Nickname
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
A nickname is a substitute for the proper name of a familiar person, place or thing. Commonly used to express affection, it is a form of endearment and amusement. It can also be used to express defamation of character, particularly by school bullies. As a concept, it is distinct from both pseudonym and stage name, and also from a title (for example, City of Fountains), although there may be overlap in these concepts. A hypocoristic is a nickname of affection between those in love or with a close emotional bond. "Moniker" is a synonym.[1]
Etymology
The compound word ekename, literally meaning "additional name", was attested as early as 1303.[2] This word was derived from the Old English phrase eac "also",[3] related to eacian "to increase".[4] By the 15th century, the misdivision of the syllables of the phrase "an ekename" led to its rephrasing as "a nekename".[5] Though the spelling has changed, the pronunciation and meaning of the word have remained relatively stable ever since.
Conventions in various languages
English nicknames are generally represented in quotes between the bearer's first and last names (e.g., Dwight David "Ike" Eisenhower, Daniel Lamont "Bubba" Franks, etc.). However, it is also common for the nickname to be identified after a comma following the full real name or later in the body of the text, such as in an obituary (e.g., Frankie Frisch, "The Fordham Flash"). Any middle name is generally omitted, especially in speech. Like English, German uses (German-style) quotation marks between the first and last names (e.g., Andreas Nikolaus "Niki" Lauda). Other languages may use other conventions; for example, Italian writes the nickname after the full name followed by button 'called' (e.g., Salvatore Schillaci to Totò), in Spanish the nickname is written in formal contexts at the end in quotes following alias (e.g. Alfonso Tostado, alias «el Abulense»), in Portuguese the nickname is written after the full name followed by vulgo (e.g. Edson Arantes do Nascimento, vulgo Pelé) and Slovenian represents nicknames after a dash or hyphen (e.g., Franc Rozman – Stane). The latter may confuse because it resembles an English convention sometimes used for married and maiden names.
Uses in various societies
In Viking societies, many people had hit, viðrnefni, or kenningarnöfn (Old Norse terms for nicknames)[6] which were used in addition to, or instead of the first name. In some circumstances, the giving of a nickname had a special status in Viking society in that it created a relationship between the name maker and the recipient of the nickname, to the extent that the creation of a nickname also often entailed a formal ceremony and an exchange of gifts known in Old Norse as naffness ('fastening a name').
In Indian society, for example, generally people have at least one nickname (call name or affection name) and these affection names are generally not related to the person's proper name.[citation needed]
In England, some nicknames are traditionally associated with a person's surname. A man with the surname 'Clark' will be nicknamed 'Nobby': the surname 'Miller' will have the nickname 'Dusty' (alluding to the flour dust of a miller at work): the surname 'Adams' has the nickname 'Nabby'. There are several other nicknames linked traditionally with a person's surname, including Chalky White, Bunny Warren, Tug Wilson, and Spud Baker. Other English nicknames allude to a person's origins. A Scotsman may be nicknamed 'Jock', an Irishman 'Paddy' (alluding to Saint Patrick, the patron saint of Ireland) or 'Mick' (alluding to the preponderance of Roman Catholicism in Ireland), and a Welshman may be nicknamed 'Taffy'. Some nicknames referred ironically to a person's physical characteristics, such as 'Lofty' for a short person, or 'Curly' for a bald man. Traditional English nicknaming - usually for men rather than women - was common through the first half of the 20th century, and was frequently used in the armed services during World War I and World War II, but has become less common since then.[citation needed]
In Chinese culture, nicknames are frequently used within a community among relatives, friends and neighbours. A typical southern Chinese nickname often begins with a "阿" followed by another character, usually, the last character of the person's given name.[7] For example, Taiwanese politician Chen Shui-bian (陳水扁) is sometimes referred as "阿扁" (A-Bian). In many Chinese communities of Southeast Asia, nicknames may also connote one's occupation or status. For example, the landlord might be known simply as Towkay (simplified Chinese: 头家; traditional Chinese: 頭家; Pe̍h-ōe-jī: thâu-ke) Hokkien for "boss") to his tenants or workers while a bread seller would be called "Mianbao Shu" 面包叔 (literally, Uncle Bread). Among Cantonese-speaking communities, the character "仔" (pronounced "Zai") may be used in a similar context of "Junior" in Western naming practices.
