Timeline of historic inventions: Difference between revisions
→Paleolithic Era: unnecessary capital letter |
Mister Pip (talk | contribs) →1950s: added integrated circuit to important inventions |
||
| Line 183: | Line 183: | ||
==== 1950s ==== |
==== 1950s ==== |
||
* December 20, 1951: First use of [[nuclear power]] to produce electricity for households in [[Arco, Idaho]]<ref name="factsheet">[http://www.inl.gov/factsheets/ebr-1.pdf Experimental Breeder Reactor 1 factsheet], Idaho National Laboratory</ref><ref>[http://www.ans.org/pubs/magazines/nn/docs/2001-11-2.pdf Fifty years ago in December: Atomic reactor EBR-I produced first electricity] American Nuclear Society Nuclear news, November 2001</ref> |
* December 20, 1951: First use of [[nuclear power]] to produce electricity for households in [[Arco, Idaho]]<ref name="factsheet">[http://www.inl.gov/factsheets/ebr-1.pdf Experimental Breeder Reactor 1 factsheet], Idaho National Laboratory</ref><ref>[http://www.ans.org/pubs/magazines/nn/docs/2001-11-2.pdf Fifty years ago in December: Atomic reactor EBR-I produced first electricity] American Nuclear Society Nuclear news, November 2001</ref> |
||
*1958-59: Co-creation of the [[integrated circuit]] by [[Jack Kilby]] and [[Robert Noyce]]. |
|||
==== 1970s ==== |
==== 1970s ==== |
||
Revision as of 19:29, 17 July 2012
This article has been shortened from a longer article which misused sources. |
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages)
No issues specified. Please specify issues, or remove this template. |

The timeline of historic inventions is a chronological list of particularly important or significant technological inventions.
Note: Dates for inventions are often controversial. Inventions are often invented by several inventors around the same time, or may be invented in an impractical form many years before another inventor improves the invention into a more practical form. Where there is ambiguity, the date of the first known working version of the invention is used here.
Paleolithic Era
Note that the dates in the Paleolithic era are approximate and refer to the earliest discovered use of an invention, and may change as new research is created and older sites are found.
- 1.8 million years ago: Fire and then cooking [2]
- 500 thousand years ago (ka): Shelter construction[3]
- 400 ka: Pigments in Zambia[4]
- 400 ka: Spears in Germany[5]
- 200 ka: Glue in Italy[6]
- 160–40 ka: Burial[7]
- 60 ka: Bow[8]
- 36 ka: Cloth woven from flax fiber[9][10]
- 35 ka: Flute in Germany[11]
- 28 ka: twisted rope[12]
- 16 ka: Pottery[13]
1st millennium BC
7th century BC
6th century BC

- c. 515 BC: Crane in Ancient Greece[16]
5th century BC
- 5th c. BC: Crank motion (rotary quern) in Celtiberian Spain[17][18]
- 5th c. BC: Cast iron in Ancient China: Confirmed by archaeological evidence, the earliest cast iron was developed in China by the early 5th century BC during the Zhou Dynasty (1122–256 BC), the oldest specimens found in a tomb of Luhe County in Jiangsu province.[19][20][21][22][23]
- 5th c. BC: Crossbow in Ancient China and Ancient Greece: In Ancient China, the earliest evidence of bronze crossbow bolts dates as early as mid-5th century BC in Yutaishan, Hubei.[24] In Ancient Greece, the terminus ante quem of the gastraphetes is 421 BC.[25][26]
- Before 421 BC: Catapult in Ancient Greece (incl. Sicily)[25][26]
- c. 480 BC: Spiral stairs (Temple A) in Selinunte, Sicily (see also List of ancient spiral stairs)[27][28]
- 408–6 BC: Wheelbarrow in Attica, Ancient Greece[29]
3rd century BC
- Early 3rd c. BC: Canal lock (possibly pound lock) in Ancient Suez Canal under Ptolemy II (283–246 BC) in Hellenistic Egypt[30][31][32]
- Early 3rd c. BC: Waterway connecting two seas (Ancient Suez Canal) by Greek engineers under Ptolemy II (283–246 BC), following earlier, probably only partly successful attempts[33]
- 3rd c. BC: Water wheel in Hellenistic kingdoms described by Philo of Byzantium (ca. 280–220 BC)[34]
- c. 240 BC: Three-masted ship (mizzen, on Syracusia) under Hiero II of Syracuse, Sicily[35]
- After 205 BC: Dry dock some time after Ptolemy IV (221–205 BC) in Hellenistic Egypt[36]
2nd century BC

- 2nd c. BC: Fore-and-aft rig (spritsail) in Ancient Greece[37]
