Epirus: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Daniel Case (talk | contribs) +protection notice |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Historical region in the Balkans}} |
|||
{{Otheruses4|the broad [[Geography|geographical]] and [[History|historical]] region of ''Epirus'', spanning [[Greece]] and [[Albania]]|other uses|Epirus}} |
|||
{{pp|small=yes}} |
|||
{{Other uses}} |
|||
{{Use dmy dates|date=April 2017}} |
|||
{{Infobox settlement |
|||
| name = Epirus |
|||
| native_name = <small>{{lang-el|Ήπειρος}}<br />{{lang-sq|Epiri}}<br />{{lang-rup|Epiru}}</small> |
|||
| native_name_lang = |
|||
| settlement_type = [[Historical region]] |
|||
| image_map = Epirus antiquus tabula.jpg |
|||
| map_alt = |
|||
| map_caption = Map of ancient Epirus by [[Heinrich Kiepert]], 1902 |
|||
| coordinates = |
|||
| coor_pinpoint = |
|||
| coordinates_footnotes = |
|||
| subdivision_type = Present status |
|||
| subdivision_name = Divided between [[Greece]] and [[Albania]] |
|||
<!-- ALL fields with measurements have automatic unit conversion --> |
|||
<!-- for references: use <ref> tags --> |
|||
| area_footnotes = |
|||
| area_note = |
|||
| area_water_percent = |
|||
<!-- square kilometers --> |
|||
| area_total_km2 = |
|||
| area_land_km2 = |
|||
| area_water_km2 = |
|||
| area_urban_km2 = |
|||
| area_rural_km2 = |
|||
| area_metro_km2 = |
|||
| dimensions_footnotes = |
|||
| elevation_footnotes = |
|||
| elevation_m = |
|||
| population_footnotes = |
|||
| population_total = |
|||
| population_as_of = |
|||
| population_density_km2 = auto |
|||
| population_note = |
|||
| timezone1 = [[Central European Time]] |
|||
| timezone2 = [[Eastern European Time]] |
|||
| utc_offset1 = |
|||
| timezone1_DST = |
|||
| utc_offset1_DST = |
|||
| footnotes = |
|||
| population_demonym = Epirote |
|||
}} |
|||
'''Epirus''' ({{IPAc-en|ᵻ|ˈ|p|aɪ|r|ə|s}}) is a [[Region#Geographical regions|geographical]] and [[historical region|historical]] region in [[southeastern Europe]], now shared between [[Greece]] and [[Albania]]. It lies between the [[Pindus Mountains]] and the [[Ionian Sea]], stretching from the [[Bay of Vlorë]] and the [[Ceraunian Mountains|Acroceraunian Mountains]] in the north to the [[Ambracian Gulf]] and the ruined [[Roman Empire|Roman]] city of [[Nicopolis]] in the south.<ref name=Britannica/><ref name="OCD527">{{harvnb|Hornblower|Spawforth|Eidinow|2012|loc="Epirus", p. 527}}.</ref> It is currently divided between the [[Modern regions of Greece|region]] of [[Epirus (region)|Epirus]] in northwestern Greece and the counties of [[Gjirokastër County|Gjirokastër]] and [[Vlorë County|Vlorë]] in southern Albania. The largest city in Epirus is [[Ioannina]], seat of the Greek region of Epirus, with [[Gjirokastër]] the largest city in the Albanian part of Epirus.<ref name=Britannica/> |
|||
'''Epirus''' is a region in south-eastern [[Europe]], currently divided between the [[Peripheries of Greece|periphery]] [[Epirus (periphery)|of Epirus]] in [[Greece]] and the prefectures of [[Gjirokastër County|Gjirokastër]], [[Vlorë County|Vlorë]], [[Berat County|Berat]], and [[Korçë County|Korçë]] in southern [[Albania]]. |
|||
[[Image:Ancient epirus map.jpg|right|thumb|250px|Map of ancient Epirus]] |
|||
A rugged and mountainous region, Epirus was the north-west area of [[ancient Greece]].<ref name="OCD527"/> It was inhabited by the Greek tribes of the [[Chaonians]], [[Molossians]], and [[Thesprotians]]. It was home to the sanctuary of [[Dodona]], the oldest [[oracle]] in ancient Greece, and the second most prestigious after [[Delphi]]. Unified into a [[Epirus (ancient state)|single state]] in 370 BC by the [[Aeacidae]] dynasty, Epirus achieved fame during the reign of [[Pyrrhus of Epirus]] who fought the [[Roman Republic]] in [[Pyrrhic War|a series of campaigns]]. Epirus subsequently became part of the Roman Republic along with the rest of Greece in 146 BC, which was followed by the [[Roman Empire]] and [[Eastern Roman Empire]]. |
|||
==Name & Etymology== |
|||
The name Epirus, from {{lang-el|Ἤπειρος}} ''Epeiros'' (in [[Doric Greek|Doric]] and the native Northwestern Greek Ἅπειρος ''Apeiros'') means 'mainland',<ref>[http://www.perseus.tufts.edu/cgi-bin/ptext?doc=Perseus%3Atext%3A1999.04.0057%3Aentry%3D%2347463 Epeiros], Henry George Liddell, Robert Scott, ''A Greek-English Lexicon'', at Perseus</ref> as contrasted with [[Ionian islands]] off the Epirote coast. It is thought to come from an [[Proto-Indo-European language|Indo-European]] root ''{{Unicode|*apero-}}'' 'coast'<ref>Babiniotis, G. ''Lexiko tis Neas Ellinikis Glossas''. Athens, 1998</ref>. It was originally applied to the whole Greek mainland. The [[Albanian language|Albanian]] name for the region is ''Epiri''. |
|||
Following the [[sack of Constantinople]] by the [[Fourth Crusade]] (1204), Epirus became the center of the [[Despotate of Epirus]], one of the successor states to the [[Byzantine Empire]]. In the 14th century, Epirus was brought under the rule of the [[Byzantine Empire under the Palaiologoi|restored Byzantine Empire]], before being briefly conquered by the [[Serbian Empire]]. The region was then divided amongst a number of despotates and political entities, including the Despotate of Epirus, the [[Despotate of Arta]], the [[Zenebishi family]], and the [[Republic of Venice]], before being conquered by the [[Ottoman Empire]] in the 15th century. Epirus became part of the semi-independent [[Pashalik of Yanina|Pashalik]] governed by the Ottoman [[Albanians|Albanian]] ruler [[Ali Pasha of Ioannina|Ali Pasha]] in the early 19th century, but the [[Sublime Porte]] re-asserted its control in 1821. Following the [[Balkan Wars]] and [[World War I]], southern Epirus became part of Greece, while [[northern Epirus]] became part of Albania. |
|||
==Name and etymology== |
|||
[[File:Epirus234bc.jpg|thumb|right|Coin of the Epirote League, depicting Zeus (left) and a lightning bolt with the word "ΑΠΕΙΡΩΤΑΝ" – of the Epirotes (right).]] |
|||
The name ''Epirus'' is derived from the {{lang-el|Ἤπειρος|translit=Ḗpeiros}} ({{lang-grc-dor|Ἄπειρος|translit=Ápeiros}}), meaning "mainland" or ''[[wikt:terra firma|terra firma]]''.<ref>{{harvnb|Liddell|Scott|1940|loc=[https://www.perseus.tufts.edu/cgi-bin/ptext?doc=Perseus%3Atext%3A1999.04.0057%3Aentry%3D%2347463 ἤπειρ-ος]}}.</ref>{{Sfn|Filos|2018|loc=p. 215, footnote #1}} It is thought to come from an [[Proto-Indo-European language|Indo-European]] root ''<nowiki>*</nowiki>apero-'' 'coast',<ref>{{harvnb|Babiniotis|1998}}</ref> and was applied to the mainland of north-west Greece opposite [[Corfu]] and the [[Ionian islands]].<ref>{{cite book |author1=David Sacks |author2=Lisa R. Brody |author3=Oswyn Murray |title= Encyclopedia of the Ancient Greek World |series=Facts on File Library of World History |date=2005 |publisher=Facts on File |isbn=0816057222 |page=85 |quote=... in a region of northwest Greece called Epirus.}}</ref><ref>{{harvnb|Winnifrith|2002|p=22}}.</ref> The local name was struck on the coinage of the [[Epirote League|unified Epirote commonwealth]]: "ΑΠΕΙΡΩΤΑΝ" ({{lang-grc|Ἀπειρωτᾶν|translit=Āpeirōtân}}, {{lang-grc-x-attic|Ἠπειρωτῶν|translit=Ēpeirōtôn}}, i.e. "of the Epirotes", see adjacent image). The [[Albanian language|Albanian]] name for the region, which derives from the Greek, is {{lang|sq|Epiri}}. Similarly, the [[Aromanian language|Aromanian]] name for Epirus, which is also Greek-derived, is {{lang|rup|Epiru}}. |
|||
==Boundaries and definitions== |
==Boundaries and definitions== |
||
[[ |
[[File:Epirus landsat.jpg|right|thumb|[[NASA]] satellite image of Epirus.]] |
||
The historical region of Epirus is generally regarded as extending from the northern end of the Llogara mountains in present-day Albania (historically the "Ceraunian mountains", from [[Ancient Greek]] Κεραύνια όρη<ref>Strabo, ''Geography'', Book VI, 3.5[http://penelope.uchicago.edu/Thayer/E/Roman/Texts/Strabo/6C*.html at LacusCurtius]</ref><ref>Strabo, ''Geography'' Book VII, 5.1 [http://penelope.uchicago.edu/Thayer/E/Roman/Texts/Strabo/7G*.html LacusCurtius]</ref> 'thunder-splitted peaks'<ref>[http://www.perseus.tufts.edu/cgi-bin/ptext?doc=Perseus%3Atext%3A1999.04.0057%3Aentry%3D%2356791 Keraunia], Henry George Liddell, Robert Scott, ''A Greek-English Lexicon'', at Perseus</ref>), located just south of the bay of Vlore, to the [[Ambracian Gulf]] (or Gulf of Arta) in Greece. The northern boundary of Classical Epirus is also given as the mouth of the Aoous (Vjosa) river, immediately to the north of the bay of Vlora.<ref> John Wilkes. [http://books.google.com/books?id=4Nv6SPRKqs8C&pg=PA92&dq=Illyrians%2Bepirus&lr=&as_brr=3&hl= The Illyrians.] Wiley-Blackwell, 1996. ISBN 9780631198079 p. 92 "Appian's description of the Illyrian territories records a southern boundary with Chaonia and Thesprotia, where ancient Epirus began south of river Aoous (Vjose)" also map [http://books.google.com/books?id=4Nv6SPRKqs8C&lpg=PP1&dq=illyrians%20wilkes&pg=PR20]</ref> Epirus' eastern boundary is defined by the [[Pindus Mountains]] that form the spine of mainland Greece and separate Epirus from [[Macedonia (Greece)|Macedonia]] and [[Thessaly]]. To the west, Epirus faces the [[Adriatic Sea]] and [[Ionian Sea]]. The island of [[Corfu]] is situated off the coast but is not regarded as part of Epirus. |
|||
Historically, the geographical area of Epirus proper is defined within the lines drawn from [[Cape of Gjuhëz|Cape Gjuhëz]] of the [[Ceraunian Mountains]] in the north-west, to [[Mount Qelqëz]] in the north-east, to [[Mount Gavrovo]] in the south-east, to the mouth of the [[Ambracian Gulf]] in the south-west.<ref>{{harvnb|Suha|2021|p=19}}</ref><ref>{{harvnb|Greenwalt|2011|p=280}}</ref> The northern boundary of ancient Epirus is alternatively given as the [[Vjosa]] river.<ref>{{harvnb|Wilkes|1995|loc=p. 92 "Appian's description of the Illyrian territories records a southern boundary with Chaonia and Thesprotia, where ancient Epirus began south of the river Aous (Vijosë)."}} ([https://books.google.com/books?id=4Nv6SPRKqs8C&dq=illyrians%20wilkes&pg=PR20 Map])</ref> Epirus's eastern boundary is defined by the [[Pindus Mountains]], that form the spine of mainland Greece and separate Epirus from [[Macedonia (Greece)|Macedonia]] and [[Thessaly]].<ref name=Britannica/> To the west, Epirus faces the [[Ionian Sea]]. The island of [[Corfu]] is situated off the Epirote coast but is not regarded as part of Epirus. |
|||
The definition of Epirus has changed over time, such that modern administrative boundaries do not correspond |
The definition of Epirus has changed over time, such that modern administrative boundaries do not correspond to the boundaries of ancient Epirus. The [[Epirus (region)|region of Epirus]] in Greece only comprises a fraction of classical Epirus and does not include its easternmost portions, which lie in Thessaly. In Albania, where the concept of Epirus is never used in an official context, the counties of Gjirokastër, [[Vlorë County|Vlorë]], and [[Berat County|Berat]] extend well beyond the northern and northeastern boundaries of classical Epirus.{{cn|date=August 2022}} |
||
==Geography and ecology== |
==Geography and ecology== |
||
[[ |
[[File:Smolikas IMG 0118.jpg|right|thumb|[[Smolikas|Mount Smolikas]] (2637m/8652f), the highest point in Epirus.]] |
||
[[ |
[[File:Zagori Vikos gorge Oxia towards Vikos.jpg|right|thumb|[[Vikos Gorge]] in [[Vikos–Aoös National Park]].]] |
||
Epirus is a rugged and mountainous region. It is largely made up of the [[Pindus Mountains]], a series of parallel [[limestone]] ridges that are a continuation of the [[Dinaric Alps]]. The Pindus mountains form the spine of mainland Greece and separate Epirus from [[Macedonia (Greece)|Macedonia]] and [[Thessaly]] to the East. Altitude increases as one moves away from the coast, reaching a maximum of 2637m at [[Smolikas|Mount Smolikas]], the highest point in Epirus. Other important ranges include, Tymfi (2496 at Mount Gamila), Lygkos (2249m), to the west and east of Smolikas, respectively, [[Gramos]] (2523m) in the northeast, Tzoumerka (2356m) in the southeast, Tomaros (1976m) in the southwest, Mitsikeli near [[Ioannina]] (1810m), Mourgana (1806m) and Nemercke/Aeoropos (2485) on the border between Greece and Albania, and Llogara (2000m) near [[Himara]] in Albania. Most of Epirus lies on the windward side of the Pindus. The winds from the Ionian Sea make the region the rainiest in Greece. |
|||
Epirus is a predominantly rugged and mountainous region. It is largely made up of the [[Pindus Mountains]], a series of parallel [[limestone]] ridges that are a continuation of the [[Dinaric Alps]].<ref name="Britannica">{{cite encyclopedia|url=https://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/190156/Epirus|title=Epirus|encyclopedia=Encyclopædia Britannica|publisher=Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.|access-date=16 November 2013}}</ref><ref>{{harvnb|Bahr|Johnston|Bloomfield|1997|p=389}}.</ref> The Pindus mountains form the spine of mainland Greece and separate Epirus from Macedonia and Thessaly to the east. The ridges of the Pindus are parallel to the sea and generally so steep that the valleys between them are mostly suitable for pasture rather than large-scale agriculture.<ref name=Britannica/> Altitude increases as one moves east, away from the coast, reaching a maximum of 2,637 m at [[Smolikas|Mount Smolikas]], the highest point in Epirus. Other important ranges include [[Tymfi]] (2,496 m at Mount Gamila), [[Lygkos]] (2,249 m), to the west and east of Smolikas respectively, [[Gramos]] (2,523 m) in the northeast, Tzoumerka (2,356 m) in the southeast, Tomaros (1,976 m) in the southwest, [[Mitsikeli]] near [[Ioannina]] (1,810 m), [[Mourgana]] (1,806 m), and [[Nemercke|Nemercke/Aeoropos]] (2,485 m) on the border between Greece and Albania, and the [[Ceraunian Mountains]] (2,000 m) near [[Himara]] in Albania. Most of Epirus lies on the windward side of the Pindus, and the prevailing winds from the Ionian Sea make the region the rainiest in mainland Greece.<ref name=Britannica/> |
|||
The main river flowing through Epirus is the Aoos/Vjosa, which flows in a northwesterly direction from the Pindus mountains in Greece to its mouth north of the bay of Vlora. Other important rivers include the the [[Acheron|Acheron river]], famous for its religious significance in ancient Greece and site of the [[Necromanteion]], the [[Arachthos river]], crossed by the historic [[Bridge of Arta]], the [[Thyamis|Kalamas river]] (anc. Thyamis), and the Voidomatis, a tributary of the Aoos known for flowing through the spectacular [[Vikos gorge]]. Vikos gorge forms the centerpiece of the [[Vikos-Aoos National Park]], known for its scenic beauty. The only significant lake in Epirus is [[Lake Pamvotis]], on whose shores lies the city of [[Ioannina]]. |
|||
Significant lowlands are to be found only near the coast, in the southwest near [[Arta, Greece|Arta]] and [[Preveza]], in the Acheron plain between [[Paramythia]] and [[Fanari, Preveza|Fanari]], between [[Igoumenitsa]] and [[Sagiada]], and also near [[Saranda]]. The [[Zagori]] area is a scenic upland plateau surrounded by mountain on all sides. |
|||
The climate of Epirus is mainly [[alpine climate|alpine]] in the interior and [[mediterranean climate|mediterranean]] along the coast. Epirus is heavily forested, mainly by coniferous species. The animal life is especially rich in this area and features, among other species, [[bear]]s, [[wolf|wolves]], [[fox]]es, [[deer]] and [[lynx]]es. |
|||
The main river flowing through Epirus is the [[Vjosë]], which flows in a northwesterly direction from the Pindus mountains in Greece to its mouth north of the [[Bay of Vlorë]] in Albania. Other important rivers include the [[Acheron|Acheron river]], famous for its religious significance in ancient Greece and site of the [[Necromanteion]], the [[Arachthos river]], crossed by the historic [[Bridge of Arta]], the [[Louros (river)|Louros]], the [[Thyamis]] or Kalamas, and the Voidomatis, a tributary of the Vjosë flowing through the [[Vikos Gorge]]. The Vikos Gorge, one of the deepest in the world, forms the centerpiece of the [[Vikos–Aoös National Park]], known for its scenic beauty. The only significant lake in Epirus is [[Lake Pamvotis]], on whose shores lies the city of [[Ioannina]], the region's largest and traditionally most important city. |
|||
The climate of Epirus is [[Mediterranean climate|Mediterranean]] along the coast and [[Alpine climate|Alpine]] in the interior. Epirus is heavily forested, mainly by coniferous species. The fauna in Epirus is especially rich and features species such as [[bear]]s, [[wolf|wolves]], [[fox]]es, [[deer]], and [[lynx]]es. |
|||
==History== |
==History== |
||
===Early |
===Early history=== |
||
[[File:Proto Greek Area reconstruction.png|thumb|left|Epirus was part of the [[Proto-Greek language|Proto-Greek]] area according to linguist [[Vladimir I. Georgiev]].]] |
|||
[[Image:EpirusMycynaen.jpg|right|thumb|200px|[[Mycenaean]] sites in Epirus.]] |
|||
[[File:EpirusMycynaen.jpg|right|thumb|[[Helladic period|Mycenaean]] sites in the [[Epirus (region)|region of Epirus]].]] |
|||
{{Main|Epirus (ancient state)}} |
|||
In the Neolithic period Epirus was populated by seafarers along the coast and by shepherds and hunters from the southwestern Balkans who brought with them the Greek language. These people buried their leaders in large mounds containing shaft graves. Similar burial chambers were subsequently used by the Mycenaean civilization, suggesting that the founders of [[Mycenae]] may have come from Epirus and central [[Albania]]. Epirus itself remained culturally backward during this time, but Mycenaean remains have been found at two religious shrines of great antiquity in the region: the Oracle of the Dead on the Acheron River, familiar to the heroes of Homer’s [[Odyssey]], and the Oracle of [[Zeus]] at Dodona, to whom Achilles prayed in the Iliad.<ref name=Britannica/> |
|||
Epirus has been occupied since at least [[Neolithic]] times, when hunters and shepherds inhabited the region and constructed large [[tumuli]] to bury their leaders.<ref>Tandy, David W. ''Prehistory and History: Ethnicity, Class and Political Economy''. Black Rose Books Ltd., 2001, ISBN 1551641887, p. 27.</ref> These tumuli bear many similarities to <ref>Tandy, David W. ''Prehistory and History: Ethnicity, Class and Political Economy''. Black Rose Books Ltd., 2001, ISBN 1551641887, p. 4.</ref> [[Mycenaean period|Mycenean tombs]],<ref>Tandy, David W. ''Prehistory and History: Ethnicity, Class and Political Economy''. Black Rose Books Ltd., 2001, ISBN 1551641887, p. 6.</ref> indicating an ancestral link<ref>Tandy, David W. ''Prehistory and History: Ethnicity, Class and Political Economy''. Black Rose Books Ltd., 2001, ISBN 1551641887, p. 17.</ref><ref>Tandy, David W. ''Prehistory and History: Ethnicity, Class and Political Economy''. Black Rose Books Ltd., 2001, ISBN 1551641887, p. 18.</ref> between Epirus<ref>Tandy, David W. ''Prehistory and History: Ethnicity, Class and Political Economy''. Black Rose Books Ltd., 2001, ISBN 1551641887, p. 22.</ref> and the Mycenean civilization.<ref name="Tandy, David W. 2001, p. 23">Tandy, David W. ''Prehistory and History: Ethnicity, Class and Political Economy''. Black Rose Books Ltd., 2001, ISBN 1551641887, p. 23.</ref><ref>Tandy, David W. ''Prehistory and History: Ethnicity, Class and Political Economy''. Black Rose Books Ltd., 2001, ISBN 1551641887, p. 24.</ref> Certainly, Mycenean remains<ref>Tandy, David W. ''Prehistory and History: Ethnicity, Class and Political Economy''. Black Rose Books Ltd., 2001, ISBN 1551641887, p. 30.</ref> have been found<ref>McHenry, Robert. ''The New Encyclopaedia Britannica''. Encyclopaedia Britannica, 1993, p. 527. "Mycenean remains have been found at two religious shrines of great antiquity in the region."</ref> in Epirus, especially at the most important ancient religious sites in the region, the [[Necromanteion]] (Oracle of the Dead) on the [[Acheron]] river, and the Oracle of [[Zeus]] at [[Dodona]].<ref name="Tandy, David W. 2001, p. 23"/> |