Computing
In the context of information technology, a nickname (usually called a nick) is a common synonym for the screen name or handle of a user. In computer networks it has become a common practice for every person to also have one or more nicknames for pseudonymity, to avoid ambiguity, or simply because the natural name or technical address would be too long to type or take too much space on the screen.
People

Nicknames are usually applied to a person and they are not always chosen by the recipient themselves. Some nicknames are derogatory name calls.
Abbreviation or modification
A nickname can be a shortened or modified variation on a person's real name.
- Contractions of longer names: Margaret to Greta.
- Initials: Using the first letters of a person's first and middle/last name, e.g. "DJ" for Daniel James
- Dropping letters: With many nicknames, one or more letters, often R, are dropped: Fanny from Frances, Walt from Walter.
- Phonetic spelling: Sometimes a nickname is created through the phonetic spelling of a name: Len from Leonard.
- Letter swapping: During the middle ages, the letter R would often be swapped for either L or D: Hal from Harry; Molly from Mary; Sadie from Sarah; Hob, Dob, Rob, Bob, and Nob from Robert; Rick, Dick, and Hick from Richard; Bill from Will (which in turn comes from William); and Peg and Meg from Margaret.
- In 19th-century frontier United States, Mary and Molly were often given the nickname Polly.
Name portions
- Front of a name. Sometimes a nickname can come from the beginning of a given name: Chris from Christopher/Christina; Ed from Edward, Edmond, Edgar or Edwin, Iz or Izzy from Isaac, Isaiah, Isidore, Isabel, or Isabella; Joe or Jo from Joseph, Josephine, or Joanna.
- End of name: Drew from Andrew; Xander from Alexander; Enzo or Renzo from Lorenzo; Beth from Elizabeth; Bel, Bell, Bella or Belle from Isabelle/Isabella
- Middle of name: Liz from Elizabeth; Tori from Victoria; Del or Della from Adelaide
- Addition of diminutives: Before the 17th century, most nicknames had the diminutive ending "-in" or "-kin", where the ending was attached to the first syllable: Watkin for Walter via Wat-kin; Hobkin from Robert via Hob-kin; or Thompkins from Thomas via Thom-Kin. While most of these have died away, a few remain, such as Robin (Rob-in, from Robert), Hank (Hen-Kin from Henry), Jack (Jan-kin from John), and Colin (Col-in from Nicolas).
- Many nicknames drop the final one or two letters and add ether ie/ee/y as a diminutive ending: Davy from David, Charlie from Charles, Mikey from Michael, Jimmy from James and Marty from Martin.
- Initialization, which forms a nickname from a person's initials: A.C. Slater from Albert Clifford Slater, or Dubya for George W. Bush, a Texan pronunciation of the name of the letter 'W', President Bush's middle initial.
- Nicknames are sometimes based on a person's last name ("Tommo" for Bill Thompson, "Campo" for David Campese) or a combination of first and last name such as "A-Rod" for Alex Rodriguez)
- Loose ties to a person's name with an attached suffix: Gazza for English footballer Paul Gascoigne (though used more widely in Australia for Gary) and similar "zza" forms (Hezza, Prezza, etc.) for other prominent personalities whose activities are frequently reported in the British press. (See also Oxford "-er" for a similar but wider phenomenon.)
- Use of the second name
- Combination of the first and middle name, or variations of a person's first and middle name. For example, a person may have the name Mary Elizabeth but has the nickname "Maz" or "Miz" by combining Mary and Liz.
