Psychology: Difference between revisions
m Removing link(s): Wikipedia:Articles for deletion/Baden Eunson closed as delete (XFDcloser) |
WebMaven2000 (talk | contribs) →{{anchor|WEIRD}}WEIRD bias: countering western bias |
||
| Line 334: | Line 334: | ||
From an anthropological perspective, scholars applied the WEIRD model to European history, arguing that a powerful Christian Church forced a radical change away from incest and cousin marriages that undermined the role of clans and created individualism in Europe by 1500 CE. They argue that a distinctive Western psychology thus emerged that valued agency, autonomy, and kindness towards strangers.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Schulz |first1=Jonathan F. |last2=Bahrami-Rad |first2=Duman |last3=Beauchamp |first3=Jonathan P. |last4=Henrich |first4=Joseph |title=The Church, intensive kinship, and global psychological variation |journal=Science |date=8 November 2019 |volume=366 |issue=6466 |pages=eaau5141 |doi=10.1126/science.aau5141|pmid=31699908 |s2cid=207943472 }}</ref> Historians were not involved in that project, and have since pointed out its historical fallacies regarding an all-powerful Church at too early a point in time, and a rejection of cousin marriage that did not happen.<ref> Brian Connolly, Hans Hummer, and Sara McDougall, "Weird Science: Incest and History" [https://www.historians.org/publications-and-directories/perspectives-on-history/may-2020/weird-science-incest-and-history ''Perspectives on History'' (May 2020)]</ref> |
From an anthropological perspective, scholars applied the WEIRD model to European history, arguing that a powerful Christian Church forced a radical change away from incest and cousin marriages that undermined the role of clans and created individualism in Europe by 1500 CE. They argue that a distinctive Western psychology thus emerged that valued agency, autonomy, and kindness towards strangers.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Schulz |first1=Jonathan F. |last2=Bahrami-Rad |first2=Duman |last3=Beauchamp |first3=Jonathan P. |last4=Henrich |first4=Joseph |title=The Church, intensive kinship, and global psychological variation |journal=Science |date=8 November 2019 |volume=366 |issue=6466 |pages=eaau5141 |doi=10.1126/science.aau5141|pmid=31699908 |s2cid=207943472 }}</ref> Historians were not involved in that project, and have since pointed out its historical fallacies regarding an all-powerful Church at too early a point in time, and a rejection of cousin marriage that did not happen.<ref> Brian Connolly, Hans Hummer, and Sara McDougall, "Weird Science: Incest and History" [https://www.historians.org/publications-and-directories/perspectives-on-history/may-2020/weird-science-incest-and-history ''Perspectives on History'' (May 2020)]</ref> |
||
In order to counter this bias, [[transnational psychology]] was developed. As first articulated by Adams, Bhatia, Else-Quest, Grabe, and Kurtis, transnational psychology counters the Western bias in the field of psychology <ref name="KurtisAdams2015">{{Cite journal | last1 = Kurtis | first1 = T. | last2 = Adams | first2 = G. | title = Decolonizing liberation: Toward a transnational feminist psychology | journal = Journal of Social and Political Psychology | volume = 3 | issue = 2| pages = 388–413 | doi = 10.5964/jspp.v3i1.326 | jstor = 3178747 | date = 2015 | ref = | url = https://kuscholarworks.ku.edu/bitstream/1808/21823/1/AdamsG_2015.pdf }}</ref><ref name="Bhatia2010">{{Cite journal | last = Bhatia | first = S. | title = Theorizing indigenous psychology | journal = Theory & Psychology | volume = 20 | pages = 137–140 | doi = 10.1177/0959354309345640| jstor = | date = 2010 | ref = }}</ref> by applying a context-sensitive [[cultural psychology]] lens to reconsider, de-naturalize, and de-universalize psychological science.<ref name="Transnational Psych">{{Cite book|last1=Collins |first1= L. H. |last2= Machizawa |first2= S. |last3=Rice |first3=K. |isbn=1-4338-3124-4|url=https://www.apa.org/pubs/books/Transnational-Psychology-of-Women-Sample-Chapter.pdf |chapter= Introduction |title=Transnational psychology of women : expanding international and intersectional approaches |publisher= American Psychological Association |location=Washington, DC|oclc=1090706835}}</ref> Transnational psychologists consider perspectives of people in the non-Western, "[[Majority World]]" (areas where the majority of the world's population lives) essential in revising traditional psychological science. Transnational psychology is also concerned with how globalization and [[capitalism]] affect people across [[nations]], [[Race (human categorization)|races]], [[genders]], [[Social class|classes]], and [[sexualities]]. The transnational academic paradigm draws from [[postcolonialism|postcolonial]] theory and methods, which critically examine how colonialist legacies shape the social, economic, and [[Political repression|political oppression]] of people across the globe. It rejects the idea that people from different regions have the same [[subjectivities]] and recognizes that global [[capitalism]] has contributed to exploitation and inequality.<ref name="Transnational Psych" /><ref name ="Practice2015">{{cite book |last1=Machizawa |first1= S. |last2= Enns |first2= C. |year= 2015 |chapter= Transnational psychological practice with women: Perspectives from East Asia and Japan |editor1-last= Enns |editor1-first= C. |editor2-last= Rice |editor2-first= J. |editor3-last= Nutt |editor3-first= R. |title= Psychological practice with women: Guidelines, diversity, empowerment | series= APA Division 35 Psychology of Women Book Series|language= English |location= Washington, DC |publisher= American Psychological Association |publication-date= 2015|pages= 225–256 |isbn=978-1433818127}}</ref><ref name ="TeachingMenaQuina">{{cite book |last=Collins |first1= L. H. |year= 2019 |chapter= Teaching cultural and transnational psychology: Taking intersectionality across the globe. |editor1-last= Mena |editor1-first= J. |editor2-last= Quina |editor2-first= K. |title= Integrating multiculturalism and intersectionality into the psychology curriculum: Strategies for instructors |language= English |location= Washington, DC |publisher= American Psychological Association |publication-date= 2015|pages= 181–196 |isbn=978-1433830075}}</ref> |
|||
=== Unscientific mental health training === |
=== Unscientific mental health training === |
||
Revision as of 18:10, 7 December 2020
| Part of a series on |
| Psychology |
|---|
Psychology is the science of mind and behavior. Psychology includes the study of conscious and unconscious phenomena, as well as feeling and thought. It is an academic discipline of immense scope. Psychologists seek an understanding of the emergent properties of brains, and all the variety of phenomena linked to those emergent properties, joining this way the broader neuro-scientific group of researchers. As a social science, it aims to understand individuals and groups by establishing general principles and researching specific cases.[1][2]
In this field, a professional practitioner or researcher is called a psychologist and can be classified as a social, behavioral, or cognitive scientist. Psychologists attempt to understand the role of mental functions in individual and social behavior, while also exploring the physiological and biological processes that underlie cognitive functions and behaviors.
Psychologists explore behavior and mental processes, including perception, cognition, attention, emotion, intelligence, subjective experiences, motivation, brain functioning, and personality. This extends to interaction between people, such as interpersonal relationships, including psychological resilience, family resilience, and other areas. Psychologists of diverse orientations also consider the unconscious mind.[3] Psychologists employ empirical methods to infer causal and correlational relationships between psychosocial variables. In addition, or in opposition, to employing empirical and deductive methods, some—especially clinical and counseling psychologists—at times rely upon symbolic interpretation and other inductive techniques. Psychology has been described as a "hub science" in that medicine tends to draw psychological research via neurology and psychiatry, whereas social sciences most commonly draws directly from sub-disciplines within psychology.[4]
While psychological knowledge is often applied to the assessment and treatment of mental health problems, it is also directed towards understanding and solving problems in several spheres of human activity. By many accounts, psychology ultimately aims to benefit society.[5][6] The majority of psychologists are involved in some kind of therapeutic role, practicing in clinical, counseling, or school settings. Many do scientific research on a wide range of topics related to mental processes and behavior, and typically work in university psychology departments or teach in other academic settings (e.g., medical schools, hospitals). Some are employed in industrial and organizational settings, or in other areas[7] such as human development and aging, sports, health, and the media, as well as in forensic investigation and other aspects of law.
