Lingam
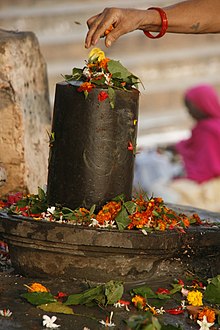
The lingam (IAST: liṅgaṃ, also linga, ling, Shiva linga, Shiv ling, meaning sign, or symbol[1][2]) is an abstract or aniconic representation of the Hindu deity, Shiva, used for worship in temples, smaller shrines, or as self-manifested natural objects.[3][4] In traditional Indian society, the lingam is seen as a symbol of the energy and potential of Shiva himself.[5][6]
The lingam is often represented alongside the yoni (Sanskrit word, literally "origin" or "source" or "womb"), a symbol of the goddess or of Shakti, female creative energy.[7] The union of lingam and yoni represents the "indivisible two-in-oneness of male and female, the passive space and active time from which all life originates".[8]
Definition

The Sanskrit term, liṅgaṃ broadly means symbol or mark, but could have different meanings based on the context.[9] In Shaivite Hindu temples, the lingam is a smooth cylindrical mass symbolising Shiva and is worshipped as a symbol of generative power. It is found at the centre of the temple often resting in the middle of a rimmed, disc-shaped yoni, a representation of Shakti.[5]
An oval shaped Lingam is also the closest representation of the formless aspect of the Divine. The shape of a Lingam maximizes the length of time for which it can hold energy in harmony and balance.[citation needed]
Origin

Anthropologist Christopher John Fuller conveys that although most sculpted images (murtis) are anthropomorphic, the aniconic Shiva Linga is an important exception.[11] Some believe that linga-worship was a feature of indigenous Indian religion.[12]
There is a hymn in the Atharvaveda which praises a pillar (Sanskrit: stambha), and this is one possible origin of linga-worship.[12] Some associate Shiva-Linga with this Yupa-Stambha, the sacrificial post. In the hymn, a description is found of the beginningless and endless Stambha or Skambha and it is shown that the said Skambha is put in place of the eternal Brahman. The sacrificial fire of the Yajna, its smoke, ashes and flames, the soma plant, and the ox that used to carry the wood for the Vedic sacrifice, gave rise to the conceptions of the brightness of Shiva's body, his tawny matted-hair, his blue throat and the riding on the bull of the Shiva. The Yupa-Skambha gave place in time to the Shiva-Linga.[13][14] In the Linga Purana the same hymn is expanded in the shape of stories, meant to establish the glory of the great Stambha and the supreme nature of Mahâdeva (the Great God, Shiva).[14]
The Hindu scripture, Shiva Purana, describes the origin of the lingam, known as Shiva-linga, as the beginning-less and endless cosmic pillar (Stambha) of fire, the cause of all causes.[15] Lord Shiva is pictured as emerging from the Lingam – the cosmic pillar of fire – proving his superiority over gods Brahma and Vishnu.[10] This is known as Lingodbhava. The Linga Purana also supports this interpretation of lingam as a cosmic pillar, symbolizing the infinite nature of Shiva.[10][13][14][16] According to Linga Purana, the lingam is a complete symbolic representation of the formless Universe Bearer - the oval shaped stone is resembling mark of the Universe and bottom base as the Supreme Power holding the entire Universe in it.[17] Similar interpretation is also found in the Skanda Purana: "The endless sky (that great void which contains the entire universe) is the Linga, the Earth is its base. At the end of time the entire universe and all the Gods finally merge in the Linga itself." [18] In yogic lore, the linga is considered the first form to arise when creation occurs, and also the last form before the dissolution of creation. It is therefore seen as an access to Shiva or that which lies beyond physical creation.[19]
Historical period

According to Shaiva Siddhanta, which was for many centuries the dominant school of Shaiva theology and liturgy across the Indian subcontinent (and beyond it in Cambodia), the linga is the ideal substrate in which the worshipper should install and worship the five-faced and ten-armed Sadāśiva, the form of Shiva who is the focal divinity of that school of Shaivism.[20]

