Bulgaria during World War I


The Kingdom of Bulgaria participated in World War I on the side of the Central Powers from 14 October 1915, when the country declared war on Serbia, until 30 September 1918, when the Armistice of Salonica came into effect.
After the Balkan wars of 1912 and 1913, Bulgaria was diplomatically isolated, surrounded by hostile neighbors and deprived of Great Power support. Negative sentiment grew particularly in France and Russia, whose officials blamed Bulgaria for the dissolution of the Balkan League, an alliance of Balkan states directed against the Ottoman Empire. Bulgarian defeat in the Second Balkan War in 1913 turned revanchism into a foreign policy focus.
When the First World War started in July 1914, Bulgaria, still recovering from the economic and demographic damage of the Balkan Wars, declared neutrality.[1] Strategic location and a strong military establishment made the country a desired ally for both warring coalitions, but its regional territorial aspirations were difficult to satisfy because they included claims against four Balkan countries. As the war progressed, the Central Powers of Austria-Hungary and the German Empire were in a better position to meet these demands. Bulgaria entered the war on the side of the Central Powers, invading Serbia in October 1915.
Although the smallest of the Central Powers, Bulgaria made vital contributions to their common war effort. Its entry heralded the defeat of Serbia, thwarted the goals of Romania,[2] and catalyzed the Ottoman war effort by providing a land and rail link from Germany to Istanbul, that is, on Via Militaris.[3]
Though the Balkan theatre saw successful campaigns of rapid movement by the Central Powers in 1915 and 1916, the conflict degraded into attritional trench warfare on both the Northern and the Southern Bulgarian Fronts after most Bulgarian goals were satisfied.[4] This period of the war further damaged the economy, creating supply problems and reducing the health and morale of Bulgarian troops. Despite achieving national territorial aspirations, Bulgaria was unable to exit what otherwise would have been a successful war, weakening its will to continue to fight. These stresses intensified with time, and in September 1918, the multinational Allied armies based in Greece broke through on the Macedonian Front during the Vardar Offensive. Part of the Bulgarian Army quickly collapsed, and open mutiny followed as rebellious troops proclaimed a republic at Radomir.[1] Forced to seek peace, Bulgaria requested an armistice with the Allies on 24 September 1918, accepting it five days later. For the second time in only five years, Bulgaria faced national catastrophe. Tsar Ferdinand I assumed responsibility, abdicating in favor of his son Boris III on 3 October.[5]
The 1919 Treaty of Neuilly formally concluded Bulgaria's participation in World War I. Stipulations included the return of all occupied territories, the cession of additional territories and the payment of heavy war reparations.
Background
The Balkan Wars

When Bulgaria proclaimed its independence from the Ottoman Empire on 22 September 1908, its status was promoted to that of a kingdom and Prince Ferdinand of Bulgaria assumed the title of Tsar. The country was now able to focus on completing its national unification by turning its attention toward the lands populated by Bulgarians that remained under Ottoman control.
To achieve its goals, the Bulgarian government, under Prime Minister Ivan Geshov, approached the governments of the other Balkan countries in hopes of creating an alliance directed against the Ottomans. His efforts culminated in a series of bilateral treaties concluded in 1912 to form the Balkan League. By summer of the same year, Ottoman grip on their Balkan provinces deteriorated rapidly in Albania and Macedonia, where open rebellions had erupted.[6][7] The Allies decided to exploit the vulnerable state of the Ottoman Empire and declared war on it in October 1912.
The opening stages of the First Balkan War began with decisive Allied victories in both Thrace and Macedonia. Within a month, the Ottomans found themselves driven back by the Bulgarians to within 40 kilometers of Constantinople and badly beaten by the Serbians and the Greeks.[8] A short armistice brought no conclusion to the conflict and fighting once again broke out in January 1913. A major Ottoman counter-offensive was defeated by the Bulgarians, who also seized the fortress of Adrianople in March and finally forced the Ottoman Empire to admit defeat and return to the peace table. While the Bulgarian army was still fighting, a new challenge arose from the north: Romania demanded territorial compensations from Bulgaria in return for its neutrality during the war.[9] A protocol, signed after several conferences held in Saint Petersburg, sought to resolve the dispute by rewarding Romania the town of Silistra, but this decision greatly antagonized both countries and sowed the seeds of further enmity between them.[10]
The formal ending of the war was marked by the signing of the Treaty of London of 1913, which awarded all Ottoman territory to the west of the Midia-Enos line, with the exception of Albania, to the Allies.[11][12]
The treaty failed to make clear provisions for the division of the former Ottoman territories between the victors, which brought about the dissolution of the Balkan League. Geshov foresaw this outcome, which signalled the collapse of his goal of forming a permanent alliance directed against the Ottoman Empire, and resigned from his post as prime minister. He was replaced by the hard-liner Stoyan Danev.[13] The new government was not willing to compromise with Bulgarian claims in Macedonia, and neither were Serbia and Greece, whose interests were frustrated by the creation of an Albanian state. Russia, which was viewed as the patron of the Balkan League, was unable to control the situation and settle the disputes between the allies. The failure of Russian diplomacy, and the Entente Cordiale among Russia, France, and Great Britain that stood behind it, was a victory for Austria-Hungary, which sought to undermine the unity between the Balkan countries. In June, the new Bulgarian government was asked by the Bulgarian General Staff to either take aggressive action or order demobilization within 10 days. The senior Bulgarian commanders were concerned by the new alliance between Serbia and Greece and the growing restlessness in the army, which had been in the field since September 1912. Danev was preparing to leave for Russia where a new attempt to solve the problem was made by Tsar Ferdinand and General Mihail Savov, who decided to make a demonstration to Serbia, Greece and the Entente by ordering two of the Bulgarian armies to attack and consolidate their positions in Macedonia on 16 June.[14] More than a day later, Danev ordered Savov to stop the fighting and the latter obeyed, despite orders for the continuation of the attack given to him by the tsar. The Serbians and Greeks, however, were not willing to let this opportunity pass and declared war on Bulgaria.[14] Perceiving an opportunity to acquire Southern Dobruja, Romania also invaded Bulgaria. The Romanian forces met with almost no resistance and was soon followed by the Ottoman Empire, which restored its control over Eastern Thrace.[15]

The eruption of this Second Balkan War tore a rift in the relations between Bulgaria and Russia and led to the downfall of the Danev government amidst the news of Bulgarian defeats in the field. A new liberal coalition government under Vasil Radoslavov took control and immediately began seeking a diplomatic solution to the crisis, looking primarily towards Germany and Austria-Hungary for help.[16] Direct negotiations with Serbia and Greece proved inconclusive, but following Bulgaria's offer to cede Southern Dobruja to Romania, both sides agreed to begin peace talks in Bucharest. At the same time, the Bulgarian army managed to stabilize the Serbian and Greek fronts and even go on the offensive. Bulgarian forces threatened to encircle the Greek army completely, but with the Romanians only a few kilometers from the Bulgarian capital of Sofia and the Ottomans in good position to invade the whole of southeastern Bulgaria, the warring countries concluded an armistice in July 1913.[17]
Following the cessation of hostilities, the peace talks in Bucharest resumed. The Bulgarian delegation found itself in almost complete isolation, with only the partial support of Russia and Austria-Hungary, which forced it to accept the coercive conditions of its opponents and sign the Treaty of Bucharest of 1913.[18] The treaty required Bulgaria to cede Southern Dobruja, most of Macedonia (including the "uncontested zone" that had previously been bestowed to it by the 1912 treaty between Bulgaria and Serbia) and the town of Kavala.
The peace treaty with the Ottomans had to be dealt with on a bilateral basis. Initially, the Bulgarian diplomacy maintained the position that the question about the possession of Adrianople and Eastern Thrace was an international matter resolved by the terms of the Treaty of London of 1913, but this line soon had to be abandoned due to the lack of support by the Great Powers and their unwillingness to pressure the Ottoman Empire. The resulting Treaty of Constantinople of 1913 restored to the Ottomans most of the lands they had re-occupied during the Second Balkan War. During the talks, the Radoslavov government for the first time sought to recover and strengthen the relations with the Ottomans by discussing an alliance directed against Serbia and Greece, but no concrete results were achieved at that point.[19]
Bulgaria in the aftermath of the Balkan Wars

The outcome of the Second Balkan War negated almost all of the territorial gains that Bulgaria secured during the First Balkan War. The failed effort to bring all Bulgarians under a single national government led to a massive influx of over 120,000 Bulgarian refugees from Eastern Thrace and the parts of Macedonia that remained under Serbian and Greek rule.[20] The Radoslavov government faced the uneasy task of integrating the new population and the acquired territories that were not ceded back, as well as rebuilding the economy and the military potential of the country.
