PSA Group: Difference between revisions
m TypoScan Project / General Fixes, typos fixed: Franche Comté → Franche-Comté using AWB |
Svgalbertian (talk | contribs) also traded as OTCQX |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
| company_logo = [[Image:PSA Peugeot Citroën.svg|220px]] |
| company_logo = [[Image:PSA Peugeot Citroën.svg|220px]] |
||
| company_type = [[S.A. (corporation)|Société Anonyme]] |
| company_type = [[S.A. (corporation)|Société Anonyme]] |
||
| traded_as = {{Euronext|UG}} |
| traded_as = {{Euronext|UG}}<BR>{{OTCQX|PEUGY}} |
||
| company_slogan = |
| company_slogan = |
||
| foundation = 1976 (Paris) |
| foundation = 1976 (Paris) |
||
Revision as of 14:28, 5 May 2012
| Company type | Société Anonyme |
|---|---|
| Euronext: UG OTCQX: PEUGY | |
| Industry | Automotive |
| Founded | 1976 (Paris) |
| Headquarters | 16th arrondissement, Paris, France |
Area served | Worldwide except North America, South Asia |
Key people | Philippe Varin (CEO) Thierry Peugeot (Chairman of the supervisory board) |
| Products | Automobiles (73.8%) Automotive parts (21%) Financing (2.8%) Logistics (2.2%) Motorcycles (0.2%)[1] |
Production output | 3,549,000 units (2011)[2] |
| Revenue | €59.912 billion (2011)[2] |
| €1.315 billion (2011)[2] | |
| €1.134 billion (2010)[2] | |
| Total assets | €68.49 billion (end 2010)[2] |
| Total equity | €14.30 billion (end 2010)[2] |
| Owner | Peugeot family 30.3%[3] |
Number of employees | 198,220 (end 2010)[2] |
| Subsidiaries | Citroën, Peugeot, Faurecia (majority stake), Gefco, Banque PSA Finance, Peugeot Motocycles, Peugeot Citroën Moteurs, Process Conception Ingénierie |
| Website | psa-peugeot-citroen.com |
PSA Peugeot Citroën (officially Peugeot S.A., informally PSA) is a French multinational manufacturer of automobiles and motorcycles sold under the Peugeot and Citroën marques. Headquartered in the 16th arrondissement of Paris, PSA is the second-largest Europe-based automaker (after Volkswagen Group) and the eighth-largest in the world measured by 2010 unit production.[4]
PSA is listed on the Euronext Paris stock exchange and is a constituent of the CAC 40 index.
History
In December 1974 Peugeot S.A. acquired a 38.2% share of Citroën. On 9 April 1976[5] they increased their stake of the then bankrupt company to 89.95%, thus creating the PSA Group (where PSA is short for Peugeot Société Anonyme), becoming PSA Peugeot Citroën.[6] Since Citroën had two successful new designs in the market at this time (the GS and CX) and Peugeot was typically prudent in its own finances, the PSA venture was a financial success from 1976 to 1979.
In late 1978, PSA purchased the failing Chrysler Europe (which was formerly Rootes and Simca), from the troubled U.S. parent firm for a nominal USD $1.00, plus assumption of outstanding debt, leading to losses for the consortium from 1980 to 1985.[7] Further investment was required because PSA decided to create a new brand for the entity for the disparate French and British models, based on the Talbot sports car last seen in the 1950s. From then on, the whole Chrysler/Simca range was sold under the Talbot badge until production of Talbot-branded passenger cars was shelved in 1987 and on commercial vehicles in 1992.[8]
All of this investment caused serious financial problems for the entire PSA group; PSA lost money from 1980 to 1985. In 1986, the company dropped the Talbot brand for passenger cars when it ceased production of the Simca-based Horizon, Alpine and Solara models. What was to have been the Talbot Arizona became the 309, with the former Rootes plant in Ryton and Simca plant in Poissy being turned over for Peugeot assembly. Producing Peugeots in Ryton was significant, as it signalled the first time that PSA would build cars in the UK. The Talbot name survived for a little longer on commercial vehicles until 1992 before being shelved completely.