- Doubling of part of a first name. For example, forming "NatNat" from Nathan/Natasha or "JamJam" from James.
Relationship
A nickname may refer to the relationship with the person. This is a term of endearment.
- In Japanese culture, Japanese honorifics are designed so that a term of endearment conveys the exact status of the relationship between two people. However, the recipient of the honorific is allowed to restrict the use when used by a certain person.
Geography
Titles of geographical places
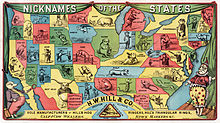
Many geographical places have titles, or alternative names, which have positive implications. Paris, for example, is the "City of Light", Venice is "La Serenissima", and New Jersey is the "Garden State". It is not correct to call these titles nicknames; these alternative names are often used to boost the status of such places, contrary to the usual role of a nickname. Many places or communities, particularly in the US, adopt titles because they can help in establishing a civic identity, help outsiders recognize a community or attract people to a community, promote civic pride, and build community unity.[8] Titles and slogans that successfully create a new community "ideology or myth"[9] are also believed to have economic value.[8] Their economic value is difficult to measure,[8] but there are anecdotal reports of cities that have achieved substantial economic benefits by "branding" themselves by adopting new slogans.[9]
By contrast, older city nicknames may be critical: London is still occasionally referred to as "The Smoke" in memory of its notorious "pea-souper" smogs (smoke-filled fogs) of the 19th and early 20th centuries, and Edinburgh was "Auld Reekie" for the same reason, as countless coal fires polluted its atmosphere.
Collective nicknames of inhabitants of a geographical place
Besides or replacing the demonym, some places have collective nicknames for their inhabitants. Many examples of this practice are found in Wallonia and in Belgium in general, where such a nickname is referred to in French as "blason populaire".
Treaties
In International relations, a typical moniker - as for UE - has "based on a city name (the Treaty of London or the Treaty of Brussels or something)".[10]
See also
- Antonomasia
- Athletic nickname
- Australian national sports team nicknames
- Calling name
- Category:Nicknames
- Epithet
- Honorific nicknames in popular music
- Legal name
- List of baseball nicknames
- List of basketball nicknames
- List of ethnic slurs by ethnicity
- List of monarchs by nickname
- List of nicknames of European Royalty and Nobility
- List of nicknames of jazz musicians
- Category:Lists of people by nickname
- List of nicknames of United States presidents
- List of North American football nicknames
- List of sportspeople by nickname
- Lists of nicknames – nickname list articles on Wikipedia
- Pet name
- Pseudonym
- Regimental nicknames of the Canadian Forces
- Category:Regional nicknames
- Sobriquet
- Synecdoche
- Terms of endearment
- Victory titles
References
- ^ "dictionary". merriam-webster.
- ^ "eke-name, n.", OED Online, Oxford University Press, June 2017, retrieved 1 September 2017
- ^ "nickname", Merriam Webster Online, retrieved 2020-06-05
- ^ "nickname", Online Etymology Dictionary, retrieved 2007-08-31
- ^ "nickname". Dictionary.com. Retrieved 10 June 2020.
- ^ Willson, Kendra Jean (2007). "Icelandic Nicknames".
- ^ Liwei, Jiao (12 November 2019). A Cultural Dictionary of The Chinese Language: 500 Proverbs, Idioms and Maxims. ISBN 9781000713022.
- ^ a b c Muench, David (December 1993) "Wisconsin Community Slogans: Their Use and Local Impacts" Archived 2013-03-09 at the Wayback Machine University of Wisconsin - Extension Retrieved April 10, 2007.
- ^ a b Andia, Alfredo (September 10, 2007) "Branding the Generic City" Archived 2008-05-21 at the Wayback Machine, MU.DOT magazine
- ^ Jon Worth, The No Deal Brexit Terminology, University College London Europe blog, 8 December 2020.