Internal bickering within the People's Liberal Party (one of the three governing coalition parties) and the lack of a majority in parliament forced the dissolution of the legislative body. General elections were called for the pre-war borders of Bulgaria in November 1913 and held for the first time under nationwide proportional representation. The government parties gained only 97 seats as compared to the 107 seats of their opponents, which prompted a new resignation of the government in December.[21] Tsar Ferdinand held consultations with several important politicians, but once again preferred to appoint a government with Radoslavov as prime minister and dissolve the newly elected parliament. When the next elections were held in March 1914, the population of the new territories was allowed to participate even though many participants had not yet received Bulgarian citizenship. During the campaign, the spokesmen of the opposition parties were practically prevented from campaigning in these lands on the grounds of the alleged threat to their safety. Ottoman officials, however, were allowed to visit the local Muslim populations and urge them to vote for the government. Despite these and other extreme measures, the liberal parties gained 116 seats, as many as their opponents, and their numbers were increased by another 16 following the completion of the verification process.[21] The government was finally able to focus its attention on more pressing internal and external matters. Radoslavov, however, remained handicapped by this fragile majority and was often forced to compromise with his coalition partners, falsify election results or simply neglect parliament.
Economic situation
Bulgarian participation in the Balkan Wars disrupted the expansion of the Bulgarian economy and proved crippling for public finances, with the financial cost of the war against the Ottoman Empire alone at over 1.3 billion francs.[22]
Agriculture, which was the leading sector of the economy, was badly affected, and overall production was reduced by about 9% compared to 1911. Still, the country avoided a large food crisis.[23] Thousands of peasant workers engaged in agricultural activities became casualties during the wars. The number of available horses, sheep, cattle and livestock was between 20% and 40% lower. The single most damaging event was the loss of Southern Dobruja: it had accounted for 20% of Bulgarian grain production before the wars and contained the largest and most developed Bulgarian farming communities.[24] This, combined with bad weather, held the harvest of all crops to 79% of the pre-war level in 1914.[24]
Unlike the agriculture sector, Bulgarian industry was less affected, even though problems occurred due to its complete dependence on foreign imports of machinery and spare parts. Production registered a modest decline and was able to maintain a constant level of capital investment that led to recovery of the sector as early as 1914.[23]
External trade fell drastically in 1913, with exports reduced by 40% and imports by 11%. This led to a soaring trade deficit of over 87 million levs by 1914.[25][26] Before the war, grain had been a leading Bulgarian export commodity with the most productive area being Dobruja. The state took special care for the development of the region; it built railways to carry grain and other exports to the port of Varna, whose facilities had been developed at great cost. In 1912, it handled more goods than Salonika.[21] Following the Second Balkan War, these advantages were lost because the port was deprived of its hinterland, and the Romanian border now ran only 15 kilometers away. The new lands gained in the south were mountainous and much poorer. They provided an outlet to the Aegean Sea at the port of Dedeagach, but the railway needed to reach it passed through Ottoman territory. Still, Western Thrace in particular was famed for its production of high quality tobacco, which proved to be a valuable asset.[23]
Foreign policy
Dealing with the international isolation that had befallen Bulgaria was a major priority of the Radoslavov government. This included re-establishing diplomatic relations with Bulgaria's neighbors, first with the Ottoman Empire in September 1913, then with Serbia in December of the same year and Greece in March 1914. Nevertheless, relations with the Balkan states remained strained due to their fear of Bulgarian revisionism and negative public opinion in Bulgaria of the country's former allies. A friendly gesture was made when Mihail Madzharov, Dimitar Stanchov and Radko Dimitriev (who were well known for their pro-Entente attitude) were appointed ambassadors to London, Paris and Saint Petersburg.[27] This showed that the liberal government was not ready to burn its bridges to the Entente powers. The Central Powers, on the other hand, were not yet willing to step into an open alliance with Bulgaria as this would have alienated the other Balkan countries that Germany and Austria-Hungary had interest in, particularly Romania and Greece.[28]
The most active Entente power in the Balkans was Russia, which sought to limit Austro-Hungarian influence in the area by creating a new Balkan League that was to include Serbia, Montenegro and possibly Romania and Bulgaria. The latter was not in the center of these plans. Though its participation was viewed as attractive enough, Russian diplomacy spent much more time and effort courting Romania, which achieved little practical results, but stirred negative emotions and further alienated Bulgaria.[29] Hints toward Serbia that it should make at least minor concessions to Bulgaria only met with stubborn resistance supported by Greece. The Russian Foreign Minister Sergey Sazonov decided that the only way to influence Bulgaria without harming Russian relations with its neighbors was through financial pressure on the Radoslavov government and its deposition by a pro-Entente government.[30]
France and the United Kingdom were willing to let Russia deal with Bulgaria and preferred not to intervene directly. Prime Minister Radoslavov, on the other hand, partially sought the support of Great Britain through the Bulgarian representative in Saint Petersburg, General Dimitriev, who asked the British ambassador to mediate the relationship between Bulgaria and Russia. The individual approached by General Dimitriev, George Buchanan, politely refused any involvement, but hinted to Sazonov that he should not risk curtailing Entente influence in Bulgaria by assuming a hard line toward the country.[31]
The most important task that faced the Radoslavov government in its foreign policy following the Treaty of Bucharest was to secure a loan that could provide the funds needed to pay the financial cost of the Balkan Wars, develop the new territories and continue paying a government debt of over 700 million golden leva.[32][33] The difficult task was entrusted to Foreign Minister Nikola Genadiev and Finance Minister Dimitar Tonchev, who were first dispatched to France, which held a considerable chunk of the Bulgarian public debt and from which Bulgaria had usually obtained loans before the Balkan Wars. The French refused to extend more loans, due to Russian pressure, despite the fact that the Bulgarian representatives were ready to accept certain unfavorable conditions and that French banks were simultaneously granting loans to Serbia, Greece, Romania and the Ottoman Empire.[32][33] In October 1913, Tonchev managed to secure a short-term loan of 30 million leva from Austrian banks, but the sum was far from sufficient. In February 1914, the Bulgarians again turned to France and were met with unacceptable conditions.
Tonchev, assisted by the German and Austro-Hungarian representatives in Sofia, Gustav Michahelles (de) and Count Adam Tarnowski von Tarnow, opened negotiations with the German Disconto-Gesellschaft bank in early 1914. Russia and France were aware of the talks, but initially dismissed the possibility of their successful conclusion. It was only in April, when the Bulgarian and German representatives had reached an understanding on the basic points of the loan, that the Entente realized that through its hard line it had pushed Bulgaria toward a serious commitment to the Central Powers. The Russian ambassador to Sofia urged the Bulgarian parliamentary opposition to resist the Radoslavov government's intention and personally met with Tsar Ferdinand, whom he promised a French loan in exchange for the removal of Radoslavov.[34] An offer for a loan from the French Banque Perier was also made, but these efforts from the Entente powers came too late and failed to change Bulgarian intentions.
In July 1914, a consortium of German banks led by the Disconto-Gesellschaft granted a 500 million golden leva loan to Bulgaria under harsh conditions. The sum would be received in two installments of 250 million each and had to be repaid within 50 years with an annual interest of 5%. The Bulgarians were obliged to grant the German consortium the contract for the construction of a new port in Porto Lagos and a railway leading to it; the Germans were also to take over the running of the state mines in Pernik and Bobov Dol.[32] The government managed to pass the loan through a vote in parliament despite furious opposition. The debate took place among numerous fist fights. The prime minister was seen to wave a revolver above his head. The government claimed the loan had been approved by show of hands.[21]
The loan agreement was a heavy defeat for Russian and French diplomacy, whose attention was also diverted by the July Crisis surrounding the assassination of the Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria. At this point, it did not yield a firm commitment by Tsar Ferdinand and Bulgaria to the cause of the Central Powers.[32]
Bulgaria at the beginning of the First World War
On 28 June 1914, Gavrilo Princip, a Bosnian-Serb student and member of Young Bosnia, assassinated the heir to the Austro-Hungarian throne, the Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria in Sarajevo, Bosnia.[35] This began a period of diplomatic manoeuvring between Austria-Hungary, Germany, Russia, France and Britain called the July Crisis. Wanting to end Serbian interference in Bosnia conclusively, Austria-Hungary delivered the July Ultimatum to Serbia, a series of ten demands that were intentionally meant to be unacceptable in order to precipitate a war with Serbia.[36] When Serbia acceded to only eight of the ten demands levied against it in the ultimatum, Austria-Hungary declared war on Serbia on 28 July 1914. Within days, the conflict spread to most of Europe and encompassed all of the major Great Powers. Many other European countries however, including Italy and Romania who had previously been affiliated with one of the major war alliances, preferred to stay neutral.
Neutrality
Immediately following the outbreak of hostilities, the Bulgarian tsar and prime minister decided to declare a policy of "strict and loyal" neutrality, a stance that was popular with both ruling and opposition parties.[21] Radoslavov also realized that the lack of proper diplomatic preparation and support from some of the Great Powers had been a major cause for the Bulgarian defeat in 1913, and he intended not to repeat the same mistakes. In order to adjust to the new reality of war, the government managed to pass a bill for the declaration of martial law and a bill for an internal loan of 50 million leva for the needs of the army.
