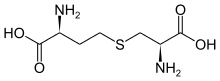
Cystathionine
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
S-((R)-2-amino-2-carboxyethyl)-L-homocysteine
| |
| Other names
L-Cystathionine; S-[(2R)-2-Amino-2-carboxyethyl]-L-homocysteine
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.269 |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | Cystathionine |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H14N2O4S | |
| Molar mass | 222.26 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Cystathionine is an intermediate in the synthesis of cysteine.
Cystathionine is produced by the transsulfuration pathway which converts homocysteine into cystathionine. Cystathionine is then used by the enzymes cystathionine gamma-lyase (CTH), cysteine dioxygenase (CDO), and sulfinoalanine decarboxylase to produce hypotaurine and then taurine.[1]
Alternately, the cysteine from the cystathionine gamma-lyase can be used by the enzymes glutamate–cysteine ligase (GCL) and glutathione synthetase (GSS) to produce glutathione.
An excess of cystathionine in the urine is called cystathioninuria.
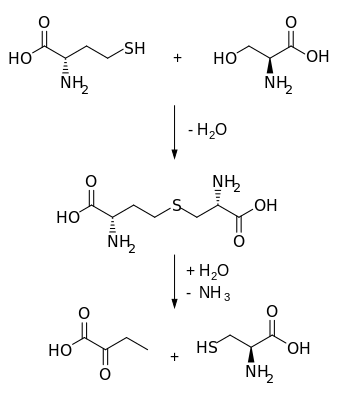
Biosynthetically, cystathionine is generated from homocysteine and serine by cystathionine beta synthase (upper reaction in the diagram below). It is then cleaved into cysteine and α-ketobutyrate by cystathionine gamma-lyase (lower reaction).