- 2nd c. BC: Paper in Ancient China: Although it is recorded that the Han Dynasty (202 BC–AD 220) court eunuch Cai Lun(b.c.50–AD 121) invented the pulp papermaking process and established the use of new raw materials used in making paper, ancient padding and wrapping paper artifacts dating to the 2nd century BC have been found in China, the oldest example of pulp papermaking being a map from Fangmatan, Tianshui.[38]
- 2nd c. BC: Sakia gear in Hellenistic Egypt[39]
1st century BC
- 1st c. BC: Segmental arch bridge (e.g. Pont-Saint-Martin or Ponte San Lorenzo) in Italy, Roman Republic[40][41]
- 1st c. BC: Arch dam (Glanum Dam) in Gallia Narbonensis, Roman Republic (see also List of Roman dams)[42][43][44][45][46]
- Before 71 BC (possibly 3rd c. BC[47][48][49]): Watermill (grain mill) by Greek engineers in Eastern Mediterranean (see also List of ancient watermills)[50][51]
1st millennium AD
1st century
- 1st c.: Multiple arch buttress dam (Esparragalejo Dam) in Hispania, Roman Empire[52][53][54][55]
- 1st–2nd c.: Buttress dam in Roman Empire[56]
2nd century
- 2nd c.: Crankshaft in Augusta Raurica, Roman Empire[57]
- 2nd c. (or 1st c. BC[58]): Lateen sail in Roman Empire[37][59][60]
- 2nd–3rd c.: Arch-gravity dam (e.g. Puy Foradado Dam or Kasserine Dam) in Roman Empire[54][61]
3rd century
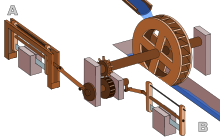
- Late 3rd c.: Crank and connecting rod (Hierapolis sawmill) in Asia Minor, Roman Empire[62][63][64]
- Late 3rd–early 4th c.: Turbine in Africa (province), Roman Empire[65][66][67]
- Ca. 300: Noria in Roman Empire[68]
4th century
- 4th–5th c.: Paddle wheel boat (in De rebus bellicis) in Roman Empire[69]
5th century
- 5th/6th c.: Pointed arch bridge (Karamagara Bridge) in Cappadocia, Eastern Roman Empire[70][71]
6th century
7th century
- 672: Greek fire in Constantinople, Byzantine Empire: Greek fire, an incendiary weapon likely based on petroleum or naphtha, was invented by Kallinikos, a Greek refugee to Constantinople, as described by Theophanes.[73] However, the historicity and exact chronology of this account is dubious,[74] and it could be that Kallinikos merely introduced an improved version of an established weapon.[75]
- 7th c.: Banknote in Tang Dynasty China: The banknote was first developed in China during the Tang and Song dynasties, starting in the 7th century. Its roots were in merchant receipts of deposit during the Tang Dynasty (618–907), as merchants and wholesalers desired to avoid the heavy bulk of copper coinage in large commercial transactions.[76][77][78]
9th century

- 9th c.: Gunpowder in Ancient China: Gunpowder was, according to prevailing academic consensus, discovered in the 9th century by Chinese alchemists searching for an elixir of immortality.[79] Evidence of gunpowder's first use in China comes from the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Period (618–907).[80] The earliest known recorded recipes for gunpowder were written by Zeng Gongliang, Ding Du, and Yang Weide in the Wujing Zongyao, a military manuscript compiled in 1044 during the Song Dynasty (960–1279).[81][82][83]
- 9th c.: Numerical zero in Ancient India: The concept of zero as a number, and not merely a symbol for separation is attributed to India.[84] In India, practical calculations were carried out using zero, which was treated like any other number by the 9th century, even in case of division.[84][85]
2nd millennium
11th century
- 1088: Movable type in Ancient China: The first record of a movable type system is in the Dream Pool Essays written in 1088, which attributed the invention of the movable type to Bi Sheng.[86][87][88][89] In the 15th century, Johannes Gutenberg independently invented the modern movable type system in Europe.[90]
12th century
- 1119: Mariner's compass (wet compass) in Ancient China: The earliest recorded use of magnetized needle for navigational purposes at sea is found in Zhu Yu's book Pingzhou Table Talks of 1119 (written from 1111 to 1117).[88][91][92][93][94][95][96] The typical Chinese navigational compass was in the form of a magnetic needle floating in a bowl of water.[97] The familiar mariner's dry compass which used a pivoting needle suspended above a compass-card in a glass box was invented in medieval Europe no later than 1300.[98]
- The first known use of gunpowder warfare in China (Song Dynasty)
- The Chinese advance weapons technology and invent cannons, grenades, land mines, rockets, and the early flamethrower.
