Linux Libertine
 | |
| Category | Serif |
|---|---|
| Classification | Transitional |
| Designer(s) | Philipp H. Poll |
| Foundry | Libertine Open Fonts Project |
| Date released | September 23, 2003 |
| Characters | 2,673 |
| Glyphs | 2,676 |
| License | GPL / OFL |
| Shown here | Version 5.3.0 |
| Website | www |
| Latest release version | 5.3.0 |
| Latest release date | July 6, 2012 |
 | |
| Category | Sans-serif |
|---|---|
| Classification | Humanist |
| Designer(s) | Philipp H. Poll |
| Foundry | Libertine Open Fonts Project |
| Date released | September 23, 2003 |
| Characters | 2,400 |
| Glyphs | 2,403 |
| License | GPL / OFL |
| Sample | |
| Shown here | Version 5.3.0 |
| Latest release version | 5.3.0 |
| Latest release date | July 6, 2012 |
Linux Libertine is a digital typeface created by the Libertine Open Fonts Project, which aims to create free and open alternatives to proprietary typefaces such as Times New Roman. It is developed with the free font editor FontForge and is licensed under the GNU General Public License and the SIL Open Font License.[1]
Characteristics
Linux Libertine is a proportional serif typeface inspired by 19th century book type and is intended as a replacement for the Times font family.[1]
The typeface has five styles: regular, bold, italic, bold italic, and small capitals, all of which are available in TrueType and OpenType format, as well as in source code. The OpenType version allows automatic positioning and substitution, including true fractions, ligatures and kerning. A display type variant, while similar in letter form, is lighter in weight and bears a closer resemblance to old-style types such as Palatino.
There is also a complementary humanist sans-serif face, Linux Biolinum, similar to Optima or Candara. It is available in bold and italic styles.
Unicode coverage
Linux Libertine contains more than 2,000 glyphs and encompasses character sets such as the Greek Alphabet, Cyrillic script, and Hebrew alphabet. Additionally, it offers several ligatures (such as ff, fi, and ct, and the capital ß). It also includes special characters such as International Phonetic Alphabet, arrows, floral symbols, Roman numbers, text figures, and small caps. The Tux mascot is included at the Unicode code point U+E000.
Usage
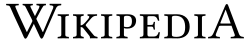
In 2010, Linux Libertine was adopted as an open-source substitute for the Hoefler Text typeface in the redesign of the Wikipedia logo, making it possible to localize the Wikipedia identity into more than 250 languages and character sets.[2] The "W" character, which had previously been used in various other places in Wikipedia (such as the favicon) and was a "distinctive part of the Wikipedia brand", had "crossed" V glyphs in the original logo, while Linux Libertine has a joined W letter shape. As a solution, the "crossed" W was added to Linux Libertine as an OpenType variant.[3][4]
Both the Linux Libertine and Linux Biolinum typefaces are used by the open-source design publication Libre Graphics Magazine.[5]
Derivative works
Németh László created a variant of fonts with additional Graphite font tables: Linux Libertine G and Linux Biolinum G.[6] Both these fonts are bundled with LibreOffice as of the suite's 3.3 release,[7] with some features added in the 3.5 release.[8] LibreOffice is the default office suite in many Linux distributions, such as Fedora,[9] Linux Mint,[10] openSUSE[11] and Ubuntu.[12]
Khaled Hosny forked Linux Libertine to create the Libertinus Serif font, which added multiple enhancements to the original font, he also created Libertinus Math based on the same font to add mathematical layout extensions. Additionally, there is Libertinus Sans which is based on Linux Biolinium and Libertinus Mono which is based on Linux Libertine Mono.[13]
See also
- Free software Unicode typefaces
- GNU General Public License
- List of typefaces
- SIL Open Font License
- Unicode fonts
References
- ^ a b Byfield, Bruce (August 28, 2006). "Linux Libertine Open Fonts offers free Times Roman alternative". Linux.com. Archived from the original on May 21, 2011. Retrieved June 18, 2012.
- ^ Walsh, Jay (May 13, 2010). "Wikipedia in 3D". Wikimedia Blog. Retrieved February 20, 2012.
- ^ Poll, Philipp H. "New Wikipedia-Logo using LinuxLibertine". Libertine Open Fonts Project. Retrieved January 30, 2011.
- ^ Walsh, Jay (May 13, 2010). "Wikimedia official marks/About the official Marks". Wikimedia Foundation. Retrieved February 20, 2012.
- ^ Carvalho, Ana Isabel; coons, ginger; Lafuente, Ricardo (2010). "Production Colophon" (PDF). Libre Graphics Magazine. 1 (1). Libre Graphics Magazine: 7. ISSN 1925-1416. Retrieved July 18, 2011.
- ^ "Linux Libertine G and Linux Biolinum G for LibreOffice and OpenOffice.org desktop publishing, OpenType to Graphite conversion". Numbertext.org. Retrieved July 9, 2018.
- ^ "Bundled Linux "Libertine G" and Linux "Biolinum G" fonts". Libreoffice.org. Retrieved September 30, 2013.
- ^ "Release Notes 3.5". The Document Foundation wiki. February 21, 2012. Retrieved February 23, 2012.
- ^ "Features/LibreOffice". fedoraproject.org. Retrieved April 2, 2011.
- ^ "Linux Mint 11 "Katya" released". The H. Heinz Heise. May 26, 2011. Retrieved May 29, 2011.
- ^ "openSUSE 11.4 Will Be First To Roll Out With LibreOffice". opensuse.org. March 7, 2011. Retrieved May 18, 2011.
- ^ "Features/Office applications". ubuntu.com. Retrieved May 3, 2011.
- ^ "libertinus-fonts/libertinus: Libertinus Font Family". GitHub. Retrieved June 27, 2018.
External links
- Official website
- Download Linux Libertine fonts
- Graphite versions of Linux Libertine G and Linux Biolinum G fonts
- Samples of Linux Biolinum at dafont.com