Etymology and definitions
The word psychology derives from Greek roots meaning study of the psyche, or soul (ψυχή psychē, "breath, spirit, soul" and -λογία -logia, "study of" or "research").[8] The Latin word psychologia was first used by the Croatian humanist and Latinist Marko Marulić in his book, Psichiologia de ratione animae humanae in the late 15th century or early 16th century.[9] The earliest known reference to the word psychology in English was by Steven Blankaart in 1694 in The Physical Dictionary which refers to "Anatomy, which treats the Body, and Psychology, which treats of the Soul."[10]
In 1890, William James defined psychology as "the science of mental life, both of its phenomena and their conditions". This definition enjoyed widespread currency for decades. However, this meaning was contested, notably by radical behaviorists such as John B. Watson, who in his 1913 manifesto defined the discipline of psychology as the acquisition of information useful to the control of behavior. Also since James defined it, the term more strongly connotes techniques of scientific experimentation.[11][12] Folk psychology refers to the understanding of ordinary people, as contrasted with that of psychology professionals.[13]
History
The ancient civilizations of Egypt, Greece, China, India, and Persia all engaged in the philosophical study of psychology. In Ancient Egypt the Ebers Papyrus mentioned depression and thought disorders.[14] Historians note that Greek philosophers, including Thales, Plato, and Aristotle (especially in his De Anima treatise),[15] addressed the workings of the mind.[16] As early as the 4th century BC, Greek physician Hippocrates theorized that mental disorders had physical rather than supernatural causes.[17]
In China, psychological understanding grew from the philosophical works of Laozi and Confucius, and later from the doctrines of Buddhism. This body of knowledge involves insights drawn from introspection and observation, as well as techniques for focused thinking and acting. It frames the universe as a division of, and interaction between, physical reality and mental reality, with an emphasis on purifying the mind in order to increase virtue and power. An ancient text known as The Yellow Emperor's Classic of Internal Medicine identifies the brain as the nexus of wisdom and sensation, includes theories of personality based on yin–yang balance, and analyzes mental disorder in terms of physiological and social disequilibria. Chinese scholarship focused on the brain advanced in the Qing Dynasty with the work of Western-educated Fang Yizhi (1611–1671), Liu Zhi (1660–1730), and Wang Qingren (1768–1831). Wang Qingren emphasized the importance of the brain as the center of the nervous system, linked mental disorder with brain diseases, investigated the causes of dreams and insomnia, and advanced a theory of hemispheric lateralization in brain function.[18]
Distinctions in types of awareness appear in the ancient thought of India, influenced by Hinduism. A central idea of the Upanishads is the distinction between a person's transient mundane self and their eternal unchanging soul. Divergent Hindu doctrines, and Buddhism, have challenged this hierarchy of selves, but have all emphasized the importance of reaching higher awareness. Yoga is a range of techniques used in pursuit of this goal. Much of the Sanskrit corpus was suppressed under the British East India Company followed by the British Raj in the 1800s. However, Indian doctrines influenced Western thinking via the Theosophical Society, a New Age group which became popular among Euro-American intellectuals.[19]
Psychology was a popular topic in Enlightenment Europe. In Germany, Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz (1646–1716) applied his principles of calculus to the mind, arguing that mental activity took place on an indivisible continuum—most notably, that among an infinity of human perceptions and desires, the difference between conscious and unconscious awareness is only a matter of degree. Christian Wolff identified psychology as its own science, writing Psychologia empirica in 1732 and Psychologia rationalis in 1734. This notion advanced further under Immanuel Kant, who established the idea of anthropology, with psychology as an important subdivision. However, Kant explicitly and notoriously rejected the idea of experimental psychology, writing that "the empirical doctrine of the soul can also never approach chemistry even as a systematic art of analysis or experimental doctrine, for in it the manifold of inner observation can be separated only by mere division in thought, and cannot then be held separate and recombined at will (but still less does another thinking subject suffer himself to be experimented upon to suit our purpose), and even observation by itself already changes and displaces the state of the observed object." In 1783, Ferdinand Ueberwasser (1752-1812) designated himself Professor of Empirical Psychology and Logic and gave lectures on scientific psychology, though these developments were soon overshadowed by the Napoleonic Wars, after which the Old University of Münster was discontinued by Prussian authorities.[20] Having consulted philosophers Hegel and Herbart, however, in 1825 the Prussian state established psychology as a mandatory discipline in its rapidly expanding and highly influential educational system. However, this discipline did not yet embrace experimentation.[21] In England, early psychology involved phrenology and the response to social problems including alcoholism, violence, and the country's well-populated mental asylums.[22]
Beginning of experimental psychology

Gustav Fechner began conducting psychophysics research in Leipzig in the 1830s, articulating the principle (Weber–Fechner law) that human perception of a stimulus varies logarithmically according to its intensity.[23] Fechner's 1860 Elements of Psychophysics challenged Kant's stricture against quantitative study of the mind.[24][21] In Heidelberg, Hermann von Helmholtz conducted parallel research on sensory perception, and trained physiologist Wilhelm Wundt. Wundt, in turn, came to Leipzig University, establishing the psychological laboratory which brought experimental psychology to the world. Wundt focused on breaking down mental processes into the most basic components, motivated in part by an analogy to recent advances in chemistry, and its successful investigation of the elements and structure of material.[25] Paul Flechsig and Emil Kraepelin soon created another influential psychology laboratory at Leipzig, this one focused on more on experimental psychiatry.[21]
Psychologists in Germany, Denmark, Austria, England, and the United States soon followed Wundt in setting up laboratories.[26] G. Stanley Hall who studied with Wundt, formed a psychology lab at Johns Hopkins University in Maryland, which became internationally influential. Hall, in turn, trained Yujiro Motora, who brought experimental psychology, emphasizing psychophysics, to the Imperial University of Tokyo.[27] Wundt's assistant, Hugo Münsterberg, taught psychology at Harvard to students such as Narendra Nath Sen Gupta—who, in 1905, founded a psychology department and laboratory at the University of Calcutta.[19] Wundt students Walter Dill Scott, Lightner Witmer, and James McKeen Cattell worked on developing tests for mental ability. Catell, who also studied with eugenicist Francis Galton, went on to found the Psychological Corporation. Wittmer focused on mental testing of children; Scott, on selection of employees.[28]
Another student of Wundt, Edward Titchener, created the psychology program at Cornell University and advanced a doctrine of "structuralist" psychology. Structuralism sought to analyze and classify different aspects of the mind, primarily through the method of introspection.[29] William James, John Dewey and Harvey Carr advanced a more expansive doctrine called functionalism, attuned more to human–environment actions. In 1890, James wrote an influential book, The Principles of Psychology, which expanded on the realm of structuralism, memorably described the human "stream of consciousness", and interested many American students in the emerging discipline.[29][30][31] Dewey integrated psychology with social issues, most notably by promoting the cause progressive education to assimilate immigrants and inculcate moral values in children.[32]

A different strain of experimentalism, with more connection to physiology, emerged in South America, under the leadership of Horacio G. Piñero at the University of Buenos Aires.[33] Russia, too, placed greater emphasis on the biological basis for psychology, beginning with Ivan Sechenov's 1873 essay, "Who Is to Develop Psychology and How?" Sechenov advanced the idea of brain reflexes and aggressively promoted a deterministic viewpoint on human behavior.[34]
Wolfgang Kohler, Max Wertheimer and Kurt Koffka co-founded the school of Gestalt psychology (not to be confused with the Gestalt therapy of Fritz Perls). This approach is based upon the idea that individuals experience things as unified wholes. Rather than breaking down thoughts and behavior into smaller elements, as in structuralism, the Gestaltists maintained that whole of experience is important, and differs from the sum of its parts. Other 19th-century contributors to the field include the German psychologist Hermann Ebbinghaus, a pioneer in the experimental study of memory, who developed quantitative models of learning and forgetting at the University of Berlin,[35] and the Russian-Soviet physiologist Ivan Pavlov, who discovered in dogs a learning process that was later termed "classical conditioning" and applied to human beings.[36]
Consolidation and funding
One of the earliest psychology societies was La Société de Psychologie Physiologique in France, which lasted 1885–1893. The first meeting of the International Congress of Psychology sponsored by the International Union of Psychological Science took place in Paris, in August 1889, amidst the World's Fair celebrating the centennial of the French Revolution. William James was one of three Americans among the four hundred attendees. The American Psychological Association (APA) was founded soon after, in 1892. The International Congress continued to be held, at different locations in Europe, with wider international participation. The Sixth Congress, Geneva 1909, included presentations in Russian, Chinese, and Japanese, as well as Esperanto. After a hiatus for World War I, the Seventh Congress met in Oxford, with substantially greater participation from the war-victorious Anglo-Americans. In 1929, the Congress took place at Yale University in New Haven, Connecticut, attended by hundreds of members of the APA.[26] Tokyo Imperial University led the way in bringing new psychology to the East, and from Japan these ideas diffused into China.[18][27]
American psychology gained status during World War I, during which a standing committee headed by Robert Yerkes administered mental tests ("Army Alpha" and "Army Beta") to almost 1.8 million soldiers.[37] Subsequent funding for behavioral research came in large part from the Rockefeller family, via the Social Science Research Council.[38][39] Rockefeller charities funded the National Committee on Mental Hygiene, which promoted the concept of mental illness and lobbied for psychological supervision of child development.[37][40] Through the Bureau of Social Hygiene and later funding of Alfred Kinsey, Rockefeller foundations established sex research as a viable discipline in the U.S.[41] Under the influence of the Carnegie-funded Eugenics Record Office, the Draper-funded Pioneer Fund, and other institutions, the eugenics movement also had a significant impact on American psychology; in the 1910s and 1920s, eugenics became a standard topic in psychology classes.[42]
During World War II and the Cold War, the U.S. military and intelligence agencies established themselves as leading funders of psychology—through the armed forces and in the new Office of Strategic Services intelligence agency. University of Michigan psychologist Dorwin Cartwright reported that university researchers began large-scale propaganda research in 1939–1941, and "the last few months of the war saw a social psychologist become chiefly responsible for determining the week-by-week-propaganda policy for the United States Government." Cartwright also wrote that psychologists had significant roles in managing the domestic economy.[43] The Army rolled out its new General Classification Test and engaged in massive studies of troop morale. In the 1950s, the Rockefeller Foundation and Ford Foundation collaborated with the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) to fund research on psychological warfare.[44] In 1965, public controversy called attention to the Army's Project Camelot—the "Manhattan Project" of social science—an effort which enlisted psychologists and anthropologists to analyze foreign countries for strategic purposes.[45][46]