|||
In the Middle Bronze Age, Epirus was inhabited by the same nomadic Hellenic tribes that went on to settle in the rest of Greece.<ref>{{harvnb|Borza|1992|pp=62, 78, 98}}; {{harvnb|Minahan|2002|p=578}}.</ref> Aristotle considered the region around Dodona to have been part of [[Ancient Greece|Hellas]] and the region where the [[Hellenes]] originated.<ref>{{harvnb|Hammond|1986|p=77}}: "The original home of the Hellenes was 'Hellas', the area round Dodona in Epirus, according to Aristotle. In the Iliad it was the home of Achilles' Hellenes."</ref><ref>Aristotle. ''Meteorologica'', [http://classics.mit.edu/Aristotle/meteorology.1.i.html 1.14] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110629061102/http://classics.mit.edu/Aristotle/meteorology.1.i.html |date=29 June 2011 }}: "Rather we must take the cause of all these changes to be that, just as winter occurs in the seasons of the year, so in determined periods there comes a great winter of a great year and with it excess of rain. But this excess does not always occur in the same place. The deluge in the time of Deucalion, for instance, took place chiefly in the Greek world and in it especially about ancient Hellas, the country about Dodona and the Achelous, a river which has often changed its course. Here the Selli dwelt and those who were formerly called Graeci and now Hellenes."</ref> According to Bulgarian linguist [[Vladimir I. Georgiev]], Epirus was part of the [[Proto-Greek language|Proto-Greek linguistic area]] during the Late Neolithic period.<ref>{{harvnb|Georgiev|1981|loc=p. 192: "''Late Neolithic Period'': in northwestern Greece the Proto-Greek language had already been formed: this is the original home of the Greeks."}}</ref> By the early 1st millennium BC, all fourteen Epirote tribes including the [[Chaonians]] in northwestern Epirus, the [[Molossians]] in the centre and the [[Thesprotians]] in the south, were speakers of a strong west Greek dialect.<ref name=Britannica/><ref name="OCD527"/><ref>{{harvnb|Hammond|1998}}; {{harvnb|Wilkes|1995|p=104}}; {{harvnb|Hammond|1994|pp=430, 434}}; {{harvnb|Hammond|1982|p=284}}.</ref> |
|||
The [[Dorians]] invaded Greece from Epirus and Macedonia at the end of the [[2nd millennium BC]] (circa 1100 BC-1000 BC), though the reasons for their migration are obscure. The region's original inhabitants were driven southward into the Greek mainland by the invasion and by the early [[1st millennium BC]] three principal clusters of Greek-speaking tribes<ref name=CAH>{{cite book|first=P. Mack|last= Crew|title= The Cambridge Ancient History - The Expansion of the Greek World, Eighth to Sixth Centuries B.C., Part 3: Volume 3 (Second Edition)|publisher=Cambridge University Press|location= Cambridge, UK|year=1982|quote=That the Molossians[...]spoke Illyrian or another barbaric tongue was nowhere suggested, although Aeschylus and Pindar wrote of Molossian lands. That they in fact spoke Greek was implied by Herodotus' inclusion of Molossi among the Greek colonists of Asia Minor, but became demonstrable only when D. Evangelides published two long inscriptions of the Molossian State, set up in 369 B.C. at Dodona, in Greek and with Greek names, Greek patronymies and Greek tribal names such as Celaethi, Omphales, Tripolitae, Triphylae, etc. As the Molossian cluster of tribes in the time of Hecataeus included the Orestae, Pelagones, Lyncestae, Tymphaei and Elimeotae, as we have argued above, we may be confident that they too were Greek-speaking.}}</ref> had emerged in Epirus. These were the [[Chaonians]] of northwestern Epirus, the [[Molossians]] in the centre and the [[Thesprotians]] in the south. |
|||
===Epirus and |
===Epirus in the Classical and Hellenistic periods=== |
||
[[ |
[[File:D70-0404-dodona.jpg|thumb|right|upright=1.6|The theater of [[Dodona]] with [[Tomaros|Mt. Tomarus]] in the background.]] |
||
[[ |
[[File:Ancient Regions Mainland Greece-es.svg|right|thumb|250px|Regions of mainland Greece and environments in antiquity.]] |
||
{{Main|Epirus (ancient state)}} |
{{Main|Epirus (ancient state)}} |
||
In antiquity, Epirus was settled by the same nomadic Hellenic tribes that went on to settle the rest of Greece <ref name=Borza>{{cite book | first= Eugene N. | last= Borza | title= In the Shadow of Olympus: the Emergence of Macedon (Revised Edition) | publisher= Princeton University Press | location= Princeton, New Jersey | year= 1992}} "Speakers of these various Greek dialects settled different parts of Greece at different times during the Middle Bronze Age, with one group, the 'northwest' Greeks, developing their own dialect and peopling central Epirus. This was the origin of the Molossian or Epirotic tribes." "[...]a proper dialect of Greek, like the dialects spoken by Dorians and Molossians." "The western mountains were peopled by the Molossians (the western Greeks of Epirus)."</ref><ref name="books.google.com">[http://books.google.com/books?id=K94wQ9MF2JsC&pg=RA1-PA577&dq=epirotes Encyclopedia of stateless nations, James Minahan, p. 578]</ref>. Unlike most other Greeks of the time, who lived in or around [[city-state]]s such as [[Athens]] or [[Sparta]], the [[Epirotes]] lived in small villages and their way of life was foreign to that of [[polis]] of southern Greeks<ref>N.G.L. Hammond. ''Epirus''. Oxford University Press, 1967.</ref>. |
|||
Their region lay on the edge of the Greek world and was far from peaceful; for many centuries, it remained a [[frontier]] area contested with the [[Illyrian]] peoples of the Adriatic coast and interior. However, Epirus had a far greater religious significance than might have been expected given its geographical remoteness, due to the presence of the shrine and oracle at Dodona - regarded as second only to the more famous oracle at [[Delphi]]. |
|||
Geographically on the edge of the Greek world, Epirus remained for the most part outside the limelight of Greek history until relatively late, much like the neighbouring Greek regions of Macedonia, Aetolia, and Acarnania, with which Epirus had political, cultural, linguistic and economic connections.{{Sfn|Filos|2018|loc=p. 215: "Epirus [...] was geographically placed on the fringe of the Greek world and remained almost until the (early) Hellenistic period on the sidelines of the political, socio-economic and cultural characteristics that characterized the southern Greek city-states and their overseas colonies from as early as the Archaic period. In that respect, Epirus shows clear similarities to neighboring Greek regions, such as Macedonia, Aetolia and Acarnania, which also stayed out of the limelight of Greek history until a relatively late period; [...] Epirus was closely related to those areas, and in fact not only in political and economic terms, but also in a cultural and linguistic manner"}} Unlike most other Greeks of this time, who lived in or around [[city-state]]s, the inhabitants of Epirus lived in small villages and their way of life was foreign to that of the [[polis|poleis]] of southern Greece.<ref name=Britannica/><ref>{{harvnb|Hammond|1967}}.</ref> Their region lay on the periphery of the Greek world<ref name=Britannica/> and was far from peaceful; for many centuries, it remained a [[frontier]] area contested with the [[Illyrian peoples]] to the north. However, Epirus had a far greater religious significance than might have been expected given its geographical remoteness, due to the presence of the shrine and oracle at [[Dodona]] – regarded as second only to the more famous oracle at [[Delphi]]. |
|||
The [[Epirotes]], though apparently speakers of an epichoric Northwest Greek dialect, different from the Dorian of the Greek colonies on the Ionian islands, and bearers of mostly Greek names, as evidenced by epigraphy, seem to have been regarded with some disdain by some classical writers. The 5th century BC Athenian historian [[Thucydides]] describes them as "[[Barbarian#Origin_of_the_term|barbarians]]",<ref>Thucydides. ''The History of the Peloponnesian War'', Book I. ([http://classics.mit.edu/Thucydides/pelopwar.mb.txt Internet Classics Archive]). "The same summer, not long after this, the Ambraciots and Chaonians, being desirous of reducing the whole of Acarnania and detaching it from Athens, persuaded the Lacedaemonians to equip a fleet from their confederacy and send a thousand heavy infantry to Acarnania, representing that, if a combined movement were made by land and sea, the coast Acarnanians would be unable to march, and the conquest of Zacynthus and Cephallenia easily following on the possession of Acarnania, the cruise round Peloponnese would be no longer so convenient for the Athenians. Besides which there was a hope of taking Naupactus."</ref> as does [[Strabo]].<ref>Strabo. ''Geography''. Book VII, 7, 1. ([http://penelope.uchicago.edu/Thayer/E/Roman/Texts/Strabo/7G*.html LacusCurtius]).</ref> Other writers, such as [[Herodotus]]<ref>Herodotus Histories 6. 127</ref>, [[Dionysius of Halicarnassus]]<ref>Dionysius of Halicarnassus. ''Roman Antiquities''. Book XX, 10 (19.11) ([http://penelope.uchicago.edu/Thayer/E/Roman/Texts/Dionysius_of_Halicarnassus/20*.html LacusCurtius]).</ref> [[Pausanias (geographer)|Pausanias]]<ref>Pausanias. ''Description of Greece'', 1.11.7-1.12.2 ([http://www.theoi.com/Text/Pausanias1A.html Theoi Project]).</ref> and [[Eutropius]],<ref>Eutropius. ''Abridgment of Roman History'' (Historiae Romanae Breviarium) Book 2, XI, XIII ([http://www.tertullian.org/fathers/eutropius_breviarium_2_text.htm Tertullian]).</ref> describe them as Greeks. Similarly, Epirote tribes/states are included in the [[Argos|Argive]] and [[Epidaurus|Epidaurian]] lists of the Greek thearodokoi.<ref>J. K. Davies, A Wholly Non-Aristotelian Universe: The Molossians as Ethnos, State and Monarchy in Alternatives to Athens: Varieties of Political Organization and Community in Ancient Greece, Oxford University Press (2000) p.234-258</ref> |
|||
The Epirotes, speakers of a [[Northwest Greek]] dialect, different from the [[Dorians|Dorian]] of the Greek colonies on the Ionian islands, and bearers of mostly Greek names, as evidenced by epigraphy, seem to have been regarded with some disdain by some classical writers. The 5th-century BC Athenian historian [[Thucydides]] describes them as "[[Barbarian#Origin of the term|barbarians]]" in his ''History of the Peloponnesian War'',<ref>Thucydides. ''The History of the Peloponnesian War'', [http://classics.mit.edu/Thucydides/pelopwar.mb.txt 1.8] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110805021537/http://classics.mit.edu/Thucydides/pelopwar.mb.txt |date=5 August 2011 }}.</ref> as does [[Strabo]] in his ''Geography'',<ref>Strabo. ''Geography'', [https://penelope.uchicago.edu/Thayer/E/Roman/Texts/Strabo/7G*.html 7.7.1].</ref> although the latter clearly distinguishes them from the neighboring [[Illyrians]].<ref>Strabo. ''Geography'', [https://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Perseus%3Atext%3A1999.01.0198%3Abook%3D7%3Achapter%3Dfragments%3Asection%3D11 7.11]</ref> Other writers, such as [[Herodotus]],<ref>Herodotus. ''Histories'', 6.127.</ref> [[Dionysius of Halicarnassus]],<ref>Dionysius of Halicarnassus. ''Roman Antiquities'', [https://penelope.uchicago.edu/Thayer/E/Roman/Texts/Dionysius_of_Halicarnassus/20*.html 20.10 (19.11)].</ref> [[Pausanias (geographer)|Pausanias]],<ref>Pausanias. ''Description of Greece'', [http://www.theoi.com/Text/Pausanias1A.html 1.11.7–1.12.2].</ref> and [[Eutropius (historian)|Eutropius]],<ref>Eutropius. ''Abridgment of Roman History'' (Historiae Romanae Breviarium), [http://www.tertullian.org/fathers/eutropius_breviarium_2_text.htm 2.11.13].</ref> describe them as Greeks. Similarly, Epirote tribes/states are included in the [[Argos, Peloponnese|Argive]] and [[Epidaurus|Epidaurian]] lists of the Greek Thearodokoi (hosts of sacred envoys).{{sfn|Davies|2002|pp=234–258}} [[Plutarch]] mentions an interesting element of Epirote folklore regarding Achilles: In his biography of King [[Pyrrhus of Epirus|Pyrrhus]], he claims that Achilles "had a divine status in Epirus and in the local dialect he was called Aspetos" (meaning ''unspeakable'', ''unspeakably great'', in [[Homeric Greek]]).<ref>{{harvnb|Cameron|2004|p=141}}: "As for Aspestos, Achilles was honored in Epirus under that name, and the patronymic [Ἀ]σπετίδης is found in a fragmentary poem found on papyrus."</ref><ref>cf. Athenian secretary: Aspetos, son of Demostratos from [[Kytheros (deme)|Kytheros]] c. 340 BC.</ref> |
|||
[[Plutarch]] mentions an interesting cultural element of the Epirotes regarding Achilles. In his biography of King [[Pyrrhus of Epirus|Pyrrhus]], he claims that Achilles "had a divine status in Epirus and in the local dialect he was called Aspetos" (meaning ''unspeakable'', ''unspeakably great'', in [[Homeric Greek]]).<ref>Cameron, Alan. ''Greek Mythography in the Roman World''. Oxford University Press US, 2004,ISBN 0195171217, p. 141. "As for Aspestos, Achilles was honored in Epirus under that name, and the patronymic [Ἀ]σπετίδης is found in a fragmentary poem found on papyrus."</ref><ref>cf. Athenian secretary: Aspetos, son of Demostratos from [[Kytheros]] ~340 BC.</ref> The Aeacidae established the [[Molossian]] dynasty, who built a state in Epirus from about 370 BC onwards, expanding their power at the expense of rival tribes. The Molossians allied themselves with the increasingly powerful kingdom of [[Macedon]] and in 359 BC the Molossian princess [[Olympias]], niece of [[Arybbas of Epirus]], married King [[Philip II of Macedon]]. She was to become the mother of [[Alexander the Great]]. |
|||
Beginning in 370 BC, the [[Molossian]] [[Aeacidae]] dynasty built a [[Epirus (ancient state)|centralized state in Epirus]] and began expanding their power at the expense of rival tribes.<ref name=Britannica/> The Aeacids allied themselves with the increasingly powerful kingdom of [[Macedon]], in part against the common threat of [[Illyrians|Illyrian]] raids,<ref name="Companion">{{harvnb|Anson|2010|p=5}}.</ref> and in 359 BC the Molossian princess [[Olympias]], niece of [[Arybbas of Epirus]], married King [[Philip II of Macedon]].<ref name=Britannica/> She was to become the mother of [[Alexander the Great]]. |
|||
On the death of Arybbas, [[Alexander of Epirus]] succeeded to the throne and the title King of Epirus. [[Aeacides of Epirus]], who succeeded Alexander, espoused the cause of Olympias against [[Cassander]], but was dethroned in 313 BC. His son [[Pyrrhus of Epirus|Pyrrhus]] came to throne in 295 BC, and for six years fought against the [[Roman Republic|Romans]] and [[Carthage (state)|Carthaginians]] in southern [[Italy]] and [[Sicily]]. His campaigns gave Epirus a new, but brief, importance and a lasting contribution to the language with the concept of a "[[Pyrrhic victory]]". |
|||
On the death of Arybbas, [[Alexander of Epirus]] succeeded to the throne and the title [[Epirus (ancient state)|King of Epirus]] in 334 BC. He invaded Italy, but was killed in battle by a [[Lucania]]n in the [[Battle of Pandosia]] against several [[Italic tribes]] 331 BC.<ref name=Britannica/><ref>Livy (1926), 8.24.8–14</ref> [[Aeacides of Epirus]], who succeeded Alexander, espoused the cause of Olympias against [[Cassander]], but was dethroned in 313 BC. His son [[Pyrrhus of Epirus|Pyrrhus]] came to throne in 295 BC, and for six years fought against the [[Roman Republic|Romans]] and [[Carthage (state)|Carthaginians]] in southern [[Italy]] and [[Sicily]]. The high cost of his victories against the Romans gave Epirus a new, but brief, importance, as well as a lasting contribution to the Greek language with the concept of a "[[Pyrrhic victory]]". Pyrrhus nonetheless brought great prosperity to Epirus, building the great theater of [[Dodona]] and a new suburb at [[Ambracia]] (now modern [[Arta, Greece|Arta]]), which he made his capital.<ref name=Britannica/> |
|||
In the 3rd century BC, Epirus remained a substantial power, unified under the auspices of the Epirote League as a federal state with its own parliament (or ''synedrion''). However, it was faced with the growing threat of the expansionist [[Roman Republic]], which fought a series of wars with Macedonia. The League remained neutral in the first two Macedonian Wars but split in the [[Third Macedonian War]] (171 BC-168 BC), with the Molossians siding with the Macedonians and the Chaones and Thesproti siding with Rome. The outcome was disastrous for Epirus; Molossia fell to Rome in 167 BC, 150,000 of its inhabitants were enslaved and the region was so thoroughly plundered that it took 500 years for central Epirus to recover fully. |
|||
The Aeacid dynasty ended in 232 BC, but Epirus remained a substantial power, unified under the auspices of the Epirote League as a federal state with its own parliament, or ''synedrion''.<ref name=Britannica/> However, it was faced with the growing threat of the expansionist [[Roman Republic]], which fought a series of wars against [[Macedon]]. The League steered an uneasy neutral course in the first two Macedonian Wars but split in the [[Third Macedonian War]] (171–168 BC), with the Molossians siding with the Macedonians and the Chaonians and Thesprotians siding with Rome.<ref name=Britannica/> The outcome was disastrous for Epirus; Molossia fell to Rome in 167 BC and 150,000 of its inhabitants were enslaved.<ref name=Britannica/> |
|||
===Roman and Byzantine rule=== |
===Roman and Byzantine rule=== |
||
====Epirus as a Roman province==== |
|||
[[Image:Epir1205-1230.png|right|200px|The [[Despotate of Epirus]] in the Middle Ages.]] |
|||
{{main|Epirus (Roman province)}} |
|||
The Roman invasion permanently ended the political independence of the Epirotes. In 146 BC Epirus became part of the [[Macedonia (Roman province)|province of Roman Macedonia]], receiving the name [[Epirus vetus]], to distinguish it from [[Epirus nova]] to the north. Its coastal regions grew wealthy from the Roman coastal trade routes, and the construction of the [[Via Egnatia]] provided a further boost to prosperity. |
|||
The region of Epirus was placed under the [[senatorial province]] of [[Achaea (Roman province)|Achaea]] in 27 BC, with the exception of its northernmost part, which remained part of the province of [[Macedonia (Roman province)|Macedonia]].{{sfn|Soustal|Koder|1981|p=47}} Under Emperor [[Trajan]], sometime between 103 and 114 AD, Epirus became a separate province, under a ''[[procurator (Roman)|procurator]] [[Augustus (honorific)|Augusti]]''. The new province extended from the Gulf of Aulon ([[Vlorë]]) and the [[Acroceraunian Mountains]] in the north to the lower course of the [[Acheloos River]] in the south, and included the northern Ionian Islands of [[Corfu]], [[Lefkada]], [[Ithaca (island)|Ithaca]], [[Cephallonia]], and [[Zakynthos]].{{sfn|Soustal|Koder|1981|p=47}} |
|||
====Late Antiquity==== |
|||
[[File:Moesia - AD 400.png|thumb|The [[Roman province|Roman provinces]] in the Balkans including ''Epirus Vetus'' and ''Epirus Nova'', ca. 400 AD.]] |