13th century
- al-Jazari's automata
- 1282: Mechanization of papermaking (paper mill) in Xàtiva, Kingdom of Aragon[99]
- 1286: Eyeglasses in Italy[100]
14th century
- 14th c.: Floating crane in Rhineland, Holy Roman Empire[101]
15th century

- 1420s: Brace in Flandres, Holy Roman Empire[102]
- 1439: Printing press in Mainz, Germany: The printing press was invented in the Holy Roman Empire by Johannes Gutenberg around 1440, based on existing screw presses. The first confirmed record of a press appeared in a 1439 lawsuit against Gutenberg.[103]
- 1470s: Parachute (with frame) in Renaissance Italy[104]
- 1480s: Mariner's astrolabe on Portuguese circumnavigation of Africa[105]
- 1494: Double-entry bookkeeping system codified by Luca Pacioli
16th century
- 1560: Floating dock in Venice, Venetian Republic[106]
17th century

- 1605: Newspaper (Relation): Johann Carolus in Strassburg, Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation (see also List of the oldest newspapers)[107][108]
18th century
- 1709: Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit invents the alcohol thermometer.
- 1712: Thomas Newcomen builds the first steam engine to pump water out of mines.[109] Newcomen's engine, unlike Thomas Savery's, used a piston.
- 1717: Sébastien Vaillant proposes that plants reproduce sexually and have male and female parts.[citation needed]
- 1733: Stephen Hales takes measurements of blood pressure.[citation needed]
- 1742: Anders Celsius develops the Centigrade temperature scale.[citation needed]
- 1764: James Hargreaves invented the spinning jenny.
19th century
1800s
- 1800-01 High pressure steam engine: Richard Trevithick and Oliver Evans, independently[110]
- 1801: Jacquard loom (loom controlled by punched card): Joseph Marie Jacquard[111]
- 1802: Arc lamp: Humphry Davy (exact date unclear; not practical as a light source until generators)[112]
- 1804: Morphine in Paderborn, Germany: Morphine was discovered as the first active alkaloid extracted from the opium poppy plant in December 1804 by Friedrich Sertürner.[113]
- 1804: Railway steam locomotive: Richard Trevithick[114]
1810s
1820s
- 1822 The pattern tracing lathe (actually more like a shaper) is completed by Thomas Blanchard for the U.S. Ordinance Dept. The lathe could copy symmetrical shapes and was used for making gun stocks, and later, ax handles. The lathe's patent was in force for 42 years, the record for any U.S. patent.[110][115]
- 1826: Friction Match: John Walker[116]
1870s
- 1878: Rebreather: Henry Fleuss was granted a patent for the first practical rebreather[117]
- 1878 The electric light bulb was first patented in England by 1878 by Joseph Swan after having experimented since about 1850. Thomas Edison in the U.S. was working on improving the bulb patented by Swan and was granted a U.S. patent in 1879.
1880s
- 1888: Wind power in an open air stream is thus proportional to the third power of the wind speed; the available power increases eightfold when the wind speed doubles. Wind turbines for grid electricity therefore need to be especially efficient at greater wind speeds. It was invented by Charles F. Brush in 1888.
20th century
1950s
- December 20, 1951: First use of nuclear power to produce electricity for households in Arco, Idaho[118][119]
- 1958-59: Co-creation of the integrated circuit by Jack Kilby and Robert Noyce.
1970s
1977: A video game console is an interactive entertainment computer or customized computer system that produces a video display signal which can be used with a display device (a television, monitor, etc.) to display a video game. The term "video game console" is used to distinguish a machine designed for people to buy and use primarily for playing video games on a TV. As of 2007, it is estimated that video game consoles have made up 75% of the world's gaming market.[120]
1980s
1985: A CD-ROM (/[invalid input: 'icon']ˌsiːˌdiːˈrɒm/, an acronym of "Compact Disc Read-only memory") is a pre-pressed compact disc that contains data accessible to, but not writable by, a computer for data storage and music playback. The 1985 “Yellow Book” standard developed by Sony and Philips adapted the format to hold any form of binary data.[121]
1990s
1990:World Wide Web by a British national in Geneva, Switzerland: The World Wide Web was first proposed on March 1989 by English engineer and computer scientist Sir Tim Berners-Lee, now the Director of the World Wide Web Consortium.[122] The project was publicly introduced in December 1990.[123]
1995: DVD is an optical disc storage format, invented and developed by Philips, Sony, Toshiba, and Panasonic in 1995. DVDs offer higher storage capacity than Compact Discs while having the same dimensions.