In Germany after World War I, psychology held institutional power through the military, and subsequently expanded along with the rest of the military under the Third Reich.[21] Under the direction of Hermann Göring's cousin Matthias Göring, the Berlin Psychoanalytic Institute was renamed the Göring Institute. Freudian psychoanalysts were expelled and persecuted under the anti-Jewish policies of the Nazi Party, and all psychologists had to distance themselves from Freud and Adler.[47] The Göring Institute was well-financed throughout the war with a mandate to create a "New German Psychotherapy". This psychotherapy aimed to align suitable Germans with the overall goals of the Reich; as described by one physician: "Despite the importance of analysis, spiritual guidance and the active cooperation of the patient represent the best way to overcome individual mental problems and to subordinate them to the requirements of the Volk and the Gemeinschaft." Psychologists were to provide Seelenführung, leadership of the mind, to integrate people into the new vision of a German community.[48] Harald Schultz-Hencke melded psychology with the Nazi theory of biology and racial origins, criticizing psychoanalysis as a study of the weak and deformed.[49] Johannes Heinrich Schultz, a German psychologist recognized for developing the technique of autogenic training, prominently advocated sterilization and euthanasia of men considered genetically undesirable, and devised techniques for facilitating this process.[50] After the war, some new institutions were created and some psychologists were discredited due to Nazi affiliation. Alexander Mitscherlich founded a prominent applied psychoanalysis journal called Psyche and with funding from the Rockefeller Foundation established the first clinical psychosomatic medicine division at Heidelberg University. In 1970, psychology was integrated into the required studies of medical students.[51]
After the Russian Revolution, psychology was heavily promoted by the Bolsheviks as a way to engineer the "New Man" of socialism. Thus, university psychology departments trained large numbers of students, for whom positions were made available at schools, workplaces, cultural institutions, and in the military. An especial focus was pedology, the study of child development, regarding which Lev Vygotsky became a prominent writer.[34] The Bolsheviks also promoted free love and embraced the doctrine of psychoanalysis as an antidote to sexual repression.[52] Although pedology and intelligence testing fell out of favor in 1936, psychology maintained its privileged position as an instrument of the Soviet Union.[34] Stalinist purges took a heavy toll and instilled a climate of fear in the profession, as elsewhere in Soviet society.[53] Following World War II, Jewish psychologists past and present (including Lev Vygotsky, A.R. Luria, and Aron Zalkind) were denounced; Ivan Pavlov (posthumously) and Stalin himself were aggrandized as heroes of Soviet psychology.[54] Soviet academics was speedily liberalized during the Khrushchev Thaw, and cybernetics, linguistics, genetics, and other topics became acceptable again. There emerged a new field called "engineering psychology" which studied mental aspects of complex jobs (such as pilot and cosmonaut). Interdisciplinary studies became popular and scholars such as Georgy Shchedrovitsky developed systems theory approaches to human behavior.[55]
Twentieth-century Chinese psychology originally modeled the U.S., with translations from American authors like William James, the establishment of university psychology departments and journals, and the establishment of groups including the Chinese Association of Psychological Testing (1930) and the Chinese Psychological Society (1937). Chinese psychologists were encouraged to focus on education and language learning, with the aspiration that education would enable modernization and nationalization. John Dewey, who lectured to Chinese audiences in 1918–1920, had a significant influence on this doctrine. Chancellor T'sai Yuan-p'ei introduced him at Peking University as a greater thinker than Confucius. Kuo Zing-yang who received a PhD at the University of California, Berkeley, became President of Zhejiang University and popularized behaviorism.[56] After the Chinese Communist Party gained control of the country, the Stalinist Soviet Union became the leading influence, with Marxism–Leninism the leading social doctrine and Pavlovian conditioning the approved concept of behavior change. Chinese psychologists elaborated on Lenin's model of a "reflective" consciousness, envisioning an "active consciousness" (pinyin: tzu-chueh neng-tung-li) able to transcend material conditions through hard work and ideological struggle. They developed a concept of "recognition" (pinyin: jen-shih) which referred the interface between individual perceptions and the socially accepted worldview (failure to correspond with party doctrine was "incorrect recognition").[57] Psychology education was centralized under the Chinese Academy of Sciences, supervised by the State Council. In 1951, the Academy created a Psychology Research Office, which in 1956 became the Institute of Psychology. Most leading psychologists were educated in the United States, and the first concern of the Academy was re-education of these psychologists in the Soviet doctrines. Child psychology and pedagogy for nationally cohesive education remained a central goal of the discipline.[58]
Disciplinary organization
Institutions
In 1920, Édouard Claparède and Pierre Bovet created a new applied psychology organization called the International Congress of Psychotechnics Applied to Vocational Guidance, later called the International Congress of Psychotechnics and then the International Association of Applied Psychology.[26] The IAAP is considered the oldest international psychology association.[59] Today, at least 65 international groups deal with specialized aspects of psychology.[59] In response to male predominance in the field, female psychologists in the U.S. formed National Council of Women Psychologists in 1941. This organization became the International Council of Women Psychologists after World War II, and the International Council of Psychologists in 1959. Several associations including the Association of Black Psychologists and the Asian American Psychological Association have arisen to promote non-European racial groups in the profession.[59]
The world federation of national psychological societies is the International Union of Psychological Science (IUPsyS), founded in 1951 under the auspices of UNESCO, the United Nations cultural and scientific authority.[26][60] Psychology departments have since proliferated around the world, based primarily on the Euro-American model.[19][60] Since 1966, the Union has published the International Journal of Psychology.[26] IAAP and IUPsyS agreed in 1976 each to hold a congress every four years, on a staggered basis.[59]
The International Union recognizes 66 national psychology associations and at least 15 others exist.[59] The American Psychological Association is the oldest and largest.[59] Its membership has increased from 5,000 in 1945 to 100,000 in the present day.[29] The APA includes 54 divisions, which since 1960 have steadily proliferated to include more specialties. Some of these divisions, such as the Society for the Psychological Study of Social Issues and the American Psychology–Law Society, began as autonomous groups.[59]
The Interamerican Society of Psychology, founded in 1951, aspires to promote psychology and coordinate psychologists across the Western Hemisphere. It holds the Interamerican Congress of Psychology and had 1,000 members in year 2000. The European Federation of Professional Psychology Associations, founded in 1981, represents 30 national associations with a total of 100,000 individual members. At least 30 other international groups organize psychologists in different regions.[59]
In some places, governments legally regulate who can provide psychological services or represent themselves as a "psychologist".[61] The APA defines a psychologist as someone with a doctoral degree in psychology.[62]
Boundaries
Early practitioners of experimental psychology distinguished themselves from parapsychology, which in the late nineteenth century enjoyed great popularity (including the interest of scholars such as William James), and indeed constituted the bulk of what people called "psychology". Parapsychology, hypnotism, and psychism were major topics of the early International Congresses. But students of these fields were eventually ostractized, and more or less banished from the Congress in 1900–1905.[26] Parapsychology persisted for a time at Imperial University, with publications such as Clairvoyance and Thoughtography by Tomokichi Fukurai, but here too it was mostly shunned by 1913.[27]
As a discipline, psychology has long sought to fend off accusations that it is a "soft" science. Philosopher of science Thomas Kuhn's 1962 critique implied psychology overall was in a pre-paradigm state, lacking the agreement on overarching theory found in mature sciences such as chemistry and physics.[63] Because some areas of psychology rely on research methods such as surveys and questionnaires, critics asserted that psychology is not an objective science. Skeptics have suggested that personality, thinking, and emotion, cannot be directly measured and are often inferred from subjective self-reports, which may be problematic. Experimental psychologists have devised a variety of ways to indirectly measure these elusive phenomenological entities.[64][65][66]
Divisions still exist within the field, with some psychologists more oriented towards the unique experiences of individual humans, which cannot be understood only as data points within a larger population. Critics inside and outside the field have argued that mainstream psychology has become increasingly dominated by a "cult of empiricism" which limits the scope of its study by using only methods derived from the physical sciences.[67] Feminist critiques along these lines have argued that claims to scientific objectivity obscure the values and agenda of (historically mostly male)[37] researchers. Jean Grimshaw, for example, argues that mainstream psychological research has advanced a patriarchal agenda through its efforts to control behavior.[68]
Major schools of thought
Biological

Psychologists generally consider the organism the basis of the mind, and therefore a vitally related area of study. Psychiatrists and neuropsychologists work at the interface of mind and body.[69] Biological psychology, also known as physiological psychology,[70] or neuropsychology is the study of the biological substrates of behavior and mental processes. Key research topics in this field include comparative psychology, which studies humans in relation to other animals, and perception which involves the physical mechanics of sensation as well as neural and mental processing.[71] For centuries, a leading question in biological psychology has been whether and how mental functions might be localized in the brain. From Phineas Gage to H.M. and Clive Wearing, individual people with mental issues traceable to physical damage have inspired new discoveries in this area.[70] Modern neuropsychology could be said to originate in the 1870s, when in France Paul Broca traced production of speech to the left frontal gyrus, thereby also demonstrating hemispheric lateralization of brain function. Soon after, Carl Wernicke identified a related area necessary for the understanding of speech.[72]
The contemporary field of behavioral neuroscience focuses on physical causes underpinning behavior. For example, physiological psychologists use animal models, typically rats, to study the neural, genetic, and cellular mechanisms that underlie specific behaviors such as learning and memory and fear responses.[73] Cognitive neuroscientists investigate the neural correlates of psychological processes in humans using neural imaging tools, and neuropsychologists conduct psychological assessments to determine, for instance, specific aspects and extent of cognitive deficit caused by brain damage or disease. The biopsychosocial model is an integrated perspective toward understanding consciousness, behavior, and social interaction. It assumes that any given behavior or mental process affects and is affected by dynamically interrelated biological, psychological, and social factors.[74]
Evolutionary psychology examines cognition and personality traits from an evolutionary perspective. This perspective suggests that psychological adaptations evolved to solve recurrent problems in human ancestral environments. Evolutionary psychology offers complementary explanations for the mostly proximate or developmental explanations developed by other areas of psychology: that is, it focuses mostly on ultimate or "why?" questions, rather than proximate or "how?" questions. "How?" questions are more directly tackled by behavioral genetics research, which aims to understand how genes and environment impact behavior.[75]
The search for biological origins of psychological phenomena has long involved debates about the importance of race, and especially the relationship between race and intelligence. The idea of white supremacy and indeed the modern concept of race itself arose during the process of world conquest by Europeans.[76] Carl von Linnaeus's four-fold classification of humans classifies Europeans as intelligent and severe, Americans as contented and free, Asians as ritualistic, and Africans as lazy and capricious. Race was also used to justify the construction of socially specific mental disorders such as drapetomania and dysaesthesia aethiopica—the behavior of uncooperative African slaves.[77] After the creation of experimental psychology, "ethnical psychology" emerged as a subdiscipline, based on the assumption that studying primitive races would provide an important link between animal behavior and the psychology of more evolved humans.[78]
Behavioral

Psychologists take human behavior as a main area of study. Much of the research in this area began with tests on mammals, based on the idea that humans exhibit similar fundamental tendencies. Behavioral research ever aspires to improve the effectiveness of techniques for behavior modification.