|||
Probably during the provincial reorganization by [[Diocletian]] (r. 284–305), the western portion of the province of Macedonia along the Adriatic coast was split off into the province of New Epirus ({{lang-la|Epirus Nova}}). Although this territory was not traditionally part of Epirus proper as defined by the ancient geographers, and was historically inhabited by Illyrian tribes and Greeks, the name reflects the fact that under Roman rule, the area had been subject to increasing Hellenization and settlement by Epirote tribes from the south.{{sfn|Soustal|Koder|1981|p=47}} |
|||
The two Epirote provinces became part of the [[Diocese of Moesia]], until it was divided in ca. 369 into the dioceses of [[Diocese of Macedonia|Macedonia]] and [[Diocese of Dacia|Dacia]], when they became part of the former.{{sfn|Soustal|Koder|1981|pp=47–48}} In the 4th century, Epirus was still a stronghold of [[paganism]], and was aided by Emperor [[Julian (emperor)|Julian]] (r. 361–363) and his [[praetorian prefect]] [[Claudius Mamertinus]] through reduction in taxes and the rebuilding of the provincial capital, [[Nicopolis]].{{sfn|Soustal|Koder|1981|p=48}} According to [[Jordanes]], in 380 the [[Visigoths]] raided the area.{{sfn|Soustal|Koder|1981|p=48}} With the division of the Empire on the death of [[Theodosius I]] in 395, Epirus became part of the Eastern Roman or [[Byzantine Empire]].{{sfn|Soustal|Koder|1981|p=48}} In 395–397, the Visigoths under [[Alaric I|Alaric]] plundered Greece. They remained in Epirus for a few years, until 401, and again in 406–407, during Alaric's alliance with the [[Western Roman]] generalissimo [[Stilicho]] in order to wrest the [[Eastern Illyricum]] from the Eastern Empire.{{sfn|Soustal|Koder|1981|p=48}} |
|||
[[File:Butrint-111198.jpg|thumb|Ruins of [[Buthrotum]]]] |
|||
The ''[[Synecdemus]]'' of [[Hierocles (author of Synecdemus)|Hierocles]], composed in ca. 527/8 AD but probably reflecting the situation in the first half of the 5th century, reports 11 cities for Old Epirus ({{lang-grc|Παλαιὰ Ἤπειρος}}, {{lang-la|Epirus Vetus}}): the capital Nicopolis, [[Dodona]], [[Euroea in Epiro|Euroea]], [[Dropull|Hadrianopolis]], [[Appon]], [[Phoenice]], [[Anchiasmos]], [[Buthrotum]], [[Photike]], Corfu Island, and Ithaca Island.{{sfn|Soustal|Koder|1981|pp=48–49}} New Epirus, with capital at [[Dyrrhachium]], comprised 9 cities.{{sfn|Soustal|Koder|1981|p=48}} From 467 on, the Ionian Islands and the coasts of Epirus became subject to raids by the [[Vandals]], who had taken over the [[North Africa]]n provinces and established their [[Kingdom of the Vandals|own kingdom]] centred on [[Carthage]]. The Vandals notably seized Nicopolis in 474 as a bargaining chip in their negotiations with Emperor [[Zeno (emperor)|Zeno]], and plundered Zakynthos, killing many of its inhabitants and ferrying off others into slavery.{{sfn|Soustal|Koder|1981|p=49}} [[Epirus Nova]] became a battleground in the rebellions of the [[Ostrogoths]] after 479.{{sfn|Soustal|Koder|1981|p=49}} In 517, a raid of the [[Getae]] or [[Antae]] reached Greece, including [[Epirus Vetus]].{{sfn|Soustal|Koder|1981|p=49}} The claim of [[Procopius of Caesarea]] in his ''Secret History'', that under [[Justinian I]] (r. 527–565) the entirety of the Balkan provinces was raided by barbarians every year, is considered rhetorical hyperbole by modern scholars; only a single Slavic raid to the environs of Dyrrhachium, in 548/9, has been documented.{{sfn|Soustal|Koder|1981|p=49}} Procopius further reports that in 551, in an attempt to interdict the Byzantines' lines of communication with Italy during the [[Gothic War (535–554)|Gothic War]], the Ostrogoth king [[Totila]] sent his fleet to raid the shores of Epirus.{{sfn|Soustal|Koder|1981|p=50}} In response to these raids, and to repair the damage done by two destructive earthquakes in 522, Justinian initiated a wide-ranging programme of reconstruction and re-fortification: Hadrianopolis was rebuilt, albeit in reduced extent, and renamed Justinianopolis, while [[Euroea in Epiro|Euroea]] was moved further inland (traditionally identified with the founding of [[Ioannina]]), while Procopius claims that no less than 36 smaller fortresses in Epirus Vetus—most of them not identifiable today—were either rebuilt or built anew.{{sfn|Soustal|Koder|1981|p=50}} |
|||
====Epirus from the Slavic invasions until 1204==== |
|||
In the late 6th century, much of Greece, including Epirus, fell under the control of the [[Pannonian Avars|Avars]] and their Slavic allies. This is placed by the ''[[Chronicle of Monemvasia]]'' in the year 587, and is further corroborated by evidence that several sees were abandoned by their bishops by 591. Thus in {{circa|590}} the bishop, clergy and people of Euroea fled their city, carrying with them the relics of their patron saint, [[Donatus of Evorea|St. Donatus]], to Cassiope in Corfu.{{sfn|Soustal|Koder|1981|p=51}} |
|||
Of the various Slavic tribes, only the [[Baiounitai]], first attested {{circa|615}}, are known by name, giving their name to their region of settlement: "[[Vagenetia]]".{{sfn|Soustal|Koder|1981|p=51}} Based on the density of the Slavic toponyms in Epirus, the Slavs must have settled in the region, although the extent of this settlement is unclear.<ref name="EllisKlusakova2007">{{harvnb|Osswald|2007|p=128}}.</ref> Slavic toponyms occur mainly in the mountainous areas of the interior and the coasts of the [[Gulf of Corinth]], indicative of the fact that this was the avenue used by most of the Slavs who crossed the Gulf into the [[Peloponnese]]. With the exception of some few toponyms on Corfu, the Ionian Islands seem to not have been affected by Slavic settlement. The linguistic analysis of the toponyms reveals that they date mostly to the early wave of Slavic settlement at the turn of the 6th/7th centuries. Due to scarcity of textual evidence, it is unclear how much the area was affected by the second wave of Slavic migration, which began in the middle of the 8th century due to [[First Bulgarian Empire|Bulgar]] pressure in the northern Balkans.{{sfn|Soustal|Koder|1981|pp=51–52}} Slavic toponyms are nearly lacking in the mountains of [[Labëria]] (on the [[Kurvelesh (region)|Kurvelesh plateau]]), in the [[Albanian Ionian Sea Coast|Ionian coast]] where today [[Lab Albanian dialect|Lab Albanian]] villages neighbour with the [[Greek language|Greek-speaking]] ones, therefore it can be assumed that the expansion of the Slavs had not reach this region.{{sfn|Desnickaja|1973|p=48}} |
|||
As in eastern Greece, the restoration of Byzantine rule seems to have proceeded from the islands, chiefly Cephallonia, which was certainly under firm Imperial control in {{circa|702}}, when [[Philippicus Bardanes]] was banished there. The gradual restoration of Imperial rule is evidenced further from the participation of local bishops in councils in [[Constantinople]]: whereas only the bishop of Dyrrhachium participated in the Ecumenical Councils of [[Third Council of Constantinople|680/1]] and [[Quinisext Council|692]], a century later the bishops of Dyrrhachium, Nicopolis, Corfu, Cephallonia, and Zakynthos are attested in the [[Second Council of Nicaea]] in 787.{{sfn|Soustal|Koder|1981|p=52}} In about the middle of the 8th century, the [[Theme of Cephallenia]] was established, but at least initially it was more oriented towards restoring Byzantine control over the Ionian and Adriatic seas, combating Saracen piracy, and securing communications with the remaining Byzantine possessions in Italy, rather than any systematic effort at subduing the Epirote mainland.{{sfn|Soustal|Koder|1981|p=52}} Nevertheless, following the onset of the [[Muslim conquest of Sicily]] in 827, the Ionian became particularly exposed to Arab raids.{{sfn|Soustal|Koder|1981|p=53}} |
|||
[[File:Byzantine Greece ca 900 AD.svg|thumb|right|Map of [[Byzantine Greece]] ca. 900 AD, with the themes and major settlements]] |
|||
The 9th century saw great progress in the restoration of Imperial control in the mainland, as evidenced by the participation of the bishops of Ioannina, [[Naupaktos]], Hadrianopolis, and Vagenetia (evidently by now organized as a ''[[Sklavinia]]'' under imperial rule) in the Ecumenical Councils of [[Fourth Council of Constantinople (Roman Catholic)|869/70]] and [[Fourth Council of Constantinople (Eastern Orthodox)|879/80]].{{sfn|Soustal|Koder|1981|p=53}} The Byzantine recovery resulted in an influx of Greeks from southern Italy and [[Asia Minor]] into the Greek interior, while remaining Slavs were Christianized and [[Hellenization|Hellenized]].{{sfn|Fine|1991|p=64}} The eventual success of the Hellenization campaign also suggests a continuity of the original Greek population, and that the Slavs had settled among many Greeks, in contrast to areas further north, in what is now Bulgaria and the former Yugoslavia, as those areas could not be Hellenized when they were recovered by the Byzantines in the early 11th century.{{sfn|Fine|1991|p=64}} Following the [[Battle of Cephalonia|great naval victory]] of admiral [[Nasar]] in 880, and the beginning of the Byzantine offensive against the Arabs in southern Italy in the 880s, the security situation improved and the [[Theme of Nicopolis]] was established, most likely after 886.{{sfn|Soustal|Koder|1981|p=53}}{{sfn|Kazhdan|1991|p=1485}} As the ancient capital of Epirus had been laid waste by the Slavs, the capital of the new theme became Naupaktos further south. The extent of the new province is unclear, but probably matched the extent of the [[Metropolis of Naupaktos]], established at about the same time, encompassing the sees of Vonditsa, Aetos, Acheloos, [[Rogoi]], Ioannina, Hadrianopolis, Photike, and Buthrotum. Vagenetia notably no longer appears as a bishopric. As the authors of the ''[[Tabula Imperii Byzantini]]'' comment, it appears that "the Byzantine administration had brought the strongly Slavic-settled areas in the mainland somewhat under its control, and a certain Re-Hellenization had set in".{{sfn|Soustal|Koder|1981|pp=53–54}} Further north, the region around [[Dyrrhachium]] existed as the [[Dyrrhachium (theme)|homonymous theme]] possibly as early as the 9th century.{{sfn|Kazhdan|1991|p=668}} |
|||
During the early 10th century, the themes of Cephallenia and Nicopolis appear mostly as bases for expeditions against southern Italy and Sicily, while [[Mardaites]] from both themes are listed in the large but unsuccessful expedition of 949 against the [[Emirate of Crete]].{{sfn|Soustal|Koder|1981|p=54}} In {{circa|930}}, the Theme of Nicopolis was raided by the Bulgarians, who even occupied some parts until driven out or subjugated by the Byzantines years later.{{sfn|Soustal|Koder|1981|p=54}} Only the extreme north of Epirus seems to have remained consistently under Bulgarian rule in the period, but under Tsar [[Samuel of Bulgaria|Samuel]], who moved the centre of Bulgarian power south and west to [[Ohrid]], probably all of Epirus down to the [[Ambracian Gulf]] came under Bulgarian rule.{{sfn|Soustal|Koder|1981|p=55}} This is evidenced from the fact that the territories that were under Bulgarian rule formed part of the [[autocephalous]] [[Archbishopric of Ohrid]] after the [[Byzantine conquest of Bulgaria]] by Emperor [[Basil II]] in 1018: thus in Epirus the sees of [[Chimara]], Hadrianopolis, Bela, Buthrotum, Ioannina, Kozyle, and Rogoi passed under the jurisdiction of Ohrid, while the Metropolitan of Naupaktos retained only the sees of Bonditza, Aetos, and Acheloos.{{sfn|Soustal|Koder|1981|p=55}} Basil II also established new, smaller themes in the region: [[Kolonje|Koloneia]], and [[Dryinopolis]] (Hadrianopolis).{{sfn|Soustal|Koder|1981|p=55}} |
|||
The region joined the [[uprising of Petar Delyan]] in 1040, and suffered in the [[First Norman invasion of the Balkans]]: Dyrrhachium was [[Battle of Dyrrhachium (1081)|occupied]] by the [[Normans]] in 1081–1084, [[Arta, Greece|Arta]] was unsuccessfully besieged, and Ioannina was captured by [[Robert Guiscard]].{{sfn|Soustal|Koder|1981|pp=55–56}} An [[Aromanians|Aromanian]] presence in Epirus is first mentioned in the late 11th century, while Jewish communities are attested throughout the medieval period in Arta and Ioannina.{{sfn|Osswald|2007|p=129}} |
|||
====Despotate of Epirus==== |
|||
[[File:Epirus 1205-1230-en.svg|thumb|alt=Map of the Balkans, with the original core of Epirus and its conquered territories shown in various shades of green|Expansion of the [[Despotate of Epirus]] in the early 13th century.]] |
|||
When [[Constantinople]] fell to the [[Fourth Crusade]] in 1204, the ''[[partitio Romaniae]]'' assigned Epirus to [[Republic of Venice|Venice]], but the Venetians were largely unable to effectively establish their authority, except over Dyrrhachium (the "[[Duchy of Durazzo (Republic of Venice)|Duchy of Durazzo]]"). The Greek noble [[Michael I Komnenos Doukas|Michael Komnenos Doukas]], who had married the daughter of a local magnate, took advantage of this, and within a few years consolidated his control over most of Epirus, first as a Venetian [[vassal]] and eventually as an independent ruler. By the time of his death in 1214/5, Michael had established a strong state, the [[Despotate of Epirus]], with the former theme of Nicopolis at its core and Arta as its capital.{{sfn|Soustal|Koder|1981|pp=59–61}}{{sfn|Osswald|2007|p=132}} Epirus, and the city of Ioannina in particular, became a haven for Greek refugees from the [[Latin Empire of Constantinople]] for the next half century.{{sfn|Osswald|2007|p=132}} |
|||
The Despotate of Epirus ruled over Epirus and western Greece as far south as Naupaktos and the Gulf of Corinth, much of Albania (including Dyrrhachium), Thessaly, and the western portion of [[Macedonia (region)|Macedonia]], extending its rule briefly over central Macedonia and most of [[Thrace]] following the aggressive expansionism of [[Theodore Komnenos Doukas]], who established the [[Empire of Thessalonica]] in 1224.{{sfn|Nicol|1984|loc="Introduction", pp. 4–5}}{{sfn|Osswald|2007|p=133}} During this time, the definition of Epirus came to encompass the entire coastal region from the Ambracian Gulf to Dyrrhachium, and the hinterland to the west up to the highest peaks of the [[Pindus]] mountain range. Some of the most important cities in Epirus, such as Gjirokastër (Argyrokastron), were founded during this period.{{sfn|Giakoumis|2002|p=176}} The oldest reference to [[Albanians]] in Epirus is from a Venetian document dating to 1210, which states that "the continent facing the island of Corfu is inhabited by Albanians". Kosta Giakoumis believes that the use of hypothetical immigrations to explain the accounts of Albanian presence in Epirote territory prior to the 13th-14th century is somewhat arbitrary.<ref>{{harvnb|Giakoumis|2002|p=176|ps=: "Are we obliged to see in this a possible earlier Albanian immigration in the Epeirote lands, as Kostas Komis did in the case of the etymology of the toponym 'Preveza'? I believe that the use of hypothetical immigrations as a basis to interpret sources that indicate the presence of Albanians in the Epeirote lands prior to the thirteenth-fourteenth century is somewhat arbitrary."}}</ref> |
|||
====14th century until the Ottoman conquest==== |
|||
In 1337, Epirus was once again brought under the rule of the [[Byzantine Empire under the Palaiologoi|restored Byzantine Empire]].{{sfn|Osswald|2007|p=133}} In 1348, taking advantage of the [[Byzantine civil war of 1341–1347|civil war]] between the Byzantine emperors [[John V Palaiologos]] and [[John VI Kantakouzenos]], the Serbian king [[Stefan Uroš IV Dušan]] conquered Epirus, with a number of Albanian mercenaries assisting him.{{sfn|Osswald|2007|p=135}} The Byzantine authorities in Constantinople soon re-established a measure of control by making the Despotate of Epirus a [[vassal state]], but Albanian clans proceeded to invade and seize most of the region. Under [[Peter Losha|Pjetër Losha]], the Albanian [[Malakasioi|Malakasi]] and [[Mazreku (Epirus)|Mazaraki]] tribes defeated [[Nikephoros II Orsini]] at the [[Battle of Achelous (1359)|Battle of Achelous]] in 1359, which won Pjetër Losha the rule of [[Arta, Greece|Arta]]; Losha then founded the [[Despotate of Arta]] (1358-1416) with the help of the Mazaraki and Malakasi clans.<ref>Epeirotica 2.220; cf. 222 f</ref> |
|||
[[File:Map of the southern Balkans, 1410.svg|thumb|right|200px|Map of the southern Balkans and western Anatolia in 1410]] |
|||
Although Albanian clans gained control of most of the region by 1366/7, their continued division into rival clans meant that they could not establish a single central authority.<ref name="mb">{{harvnb|Fine|1994|pp=348–351}}.</ref> Ioannina became a center of Greek resistance to the Albanian clans. The Greeks of Ioannina offered power to three foreign rulers during this time, beginning with [[Thomas II Preljubović]] (1367–1384), whose rule was marked by hostilities in the region, as Ioannina came under constant siege by the Mazaraki and Malakasi clans under Losha. These tribes would besiege Ioannina a second time in 1374–1375.{{sfn|Sansaridou-Hendrickx|2017|p=294}}{{sfn|Nicol|1984|pp=142–145}}<ref name="Sakellariou1997">{{cite book|author=M. V. Sakellariou|title=Epirus, 4000 years of Greek history and civilization|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=UV1oAAAAMAAJ|year=1997|publisher=Ekdotikē Athēnōn|isbn=978-960-213-371-2|quote=For the Albanian tribes of the Mazarakaioi and the Malakasioi, led by Peter Losha the despot of Arta,}}</ref> A truce was signed when Pjetër's son Gjin was betrothed to Thomas's daughter Irina, but she would soon die in the 1375 plague and hostilities would recommence.{{sfnm|Nicol|1984|1pp=142–145|Fine|1994|2pp=351–352|Sansaridou-Hendrickx|2017|3p=294}} Preljubović attempted to pacify the Albanians of Epirus; however, under [[Gjin Bua Shpata]], the Albanians defeated him.<ref>[https://books.google.com/books?id=_VBoAAAAMAAJ Hammond, 1976 & ps]''"The Albanians and in particular the Mazarakii of the Kalamas valley held firm against him. In 1385 he was assassinated by some of his own bodyguards"'' (Epeirotica 2.230), p. 59.</ref> |
|||
The reign of [[Esau de' Buondelmonti]] (1385–1411) in Ioannina followed, and with an army that consisted of the Albanian tribes of the Mazaraki and Malakasi, he marched against the [[Principality of Gjirokastër]]. He was defeated and captured by Albanian nobleman [[Gjon Zenebishi]], and ransomed for 10,000 gold pieces on the intervention of the Venetian governor of [[Corfu]].<ref>{{cite book |last1=Hutchinson |first1=Richard Wyatt |title=The Lord of Patras |date=1956 |publisher=A.G. Kalokairinos |page=343 |url=https://ir.lib.uth.gr/xmlui/bitstream/handle/11615/10744/article.pdf?sequence=1}}</ref> At the time the Zenebishi clan controlled the area around Gjirokastër (1386–1411), while only the city of Ioannina remained under Greek control.{{sfn|Osswald|2007|p=134}} |
|||
[[Carlo I Tocco]] (1411–1429) then assumed control of Ioannina, commencing heavy conflicts with [[Yaqub Spata|Jakob]] and [[Maurice Spata|Muriq]] Shpata, the Albanian leaders of the [[Despotate of Arta]]. The Shpata were originally defeated by Carlo's brother [[Leonardo II Tocco]] at Mazoma near ancient [[Nicopolis]], but Carlo's son Torno was in turn defeated by the Albanians.{{sfn|PLP|loc=26521. Σπάτας Γιαγούπης}}{{sfn|Nicol|1984|p=186}} After the Tocchi succeeded in capturing Rhiniasa, Leonardo tried to take Rogoi and Carlo attempted to take Arta, but Jakob and Muriq succeeded in defending their capital for the time being. Carlo withdrew to Ioannina, but soon after was able to lure Jakob to an ambush near Vobliana: Jakob was captured and immediately executed (1 October 1416).{{sfn|PLP|loc=26521. Σπάτας Γιαγούπης}}{{sfn|Nicol|1984|p=186}} Carlo had effectively ended the rule of the Albanian clans in southernmost Epirus.{{sfn|Osswald|2007|p=136}} |
