November 1932 German federal election
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
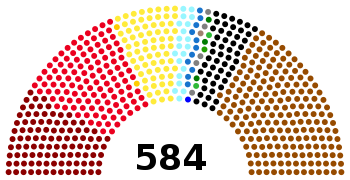
All 584 seats in the Reichstag 293 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Registered | 44,374,085 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Turnout | 35,758,259 (80.58%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
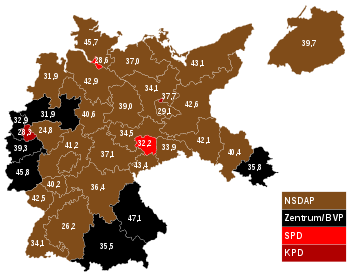 Results map | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| This article is part of a series on the |
| Politics of Germany |
|---|
 |
Federal elections were held in Germany on 6 November 1932.[1] The Nazi Party saw its vote share fall by four percent, while there were slight increases for the Communist Party of Germany and the national conservative German National People's Party. The results were a great disappointment for the Nazis, who lost 34 seats and failed to form a coalition government in the Reichstag.
Previously Chancellor Franz von Papen, a former member of the Catholic Centre Party, had governed without parliamentary support by relying on legislative decrees promulgated by President Paul von Hindenburg under Article 48 of the Weimar Constitution. However, on 12 September 1932 Papen had to ask Hindenburg to dissolve parliament in order to pre-empt a motion of no confidence tabled by the Communist Party, which was expected to pass since the Nazis were also expected to support it due to their desire for fresh elections.
After the election, Papen urged Hindenburg to continue to govern by emergency decree. However, on 3 December, he was replaced by Defence Minister Kurt von Schleicher, who held talks with the left wing of the Nazi Party led by Gregor Strasser in an attempt at a Third Position (Querfront) strategy. The plans failed when Hitler disempowered Strasser and approached Papen for coalition talks. Papen obtained Hindenburg's consent to form the Hitler Cabinet on 30 January 1933.
The elections were the last free and fair all-German election before the Nazi seizure of power on 30 January 1933 since the elections in March 1933 saw massive suppression, especially against Communist and SPD politicians. The next free elections were not held until 1949 in West Germany and 1946 in East Germany. The next free all-German elections took place in December 1990, after reunification.
Results
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Votes | % | Seats | +/– |
| National Socialist German Workers Party | 11,737,021 | 33.09 | 196 | –34 |
| Social Democratic Party of Germany | 7,247,901 | 20.43 | 121 | –12 |
| Communist Party of Germany | 5,980,239 | 16.86 | 100 | +11 |
| Centre Party | 4,230,545 | 11.93 | 70 | –5 |
| German National People's Party | 2,959,053 | 8.34 | 51 | +14 |
| Bavarian People's Party | 1,094,597 | 3.09 | 20 | –2 |
| German People's Party | 660,889 | 1.86 | 11 | +4 |
| Christian Social People's Service | 403,666 | 1.14 | 5 | +2 |
| German State Party | 336,447 | 0.95 | 2 | –2 |
| German Farmers' Party | 149,026 | 0.42 | 3 | +1 |
| Agricultural League | 105,220 | 0.30 | 2 | 0 |
| Reich Party of the German Middle Class | 110,309 | 0.31 | 1 | –1 |
| German-Hanoverian Party | 63,966 | 0.18 | 1 | +1 |
| Radical Middle Class | 60,246 | 0.17 | 0 | 0 |
| Thuringian Agricultural League | 60,062 | 0.17 | 1 | New |
| Christian-National Peasants' and Farmers' Party | 46,382 | 0.13 | 0 | –1 |
| People's Justice Party | 46,202 | 0.13 | 0 | –1 |
| Socialist Workers' Party of Germany | 45,201 | 0.13 | 0 | 0 |
| Poland List | 32,988 | 0.09 | 0 | 0 |
| For Hindenberg and Pope | 27,752 | 0.08 | 0 | New |
| Kleinrentner, Inflationsgeschädigte und Vorkriegsgeldbesitzer | 15,727 | 0.04 | 0 | 0 |
| Free Economy Party of Germany | 11,002 | 0.03 | 0 | 0 |
| Schicksalsgemeinschaft deutscher Erwerbslosen, Kleinhandel und Gewerbe | 9,250 | 0.03 | 0 | New |
| Social Republican Party of Germany | 8,395 | 0.02 | 0 | New |
| Handwerker, Handel- und Gewerbetreibende | 5,189 | 0.01 | 0 | 0 |
| Radical Democratic Party | 3,789 | 0.01 | 0 | New |
| Kampfgemeinschaft der Arbeiter und Bauern | 3,308 | 0.01 | 0 | 0 |
| National Social Party of the Middle Class | 3,052 | 0.01 | 0 | New |
| Enteigneter Mittelstand | 2,737 | 0.01 | 0 | 0 |
| National Freedom Party of Germany | 1,810 | 0.01 | 0 | 0 |
| Schleswig Home | 1,694 | 0.00 | 0 | 0 |
| Greater Germany People's Party | 1,311 | 0.00 | 0 | 0 |
| Interessengemeinschaft der Kleinrentner und Inflationsgeschädigten | 1,086 | 0.00 | 0 | 0 |
| Nationalist Party | 588 | 0.00 | 0 | New |
| People's Socialists | 518 | 0.00 | 0 | New |
| Haus- und Landwirtepartei | 461 | 0.00 | 0 | New |
| National Communist Party of Germany | 381 | 0.00 | 0 | New |
| German Social Monarchist Party | 355 | 0.00 | 0 | 0 |
| German Reform Party | 352 | 0.00 | 0 | 0 |
| German Workers Party | 308 | 0.00 | 0 | 0 |
| Unitarianist Union of Germany | 290 | 0.00 | 0 | 0 |
| Greater German Middle Class Party for Middle Class Dictatorship | 286 | 0.00 | 0 | New |
| Gerechtigkeits-Bewegung-Meißner | 280 | 0.00 | 0 | New |
| German National Citizen Bloc | 192 | 0.00 | 0 | New |
| Party for the Unemployed for Work and Bread | 140 | 0.00 | 0 | 0 |
| National German Catholic Reich Party | 137 | 0.00 | 0 | New |
| German Socialist Struggle Movement | 101 | 0.00 | 0 | 0 |
| German Reich against Interest Rate Movement | 97 | 0.00 | 0 | New |
| Freiheitsbewegung Schwarz-Weiß-Rot | 92 | 0.00 | 0 | New |
| Middle Class Party | 85 | 0.00 | 0 | New |
| Kampfbund der Lohn- und Gehaltsabgebauten | 63 | 0.00 | 0 | New |
| Invalid/blank votes | 287,471 | – | – | – |
| Total | 35,758,259 | 100 | 584 | –24 |
| Registered voters/turnout | 44,374,085 | 80.58 | – | – |
| Source: Gonschior.de | ||||
References
- ^ Dieter Nohlen & Philip Stöver (2010) Elections in Europe: A data handbook, p762 ISBN 978-3-8329-5609-7