21st century
2000s
See also
- Accelerating change
- List of emerging technologies
- List of inventors
- Outline of prehistoric technology
Footnotes
- ^ See People of the Millennium for an overview of the wide acclaim. In 1999, the A&E Network ranked Gutenberg no. 1 on their "People of the Millennium" countdown. In 1997, Time–Life magazine picked Gutenberg's invention as the most important of the second millennium; the same did four prominent US journalists in their 1998 resume 1,000 Years, 1,000 People: Ranking The Men and Women Who Shaped The Millennium. The Johann Gutenberg entry of the Catholic Encyclopedia describes his invention as having made a practically unparalleled cultural impact in the Christian era.
- ^ Harvard Gazette, Invention of cooking drove evolution of the human species
- ^ Hadfield, Peter, Gimme Shelter
- ^ Earliest evidence of art found
- ^ Kouwenhoven, Arlette P., World's Oldest Spears
- ^ Mazza, P; Martini, F; Sala, B; Magi, M; Colombini, M; Giachi, G; Landucci, F; Lemorini, C; Modugno, F (2006). "A new Palaeolithic discovery: tar-hafted stone tools in a European Mid-Pleistocene bone-bearing bed". Journal of Archaeological Science. 33 (9): 1310. doi:10.1016/j.jas.2006.01.006.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - ^ Evolving in their graves: early burials hold clues to human origins
- ^ Jennifer Viegas (31 March 2008). "Early Weapon Evidence Reveals Bloody Past". Discovery News.
- ^ Balter, M. (2009). "Clothes Make the (Hu) Man". Science. 325 (5946): 1329. doi:10.1126/science.325_1329a. PMID 19745126.
{{cite journal}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|author-name-separator=(help); Invalid|ref=harv(help); Unknown parameter|author-separator=ignored (help)CS1 maint: postscript (link) - ^ Kvavadze, E; Bar-Yosef, O; Belfer-Cohen, A; Boaretto, E; Jakeli, N; Matskevich, Z; Meshveliani, T. (2009). "30,000-Year-Old Wild Flax Fibers". Science. 325 (5946): 1359. doi:10.1126/science.1175404. PMID 19745144.
{{cite journal}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|author-name-separator=(help); Invalid|ref=harv(help); Unknown parameter|author-separator=ignored (help)CS1 maint: postscript (link) - ^ 'Oldest musical instrument' found, Pallab Ghosh, BBC News, June 25, 2009. Accessed on line August 26, 2009.
- ^ Small, Meredith F. (April 2002). "String theory: the tradition of spinning raw fibers dates back 28,000 years. (At The Museum)". Natural History. 111.3: 14(2)Template:Inconsistent citations
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help)CS1 maint: postscript (link) - ^ "Chinese pottery may be earliest discovered." Associated Press. 2009-06-01
- ^ Turfa, J. MacIntosh; Steinmayer, A. G. (1999): "The Earliest Foresail, on Another Etruscan Vase", The International Journal of Nautical Archaeology, Vol. 28, No. 3, pp. 292-296 (295)
- ^ Hans-Liudger, Dienel; Wolfgang, Meighörner (1997): "Der Tretradkran", Technikgeschichte series, 2nd ed., Deutsches Museum, München, p. 13
- ^ Coulton, J. J. (1974): "Lifting in Early Greek Architecture", The Journal of Hellenic Studies, Vol. 94, pp. 1–19 (7, 16)
- ^ Frankel, Rafael (2003): "The Olynthus Mill, Its Origin, and Diffusion: Typology and Distribution", American Journal of Archaeology, Vol. 107, No. 1, pp. 1–21 (17–19)
- ^ Ritti, Tullia; Grewe, Klaus; Kessener, Paul (2007): "A Relief of a Water-powered Stone Saw Mill on a Sarcophagus at Hierapolis and its Implications", Journal of Roman Archaeology, Vol. 20, pp. 138–163 (159)
- ^ Wagner (2001), 7, 36–37, 64–68.
- ^ Ebrey, Walthall, and Palais (2006), 30.
- ^ Gernet (1996), 69.
- ^ Wagner (1993), 335.
- ^ Pigott (1999), 177.
- ^ Wagner (1993), 153, 157–158.
- ^ a b Campbell, Duncan B. (2003): Greek and Roman Artillery 399 BC–AD 363, Osprey Publishing, Oxford, ISBN 978-1-84176-634-8, pp. 3ff.
- ^ a b Schellenberg, Hans Michael (2006): "Diodor von Sizilien 14,42,1 und die Erfindung der Artillerie im Mittelmeerraum", Frankfurter Elektronische Rundschau zur Altertumskunde, Vol. 3, pp. 14–23 (18f.)