The oldest example of a lingam which is still used for worship is in Gudimallam. According to Klaus Klostermaier, it is clearly a phallic object, and dates to the 2nd century BC.[21] A figure of Shiva is carved into the front of the lingam.[22]
Modern period
In 1825 Horace Hayman Wilson's work on the lingayat sect of South India attempted to refute British notions that the lingam graphically represented a human organ and that it aroused erotic emotions in its devotees.[23]
Monier-Williams wrote in Brahmanism and Hinduism that the symbol of linga is "never in the mind of a Shaiva (or Shiva-worshipper) connected with indecent ideas, nor with sexual love."[24] According to Jeaneane Fowler, the linga is "a phallic symbol which represents the potent energy which is manifest in the cosmos."[4] Some scholars, such as David James Smith, believe that throughout its history the lingam has represented the phallus; others, such as N. Ramachandra Bhatt, believe the phallic interpretation to be a later addition.[25] M.K.V. Narayan distinguishes the Siva-linga from anthropomorphic representations of Shiva, and notes its absence from Vedic literature, and its interpretation as a phallus in Tantric sources.[26]
Ramakrishna practiced Jivanta-linga-puja, or "worship of the living lingam".[27][28] At the Paris Congress of the History of Religions in 1900, Ramakrishna's follower Swami Vivekananda argued that the Shiva-Linga had its origin in the idea of the Yupa-Stambha or Skambha—the sacrificial post, idealized in Vedic ritual as the symbol of the Eternal Brahman.[13][14][29] This was in response to a paper read by Gustav Oppert, a German Orientalist, who traced the origin of the Shalagrama-Shila and the Shiva-Linga to phallicism.[30] According to Vivekananda, the explanation of the Shalagrama-Shila as a phallic emblem was an imaginary invention. Vivekananda argued that the explanation of the Shiva-Linga as a phallic emblem was brought forward by the most thoughtless, and was forthcoming in India in her most degraded times, those of the downfall of Buddhism.[14]
According to Swami Sivananda, the view that the Shiva lingam represents the phallus is a mistake;[17] The same sentiments have also been expressed by H. H. Wilson in 1840.[31]
According to Hélène Brunner,[32] the lines traced on the front side of the linga, which are prescribed in medieval manuals about temple foundation and are a feature even of modern sculptures, appear to be intended to suggest a stylised glans, and some features of the installation process seem intended to echo sexual congress. Scholars like S. N. Balagangadhara have disputed the sexual meaning of lingam.[33]
Naturally occurring lingams

An ice lingam at Amarnath in the western Himalayas forms every winter from ice dripping on the floor of a cave and freezing like a stalagmite. It is very popular with pilgrims.
Shivling (6543m) is also a mountain in Uttarakhand (the Garhwal region of Himalayas). It arises as a sheer pyramid above the snout of the Gangotri Glacier. The mountain resembles a Shiva linga when viewed from certain angles, especially when travelling or trekking from Gangotri to Gomukh as a part of a traditional Hindu pilgrimage.
A lingam is also the base for the legend of formation (and name) of the Borra Caves in Andhra Pradesh.
See also
- Banalinga
- Spatika Lingam
- Axis mundi
- Hindu iconography
- Lingayatism
- Jyotirlinga
- Mukhalinga
- Pancharamas
- Shaligram
References
- ^ Spoken Sanskrit Dictionary
- ^ A Practical Sanskrit Dictionary
- ^ Johnson, W.J. (2009). A dictionary of Hinduism (1st ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780191726705. Retrieved 5 January 2016.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|subscription=ignored (|url-access=suggested) (help)(subscription or UK public library membership required) - ^ a b Fowler, Jeaneane (1997). Hinduism : beliefs and practices. Brighton [u.a.]: Sussex Acad. Press. pp. 42–43. ISBN 9781898723608.