Early behavioral researchers studied stimulus–response pairings, now known as classical conditioning. They demonstrated that behaviors could be linked through repeated association with stimuli eliciting pain or pleasure. Ivan Pavlov—known best for inducing dogs to salivate in the presence of a stimulus previously linked with food—became a leading figure in the Soviet Union and inspired followers to use his methods on humans.[34] In the United States, Edward Lee Thorndike initiated "connectionism" studies by trapping animals in "puzzle boxes" and rewarding them for escaping. Thorndike wrote in 1911: "There can be no moral warrant for studying man's nature unless the study will enable us to control his acts."[79] From 1910–1913 the American Psychological Association went through a sea change of opinion, away from mentalism and towards "behavioralism", and in 1913 John B. Watson coined the term behaviorism for this school of thought.[80] Watson's famous Little Albert experiment in 1920 demonstrated that repeated use of upsetting loud noises could instill phobias (aversions to other stimuli) in an infant human.[12][81] Karl Lashley, a close collaborator with Watson, examined biological manifestations of learning in the brain.[70]
Embraced and extended by Clark L. Hull, Edwin Guthrie, and others, behaviorism became a widely used research paradigm.[29] A new method of "instrumental" or "operant" conditioning added the concepts of reinforcement and punishment to the model of behavior change. Radical behaviorists avoided discussing the inner workings of the mind, especially the unconscious mind, which they considered impossible to assess scientifically.[82] Operant conditioning was first described by Miller and Kanorski and popularized in the U.S. by B.F. Skinner, who emerged as a leading intellectual of the behaviorist movement.[83][84]
Noam Chomsky delivered an influential critique of radical behaviorism on the grounds that it could not adequately explain the complex mental process of language acquisition.[85][86][87] Martin Seligman and colleagues discovered that the conditioning of dogs led to outcomes ("learned helplessness") that opposed the predictions of behaviorism.[88][89] Skinner's behaviorism did not die, perhaps in part because it generated successful practical applications.[85] Edward C. Tolman advanced a hybrid "cognitive behavioral" model, most notably with his 1948 publication discussing the cognitive maps used by rats to guess at the location of food at the end of a modified maze.[90]
The Association for Behavior Analysis International was founded in 1974 and by 2003 had members from 42 countries. The field has been especially influential in Latin America, where it has a regional organization known as ALAMOC: La Asociación Latinoamericana de Análisis y Modificación del Comportamiento. Behaviorism also gained a strong foothold in Japan, where it gave rise to the Japanese Society of Animal Psychology (1933), the Japanese Association of Special Education (1963), the Japanese Society of Biofeedback Research (1973), the Japanese Association for Behavior Therapy (1976), the Japanese Association for Behavior Analysis (1979), and the Japanese Association for Behavioral Science Research (1994).[91] Today the field of behaviorism is also commonly referred to as behavior modification or behavior analysis.[91]
Cognitive
Green Red Blue
Purple Blue Purple
Blue Purple Red
Green Purple Green
The Stroop effect refers to the fact that naming the color of the first set of words is easier and quicker than the second.
Cognitive psychology studies cognition, the mental processes underlying mental activity. Perception, attention, reasoning, thinking, problem solving, memory, learning, language, and emotion are areas of research. Classical cognitive psychology is associated with a school of thought known as cognitivism, whose adherents argue for an information processing model of mental function, informed by functionalism and experimental psychology.

Starting in the 1950s, the experimental techniques developed by Wundt, James, Ebbinghaus, and others re-emerged as experimental psychology became increasingly cognitivist—concerned with information and its processing—and, eventually, constituted a part of the wider cognitive science.[92] Some called this development the cognitive revolution because it rejected the anti-mentalist dogma of behaviorism as well as the strictures of psychoanalysis.[92]
Social learning theorists, such as Albert Bandura, argued that the child's environment could make contributions of its own to the behaviors of an observant subject.[93]

Technological advances also renewed interest in mental states and representations. English neuroscientist Charles Sherrington and Canadian psychologist Donald O. Hebb used experimental methods to link psychological phenomena with the structure and function of the brain. The rise of computer science, cybernetics and artificial intelligence suggested the value of comparatively studying information processing in humans and machines. Research in cognition had proven practical since World War II, when it aided in the understanding of weapons operation.[94]
A popular and representative topic in this area is cognitive bias, or irrational thought. Psychologists (and economists) have classified and described a sizeable catalogue of biases which recur frequently in human thought. The availability heuristic, for example, is the tendency to overestimate the importance of something which happens to come readily to mind.[95]
Elements of behaviorism and cognitive psychology were synthesized to form cognitive behavioral therapy, a form of psychotherapy modified from techniques developed by American psychologist Albert Ellis and American psychiatrist Aaron T. Beck.
On a broader level, cognitive science is an interdisciplinary enterprise of cognitive psychologists, cognitive neuroscientists, researchers in artificial intelligence, linguists, human–computer interaction, computational neuroscience, logicians and social scientists. The discipline of cognitive science covers cognitive psychology as well as philosophy of mind, computer science, and neuroscience.[citation needed] Computer simulations are sometimes used to model phenomena of interest.
Social

Social psychology is the study of how humans think about each other and how they relate to each other. Social psychologists study such topics as the influence of others on an individual's behavior (e.g. conformity, persuasion), and the formation of beliefs, attitudes, and stereotypes about other people. Social cognition fuses elements of social and cognitive psychology in order to understand how people process, remember, or distort social information. The study of group dynamics reveals information about the nature and potential optimization of leadership, communication, and other phenomena that emerge at least at the microsocial level. In recent years, many social psychologists have become increasingly interested in implicit measures, mediational models, and the interaction of both person and social variables in accounting for behavior. The study of human society is therefore a potentially valuable source of information about the causes of psychiatric disorder. Some sociological concepts applied to psychiatric disorders are the social role, sick role, social class, life event, culture, migration, social, and total institution.[96]
Psychoanalysis

Psychoanalysis comprises a method of investigating the mind and interpreting experience; a systematized set of theories about human behavior; and a form of psychotherapy to treat psychological or emotional distress, especially conflict originating in the unconscious mind.[97] This school of thought originated in the 1890s with Austrian medical doctors including Josef Breuer (physician), Alfred Adler (physician), Otto Rank (psychoanalyst), and most prominently Sigmund Freud (neurologist). Freud's psychoanalytic theory was largely based on interpretive methods, introspection and clinical observations. It became very well known, largely because it tackled subjects such as sexuality, repression, and the unconscious. These subjects were largely taboo at the time, and Freud provided a catalyst for their open discussion in polite society.[52] Clinically, Freud helped to pioneer the method of free association and a therapeutic interest in dream interpretation.[98][99]
Swiss psychiatrist Carl Jung, influenced by Freud, elaborated a theory of the collective unconscious—a primordial force present in all humans, featuring archetypes which exerted a profound influence on the mind. Jung's competing vision formed the basis for analytical psychology, which later led to the archetypal and process-oriented schools. Other well-known psychoanalytic scholars of the mid-20th century include Erik Erikson, Melanie Klein, D.W. Winnicott, Karen Horney, Erich Fromm, John Bowlby, and Sigmund Freud's daughter, Anna Freud. Throughout the 20th century, psychoanalysis evolved into diverse schools of thought which could be called Neo-Freudian. Among these schools are ego psychology, object relations, and interpersonal, Lacanian, and relational psychoanalysis.[citation needed]
Psychologists such as Hans Eysenck and philosophers including Karl Popper criticized psychoanalysis. Popper argued that psychoanalysis had been misrepresented as a scientific discipline,[100] whereas Eysenck said that psychoanalytic tenets had been contradicted by experimental data. By the end of 20th century, psychology departments in American universities mostly marginalized Freudian theory, dismissing it as a "desiccated and dead" historical artifact.[101] However, researchers in the emerging field of neuro-psychoanalysis today defend some of Freud's ideas on scientific grounds,[102] while scholars of the humanities maintain that Freud was not a "scientist at all, but ... an interpreter".[101]
Existential-humanistic theories
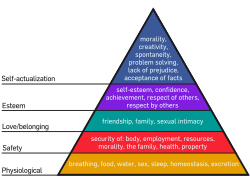
Humanistic psychology developed in the 1950s as a movement within academic psychology, in reaction to both behaviorism and psychoanalysis.[104] The humanistic approach sought to glimpse the whole person, not just fragmented parts of the personality or isolated cognitions.[105] Humanism focused on uniquely human issues, such as free will, personal growth, self-actualization, self-identity, death, aloneness, freedom, and meaning. It emphasized subjective meaning, rejection of determinism, and concern for positive growth rather than pathology.[citation needed] Some founders of the humanistic school of thought were American psychologists Abraham Maslow, who formulated a hierarchy of human needs, and Carl Rogers, who created and developed client-centered therapy. Later, positive psychology opened up humanistic themes to scientific modes of exploration.
