Dâmbovița (river)
| Dâmbovița | |
|---|---|
 The Dâmbovița in Bucharest | |
 | |
| Location | |
| Country | Romania |
| Counties | Argeș, Dâmbovița, Ilfov, Bucharest, Călărași |
| Cities | Bucharest |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | Curmătura Oticu |
| • location | Făgăraș Mountains |
| • coordinates | 45°29′54″N 24°56′14″E / 45.49833°N 24.93722°E |
| • elevation | 1,800 m (5,900 ft) |
| Mouth | Argeș |
• location | Budești |
• coordinates | 44°13′40″N 26°28′16″E / 44.22778°N 26.47111°E |
• elevation | 43 m (141 ft) |
| Length | 286 km (178 mi) |
| Basin size | 2,824 km2 (1,090 sq mi) |
| Basin features | |
| Progression | Argeș→ Danube→ Black Sea |
| Tributaries | |
| • left | Ilfov, Colentina |
| River code | X.1.25 |
 | |
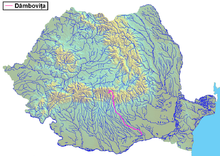
The Dâmbovița (Romanian pronunciation: [ˈdɨmbovitsa] ) is a river in Romania.[1][2] It has its sources on the Curmătura Oticului, a mountain pass that separates the Iezer Mountains from the Făgăraș Mountains proper. It passes through Bucharest and flows into the river Argeș near Budești, in Călărași County. Its length is 286 km (178 mi) and its basin size is 2,824 km2 (1,090 sq mi).[2][3] Dâmbovița County is named after the river.
Name
[edit]The name of the Dâmbovița is of Slavic origin, derived from Common Slavic dǫbŭ (дѫбъ), meaning "oak", as it once flowed through the oak forests of the Wallachian Plain.[4] Its upper course, upstream from the Valea Vladului, is also called Valea Boarcășului.
Dâmbovița in Bucharest
[edit]For centuries, Dâmbovița was the main source of drinking water for the city of Bucharest. While there were a few dozen water wells, most of the water in Bucharest was distributed by water-carriers.[5]
Bucharest folklore mentions the waters of Dâmbovița as "sweet", and even at the beginning of the 18th century, Anton Maria del Chiaro considered it "light and clean". However, toward the end of the 18th century, as the population of Bucharest increased, the river ceased to be as clean, and hence the need of the aqueducts. The earliest aqueducts with public fountains (cișmele) were built during the rule of Prince Alexander Ypsilantis.[5]
Many watermills were built on the Dâmbovița, most of them owned by the prince, the monasteries or boyars.
Dâmbovița used to have two tributaries in Bucharest:
- Dâmbovicioara, on the right bank, which probably flowed in what is the area where Sființii Apostoli street is located.
- Bucureștioara, which rose from a pond located in what is now Grădina Icoanei.
Additionally, there was a branch, Gârlița, which formed an island, Ostrovu.
The Dâmbovița often flooded Bucharest, especially the left bank, which was lower. After the great 1775 flood, Ypsilantis ordered a branch canal to be built, in order to prevent, or at least diminish the effects of such flooding; in 1813, Prince Ioan Caragea decided to clean up the river bed.[5] The portion of the river flowing through the capital was channelled twice: in 1883 (to combat regular floods), and in the late 1970s, to aid in the replanning of the Central area and the construction of the Bucharest Metro. To prevent floods, in 1986 a dam was built between the Crângași and Militari quarters, and Morii Lake artificial lake was created.[6]
Dâmbovița has never been navigable, but there has been an unsuccessful attempt in 1902 to introduce boats on the river.[7]
Early in its history, Bucharest had few bridges over the Dâmbovița, as the right bank was only sparsely populated. The estates of some boyars used to extend on both banks of the river and they had footbridges.[5] Currently, there are sixteen bridges over Dâmbovița River in central Bucharest.
Glina Wastewater Station
[edit]The Dâmbovița was polluted before the opening in 2011 of the Glina Wastewater Station, the biggest ecological project in Romania, which treats the sewage water that pours into the channel which is built below the river floor. Before entering Bucharest, the river's water is already treated by the company "Compania de Apă Târgoviște".[8] After exiting Bucharest, the Dâmbovița water were polluted, due to the hundreds of millions of cubic meters of raw sewage that were dumped every year directly into the channel below the river, but now the quality of water is much improved.[9][10]
In Bucharest, the river is vertically divided into 2 separated parts. In the lower part, under the Dâmbovița river floor, there is a channel which contains the sewage from the city. The two flows join into a single flow when exiting Bucharest. There are river plants and fish that live in the upper side of the river and sometimes one can even see some fishermen on the shores.
