United Nations Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean: Difference between revisions
Cantab1985 (talk | contribs) |
Rescuing 1 sources and tagging 0 as dead. #IABot (v1.1) |
||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
The '''United Nations Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean''', known as ECLAC, UNECLAC or in Spanish CEPAL, is a [[United Nations]] [[United_Nations_Economic_and_Social_Council#Regional_commissions|regional commission]] to encourage economic cooperation. ECLAC includes 45 member States (20 in [[Latin America]], 13 in the [[Caribbean]] and 12 from outside the region), and 13 associate members which are various non-independent territories, associated island countries and a commonwealth in the Caribbean. ECLAC publishes statistics covering the countries of the region<ref name=cepalstat>[http://www.eclac.org/estadisticas/default.asp?idioma=IN CEPALSTAT] page at official ECLAC site</ref> and makes cooperative agreements with nonprofit institutions.<ref name=newsrelease1>[http://www.eclac.org/cgi-bin/getProd.asp?xml=/prensa/noticias/comunicados/6/47586/P47586.xml&xsl=/prensa/tpl-i/p6f.xsl&base=/tpl-i/top-bottom.xsl ECLAC signed a cooperation agreement to promote science and technology in the region] (with Brazilian Center for Strategic Studies and Management) at ECLAC.org</ref> ECLAC's headquarters is in [[Santiago de Chile|Santiago]], Chile. |
The '''United Nations Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean''', known as ECLAC, UNECLAC or in Spanish CEPAL, is a [[United Nations]] [[United_Nations_Economic_and_Social_Council#Regional_commissions|regional commission]] to encourage economic cooperation. ECLAC includes 45 member States (20 in [[Latin America]], 13 in the [[Caribbean]] and 12 from outside the region), and 13 associate members which are various non-independent territories, associated island countries and a commonwealth in the Caribbean. ECLAC publishes statistics covering the countries of the region<ref name=cepalstat>[http://www.eclac.org/estadisticas/default.asp?idioma=IN CEPALSTAT] {{wayback|url=http://www.eclac.org/estadisticas/default.asp?idioma=IN |date=20120519021707 }} page at official ECLAC site</ref> and makes cooperative agreements with nonprofit institutions.<ref name=newsrelease1>[http://www.eclac.org/cgi-bin/getProd.asp?xml=/prensa/noticias/comunicados/6/47586/P47586.xml&xsl=/prensa/tpl-i/p6f.xsl&base=/tpl-i/top-bottom.xsl ECLAC signed a cooperation agreement to promote science and technology in the region] (with Brazilian Center for Strategic Studies and Management) at ECLAC.org</ref> ECLAC's headquarters is in [[Santiago de Chile|Santiago]], Chile. |
||
ECLAC was established in 1948 as the UN Economic Commission for [[Latin America]],<ref>{{cite book |last1=Cypher |first1= James M. |last2=Dietz |first2= James L. |date=2009 |title=The process of economic development |url= |location= |publisher=London & New York: Routledge |page= |isbn= 978-0-415-77103-0|accessdate= }}</ref> or UNECLA. In 1984, a resolution was passed to include the countries of the [[Caribbean]] in the name.<ref name=official-history>[http://www.eclac.cl/cgi-bin/getprod.asp?xml=/noticias/paginas/4/43024/P43024.xml ABOUT ECLAC] at official ECLAC site</ref> It reports to the [[UN Economic and Social Council]] (ECOSOC). |
ECLAC was established in 1948 as the UN Economic Commission for [[Latin America]],<ref>{{cite book |last1=Cypher |first1= James M. |last2=Dietz |first2= James L. |date=2009 |title=The process of economic development |url= |location= |publisher=London & New York: Routledge |page= |isbn= 978-0-415-77103-0|accessdate= }}</ref> or UNECLA. In 1984, a resolution was passed to include the countries of the [[Caribbean]] in the name.<ref name=official-history>[http://www.eclac.cl/cgi-bin/getprod.asp?xml=/noticias/paginas/4/43024/P43024.xml ABOUT ECLAC] at official ECLAC site</ref> It reports to the [[UN Economic and Social Council]] (ECOSOC). |
||
Revision as of 23:51, 20 July 2016
 ECLAC headquarters in Santiago, Chile | |
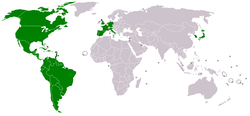 Map showing United Nations Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean members | |
| Established | 1948 |
|---|---|
| Type | Primary Organ - Regional Branch |
| Legal status | Active |
| Headquarters | |
| Website | English version |
The United Nations Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean, known as ECLAC, UNECLAC or in Spanish CEPAL, is a United Nations regional commission to encourage economic cooperation. ECLAC includes 45 member States (20 in Latin America, 13 in the Caribbean and 12 from outside the region), and 13 associate members which are various non-independent territories, associated island countries and a commonwealth in the Caribbean. ECLAC publishes statistics covering the countries of the region[2] and makes cooperative agreements with nonprofit institutions.[3] ECLAC's headquarters is in Santiago, Chile.