In October 2011, PSA has announced to cut 5,000 non-production jobs in Europe in a cost-cutting effort. There are no cut for production employees, although the two-companies are planning temporary work stoppages at some factories inline with reducing demand of vehicles caused by the European sovereign debt crisis.[9]
On 29 February 2012, PSA formally announced the creation of a major alliance with General Motors (GM), as part of which GM became PSA's second-largest shareholder, after the Peugeot family, with a holding of 7%. The alliance is intended to enable £1.3 billion per year of cost savings through platform sharing, common purchasing and other economies of scale.[10]
Operations
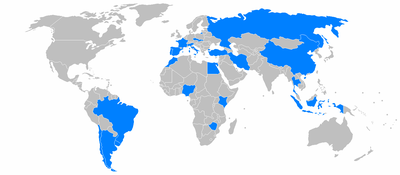
The Peugeot and Citroën brands retain separate sales and marketing structures, but share common technology, development and assembling assets.
PSA is actively committed to develop its market presence and sales in many fast growing developing countries and regions of the world. This led to huge investments and partnerships in South America, Iran (Iran Khodro) and China (Dongfeng Peugeot-Citroën Automobile). It announced plans to invest € 650 million in a manufacturing plant in Sanand, India. With a capacity of 170,000 vehicles, the Sanand plant is expected to be operational by 2014.[11]
Jean-Martin Folz was PSA's CEO between 1996 and early 2007, when he was replaced by former Airbus head Christian Streiff. Streiff was sacked on 29 March 2009, a day after the company posted a full year loss for 2008.[12] Streiff was replaced by Corus Group chief executive Philippe Varin.[12]
Peugeot Citroën Automobiles SA
The manufacturer of Peugeot and Citroën branded cars and vans, 100% owned by PSA Peugeot Citroën and formed from the combination of Automobiles Citroën and Automobiles Peugeot. Automobiles Citroën and Automobiles Peugeot remain in operation in relation to specific retail operations in various countries but not in the development or manufacture of vehicles.
Peugeot Citroën Moteurs
Peugeot Citroën Moteurs is a manufacturer of petrol and diesel engines for a range of companies including Citroën, Ford, Jaguar, Mini and Peugeot. Initially founded by Peugeot in 1898 in Lille and subsequently named Compagnie Lilloise de moteurs (CLM). In 1992 SCM-CLM as it was then known became Peugeot Citroën Moteurs.[13]
The company has a partnership with Ford Motor Company since 1998,[14] currently supplies and receives a range of petrol and diesel engines to Ford and its subsidiaries.
PSA and BMW have an agreement to develop the Prince engine. PSA also sell their engines, gearboxes and other parts for minor companies like Side-Bike, DeLaChapelle, PGO and others.[citation needed]
Process Conception Ingénierie
Process Conception Ingénierie (PCI) is a French based manufacturer of machine-tools for the automotive and aircraft industry.[15]
Peugeot Motocycles
Peugeot Motocycles is 99.9% owned by PSA and manufacturers a range of mopeds and scooters. The subsidiary owns 50% of the Chinese Jinan Quigqu Peugeot Motocycles joint venture.
Faurecia
PSA owns 57.43% of automotive supplier Faurecia,[16] a company created by a 1997 merger between Bertrand Faure and PSA-owned ECIA. It provides various components to Citroen and Peugeot together with significant interior and exterior parts to companies such as Audi, BMW and Mercedes-Benz.[17]
Gefco
Gefco is a large international logistics company,[18] wholly owned by PSA.[19] It was established by Peugeot in 1949 and was originally named Les Groupages Express de Franche-Comté.
Motaquip
Motaquip is an aftermarket parts company established in the UK in 1981[20]
Financial services
PSA wholly owns Banque PSA Finance which provides financial services and also 98.67% of GIE PSA Tresorerie which was founded in 1990 as a treasury and cash management services division.
