counter Derivatives Markets and the Commodity Exchange Act: Report of The President's Working Group on Financial Markets" (PDF): 1. Retrieved July 20, 2009.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Cite journal requires|journal=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ "Forbes-Geithner's Plan for Derivatives". Forbes. May 18, 2009. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ "The Economist-Derivatives-A Nuclear Winter?". The Economist. September 18, 2008. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ "BBC-Buffet Warns on Investment Time Bomb". BBC News. March 4, 2003. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ a b "Greenspan Kennedy Report - Table 2 - Sources and Uses of Equity Extracted from Homes" (PDF). Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ a b "Equity extraction - Charts". Seekingalpha.com. April 25, 2007. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ a b "Reuters-Spending Boosted by Home Equity Loans". Reuters.com. April 23, 2007. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ a b Barr, Colin (May 27, 2009). "Fortune-The $4 trillion housing headache". CNN. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ "The End of the Affair". Economist. October 30, 2008. Retrieved February 27, 2009.
- ^ "FT-Wolf Japan's Lessons". Financial Times. February 17, 2009. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ Labaton, Stephen (October 3, 2008). "Agency's '04 Rule Let Banks Pile Up New Debt, and Risk". The New York Times. Retrieved May 2, 2010.
- ^ "AEI-The Last Trillion Dollar Commitment". Aei.org. Retrieved February 27, 2009. American Enterprise Institute is a conservative organization with a right- of-center political agenda .
- ^ "Bloomberg-U.S. Considers Bringing Fannie & Freddie Onto Budget". Bloomberg. September 11, 2008. Retrieved February 27, 2009.
- ^ "FT Martin Wolf - Reform of Regulation and Incentives". Financial Times. June 23, 2009. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ "paulw's Blog | Talking Points Memo | The power of belief". Tpmcafe.talkingpointsmemo.com. March 2, 2009. Retrieved November 11, 2009.
- ^ "Bloomberg-Credit Swap Disclosure Obscures True Financial Risk". Bloomberg. November 6, 2008. Retrieved February 27, 2009.
- ^ Byrnes, Nanette (March 17, 2009). "Business Week-Who's Who on AIG List of Counterparties". BusinessWeek. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ Regnier, Pat (February 27, 2009). "New theories attempt to explain the financial crisis - Personal Finance blog - Money Magazine's More Money". Moneyfeatures.blogs.money.cnn.com. Retrieved November 11, 2009.
- ^ a b c Salmon, Felix (February 23, 2009). "Recipe for Disaster: The Formula That Killed Wall Street". Wired Magazine. No. 17.03. Retrieved March 8, 2009.
- ^ Floyd Norris (2008). News Analysis: Another Crisis, Another Guarantee, The New York Times, November 24, 2008
- ^ Soros, George (January 22, 2008). "The worst market crisis in 60 years". Financial Times. London, UK. Retrieved March 8, 2009.
- ^ Calomiris, Charles (Spring 2009). "The Subprime Turmoil: What's Old, What's New, and What's Next" (PDF). Journal of Structured Finance. 15 (1). Institutional Investor Journals: 6–52. doi:10.3905/JSF.2009.15.1.006. Retrieved August 19, 2010.
{{cite journal}}: Check|authorlink=value (help); External link in|authorlink= - ^ Lipton, A., and A. Rennie, (Editors) (2007), Credit Correlation: Life after Copulas, World Scientific
{{citation}}:|first=has generic name (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Donnelly, C, Embrechts, P, (2010), The devil is in the tails: actuarial mathematics and the subprime mortgage crisis, ASTIN Bulletin 40(1), 1-33
{{citation}}: CS1 maint: extra punctuation (link) CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Brigo, D, Pallavicini, A, and Torresetti, R, (2010), Credit Models and the Crisis: A Journey into CDOs, Copulas, Correlations and dynamic Models, Wiley and Sons
{{citation}}: CS1 maint: extra punctuation (link) CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Search Site. "Nicole Gelinas-Can the Fed's Uncrunch Credit?". City-journal.org. Retrieved February 27, 2009.
- ^ Brookings Institute - U.S. Financial and Economic Crisis June 2009 PDF Page 14
- ^ Testimony of Mark Zandi to Financial Crisis Inquiry Commission-January 2010
- ^ "Light Crude Oil Chart". Futures.tradingcharts.com. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ Conway, Edmund (May 26, 2008). "Soros - Rocketing Oil Price is a Bubble". The Daily Telegraph. London. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ "Mises Institute-The Oil Price Bubble". Mises.org. June 2, 2008. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ Tom Therramus, (editor, Gail the Actuary) - Was Volatility in the Price of Oil a Cause of the 2008 Financial Crisis?