- ^ Beckmann, Martin (2002): "The 'Columnae Coc(h)lides' of Trajan and Marcus Aurelius", Phoenix, Vol. 56, No. 3/4, pp. 348–357 (354)
- ^ Ruggeri, Stefania (2006): "Selinunt", Edizioni Affinità Elettive, Messina, ISBN 88-8405-079-0, p. 77
- ^ Lewis, M. J. T. (1994): "The Origins of the Wheelbarrow", Technology and Culture, Vol. 35, No. 3, pp. 453–475
- ^ Moore, Frank Gardner (1950): "Three Canal Projects, Roman and Byzantine", American Journal of Archaeology, Vol. 54, No. 2, pp. 97–111 (99–101)
- ^ Froriep, Siegfried (1986): "Ein Wasserweg in Bithynien. Bemühungen der Römer, Byzantiner und Osmanen", Antike Welt, 2nd Special Edition, pp. 39–50 (46)
- ^ Schörner, Hadwiga (2000): "Künstliche Schiffahrtskanäle in der Antike. Der sogenannte antike Suez-Kanal", Skyllis, Vol. 3, No. 1, pp. 28–43 (33–35, 39)
- ^ Schörner, Hadwiga (2000): "Künstliche Schiffahrtskanäle in der Antike. Der sogenannte antike Suez-Kanal", Skyllis, Vol. 3, No. 1, pp. 28–43 (29–36)
- ^ Oleson, John Peter (2000): "Water-Lifting", in: Wikander, Örjan: "Handbook of Ancient Water Technology", Technology and Change in History, Vol. 2, Brill, Leiden, ISBN 90-04-11123-9, pp. 217–302 (233)
- ^ Casson, Lionel (1995): "Ships and Seamanship in the Ancient World", Johns Hopkins University Press, ISBN 978-0-8018-5130-8, pp. 242, fn. 75
- ^ Athenaeus of Naucratis: "Deipnosophistae", V 204c–d
- ^ a b c Casson, Lionel (1995): "Ships and Seamanship in the Ancient World", Johns Hopkins University Press, ISBN 978-0-8018-5130-8, pp. 243–245
- ^ Buisseret (1998), 12.
- ^ Oleson, John Peter (2000): "Water-Lifting", in: Wikander, Örjan: "Handbook of Ancient Water Technology", Technology and Change in History, Vol. 2, Brill, Leiden, ISBN 90-04-11123-9, pp. 217–302 (234, 270)
- ^ O’Connor, Colin: Roman Bridges, Cambridge University Press, 1993, ISBN 0-521-39326-4, p. 171
- ^ Galliazzo, Vittorio (1995): "I ponti romani", Vol. 1, Edizioni Canova, Treviso, ISBN 88-85066-66-6, pp. 429–437
- ^ Smith, Norman (1971): "A History of Dams", Peter Davies, London, ISBN 978-0-432-15090-0, pp. 25–49 (33–35)
- ^ Schnitter, Niklaus (1978): "Römische Talsperren", Antike Welt, Vol. 8, No. 2, pp. 25–32 (31f.)
- ^ Schnitter, Niklaus (1987): "Verzeichnis geschichtlicher Talsperren bis Ende des 17. Jahrhunderts", in: Garbrecht, Günther (ed.): Historische Talsperren, Verlag Konrad Wittwer, Stuttgart, Vol. 1, ISBN 3-87919-145-X, pp. 9–20 (12)
- ^ Schnitter, Niklaus (1987): "Die Entwicklungsgeschichte der Bogenstaumauer", Garbrecht, Günther (ed.): Historische Talsperren, Vol. 1, Verlag Konrad Wittwer, Stuttgart, ISBN 3-87919-145-X, pp. 75–96 (80)
- ^ Hodge, A. Trevor (2000): "Reservoirs and Dams", in: Wikander, Örjan: Handbook of Ancient Water Technology, Technology and Change in History, Vol. 2, Brill, Leiden, ISBN 90-04-11123-9, pp. 331–339 (332, fn. 2)
- ^ Wikander, Örjan (2000): "The Water-Mill" in: Wikander, Örjan (ed.): Handbook of Ancient Water Technology, Technology and Change in History, Vol. 2, Brill, Leiden, ISBN 90-04-11123-9, pp. 371–400 (396f.)
- ^ Donners, K.; Waelkens, M.; Deckers, J. (2002): "Water Mills in the Area of Sagalassos: A Disappearing Ancient Technology", Anatolian Studies, Vol. 52, pp. 1–17 (11)
- ^ Wilson, Andrew (2002): "Machines, Power and the Ancient Economy", The Journal of Roman Studies, Vol. 92, pp. 1–32 (7f.)