|||
Epirus became the westernmost province of the Eastern Roman Empire (subsequently the Greek-speaking [[Byzantine Empire]]), ruled from [[Constantinople]] when the empire was divided in two in 395 AD. When Constantinople fell to the [[Fourth Crusade]] in 1204, [[Michael I Ducas|Michael Angelos Komnenos Ducas]] seized [[Aetolia]] and Epirus and established an independent state known as the [[Despotate of Epirus]]. The rulers of the Despotate controlled a substantial area corresponding to a large swathe of northwestern Greece, much of modern Albania and parts of the modern [[Republic of Macedonia]]. During this time, the definition of Epirus came to encompass the entire region from the Ambracian Gulf to [[Dyrrachium]] (modern-day Durrës, in Albania). Some of the most important cities in Epirus, such as [[Gjirokastër]] (Argyrokastron), were founded during this period. |
|||
Nevertheless, internal dissension eased the Ottoman conquest, which began with the capture of Ioannina in 1430 and continued with Arta in 1449, [[Angelokastro, Aetolia-Acarnania|Angelokastro]] in 1460, [[Riniasa Castle]] and its environs (in what is now [[Preveza]]) in 1463,<ref>{{harvnb|Karabelas|2015|pp=972–975}}.</ref> and finally [[Vonitsa]] in 1479. With the exception of several coastal Venetian possessions, this was also the end of Latin rule in mainland Greece. |
|||
In 1318, Epirus was attacked by [[Serbs]] in one of a series of uprisings. Following an Albanian uprising in 1359, in which the Despot [[Nicephorus II]] was killed, the Byzantines authorities in Constantinople re-established a measure of control by making the despotate a vassal state. However, The Ottoman Turks annexed Epirus to their expanding empire following a long campaign between 1430 and 1440. Epirus would remain under Ottoman rule for almost the next 500 years. During this period Epirus was inhabited mainly by Greeks but also by Slavs, Albanians, Vlachs, Armenians, Jews, Latins and Turks.<ref>The Oxford Dictionary of Byzantium (1991), ''Epiros, Despotate of'', p. 716</ref> |
|||
===Ottoman rule=== |
===Ottoman rule=== |
||
{{POV section|date=June 2023}} |
|||
[[Image:Epirus ethnic (Greek point of view).JPG|thumb|200px|Ethnographic map of the [[Epirus]] region, 1878. Pink - Greek speakers, Blue - Greek and Vlach speakers, Orange - Greek and Albanian speakers, Yellow - Albanian speakers]] |
|||
[[File:Ethnographic map of Epirus, based on P. Aravandinos, 1878.jpg|thumb|upright=1.15|Linguistic (big) and religious (small) map of the Epirus region, 1878. German maker, H. Kiepert; information provided by Greek scholar, P. Aravandinos. |
|||
{{legend|#FFC0CB|Greek speakers}} |
|||
{{legend|#99BADD|Greek and Vlach speakers}} |
|||
{{legend|#FFBF00|Greek and Albanian speakers}} |
|||
{{legend|#FBEC5D|Albanian speakers}} |
|||
{{legend|#1E90FF|Greek Orthodox entirely}} |
|||
{{legend|#008080|Greek Orthodox majority}} |
|||
{{legend|#4F7942|Greek Orthodox – Muslim equivalence}} |
|||
{{legend|#addfad|Muslim majority}} |
|||
{{legend|#FBEC5D|Muslim entirely}} |
|||
]] |
|||
The [[Ottoman Empire|Ottomans]] ruled Epirus for almost 500 years. Their rule in Epirus proved particularly damaging; the region was subjected to deforestation and excessive cultivation, which damaged the soil and drove many Epirotes to emigrate so as to escape the region's pervasive poverty.<ref name=Britannica/> Nonetheless, the Ottomans did not enjoy total control of Epirus. The [[Himara]] and [[Zagori]] regions managed to successfully resist Ottoman rule and maintained a degree of independence throughout this period. The Ottomans expelled the Venetians from almost the whole area in the late 15th century. |
|||
Between the 16th and 19th centuries, the city of Ioannina attained great prosperity and became a major center of the [[modern Greek Enlightenment]].<ref>{{harvnb|Sakellariou|1997|p=268}}.</ref><ref name=Fleming>{{harvnb|Fleming|1999|pp=63–66}}.</ref><ref>''[http://www.greece2001.gr/docs/67-132.pdf The Era of Enlightenment (Late 7th century–1821)]''. Εθνικό Kέντρο Bιβλίου, p. 13.</ref><ref>Υπουργείο Εσωτερικών, Αποκέντρωσης και Ηλεκρονικής Διακυβέρνησης [http://www.epirus.gov.gr/portal/index.php/epirus/genika-stoixeia/the-epirus.html Περιφέρεια Ηπείρου]: "Στη δεκαετία του 1790 ο νεοελληνικός διαφωτισμός έφθασε στο κορύφωμά του. Φορέας του πνεύματος στα Ιωάννινα είναι ο Αθανάσιος Ψαλίδας."</ref> Numerous schools were founded, such as the Balaneios, [[Maroutsaia School|Maroutsaia]], [[Kaplaneios School|Kaplaneios]], and [[Zosimaia School|Zosimaia]], teaching subjects such as literature, philosophy, mathematics and physical sciences. In the 18th century, as the power of the Ottoman Empire declined, Epirus became a ''de facto'' independent region under the despotic rule of [[Ali Pasha of Tepelena]], a Muslim [[Albanians|Albanian]] brigand who rose to become the provincial governor of Ioannina in 1788.<ref name=Britannica/> At the height of his power, he controlled all of Epirus, and much of the [[Peloponnese]], central Greece, and parts of western [[Macedonia (region)|Macedonia]]<ref name=Britannica/> Ali Pasha's campaign to subjugate the confederation of the settlements of [[Souli]] met with fierce resistance by the [[Souliotes|Souliot]] warriors of the mountainous area. After numerous failed attempts to defeat the Souliotes, his troops succeeded in conquering the area in 1803. On the other hand, Ali, who used Greek as official language, witnessed an increase of Greek cultural activity with the establishment of several educational institutions.{{sfn|Fleming|1999|p=64}} |
|||
When the [[Greek War of Independence]] broke out, the inhabitants of Epirus contributed greatly. Two of the founding members of the [[Filiki Eteria]] (the secret society of the Greek revolutionaries), [[Nikolaos Skoufas]] and Athanasios Tsakalov, came from the [[Arta (regional unit)|Arta]] area and the city of [[Ioannina]], respectively. Greece's first constitutional prime minister (1844–1847), [[Ioannis Kolettis]], was a native of the village of Syrrako in Epirus and was a former personal physician to Ali Pasha. Ali Pasha tried to use the war as an opportunity to make himself a fully independent ruler, but was assassinated by Ottoman agents in 1822. When Greece became independent in 1830, however, Epirus remained under Ottoman rule. In 1854, during the [[Crimean War]], a major local [[Epirus Revolt of 1854|rebellion broke out]]. Although the newly found Greek state tried tacitly to support it, the rebellion was suppressed by Ottoman forces after a few months.{{sfn|Reid|2000}} Another failed rebellion by local Greeks [[Epirus revolt of 1878|broke out in 1878]]. During this period, the [[Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople]] managed to shut down the few Albanian schools, considering teaching in Albanian a factor that would diminish its influence and lead to the creation of separate Albanian church, while publications in Albanian were banned by the Ottoman Empire.{{sfn|Jelavich|Jelavich|1977|p=226}}<ref name="Ramet1998">{{harvnb|Ramet|1998|p=205}}.</ref> In the late 19th century, the Kingdom of Italy opened various schools in the regions of [[Ioannina]] and [[Preveza]] in order to influence the local population. These schools began to attract students from the Greek language schools, but were ultimately closed after intervention and harassment by the Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople.{{sfn|Blumi|2002|p=57}} Throughout, the late period of Ottoman rule (from the 18th century) Greek and Aromanian population of the region suffered from Albanians raiders, that sporadically continued after Ali Pasha's death, until 1912–1913.{{sfn|Hammond|1976|loc=p. 41: "Throughout this period bands of Albanians raiders pillaged and destroyed the villages of the Vlachs and the Greeks in Epirus, northern Pindus, the lakeland of Prespa and Ochrid, and parts of western Macedonia. One Albanian leader, 'Ali the Lion', emulated the achievements of 'John the Sword' and 'Peter the Pockmark' when he established himself as Ali Pasha, independent ruler of Ioannina. He and his Albanian soldiers, recruited mainly from his homeland in the Kurvelesh and the Drin valley of North Epirus, controlled the whole of Epirus and carried their raids far into western Macedonia and Thessaly. As we have seen, they destroyed the Vlach settlements in the lakeland and weakened those farther south. After the assassination of Ali Pasha in 1822 sporadic raids by bands of Albanians were a feature of life in northern Greece until the liberation of 1912–13"}} |
|||
Ottoman rule proved particularly damaging in Epirus; the region was subjected to deforestation and excessive cultivation, which damaged the soil and drove many [[Epirotes]] to emigrate to escape the region's pervasive poverty. Nonetheless, the Ottomans did not enjoy total control of Epirus. In 1443 the northernmost part of Epirus was briefly conquered by Gjergj Kastrioti [[Skenderbeg]] as part of his revolt against the Ottoman Empire, but on his death it fell to [[Venice]]. The Ottomans expelled the Venetians from almost the whole area in the late 15th century. |
|||
===20th-century Epirus=== |
|||
In the 18th century, as the power of the Ottomans declined, Epirus became a virtually independent region under the despotic rule of [[Ali Pasha]] Tepelena, an [[Albania]]n brigand who became the provincial governor of Ioannina in 1788. At the height of his power, he controlled much of western Greece, the [[Peloponnese]] and (southern) Albania. Ali Pasha's campaigns to subjugate the confederation of the [[Souli]] settlements is a well known incident of his rule. His forces met fierce resistance by the [[Souliotes]] warriors of the mountainous area. After numerous failed attempts to defeat the Souliotes, his troops succeeded in conquering the area in 1803. When the [[Greek War of Independence]] broke out, the inhabitants of the region contributed greatly, and Ali Pasha tried to make himself an independent ruler, but he was deposed and murdered by Ottoman agents in 1822. |
|||
{{POV section|date=June 2023}} |
|||
[[File:Epirote women Aug1914.jpg|left|thumb|Detachment of armed Epirote women in the [[Autonomous Republic of Northern Epirus]].]] |
|||
While the [[Treaty of Berlin (1878)]] awarded large parts of Epirus to Greece, opposition by the Ottomans and the [[League of Prizren]] resulted in only the region of [[Arta (regional unit)|Arta]] being ceded to Greece in 1881.<ref name="Gawrych2006">{{harvnb|Gawrych|2006|pp=68–69}}.</ref> It was only following the [[First Balkan War]] of 1912–1913 and the [[Treaty of London (1913)|Treaty of London]] that the rest of southern Epirus, including [[Ioannina]], was incorporated into Greece.<ref>{{harvnb|Clogg|2002|p=105}}: "In February 1913 the Greek Army seized Ioannina, the capital of Epirus. The Turks recognized the gains of the Balkan allies by the Treaty of London, in May 1913."</ref> Greece had also seized northern Epirus during the [[Balkan Wars]], but the [[Treaty of Bucharest (1913)|Treaty of Bucharest]], which concluded the [[Second Balkan War]], assigned [[Northern Epirus]] to Albania.{{sfn|Clogg|2002|loc=p. 105 "The Second Balkan War had short duration and the Bulgarians were soon dragged to the table of negotiations. By the Treaty of Bucharest (August 1913) Bulgaria was forced to accept a little favourable regulation of the borders, even if she kept a way to the Aegean, in Degeagatch (modern Alexandroupolis). The sovereignty of Greece over Crete was now recognised, but her ambition to annex Northern Epirus with its large Greek population was stopped by the annexation of the area to an independent Albania"}} |
|||
When Greece became independent, Epirus remained under Ottoman rule. Two of the founding members of the [[Filiki Eteria]] (secret patriotic society), [[Nikolaos Skoufas]] and Athanasios Tsakalov, came from the [[Arta Prefecture|Arta]] area and the city of [[Ioannina]] respectively. Greece's first constitutional prime minister (1844–47), [[Ioannis Kolettis]], was a native of the [[Aromanians|Aromanian]] Greek village of Syrrako in Epirus and a former personal doctor to Ali Pasha. In 1854, during the [[Crimean War]], a major local [[Epirus Revolt of 1854|rebellion broke out]]. Although, the newly found Greek state tried tacitly to support it, after a few months period of uprising the rebellion was suppressed by Ottoman forces<ref>{{cite book |last=Reid |first=James J.|title=Crisis of the Ottoman Empire: prelude to collapse 1839-1878 |publisher=Franz Steiner Verlag|year=2000 | pages = | ref=Reid |isbn=9783515076876 |url=http://books.google.com/books?id=Zgg6c_Ndtu4C&pg=PA182&dq=Russo-Turkish+War+1878+Greeks&lr=&as_brr=0&hl=}}</ref>. Another failed rebellion by local Greeks [[Epirus revolt of 1878|broke out in 1878]]. |
|||
This outcome was unpopular among local Greeks, as a substantial Greek population existed on the Albanian side of the border.<ref>{{harvnb|Pettifer|2001|p=4}}.</ref> Among Greeks, [[northern Epirus]] was henceforth regarded as ''[[irredentism|terra irredenta]]''.<ref name="Konidaris">{{harvnb|Konidaris|2013||pp=64–92}}.</ref> Local Greeks in northern Epirus revolted, declared [[Northern Epirote Declaration of Independence|their independence]] and proclaimed the [[Autonomous Republic of Northern Epirus]] in February 1914.{{sfn|Winnifrith|2002|p=130}} After fierce guerrilla fighting, they managed to gain full autonomy under the terms of the [[Protocol of Corfu]], signed by Albanian and Northern Epirote representatives and approved by the Great Powers. The signing of the Protocol ensured that the region would have its own administration, recognized the rights of the local Greeks and provided self-government under nominal Albanian sovereignty.<ref name="Triadafilopoulos">{{harvnb|Triadafilopoulos|2000|p=152}}.</ref> The Republic, however, was short-lived, as when [[World War I]] broke out, Albania collapsed, and northern Epirus was alternately controlled by Greece, Italy and France at various intervals.<ref name="Konidaris"/><ref name="TuckerRoberts2005">{{harvnb|Tucker|Roberts|2005|p=77}}.</ref> |
|||
===20th century Epirus=== |
|||
{|class="infobox" width="180px" |
|||
|- |
|||
|[[Image:Epirus across Greece Albania4.svg|180px]] |
|||
|- |
|||
|The region of Epirus in the 20th century, divided between Greece and Albania. |
|||
<small> |
|||
'''Grey''': approx. extent of Epirus in antiquity; '''Orange''': Greek [[Epirus (periphery)|periphery of Epirus]]; '''Green''': approx. extent of largest concentration of Greeks in "Northern Epirus", early 20th cent.<ref>Following G. Soteriadis: “An Ethnological Map Illustrating Hellenism In The Balkan Peninsula And Asia Minor” London: Edward Stanford, 1918. [[:Image:Hellenism in the Near East 1918.jpg]]</ref> '''Red dotted line''': territory of autonomous state of Northern Epirus</small> |
|||
|} |
|||
The [[Treaty of Berlin]] of 1881 gave Greece parts of southern Epirus, but it was not until the [[First Balkan War]] of 1912–13 and the [[Treaty of London (1913)|Treaty of London]]<ref>Clogg, Richard. ''Concise History of Greece 1770–2000''. Cambridge University Press, 2002, ISBN 9607778618. "In February 1913 the Greek Army seized Ioannina, the capital of Epirus. The Turks recognised the gains of the Balkan allies by the Treaty of London, in May 1913."</ref> that the rest of southern Epirus to joined Greece. The [[Treaty of Bucharest (1913)|Treaty of Bucharest]], which concluded the [[Second Balkan War]], gave Northern Epirus to Albania.<ref>Clogg, Richard. ''Concise History of Greece 1770–2000''. Cambridge University Press, 2002, ISBN 9607778618. "The Second Balkan War had short duration and the Bulgarians were soon dragged to the table of negotiations. By the Treaty of Bucharest (August 1913) Bulgaria was forced to accept a little favourable regulation of the borders, even if she kept a way to the Aegean, in Degeagatch (modern Alexandroupolis). The sovereignty of Greece on Crete was now recognised, but her ambition to annex Northern Epirus with its large Greek population was stopped by the annexation of the area to an independent Albania."</ref>. This outcome was unpopular among both Greeks and Albanians, as settlements of the two people existed on both sides of the border. Among Greeks, northern Epirus was regarded as ''[[irredentism|terra irredenta]]''. When [[World War I]] broke out in 1914, Albania collapsed. Under a March 1915 agreement among the [[Allies of World War I|Allies]], Italy seized northern Albania and local Greeks set up an autonomous state in [[Northern Epirus]] in the southern part of the country. Although short-lived, the [[Autonomous Republic of Northern Epirus]] managed to leave behind a number of historical records of its existence, including its own postage stamps; see [[Postage stamps and postal history of Epirus]]. |
|||
[[Image:Epirote women Aug1914.jpg|right|200px|thumb|Detachment of armed Epirote women in the [[Autonomous Republic of Northern Epirus]].]] |
|||
Although the [[Paris Peace Conference, 1919|Paris Peace Conference]] of 1919 awarded the area to Greece after World War I, political developments such as the Greek defeat in the [[Greco-Turkish War (1919–1922)|Greco-Turkish War]] and, crucially, Italian lobbying in favour of Albania meant that Greece could not claim Northern Epirus. The area was finally ceded to Albania in 1924. |
|||
[[File:Epirus across Greece Albania4.svg|thumb|upright=1.15|The region of Epirus in the 20th century, divided between Greece and Albania. |
|||
Italy [[Italian invasion of Albania|occupied Albania]] in 1939 and in 1940 invaded Greece. The Italians were, however, driven back into Albania and Greek forces again took control of northern Epirus. The conflict, known as the [[Greco-Italian War]], marked one of the first tactical victories of the [[Allies of World War II|Allies]] in [[World War II]]. [[Benito Mussolini]] himself supervised the massive counter-attack of his divisions in spring 1941, only to be decisively defeated again by the poorly equipped, but determined, Greeks. [[Nazi Germany]] intervened in April 1941 to avert an embarrassing Italian defeat. The German military performed rapid military maneuvers through [[Kingdom of Yugoslavia|Yugoslavia]] and forced the encircled Greek forces to surrender. |
|||
{{legend|#fcc45f|Greek [[Epirus (region)|region of Epirus]]}} |
|||
{{legend|#dcc9a7|approx. extent of Epirus in antiquity}} |
|||
{{legend|#77da9b|approx. extent of largest concentration of Greeks in "Northern Epirus", early 20th century<ref>{{harvnb|Soteriades|1918}}: [[:File:Hellenism in the Near East 1918.jpg|Map]]</ref>{{unreliable source?|date=May 2020}}}}<br/>'''Red dotted line''': Territory of Autonomous State of Northern Epirus]] |
|||
Although the [[Paris Peace Conference, 1919|Paris Peace Conference]] of 1919 awarded Northern Epirus to Greece, developments such as the Greek defeat in the [[Greco-Turkish War (1919–1922)|Greco-Turkish War]] and, crucially, Italian lobbying in favor of Albania meant that Greece would not keep Northern Epirus. In 1924, the area was again ceded to Albania.<ref name="Miller">{{harvnb|Miller|1966|pp=543–544}}.</ref> |