The American Association for Humanistic Psychology, formed in 1963, declared:
Humanistic psychology is primarily an orientation toward the whole of psychology rather than a distinct area or school. It stands for respect for the worth of persons, respect for differences of approach, open-mindedness as to acceptable methods, and interest in exploration of new aspects of human behavior. As a "third force" in contemporary psychology, it is concerned with topics having little place in existing theories and systems: e.g., love, creativity, self, growth, organism, basic need-gratification, self-actualization, higher values, being, becoming, spontaneity, play, humor, affection, naturalness, warmth, ego-transcendence, objectivity, autonomy, responsibility, meaning, fair-play, transcendental experience, peak experience, courage, and related concepts.[106]
In the 1950s and 1960s, influenced by philosophers Søren Kierkegaard and Martin Heidegger and, psychoanalytically trained American psychologist Rollo May pioneered an existential branch of psychology, which included existential psychotherapy: a method based on the belief that inner conflict within a person is due to that individual's confrontation with the givens of existence. Swiss psychoanalyst Ludwig Binswanger and American psychologist George Kelly may also be said to belong to the existential school.[107] Existential psychologists differed from more "humanistic" psychologists in their relatively neutral view of human nature and their relatively positive assessment of anxiety.[108] Existential psychologists emphasized the humanistic themes of death, free will, and meaning, suggesting that meaning can be shaped by myths, or narrative patterns,[109] and that it can be encouraged by an acceptance of the free will requisite to an authentic, albeit often anxious, regard for death and other future prospects.
Austrian existential psychiatrist and Holocaust survivor Viktor Frankl drew evidence of meaning's therapeutic power from reflections garnered from his own internment.[110] He created a variation of existential psychotherapy called logotherapy, a type of existentialist analysis that focuses on a will to meaning (in one's life), as opposed to Adler's Nietzschean doctrine of will to power or Freud's will to pleasure.[111]
Themes
Personality
Personality psychology is concerned with enduring patterns of behavior, thought, and emotion—commonly referred to as personality—in individuals. Theories of personality vary across different psychological schools and orientations. They carry different assumptions about such issues as the role of the unconscious and the importance of childhood experience. According to Freud, personality is based on the dynamic interactions of the id, ego, and super-ego.[112] In order to develop a taxonomy of personality constructs, trait theorists, in contrast, attempt to describe the personality sphere in terms of a discrete number of key traits using the statistical data-reduction method of factor analysis. Although the number of proposed traits has varied widely, an early biologically-based model proposed by Hans Eysenck, the 3rd mostly highly cited psychologist of the 20th Century (after Freud, and Piaget respectively), suggested that at least three major trait constructs are necessary to describe human personality structure: extraversion–introversion, neuroticism-stability, and psychoticism-normality. Raymond Cattell, the 7th most highly cited psychologist of the 20th Century (based on the scientific peer-reviewed journal literature)[113] empirically derived a theory of 16 personality factors at the primary-factor level, and up to 8 broader second-stratum factors (at the Eysenckian level of analysis), rather than the "Big Five" dimensions.[114][115][116][117] Dimensional models of personality are receiving increasing support, and a version of dimensional assessment has been included in the DSM-V. However, despite a plethora of research into the various versions of the "Big Five" personality dimensions, it appears necessary to move on from static conceptualizations of personality structure to a more dynamic orientation, whereby it is acknowledged that personality constructs are subject to learning and change across the lifespan.[118][119]
An early example of personality assessment was the Woodworth Personal Data Sheet, constructed during World War I. The popular, although psychometrically inadequate Myers–Briggs Type Indicator[120] sought to assess individuals' "personality types" according to the personality theories of Carl Jung. Behaviorist resistance to introspection led to the development of the Strong Vocational Interest Blank and Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory (MMPI), in an attempt to ask empirical questions that focused less on the psychodynamics of the respondent.[121] However, the MMPI has been subjected to critical scrutiny, given that it adhered to archaic psychiatric nosology, and since it required individuals to provide subjective, introspective responses to the hundreds of items pertaining to psychopathology.[122]
Unconscious mind
Study of the unconscious mind, a part of the psyche outside the awareness of the individual which nevertheless influenced thoughts and behavior was a hallmark of early psychology. In one of the first psychology experiments conducted in the United States, C.S. Peirce and Joseph Jastrow found in 1884 that subjects could choose the minutely heavier of two weights even if consciously uncertain of the difference.[123] Freud popularized this concept, with terms like Freudian slip entering popular culture, to mean an uncensored intrusion of unconscious thought into one's speech and action. His 1901 text The Psychopathology of Everyday Life catalogues hundreds of everyday events which Freud explains in terms of unconscious influence. Pierre Janet advanced the idea of a subconscious mind, which could contain autonomous mental elements unavailable to the scrutiny of the subject.[124]
Behaviorism notwithstanding, the unconscious mind has maintained its importance in psychology. Cognitive psychologists have used a "filter" model of attention, according to which much information processing takes place below the threshold of consciousness, and only certain processes, limited by nature and by simultaneous quantity, make their way through the filter. Copious research has shown that subconscious priming of certain ideas can covertly influence thoughts and behavior.[124] A significant hurdle in this research is proving that a subject's conscious mind has not grasped a certain stimulus, due to the unreliability of self-reporting. For this reason, some psychologists prefer to distinguish between implicit and explicit memory. In another approach, one can also describe a subliminal stimulus as meeting an objective but not a subjective threshold.[125]
The automaticity model, which became widespread following exposition by John Bargh and others in the 1980s, describes sophisticated processes for executing goals which can be selected and performed over an extended duration without conscious awareness.[126][127] Some experimental data suggests that the brain begins to consider taking actions before the mind becomes aware of them.[125][128] This influence of unconscious forces on people's choices naturally bears on philosophical questions free will. John Bargh, Daniel Wegner, and Ellen Langer are some prominent contemporary psychologists who describe free will as an illusion.[126][127][129]
Motivation
Psychologists such as William James initially used the term motivation to refer to intention, in a sense similar to the concept of will in European philosophy. With the steady rise of Darwinian and Freudian thinking, instinct also came to be seen as a primary source of motivation.[130] According to drive theory, the forces of instinct combine into a single source of energy which exerts a constant influence. Psychoanalysis, like biology, regarded these forces as physical demands made by the organism on the nervous system. However, they believed that these forces, especially the sexual instincts, could become entangled and transmuted within the psyche. Classical psychoanalysis conceives of a struggle between the pleasure principle and the reality principle, roughly corresponding to id and ego. Later, in Beyond the Pleasure Principle, Freud introduced the concept of the death drive, a compulsion towards aggression, destruction, and psychic repetition of traumatic events.[131] Meanwhile, behaviorist researchers used simple dichotomous models (pleasure/pain, reward/punishment) and well-established principles such as the idea that a thirsty creature will take pleasure in drinking.[130][132] Clark Hull formalized the latter idea with his drive reduction model.[133]
Hunger, thirst, fear, sexual desire, and thermoregulation all seem to constitute fundamental motivations for animals.[132] Humans also seem to exhibit a more complex set of motivations—though theoretically these could be explained as resulting from primordial instincts—including desires for belonging, self-image, self-consistency, truth, love, and control.[134][135]
Motivation can be modulated or manipulated in many different ways. Researchers have found that eating, for example, depends not only on the organism's fundamental need for homeostasis—an important factor causing the experience of hunger—but also on circadian rhythms, food availability, food palatability, and cost.[132] Abstract motivations are also malleable, as evidenced by such phenomena as goal contagion: the adoption of goals, sometimes unconsciously, based on inferences about the goals of others.[136] Vohs and Baumeister suggest that contrary to the need-desire-fulfilment cycle of animal instincts, human motivations sometimes obey a "getting begets wanting" rule: the more you get a reward such as self-esteem, love, drugs, or money, the more you want it. They suggest that this principle can even apply to food, drink, sex, and sleep.[137]
Development

Mainly focusing on the development of the human mind through the life span, developmental psychology seeks to understand how people come to perceive, understand, and act within the world and how these processes change as they age. This may focus on cognitive, affective, moral, social, or neural development. Researchers who study children use a number of unique research methods to make observations in natural settings or to engage them in experimental tasks. Such tasks often resemble specially designed games and activities that are both enjoyable for the child and scientifically useful, and researchers have even devised clever methods to study the mental processes of infants. In addition to studying children, developmental psychologists also study aging and processes throughout the life span, especially at other times of rapid change (such as adolescence and old age). Developmental psychologists draw on the full range of psychological theories to inform their research.[citation needed]
Genes and environment
All researched psychological traits are influenced by both genes and environment, to varying degrees.[138][139] These two sources of influence are often confounded in observational research of individuals or families. An example is the transmission of depression from a depressed mother to her offspring. Theory may hold that the offspring, by virtue of having a depressed mother in his or her (the offspring's) environment, is at risk for developing depression. However, risk for depression is also influenced to some extent by genes. The mother may both carry genes that contribute to her depression but will also have passed those genes on to her offspring thus increasing the offspring's risk for depression. Genes and environment in this simple transmission model are completely confounded. Experimental and quasi-experimental behavioral genetic research uses genetic methodologies to disentangle this confound and understand the nature and origins of individual differences in behavior.[75] Traditionally this research has been conducted using twin studies and adoption studies, two designs where genetic and environmental influences can be partially un-confounded. More recently, the availability of microarray molecular genetic or genome sequencing technologies allows researchers to measure participant DNA variation directly, and test whether individual genetic variants within genes are associated with psychological traits and psychopathology through methods including genome-wide association studies. One goal of such research is similar to that in positional cloning and its success in Huntington's: once a causal gene is discovered biological research can be conducted to understand how that gene influences the phenotype. One major result of genetic association studies is the general finding that psychological traits and psychopathology, as well as complex medical diseases, are highly polygenic,[140][141][142][143][144] where a large number (on the order of hundreds to thousands) of genetic variants, each of small effect, contribute to individual differences in the behavioral trait or propensity to the disorder. Active research continues to understand the genetic and environmental bases of behavior and their interaction.