- ^ "Energy Market Manipulation and Federal Enforcement Regimes". Digitalcommons.law.umaryland.edu. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ "ICE History". Digitalcommons.law.umaryland.edu. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ "Historical Copper Prices, Copper Prices History". Dow-futures.net. January 22, 2007. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ "Business | Miner BHP to lay off 6,000 staff". BBC News. January 21, 2009. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ "(AU) - Mincor's result reflects a return to better days for sulphide nickel". Proactive Investors. February 18, 2010. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ a b Irwin SH, Sanders DR. (2010). The Impact of Index and Swap Funds on Commodity Futures Markets. OECD Working Paper. doi:10.1787/5kmd40wl1t5f-en
- ^ McMurty, John (1999). The Cancer Stage of Capitalism. ISBN 0-7453-1347-7.
- ^ "Samir AMIN". Ismea.org. August 22, 1996. Retrieved November 11, 2009.
- ^ Amin, Samir (November 23, 2008). "Financial Collapse, Systemic Crisis?". Globalresearch.ca. Retrieved November 11, 2009.
- ^ "The Financialization of Capital and the Crisis". Monthly Review. Retrieved November 11, 2009.
- ^ Bogle, John (2005). The Battle for the Soul of Capitalism. Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0-300-11971-8.
- ^ "Battle for the Soul of Capitalism". Video.google.com. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ Reich, Robert (July 25, 2008). "The Heart of the Economic Mess". Retrieved June 28, 2010.
- ^ Bezemer, Dirk J (June 2009). ""No One Saw This Coming": Understanding Financial Crisis Through Accounting Models". Munich Personal RePEc Archive. Retrieved October 23, 2009.
- ^ "Recession in America," The Economist, November 15, 2007.
- ^ Richard Berner, "Perfect Storm for the American Consumer," Morgan Stanley Global Economic Forum, November 12, 2007.
- ^ Kabir Chibber, "Goldman Sees Subprime Cutting $2 Trillion in Lending," Bloomberg.com, November 16, 2007.
- ^ Coy, Peter (April 16, 2009). "Businessweek Magazine". BusinessWeek. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ "Why Economists Failed to Predict the Financial Crisis - Knowledge@Wharton". Knowledge.wharton.upenn.edu. Retrieved November 11, 2009.
- ^ "Dr. Doom", By Stephen Mihm, August 15, 2008, New York Times Magazine
- ^ Emma Brockes (January 24, 2009). "Emma Brockes, "He Told Us So," The Guardian, January 24, 2009". Guardian. London. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ "John Cochrane's Response to Paul Krugman: Full Text « Modeled Behavior". Modeledbehavior.com. September 11, 2009. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ http://www.huffingtonpost.com/pablo-triana/why-nassim-taleb-is-the-t_b_263194.html
- ^ http://www.fooledbyrandomness.com/imbeciles.htm
- ^ Nocera, Joe (January 4, 2009). "Risk Mismanagement". The New York Times.
- ^ Brooks, David (October 28, 2008). "The Behavioral Revolution". The New York Times.
- ^ "Bloomberg-U.S. European Bank Writedowns & Losses-November 5, 2009". Reuters.com. November 5, 2009. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ HM Treasury, Bank of England and Financial Services Authority (September 14, 2007). "News Release: Liquidity Support Facility for Northern Rock plc".
- ^ a b Roger C. Altman. "Altman - The Great Crash". Foreign Affairs. Retrieved February 27, 2009.
- ^ Gullapalli, Diya (September 20, 2008). "NYT". The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ "3 year chart" TED spread Bloomberg.com "Investment Tools"
- ^ NYT The Reckoning - As Crisis Spiraled, Alarm Led to Action
- ^ Raum, Tom (October 3, 2008) Bush signs $700 billion bailout bill[dead link]. NPR
- ^ Search Site. "Nicole Gelinas-Can the Fed's Uncrunch Credit?". City-journal.org. Retrieved February 27, 2009.
- ^ June 15, 2009 — (June 15, 2009). "Brookings Institute - U.S. Financial and Economic Crisis June 2009 PDF Page 14". Brookings.edu. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ Roger C. Altman. "The Great Crash, 2008 - Roger C. Altman". Foreign Affairs. Retrieved February 27, 2009.