|||
The whole of Epirus was then placed under Italian [[Axis Occupation of Greece|occupation]] until 1943, when the Germans took over following the [[Italian armistice|Italian surrender]] to the Allies. The highlands of Epirus became the major theatre of guerrilla infighting between the leftist [[National People's Liberation Army (Greece)|National People's Liberation Army]] (ELAS) and the right-wing [[National Republican Greek League]] (EDES). At the same time, the Germans carried out successive anti-partisan sweeps, which resulted in several atrocities against the civilian population. Following the German withdrawal from Greece in 1944, EDES forces also [[Chameria issue|expelled]] several thousand [[Cham Albanians]] as Nazi [[collaborationism|collaborators]]. On the other hand collaboranists Albanian bands of the [[Balli Kombetar]] launched a major offensive against towns and villages in Northern Epirus with devastating results<ref>{{citation |
|||
|last=Ruches |
|||
|first=Pyrros |
|||
|title=Albania's Captives |
|||
|year=1965 |
|||
|journal= |
|||
|volume= |
|||
|publisher=Argonaut |
|||
|pages=162-167 |
|||
|place=Chicago, USA |
|||
}}</ref>. In subsequent years (1945-1949), the mountains of Epirus became the scene of some of the fiercest fighting of the [[Greek Civil War]]. The final episode of the Greek Civil War took place on [[Gramos|Mount Grammos]] in 1949, ending with the defeat of the Communists. Peace returned to the region in 1949, although the formal state of war between Greece and Albania remained until 1987. During the Communist rule in Albania, the Greeks in northern [[Epirus]] experienced forced [[Albanisation]].<ref>[http://www.da.mod.uk/colleges/arag/document-listings/balkan/G97 Pettifer, James. "The Greek Minority in Albania - In the Aftermath of Communism". Conflict Studies Research Centre, July 2001, ISBN 1-903584-35-3], p. 7.</ref> |
|||
In 1939, Italy [[Italian invasion of Albania|occupied Albania]], and in 1940 [[Greco-Italian War|invaded Greece]]. The Italians were driven back into Albania, however, and Greek forces again took control of northern Epirus. The conflict marked the first tactical victory of the [[Allies of World War II|Allies]] in [[World War II]]. [[Benito Mussolini]] himself supervised the spring counter-offensive of his divisions in spring 1941, only to be repulsed again by the poorly equipped, but determined, Greeks. [[Nazi Germany]] then [[Battle of Greece|intervened]] in April 1941 to avert an Italian defeat. The German military performed rapid military maneuvers through [[Kingdom of Yugoslavia|Yugoslavia]] and forced the encircled Greek forces of the Epirus front to surrender. |
|||
The collapse of the communist regime in Albania in 1990-1991 triggered a massive migration of Albanian citizens to Greece, which included many members of the Greek community of Northen Epirus. Since the end of the [[Cold War]], many Greeks in northern Epirus are re-discovering their Greek heritage thanks to the opening of Greek schools in the region, while the Cham Albanians have called for compensation for their lost lands{{Citation needed|date=August 2009}}. |
|||
The whole of Epirus was then placed under Italian [[Axis Occupation of Greece|occupation]] until 1943, when the Germans took over following the [[Italian armistice|Italian surrender]] to the Allies. Due to the extensive activity of the anti-Nazi Greek resistance (mainly under [[EDES]]), the Germans carried out large scaled anti-partisan sweeps, making wide use of [[Axis-Cham Albanian collaboration|Nazi-collaborationist bands]] of [[Cham Albanians]], who committed numerous atrocities against the civilian population.{{sfn|Konidaris|2013|p=67}} They fought fiercely against the Greek partisans of the EDES, the latter being ordered by the Allied command to push them out of Greece into Albania. The violent clashes and the reprisals that followed by the Greek guerillas resulted in the [[Expulsion of Cham Albanians|expulsion]] to Albania of almost the entire Cham population.{{sfn|Konidaris|2013|p=67}} |
|||
With the liberation of Greece and the start of the first round of the [[Greek Civil War]] at the end of 1944, the highlands of Epirus became a major theater of guerrilla warfare between the leftist [[Greek People's Liberation Army]] (ELAS) and the right-wing [[National Republican Greek League]] (EDES). In subsequent years (1945–1949), the mountains of Epirus also became the scene of some of the fiercest fighting of the second and bloodier round of the Greek Civil War. The final episode of the war took place on [[Gramos|Mount Grammos]] in 1949, ending with the defeat of the Communists. Peace returned to the region in 1949, although because of official Albanian active involvement in the civil war on the side of the communists, the formal state of war between Greece and Albania remained in effect until 1987. Another reason for the continuation of the state of war until 1987 was that during the entire period of Communist rule in Albania, the Greek population of [[Northern Epirus]] experienced forced [[Albanisation]].{{sfn|Pettifer|2001|p=7}} Although a Greek minority was recognized by the Hoxha regime, this recognition only applied to an "official minority zone" consisting of 99 villages, leaving out important areas of Greek settlement, such as [[Himara]].<ref name="Konidaris"/> People outside the official minority zone received no education in the Greek language, which was prohibited in public.<ref name="Konidaris"/> The Hoxha regime also diluted the ethnic demographics of the region by relocating Greeks living there and settling in their stead Albanians from other parts of the country.<ref name="Konidaris"/> Relations began to improve in the 1980s with Greece's abandonment of any territorial claims over Northern Epirus and the lifting of the official state of war between the two countries.<ref name="Konidaris"/> |
|||
== Gallery == |
|||
<gallery> |
|||
==Economy== |
|||
File:Brücke Arta.jpg |
|||
[[File:New port of igoumenitsa.JPG|thumb|right|[[Igoumenitsa]] is the main port in Epirus, and links the region to [[Italy]].]] |
|||
File:Aetomilitsa-Densko.jpg |
|||
File:Vikos_river,_Epirus,_Greece.jpg |
|||
A rugged topography, poor soils, and fragmented landholdings have kept agricultural production low and have resulted in a low population density.<ref name=Britannica/> Animal husbandry is the main industry and corn the chief crop.<ref name=Britannica/> Oranges and olives are grown in the western lowlands, while tobacco is grown around Ioannina.<ref name=Britannica/> Epirus has few natural resources and industries, and the population has been depleted by migration.<ref name=Britannica/> The population is centered around Ioannina, which has the largest number of industrial establishments.<ref name=Britannica/> |
|||
File:Vikos Gorge from Beloe.jpg |
|||
File:120 2821-Aoos-Onno-Zweers.jpg |
|||
==Transportation== |
|||
File:Zagori Dragonlake and Gamila summit.jpg |
|||
Epirus has historically been a remote and isolated region due to its location between the Pindus mountains and the sea. In antiquity, the Roman [[Via Egnatia]] passed through [[Epirus Nova]], which linked Byzantium and Thessalonica to [[Dyrrachium]] on the [[Adriatic Sea]]. The modern [[Egnatia Odos (modern road)|Egnatia Odos highway]], which links [[Ioannina]] to the Greek province of Macedonia and terminating at [[Igoumenitsa]], is the only highway through the Pindus mountains and has served to greatly reduce the region's isolation from the east, while the [[Ionia Odos|Ionia Odos highway]], connecting Epirus with [[Western Greece]], helped reducing the region's isolation from the south. Also, the [[Aktio-Preveza Undersea Tunnel]] connects the southernmost tip of Epirus, near [[Preveza]], with [[Aetolia-Acarnania]] in western Greece. Ferry services from [[Igoumenitsa]] to the [[Ionian islands]] and [[Italy]] exist. The only airport in Epirus is the [[Ioannina National Airport]], while the [[Aktion National Airport]] is located just south of Preveza in [[Aetolia-Acarnania]]. There are no railroads in Epirus. |
|||
File:Acherons_utsprång,_Grekland.JPG |
|||
File:Ioannina Greece.jpg |
|||
==Gallery== |
|||
File:Sirako_Village_in_Epirus,_Greece.jpg |
|||
<gallery class="center"> |
|||
File:Nicopolis_LR_wall.jpg |
|||
File:Brücke Arta.jpg|The [[Bridge of Arta]]. |
|||
File:Dodona_Theatre_1.jpg |
|||
File:Aetomilitsa-Densko.jpg|The village of Aetomilitsa on Mount [[Gramos]], in the [[Pindus mountains]]. |
|||
File:Sheep in shadow, Konitsa, Ioannina prefecture, Greece.jpg |
|||
File:Vikos river, Epirus, Greece.jpg|The Vikos river, [[Vikos–Aoös National Park]]. |
|||
File:BaiedeParga.jpg |
|||
File: |
File:Vikos Gorge from Beloe.jpg|The [[Vikos Gorge]]. |
||
File:120 2821-Aoos-Onno-Zweers.jpg|The old bridge of [[Konitsa]] over the [[Vjosa|Aoos]] river. |
|||
File:07Vjosa02.jpg |
|||
File:Zagori Dragonlake and Gamila summit.jpg|The high altitude [[Drakolimni|Lake Drakolimni]] (Dragon Lake), on Mount Gamila in the [[Pindus mountains]]. |
|||
File:A2 Motorway, Greece - Section Paramythia-Igoumenitsa - 16.jpg |
|||
File:Acherons utsprång, Grekland.JPG|A canyon of the [[Acheron]] river. |
|||
File:Sirrako Village in Epirus, Greece.jpg|The village of [[Sirako]]. |
|||
File:Nicopolis LR wall.jpg|The walls of ancient [[Nicopolis]]. |
|||
File:Dodona Theatre 1.jpg|The Hellenistic theater of [[Dodona]]. |
|||
File:Sheep in shadow, Konitsa, Ioannina prefecture, Greece.jpg|Sheep under the shade of a tree near [[Konitsa]]. |
|||
File:BaiedeParga.jpg|The bay of [[Parga]]. |
|||
File:ALB 20070718 img 1368.jpg|The region of [[Himara]] seen from the Llogara pass. |
|||
File:07Vjosa02.jpg|The [[Vjosa]] river near [[Tepelena]]. |
|||
File:A2 Motorway, Greece - Section Paramythia-Igoumenitsa - 16.jpg|Section of the [[Egnatia Odos (modern road)|Egnatia Odos]], the only motorway in Epirus, near [[Igoumenitsa]]. |
|||
File:Gjirokastra01.jpg|[[Gjirokaster]], a [[UNESCO World Heritage Site]]. |
|||
File:Preveza Greece from above dsc06080.jpg|[[Preveza]] seen from the air. |
|||
</gallery> |
</gallery> |
||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
*[[ |
* [[List of cities in ancient Epirus]] |
||
*[[ |
* [[List of Epirotes]] |
||
*[[Chaonians]] |
|||
*[[Despotate of Epirus]] |
|||
*[[Dodona]] |
|||
*[[Epirus (periphery)]] in [[Greece]] |
|||
*[[Greco-Italian War]] |
|||
*[[Himara]] |
|||
*[[Ioannina]] |
|||
*[[List of Epirotes]] |
|||
*[[Molossians]] |
|||
*[[Northern Epirus]] |
|||
*[[Northern Epirotes]] |
|||
*[[Pindus Mountains]] |
|||
*[[Protocol of Corfu]]. |
|||
*[[Pyrrhus of Epirus]] |
|||
*[[Souliotes]] |
|||
*[[Thesprotians]] |
|||
*[[Vikos-Aoos National Park]] |
|||
==References== |
== References == |
||
=== Citations === |
|||
{{reflist}} |
|||
{{Reflist}} |
|||
=== General and cited sources === |
|||
{{sfn whitelist |CITEREFHammond1982 |CITEREFHammond1994}} |
|||
{{Refbegin|30em}} |
|||
*{{cite book | last=Anson | first=Edward M. | chapter=Why Study Ancient Macedonia and What This Companion is About | editor-last1=Roisman | editor-first1=Joseph | editor-last2=Worthington | editor-first2=Ian | title=A Companion to Ancient Macedonia | pages=3–20 | location=Oxford, Chichester, & Malden | publisher=Wiley-Blackwell | year=2010 | isbn=978-1-4051-7936-2 | chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=lkYFVJ3U-BIC }} |
|||
*{{cite book | last=Antoniadis | first=Vyron | year=2016 | title=Tabula Imperii Romani : J 34 - Athens : Epirus | location=Athens | publisher=Academy of Athens | isbn=978-960-404-308-8 | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=S99NvgAACAAJ }} |
|||
*{{cite book | last=Babiniotis | first=Georgios | title=Lexiko tis Neas Ellinikis Glossas | location=Athens, Greece | publisher=Kentro Lexikologias | year=1998 | isbn=960-86190-0-9 | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=VpJiAAAAMAAJ}} |
|||
*{{cite book | last1=Bahr | first1=Lauren S. | last2=Johnston | first2=Bernard | last3=Bloomfield | first3=Louise A. | title=Collier's Encyclopedia | volume=11 | location=New York, NY | publisher=Collier | year=1997 | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0EgUAQAAIAAJ }} |
|||
*{{cite book | last=Blumi | first=Isa | chapter=The Role of Education in the Albanian Identity and its Myths | pages=49–59 | editor-last1=Schwandner-Sievers | editor-first1=Stephanie | editor-last2=Fischer | editor-first2=Bernd Jürgen | title=Albanian Identities: Myth and History | location=Bloomington, IN | publisher=Indiana University Press | year=2002 | isbn=0-253-21570-6 | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=RnDeHFOX8yIC }} |
|||
*{{cite book | last=Borza | first=Eugene N. | title=In the Shadow of Olympus: The Emergence of Macedon | location=Princeton, NJ | publisher=Princeton University Press | year=1992 | isbn=0-691-00880-9 | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=614pd07OtfQC | edition=Revised }} |
|||
*{{cite book | last=Bowden | first=William | title=Epirus Vetus: The Archaeology of a Late Antique Province | year=2003 | location=London | publisher=Gerald Duckworth & Co. Limited | isbn=0-7156-3116-0 | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=ElFoAAAAMAAJ }} |
|||
*{{cite book | last=Cameron | first=Alan | title=Greek Mythography in the Roman World | location=New York and Oxford | publisher=Oxford University Press | year=2004 | isbn=0-19-517121-7 | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=A3H_51913RkC }} |
|||
*{{cite book | last=Clogg | first=Richard | title=A Concise History of Greece | edition=2nd | year=2002 | orig-year=1992 | location=Cambridge and New York | publisher=Cambridge University Press | isbn=978-0-52-100479-4 | url=https://archive.org/details/concisehistoryof00clog_0 | url-access=registration }} |
|||
*{{cite book | last=Davies | first=J. K. | chapter=13. A Wholly Non-Aristotelian Universe: The Molossians as Ethnos, State, and Monarchy | pages=234–258 | editor-last1=Brock | editor-first1=Roger | editor-last2=Hodkinson | editor-first2=Stephen | title=Alternatives to Athens: Varieties of Political Organization and Community in Ancient Greece | location=Oxford | publisher=Oxford University Press | year=2002 | isbn=0-19-925810-4 | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=J5Jg8raPTZsC }} |
|||
*{{cite journal|last=Desnickaja|first=A. V.|title=Language Interferences and Historical Dialectology|journal=Linguistics|volume=11|number=113|year=1973|doi=10.1515/ling.1973.11.113.41|pages=41–52|s2cid=144569294}} |
|||
*{{cite book | last=Fleming | first=Katherine Elizabeth | title=The Muslim Bonaparte: Diplomacy and Orientalism in Ali Pasha's Greece | location=Princeton, NJ | publisher=Princeton University Press | year=1999 | isbn=0-691-00194-4 | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=zZqbA6Jk0uUC }} |
|||
*{{cite book | last=Filos | first=Panagiotis | chapter=The Dialectal Variety of Epirus | pages=215–248 | editor1-last=Giannakis | editor1-first=Georgios | editor2-last=Crespo | editor2-first=Emilio | editor3-last=Filos | editor3-first=Panagiotis | title=Studies in Ancient Greek Dialects: From Central Greece to the Black Sea | year=2018 | location=Berlin and Boston | publisher=Walter de Gruyter | isbn=9783110532135 | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=UrxGDwAAQBAJ }} |
|||
*{{The Early Medieval Balkans}} |
|||
*{{The Late Medieval Balkans}} |
|||
*{{cite book | last=Gawrych | first=George Walter | title=The Crescent and the Eagle: Ottoman Rule, Islam and the Albanians, 1874–1913 | location=New York and London | publisher=I.B. Tauris | year=2006 | isbn=1-84511-287-3 | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=wPOtzk-unJgC }} |
|||
*{{cite book | last=Georgiev | first=Vladimir Ivanov | title=Introduction to the History of the Indo-European Languages | year=1981 | location=Sofia | publisher=Bulgarian Academy of Sciences | isbn=9789535172611 | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=xmZiAAAAMAAJ }} |
|||
*{{cite journal | last=Giakoumis | first=Kosta | title=Fourteenth-century Albanian migration and the 'relative autochthony' of the Albanians in Epeiros. The case of Gjirokastër | journal=Byzantine and Modern Greek Studies | volume=27 | year=2002 | pages=171–183 | doi=10.1179/byz.2003.27.1.171 | url=https://www.researchgate.net/publication/233673710 }} |
|||
*{{cite book|last=Greenwalt|first=William S.|editor-last1=Roisman|editor-first1=Joseph|editor-last2=Worthington|editor-first2=Ian|title=A Companion to Ancient Macedonia|chapter=Macedonia, Illyria and Epirus|pages=279–305|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=QsJ183uUDkMC|year=2011|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|isbn=978-1-4443-5163-7}} |
|||
*{{cite book | last=Hammond | first=Nicholas Geoffrey Lemprière | title=Epirus: The Geography, the Ancient Remains, the History and the Topography of Epirus and Adjacent Areas | location=Oxford | publisher=The Clarendon Press | year=1967 | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=xmKSQgAACAAJ }} |
|||
*{{cite book | last=Hammond | first=Nicholas Geoffrey Lemprière | title=Migrations and Invasions in Greece and Adjacent Areas | location=Park Ridge, NJ | publisher=Noyes Press | year=1976 | isbn=0-8155-5047-2 | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=_VBoAAAAMAAJ }} |
|||
*{{Cambridge Ancient History | volume = 3c | last=Hammond | first=Nicholas Geoffrey Lemprière | chapter=ILLYRIS, EPIRUS AND MACEDONIA | pages=261–285 }} |
|||
*{{cite book | last=Hammond | first=Nicholas Geoffrey Lemprière | title=A History of Greece to 322 B.C | location=Oxford | publisher=Clarendon Press | year=1986 | isbn=0-19-873096-9 | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=KwHBQgAACAAJ }} |
|||
* {{Cambridge Ancient History | volume = 6 | last=Hammond | first=Nicholas Geoffrey Lemprière | chapter=ILLYRIANS AND NORTH-WEST GREEKS | pages=422–443 }} |
|||
*{{cite book | last=Hammond | first=Nicholas Geoffrey Lemprière | title=Philip of Macedon | location=London | publisher=Duckworth | year=1998 | isbn=0-7156-2829-1 | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0XF5OwAACAAJ }} |
|||
*{{cite book | last1=Hornblower | first1=Simon | last2=Spawforth | first2=Antony | last3=Eidinow | first3=Esther | title=The Oxford Classical Dictionary | year=2012 | edition=4th | orig-year=1949 | location=Oxford | publisher=Oxford University Press | isbn=978-0-19-954556-8 | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=bVWcAQAAQBAJ }} |
|||
*{{cite book | last1=Jelavich | first1=Charles | last2=Jelavich | first2=Barbara | title=The Establishment of the Balkan National States, 1804–1920: A History of East Central Europe | volume=VIII | location=Seattle, WA | publisher=University of Washington Press | year=1977 | isbn=0-295-96413-8 | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=LBYriPYyfUoC }} |
|||
*{{cite conference |url=https://www.academia.edu/1478948 |title=The Ottoman Conquest of Preveza and its First Castle |first=Nikos D. |last=Karabelas |year=2015 |conference=XVIth Turkish Congress of History, organised by the Turkish Historical Society, in Ankara, 20–24 September 2010 |series=Kongreye Sunulan Bildiriler, Volume 4, Part 2, Osmanli Tarihi |location=Ankara |publisher=Türk Tarih Kurumu |pages=967–998 |isbn=978-975-16-2982-1 }} |
|||
*{{Oxford Dictionary of Byzantium}} |
|||