- ^ a b "lingam". Encyclopædia Britannica. 2010.
- ^ Sivananda (1996). Lord Siva and His Worship. Worship of Siva Linga: The Divine Life Trust Society. ISBN 81-7052-025-8.
- ^ Zimmer, Heinrich Robert (1946). Campbell, Joseph (ed.). Myths and symbols in Indian art and civilization. Princeton, New Jersey: Princeton University Press. p. 126. ISBN 0-691-01778-6.
But the basic and most common object of worship in Shiva shrines is the lingam.
- ^ Jansen, Eva Rudy (2003) [1993]. The book of Hindu imagery: gods, manifestations and their meaning. Binkey Kok Publications. pp. 46, 119. ISBN 90-74597-07-6.
- ^ "Sanskrit Dictionary for Spoken Sanskrit (". Spoken Sanskrit. Retrieved 6 May 2016.
- ^ a b c Blurton, T. R. (1992). "Stone statue of Shiva as Lingodbhava". Extract from Hindu art (London, The British Museum Press). British Museum site. Retrieved 2 July 2010.
- ^ The Camphor Flame: Popular Hinduism and society in India, pg. 58 at Books.Google.com
- ^ a b Singh, Nagendra Kr. (1997). Encyclopaedia of Hinduism (1st ed.). New Delhi: Centre for International Religious Studies. p. 1567. ISBN 9788174881687.
- ^ a b c Harding, Elizabeth U. (1998). "God, the Father". Kali: The Black Goddess of Dakshineswar. Motilal Banarsidass. pp. 156–157. ISBN 978-81-208-1450-9.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ a b c d e Vivekananda, Swami. "The Paris Congress of the History of Religions". The Complete Works of Swami Vivekananda. Vol. Vol.4.
{{cite book}}:|volume=has extra text (help); External link in|chapterurl=|chapterurl=ignored (|chapter-url=suggested) (help) - ^ Chaturvedi. Shiv Purana (2006 ed.). Diamond Pocket Books. p. 11. ISBN 978-81-7182-721-3.
- ^ "The linga Purana". astrojyoti. Retrieved 10 April 2012.
. It was almost as if the linga had emerged to settle Brahma and Vishnu's dispute. The linga rose way up into the sky and it seemed to have no beginning or end.
- ^ a b Sivananda, Swami (1996). "Worship of Siva Linga". Lord Siva and His Worship. The Divine Life Trust Society.
- ^ http://is1.mum.edu/vedicreserve/skanda.htm
- ^ "Linga – A Doorway to No-thing". 18 July 2013. Retrieved 11 April 2014.
- ^ Dominic Goodall, Nibedita Rout, R. Sathyanarayanan, S.A.S. Sarma, T. Ganesan and S. Sambandhasivacarya, The Pañcāvaraṇastava of Aghoraśivācārya: A twelfth-century South Indian prescription for the visualisation of Sadāśiva and his retinue, Pondicherry, French Institute of Pondicherry and Ecole française d'Extréme-Orient, 2005, p.12.
- ^ Klostermaier, Klaus K. (2007). A Survey of Hinduism (3. ed. ed.). Albany, N.Y.: State University of New York Press. p. 111. ISBN 9780791470824.
{{cite book}}:|edition=has extra text (help) - ^ Elgood, Heather (2000). Hinduism and the religious arts. London: Cassell. p. 47. ISBN 9780826498656.
- ^ p132
- ^ Carus, Paul (1969). The History of the Devil and the Idea of Evil. Forgotten Books. p. 82. ISBN 978-1-60506-556-4.
- ^ Hinduism and Modernity by David James Smith p. 119
- ^ Flipside of Hindu symbolism, pp. 86–87, by M. K. V. Narayan, Books.Google.com
- ^ Ramakrishna Kathamrita Section XV Chapter II kathamrita.org
- ^ Kripal, Jeffrey J. (1995). Kali's child : the mystical and the erotic in the life and teachings of Ramakrishna (2nd ed.). Chicago: University of Chicago Press. pp. 159–163. ISBN 9780226453774.