- ^ Americans' wealth drops $1.3 trillion. CNNMoney.com. June 11, 2009
- ^ "Government Support for Financial Assets and Liabilities Announced in 2008 and Soon Thereafter ($ in billions). Page 7. FDIC Supervisory Insights Summer 2009" (PDF). Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ Baker, Dean (November 29, 2008). "It's Not the Credit Crisis, Damn It!". Retrieved March 8, 2009.
- ^ Uchitelle, Louis (September 18, 2008). "Pain Spreads as Credit Vise Grows Tighter". The New York Times. pp. A1. Retrieved March 8, 2009.
- ^ "Lehman Files for Bankruptcy; Merrill Is Sold" article by Andrew Ross Sorkin in The New York Times September 14, 2008
- ^ "Lloyds Bank Is Discussing Purchase of British Lender" article by Julia Werdigier in The New York Times September 17, 2008
- ^ Norris, Floyd (October 24, 2008). "United Panic". The New York Times. Retrieved October 24, 2008.
{{cite news}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ Evans-Pritchard, Ambrose (July 25, 2007). "Dollar tumbles as huge credit crunch looms". The Daily Telegraph. London: Telegraph Media Group Limited. Retrieved October 15, 2008.
{{cite news}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ Central banks act to calm markets, The Financial Times, September 18, 2008
- ^ Landler, Mark (October 23, 2008). "West Is in Talks on Credit to Aid Poorer Nations". The New York Times. Retrieved October 24, 2008.
{{cite news}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ Fackler, Martin (October 23, 2008). "Trouble Without Borders". The New York Times. Retrieved October 24, 2008.
{{cite news}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ Goodman, Peter S. (September 26, 2008). "Credit Enters a Lockdown". The New York Times. pp. A1. Retrieved March 8, 2009.
- ^ Cho, David; Appelbaum, Binyamin (October 7, 2008). "Unfolding Worldwide Turmoil Could Reverse Years of Prosperity". The Washington Post. pp. A01. Retrieved March 8, 2009.
- ^ Since 1934, FDIC has closed more than 3,500 banks. More than 82% failed during the savings-and-loan crisis (chart)."Bank on this: bank failures will rise in next year". Associated Press. October 5, 2008.[dead link]
- ^ UBS AG. "Recession". There is no alternative. Daily roundup for October 6, 2008. Retrieved October 12, 2008. 'global growth at 2.2% yoy (previously 2.8%). The IMF brands 2.5% yoy a "recession".' 'global collapse is inevitable' ... 'at least two years before we can talk of a normalisation in economic activity'
- ^ UBS AG. A plan to save the world. Daily roundup for October 9, 2008. Retrieved October 13, 2008. "The actions yesterday can not stop a significant economic downturn."
- ^ UBS AG. Fears of recession loom. Daily roundup for October 9, 2008. Retrieved October 17, 2008. "short by historical standards"
- ^ "Cracks in the crust". The Economist. December 11, 2008. Retrieved November 11, 2009.
- ^ UBS AG.The IMF in March, 2009 forecast that it would be the first occasion since the great depression that the world economy as a whole would contract. Be afraid. Be very afraid. Daily roundup for October 31, 2008. Retrieved November 2, 2008. "NEGATIVE growth in 2009 for the US, UK, Euro area. Japan is the fastest growing G7 economy at 0.1% growth, Followed close behind by Canada with .098% growth. Global growth in 2009 forecast at 1.3%."
- ^ "Untold Stories: Latvia: Sobering Lessons in Unregulated Lending". Pulitzercenter.typepad.com. May 18, 2009. Retrieved November 11, 2009. [dead link]
- ^ Baily, Martin Neil & Elliott, Douglas J. (June 15, 2009). "The U.S. Financial and Economic Crisis: Where Does It Stand and Where Do We Go From Here?". Brookings.edu. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Dirk Willem te Velde(2009) Briefing Paper 54 - The global financial crisis and developing countries: taking stock, taking action. London: Overseas Development Institute
- ^ Dina Elnaggar. (February 1, 2009). "Update on the Impact of the Global Financial Crisis on Arab Countries". World Bank. Retrieved November 5, 2010.
- ^ "BEA Press Releases". Bea.gov. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ "BLS-Historical Unemployment Rate Table". Data.bls.gov. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ Herbst, Moira (July 10, 2009). "Business Week-Unemployed lose with hour and wage cuts". BusinessWeek. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ Matt Taibbi. Griftopia. Spiegel & Grau, 2010. p. 12. ISBN 978-0-385-52995-2.