Applications
Psychology encompasses many subfields and includes different approaches to the study of mental processes and behavior:
Mental testing
Psychological testing has ancient origins, such as examinations for the Chinese civil service dating back to 2200 BC. Written exams began during the Han dynasty (202 BC – AD 200). By 1370, the Chinese system required a stratified series of tests, involving essay writing and knowledge of diverse topics. The system was ended in 1906.[145] In Europe, mental assessment took a more physiological approach, with theories of physiognomy—judgment of character based on the face—described by Aristotle in 4th century BC Greece. Physiognomy remained current through the Enlightenment, and added the doctrine of phrenology: a study of mind and intelligence based on simple assessment of neuroanatomy.[146]
When experimental psychology came to Britain, Francis Galton was a leading practitioner, and, with his procedures for measuring reaction time and sensation, is considered an inventor of modern mental testing (also known as psychometrics).[147] James McKeen Cattell, a student of Wundt and Galton, brought the concept to the United States, and in fact coined the term "mental test".[148] In 1901, Cattell's student Clark Wissler published discouraging results, suggesting that mental testing of Columbia and Barnard students failed to predict their academic performance.[148] In response to 1904 orders from the Minister of Public Instruction, French psychologists Alfred Binet and Théodore Simon elaborated a new test of intelligence in 1905–1911, using a range of questions diverse in their nature and difficulty. Binet and Simon introduced the concept of mental age and referred to the lowest scorers on their test as idiots. Henry H. Goddard put the Binet-Simon scale to work and introduced classifications of mental level such as imbecile and feebleminded. In 1916 (after Binet's death), Stanford professor Lewis M. Terman modified the Binet-Simon scale (renamed the Stanford–Binet scale) and introduced the intelligence quotient as a score report.[149] From this test, Terman concluded that mental retardation "represents the level of intelligence which is very, very common among Spanish-Indians and Mexican families of the Southwest and also among negroes. Their dullness seems to be racial."[150]
Following the Army Alpha and Army Beta tests for soldiers in World War I, mental testing became popular in the US, where it was soon applied to school children. The federally created National Intelligence Test was administered to 7 million children in the 1920s, and in 1926 the College Entrance Examination Board created the Scholastic Aptitude Test to standardize college admissions.[151] The results of intelligence tests were used to argue for segregated schools and economic functions—i.e. the preferential training of Black Americans for manual labor. These practices were criticized by black intellectuals such a Horace Mann Bond and Allison Davis.[150] Eugenicists used mental testing to justify and organize compulsory sterilization of individuals classified as mentally retarded.[42] In the United States, tens of thousands of men and women were sterilized. Setting a precedent which has never been overturned, the U.S. Supreme Court affirmed the constitutionality of this practice in the 1907 case Buck v. Bell.[152]
Today mental testing is a routine phenomenon for people of all ages in Western societies.[153] Modern testing aspires to criteria including standardization of procedure, consistency of results, output of an interpretable score, statistical norms describing population outcomes, and, ideally, effective prediction of behavior and life outcomes outside of testing situations.[154]
Mental health care
The provision of psychological health services is generally called clinical psychology in the U.S. The definitions of this term are various and may include school psychology and counseling psychology. Practitioners typically includes people who have graduated from doctoral programs in clinical psychology but may also include others. In Canada, the above groups usually fall within the larger category of professional psychology. In Canada and the US, practitioners get bachelor's degrees and doctorates, then spend one year in an internship and one year in postdoctoral education. In Mexico and most other Latin American and European countries, psychologists do not get bachelor's and doctorate degrees; instead, they take a three-year professional course following high school.[62] Clinical psychology is at present the largest specialization within psychology.[155] It includes the study and application of psychology for the purpose of understanding, preventing, and relieving psychologically based distress, dysfunction or mental illness and to promote subjective well-being and personal development. Central to its practice are psychological assessment and psychotherapy although clinical psychologists may also engage in research, teaching, consultation, forensic testimony, and program development and administration.[156]
Credit for the first psychology clinic in the United States typically goes to Lightner Witmer, who established his practice in Philadelphia in 1896. Another modern psychotherapist was Morton Prince.[155] For the most part, in the first part of the twentieth century, most mental health care in the United States was performed by specialized medical doctors called psychiatrists. Psychology entered the field with its refinements of mental testing, which promised to improve diagnosis of mental problems. For their part, some psychiatrists became interested in using psychoanalysis and other forms of psychodynamic psychotherapy to understand and treat the mentally ill.[37] In this type of treatment, a specially trained therapist develops a close relationship with the patient, who discusses wishes, dreams, social relationships, and other aspects of mental life. The therapist seeks to uncover repressed material and to understand why the patient creates defenses against certain thoughts and feelings. An important aspect of the therapeutic relationship is transference, in which deep unconscious feelings in a patient reorient themselves and become manifest in relation to the therapist.[157]
Psychiatric psychotherapy blurred the distinction between psychiatry and psychology, and this trend continued with the rise of community mental health facilities and behavioral therapy, a thoroughly non-psychodynamic model which used behaviorist learning theory to change the actions of patients. A key aspect of behavior therapy is empirical evaluation of the treatment's effectiveness. In the 1970s, cognitive-behavior therapy arose, using similar methods and now including the cognitive constructs which had gained popularity in theoretical psychology. A key practice in behavioral and cognitive-behavioral therapy is exposing patients to things they fear, based on the premise that their responses (fear, panic, anxiety) can be deconditioned.[158]
Mental health care today involves psychologists and social workers in increasing numbers. In 1977, National Institute of Mental Health director Bertram Brown described this shift as a source of "intense competition and role confusion".[37] Graduate programs issuing doctorates in psychology (PhD or PsyD) emerged in the 1950s and underwent rapid increase through the 1980s. This degree is intended to train practitioners who might conduct scientific research.[62]
Some clinical psychologists may focus on the clinical management of patients with brain injury—this area is known as clinical neuropsychology. In many countries, clinical psychology is a regulated mental health profession. The emerging field of disaster psychology (see crisis intervention) involves professionals who respond to large-scale traumatic events.[159]
The work performed by clinical psychologists tends to be influenced by various therapeutic approaches, all of which involve a formal relationship between professional and client (usually an individual, couple, family, or small group). Typically, these approaches encourage new ways of thinking, feeling, or behaving. Four major theoretical perspectives are psychodynamic, cognitive behavioral, existential–humanistic, and systems or family therapy. There has been a growing movement to integrate the various therapeutic approaches, especially with an increased understanding of issues regarding culture, gender, spirituality, and sexual orientation. With the advent of more robust research findings regarding psychotherapy, there is evidence that most of the major therapies have equal effectiveness, with the key common element being a strong therapeutic alliance.[160][161] Because of this, more training programs and psychologists are now adopting an eclectic therapeutic orientation.[162][163][164][165][166]
Diagnosis in clinical psychology usually follows the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM), a handbook first published by the American Psychiatric Association in 1952. New editions over time have increased in size and focused more on medical language.[167] The study of mental illnesses is called abnormal psychology.
Education

Educational psychology is the study of how humans learn in educational settings, the effectiveness of educational interventions, the psychology of teaching, and the social psychology of schools as organizations. The work of child psychologists such as Lev Vygotsky, Jean Piaget, and Jerome Bruner has been influential in creating teaching methods and educational practices. Educational psychology is often included in teacher education programs in places such as North America, Australia, and New Zealand.