- ^ Wikander, Örjan (1985): "Archaeological Evidence for Early Water-Mills. An Interim Report", History of Technology, Vol. 10, pp. 151–179 (160)
- ^ Wikander, Örjan (2000): "The Water-Mill" in: Wikander, Örjan (ed.): Handbook of Ancient Water Technology, Technology and Change in History, Vol. 2, Brill, Leiden, ISBN 90-04-11123-9, pp. 371–400 (396)
- ^ Schnitter, Niklaus (1978): "Römische Talsperren", Antike Welt, Vol. 8, No. 2, pp. 25–32 (29)
- ^ Schnitter, Niklaus (1987): "Die Entwicklungsgeschichte der Pfeilerstaumauer", in: Garbrecht, Günther (ed.): Historische Talsperren, Vol. 1, Verlag Konrad Wittwer, Stuttgart, ISBN 3-87919-145-X, pp. 57–74 (60, table 1, 62)
- ^ a b James, Patrick; Chanson, Hubert (2002): "Historical Development of Arch Dams. From Roman Arch Dams to Modern Concrete Designs", Australian Civil Engineering Transactions, Vol. CE43, pp. 39–56
- ^ Arenillas, Miguel; Castillo, Juan C. (2003): "Dams from the Roman Era in Spain. Analysis of Design Forms (with Appendix)", 1st International Congress on Construction History [20th–24th January], Madrid
- ^ Schnitter, Niklaus (1987): "Die Entwicklungsgeschichte der Pfeilerstaumauer", in: Garbrecht, Günther (ed.): Historische Talsperren, Vol. 1, Verlag Konrad Wittwer, Stuttgart, ISBN 3-87919-145-X, pp. 57–74 (59–62)
- ^ Schiöler, Thorkild (2009): "Die Kurbelwelle von Augst und die römische Steinsägemühle", Helvetia Archaeologica, Vol. 40, No. 159/160, pp. 113–124 (113f.)
- ^ Basch, Lucien (2001): "La voile latine, son origine, son évolution et ses parentés arabes", in: Tzalas, H. (ed.): Tropis VI, 6th International Symposium on Ship Construction in Antiquity, Lamia 1996 proceedings, Hellenic Institute for the Preservation of Nautical Tradition, pp. 55–85 (63)
- ^ Casson, Lionel (1954): "The Sails of the Ancient Mariner", Archaeology, Vol. 7, No. 4, pp. 214–219
- ^ Whitewright, Julian (2009): "The Mediterranean Lateen Sail in Late Antiquity", The International Journal of Nautical Archaeology, Vol. 38, No. 1, pp. 97–104
- ^ Hodge, A. Trevor (2000): "Reservoirs and Dams", in: Wikander, Örjan: Handbook of Ancient Water Technology, Technology and Change in History, Vol. 2, Brill, Leiden, ISBN 90-04-11123-9, pp. 331–339 (332)
- ^ a b Ritti, Tullia; Grewe, Klaus; Kessener, Paul (2007): "A Relief of a Water-powered Stone Saw Mill on a Sarcophagus at Hierapolis and its Implications", Journal of Roman Archaeology, Vol. 20, pp. 138–163 (140, 161)
- ^ a b Grewe, Klaus (2009): "Die Reliefdarstellung einer antiken Steinsägemaschine aus Hierapolis in Phrygien und ihre Bedeutung für die Technikgeschichte. Internationale Konferenz 13.−16. Juni 2007 in Istanbul", in: Bachmann, Martin (ed.): Bautechnik im antiken und vorantiken Kleinasien, Byzas, Vol. 9, Ege Yayınları/Zero Prod. Ltd., Istanbul, ISBN 978-975-8072-23-1, pp. 429–454 (429)
- ^ a b Grewe, Klaus (2010): "La máquina romana de serrar piedras. La representación en bajorrelieve de una sierra de piedras de la antigüedad, en Hierápolis de Frigia y su relevancia para la historia técnica (translation by Miguel Ordóñez)", in: Las técnicas y las construcciones de la Ingeniería Romana, V Congreso de las Obras Públicas Romanas, pp. 381–401
- ^ Wilson, Andrew (1995): "Water-Power in North Africa and the Development of the Horizontal Water-Wheel", Journal of Roman Archaeology, Vol. 8, pp. 499–510 (507f.)