- ^ Nathaniel Schmidt (December 1900). "The Paris Congress of the History of Religion". The Biblical World. 16 (6): 447–450. doi:10.1086/472718. JSTOR 3136952.
- ^ Sen, Amiya P. (2006). "Editor's Introduction". The Indispensable Vivekananda. Orient Blackswan. pp. 25–26.
During September–October 1900, he [Vivekananda] was a delegate to the Religious Congress at Paris, though oddly, the organizers disallowed discussions on any particular religious tradition. It was rumoured that his had come about largely through the pressure of the Catholic Church, which worried over the 'damaging' effects of Oriental religion on the Christian mind. Ironically, this did not stop Western scholars from making surreptitious attacks on traditional Hinduism. Here, Vivekananda strongly contested the suggestion made by the German Indologist Gustav Oppert that the Shiva Linga and the Salagram Shila, stone icons representing the gods Shiva and Vishnu respectively, were actually crude remnants of phallic worship.
- ^ Wilson, HH. "Classification of Puranas". Vishnu Purana. John Murray, London, 2005. pp. xli–xlii.
- ^ Hélène Brunner, The sexual Aspect of the linga Cult according to the Saiddhāntika Scriptures, pp.87–103 in Gerhard Oberhammer's Studies in Hinduism II, Miscellanea to the Phenomenon of Tantras, Vienna, Verlag der oesterreichischen Akademie der Wissenschaften, 1998.
- ^ Balagangadhara, S. N. (2007). Invading the Sacred. Rupa & Co. pp. 431–433. ISBN 978-81-291-1182-1.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|editors=ignored (|editor=suggested) (help)
Sources
- Basham, A. L. The Wonder That Was India: A survey of the culture of the Indian Sub-Continent before the coming of the Muslims, Grove Press, Inc., New York (1954; Evergreen Edition 1959).
- Schumacher, Stephan and Woerner, Gert. The Encyclopedia of Eastern Philosophy and Religion, Buddhism, Taoism, Zen, Hinduism, Shambhala, Boston, (1994) ISBN 0-87773-980-3.
- Chakravarti, Mahadev. The Concept of Rudra-Śiva Through the Ages, Delhi: Motilal Banarasidass (1986), ISBN 8120800532.
- Davis, Richard H. (1992). Ritual in an Oscillating Universe: Worshipping Śiva in Medieval India. Princeton, New Jersey: Princeton University Press. ISBN 9780691073866.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - Drabu, V.N. Śaivāgamas: A Study in the Socio-economic Ideas and Institutions of Kashmir (200 B.C. to A.D. 700), New Delhi: Indus Publishing (1990), ISBN 8185182388.
- Ram Karan Sharma. Śivasahasranāmāṣṭakam: Eight Collections of Hymns Containing One Thousand and Eight Names of Śiva. With Introduction and Śivasahasranāmākoṣa (A Dictionary of Names). (Nag Publishers: Delhi, 1996). ISBN 81-7081-350-6. This work compares eight versions of the Śivasahasranāmāstotra. The preface and introduction Template:En icon by Ram Karan Sharma provide an analysis of how the eight versions compare with one another. The text of the eight versions is given in Sanskrit.
- Kramrisch, Stella (1988). The Presence of Siva. Delhi: Motilal Banarsidass. ISBN 9788120804913.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help)
Further reading
- Daniélou, Alain (1991). The Myths and Gods of India: The Classic Work on Hindu Polytheism. Inner Traditions / Bear & Company. pp. 222–231. ISBN 0-89281-354-7Template:Inconsistent citations
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: postscript (link) - Versluis, Arthur (2008), The Secret History of Western Sexual Mysticism: Sacred Practices and Spiritual Marriage, Destiny Books, ISBN 978-1-59477-212-2
External links