- ^ "FOMC Statement June 24, 2009". Federalreserve.gov. June 24, 2009. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ "Minutes of the FOMC April 2009" (PDF). Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ http://www.ibtimes.com/articles/35240/20100713/portugal-cut-by-all-3-agencies-faces-serious-challenges.htm Moody's followed suit on Tuesday and became the third and final international ratings agency to cut the sovereign debt of Portugal, which, like other PIGS (Portugal, Italy, Greece, Spain) countries, faces formidable economic and fiscal challenges.
- ^ "BBC - Stimulus Package 2009". BBC News. February 14, 2009. Retrieved February 27, 2009.
- ^ Stiglitz, Joseph (November 5, 2010). "New $600B Fed Stimulus Fuels Fears of US Currency War". Democracy Now. Retrieved November 5, 2010.
- ^ Wheatley, Jonathan; Peter Garnham (November 5, 2010). "Brazil in 'currency war' alert". Financial Times. Retrieved November 5, 2010.
- ^ Tim Wafa (J.D.). "When Policies Collide: A Decision Making Framework for Financial System Overhaul in the 21st Century". Social Science Research Network (SSRN), October 2010.
- ^ "Remarks of the President on Regulatory Reform | The White House". Whitehouse.gov. June 17, 2009. Retrieved November 11, 2009.
- ^ View all comments that have been posted about this article. (June 14, 2009). "Geithner & Summers - A New Financial Foundation". Washington Post. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ "Treasury Department Report - Financial Regulatory Reform". Financialstability.gov. March 22, 2010. Retrieved May 1, 2010. [dead link]
- ^ Uchitelle, Louis (January 22, 2010), "Glass-Steagall vs. the Volcker Rule", The New York Times, retrieved January 27, 2010
- ^ a b David Cho, and Binyamin Appelbaum (January 22). "Obama's 'Volcker Rule' shifts power away from Geithner". The Washington Post. Retrieved February 13, 2010.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ New, The (May 20, 2010). "New York Times-Major Parts of the Financial Regulation Overhaul-May 2010". The New York Times. Retrieved June 27, 2010.
- ^ "Bernanke Remarks". Federalreserve.gov. December 1, 2008. Retrieved February 27, 2009.
- ^ "Stigliz Recommendations". CNN. September 17, 2008. Retrieved May 2, 2010.
- ^ Stiglitz, Joseph E. (October 20, 2009). "Stiglitz - Vanity Fair - Capitalist Fools". Vanity Fair. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ Jackson, Maya (April 22, 2009). "WSJ-Economists Seek Breakup of Big Banks". The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ "Greenspan-We need a better cushion against risk". Financial Times. March 26, 2009. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ "Warren Buffet-2008 Shareholder's Letter Summary". Reuters.com. February 28, 2009. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ "Dinallo-We Modernized Ourselves Into This Ice Age". Financial Times. March 30, 2009. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ "The Economist-Rajan-Cycle Proof Regulation". The Economist. April 8, 2009. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ "VOX-Portes-Risk, reward and responsibility: The financial sector and society". Voxeu.org. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ "Alon Raviv, Bank Stability and Market Discipline: Debt-for-Equity Swap versus Subordinated Notes". Papers.ssrn.com. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ "PIMCO-Lessons from the Crisis". Pimco.com. November 26, 2008. Retrieved February 27, 2009. [dead link]
- ^ "Jeffrey Sachs-Our Wall Street Besotted Public Policy". Realclearpolitics.com. March 31, 2009. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ "FT-Ferguson-Beyond the Age of Leverage". Financial Times. February 2, 2009. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ "Roubini-Charlie Rose Interview". Charlierose.com. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ "Risks to Global Growth". Forbes. May 27, 2009. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ^ "How to tame global finance". Prospect Magazine.
- ^ Daniel Pimlott (November 8, 2009). "Q & A on Tobin tax". The Financial Times. Retrieved December 11, 2009.
- ^ George Parker, Daniel Pimlott, Kate Burgess, Lina Saigol and Jim Pickard (August 28, 2009). "Turner relishes role on City front line". Financial Times. Retrieved December 31, 2009.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Matt Cover (December 7, 2009). "Pelosi Endorses 'Global' Tax on Stocks, Bonds, and other Financial Transactions". CNSNews.com. Retrieved February 13, 2010. [dead link]
- ^ GovTrack - A civic project to track Congress (December 3, 2009). "Text of H.R. 4191: Let Wall Street Pay for the Restoration of Main Street Act of 2009". GovTrack. Retrieved February 13, 2010.