*{{cite book |last=Konidaris |first=Gerasimos |chapter=Examining Policy Responses to Immigration in the Light of Interstate Relations and Foreign Policy Objectives: Greece and Albania |pages=64–92 |editor-last1=King |editor-first1=Russell |editor-last2=Mai |editor-first2=Nicola |editor-last3=Schwandner-Sievers |editor-first3=Stephanie |title=The New Albanian Migration |location=Portland, OR |publisher=Sussex Academic Press |date=2013 |isbn=9781837641932 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=W3LEEAAAQBAJ |language=en}} |
|||
*{{cite book | last1=Liddell | first1=Henry George | last2=Scott | first2=Robert | title=A Greek-English Lexicon | location=Oxford | publisher=Clarendon Press | year=1940 | url=https://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Perseus:text:1999.04.0057 }} |
|||
*{{cite book | last=McHenry | first=Robert | title=The New Encyclopædia Britannica | year=2003 | location=Chicago, IL | publisher=Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. | edition=15th | isbn=978-0-85229-961-6 | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=rIQxAQAAIAAJ }} |
|||
*{{cite book | last=Miller | first=William | title=The Ottoman Empire and Its Successors, 1801–1927 | location=New York and London | publisher=Frank Cass | year=1966 | isbn=978-0-7146-1974-3 | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=HaA18-u7mMMC }} |
|||
*{{cite book | last=Minahan | first=James | title=Encyclopedia of the Stateless Nations: Ethnic and National Groups around the World | location=Westport, CT | publisher=Greenwood Press | year=2002 | isbn=978-0313076961 | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=ZfnWCQAAQBAJ}} |
|||
*{{cite book | last=Nicol | first=Donald MacGillivray | title=The Despotate of Epiros, 1267–1479: A Contribution to the History of Greece | year=1984 | location=Cambridge | publisher=Cambridge University Press | isbn=978-0-521-26190-6 | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=XIj0FfKto9AC }} |
|||
*{{cite book | last=Osswald | first=Brendan | chapter=The Ethnic Composition of Medieval Epirus | pages=125–154 | editor1-last=Ellis | editor1-first=Steven G. | editor2-last=Klusáková | editor2-first=Lud'a | title=Imagining Frontiers, Contesting Identities | location=Pisa | publisher=Edizioni Plus – Pisa University Press | year=2007 | isbn=978-88-8492-466-7 | chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=3zXFCs9EfEYC&pg=PA125 }} |
|||
*{{cite book | last=Pettifer | first=James | title=The Greek Minority in Albania – In the Aftermath of Communism | location=Camberley, Surrey | publisher=Conflict Studies Research Centre, Royal Military Academy Sandhurst | format=PDF | year=2001 | isbn=1-903584-35-3 | url=http://www.da.mod.uk/colleges/arag/document-listings/balkan/G97 | url-status=dead | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100521003813/http://www.da.mod.uk/colleges/arag/document-listings/balkan/G97 | archive-date=21 May 2010 | df=dmy-all }} |
|||
* {{Prosopographisches Lexikon der Palaiologenzeit}} |
|||
*{{cite book | last=Ramet | first=Sabrina P. | title=Nihil Obstat: Religion, Politics, and Social Change in East-Central Europe and Russia | location=Durham, NC | publisher=Duke University Press | year=1998 | isbn=0-8223-2070-3 | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=ZvMi6paTOlcC }} |
|||
*{{cite book | last=Reid | first=James J. | title=Crisis of the Ottoman Empire: Prelude to Collapse 1839–1878 | location=Stuttgart | publisher=Franz Steiner Verlag | year=2000 | isbn=3-515-07687-5 | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Zgg6c_Ndtu4C }} |
|||
*{{cite book | last=Ruches | first=Pyrrhus J. | title=Albania's Captives | location=Chicago, IL | publisher=Argonaut Incorporated, Publishers | year=1965 | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=2k9pAAAAMAAJ }} |
|||
*{{cite book | last=Sakellariou | first=M. V. | title=Epirus, 4000 Years of Greek History and Civilization | location=Athens, Greece | publisher=Ekdotikē Athēnōn | year=1997 | isbn=960-213-371-6 | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=UV1oAAAAMAAJ }} |
|||
*{{cite journal |last1=Sansaridou-Hendrickx |first1=Thekla |title=The Albanians in the Chronicle(s) of Ioannina: An Anthropological Approach |journal=Acta Patristica et Byzantina |date=2017 |volume=21 |issue=2 |pages=287–306 |doi=10.1080/10226486.2010.11879131 |s2cid=163742869 |url=https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/10226486.2010.11879131}} |
|||
*{{cite book | last=Soteriades | first=Georgios | title=An Ethnological Map Illustrating Hellenism in the Balkan Peninsula and Asia Minor | location=London | publisher=Edward Stanford | year=1918 | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=m02ZQAAACAAJ }} |
|||
*{{Tabula Imperii Byzantini | volume = 3}} |
|||
*{{cite thesis|last=Suha|first=Mikko|title=Late Classical – Hellenistic Fortifications in Epirus: Fourth to Second Century BC|publisher=Unigrafia, University of Helsinki|year=2021|isbn=978-951-51-7673-8}} |
|||
*{{cite book | last=Tandy | first=David W. | title=Prehistory and History: Ethnicity, Class and Political Economy | location=Montréal, Québec, Canada | publisher=Black Rose Books Limited | year=2001 | isbn=1-55164-188-7 | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=BiqTCaFkvdYC&q=david+tandy }} |
|||
*{{cite journal |last1=Triadafilopoulos |first1=Triadafilos |title=Power politics and nationalist discourse in the struggle for 'Northern Epirus': 1919-1921 |journal=Journal of Southern Europe and the Balkans |date=November 2000 |volume=2 |issue=2 |pages=149–162 |doi=10.1080/713683343 |s2cid=140687333 |url=https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/713683343 |access-date=17 June 2023 |language=en |issn=1461-3190}} |
|||
*{{cite book | last1=Tucker | first1=Spencer | last2=Roberts | first2=Priscilla Mary | title=World War I: Encyclopedia | year=2005 | location=Santa Barbara, CA | publisher=ABC-CLIO Incorporated | isbn=1-85109-420-2 | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=2YqjfHLyyj8C }} |
|||
*{{cite book | last=Wilkes | first=John J. | title=The Illyrians | location=Oxford | publisher=Blackwell Publishers Limited | year=1995 | isbn=0-631-19807-5 | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=4Nv6SPRKqs8C }} |
|||
*{{cite book | last=Winnifrith | first=Tom | title=Badlands, Borderlands: A History of Northern Epirus/Southern Albania | location=London | publisher=Duckworth | year=2002 | isbn=0-7156-3201-9 | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=dkRoAAAAMAAJ }} |
|||
{{Refend}} |
|||
==External links== |
==External links== |
||
*[http://www.ucc.ie/staff/jprodr/macedonia/epeanchis.html Ancient Epirus] |
|||
*[http://www.lysimachos.com/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=116&Itemid=27 Etymology of the 70 most famous ancient Epirotan names] |
|||
*[http://www.historyofepirus.org/ Articles about Epirus History] |
|||
*[http://www.epirus.info/ Epirus Info Guide] |
|||
*[http://www.macedonian-heritage.gr/HellenicMacedonia/en/img_A163a.html Didrachm of the Epirote League] |
*[http://www.macedonian-heritage.gr/HellenicMacedonia/en/img_A163a.html Didrachm of the Epirote League] |
||
*[http://www.epirus.info/ Epirus Info Guide] |
|||
*[http://panepirotic.org/ Panepirotic Federation of America] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080611160243/http://www.panepirotic.org/ |date=11 June 2008 }} |
|||
*[http://www.panepirotiki.com/ Panepirotic Federation of Greece] |
*[http://www.panepirotiki.com/ Panepirotic Federation of Greece] |
||
*[http:// |
*[https://web.archive.org/web/20131126113309/http://www.panipirotikos-kairou.org/greek/ Panepirotic Society of Cairo] |
||
*[https://longreads.com/2018/09/14/the-dead-end-on-my-record-shelf/ Folk music in Epirus] by musicologist Christopher C. King |
|||
*[http://www.panipirotikos-kairou.org/greek/ Panepirotic Society of Cairo] |
|||
{{Authority control}} |
|||
{{DEFAULTSORT:Epirus (Region)}} |
{{DEFAULTSORT:Epirus (Region)}} |
||
[[Category:Epirus]] |
[[Category:Epirus| ]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:Balkans]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:Geography of Europe]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:Historical regions in Albania]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:Historical regions in Greece]] |
||
[[Category:Historical regions]] |
[[Category:Historical regions]] |
||
[[Category:Traditional geographic divisions of Greece]] |
|||
[[bg:Епир]] |
|||
[[ca:Regió de l'Epir]] |
|||
[[cy:Epirus]] |
|||
[[de:Epirus (historische Region)]] |
|||
[[el:Ήπειρος]] |
|||
[[es:Reino de Epiro]] |
|||
[[eo:Epiro (regiono)]] |
|||
[[fr:Épire]] |
|||
[[hr:Epir (pokrajina)]] |
|||
[[la:Epirus (provincia Romana)]] |
|||
[[lv:Epīra]] |
|||
[[ja:イピロス]] |
|||
[[sq:Epiri]] |
|||
[[sk:Epirus]] |
|||
[[sl:Epir]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 04:41, 27 May 2024
Epirus
| |
|---|---|
 Map of ancient Epirus by Heinrich Kiepert, 1902 | |
| Present status | Divided between Greece and Albania |
| Demonym | Epirote |
| Time zones | Central European Time |
| Eastern European Time | |
Epirus (/ɪˈpaɪrəs/) is a geographical and historical region in southeastern Europe, now shared between Greece and Albania. It lies between the Pindus Mountains and the Ionian Sea, stretching from the Bay of Vlorë and the Acroceraunian Mountains in the north to the Ambracian Gulf and the ruined Roman city of Nicopolis in the south.[1][2] It is currently divided between the region of Epirus in northwestern Greece and the counties of Gjirokastër and Vlorë in southern Albania. The largest city in Epirus is Ioannina, seat of the Greek region of Epirus, with Gjirokastër the largest city in the Albanian part of Epirus.[1]
A rugged and mountainous region, Epirus was the north-west area of ancient Greece.[2] It was inhabited by the Greek tribes of the Chaonians, Molossians, and Thesprotians. It was home to the sanctuary of Dodona, the oldest oracle in ancient Greece, and the second most prestigious after Delphi. Unified into a single state in 370 BC by the Aeacidae dynasty, Epirus achieved fame during the reign of Pyrrhus of Epirus who fought the Roman Republic in a series of campaigns. Epirus subsequently became part of the Roman Republic along with the rest of Greece in 146 BC, which was followed by the Roman Empire and Eastern Roman Empire.
Following the sack of Constantinople by the Fourth Crusade (1204), Epirus became the center of the Despotate of Epirus, one of the successor states to the Byzantine Empire. In the 14th century, Epirus was brought under the rule of the restored Byzantine Empire, before being briefly conquered by the Serbian Empire. The region was then divided amongst a number of despotates and political entities, including the Despotate of Epirus, the Despotate of Arta, the Zenebishi family, and the Republic of Venice, before being conquered by the Ottoman Empire in the 15th century. Epirus became part of the semi-independent Pashalik governed by the Ottoman Albanian ruler Ali Pasha in the early 19th century, but the Sublime Porte re-asserted its control in 1821. Following the Balkan Wars and World War I, southern Epirus became part of Greece, while northern Epirus became part of Albania.
Name and etymology

The name Epirus is derived from the Greek: Ἤπειρος, romanized: Ḗpeiros (Doric Greek: Ἄπειρος, romanized: Ápeiros), meaning "mainland" or terra firma.[3][4] It is thought to come from an Indo-European root *apero- 'coast',[5] and was applied to the mainland of north-west Greece opposite Corfu and the Ionian islands.[6][7] The local name was struck on the coinage of the unified Epirote commonwealth: "ΑΠΕΙΡΩΤΑΝ" (Ancient Greek: Ἀπειρωτᾶν, romanized: Āpeirōtân, Attic Greek: Ἠπειρωτῶν, romanized: Ēpeirōtôn, i.e. "of the Epirotes", see adjacent image). The Albanian name for the region, which derives from the Greek, is Epiri. Similarly, the Aromanian name for Epirus, which is also Greek-derived, is Epiru.
Boundaries and definitions

Historically, the geographical area of Epirus proper is defined within the lines drawn from Cape Gjuhëz of the Ceraunian Mountains in the north-west, to Mount Qelqëz in the north-east, to Mount Gavrovo in the south-east, to the mouth of the Ambracian Gulf in the south-west.[8][9] The northern boundary of ancient Epirus is alternatively given as the Vjosa river.[10] Epirus's eastern boundary is defined by the Pindus Mountains, that form the spine of mainland Greece and separate Epirus from Macedonia and Thessaly.[1] To the west, Epirus faces the Ionian Sea. The island of Corfu is situated off the Epirote coast but is not regarded as part of Epirus.
The definition of Epirus has changed over time, such that modern administrative boundaries do not correspond to the boundaries of ancient Epirus. The region of Epirus in Greece only comprises a fraction of classical Epirus and does not include its easternmost portions, which lie in Thessaly. In Albania, where the concept of Epirus is never used in an official context, the counties of Gjirokastër, Vlorë, and Berat extend well beyond the northern and northeastern boundaries of classical Epirus.[citation needed]
Geography and ecology


Epirus is a predominantly rugged and mountainous region. It is largely made up of the Pindus Mountains, a series of parallel limestone ridges that are a continuation of the Dinaric Alps.[1][11] The Pindus mountains form the spine of mainland Greece and separate Epirus from Macedonia and Thessaly to the east. The ridges of the Pindus are parallel to the sea and generally so steep that the valleys between them are mostly suitable for pasture rather than large-scale agriculture.[1] Altitude increases as one moves east, away from the coast, reaching a maximum of 2,637 m at Mount Smolikas, the highest point in Epirus. Other important ranges include Tymfi (2,496 m at Mount Gamila), Lygkos (2,249 m), to the west and east of Smolikas respectively, Gramos (2,523 m) in the northeast, Tzoumerka (2,356 m) in the southeast, Tomaros (1,976 m) in the southwest, Mitsikeli near Ioannina (1,810 m), Mourgana (1,806 m), and Nemercke/Aeoropos (2,485 m) on the border between Greece and Albania, and the Ceraunian Mountains (2,000 m) near Himara in Albania. Most of Epirus lies on the windward side of the Pindus, and the prevailing winds from the Ionian Sea make the region the rainiest in mainland Greece.[1]
Significant lowlands are to be found only near the coast, in the southwest near Arta and Preveza, in the Acheron plain between Paramythia and Fanari, between Igoumenitsa and Sagiada, and also near Saranda. The Zagori area is a scenic upland plateau surrounded by mountain on all sides.
The main river flowing through Epirus is the Vjosë, which flows in a northwesterly direction from the Pindus mountains in Greece to its mouth north of the Bay of Vlorë in Albania. Other important rivers include the Acheron river, famous for its religious significance in ancient Greece and site of the Necromanteion, the Arachthos river, crossed by the historic Bridge of Arta, the Louros, the Thyamis or Kalamas, and the Voidomatis, a tributary of the Vjosë flowing through the Vikos Gorge. The Vikos Gorge, one of the deepest in the world, forms the centerpiece of the Vikos–Aoös National Park, known for its scenic beauty. The only significant lake in Epirus is Lake Pamvotis, on whose shores lies the city of Ioannina, the region's largest and traditionally most important city.
The climate of Epirus is Mediterranean along the coast and Alpine in the interior. Epirus is heavily forested, mainly by coniferous species. The fauna in Epirus is especially rich and features species such as bears, wolves, foxes, deer, and lynxes.
History
Early history


In the Neolithic period Epirus was populated by seafarers along the coast and by shepherds and hunters from the southwestern Balkans who brought with them the Greek language. These people buried their leaders in large mounds containing shaft graves. Similar burial chambers were subsequently used by the Mycenaean civilization, suggesting that the founders of Mycenae may have come from Epirus and central Albania. Epirus itself remained culturally backward during this time, but Mycenaean remains have been found at two religious shrines of great antiquity in the region: the Oracle of the Dead on the Acheron River, familiar to the heroes of Homer’s Odyssey, and the Oracle of Zeus at Dodona, to whom Achilles prayed in the Iliad.[1]
In the Middle Bronze Age, Epirus was inhabited by the same nomadic Hellenic tribes that went on to settle in the rest of Greece.[12] Aristotle considered the region around Dodona to have been part of Hellas and the region where the Hellenes originated.[13][14] According to Bulgarian linguist Vladimir I. Georgiev, Epirus was part of the Proto-Greek linguistic area during the Late Neolithic period.[15] By the early 1st millennium BC, all fourteen Epirote tribes including the Chaonians in northwestern Epirus, the Molossians in the centre and the Thesprotians in the south, were speakers of a strong west Greek dialect.[1][2][16]
Epirus in the Classical and Hellenistic periods


Geographically on the edge of the Greek world, Epirus remained for the most part outside the limelight of Greek history until relatively late, much like the neighbouring Greek regions of Macedonia, Aetolia, and Acarnania, with which Epirus had political, cultural, linguistic and economic connections.[17] Unlike most other Greeks of this time, who lived in or around city-states, the inhabitants of Epirus lived in small villages and their way of life was foreign to that of the poleis of southern Greece.[1][18] Their region lay on the periphery of the Greek world[1] and was far from peaceful; for many centuries, it remained a frontier area contested with the Illyrian peoples to the north. However, Epirus had a far greater religious significance than might have been expected given its geographical remoteness, due to the presence of the shrine and oracle at Dodona – regarded as second only to the more famous oracle at Delphi.
The Epirotes, speakers of a Northwest Greek dialect, different from the Dorian of the Greek colonies on the Ionian islands, and bearers of mostly Greek names, as evidenced by epigraphy, seem to have been regarded with some disdain by some classical writers. The 5th-century BC Athenian historian Thucydides describes them as "barbarians" in his History of the Peloponnesian War,[19] as does Strabo in his Geography,[20] although the latter clearly distinguishes them from the neighboring Illyrians.[21] Other writers, such as Herodotus,[22] Dionysius of Halicarnassus,[23] Pausanias,[24] and Eutropius,[25] describe them as Greeks. Similarly, Epirote tribes/states are included in the Argive and Epidaurian lists of the Greek Thearodokoi (hosts of sacred envoys).[26] Plutarch mentions an interesting element of Epirote folklore regarding Achilles: In his biography of King Pyrrhus, he claims that Achilles "had a divine status in Epirus and in the local dialect he was called Aspetos" (meaning unspeakable, unspeakably great, in Homeric Greek).[27][28]
Beginning in 370 BC, the Molossian Aeacidae dynasty built a centralized state in Epirus and began expanding their power at the expense of rival tribes.[1] The Aeacids allied themselves with the increasingly powerful kingdom of Macedon, in part against the common threat of Illyrian raids,[29] and in 359 BC the Molossian princess Olympias, niece of Arybbas of Epirus, married King Philip II of Macedon.[1] She was to become the mother of Alexander the Great.