The news of Bulgarian neutrality was received well in Entente capitals, even if their approach towards the country differed. Initially, these powers thought the war would be short. Bulgaria was not given an important role in their plans, as its diplomatic isolation was viewed as weakness. Romania, with its large population, substantial oil reserves and strategic position on the flank of Austria-Hungary, was reckoned a more attractive ally.[37] This was especially the case in France, whose ambassador in Bucharest was heavily engaged in fighting German and Austrian influence in the country. Great Britain also hoped that a Romanian entry into the war on its side would force Bulgaria and even the Ottoman Empire to at least remain neutral, while Greece might brave itself to support Serbia openly. The mood in Saint Petersburg was far less optimistic, as the Russians were aware that the price tag of Romania's entry into the war would include Bessarabia and also feared that its intervention would only extend the already huge Eastern Front.[37]
The initial reaction of the Central Powers to the declaration of neutrality was similar to that of the Entente. Germany and Austria-Hungary in particular were weighing the possibility of encouraging immediate Bulgarian intervention against Serbia, because the neutrality of Italy and Romania, countries that had been their allies prior to the outbreak of the war, was a major defeat for German and Austrian diplomacy. Radoslavov, who was generally pro-German, engaged in talks with the German and Austro-Hungarian ambassadors as early as July 1914, but in the end he preferred to reaffirm Bulgaria's neutrality. On other diplomatic fronts, the prime minister achieved greater results with the signing of a secret treaty between Bulgaria and the Ottoman Empire on 6 August 1914.[38] This was a mutual defense pact that would come into effect if either party was attacked by another Balkan power. Both countries pledged not to attack other Balkan countries without consultation with each other. In the absence of such consultation, the parties pledged benevolent neutrality in such a conflict. Bulgaria additionally agreed to notify the Ottoman Empire of any impending military mobilization. The treaty was kept in deep secrecy, and it remained unknown to most other powers; Germany was made aware of its existence in December 1914.[38] When the Ottomans entered the war on the side of the Central Powers in October 1914, Bulgaria reaffirmed its neutrality.
Foreign diplomatic activity in Bulgaria
German and Austro-Hungarian diplomats began probing the Bulgarian government's intentions immediately following the initial declaration of neutrality. The two countries presented Tsar Ferdinand with a draft of a military agreement between the Central Powers and Bulgaria.[39] The German ambassador Michahelles also initiated negotiations for a military agreement with Prime Minister Radoslavov in August 1914. These steps did not lead to any concrete commitments by the Bulgarian government, which realized the country was not yet ready for a war. The Austrian defeat in the Battle of Cer in Serbia also undermined the attempts of Austria-Hungary to secure an explcit alliance with Bulgaria. In early September 1914, Duke John Albert of Mecklenburg visited Bulgaria as a personal representative of Kaiser Wilhelm II, but he also failed to sway the firm position of the Bulgarian government.
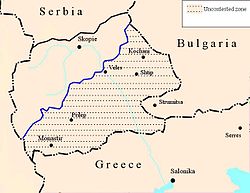
Entente diplomats did not sit idly by either. Russia was still trying to build a new Balkan League that would include Serbia, Montenegro, and Bulgaria.[37] On 31 July, Sazonov asked the Serbian government to determine what territory it would be willing to give to Bulgaria in exchange for its neutrality or military cooperation, but received no reaction from the Serbian prime minister.[37] A few days later, Sazonov suggested that Serbia should cede parts of the uncontested zone of Macedonia to Bulgaria for joining the Entente, and eventually cede the entire zone if the Entente won.[40] Though the Serbians were not willing to antagonize their Russian patrons, they decided not to yield. Serbian policy on this matter was not led by ethnographic motives, but by a geopolitical theory that held that the dominant position in the Balkan Peninsula would be held by the country that controlled the valleys of the rivers Morava and Vardar.[41] Thus Serbia preferred to face Austria-Hungary on their own, with benevolent Bulgarian neutrality for which they offered to cede about a quarter of the uncontested zone, while keeping total control of the Vardar. This however did not deter Sazonov from ordering Savinsky to offer vague territorial acquisitions to Ferdinand and Radoslavov in exchange for Bulgaria's cooperation.
The Russians were also restrained in their activity by their allies, especially France, which preferred the cooperation of Romania rather than Bulgaria. Fresh diplomatic initiatives from France were expected following the appointment on 26 August 1914 of Théophile Delcassé, a diplomat with extensive experience regarding Balkan matters, as French foreign minister. French diplomacy, like Russian diplomacy, also toyed with the idea of a new Balkan League directed against the Ottoman and believed that Bulgaria could be offered Eastern Thrace up to the Midia-Enos line.[42] Still, France's prestige and influence were greatly reduced in Bulgaria, due to its behavior during the Balkan Wars. This forced the French to admit the leading role of Russia in all attempts of gaining Bulgarian support and limit themselves to cautious support of Russian proposals.
Britain government thought it best to avoid any complications in the Balkans, feeling that a Balkan alliance of neutral countries was better suited to its interests This conflicted with Russian ideas of getting Bulgarian military support in exchange for territorial concessions by it neighbors.[43] Great Britain was thus unwilling to pressure Bulgaria's neighbors to satisfy Bulgarian territorial demands. To further Entente ideas of a Balkan League, the British government dispatched the Liberal MPs Noel and Charles Buxton to meet unofficially with leading Bulgarian statesmen.[44] When they arrived in Bulgaria, the brothers were greeted warmly and first met in September with Tsar Ferdinand, Prime Minister Radoslavov, and minister Tonchev, from whom they received firm assurances of Bulgaria's strict neutrality. After that, they turned their attention to the Bulgarian opposition leaders and met with Aleksandar Stamboliyski, Ivan Geshov, Yanko Sakazov, and others. During their stay in the country, the Buxtons found the Bulgarians, even the pro-Entente ones, to be very cautious when it came to aligning the country to Britain. The unofficial character of the visit also made it look like it was a private enterprise rather than one backed by serious British intentions. The brothers however continued their work in Bulgaria and advocated a declaration by the Entente powers promising support for Bulgaria's claim to the uncontested zone of Macedonia in return for its benevolent neutrality towards Romania and Serbia. Despite having the support of all Allied representatives in Sofia, the Buxtons were unable to impress British Prime Minister H. H. Asquith, who considered it out of the question to force Serbia to cede land. Shortly after Noel Buxton was shot and seriously wounded by a Turkish assassin while visiting Bucharest, he and his brother were forced to cease their diplomatic activities temporarily.[45]
In October 1914, the Ottoman Empire entered the war on the side of the Central Powers, which considerably altered the political and military situation in the Balkans. Radoslavov realized that Bulgaria's value as a potential ally had now increased substantially. The new situation also increased the bargaining power of Germany and Austria-Hungary in the remaining neutral Balkan capitals, but it did not enhance the Entente's cause in its negotiations with Bulgaria.[46] All the Allies could do was send a note to Radoslavov promising unspecified territorial gains in exchange for strict neutrality and further gains if Bulgaria joined the Entente in the war.[47] The Bulgarian prime minister could not accept such a vague offer in the face of Serbia's continued determination not to cede lands to Bulgaria. On 9 December, the Allies, who realized their previous mistake, sent a new declaration promising Bulgaria Ottoman Eastern Thrace up to the Midia-Enos line and "fair" territorial gains in Macedonia in exchange for its neutrality.[48][49] Radoslavov again refused to make any commitments and confirmed his intention to keep Bulgaria on the already established course.
The End of Neutrality
As 1914 came to an end, Bulgaria remained on the sidelines of World War I. Popular opinion lacked enthusiasm for entering the conflict and supported the country's stance of neutrality. At this point, Prime Minister Radoslavov adopted a "wait and see" policy while at the same time he successfully probed the abilities of the warring alliances to satisfy Bulgarian territorial ambitions. A final commitment could be made only when one of the sides had gained a decisive military advantage and had firmly guaranteed the fulfillment of Bulgarian national ideals.
On the battlefields far from Bulgaria, the war had entered a long period of stalemate with no side appearing to gain the upper hand. On the Western Front in February 1915, the French failed to break the German lines at the First Battle of Champagne, while further attempts at the Second Battle of Artois during May also came to an unsuccessful conclusion.[50] The Germans had decided to focus their efforts on the Eastern Front, where they had considerable success against the Russians in the Second Battle of the Masurian Lakes in February 1915, but their gains were largely negated at the Siege of Przemyśl in March.[50] The Germans and Austrians then undertook new counterattacks to restore their positions. Finally, in May 1915, Italy entered the war on the side of the Entente. Under these circumstances, the military and political value of the neutral Balkan countries increased significantly.
The military successes of each warring side were often a major asset in their diplomatic courtship of Bulgaria. Thus when Przemyśl fell and the Anglo-French landed in the Dardanelles, Radoslavov expressed greater interest in negotiations with the Entente.[51] The leading role of Britain in the Gallipoli Campaign of 1915 made it a natural driving force behind the revival of Entente attempts to acquire Bulgaria as an ally.[52] The British realized that the key to winning Bulgaria was in Vardar Macedonia, and they suggested to Sazonov that Serbia should be prepared to cede the uncontested zone in exchange for Austrian territory. The Russian foreign minister decided to stand behind this proposition, even though he found it rather vague, as long as it could turn Bulgaria against the Ottoman Empire. Serbia however remained adamant and Crown Prince George of Serbia even declared that the country would rather give up Bosnia than hand over Vardar Macedonia to Bulgaria.[53]
At the same time, Germany hoped in vain to use the payment of a 150 million installment of the 1914 loan as means of exerting influence on the Bulgarian government, and Radoslavov turned his attention in an unexpected direction by sending Genadiev to Rome. The purpose of this move was unclear to foreign observers and speculations soon arose that Radoslavov was only trying to remove a potent contender for his post.[54] Whatever the reason, Genadiev became convinced that Italy was preparing to throw in its lot with the Entente during his two-month stay in the Italian capital.[54] Radoslavov was not pleased by this news and thought that his coalition partner might undermine the ruling government coalition had he read the report on his foreign visit to the Council of Ministers of Bulgaria.[55] To prevent this, the prime minister made sure that Genadiev would not be able to share his impressions with his colleagues, and most ministers were left completely unaware of his report. The foreign minister's prediction about Italy entering the war on the side of the Entent became reality in May 1915, but it also presented an unforeseen complication for the Allied diplomacy as Italy and Serbia both had claims in Dalmatia, which made the latter even more uncompromising when asked to make concession to Bulgaria.