ECLAC was established in 1948 as the UN Economic Commission for Latin America,[4] or UNECLA. In 1984, a resolution was passed to include the countries of the Caribbean in the name.[5] It reports to the UN Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC).
Member states
The member states are Antigua and Barbuda, Argentina, Bahamas, Barbados, Belize, Bolivia, Brazil, Canada, Chile, Colombia, Costa Rica, Cuba, Dominica, Dominican Republic, Ecuador, El Salvador, France, Germany, Grenada, Guatemala, Guyana, Haiti, Honduras, Italy, Jamaica, Japan, Mexico, Netherlands, Nicaragua, Norway, Panama, Paraguay, Peru, Portugal, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, South Korea, Spain, Suriname, Trinidad and Tobago, United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, United States of America, Uruguay, and Venezuela. The associate members are Anguilla, Aruba, Bermuda, British Virgin Islands, Cayman Islands, Curaçao, Guadeloupe, Martinique, Montserrat, Puerto Rico, Sint Maarten, Turks and Caicos Islands, and United States Virgin Islands. [6]
Locations
- Santiago, Chile (headquarters)
- Mexico City, Mexico (Central American subregional headquarters)
- Port of Spain, Trinidad and Tobago (Caribbean subregional headquarters)
- Buenos Aires, Argentina (country office)
- Brasília, Brazil (country office)
- Montevideo, Uruguay (country office)
- Bogotá, Colombia (country office)
- Washington, DC, United States of America (liaison office)
Executive Secretaries of ECLAC

| Name | Country | Served |
|---|---|---|
| Alicia Bárcena Ibarra | July 2008 - present | |
| José Luis Machinea | December 2003 - June 2008 | |
| José Antonio Ocampo | January 1998 – August 2003 | |
| Gert Rosenthal | January 1988 – December 1997 | |
| Norberto González | March 1985 – December 1987 | |
| Enrique V. Iglesias | April 1972 – February 1985 | |
| Carlos Quintana | January 1967 – March 1972 | |
| José Antonio Mayobre | August 1963 – December 1966 | |
| Raúl Prebisch | May 1950 – July 1963 | |
| Gustavo Martínez Cabañas | December 1948 – April 1950 |
See also
- United Nations System
- eLAC eLAC2007, eLAC2010 and eLAC2015: Strategies for the Information Society in Latin America and the Caribbean
References
- ^ eclac.cl, ECLAC: Office of the Executive Secretary
- ^ CEPALSTAT Archived 2012-05-19 at the Wayback Machine page at official ECLAC site
- ^ ECLAC signed a cooperation agreement to promote science and technology in the region (with Brazilian Center for Strategic Studies and Management) at ECLAC.org
- ^ Cypher, James M.; Dietz, James L. (2009). The process of economic development. London & New York: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-77103-0.
- ^ ABOUT ECLAC at official ECLAC site
- ^ "ABOUT ECLAC – Member States and associate members of ECLAC". CEPAL. Retrieved 15 June 2013.
Bibliography
- Paul Berthoud, A Professional Life Narrative, 2008, worked with CEPAL-ECLAC and offers testimony from the inside of the early years of the organization.
- José Briceño Ruiz, María Liliana Quintero Rizzuto and Dyanna de Benítez (June 2013). "The ECLAC's structuralist thinking on development and Latin American integration: reflections on the contemporary relevance". Aportes para la Integración Latinoamericana (in Spanish). XIX (28): 1–324. ISSN 1667-8613. Retrieved 29 April 2014.