- ^ "Defazio introduces legislation invoking wall street 'transaction tax'". Website of Peter DeFazio. Retrieved February 13, 2010.
- ^ http://www.whitehouse.gov/the-press-office/president-obama-proposes-financial-crisis-responsibility-fee-recoup-every-last-penn
- ^ Richard T. Page, "Foolish Revenge or Shrewd Regulation? Financial-Industry Tax Law Reforms Proposed in the Wake of the Financial Crisis?" 85 Tul. L. Rev. 191, 197-98, 205-14 (2010).
- ^ "IMF proposes two big new bank taxes to fund bail-outs". BBC. April 21, 2010. Retrieved April 22, 2010.
- ^ Peter Thal Larsen (April 23, 2010). "Low-FAT diet". Reuters Breaking News. Retrieved April 23, 2010.
- ^ International Monetary Fund (April 16, 2010). "A Fair and Substantial Contribution by the Financial Sector Interim Report for the G-20". International Monetary Fund; Excerpt and LINK TO FULL REPORT as a PDF - republished online by Global Print Monitor on April 22, 2010. Retrieved June 25, 2010.
- ^ Dietl, H., Duschl, T. and Lang, M. (2010): "Executive Salary Caps: What Politicians, Regulators and Managers Can Learn from Major Sports Leagues", University of Zurich, ISU Working Paper Series No. 129.
- ^ http://www.opencongress.org/bill/111-h4173/show
- ^ http://www.opencongress.org/bill/111-s3217/show
- ^ "Bill Summary & Status - 111th Congress (2009 - 2010) - H.R.4173 - All Information - THOMAS (Library of Congress)". Library of Congress. Retrieved July 22, 2010.
- ^ http://www.marketwatch.com/story/senate-defeats-filibuster-threat-on-bank-bill-2010-07-15 Bank-reform bill sent to Obama
- ^ http://www.cato.org/events/100517screening.html
- ^ Askar Akayev, Alexey Fomin, Sergey Tsirel, and Andrey Korotayev. Log-Periodic Oscillation Analysis Forecasts the Burst of the “Gold Bubble” in April – June 2011 // Structure and Dynamics 4/3 (2010): 1-11. For a more technically sophisticated (but less easily understandable for a general audience) treatment of this subject see Log-Periodic Oscillation Analysis and Possible Burst of the "Gold Bubble" in April - June 2011 by Sergey Tsirel, Askar Akayev, Alexey Fomin, and Andrey Korotayev.
The initial articles and some subsequent material were adapted from the Wikinfo article Financial crisis of 2007-2008 released under the GNU Free Documentation License Version 1.2
External links and further reading
- Times of Crisis - Reuters: Multimedia interactive charting the year of global change
- PBS Frontline - Inside the Meltdown
- Economic Crisis and Stimulus from UCB Libraries GovPubs
- Credit Crisis—The Essentials topic page from The New York Times
- Fengbo Zhang (2008): 1. Perspective on the United States Sub-prime Mortgage Crisis , 2. Accurately Forecasting Trends of the Financial Crisis , 3. Stop Arguing about Socialism versus Capitalism .
- NYU Stern on Finance - Understanding the Financial Crisis
- How nations around the world are responding to the global financial crisis from PBS
- In depth: Global financial crisis from the Financial Times
- Timeline: Global credit crunch Published in BBC News on October 6, 2008.
- ILO Job Crisis Observatory
- Financial Crisis-IMF
- Financial Crisis-World Bank Group
- Global Financial Crisis-Asian Development Bank
- High Anxieties - The Mathematics of Chaos (2008) BBC documentary by David Malone looking at how chaos theory can help explain the roots of the financial crisis.
- Askar Akayev's research group predicts the start of the second wave of the crisis in April – June 2011.
- Articles with minor POV problems from October 2010
- Use mdy dates from August 2010
- Financial crisis of 2007–2010
- 2000s economic history
- 2010s economic history
- 2007 in economics
- 2008 in economics
- 2009 in economics
- 2010 in economics
- Economic bubbles
- Economy of the United States
- Financial crises
- Presidency of Barack Obama
- Presidency of George W. Bush
- Stock market crashes