On 29 May, not long after Italy's entry into the war, the Allied representatives in Sofia independently presented an identical note proposing an alliance in exchange for Bulgaria's immediate attack on the Ottoman Empire. In return, Bulgaria would receive Eastern Thrace to the Enos-Midia line and the uncontested zone in Macedonia. Bulgaria could occupy Thrace at its earliest convenience, and the gains in Macedonia were contingent upon Serbia receiving land in Bosnia and an outlet on the Adriatic coast. The Allies also promised substantial financial assistance and full support in pressuring Greece to cede Kavalla, whereas Romania was to return Southern Dobruja.[56] In many respects, this proposal represented a turning point in the relationship between the Entente and Bulgaria as it offered for the first time a reward close to satisfying all Bulgarian demands. The Allied proposals however had been coordinated with neither Serbia nor Greece and provoked fierce protests from those countries. Naturally this left the Bulgarians with serious doubts about Allied intentions. Radoslavov's reply was received only on 15 June and although friendly, it asked for further clarifications and no commitments at all.[56] In addition, the changing military situation also affected Bulgarian opinions as Italy's entry into the war failed to break Austria-Hungary, the Russians suffered reverses in Galicia and the Allied landings in the Dardanelles proved less successful than expected.
The Central Powers were aware of the Allied overtures to Bulgaria and only a few days before the Allied proposal of 29 May came up with an offer of their own. The Austrian and Germans would guarantee both the contested and uncontested zones of Macedonia in exchange for Bulgarian neutrality and if a war with Greece and Romania resulted, then Bulgaria could expect the lands that it had lost in 1913.[56] Tsar Ferdinand issued a speedy reply, but at this point he too preferred not to commit the country to the war.
The Allies struggled to give a unified reply to Radoslavov's questions as their positions began to diverge. Britain's foreign minister Edward Grey had doubts about the true Bulgarian intentions and wished to scale down the promises made to Bulgaria. His views, however, were met with disapproval even in his own cabinet; David Lloyd George and Winston Churchill thought that a high price, mostly at Greek expense, was worth paying.[57] France and Russia feared that Grey's ideas might push Ferdinand and Radoslavov further away and also disagreed.[58] Unlike their British colleague, both Sazanov and Delcassé were also willing to exert greater pressure on Greece to make appropriate concessions in exchange for future compensations in Asia Minor. The Russians wanted to put a time limit for Bulgarian acceptance, because its military intervention would be most useful before the autumn mud put an end to the heavy fighting on the Eastern Front. As the spring of 1915 passed, the Allies missed the most promising opportunity of winning Bulgaria for their cause.
"The Bulgarian Summer" of 1915

The summer months of 1915 saw a decisive clash between the diplomacy of the Entente and the Central Powers. Marcel Dunan, a young French historian, reporter for the French press and witness of the critical events, summarized the importance of this period for the entire course of the war by simply naming it the "Bulgarian Summer" of 1915.[59] Bulgaria's strategic geographic position and strong army now, more than ever, could provide a decisive advantage to the side that managed to win its support. For the Allies, Bulgaria could provide needed support to Serbia, shore up Russia's defenses, and effectively neutralize the Ottoman Empire, while it could ensure the defeat of Serbia for the Central Powers, cut off Russia from its allies and open the way to Constantinople, thus securing the continuous Ottoman war effort.[60] Both sides had promised more or less the fulfillment of Bulgaria's national aspirations, and the only problem facing the Bulgarian prime minister was how to secure maximum gains in exchange for minimum commitments.
During this time, many Entente and Central Powers dignitaries were sent to Sofia in an effort to secure Bulgaria's friendship and support. Allied representatives met with the leaders of the Bulgarian opposition parties and also provided generous financial support for opposition newspapers; they even attempted to bribe high-ranking government officials.[61] Germany and Austria-Hungary were not willing to remain on the sidelines and dispatched to Bulgaria Duke John Albert of Mecklenburg, the former ambassador to the Ottoman Empire Hans Freiherr von Wangenheim and Prince Hohenlohe, who openly declared that after the defeat of Serbia, Bulgaria would assume hegemony of the Balkans.[62] What seized Bulgarian interest the most was indeed the balance of military power. The situation on the major European fronts was at that time developing markedly in favor of the Central Powers, and while the Allied operation in Gallipoli turned into a costly stalemate, the Russians were being driven out of Galicia and Poland. Under these circumstances. The Central Powers were hoping to secure Bulgaria at last.
Still, it took Entente diplomacy more than a month to give an answer to Radoslavov's questions and the reply proved far from satisfactory. In reality, it hardly differed from the offer the Allies presented in May. Once again the promises lacked a clear guarantee that Serbia would cede the desired lands and there was not even a mention of Southern Dobruja. In the eyes of the Bulgarians, this was a manifestation of Entente helplessness in the face of the conflicting ambitions of its smaller Balkan allies. The diplomatic positions of the Central Powers in Sofia were strengthened immensely, forcing the Bulgarian tsar and prime minister to assume a course towards a final alignment of the country to the side of the Central Powers. In August, a Bulgarian military mission led by Colonel Petar Ganchev, a former military attaché in Berlin, was dispatched to Germany to work out the details for a military convention.[63][64] Almost at the same time, the Minister of War Lieutenant General Ivan Fichev resigned and was replaced as minister by the pro-German Major General Nikola Zhekov.[62][63] Radoslavov also entered into talks with the Ottoman Empire, trying to gain concessions in exchange for Bulgarian benevolent neutrality. In this situation, Germany, unlike the Allies, was able to persuade its ally at least to consider seriously the notion of ceding some land to gain Bulgarian support. Still, the Ottomans were willing to conclude the deal only after Bulgaria entered into an agreement with the Central Powers.[64]
Throughout the month of August, the Allied diplomatic activity grew more incoherent. British and French diplomats began to realize that in the face of the stubborn Serbian and Greek refusals of any immediate concessions that the best they could hope for was to keep Bulgaria neutral. In the face of its diplomatic failure, the Entente even resorted to more unusual means of keeping Bulgaria on the sidelines. The Allies and their Bulgarian political sympathizers attempted to buy out the country's grain harvest and create a food crisis. This affair was revealed to the Bulgarian government, and the perpetrators were arrested. Entente diplomats continued to pressure the Serbian government, finally forcing it to assume a more yielding attitude. On 1 September 1915, the Serbian prime minister agreed to cede about half of the uncontested zone, but he demanded that Serbia should keep most of the land to the west of the Vardar, including the towns of Prilep, Ohrid and Veles.[65] In return for these territorial concessions, the Allied Powers had to allow Serbia to absorb Croatia and Slovenia and demand Bulgaria to attack the Ottoman Empire.[65][66] The Serbian offer was unacceptable, and most of its demands were rejected. At the same time, the Entente was unaware that the negotiations between Bulgaria and the Central Powers had reached a critical phase.