Former subsidiaries
- Cycles Peugeot - Produced bicycle from the 1882 until 2005. In 1987 ProCycle of Canada acquired rights to distribute French-made Peugeots in North America and in 1990, Cycles Peugeot sold the North American rights to market bicycles under the Peugeot name to the Canadian firm ProCycle. In 2001, ProCycle discontinued the Peugeot bicycle brand. In Europe, the license to produce Peugeot-branded bicycles was sold to Cycleurope, a company making bicycles under different names, on condition that it would be reconsidered in 2004. That license was later withdrawn for Europe, though production of bicycles for export continued for another year.
- Citer SA - French based car rental company originally established by Citroën in 1968 was sold to Enterprise Holdings in 2011.[21]
Joint ventures and collaborations
Sevel SpA
Seval (Société Européenne de Véhicules Légers SA and Società Europea Veicoli Leggeri-Sevel S.p.A.) was established in 1978 and is equally owned by Peugeot Citroen and Fiat. As a result of this, two factories have been built assembling three ranges of vehicles, Sevel Nord and Sevel Sud. Peugeot and Fiat's Argentinian operations were also joined under the name of Sevel Argentina S.A. (Sociedad Europea de Vehículos para Latinoamérica), although Fiat withdrew in 1995. Currently Sevel builds the Fiat Ducato, Peugeot Boxer and Citroen Dispatch vans.
Dongfeng Peugeot Citroën Automobile Company
The joint venture with the Chinese company Dongfeng was established in 1992 and produces the 207, 307 and 408 models at factories in Wuhan and Xiangyang.[22]
Toyota Peugeot Citroën Automobile
In 2002 the joint venture with Toyota Motor Corporation for the development and manufacturing of a series of city cars in a new factory in the Czech Republic was signed. The resulting company is called TPCA (Toyota Peugeot Citroën Automobile) and it currently manufactures the Citroën C1, Peugeot 107 and Toyota Aygo.[23]
Peugeot Citroën Mitsubishi Automotiv Rus
The Kaluga factory was built by the Russian based joint venture between PSA Peugeot Citroën (70%) and Mitsubishi Motors (30%) established in 2011. The site builds the joint venture Peugeot 4007, Citroën C-Crosser and Mitsubishi Outlander, and the Peugeot 308 and Citroën C4.[24]
BMW Peugeot Citroën Electrification
In 2011 PSA Peugeot Citroën and BMW agreed an equal joint venture to develop and manufacturer hybrid components including battery packs, generators, power electronics and chargers, and software for hybrid systems.[25]
Changan PSA Automobile
A 50-50 joint venture with the Chinese Chang'an Automobile Group. Based in Shenzhen with an initial annual production capacity of 200,000 vehicles & engines.[26]
Other interests
In 2008 the company investigated the option to buy Mitsubishi Motors but a deal could not be concluded and was called off in 2010.[27] One outcome of the talks resulted in the Mitsubishi Outlander and Mitsubishi i-MiEV to be sold as Peugeot and Citroen in Europe from 2010.[28]
Former joint ventures
- Guangzhou Peugeot Automobile Company (GPAC) was in operation from 1985 to 1997[29] and produced the Peugeot 504 and 505.
Locations
Head office
The head office of PSA Peugeot Citroën is located in the 16th arrondissement of Paris.[30][31] The 50,000-square-metre (540,000 sq ft) 1961 building houses around 2,000 employees. 900 square metres (9,700 sq ft) of space in the lobby includes an automobile showroom.[31]
Other locations
PSA has a number of manufacturing and development sites around the world. Vigo, in Galicia has PSA's biggest factory in the world.
PSA invested ₹4 billion establishing new plant in Chennai, India[32]
European Car of the Year
Peugeot S.A., Citroën and PSA have produced a number of European Car of the Year winners:[33]
- 1969 - Peugeot 504
- 1971 - Citroën GS
- 1975 - Citroën CX
- 1988 - Peugeot 405
- 1990 - Citroën XM
- 2002 - Peugeot 307
See also
Notes
- ^ "Peugeot Company Information". NYSE EURONEXT. Retrieved 4 January 2012.