School psychology combines principles from educational psychology and clinical psychology to understand and treat students with learning disabilities; to foster the intellectual growth of gifted students; to facilitate prosocial behaviors in adolescents; and otherwise to promote safe, supportive, and effective learning environments. School psychologists are trained in educational and behavioral assessment, intervention, prevention, and consultation, and many have extensive training in research.[168]
Work
Industrialists soon brought the nascent field of psychology to bear on the study of scientific management techniques for improving workplace efficiency. This field was at first called economic psychology or business psychology; later, industrial psychology, employment psychology, or psychotechnology.[169] An important early study examined workers at Western Electric's Hawthorne plant in Cicero, Illinois from 1924–1932. With funding from the Laura Spelman Rockefeller Fund and guidance from Australian psychologist Elton Mayo, Western Electric experimented on thousands of factory workers to assess their responses to illumination, breaks, food, and wages. The researchers came to focus on workers' responses to observation itself, and the term Hawthorne effect is now used to describe the fact that people work harder when they think they're being watched.[170]
The name industrial and organizational psychology (I–O) arose in the 1960s and became enshrined as the Society for Industrial and Organizational Psychology, Division 14 of the American Psychological Association, in 1973.[169] The goal is to optimize human potential in the workplace. Personnel psychology, a subfield of I–O psychology, applies the methods and principles of psychology in selecting and evaluating workers. I–O psychology's other subfield, organizational psychology, examines the effects of work environments and management styles on worker motivation, job satisfaction, and productivity.[171] The majority of I–O psychologists work outside of academia, for private and public organizations and as consultants.[169] A psychology consultant working in business today might expect to provide executives with information and ideas about their industry, their target markets, and the organization of their company.[172][173]
Military and intelligence
One role for psychologists in the military is to evaluate and counsel soldiers and other personnel. In the U.S., this function began during World War I, when Robert Yerkes established the School of Military Psychology at Fort Oglethorpe in Georgia, to provide psychological training for military staff military.[37][174] Today, U.S Army psychology includes psychological screening, clinical psychotherapy, suicide prevention, and treatment for post-traumatic stress, as well as other aspects of health and workplace psychology such as smoking cessation.[175]
Psychologists may also work on a diverse set of campaigns known broadly as psychological warfare. Psychological warfare chiefly involves the use of propaganda to influence enemy soldiers and civilians. In the case of so-called black propaganda the propaganda is designed to seem like it originates from a different source.[176] The CIA's MKULTRA program involved more individualized efforts at mind control, involving techniques such as hypnosis, torture, and covert involuntary administration of LSD.[177] The U.S. military used the name Psychological Operations (PSYOP) until 2010, when these were reclassified as Military Information Support Operations (MISO), part of Information Operations (IO).[178] Psychologists are sometimes involved in assisting the interrogation and torture of suspects, though this has sometimes been denied by those involved and sometimes opposed by others.[179]
Health, well-being, and social change
Medical facilities increasingly employ psychologists to perform various roles. A prominent aspect of health psychology is the psychoeducation of patients: instructing them in how to follow a medical regimen. Health psychologists can also educate doctors and conduct research on patient compliance.[180]
Psychologists in the field of public health use a wide variety of interventions to influence human behavior. These range from public relations campaigns and outreach to governmental laws and policies. Psychologists study the composite influence of all these different tools in an effort to influence whole populations of people.[181]
Black American psychologists Kenneth and Mamie Clark studied the psychological impact of segregation and testified with their findings in the desegregation case Brown v. Board of Education (1954).[182]
Positive psychology is the study of factors which contribute to human happiness and well-being, focusing more on people who are currently healthy. In 2010, Clinical Psychological Review published a special issue devoted to positive psychological interventions, such as gratitude journaling and the physical expression of gratitude. Positive psychological interventions have been limited in scope, but their effects are thought to be superior to that of placebos, especially with regard to helping people with body image problems.
Research methods
Quantitative psychological research lends itself to the statistical testing of hypotheses. Although the field makes abundant use of randomized and controlled experiments in laboratory settings, such research can only assess a limited range of short-term phenomena. Thus, psychologists also rely on creative statistical methods to glean knowledge from clinical trials and population data.[183] These include the Pearson product–moment correlation coefficient, the analysis of variance, multiple linear regression, logistic regression, structural equation modeling, and hierarchical linear modeling. The measurement and operationalization of important constructs is an essential part of these research designs.
Controlled experiments
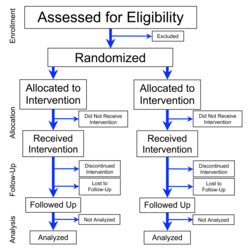
A true experiment with random allocation of subjects to conditions allows researchers to make strong inferences about causal relationships. In an experiment, the researcher alters parameters of influence, called independent variables, and measures resulting changes of interest, called dependent variables. Prototypical experimental research is conducted in a laboratory with a carefully controlled environment.
Repeated-measures experiments are those which take place through intervention on multiple occasions. In research on the effectiveness of psychotherapy, experimenters often compare a given treatment with placebo treatments, or compare different treatments against each other. Treatment type is the independent variable. The dependent variables are outcomes, ideally assessed in several ways by different professionals.[186] Using crossover design, researchers can further increase the strength of their results by testing both of two treatments on two groups of subjects.
Quasi-experimental design refers especially to situations precluding random assignment to different conditions. Researchers can use common sense to consider how much the nonrandom assignment threatens the study's validity.[187] For example, in research on the best way to affect reading achievement in the first three grades of school, school administrators may not permit educational psychologists to randomly assign children to phonics and whole language classrooms, in which case the psychologists must work with preexisting classroom assignments. Psychologists will compare the achievement of children attending phonics and whole language classes.
Experimental researchers typically use a statistical hypothesis testing model which involves making predictions before conducting the experiment, then assessing how well the data supports the predictions. (These predictions may originate from a more abstract scientific hypothesis about how the phenomenon under study actually works.) Analysis of variance (ANOVA) statistical techniques are used to distinguish unique results of the experiment from the null hypothesis that variations result from random fluctuations in data. In psychology, the widely used standard ascribes statistical significance to results which have less than 5% probability of being explained by random variation.[188]
Other forms of statistical inference
Statistical surveys are used in psychology for measuring attitudes and traits, monitoring changes in mood, checking the validity of experimental manipulations, and for other psychological topics. Most commonly, psychologists use paper-and-pencil surveys. However, surveys are also conducted over the phone or through e-mail. Web-based surveys are increasingly used to conveniently reach many subjects.
Neuropsychological tests, such as the Wechsler scales and Wisconsin Card Sorting Test, are mostly questionnaires or simple tasks used which assess a specific type of mental function in the respondent. These can be used in experiments, as in the case of lesion experiments evaluating the results of damage to a specific part of the brain.[189]
Observational studies analyze uncontrolled data in search of correlations; multivariate statistics are typically used to interpret the more complex situation. Cross-sectional observational studies use data from a single point in time, whereas longitudinal studies are used to study trends across the life span. Longitudinal studies track the same people, and therefore detect more individual, rather than cultural, differences. However, they suffer from lack of controls and from confounding factors such as selective attrition (the bias introduced when a certain type of subject disproportionately leaves a study).
Exploratory data analysis refers to a variety of practices which researchers can use to visualize and analyze existing sets of data. In Peirce's three modes of inference, exploratory data analysis corresponds to abduction, or hypothesis formation.[190] Meta-analysis is the technique of integrating the results from multiple studies and interpreting the statistical properties of the pooled dataset.[191]
Technological assays

A classic and popular tool used to relate mental and neural activity is the electroencephalogram (EEG), a technique using amplified electrodes on a person's scalp to measure voltage changes in different parts of the brain. Hans Berger, the first researcher to use EEG on an unopened skull, quickly found that brains exhibit signature "brain waves": electric oscillations which correspond to different states of consciousness. Researchers subsequently refined statistical methods for synthesizing the electrode data, and identified unique brain wave patterns such as the delta wave observed during non-REM sleep.[192]
Newer functional neuroimaging techniques include functional magnetic resonance imaging and positron emission tomography, both of which track the flow of blood through the brain. These technologies provide more localized information about activity in the brain and create representations of the brain with widespread appeal. They also provide insight which avoids the classic problems of subjective self-reporting. It remains challenging to draw hard conclusions about where in the brain specific thoughts originate—or even how usefully such localization corresponds with reality. However, neuroimaging has delivered unmistakable results showing the existence of correlations between mind and brain. Some of these draw on a systemic neural network model rather than a localized function model.[193][194][195]
Psychiatric interventions such as transcranial magnetic stimulation and drugs also provide information about brain–mind interactions. Psychopharmacology is the study of drug-induced mental effects.
Computer simulation
Computational modeling is a tool used in mathematical psychology and cognitive psychology to simulate behavior.[196] This method has several advantages. Since modern computers process information quickly, simulations can be run in a short time, allowing for high statistical power. Modeling also allows psychologists to visualize hypotheses about the functional organization of mental events that couldn't be directly observed in a human. Computational neuroscience uses mathematical models to simulate the brain. Another method is symbolic modeling, which represents many mental objects using variables and rules. Other types of modeling include dynamic systems and stochastic modeling.
Animal studies

Animal experiments aid in investigating many aspects of human psychology, including perception, emotion, learning, memory, and thought, to name a few. In the 1890s, Russian physiologist Ivan Pavlov famously used dogs to demonstrate classical conditioning. Non-human primates, cats, dogs, pigeons, rats, and other rodents are often used in psychological experiments. Ideally, controlled experiments introduce only one independent variable at a time, in order to ascertain its unique effects upon dependent variables. These conditions are approximated best in laboratory settings. In contrast, human environments and genetic backgrounds vary so widely, and depend upon so many factors, that it is difficult to control important variables for human subjects. There are pitfalls in generalizing findings from animal studies to humans through animal models.[197]
Comparative psychology refers to the scientific study of the behavior and mental processes of non-human animals, especially as these relate to the phylogenetic history, adaptive significance, and development of behavior. Research in this area explores the behavior of many species, from insects to primates. It is closely related to other disciplines that study animal behavior such as ethology.[198] Research in comparative psychology sometimes appears to shed light on human behavior, but some attempts to connect the two have been quite controversial, for example the Sociobiology of E.O. Wilson.[199] Animal models are often used to study neural processes related to human behavior, e.g. in cognitive neuroscience.