Bulgaria enters the war
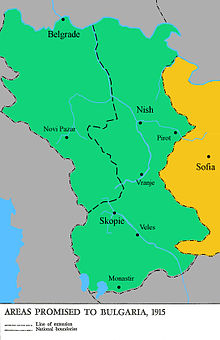
On 6 September 1915, Bulgaria formalized its affiliation with the Central Powers by concluding three separate documents of political and military character. The first document was signed by Prime Minister Radoslavov and the German ambassador Michahelles in Sofia: the Treaty of Amity and Alliance between the Kingdom of Bulgaria and the German Empire. It consisted of five articles that were to remain in force for five years. According to the treaty, each of the contracting sides agreed not to enter an alliance or agreement directed against the other. Germany was obliged to protect Bulgarian political independence and territorial integrity against all attack that could result without provocation on the side of the Bulgarian government. In exchange, Bulgaria was obligated to take action against any of its neighboring states if they attacked Germany.[67]

The second important document was a secret annex to the Treaty of Alliance. It specified the territorial acquisitions that Germany guaranteed to Bulgaria: the whole of Vardar Macedonia, including the so-called contested and uncontested zones, plus the part of Old Serbia to the east of the Morava river.[67] In case Romania or Greece attacked Bulgaria or its allies without provocation, Germany would agree to Bulgarian annexation of the lands lost to these countries by the Treaty of Bucharest of 1913, and to a rectification of the Bulgarian-Romanian border as delimited by the Treaty of Berlin of 1878. In addition, Germany and Austria-Hungary guaranteed the Bulgarian government a war loan of 200,000,000 francs and in case the war lasted longer than four months, they guaranteed an additional supplementary loan.[67]
The third document was concluded at the German Eastern military headquarters in Pless by the Chief of the German General Staff Erich von Falkenhayn, the Chief of the Austro-Hungarian General Staff Count Franz Conrad von Hötzendorf and the delegate of the Bulgarian government, Colonel Peter Ganchev.[68] It was a military convention detailing the plan for the final defeat and conquest of Serbia. Germany and Austria-Hungary were obliged to act against Serbia within thirty days of the signing of the convention, while Bulgaria had to do the same within 35 days of that date. Germany and Austria-Hungary were to field at least six infantry divisions for the attack, and Bulgaria at least four infantry divisions according to their established tables and organization.[a] All these forces were to be placed under the command of Generalfeldmarschall August von Mackensen, whose task was "to fight the Serbian Army wherever he finds it and to open and insure as soon as possible a land connection between Hungary and Bulgaria".[68] Germany also pledged to assist with whatever war materiel that Bulgaria needed, unless it harmed Germany's own needs. Bulgaria was to mobilize the four divisions within 15 days of the signing of the convention and furnish at least one more division (outside of Mackensen's command and forces) that was to occupy Vardar Macedonia.[68] Bulgaria also pledged to keep strict neutrality against Greece and Romania for the duration of the war operations against Serbia, as long as the two countries remained neutral themselves. The Ottoman Empire was given the right to adhere to all points of the military convention and Falkenhayn was to open immediate negotiations with its representatives. For its part, Bulgaria agreed to give full passage to all materials and soldiers sent from Germany and Austria-Hungary to the Ottoman Empire as soon as a connection through Serbia, the Danube or Romania had been opened.[68]
On the same day, Bulgaria and the Ottoman Empire concluded a separate agreement that granted Bulgaria the possession of the remaining Ottoman lands west of the river Maritsa, including a 2-kilometer stretch on its eastern bank that ran along the entire length of the river. This placed the railway to the Aegean port of Dedeagach and some 2,587 square kilometers (999 square miles) under Bulgarian control.[69]
The Allies were unaware of the treaty between Bulgaria and Germany and on September 13 made a new attempt to gain Bulgarian support by offering the occupation of the uncontested zone by Allied troops as a guarantee that Bulgaria would receive it after it had attacked the Ottoman Empire.[70] This offer, however, was a sign of desperation and even the British foreign minister considered it inadequate.[70] Radoslavov decided to play along and asked for further clarification.
On September 22, Bulgaria declared general mobilization and Radoslavov stated that country would assume a state of "armed neutrality" that its neighbors should not perceive as a threat.[70] This event was indicative of Bulgarian intentions and prompted the Serbians to ask the Entente to support them in a pre-emptive strike on Bulgaria. The Allies were not yet ready to help Serbia in a military way and refused, focusing their efforts instead on finding ways to delay as much as possible the seemingly imminent Bulgarian attack. Sazonov, angered by this "Bulgarian betrayal", insisted that a clear ultimatum should be issued to the Balkan country. The French and the British resisted at first but eventually fell in line with the Russians and on 4 October, the Entente presented an ultimatum demanding all German officers attached to the Bulgarian army be sent back to home within 24 hours.[71] On the previous day, a small Allied force had landed in Salonika. Radoslavov did not reply and on 5 October the Allied representatives asked for their passports and left Sofia.
On 14 October, Bulgaria declared war on Serbia and the Bulgarian Army invaded Serbian territory. British Prime Minister H. H. Asquith concluded that "one of the most important chapters in the history of diplomacy" had ended.[72] He blamed this heavy Allied diplomatic defeat on Russia and most of all on Serbia and its "obstinacy and cupidity". In military terms, Bulgaria's involvement also made the position of the Allies in Gallipoli untenable.
The Bulgarian Army
Organization and state of the army
The demobilization of the Bulgarian Army following the formal end of the Second Balkan War took place under the difficult conditions created by the Ottoman military threat hanging over Southern Bulgaria and the Romanian occupation of Northern Bulgaria. Many of the divisions had to be brought down to their usual peace strength and re-deployed to cover the Ottoman border. It was only after the signing of the Treaty of Constantinople that the army was able to complete the process of its demobilization and assume its peacetime organization. The old nine regular infantry divisions were returned to their garrison areas; the 10th Aegean Division, that had been formed in the First Balkan War, was settled in the newly acquired territories in the Rhodope Mountains and Western Thrace; the 11th Infantry Division was reduced to minimal size and reformed into a cadre division used for the training of new recruits.[73] On 8 December the demobilization was completed and the peacetime army now comprised 66,887 men, out of whom 36,976 were in the interior of Bulgaria and 27,813 in the new territories.[73]
In peacetime, the Bulgarian Land Forces consisted of three armies, ten infantry divisions, forty infantry regiments, nineteen artillery regiments, eleven cavalry regiments, five battalions of engineers, one railway battalion, one telegraph battalion and one technical battalion.[74] These forces retained the territorial organization established prior to the First Balkan War. The country was divided in three army inspectorates, ten Division districts and forty Regiment districts. During wartime, the staff of each of these administrative units formed the headquarters and staff of a separate army, division and regiment. All male Bulgarian subjects were eligible to serve in the army when they reached the age of 20. At that age, they were conscripted for a period of two years in the infantry and three years in other branches of the Active (Standing) Army. Following this period, a person was enrolled for another 18 years in the infantry or 16 years in other branches of the Active Army Reserve. This Reserve was the heart of the army, as it encompassed the bulk of the available manpower and reached a size of 374,613 men by the end of 1914.[75] Finally, the men between 40 and 48 years served in the National Militia (Narodno Opalchenie) which was divided in two "Ban's". Initially, the First Ban was composed of men 41 to 44 years old and the Second Ban was composed of men 45 to 48 old. Around 1914, due to the experience of the Balkan Wars, the men between 45 and 46 years old that belonged to the Second Ban were formed into separate Etappe Troops. By early 1915, the Bulgarian Army could rely altogether on some 577,625 trained men aged 20 to 48.[75] A special inquiry also determined that another 231,572 men were eligible for military service but had not received their training. Many of those were called up and received training in 1915. The principal firearm used by the Bulgarian infantry since the end of the 19th century was the Mannlicher magazine rifle, notably the M95 model but also the 1888 and 1890 models. Other rifles in use by the army include the Mosin–Nagant 1891 model, the Berdan II and a number of Mauser rifles captured from the Ottomans during the First Balkan War. Officers were armed with a variety of pistols and revolvers, including the Parabellum 1908 and Smith & Wesson. Since 1908, the infantry was also armed with the heavy Maxim machine gun.
The Bulgarian cavalry was armed with sabers for close combat and with the Mannlicher M.1890 carbine. The Balkan Wars had revealed that horse-breeding in Bulgaria was not developed enough to satisfy the wartime requirements of the army, and in order to compensate for the deficiency of strong cavalry and artillery horses by October 1915, the authorities imported about 300 animals.[75]
| Weapon system | Quantity | Ammunition stock | Ammunition per single weapon |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mannlicher rifles | 251,713 | 150,810,600 | 600 |
| Mannlicher carbines | 9,513 | 1,781,800 | 187 |
| Mosin–Nagant rifles | 46,056 | 42,750,000 | 928 |
| Berdan rifles | 54,912 | 27,757,340 | 500 |
| Mauser rifles | 12,918 | 11,188,000 | 860 |
| Martini–Henry rifles | 3,614 | 900,000 | 250 |
| Captured Serbian rifles | 995 | 86,000 | 86 |
| Krnka rifles | 12,800 | 1,224,000 | 95 |
| Parabellum 1908 pistols | 3,957 | 273,000 | 69 |
| Smith & Wesson revolvers | 1,112 | 105,320 | 94 |
| Maxim machine guns | 248 | 10,667,763 | 43,000 |
| Sabres | 19,000 | - | - |

The artillery consisted of various field, mountain and fortress guns, most of it produced by the two world-leading manufacturers Schneider and Krupp. During the Second Balkan War, the Bulgarian army had lost a sizable quantity of its artillery, but by 1915 the country managed to recover its losses and even increase the number of available guns, so that by October 1915, the artillery park consisted of 1,211 pieces, of which 418 were not quick-firing guns.[78] The ammunition for the artillery was however in short supply, and the lack of any large home-based manufacturing capability left the army with only about 500 shells per gun, enough to satisfy the artillery's needs for about two months.