- ^ a b c d e f g "Annual Report 2010" (PDF). PSA Peugeot Citroën. Retrieved 25 April 2011.
- ^ "Ownership structure". PSA Peugeot Citroen website. 31 December 2010. Retrieved 4 January 2012.
- ^ "WORLD RANKING OF MANUFACTURERS 2010" (PDF). oica.net. Retrieved 6 October 2011.
- ^ http://news.google.com/newspapers?id=MZxAAAAAIBAJ&sjid=GKUMAAAAIBAJ&pg=6208,1716150&dq=citroen&hl=en
- ^ Peugeot Motion and Emotion, Corporate interactive history, Undated. Retrieved: 9 April 2012.
- ^ "Development of the Simca 180 cars". Rootes-Chrysler.co.uk. Retrieved 11 June 2006.
- ^ "Austin Rover Online". Aronline.co.uk. Retrieved 2 May 2011.
- ^ "Peugeot Citroën may cut 5000 jobs in Europe". Retrieved 26 October 2011.
- ^ "GM and Peugeot announce alliance". BBC News. 29 February 2012. Retrieved 29 February 2012.
- ^ Pearson, David (1 September 2011). "Peugeot-Citroen to Invest €650 Million in Indian Assembly Plant". Wall Street Journal. Retrieved 2 September 2011.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) [dead link] - ^ a b "French carmaker Peugeot fires CEO to weather crisis". Reuters. 30 March 2009. Retrieved 1 October 2010.
- ^ "Official website". Peugeot Citroen Moteurs. Retrieved 6 January 2012.
- ^ "Ford And PSA Peugeot Citroen Announce Plans For Expansion Of Diesel Engine Production". Carpages.co.uk. Retrieved 30 September 2010.
- ^ "Official website". PCI. Retrieved 6 January 2012.
- ^ "2010 Registration Document" (PDF). PSA Peugeot Citroen. Retrieved 6 January 2012.
- ^ "Geneva 2011 press pack" (PDF). Faurecia. Retrieved 6 January 2012.
- ^ "Official website". Gefco. Retrieved 6 January 2012.
- ^ "Gefco SA". Funding Universe. Retrieved 6 January 2012.
- ^ "About Motaquip". Motaquip. Retrieved 4 January 2012.
- ^ Webb, Alex (21 November 2011). "Enterprise Buys Peugeot Rental-Car Unit". Bloomberg. Retrieved 6 January 2012.
- ^ "China : Wuhan". PSA Peugeot Citroen. Retrieved 4 January 2012.
- ^ "About us". TPCA website. Retrieved 4 January 2012.
- ^ "PSA Peugeot Citroën and Mitsubishi Motors Corporation begin production at their jointly owned plant in Kaluga". PSA Peugeot Citroën press release. 23 April 2010. Retrieved 4 January 2012.
- ^ "BMW Group and PSA Peugeot Citroën Create Joint Venture to Enhance Cooperation on Hybrid Technologies". BMW Press release. Retrieved 4 January 2012.
- ^ "FIRST HALF RESULTS" (PDF). 2011 FIRST HALF RESULTS - July 27th, 2011. PSA Peugeot Citroen. Retrieved 4 January 2012.
- ^ "Mitsubishi left at the altar – again". Go Auto. 11 March 2010. Retrieved 4 January 2012.
- ^ Lawrence J. Speer (2009). "PSA to launch electric cars next year". autonews.com. Retrieved 30 September 2010.
- ^ "China Press Kit – September 2010" (PDF). PSA Peugeot Citroen. Retrieved 8 January 2012.
- ^ "Contact." PSA Peugeot Citroën. Retrieved on 7 July 2010.
- ^ a b "Axa allie patrimoine et modernité." Le Journal du Net. Retrieved on 7 July 2010.
- ^ "Peugeot to set up Rs 4,000-cr plant in Tamil Nadu". The Times Of India. 30 June 2011.
- ^ "European Car of the Year webpage" (in Template:Es icon). Caroftheyear.org. Retrieved 6 January 2012.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link)
External links