- ^ Wikander, Örjan (2000): "The Water-Mill" in: Wikander, Örjan (ed.): Handbook of Ancient Water Technology, Technology and Change in History, Vol. 2, Brill, Leiden, ISBN 90-04-11123-9, pp. 371–400 (377)
- ^ Donners, K.; Waelkens, M.; Deckers, J. (2002): "Water Mills in the Area of Sagalassos: A Disappearing Ancient Technology", Anatolian Studies, Vol. 52, pp. 1–17 (13)
- ^ Oleson, John Peter (2000): "Water-Lifting", in: Wikander, Örjan: "Handbook of Ancient Water Technology", Technology and Change in History, Vol. 2, Brill, Leiden, ISBN 90-04-11123-9, pp. 217–302 (235)
- ^ De Rebus Bellicis (anon.), chapter XVII, text edited by Robert Ireland, in: BAR International Series 63, part 2, p. 34
- ^ Galliazzo, Vittorio (1995): "I ponti romani", Vol. 1, Edizioni Canova, Treviso, ISBN 88-85066-66-6, p. 92
- ^ Warren, John (1991): "Creswell's Use of the Theory of Dating by the Acuteness of the Pointed Arches in Early Muslim Architecture", Muqarnas, Vol. 8, pp. 59–65 (61–63)
- ^ Heinle, Erwin; Schlaich, Jörg (1996): "Kuppeln aller Zeiten, aller Kulturen", Deutsche Verlags-Anstalt, Stuttgart, ISBN 3-421-03062-6, pp. 30–32
- ^ Pryor & Jeffreys 2006, pp. 607–609
- ^ Theophanes & Turtledove 1982, p. 52
- ^ Roland 1992, p. 657; Pryor & Jeffreys 2006, p. 608
- ^ Ebrey, Walthall, and Palais (2006), 156.
- ^ Bowman (2000), 105.
- ^ Gernet (1962), 80.
- ^ Jack Kelly Gunpowder: Alchemy, Bombards, and Pyrotechnics: The History of the Explosive that Changed the World, Perseus Books Group: 2005, ISBN :0465037224, 9780465037223: pp. 2-5
- ^ Needham, Volume 5, Part 7, 8–9, 80–82.
- ^ Needham (1987), Volume 5, Part 7, 70–73, 120–124.
- ^ Gernet (1996), 311.
- ^ Day & McNeil (1996), 785.
- ^ a b Bourbaki (1998), page 46
- ^ Britannica Concise Encyclopedia (2007). algebra
- ^ Needham, Volume 5, Part 1, 201–202.
- ^ Gernet (1996), 335.
- ^ a b Bowman (2000), 599.
- ^ Day & McNeil (1996), 70.
- ^ Encyclopaedia Britannica. Retrieved November 27, 2006, from Encyclopaedia Britannica Ultimate Reference Suite DVD—entry 'printing'
- ^ Gernet (1962), 77.
- ^ Sivin (1995), III, 21–22.
- ^ Needham (1986), Volume 4, Part 1, 279.
- ^ Elisseeff (2000), 296.
- ^ Gernet (1996), 328.
- ^ Day & McNeil (1996), 636.
- ^ Kreutz, p. 373
- ^ Frederic C. Lane, “The Economic Meaning of the Invention of the Compass,” The American Historical Review, Vol. 68, No. 3. (Apr., 1963), p.615ff.
- ^ Burns, Robert I. (1996): "Paper Comes to the West, 800−1400", in: Lindgren, Uta (ed.): Europäische Technik im Mittelalter. 800 bis 1400. Tradition und Innovation, 4th ed., Gebr. Mann Verlag, Berlin, ISBN 3-7861-1748-9, pp. 413–422 (417f.)
- ^ Vincent Ilardi, Renaissance Vision from Spectacles to Telescopes (Philadelphia, Pennsylvania: American Philosophical Society, 2007), page 5.
- ^ Matheus, Michael (1996): "Mittelalterliche Hafenkräne", in: Lindgren, Uta (ed.): Europäische Technik im Mittelalter. 800 bis 1400. Tradition und Innovation, 4th ed., Gebr. Mann Verlag, Berlin, ISBN 3-7861-1748-9, pp. 345–348 (346)
- ^ a b White, Lynn (1962): "Medieval Technology and Social Change", At the Clarendon Press, Oxford, p. 112
- ^ Meggs, Philip B. A History of Graphic Design. John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1998. (pp 58–69) ISBN 0-471-29198-6
- ^ White, Lynn (1968): "The Invention of the Parachute", Technology and Culture, Vol. 9, No. 3, pp. 462–467 (462f.)
- ^ Stimson, Alan (1985): "The Mariner's Astrolabe. A Survey of 48 Surviving Examples", UC Biblioteca Geral, Coimbra, p. 576
- ^ Sarton, George (1946): "Floating Docks in the Sixteenth Century", Isis, Vol. 36, No. 3/4, pp. 153–154 (153f.)
- ^ a b World Association of Newspapers: "Newspapers: 400 Years Young!"
- ^ a b Weber, Johannes (2006): "Strassburg, 1605: The Origins of the Newspaper in Europe", German History, Vol. 24, No. 3, pp. 387–412 (396f.)