Bulgaria possessed a small naval force of torpedo gunboats and patrol boats that were restricted to operating only in the coastal areas of the Black Sea and along the river Danube. Following the Second Balkan War, the country acquired an outlet on the Aegean Sea, and in January 1915 the "Aegean" Section of the Bulgarian Navy was created by a royal decree. Initially, only 78 soldiers were assigned to the small force and were given a task to observe and defend the coastline by laying naval mines.[79] These activities were centered on the ports of Porto Lagos and Dedeagach, but the true development of the facilities there was hampered by financial difficulties.[79]
The Bulgarian air force had gained some experience during the First Balkan War, but its development was halted following the defeat in the Second Balkan War. The airplane and balloon sections were reduced to two companies and made part of a technical battalion that was attached to the army's engineers. The airplane section, which included 5 functional aircraft and 124 men (including 8 pilots), was stationed on an airfield outside of Sofia. Despite the difficult conditions, the command took measures to improve the material and personnel situation of the air troops by building a special repair workshop and opening a specialized school for the training of pilots, observers and technicians.[80] Bulgaria's hostile neighbors practically isolated it from the big airplane manufacturers and prevented it from receiving new aircraft. Under these circumstances, an alternative had to be provided by a few Bulgarian air enthusiasts who attempted to build a fully functional Bulgarian airplane. In the summer of 1915, Assen Jordanoff was the first to succeed in this task by designing and building the first Bulgarian-made airplane, which was later named Diplane Yordanov-1.[80] Still, in September 1915, the airplane section had only two German-made Albatros B.I, two French-made Blériot IX-2 and one Blériot IX-bis. They were however joined by three German Fokker-Е80Е-III and their German crew, whose task was to defend Sofia from any attacks. It was only after Bulgaria entered the war that the air force was able to receive new aircraft.[81]
1915 also saw the birth of the anti-aircraft component of the Bulgarian armed forces. The first such specialized formation was a mixed battery of six guns (2 quick-firing 75 mm Krupp guns and 4 not quick-firing 87 mm Krupp guns), seven machine guns (five Madsen and two Hotchkiss), which was deployed around Sofia.[81]
Mobilization

The decree for general mobilization of the Bulgarian Army was issued by the Bulgarian government on 22 September 1915, but as this happened late in the evening, the orders reached the local authorities only on the next day. Around this time the total surface area of the kingdom was 114,424 square kilometers and its population stood at 4,930,151 people, out of whom 2,484,122 were males.[82]
The mobilization was carried out behind the established schedule because the nature of Colonel Ganchev's mission to Germany was held in great secrecy to the last moment, even from the Bulgarian General Staff, which was left out of the negotiations completely. The whole mobilization period, which lasted for 17 or 18 days, was accompanied with some difficulties of material character due to the insufficient quantities of uniforms, horses and carts. Even though there was no serious manpower shortage, the absence of the enthusiasm demonstrated during the mobilization prior the First Balkan War was visible. By the beginning of October, the total number of mobilized personnel reached 616,680 men,[83] which represented over 12 percent of the population and almost a quarter of the male inhabitants of the country. Instead of the five divisions required by the military convention, Bulgaria mobilized 11 infantry and one cavalry division as well as numerous auxiliary and militia units. Most of these forces were deployed in three field armies, two of which concentrated on the Serbian border and one on the Romanian border.[84][85]
The Bulgarian constitution designated the monarch as commander-in-chief of the Bulgarian armed forces in time of peace and in time war. In practice, however, the Bulgarian tsar could delegate this function in wartime by granting all the powers of the commander-in-chief to a different person.[86] During the First Balkan War, Tsar Ferdinand had remained acting supreme commander, but his lack of military education and experience forced him to rely heavily on his assistant commander-in-chief Lieutenant General Mihail Savov.

The experience of the Balkan Wars convinced the tsar in 1915 to delegate the title and its powers entirely to a different person. Out of the few appropriate candidates that were available, Ferdinand chose the pro-German Minister of War Major General Nikola Zhekov. The powers of the commander-in-chief were not regulated by law and even from the beginning, this caused some friction with the government. In his new role, General Zhekov exercised direct control over all forces except those that remained in the interior of the country, which were placed under the command of the new Minister of War Major General Kalin Naydenov.[87] At the same time, Major General Konstantin Zhostov succeeded Lieutenant General Kliment Boyadzhiev, who was appointed commander of the 1st Army as Chief of the Bulgarian General Staff.
The military convention between Bulgaria and the Central Powers laid down the general plan for its campaign against the Kingdom of Serbia. It severely limited the control of the Bulgarian High Command over the Bulgarian 1st Army, which was designated part of a combined German, Bulgarian and Austro-Hungarian force commanded by Field Marshal August von Mackensen. He had recently led the German and Austro-Hungarian armies in the highly successful and victorious Gorlice–Tarnów Offensive of the Central Powers against the Russian army on the Eastern Front. His army group was created specifically to wage war against the Serbian army in the pre-1913 borders of the country ("Old Serbia"), to defeat it wherever it found it and to open the land route between Hungary and Bulgaria. As commander, Mackensen acted independently and received his directives only from the German High Command. However, the field marshal's orders to his Bulgarian forces had to be relayed to the commander of the 1st Army by the Bulgarian General Staff, which left room for the latter to intervene when needed. According to the convention, the Bulgarian commander-in- chief retained full and direct control over the Bulgarian 2nd Army and its operations in Vardar Macedonia.
Bulgaria at war
Military operations

Conquest of Serbia
The general mobilization of the Bulgarian Army caused great concern in Serbia, but its military leaders were quick to respond by drafting a plan to deter Bulgaria from entering into the war. The build-up of Serbian forces along the Bulgarian border peaked by the first week of October 1915, when 145 battalions, 25 squadrons and 316 guns were concentrated and prepared for operations against Bulgaria.[88] These forces represented half the entire Serbian Army of 288 battalions, 40 squadrons and 678 guns.[89] The plan relied heavily on the support of the Allies, from whom the Serbians expected to draw another 150,000 men for the defense of Vardar Macedonia. The Serbian government pressed this issue before the governments of the major Entente powers, but was not able to negotiate any commitment on their part. France, Britain and Russia were unable and unwilling to dispatch large numbers of troops, and instead felt that Greece, which had a defensive treaty with Serbia, should act in case of a Bulgarian attack.
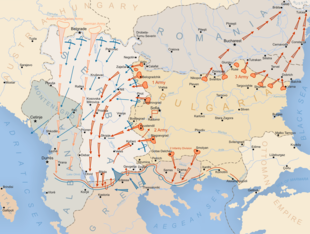
Allied inactivity allowed the Central Powers to continue their preparations for the offensive undisturbed. By early October, however, the Austro-Hungarians were unable to furnish the required minimum of 6 divisions for the attack, so the Germans had to step in with additional forces. The forces, under the overall command of Field Marshal Mackensen, were deployed in the German 11th Army, with 7 German divisions led by General Max von Gallwitz, and the Austro-Hungarian 3rd Army, with 4 Austro-Hungarian and 3 German divisions led by General Hermann Kövess von Kövessháza. On 6 October 1915, Mackensen opened the offensive, as scheduled, with a powerful artillery barrage along the Sava–Danube front and on the next day, the main body of his forces crossed the rivers.
According to the convention, Bulgaria was obliged to move against Serbia within five days of the German and Austro-Hungarian attack, but owing to a delay in the concentration of some of the forces needed, the schedule could not be kept. The Serbians were surprised by Bulgarian inactivity and were forced to begin shifting part of their forces from the Bulgarian border to face the Germans and Austro-Hungarians to the north, which eventually allowed their eastern neighbors to finish their preparations undisturbed. The Bulgarians deployed two field armies with a combined strength of almost 300,000 men.[90] The Bulgarian 1st Army had a ration strength of 195,820 men. The 2nd Army, which remained under the direct control of the Bulgarian commander-in-chief, consisted of two infantry and one cavalry division under the command of Lieutenant General Georgi Todorov.[91] The two armies were to operate against Old Serbia and Vardar Macedonia on a front stretching over 300 kilometers.[92]
On 14 October, with most of the preparations completed, Bulgaria finally declared war on Serbia and officially entered the First World War. Around this time, the Germans and Austro-Hungarians had penetrated into Serbia on a front that was 140 kilometers in length and 15 kilometers in depth. In order to close the 90-kilometer gap between the flanks of the German 11th Army and the Bulgarian 1st Army, Mackensen ordered the latter to invade the valley of the river Morava and take Niš and Aleksinac. In accordance with this order, the Bulgarians attacked along the entire front of their 1st Army, quickly driving out the Serbian units and taking control of the border area.