On the death of Arybbas, Alexander of Epirus succeeded to the throne and the title King of Epirus in 334 BC. He invaded Italy, but was killed in battle by a Lucanian in the Battle of Pandosia against several Italic tribes 331 BC.[1][30] Aeacides of Epirus, who succeeded Alexander, espoused the cause of Olympias against Cassander, but was dethroned in 313 BC. His son Pyrrhus came to throne in 295 BC, and for six years fought against the Romans and Carthaginians in southern Italy and Sicily. The high cost of his victories against the Romans gave Epirus a new, but brief, importance, as well as a lasting contribution to the Greek language with the concept of a "Pyrrhic victory". Pyrrhus nonetheless brought great prosperity to Epirus, building the great theater of Dodona and a new suburb at Ambracia (now modern Arta), which he made his capital.[1]
The Aeacid dynasty ended in 232 BC, but Epirus remained a substantial power, unified under the auspices of the Epirote League as a federal state with its own parliament, or synedrion.[1] However, it was faced with the growing threat of the expansionist Roman Republic, which fought a series of wars against Macedon. The League steered an uneasy neutral course in the first two Macedonian Wars but split in the Third Macedonian War (171–168 BC), with the Molossians siding with the Macedonians and the Chaonians and Thesprotians siding with Rome.[1] The outcome was disastrous for Epirus; Molossia fell to Rome in 167 BC and 150,000 of its inhabitants were enslaved.[1]
Roman and Byzantine rule
Epirus as a Roman province
The region of Epirus was placed under the senatorial province of Achaea in 27 BC, with the exception of its northernmost part, which remained part of the province of Macedonia.[31] Under Emperor Trajan, sometime between 103 and 114 AD, Epirus became a separate province, under a procurator Augusti. The new province extended from the Gulf of Aulon (Vlorë) and the Acroceraunian Mountains in the north to the lower course of the Acheloos River in the south, and included the northern Ionian Islands of Corfu, Lefkada, Ithaca, Cephallonia, and Zakynthos.[31]
Late Antiquity
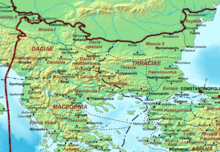
Probably during the provincial reorganization by Diocletian (r. 284–305), the western portion of the province of Macedonia along the Adriatic coast was split off into the province of New Epirus (Latin: Epirus Nova). Although this territory was not traditionally part of Epirus proper as defined by the ancient geographers, and was historically inhabited by Illyrian tribes and Greeks, the name reflects the fact that under Roman rule, the area had been subject to increasing Hellenization and settlement by Epirote tribes from the south.[31]
The two Epirote provinces became part of the Diocese of Moesia, until it was divided in ca. 369 into the dioceses of Macedonia and Dacia, when they became part of the former.[32] In the 4th century, Epirus was still a stronghold of paganism, and was aided by Emperor Julian (r. 361–363) and his praetorian prefect Claudius Mamertinus through reduction in taxes and the rebuilding of the provincial capital, Nicopolis.[33] According to Jordanes, in 380 the Visigoths raided the area.[33] With the division of the Empire on the death of Theodosius I in 395, Epirus became part of the Eastern Roman or Byzantine Empire.[33] In 395–397, the Visigoths under Alaric plundered Greece. They remained in Epirus for a few years, until 401, and again in 406–407, during Alaric's alliance with the Western Roman generalissimo Stilicho in order to wrest the Eastern Illyricum from the Eastern Empire.[33]

The Synecdemus of Hierocles, composed in ca. 527/8 AD but probably reflecting the situation in the first half of the 5th century, reports 11 cities for Old Epirus (Ancient Greek: Παλαιὰ Ἤπειρος, Latin: Epirus Vetus): the capital Nicopolis, Dodona, Euroea, Hadrianopolis, Appon, Phoenice, Anchiasmos, Buthrotum, Photike, Corfu Island, and Ithaca Island.[34] New Epirus, with capital at Dyrrhachium, comprised 9 cities.[33] From 467 on, the Ionian Islands and the coasts of Epirus became subject to raids by the Vandals, who had taken over the North African provinces and established their own kingdom centred on Carthage. The Vandals notably seized Nicopolis in 474 as a bargaining chip in their negotiations with Emperor Zeno, and plundered Zakynthos, killing many of its inhabitants and ferrying off others into slavery.[35] Epirus Nova became a battleground in the rebellions of the Ostrogoths after 479.[35] In 517, a raid of the Getae or Antae reached Greece, including Epirus Vetus.[35] The claim of Procopius of Caesarea in his Secret History, that under Justinian I (r. 527–565) the entirety of the Balkan provinces was raided by barbarians every year, is considered rhetorical hyperbole by modern scholars; only a single Slavic raid to the environs of Dyrrhachium, in 548/9, has been documented.[35] Procopius further reports that in 551, in an attempt to interdict the Byzantines' lines of communication with Italy during the Gothic War, the Ostrogoth king Totila sent his fleet to raid the shores of Epirus.[36] In response to these raids, and to repair the damage done by two destructive earthquakes in 522, Justinian initiated a wide-ranging programme of reconstruction and re-fortification: Hadrianopolis was rebuilt, albeit in reduced extent, and renamed Justinianopolis, while Euroea was moved further inland (traditionally identified with the founding of Ioannina), while Procopius claims that no less than 36 smaller fortresses in Epirus Vetus—most of them not identifiable today—were either rebuilt or built anew.[36]
Epirus from the Slavic invasions until 1204
In the late 6th century, much of Greece, including Epirus, fell under the control of the Avars and their Slavic allies. This is placed by the Chronicle of Monemvasia in the year 587, and is further corroborated by evidence that several sees were abandoned by their bishops by 591. Thus in c. 590 the bishop, clergy and people of Euroea fled their city, carrying with them the relics of their patron saint, St. Donatus, to Cassiope in Corfu.[37]
Of the various Slavic tribes, only the Baiounitai, first attested c. 615, are known by name, giving their name to their region of settlement: "Vagenetia".[37] Based on the density of the Slavic toponyms in Epirus, the Slavs must have settled in the region, although the extent of this settlement is unclear.[38] Slavic toponyms occur mainly in the mountainous areas of the interior and the coasts of the Gulf of Corinth, indicative of the fact that this was the avenue used by most of the Slavs who crossed the Gulf into the Peloponnese. With the exception of some few toponyms on Corfu, the Ionian Islands seem to not have been affected by Slavic settlement. The linguistic analysis of the toponyms reveals that they date mostly to the early wave of Slavic settlement at the turn of the 6th/7th centuries. Due to scarcity of textual evidence, it is unclear how much the area was affected by the second wave of Slavic migration, which began in the middle of the 8th century due to Bulgar pressure in the northern Balkans.[39] Slavic toponyms are nearly lacking in the mountains of Labëria (on the Kurvelesh plateau), in the Ionian coast where today Lab Albanian villages neighbour with the Greek-speaking ones, therefore it can be assumed that the expansion of the Slavs had not reach this region.[40]
As in eastern Greece, the restoration of Byzantine rule seems to have proceeded from the islands, chiefly Cephallonia, which was certainly under firm Imperial control in c. 702, when Philippicus Bardanes was banished there. The gradual restoration of Imperial rule is evidenced further from the participation of local bishops in councils in Constantinople: whereas only the bishop of Dyrrhachium participated in the Ecumenical Councils of 680/1 and 692, a century later the bishops of Dyrrhachium, Nicopolis, Corfu, Cephallonia, and Zakynthos are attested in the Second Council of Nicaea in 787.[41] In about the middle of the 8th century, the Theme of Cephallenia was established, but at least initially it was more oriented towards restoring Byzantine control over the Ionian and Adriatic seas, combating Saracen piracy, and securing communications with the remaining Byzantine possessions in Italy, rather than any systematic effort at subduing the Epirote mainland.[41] Nevertheless, following the onset of the Muslim conquest of Sicily in 827, the Ionian became particularly exposed to Arab raids.[42]

The 9th century saw great progress in the restoration of Imperial control in the mainland, as evidenced by the participation of the bishops of Ioannina, Naupaktos, Hadrianopolis, and Vagenetia (evidently by now organized as a Sklavinia under imperial rule) in the Ecumenical Councils of 869/70 and 879/80.[42] The Byzantine recovery resulted in an influx of Greeks from southern Italy and Asia Minor into the Greek interior, while remaining Slavs were Christianized and Hellenized.[43] The eventual success of the Hellenization campaign also suggests a continuity of the original Greek population, and that the Slavs had settled among many Greeks, in contrast to areas further north, in what is now Bulgaria and the former Yugoslavia, as those areas could not be Hellenized when they were recovered by the Byzantines in the early 11th century.[43] Following the great naval victory of admiral Nasar in 880, and the beginning of the Byzantine offensive against the Arabs in southern Italy in the 880s, the security situation improved and the Theme of Nicopolis was established, most likely after 886.[42][44] As the ancient capital of Epirus had been laid waste by the Slavs, the capital of the new theme became Naupaktos further south. The extent of the new province is unclear, but probably matched the extent of the Metropolis of Naupaktos, established at about the same time, encompassing the sees of Vonditsa, Aetos, Acheloos, Rogoi, Ioannina, Hadrianopolis, Photike, and Buthrotum. Vagenetia notably no longer appears as a bishopric. As the authors of the Tabula Imperii Byzantini comment, it appears that "the Byzantine administration had brought the strongly Slavic-settled areas in the mainland somewhat under its control, and a certain Re-Hellenization had set in".[45] Further north, the region around Dyrrhachium existed as the homonymous theme possibly as early as the 9th century.[46]
During the early 10th century, the themes of Cephallenia and Nicopolis appear mostly as bases for expeditions against southern Italy and Sicily, while Mardaites from both themes are listed in the large but unsuccessful expedition of 949 against the Emirate of Crete.[47] In c. 930, the Theme of Nicopolis was raided by the Bulgarians, who even occupied some parts until driven out or subjugated by the Byzantines years later.[47] Only the extreme north of Epirus seems to have remained consistently under Bulgarian rule in the period, but under Tsar Samuel, who moved the centre of Bulgarian power south and west to Ohrid, probably all of Epirus down to the Ambracian Gulf came under Bulgarian rule.[48] This is evidenced from the fact that the territories that were under Bulgarian rule formed part of the autocephalous Archbishopric of Ohrid after the Byzantine conquest of Bulgaria by Emperor Basil II in 1018: thus in Epirus the sees of Chimara, Hadrianopolis, Bela, Buthrotum, Ioannina, Kozyle, and Rogoi passed under the jurisdiction of Ohrid, while the Metropolitan of Naupaktos retained only the sees of Bonditza, Aetos, and Acheloos.[48] Basil II also established new, smaller themes in the region: Koloneia, and Dryinopolis (Hadrianopolis).[48]
The region joined the uprising of Petar Delyan in 1040, and suffered in the First Norman invasion of the Balkans: Dyrrhachium was occupied by the Normans in 1081–1084, Arta was unsuccessfully besieged, and Ioannina was captured by Robert Guiscard.[49] An Aromanian presence in Epirus is first mentioned in the late 11th century, while Jewish communities are attested throughout the medieval period in Arta and Ioannina.[50]
Despotate of Epirus

When Constantinople fell to the Fourth Crusade in 1204, the partitio Romaniae assigned Epirus to Venice, but the Venetians were largely unable to effectively establish their authority, except over Dyrrhachium (the "Duchy of Durazzo"). The Greek noble Michael Komnenos Doukas, who had married the daughter of a local magnate, took advantage of this, and within a few years consolidated his control over most of Epirus, first as a Venetian vassal and eventually as an independent ruler. By the time of his death in 1214/5, Michael had established a strong state, the Despotate of Epirus, with the former theme of Nicopolis at its core and Arta as its capital.[51][52] Epirus, and the city of Ioannina in particular, became a haven for Greek refugees from the Latin Empire of Constantinople for the next half century.[52]
The Despotate of Epirus ruled over Epirus and western Greece as far south as Naupaktos and the Gulf of Corinth, much of Albania (including Dyrrhachium), Thessaly, and the western portion of Macedonia, extending its rule briefly over central Macedonia and most of Thrace following the aggressive expansionism of Theodore Komnenos Doukas, who established the Empire of Thessalonica in 1224.[53][54] During this time, the definition of Epirus came to encompass the entire coastal region from the Ambracian Gulf to Dyrrhachium, and the hinterland to the west up to the highest peaks of the Pindus mountain range. Some of the most important cities in Epirus, such as Gjirokastër (Argyrokastron), were founded during this period.[55] The oldest reference to Albanians in Epirus is from a Venetian document dating to 1210, which states that "the continent facing the island of Corfu is inhabited by Albanians". Kosta Giakoumis believes that the use of hypothetical immigrations to explain the accounts of Albanian presence in Epirote territory prior to the 13th-14th century is somewhat arbitrary.[56]
14th century until the Ottoman conquest
In 1337, Epirus was once again brought under the rule of the restored Byzantine Empire.[54] In 1348, taking advantage of the civil war between the Byzantine emperors John V Palaiologos and John VI Kantakouzenos, the Serbian king Stefan Uroš IV Dušan conquered Epirus, with a number of Albanian mercenaries assisting him.[57] The Byzantine authorities in Constantinople soon re-established a measure of control by making the Despotate of Epirus a vassal state, but Albanian clans proceeded to invade and seize most of the region. Under Pjetër Losha, the Albanian Malakasi and Mazaraki tribes defeated Nikephoros II Orsini at the Battle of Achelous in 1359, which won Pjetër Losha the rule of Arta; Losha then founded the Despotate of Arta (1358-1416) with the help of the Mazaraki and Malakasi clans.[58]

Although Albanian clans gained control of most of the region by 1366/7, their continued division into rival clans meant that they could not establish a single central authority.[59] Ioannina became a center of Greek resistance to the Albanian clans. The Greeks of Ioannina offered power to three foreign rulers during this time, beginning with Thomas II Preljubović (1367–1384), whose rule was marked by hostilities in the region, as Ioannina came under constant siege by the Mazaraki and Malakasi clans under Losha. These tribes would besiege Ioannina a second time in 1374–1375.[60][61][62] A truce was signed when Pjetër's son Gjin was betrothed to Thomas's daughter Irina, but she would soon die in the 1375 plague and hostilities would recommence.[63] Preljubović attempted to pacify the Albanians of Epirus; however, under Gjin Bua Shpata, the Albanians defeated him.[64]
The reign of Esau de' Buondelmonti (1385–1411) in Ioannina followed, and with an army that consisted of the Albanian tribes of the Mazaraki and Malakasi, he marched against the Principality of Gjirokastër. He was defeated and captured by Albanian nobleman Gjon Zenebishi, and ransomed for 10,000 gold pieces on the intervention of the Venetian governor of Corfu.[65] At the time the Zenebishi clan controlled the area around Gjirokastër (1386–1411), while only the city of Ioannina remained under Greek control.[66]
Carlo I Tocco (1411–1429) then assumed control of Ioannina, commencing heavy conflicts with Jakob and Muriq Shpata, the Albanian leaders of the Despotate of Arta. The Shpata were originally defeated by Carlo's brother Leonardo II Tocco at Mazoma near ancient Nicopolis, but Carlo's son Torno was in turn defeated by the Albanians.[67][68] After the Tocchi succeeded in capturing Rhiniasa, Leonardo tried to take Rogoi and Carlo attempted to take Arta, but Jakob and Muriq succeeded in defending their capital for the time being. Carlo withdrew to Ioannina, but soon after was able to lure Jakob to an ambush near Vobliana: Jakob was captured and immediately executed (1 October 1416).[67][68] Carlo had effectively ended the rule of the Albanian clans in southernmost Epirus.[69]
Nevertheless, internal dissension eased the Ottoman conquest, which began with the capture of Ioannina in 1430 and continued with Arta in 1449, Angelokastro in 1460, Riniasa Castle and its environs (in what is now Preveza) in 1463,[70] and finally Vonitsa in 1479. With the exception of several coastal Venetian possessions, this was also the end of Latin rule in mainland Greece.
Ottoman rule

The Ottomans ruled Epirus for almost 500 years. Their rule in Epirus proved particularly damaging; the region was subjected to deforestation and excessive cultivation, which damaged the soil and drove many Epirotes to emigrate so as to escape the region's pervasive poverty.[1] Nonetheless, the Ottomans did not enjoy total control of Epirus. The Himara and Zagori regions managed to successfully resist Ottoman rule and maintained a degree of independence throughout this period. The Ottomans expelled the Venetians from almost the whole area in the late 15th century.
Between the 16th and 19th centuries, the city of Ioannina attained great prosperity and became a major center of the modern Greek Enlightenment.[71][72][73][74] Numerous schools were founded, such as the Balaneios, Maroutsaia, Kaplaneios, and Zosimaia, teaching subjects such as literature, philosophy, mathematics and physical sciences. In the 18th century, as the power of the Ottoman Empire declined, Epirus became a de facto independent region under the despotic rule of Ali Pasha of Tepelena, a Muslim Albanian brigand who rose to become the provincial governor of Ioannina in 1788.[1] At the height of his power, he controlled all of Epirus, and much of the Peloponnese, central Greece, and parts of western Macedonia[1] Ali Pasha's campaign to subjugate the confederation of the settlements of Souli met with fierce resistance by the Souliot warriors of the mountainous area. After numerous failed attempts to defeat the Souliotes, his troops succeeded in conquering the area in 1803. On the other hand, Ali, who used Greek as official language, witnessed an increase of Greek cultural activity with the establishment of several educational institutions.[75]
When the Greek War of Independence broke out, the inhabitants of Epirus contributed greatly. Two of the founding members of the Filiki Eteria (the secret society of the Greek revolutionaries), Nikolaos Skoufas and Athanasios Tsakalov, came from the Arta area and the city of Ioannina, respectively. Greece's first constitutional prime minister (1844–1847), Ioannis Kolettis, was a native of the village of Syrrako in Epirus and was a former personal physician to Ali Pasha. Ali Pasha tried to use the war as an opportunity to make himself a fully independent ruler, but was assassinated by Ottoman agents in 1822. When Greece became independent in 1830, however, Epirus remained under Ottoman rule. In 1854, during the Crimean War, a major local rebellion broke out. Although the newly found Greek state tried tacitly to support it, the rebellion was suppressed by Ottoman forces after a few months.[76] Another failed rebellion by local Greeks broke out in 1878. During this period, the Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople managed to shut down the few Albanian schools, considering teaching in Albanian a factor that would diminish its influence and lead to the creation of separate Albanian church, while publications in Albanian were banned by the Ottoman Empire.[77][78] In the late 19th century, the Kingdom of Italy opened various schools in the regions of Ioannina and Preveza in order to influence the local population. These schools began to attract students from the Greek language schools, but were ultimately closed after intervention and harassment by the Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople.[79] Throughout, the late period of Ottoman rule (from the 18th century) Greek and Aromanian population of the region suffered from Albanians raiders, that sporadically continued after Ali Pasha's death, until 1912–1913.[80]
20th-century Epirus

While the Treaty of Berlin (1878) awarded large parts of Epirus to Greece, opposition by the Ottomans and the League of Prizren resulted in only the region of Arta being ceded to Greece in 1881.[81] It was only following the First Balkan War of 1912–1913 and the Treaty of London that the rest of southern Epirus, including Ioannina, was incorporated into Greece.[82] Greece had also seized northern Epirus during the Balkan Wars, but the Treaty of Bucharest, which concluded the Second Balkan War, assigned Northern Epirus to Albania.[83]
This outcome was unpopular among local Greeks, as a substantial Greek population existed on the Albanian side of the border.[84] Among Greeks, northern Epirus was henceforth regarded as terra irredenta.[85] Local Greeks in northern Epirus revolted, declared their independence and proclaimed the Autonomous Republic of Northern Epirus in February 1914.[86] After fierce guerrilla fighting, they managed to gain full autonomy under the terms of the Protocol of Corfu, signed by Albanian and Northern Epirote representatives and approved by the Great Powers. The signing of the Protocol ensured that the region would have its own administration, recognized the rights of the local Greeks and provided self-government under nominal Albanian sovereignty.[87] The Republic, however, was short-lived, as when World War I broke out, Albania collapsed, and northern Epirus was alternately controlled by Greece, Italy and France at various intervals.[85][88]

Red dotted line: Territory of Autonomous State of Northern Epirus
Although the Paris Peace Conference of 1919 awarded Northern Epirus to Greece, developments such as the Greek defeat in the Greco-Turkish War and, crucially, Italian lobbying in favor of Albania meant that Greece would not keep Northern Epirus. In 1924, the area was again ceded to Albania.[90]
In 1939, Italy occupied Albania, and in 1940 invaded Greece. The Italians were driven back into Albania, however, and Greek forces again took control of northern Epirus. The conflict marked the first tactical victory of the Allies in World War II. Benito Mussolini himself supervised the spring counter-offensive of his divisions in spring 1941, only to be repulsed again by the poorly equipped, but determined, Greeks. Nazi Germany then intervened in April 1941 to avert an Italian defeat. The German military performed rapid military maneuvers through Yugoslavia and forced the encircled Greek forces of the Epirus front to surrender.
The whole of Epirus was then placed under Italian occupation until 1943, when the Germans took over following the Italian surrender to the Allies. Due to the extensive activity of the anti-Nazi Greek resistance (mainly under EDES), the Germans carried out large scaled anti-partisan sweeps, making wide use of Nazi-collaborationist bands of Cham Albanians, who committed numerous atrocities against the civilian population.[91] They fought fiercely against the Greek partisans of the EDES, the latter being ordered by the Allied command to push them out of Greece into Albania. The violent clashes and the reprisals that followed by the Greek guerillas resulted in the expulsion to Albania of almost the entire Cham population.[91]
With the liberation of Greece and the start of the first round of the Greek Civil War at the end of 1944, the highlands of Epirus became a major theater of guerrilla warfare between the leftist Greek People's Liberation Army (ELAS) and the right-wing National Republican Greek League (EDES). In subsequent years (1945–1949), the mountains of Epirus also became the scene of some of the fiercest fighting of the second and bloodier round of the Greek Civil War. The final episode of the war took place on Mount Grammos in 1949, ending with the defeat of the Communists. Peace returned to the region in 1949, although because of official Albanian active involvement in the civil war on the side of the communists, the formal state of war between Greece and Albania remained in effect until 1987. Another reason for the continuation of the state of war until 1987 was that during the entire period of Communist rule in Albania, the Greek population of Northern Epirus experienced forced Albanisation.[92] Although a Greek minority was recognized by the Hoxha regime, this recognition only applied to an "official minority zone" consisting of 99 villages, leaving out important areas of Greek settlement, such as Himara.[85] People outside the official minority zone received no education in the Greek language, which was prohibited in public.[85] The Hoxha regime also diluted the ethnic demographics of the region by relocating Greeks living there and settling in their stead Albanians from other parts of the country.[85] Relations began to improve in the 1980s with Greece's abandonment of any territorial claims over Northern Epirus and the lifting of the official state of war between the two countries.[85]
Economy

A rugged topography, poor soils, and fragmented landholdings have kept agricultural production low and have resulted in a low population density.[1] Animal husbandry is the main industry and corn the chief crop.[1] Oranges and olives are grown in the western lowlands, while tobacco is grown around Ioannina.[1] Epirus has few natural resources and industries, and the population has been depleted by migration.[1] The population is centered around Ioannina, which has the largest number of industrial establishments.[1]
Transportation
Epirus has historically been a remote and isolated region due to its location between the Pindus mountains and the sea. In antiquity, the Roman Via Egnatia passed through Epirus Nova, which linked Byzantium and Thessalonica to Dyrrachium on the Adriatic Sea. The modern Egnatia Odos highway, which links Ioannina to the Greek province of Macedonia and terminating at Igoumenitsa, is the only highway through the Pindus mountains and has served to greatly reduce the region's isolation from the east, while the Ionia Odos highway, connecting Epirus with Western Greece, helped reducing the region's isolation from the south. Also, the Aktio-Preveza Undersea Tunnel connects the southernmost tip of Epirus, near Preveza, with Aetolia-Acarnania in western Greece. Ferry services from Igoumenitsa to the Ionian islands and Italy exist. The only airport in Epirus is the Ioannina National Airport, while the Aktion National Airport is located just south of Preveza in Aetolia-Acarnania. There are no railroads in Epirus.
Gallery
-
The Bridge of Arta.
-
The village of Aetomilitsa on Mount Gramos, in the Pindus mountains.
-
The Vikos river, Vikos–Aoös National Park.