- ^ McNeil, Ian (1990). An Encyclopedia of the History of Technology. London: Routledge. ISBN 0-415-14792-1.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ a b Thomson, Ross (2009). Structures of Change in the Mechanical Age: Technological Invention in the United Sates 1790-1865. Baltimore, MD: The Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 978-0-8018-9141-0.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ http://www.ideafinder.com/history/inventions/jacquard.htm
- ^ http://archives.theiet.org/about/Arclamps/arclamps.htm
- ^ Andreas Luch (2009). Molecular, clinical and environmental toxicology. Springer. p. 20. ISBN 3-7643-8335-6.
- ^ http://www.museumwales.ac.uk/en/rhagor/article/trevithic_loco/
- ^ Hounshell 1984, p. 35
- ^ "John Walker's Friction Light". BBC. Retrieved 2011-08-25.
- ^ Quick, D. (1970). "A History Of Closed Circuit Oxygen Underwater Breathing Apparatus". Royal Australian Navy, School of Underwater Medicine. RANSUM-1-70. Retrieved 2011-08-25.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - ^ Experimental Breeder Reactor 1 factsheet, Idaho National Laboratory
- ^ Fifty years ago in December: Atomic reactor EBR-I produced first electricity American Nuclear Society Nuclear news, November 2001
- ^ "The World’s Technological Capacity to Store, Communicate, and Compute Information", Martin Hilbert and Priscila López (2011), Science (journal), 332(6025), 60-65; free access to the article through here martinhilbert.net/WorldInfoCapacity.html
- ^ EP 689208 "Method for block oriented addressing" – for block layouts see columns 1 and 2
- ^ "Tim Berners Lee - Time 100 People of the Century". Time Magazine. Retrieved 17 May 2010.
He wove the World Wide Web and created a mass medium for the 21st century. The World Wide Web is Berners-Lee's alone. He designed it. He loosed it on the world. And he more than anyone else has fought to keep it open, nonproprietary and free. .
- ^ Berners-Lee, Tim. "Pre-W3C Web and Internet Background". World Wide Web Consortium. Retrieved April 21, 2009.
References
- Bourbaki, Nicolas (1998). Elements of the History of Mathematics. Berlin, Heidelberg, and New York: Springer-Verlag. ISBN 3-540-64767-8.
- Bowman, John S. (2000). Columbia Chronologies of Asian History and Culture. New York: Columbia University Press. ISBN 0-231-11004-9.
- Buisseret, David. (1998). Envisioning the City: Six Studies in Urban Cartography. Chicago: University Of Chicago Press. ISBN 0-226-07993-7.
- Day, Lance and Ian McNeil. (1996). Biographical Dictionary of the History of Technology. New York: Routledge. ISBN 0-415-06042-7.
- Ebrey, Walthall, Palais, (2006). East Asia: A Cultural, Social, and Political History. Boston: Houghton Mifflin Company.
- Elisseeff, Vadime. (2000). The Silk Roads: Highways of Culture and Commerce. New York: Berghahn Books. ISBN 1-57181-222-9.
- Gernet, Jacques (1962). Daily Life in China on the Eve of the Mongol Invasion, 1250-1276. Translated by H.M. Wright. Stanford: Stanford University Press. ISBN 0-8047-0720-0.
- Gernet, Jacques. (1996). A History of Chinese Civilization. Translated by J.R. Foster and Charles Hartman. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-49781-7.
- Kreutz, Barbara M. (1973) "Mediterranean Contributions to the Medieval Mariner's Compass", Technology and Culture, 14 (3: July), p. 367–383
- Needham, Joseph (1962). Science and Civilization in China: Volume 4, Physics and Physical Technology; Part 1, Physics. Cambridge University Press., reprinted Taipei: Caves Books, Ltd.(1986)
- Needham, Joseph and Tsien Tsuen-Hsuin. (1985). Science and Civilization in China: Volume 5, Chemistry and Chemical Technology, Part 1, Paper and Printing. Cambridge University Press., reprinted Taipei: Caves Books, Ltd.(1986)
- Needham, Joseph. (1987). Science and Civilization in China: Volume 5, Chemistry and Chemical Technology, Part 7, Military Technology; the Gunpowder Epic. Cambridge University Press.
- Pigott, Vincent C. (1999). The Archaeometallurgy of the Asian Old World. Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Museum of Archaeology and Anthropology. ISBN 0-924171-34-0.
- Sivin, Nathan (1995). Science in Ancient China: Researches and Reflections. Brookfield, Vermont: VARIORUM, Ashgate Publishing.
- Wagner, Donald B. (1993). Iron and Steel in Ancient China: Second Impression, With Corrections. Leiden: E.J. Brill. ISBN 90-04-09632-9.
- Wagner, Donald B. (2001). The State and the Iron Industry in Han China. Copenhagen: Nordic Institute of Asian Studies Publishing. ISBN 87-87062-83-6.