Following this easy success, the speed of the advance was much reduced due to the bad weather, which turned roads into mud, and a dense fog that sometimes limited visibility to 50 meters. In addition, the stiffening Serbian resistance and the mountainous character of the area caused the flanks of the 1st Army to halt before the fortresses of Pirot and Zaječar that were only 15 kilometers from the border. A breakthrough in the centre of the front forced the Serbians to retreat, and the two towns were occupied on 26 October.[93]
Despite its smaller size, the Bulgarian 2nd Army achieved much greater success and completed its first objective as early as 16 October by taking the town of Vranje and severing all railway communications between Serbia and Vardar Macedonia. A small part of the army was then directed in the direction of Niš with the idea of assisting the 1st Army and cutting off the Serbian retreat routes. The remaining units advanced further west, reaching Veles and Kumanovo on 20 October. During the fighting around Veles, other Bulgarian troops located around Krivolak and Strumitsa for the first time met French forces that were finally advancing north in an attempt to aid the Serbians (See: Battle of Krivolak). The appearance of this new threat to the south forced the Bulgarian High Command to prepare the transportation of two more infantry divisions to Macedonia and divide the 2nd Army in two groups: a northern group operating against the Serbians and a southern group operating against the Allies.[94] On 22 October, following a brief confrontation between Serbian and Bulgarian forces, the town of Skopje was taken, and a detachment was sent to occupy the Kacanik pass and block the Serbian retreat. The rapid advance of the Bulgarian 2nd Army created favorable conditions for the encirclement of the entire Serbian Army fighting in Old Serbia. The Bulgarian High Command decided to focus this objective and ordered the forces operating against the Allies to the south to assume defensive positions.[95]
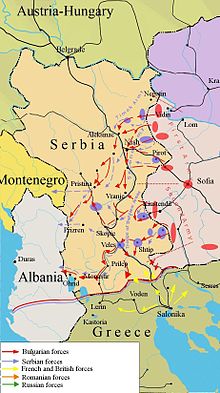
The exploits of the Bulgarian 2nd Army in Macedonia convinced the Serbians that the danger of complete encirclement was high and forced them to begin withdrawing their forces to Kosovo while offering stiff resistance to Army Group Mackensen. On 1 November, Kragujevac fell to the Germans, who began pursuing their opponents down the river Great Morava. Mackensen ordered his forces to "push the main body of the Serbian Army back and decisively beat it in the interior of Serbia".[96] In accordance, the Bulgarian 1st Army continued its advance and captured Niš, the wartime capital of Serbia, taking around 5,000 prisoners on 5 November. On the same day, the flanks of the German 11th Army and the Bulgarian 1st Army joined in a single line, closing the gap between them. Thus the main objectives of the Bulgarian Morava Offensive were completed, but more importantly, the main objective of the entire campaign was also completed and the land route from Austria-Hungary to Bulgaria was opened permanently.
The Serbian Army was now retreating and concentrating on the Kosovo plain, where they hoped to make a stand and buy time either to breakthrough and join the Allies in Macedonia or escape an encirclement. Under these circumstances, the Bulgarian High Command and the headquarters of Army Group Mackensen agreed to pursue the retreating Serbians relentlessly, to cut their possible retreat routes and to undertake a decisive advance towards Pristina.[97] The plan required the Bulgarian 1st Army to attack from the east, the reinforced Northern Operations Group of the Bulgarian 2nd Army from the south, parts of the German 11th army from the north and finally the main forces of the Austro-Hungarian 3rd Army from the northwest. The plan however did not take into account the swollen waters of the river Morava, which slowed down its crossing. As a result of this delay, the Serbians concentrated greater forces against the Bulgarian 2nd Army, which was the main obstacle sitting between them and the Allies, but also the greatest threat to their retreat routes leading to Albania. Thus, when the operation started, the Serbians were not only able to resist the 2nd Army, but also launch a desperate attempt to break through it at Kacanik and reach the Allies. They succeeded in doing so because of the slow advance of the Austro-German and Bulgarian forces from the north and east due to the bad weather, bad roads and overextended supply lines. Mackensen had even pulled back most of the 11th Army, leaving only two divisions in the first line, which greatly reduced the already weak will of the German forces to advance rapidly. Despite this, the exhausted Serbians were not able to break through the northern group of the 2nd Army and retreated. Bulgarian attempts to cut their retreat from the south were thwarted, and when the Bulgarian 1st Army and the German 11th Army took Pristina on 23 November, the Serbian High Command was able to order a general retreat of the entire army to Albania in order to avoid its complete destruction. The pursuit of the retreating opponent was left mostly to Bulgarian and Austro-Hungarian forces and on 29 November, the 3rd "Balkan" division took Prizren. Within days, the towns of Debar, Struga, Ohrid were also occupied. Finally, on 4 December, the Bulgarians entered Bitola.[98] This marked the end of the operations against the Serbian Army, which continued its retreat through the Albanian mountains, and lost around 55,000 men in the process.[99]

Around 150,000 Serbian troops gathered in different Albanian ports and were evacuated by Allied ships to the island of Korfu. This beaten and demoralized force had lost practically all its equipment and had to be rebuilt from scratch.
In November, while the decisive Serbian defeat unfolded, the French attempted to exert pressure on the Bulgarian 2nd Army, but were soon forced to halt their attempts to drive north. The forces of General Maurice Sarrail that consisted of three French and one British division dug in along an 80-kilometer front from the river Cherna to Lake Doiran.[100] With the fall of Pristina, General Sarrail realized that the Allies could no longer help the Serbians and decided to begin pulling back his forces to Salonika. The Bulgarian High Command shifted its focus to the Allies in Macedonia and decided that the time was right to go on the offensive. Several days were lost, however, in scouting, and it was only on 3 December that the 2nd army commenced a general advance. Nonetheless, the French were able to retreat in good order towards Salonika. They were soon followed by the British, who were defeated at the Battle of Kosturino. On 11 December, the Bulgarian divisions reached the Greek border, where they were ordered to halt and warned repeatedly not to cross.[101]
By the middle of December, the entire Kingdom of Serbia was occupied by the armies of the Central Powers and the Allies were pushed back to Salonika by the Bulgarians. Within two months of its entry into the war, Bulgaria achieved its main war goal: the conquest of Vardar Macedonia. For the duration of military operations against Serbia and the Entente in 1915, the Bulgarian Army committed a total of around 424,375 men,[102] while its casualties were held to around 37,000 men.[103]
By the end of 1915, the Central Powers had established firm and unbroken control over a vast territory that stretched from the North Sea to Mesopotamia. They also drew great political and military dividends from the defeat and occupation of Serbia. Bulgaria conquered almost all the territory it desired, Germany gained unrestricted access to the natural resources of Ottoman Asia, the Ottomans received much needed German matériel assistance and Austria-Hungary secured its southern flank and could completely focus its attention on the Russian and Italian fronts.[99]
Bulgarian war crimes in Serbia
Since November 1915, when Serbia was occupied, the Bulgarian army launched crimes against the civilian population. The use of the Serbian language was banned and books in the Serbian language were burned in Niš and Leskovac. Bulgarian soldiers publicly executed those that declared themselves Serbian, the worst example being the Surdulica massacre, where an estimated 2,000–3,000 Serbian men were executed in two years. Bulgarian atrocities purportedly sparked the Toplica Uprising in 1917. Bulgarian forces swiftly suppressed the insurrection, killing over 20,000 civilians and guerrillas in retribution. Bulgarians have deflected blame for these atrocities onto the Austro-Hungarians, though reliable sources confirm their culpability. Following the Allied breakthrough on the Macedonian front, Serbia pressed for an invasion of Bulgaria; this proposal was blocked by the British who feared the Serbs would take revenge on the Bulgarian population.[104][105]

Establishment and development of the Macedonian front during 1916
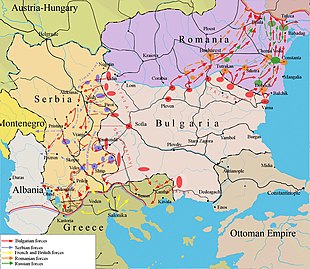
The Romanian campaign
1917 – Stalemate on the Macedonian front
1918 – End of the War

In September 1918 the French, British, Italians, Serbs and Greeks broke through on the Macedonian front during the Vardar Offensive and Tsar Ferdinand was forced to sue for peace. Under the terms of the Armistice of Salonica, Bulgarian troops had to evacuate all occupied Greek and Serbian territory; agree to surrender all of its arms and weapons of war; and the evacuation of all German and Austrian troops and Allied occupation of strategic points inside Bulgaria. With revolts occurring throughout the country, the Bulgarian Agrarian National Union leader Aleksandar Stamboliyski was released from prison in hopes of quelling the discontent. In order to head off the revolutionaries, he persuaded Ferdinand to abdicate in favour of his son Boris III. The revolutionaries were suppressed and the army disbanded.
Images
-
the nationalities in Northern Dobruja at the beginning of the 20th century.
-
The Dobruja after 1878.
-
Western Thrace within Greece.
See also
- 1910s in Bulgaria
- Bulgarian irredentism
- Diplomatic history of World War I#Bulgaria
- Romania in World War I
- Serbia in World War I
- Greece during World War I
- Western Rumelia
- Eastern Rumelia
- Macedonia (region)
In literature
The story ¨Kradetzat na praskovi¨ (English: "The Peach Thief") depicts the love story between a Bulgarian colonel's wife and a Serbian prisoner of war. The First World War is so far best presented in that story by the late Emiliyan Stanev, one of the greatest Bulgarian writers.
Notes
- ^ Bulgarian infantry divisions were significantly larger than their German and Austrian counterparts.
References
- ^ a b Tucker (1996), p. 151.
- ^ (Erickson 2001, pp. 20)
- ^ (Erickson 2001, pp. 91)
- ^ Crampton, pg.139
- ^ Crampton, pg.143
- ^ Crampton, pg.132
- ^ Hall, The Balkan Wars... pg.132
- ^ Hall, The Balkan Wars... pp.43,66–67
- ^ Crampton, pg.133
- ^ Hall, The Balkan Wars... pp.97
- ^ Crampton, pg.134
- ^ Hall, The Balkan Wars... pp.111
- ^ Hall, The Balkan Wars... pp.102
- ^ a b Stavrinos pg.539
- ^ Hall, The Balkan Wars... pp.117–119
- ^ Hall, The Balkan Wars... pp.118–119
- ^ Hall, The Balkan Wars... pp.120–122
- ^ Hall, The Balkan Wars... pp.123–125
- ^ Hall, The Balkan Wars... pp.125–126
- ^ Michael Robert Marrus. The unwanted: European refugees from the First World War through the Cold War. Temple University Press, 2002, pg. 46.