The quality of the water was very much improved as of October 10, 2011 with the opening of Glina Wastewater Station, which is the first sewage treatment plant of Bucharest, with a capacity of 10 m3/s (350 cu ft/s), while a second one, which will clean all the water (with a capacity of 12 m3/s) should be finalized by 2015.[10]
Tributaries
[edit]The following rivers are tributaries to the river Dâmbovița (from source to mouth):[2]
Left: Valea Vladului, Berevoiu, Luțele Mari, Luțele Mici, Valea lui Aron (Comisu), Valea Comisului, Pârâul Nemțoaicelor, Răchita, Valea lui Stanciu, Valea Turcilor, Tămașul, Valea Dragoslăvenilor, Valea lui Ivan, Valea Largă, Valea Seacă, Valea Speriatei, Valea Gruiului, Berila, Dâmbovicioara, Valea Orățiilor, Valea Cheii, Ghimbav, Valea Luncii, Valea Caselor, Hotarul, Olăneasca, Valea Runcului, Valea Jocii, Valea Bădenilor, Valea Grecului, Valea lui Coman, Valea Chiliilor, Valea Pleșei, Valea Măgurii, Valea Vlazilor, Valea Ulmului, Valea Largă, Râul Alb, Gârlița Satului, Ilfov, Bâldana, Colentina, Pasărea
Right: Colții lui Andrei, Izvorul Foișorului, Valea Barbului, Izvorul Hotarului, Pârâul Larg, Valea lui Aron (Dracsin), Bălțatul, Dracsin, Cascue, Pârâul Căciulelor, Valea Șaului, Clăbucet, Oncioaia, Valea Arșiței, Râușor, Valea Frasinului, Stoeneasca, Mușcel, Aninoasa, Câlnău, Gruiu
Localities
[edit]The river flows through the following communes, towns and cities: Rucăr, Dragoslavele, Stoenești, Malu cu Flori, Cândești, Vulcana-Băi, Voinești, Mănești, Dragomirești, Lucieni, Nucet, Conțești, Lungulețu, Chiajna, Bucharest (city), Plătărești, Vasilați, Budești (town).
Gallery
[edit]-
Dâmbovița in Bucharest, an aquarelle by Amedeo Preziosi (1868)
-
Systematization of the Dâmbovița in Bucharest (1880s)
-
The Dâmbovița watermills on the outskirts of Bucharest (1837), in the background: Dealul Spirii
-
Dâmbovița and the Bucharest Tribunal (1901)
-
Look on the Dâmbovița in Bucharest
References
[edit]- ^ "Planul național de management. Sinteza planurilor de management la nivel de bazine/spații hidrografice, anexa 7.1" (PDF, 5.1 MB). Administrația Națională Apele Române. 2010. pp. 765–768.
- ^ a b c Atlasul cadastrului apelor din România. Partea 1 (in Romanian). Bucharest: Ministerul Mediului. 1992. pp. 337–340. OCLC 895459847. River code: X.1.25
- ^ 2017 Romanian Statistical Yearbook Archived 2018-06-12 at the Wayback Machine, p. 13
- ^ Constantin C. Giurescu, Istoria Bucureștilor. Din cele mai vechi timpuri pînă în zilele noastre, Bucharest, 1966, p.38
- ^ a b c d Ștefan Ionescu, Bucureștii în vremea fanarioților, Editura Dacia, Cluj, 1974. p. 28-30
- ^ Kadinsky, Sergey (December 28, 2016). "Dâmbovița River, Bucharest". Hidden Waters Blog. Archived from the original on January 7, 2017. Retrieved January 6, 2017.
- ^ Florian Georgescu et al. Istoria Orașului București, Muzeul de Istorie al Orașului București, 1965, p.392
- ^ "CE a aprobat proiectul major pentru sistemul de alimentare cu apă, canalizare și epurare din județul Dâmbovița" Archived 2012-04-25 at the Wayback Machine, Fonduri Structurale, retrieved on October 27, 2011
- ^ "Dâmbovița, râul ucis de deversările Capitalei" Archived 2009-04-11 at the Wayback Machine, Evenimentul Zilei, April 8, 2009
- ^ a b "Sorin Oprescu: "Dâmbovița e mai curată de ieri" Archived 2011-10-11 at the Wayback Machine, Jurnalul Național, October 11, 2011





