Western Qin
Appearance
This article needs additional citations for verification. (December 2015) |
Western Qin (西秦) 苑川 (387-388) 河南 (388-389, 394, 411-414) 金城 (389-394) 梁 (394-395) 秦 (395-400, 409-411, 414-431) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 385–431 | |||||||||||||
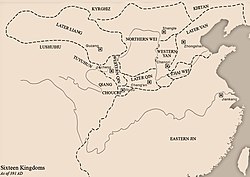 Western Qin and its neighbors in 391 AD | |||||||||||||
| Status | Vassal of Former Qin, Later Qin, Jin Dynasty (265-420), Northern Wei | ||||||||||||
| Capital | Yongshicheng (385-386) Wanchuan (386-388, 400, 410-412) Jincheng (388-395) Xicheng (395-400) Dujianshan (409-410) Tanjiao (412), Fuhan (412-429) Dinglian (429-430) Nan'an (430-431) | ||||||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||||||
| King | |||||||||||||
• 385-388 | Qifu Guoren | ||||||||||||
• 388-400, 409-412 | Qifu Gangui | ||||||||||||
• 412-428 | Qifu Chipan | ||||||||||||
• 428-431 | Qifu Mumo | ||||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||||
• Qifu Guoren's rebellion against Former Qin | 383 | ||||||||||||
• Established | 385 | ||||||||||||
• Qifu Gangui's surrender to Southern Liang | 400 | ||||||||||||
• Qifu Gangui's reassertion of independence | 409 | ||||||||||||
• Qifu Gangui's assassination by Qifu Gongfu | 412 | ||||||||||||
• Disestablished | 431 | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
The Western Qin (Chinese: 西秦; pinyin: Xīqín; 385-400, 409-431) was a state of Xianbei ethnicity during the era of Sixteen Kingdoms in China.[1] Note that the Western Qin is entirely distinct from the ancient Qin Dynasty, the Former Qin, and the Later Qin.
All rulers of the Western Qin declared themselves "wang", translatable as either "king" or "prince." They ruled the area that is now southwest part of Gansu province in Northwest China.
Rulers of the Western Qin
| Temple names | Posthumous names | Family names and given name | Durations of reigns | Era names and their according durations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese convention: use family and given names | ||||
| Liezu (烈祖 Lièzǔ) | Xuanlie (宣烈 Xuānliè) | 乞伏國仁 Qǐfú Guórén | 385-388 | Jianyi (建義 Jiànyì) 385-388 |
| Gaozu (高祖 Gāozǔ) | Wuyuan (武元 Wǔyuán) | 乞伏乾歸 Qǐfú Gānguī | 388-400, 409-412 | Taichu (太初 Taìchū) 388-400 Gengshi (更始 Gèngshǐ) 409-412 |
| Taizu (太祖 Taìzǔ) | Wenzhao (文昭 Wénzhāo) | 乞伏熾磐 Qǐfú Chìpán | 412-428 | Yongkang (永康 Yǒngkāng) 412-419 Jianhong (建弘 Jiànhóng) 420-428 |
| Did not exist | Houzhu (後主 Hoùzhǔ) | 乞伏暮末 Qǐfú Mùmò | 428-431 | Yonghong (永弘 Yǒnghóng) 428-431 |
The family tree of Western Qin rulers
| Western Qin | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See also
References
- ^ Grousset, Rene (1970). The Empire of the Steppes. Rutgers University Press. pp. 59–60. ISBN 0-8135-1304-9.