- ^ a b c d e Crampton, R. J. (2007). Bulgaria. Oxford History of Modern Europe. Oxford University Press. pp. 203–206. ISBN 978-0-19-820514-2 – via Google Books.
- ^ Hall, The Balkan Wars... pp.138
- ^ a b c "Българското стопанство в годините на войните /1912 1918 г./" [The Bulgarian Economy during the War Years 1912–1918] (in Bulgarian). Archived from the original on 27 March 2016.
- ^ a b Lampre, pp.42–43
- ^ Панайотов, pg.355
- ^ Ганчев p. 369
- ^ Илчев, pp.37-38
- ^ Илчев, pp.37–38
- ^ Hamilton, pp.401
- ^ Илчев, pp.44
- ^ Илчев, pp.45
- ^ a b c d Crampton, A concise history of Bulgaria pg.137
- ^ a b Илчев, pp.46
- ^ Илчев, pp.52
- ^ Willmott 2003, p. 26
- ^ Willmott 2003, p. 27
- ^ a b c d Илчев, pp.64
- ^ a b (Erickson 2001, pp. 31)
- ^ Lalkov, Балканската политика на Австро-Унгария, 1983. Sofia pp.175
- ^ Дерменджиева, pp.235
- ^ Илчев, pg,71–72
- ^ Илчев, pg,76
- ^ Илчев, pg,79
- ^ Roberts, pg,222
- ^ Roberts, pg,223
- ^ Илчев, pg,94
- ^ Дерменджиева, pp.237
- ^ Roberts, pg,225
- ^ Илчев, pg,103
- ^ a b Ганчев, pg,362
- ^ Hamilton, pp.398
- ^ Илчев, pg,125
- ^ Илчев, pg,127
- ^ a b Илчев, pg,146
- ^ Илчев, pg,147
- ^ a b c Roberts, pg,230
- ^ Roberts, pg,231
- ^ Илчев, pp,185–186
- ^ Dunan, Marcel (April 12, 1917). "L'été bulgare, notes d'un témoin- juil-let-Octobre 1915". Paris, Chapelot – via Internet Archive.
- ^ Yokell, pg,61
- ^ Илчев, pg.194
- ^ a b Roberts, pg,233
- ^ a b Илчев, pg.210
- ^ a b Yokell, pg,87
- ^ a b Илчев, pg.205
- ^ Yokell, pg,82
- ^ a b c Yokell, pp 102–103
- ^ a b c d Lutz, pp 745–746
- ^ Ганчев, pг,364
- ^ a b c Илчев, pg. 207
- ^ Roberts, pg 237
- ^ Roberts, pg,238
- ^ a b Крапчански, pp,94–95
- ^ Крапчански, pg,104
- ^ a b c Крапчански, pg 108
- ^ Крапчански, pg 202
- ^ "Between two wars 1913-1915". Bulgarian Artillery.
- ^ Крапчански, pg 109
- ^ a b Prokopiev, pg,109
- ^ a b Nedyalkov, pg,40
- ^ a b Nedyalkov, pg,41
- ^ Ганчев, p.370
- ^ Крапчански p. 112
- ^ Нойков p. 48
- ^ Ганчев, pp,374–375
- ^ Нойков p. 31
- ^ Ганчев, pg 379
- ^ Българската армия в Световната война, vol. II , pg. 14; Държавна печатница,София 1938
- ^ Българската армия в Световната война, vol. II (1936), pg. 14
- ^ Българската армия в Световната война, vol. II (1936), pg. 904.
- ^ Hall. Balkan Breakthrough..., pp,44–45
- ^ Ганчев, pg,380
- ^ Ганчев, pg,388
- ^ Нойков p. 60
- ^ Българската армия в Световната война 1915 – 1918, Vol. III (1938), pg. 652
- ^ Ганчев, pg 390
- ^ Нойков p. 64
- ^ Нойков pp. 66–67
- ^ a b История первой мировой войны 1914–1918 гг.
- ^ Ганчев, pg 401
- ^ Hall. Balkan Breakthrough..., pg 50
- ^ Българската армия в Световната война 1915 – 1918, Vol. III (1938), pg. 1146 – During the campaign the Bulgarians reinforced their forces with three additional infantry divisions, or some 129,061 men.
- ^ Бакалов, Георги (2009). История на българите [History of the Bulgarians] (in Bulgarian). TRUD Publishers. p. 463. ISBN 9789545287527 – via Google Books.
- ^ "Сурдулица 1915-1918 - www.zlocininadsrbima.com". www.zlocininadsrbima.com. Retrieved 2020-02-07.
- ^ Mitrović, Andrej (1993). Топлички устанак: место у српској историји (in Serbian). САНУ. ISBN 9788670251717.
External links
- Articles relating to Bulgaria at 1914-1918-online. International Encyclopedia of the First World War.
Further reading
In English:
- Gilbert, Martin. The First World War, (2008) p. 468
- Hall, Richard C. "Bulgaria in the First World War," Historian, (Summer 2011) 73#2 pp 300–315 online
- Hall, Richard C. "'The Enemy is Behind Us': The Morale Crisis in the Bulgarian Army during the Summer of 1918," War in History, (April 2004), 11#2 pp 209–219,
- Tucker, Spencer (1996). The European powers in the First World War: an encyclopedia. Taylor & Francis. ISBN 978-0-8153-0399-2.
- Tucker, Spencer (2005). World War I: encyclopedia, Volume 1. ABC-CLIO. ISBN 978-1-85109-420-2.
- Erickson, Edward J. (2001). Ordered to Die: A History of the Ottoman Army in the First World War. Greenwood Publishing Group. ISBN 978-0-313-31516-9.
- R. J. Crampton (2005). A concise history of Bulgaria. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-61637-9.
- R. J. Crampton (1987). A short history of modern Bulgaria. CUP Archive. ISBN 978-0-521-27323-7.
history of bulgaria.
- Hall, Richard C. (2000). The Balkan Wars, 1912–1913: Prelude to the First World War. Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-22946-3.
- Stavrinos, Leften (2008). The Balkans since 1453. C. Hurst & Co. Publishers. ISBN 978-1-85065-551-0.
- Lampe, John (1986). The Bulgarian economy in the twentieth century. Routledge. ISBN 978-0-7099-1644-4.
- Roberts, Keith (1994). Politicians, diplomacy, and war in modern British history. Continuum International Publishing Group. ISBN 978-1-85285-111-8.
- Hamilton, Richard (2003). Origins of World War One. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-81735-6.
- Matthew, YOKELL (2010). SOLD TO THE HIGHEST BIDDER? AN INVESTIGATION OF THE DIPLOMACY REGARDING BULGARIA'S ENTRY INTO WORLD WAR I. Richmond University.
- Lutz. Fall of the German Empire 1914–1918, Volume I. Stanford University Press. ISBN 978-0-8047-2380-0.
- Hall, Richard (2010). Balkan Breakthrough: The Battle of Dobro Pole 1918. Indiana University Press. ISBN 978-0-253-35452-5.
- Willmott, H.P. (2003). World War I. Dorling Kindersley. ISBN 978-0-7894-9627-0. OCLC 52541937.
In Bulgarian:
- В., Крапчански (1961). Кратък обзор на бойния състав, организацията, попълването и мобилизацията на българската армия от 1878 до 1944г. военно издателство, София. Archived from the original on 2007-08-12. Retrieved 2011-02-28.
- Панайотов, Филип (1999). България в 20ти век. Алманах. Труд. ISBN 978-954-528-146-4.
- Ганчев, Атанас. Войнитъ презъ Третото Българско Царство. Родна Мисълъ. Archived from the original on 2013-02-21. Retrieved 2011-02-28.
- Bulgarian Economy during the wars 1912–1918.
- Илчев, Иван (1990). България и Антантата през Първата световна война. Наука и изкуство.
- Нойков, Стефан (1922). Защо не победихме. Печатница на Армейския военно-издателския фонд, София.
- РУСИЯ И БЪЛГАРСКИЯТ НЕУТРАЛИТЕТ (1914–1915) Т. Астарджиева
- Prokopiev, Anatlii. THE AEGEAN FORMATION OF BULGARIAN NAVY IN THE FIRST WORLD WAR, ВИС кн. 1, С., 2004 г.[permanent dead link]
- Nedyalkov, Dimiter. BULGARIAN AVIATION IN THE FIRST WORLD WAR, ВИС кн. 4, С., 2005 г.
- Министерство на войната – Щаб на армията. "Българската армия в Световната война, vol. II. Войната срещу Сърбия през 1915"; Държавна печатница, София 1936
- Министерство на войната, Щаб на войската (1938). Българската армия в Световната война 1915 – 1918, Vol. III. Държавна печатница, София.
In Russian
- Корсун (1939). Балканский фронт. Воениздат НКО СССР.
- А.М. Агеев; Д.В. Вержховский; В.И. Виноградов; В.П. Глухов; et al. (1975). История первой мировой войны 1914–1918 гг. Наука.