-
The Vikos Gorge.
-
The high altitude Lake Drakolimni (Dragon Lake), on Mount Gamila in the Pindus mountains.
-
A canyon of the Acheron river.
-
The village of Sirako.
-
The walls of ancient Nicopolis.
-
The Hellenistic theater of Dodona.
-
Sheep under the shade of a tree near Konitsa.
-
The bay of Parga.
-
The region of Himara seen from the Llogara pass.
-
Section of the Egnatia Odos, the only motorway in Epirus, near Igoumenitsa.
-
Preveza seen from the air.
See also
References
Citations
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y "Epirus". Encyclopædia Britannica. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. Retrieved 16 November 2013.
- ^ a b c Hornblower, Spawforth & Eidinow 2012, "Epirus", p. 527.
- ^ Liddell & Scott 1940, ἤπειρ-ος.
- ^ Filos 2018, p. 215, footnote #1.
- ^ Babiniotis 1998
- ^ David Sacks; Lisa R. Brody; Oswyn Murray (2005). Encyclopedia of the Ancient Greek World. Facts on File Library of World History. Facts on File. p. 85. ISBN 0816057222.
... in a region of northwest Greece called Epirus.
- ^ Winnifrith 2002, p. 22.
- ^ Suha 2021, p. 19
- ^ Greenwalt 2011, p. 280
- ^ Wilkes 1995, p. 92 "Appian's description of the Illyrian territories records a southern boundary with Chaonia and Thesprotia, where ancient Epirus began south of the river Aous (Vijosë)." (Map)
- ^ Bahr, Johnston & Bloomfield 1997, p. 389.
- ^ Borza 1992, pp. 62, 78, 98; Minahan 2002, p. 578.
- ^ Hammond 1986, p. 77: "The original home of the Hellenes was 'Hellas', the area round Dodona in Epirus, according to Aristotle. In the Iliad it was the home of Achilles' Hellenes."
- ^ Aristotle. Meteorologica, 1.14 Archived 29 June 2011 at the Wayback Machine: "Rather we must take the cause of all these changes to be that, just as winter occurs in the seasons of the year, so in determined periods there comes a great winter of a great year and with it excess of rain. But this excess does not always occur in the same place. The deluge in the time of Deucalion, for instance, took place chiefly in the Greek world and in it especially about ancient Hellas, the country about Dodona and the Achelous, a river which has often changed its course. Here the Selli dwelt and those who were formerly called Graeci and now Hellenes."
- ^ Georgiev 1981, p. 192: "Late Neolithic Period: in northwestern Greece the Proto-Greek language had already been formed: this is the original home of the Greeks."
- ^ Hammond 1998; Wilkes 1995, p. 104; Hammond 1994, pp. 430, 434; Hammond 1982, p. 284.
- ^ Hammond 1967.
- ^ Thucydides. The History of the Peloponnesian War, 1.8 Archived 5 August 2011 at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ Strabo. Geography, 7.7.1.
- ^ Strabo. Geography, 7.11
- ^ Herodotus. Histories, 6.127.
- ^ Dionysius of Halicarnassus. Roman Antiquities, 20.10 (19.11).
- ^ Pausanias. Description of Greece, 1.11.7–1.12.2.
- ^ Eutropius. Abridgment of Roman History (Historiae Romanae Breviarium), 2.11.13.
- ^ Davies 2002, pp. 234–258.
- ^ Cameron 2004, p. 141: "As for Aspestos, Achilles was honored in Epirus under that name, and the patronymic [Ἀ]σπετίδης is found in a fragmentary poem found on papyrus."
- ^ cf. Athenian secretary: Aspetos, son of Demostratos from Kytheros c. 340 BC.
- ^ Anson 2010, p. 5.
- ^ Livy (1926), 8.24.8–14
- ^ a b c Soustal & Koder 1981, p. 47.
- ^ Soustal & Koder 1981, pp. 47–48.
- ^ a b c d e Soustal & Koder 1981, p. 48.
- ^ Soustal & Koder 1981, pp. 48–49.
- ^ a b c d Soustal & Koder 1981, p. 49.
- ^ a b Soustal & Koder 1981, p. 50.
- ^ a b Soustal & Koder 1981, p. 51.
- ^ Osswald 2007, p. 128.
- ^ Soustal & Koder 1981, pp. 51–52.
- ^ Desnickaja 1973, p. 48.
- ^ a b Soustal & Koder 1981, p. 52.
- ^ a b c Soustal & Koder 1981, p. 53.
- ^ a b Fine 1991, p. 64.
- ^ Kazhdan 1991, p. 1485.
- ^ Soustal & Koder 1981, pp. 53–54.
- ^ Kazhdan 1991, p. 668.
- ^ a b Soustal & Koder 1981, p. 54.
- ^ a b c Soustal & Koder 1981, p. 55.
- ^ Soustal & Koder 1981, pp. 55–56.
- ^ Osswald 2007, p. 129.
- ^ Soustal & Koder 1981, pp. 59–61.
- ^ a b Osswald 2007, p. 132.
- ^ Nicol 1984, "Introduction", pp. 4–5.
- ^ a b Osswald 2007, p. 133.
- ^ Giakoumis 2002, p. 176.
- ^ Giakoumis 2002, p. 176: "Are we obliged to see in this a possible earlier Albanian immigration in the Epeirote lands, as Kostas Komis did in the case of the etymology of the toponym 'Preveza'? I believe that the use of hypothetical immigrations as a basis to interpret sources that indicate the presence of Albanians in the Epeirote lands prior to the thirteenth-fourteenth century is somewhat arbitrary."
- ^ Osswald 2007, p. 135.
- ^ Epeirotica 2.220; cf. 222 f
- ^ Fine 1994, pp. 348–351.
- ^ Sansaridou-Hendrickx 2017, p. 294.
- ^ Nicol 1984, pp. 142–145.
- ^ M. V. Sakellariou (1997). Epirus, 4000 years of Greek history and civilization. Ekdotikē Athēnōn. ISBN 978-960-213-371-2.
For the Albanian tribes of the Mazarakaioi and the Malakasioi, led by Peter Losha the despot of Arta,
- ^ Nicol 1984, pp. 142–145; Fine 1994, pp. 351–352; Sansaridou-Hendrickx 2017, p. 294.
- ^ Hammond, 1976 & ps"The Albanians and in particular the Mazarakii of the Kalamas valley held firm against him. In 1385 he was assassinated by some of his own bodyguards" (Epeirotica 2.230), p. 59.
- ^ Hutchinson, Richard Wyatt (1956). The Lord of Patras (PDF). A.G. Kalokairinos. p. 343.
- ^ Osswald 2007, p. 134.
- ^ a b PLP, 26521. Σπάτας Γιαγούπης.
- ^ a b Nicol 1984, p. 186.
- ^ Osswald 2007, p. 136.
- ^ Karabelas 2015, pp. 972–975.
- ^ Sakellariou 1997, p. 268.
- ^ Fleming 1999, pp. 63–66.
- ^ The Era of Enlightenment (Late 7th century–1821). Εθνικό Kέντρο Bιβλίου, p. 13.
- ^ Υπουργείο Εσωτερικών, Αποκέντρωσης και Ηλεκρονικής Διακυβέρνησης Περιφέρεια Ηπείρου: "Στη δεκαετία του 1790 ο νεοελληνικός διαφωτισμός έφθασε στο κορύφωμά του. Φορέας του πνεύματος στα Ιωάννινα είναι ο Αθανάσιος Ψαλίδας."
- ^ Fleming 1999, p. 64.
- ^ Reid 2000.
- ^ Jelavich & Jelavich 1977, p. 226.
- ^ Ramet 1998, p. 205.
- ^ Blumi 2002, p. 57.
- ^ Hammond 1976, p. 41: "Throughout this period bands of Albanians raiders pillaged and destroyed the villages of the Vlachs and the Greeks in Epirus, northern Pindus, the lakeland of Prespa and Ochrid, and parts of western Macedonia. One Albanian leader, 'Ali the Lion', emulated the achievements of 'John the Sword' and 'Peter the Pockmark' when he established himself as Ali Pasha, independent ruler of Ioannina. He and his Albanian soldiers, recruited mainly from his homeland in the Kurvelesh and the Drin valley of North Epirus, controlled the whole of Epirus and carried their raids far into western Macedonia and Thessaly. As we have seen, they destroyed the Vlach settlements in the lakeland and weakened those farther south. After the assassination of Ali Pasha in 1822 sporadic raids by bands of Albanians were a feature of life in northern Greece until the liberation of 1912–13".
- ^ Gawrych 2006, pp. 68–69.
- ^ Clogg 2002, p. 105: "In February 1913 the Greek Army seized Ioannina, the capital of Epirus. The Turks recognized the gains of the Balkan allies by the Treaty of London, in May 1913."
- ^ Clogg 2002, p. 105 "The Second Balkan War had short duration and the Bulgarians were soon dragged to the table of negotiations. By the Treaty of Bucharest (August 1913) Bulgaria was forced to accept a little favourable regulation of the borders, even if she kept a way to the Aegean, in Degeagatch (modern Alexandroupolis). The sovereignty of Greece over Crete was now recognised, but her ambition to annex Northern Epirus with its large Greek population was stopped by the annexation of the area to an independent Albania".
- ^ Pettifer 2001, p. 4.
- ^ a b c d e f Konidaris 2013, pp. 64–92.
- ^ Winnifrith 2002, p. 130.
- ^ Triadafilopoulos 2000, p. 152.
- ^ Tucker & Roberts 2005, p. 77.
- ^ Soteriades 1918: Map
- ^ Miller 1966, pp. 543–544.
- ^ a b Konidaris 2013, p. 67.
- ^ Pettifer 2001, p. 7.
General and cited sources
- Anson, Edward M. (2010). "Why Study Ancient Macedonia and What This Companion is About". In Roisman, Joseph; Worthington, Ian (eds.). A Companion to Ancient Macedonia. Oxford, Chichester, & Malden: Wiley-Blackwell. pp. 3–20. ISBN 978-1-4051-7936-2.
- Antoniadis, Vyron (2016). Tabula Imperii Romani : J 34 - Athens : Epirus. Athens: Academy of Athens. ISBN 978-960-404-308-8.
- Babiniotis, Georgios (1998). Lexiko tis Neas Ellinikis Glossas. Athens, Greece: Kentro Lexikologias. ISBN 960-86190-0-9.
- Bahr, Lauren S.; Johnston, Bernard; Bloomfield, Louise A. (1997). Collier's Encyclopedia. Vol. 11. New York, NY: Collier.
- Blumi, Isa (2002). "The Role of Education in the Albanian Identity and its Myths". In Schwandner-Sievers, Stephanie; Fischer, Bernd Jürgen (eds.). Albanian Identities: Myth and History. Bloomington, IN: Indiana University Press. pp. 49–59. ISBN 0-253-21570-6.
- Borza, Eugene N. (1992). In the Shadow of Olympus: The Emergence of Macedon (Revised ed.). Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. ISBN 0-691-00880-9.
- Bowden, William (2003). Epirus Vetus: The Archaeology of a Late Antique Province. London: Gerald Duckworth & Co. Limited. ISBN 0-7156-3116-0.
- Cameron, Alan (2004). Greek Mythography in the Roman World. New York and Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-517121-7.
- Clogg, Richard (2002) [1992]. A Concise History of Greece (2nd ed.). Cambridge and New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-52-100479-4.
- Davies, J. K. (2002). "13. A Wholly Non-Aristotelian Universe: The Molossians as Ethnos, State, and Monarchy". In Brock, Roger; Hodkinson, Stephen (eds.). Alternatives to Athens: Varieties of Political Organization and Community in Ancient Greece. Oxford: Oxford University Press. pp. 234–258. ISBN 0-19-925810-4.
- Desnickaja, A. V. (1973). "Language Interferences and Historical Dialectology". Linguistics. 11 (113): 41–52. doi:10.1515/ling.1973.11.113.41. S2CID 144569294.
- Fleming, Katherine Elizabeth (1999). The Muslim Bonaparte: Diplomacy and Orientalism in Ali Pasha's Greece. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. ISBN 0-691-00194-4.
- Filos, Panagiotis (2018). "The Dialectal Variety of Epirus". In Giannakis, Georgios; Crespo, Emilio; Filos, Panagiotis (eds.). Studies in Ancient Greek Dialects: From Central Greece to the Black Sea. Berlin and Boston: Walter de Gruyter. pp. 215–248. ISBN 9783110532135.
- Fine, John V. A. Jr. (1991) [1983]. The Early Medieval Balkans: A Critical Survey from the Sixth to the Late Twelfth Century. Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Press. ISBN 0-472-08149-7.
- Fine, John V. A. Jr. (1994) [1987]. The Late Medieval Balkans: A Critical Survey from the Late Twelfth Century to the Ottoman Conquest. Ann Arbor, Michigan: University of Michigan Press. ISBN 0-472-08260-4.
- Gawrych, George Walter (2006). The Crescent and the Eagle: Ottoman Rule, Islam and the Albanians, 1874–1913. New York and London: I.B. Tauris. ISBN 1-84511-287-3.
- Georgiev, Vladimir Ivanov (1981). Introduction to the History of the Indo-European Languages. Sofia: Bulgarian Academy of Sciences. ISBN 9789535172611.
- Giakoumis, Kosta (2002). "Fourteenth-century Albanian migration and the 'relative autochthony' of the Albanians in Epeiros. The case of Gjirokastër". Byzantine and Modern Greek Studies. 27: 171–183. doi:10.1179/byz.2003.27.1.171.
- Greenwalt, William S. (2011). "Macedonia, Illyria and Epirus". In Roisman, Joseph; Worthington, Ian (eds.). A Companion to Ancient Macedonia. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 279–305. ISBN 978-1-4443-5163-7.
- Hammond, Nicholas Geoffrey Lemprière (1967). Epirus: The Geography, the Ancient Remains, the History and the Topography of Epirus and Adjacent Areas. Oxford: The Clarendon Press.
- Hammond, Nicholas Geoffrey Lemprière (1976). Migrations and Invasions in Greece and Adjacent Areas. Park Ridge, NJ: Noyes Press. ISBN 0-8155-5047-2.
- Hammond, Nicholas Geoffrey Lemprière (1982). "ILLYRIS, EPIRUS AND MACEDONIA". In Boardman, John; Hammond, N. G. L. (eds.). The Cambridge Ancient History, Volume III, Part 3: The Expansion of the Greek World, Eighth to Sixth Centuries B.C. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 261–285. ISBN 978-0-5212-3447-4.
- Hammond, Nicholas Geoffrey Lemprière (1986). A History of Greece to 322 B.C. Oxford: Clarendon Press. ISBN 0-19-873096-9.
- Hammond, Nicholas Geoffrey Lemprière (1994). "ILLYRIANS AND NORTH-WEST GREEKS". In Lewis, David M.; Boardman, John; Hornblower, Simon; Ostwald, M. (eds.). The Cambridge Ancient History, Volume VI: The Fourth Century B.C. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 422–443. ISBN 978-0-5212-3348-4.
- Hammond, Nicholas Geoffrey Lemprière (1998). Philip of Macedon. London: Duckworth. ISBN 0-7156-2829-1.
- Hornblower, Simon; Spawforth, Antony; Eidinow, Esther (2012) [1949]. The Oxford Classical Dictionary (4th ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-954556-8.
- Jelavich, Charles; Jelavich, Barbara (1977). The Establishment of the Balkan National States, 1804–1920: A History of East Central Europe. Vol. VIII. Seattle, WA: University of Washington Press. ISBN 0-295-96413-8.
- Karabelas, Nikos D. (2015). The Ottoman Conquest of Preveza and its First Castle. XVIth Turkish Congress of History, organised by the Turkish Historical Society, in Ankara, 20–24 September 2010. Kongreye Sunulan Bildiriler, Volume 4, Part 2, Osmanli Tarihi. Ankara: Türk Tarih Kurumu. pp. 967–998. ISBN 978-975-16-2982-1.
- Kazhdan, Alexander, ed. (1991). The Oxford Dictionary of Byzantium. Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-504652-8.
- Konidaris, Gerasimos (2013). "Examining Policy Responses to Immigration in the Light of Interstate Relations and Foreign Policy Objectives: Greece and Albania". In King, Russell; Mai, Nicola; Schwandner-Sievers, Stephanie (eds.). The New Albanian Migration. Portland, OR: Sussex Academic Press. pp. 64–92. ISBN 9781837641932.
- Liddell, Henry George; Scott, Robert (1940). A Greek-English Lexicon. Oxford: Clarendon Press.
- McHenry, Robert (2003). The New Encyclopædia Britannica (15th ed.). Chicago, IL: Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. ISBN 978-0-85229-961-6.
- Miller, William (1966). The Ottoman Empire and Its Successors, 1801–1927. New York and London: Frank Cass. ISBN 978-0-7146-1974-3.
- Minahan, James (2002). Encyclopedia of the Stateless Nations: Ethnic and National Groups around the World. Westport, CT: Greenwood Press. ISBN 978-0313076961.
- Nicol, Donald MacGillivray (1984). The Despotate of Epiros, 1267–1479: A Contribution to the History of Greece. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-26190-6.
- Osswald, Brendan (2007). "The Ethnic Composition of Medieval Epirus". In Ellis, Steven G.; Klusáková, Lud'a (eds.). Imagining Frontiers, Contesting Identities. Pisa: Edizioni Plus – Pisa University Press. pp. 125–154. ISBN 978-88-8492-466-7.
- Pettifer, James (2001). The Greek Minority in Albania – In the Aftermath of Communism. Camberley, Surrey: Conflict Studies Research Centre, Royal Military Academy Sandhurst. ISBN 1-903584-35-3. Archived from the original (PDF) on 21 May 2010.
- Trapp, Erich; Beyer, Hans-Veit; Walther, Rainer; Sturm-Schnabl, Katja; Kislinger, Ewald; Leontiadis, Ioannis; Kaplaneres, Sokrates (1976–1996). Prosopographisches Lexikon der Palaiologenzeit (in German). Vienna: Verlag der Österreichischen Akademie der Wissenschaften. ISBN 3-7001-3003-1.
- Ramet, Sabrina P. (1998). Nihil Obstat: Religion, Politics, and Social Change in East-Central Europe and Russia. Durham, NC: Duke University Press. ISBN 0-8223-2070-3.
- Reid, James J. (2000). Crisis of the Ottoman Empire: Prelude to Collapse 1839–1878. Stuttgart: Franz Steiner Verlag. ISBN 3-515-07687-5.
- Ruches, Pyrrhus J. (1965). Albania's Captives. Chicago, IL: Argonaut Incorporated, Publishers.
- Sakellariou, M. V. (1997). Epirus, 4000 Years of Greek History and Civilization. Athens, Greece: Ekdotikē Athēnōn. ISBN 960-213-371-6.
- Sansaridou-Hendrickx, Thekla (2017). "The Albanians in the Chronicle(s) of Ioannina: An Anthropological Approach". Acta Patristica et Byzantina. 21 (2): 287–306. doi:10.1080/10226486.2010.11879131. S2CID 163742869.
- Soteriades, Georgios (1918). An Ethnological Map Illustrating Hellenism in the Balkan Peninsula and Asia Minor. London: Edward Stanford.
- Soustal, Peter; Koder, Johannes (1981). Tabula Imperii Byzantini, Band 3: Nikopolis und Kephallēnia (in German). Vienna: Verlag der Österreichischen Akademie der Wissenschaften. ISBN 978-3-7001-0399-8.
- Suha, Mikko (2021). Late Classical – Hellenistic Fortifications in Epirus: Fourth to Second Century BC (Thesis). Unigrafia, University of Helsinki. ISBN 978-951-51-7673-8.
- Tandy, David W. (2001). Prehistory and History: Ethnicity, Class and Political Economy. Montréal, Québec, Canada: Black Rose Books Limited. ISBN 1-55164-188-7.
- Triadafilopoulos, Triadafilos (November 2000). "Power politics and nationalist discourse in the struggle for 'Northern Epirus': 1919-1921". Journal of Southern Europe and the Balkans. 2 (2): 149–162. doi:10.1080/713683343. ISSN 1461-3190. S2CID 140687333. Retrieved 17 June 2023.
- Tucker, Spencer; Roberts, Priscilla Mary (2005). World War I: Encyclopedia. Santa Barbara, CA: ABC-CLIO Incorporated. ISBN 1-85109-420-2.
- Wilkes, John J. (1995). The Illyrians. Oxford: Blackwell Publishers Limited. ISBN 0-631-19807-5.
- Winnifrith, Tom (2002). Badlands, Borderlands: A History of Northern Epirus/Southern Albania. London: Duckworth. ISBN 0-7156-3201-9.
External links
- Didrachm of the Epirote League
- Epirus Info Guide
- Panepirotic Federation of America Archived 11 June 2008 at the Wayback Machine
- Panepirotic Federation of Greece
- Panepirotic Society of Cairo
- Folk music in Epirus by musicologist Christopher C. King

