Qualitative and descriptive research
Research designed to answer questions about the current state of affairs such as the thoughts, feelings, and behaviors of individuals is known as descriptive research. Descriptive research can be qualitative or quantitative in orientation. Qualitative research is descriptive research that is focused on observing and describing events as they occur, with the goal of capturing all of the richness of everyday behavior and with the hope of discovering and understanding phenomena that might have been missed if only more cursory examinations have been made.
Qualitative psychological research methods include interviews, first-hand observation, and participant observation. Creswell (2003) identifies five main possibilities for qualitative research, including narrative, phenomenology, ethnography, case study, and grounded theory. Qualitative researchers[200] sometimes aim to enrich interpretations or critiques of symbols, subjective experiences, or social structures. Sometimes hermeneutic and critical aims can give rise to quantitative research, as in Erich Fromm's study of Nazi voting[citation needed] or Stanley Milgram's studies of obedience to authority.

Just as Jane Goodall studied chimpanzee social and family life by careful observation of chimpanzee behavior in the field, psychologists conduct naturalistic observation of ongoing human social, professional, and family life. Sometimes the participants are aware they are being observed, and other times the participants do not know they are being observed. Strict ethical guidelines must be followed when covert observation is being carried out.
Program Evaluation
Program Evaluation is a systematic method for collecting, analyzing, and using information to answer questions about projects, policies and programs,[202] particularly about their effectiveness and efficiency. In both the public and private sectors, stakeholders often want to know whether the programs they are funding, implementing, voting for, receiving or objecting to are producing the intended effect. While program evaluation first focuses around this definition, important considerations often include how much the program costs per participant, how the program could be improved, whether the program is worthwhile, whether there are better alternatives, if there are unintended outcomes, and whether the program goals are appropriate and useful.[203]
Contemporary issues in methodology and practice
Metascience
The field of metascience has revealed significant problems with the methodology of psychological research. Psychological research suffers from high bias,[204] low reproducibility,[205] and widespread misuse of statistics.[206] These finding have led to calls for reform from within and from outside the scientific community.[207]
Confirmation bias
In 1959, statistician Theodore Sterling examined the results of psychological studies and discovered that 97% of them supported their initial hypotheses, implying a possible publication bias.[208][209][210] Similarly, Fanelli (2010)[211] found that 91.5% of psychiatry/psychology studies confirmed the effects they were looking for, and concluded that the odds of this happening (a positive result) was around five times higher than in fields such as space- or geosciences. Fanelli argues that this is because researchers in "softer" sciences have fewer constraints to their conscious and unconscious biases.
Replication
Over the subsequent few years, a replication crisis in psychology was identified, where it was publicly noted that many notable findings in the field had not been replicated and with some researchers being accused of outright fraud in their results.[212][213][214] More systematic efforts to assess the extent of the problem, such as the Reproducibility Project of the Center for Open Science, found that as many as two-thirds of highly publicized findings in psychology had failed to be replicated,[215] with reproducibility being generally stronger in studies and journals representing cognitive psychology than social psychology topics,[215] and the subfields of differential psychology (including general intelligence and Big Five personality traits research),[216][217] behavioral genetics (except for candidate gene and candidate gene-by-environment interaction research on behavior and mental illness),[218][219] and the related field of behavioral economics being largely unaffected by the replication crisis.[220] Other subfields of psychology that have been implicated by the replication crisis are clinical psychology,[221][222] developmental psychology (particularly cognitive and personality development),[223][224][225] and a field closely related to psychology that has also been implicated is educational research.[226][227][228][229]
Focus on the replication crisis has led to other renewed efforts in the discipline to re-test important findings,[230][231] and in response to concerns about publication bias and p-hacking, more than 140 psychology journals have adopted result-blind peer review where studies are accepted not on the basis of their findings and after the studies are completed, but before the studies are conducted and upon the basis of the methodological rigor of their experimental designs and the theoretical justifications for their statistical analysis techniques before data collection or analysis is done.[232] In addition, large-scale collaborations between researchers working in multiple labs in different countries and that regularly make their data openly available for different researchers to assess have become much more common in the field.[233] Early analysis of such reforms has estimated that 61 percent of result-blind studies have led to null results, in contrast to an estimated 5 to 20 percent in earlier research.[234]
Misuse of statistics
Some critics view statistical hypothesis testing as misplaced. Psychologist and statistician Jacob Cohen wrote in 1994 that psychologists routinely confuse statistical significance with practical importance, enthusiastically reporting great certainty in unimportant facts.[235] Some psychologists have responded with an increased use of effect size statistics, rather than sole reliance on p-values.[citation needed]
WEIRD bias
In 2008, Arnett pointed out that most articles in American Psychological Association journals were about US populations when U.S. citizens are only 5% of the world's population. He complained that psychologists had no basis for assuming psychological processes to be universal and generalizing research findings to the rest of the global population.[236] In 2010, Henrich, Heine, and Norenzayan reported a systemic bias in conducting psychology studies with participants from "WEIRD" (western, educated, industrialized, rich and democratic) societies.[237][238] Although only 1/8 people worldwide live in regions that fall into the WEIRD classification, the researchers claimed that 60–90% of psychology studies are performed on participants from these areas. The article gave examples of results that differ significantly between people from WEIRD and tribal cultures, including the Müller-Lyer illusion. Arnett (2008), Altmaier and Hall (2008), and Morgan-Consoli et al. (2018) saw the Western bias in research and theory as a serious problem considering psychologists are increasingly applying psychological principles developed in WEIRD regions in their research, clinical work, and consultation with populations around the world.[236][239][240] In 2018, Rad, Martingano & Ginges showed that nearly a decade after Henrich et al.'s paper, over 80% of the samples used in studies published in the journal, Psychological Science, were from the WEIRD population. Moreover, their analysis showed that several studies did not fully disclose the origin of their samples, and the authors offer a set of recommendations to editors and reviewers to reduce the WEIRD bias.[241]
From an anthropological perspective, scholars applied the WEIRD model to European history, arguing that a powerful Christian Church forced a radical change away from incest and cousin marriages that undermined the role of clans and created individualism in Europe by 1500 CE. They argue that a distinctive Western psychology thus emerged that valued agency, autonomy, and kindness towards strangers.[242] Historians were not involved in that project, and have since pointed out its historical fallacies regarding an all-powerful Church at too early a point in time, and a rejection of cousin marriage that did not happen.[243]
In order to counter this bias, transnational psychology was developed. As first articulated by Adams, Bhatia, Else-Quest, Grabe, and Kurtis, transnational psychology counters the Western bias in the field of psychology [244][245] by applying a context-sensitive cultural psychology lens to reconsider, de-naturalize, and de-universalize psychological science.[246] Transnational psychologists consider perspectives of people in the non-Western, "Majority World" (areas where the majority of the world's population lives) essential in revising traditional psychological science. Transnational psychology is also concerned with how globalization and capitalism affect people across nations, races, genders, classes, and sexualities. The transnational academic paradigm draws from postcolonial theory and methods, which critically examine how colonialist legacies shape the social, economic, and political oppression of people across the globe. It rejects the idea that people from different regions have the same subjectivities and recognizes that global capitalism has contributed to exploitation and inequality.[246][247][248]
Unscientific mental health training
Some observers perceive a gap between scientific theory and its application—in particular, the application of unsupported or unsound clinical practices.[249] Critics say there has been an increase in the number of mental health training programs that do not instill scientific competence.[250] Practices such as "facilitated communication for infantile autism"; memory-recovery techniques including body work; and other therapies, such as rebirthing and reparenting, may be dubious or even dangerous, despite their popularity.[251] In 1984, Allen Neuringer made a similar point[vague] regarding the experimental analysis of behavior.[252] Psychologists, sometimes divided along the lines of laboratory vs. clinic, continue to debate these issues.[253]
Ethics
Ethical standards in the discipline have changed over time. Some famous past studies are today considered unethical and in violation of established codes (the Canadian Code of Conduct for Research Involving Humans, and the Belmont Report).
The most important contemporary standards are informed and voluntary consent. After World War II, the Nuremberg Code was established because of Nazi abuses of experimental subjects. Later, most countries (and scientific journals) adopted the Declaration of Helsinki. In the U.S., the National Institutes of Health established the Institutional Review Board in 1966, and in 1974 adopted the National Research Act (HR 7724). All of these measures encouraged researchers to obtain informed consent from human participants in experimental studies. A number of influential studies led to the establishment of this rule; such studies included the MIT and Fernald School radioisotope studies, the Thalidomide tragedy, the Willowbrook hepatitis study, and Stanley Milgram's studies of obedience to authority.
Humans
University psychology departments have ethics committees dedicated to the rights and well-being of research subjects. Researchers in psychology must gain approval of their research projects before conducting any experiment to protect the interests of human participants and laboratory animals.[254]
The ethics code of the American Psychological Association originated in 1951 as "Ethical Standards of Psychologists". This code has guided the formation of licensing laws in most American states. It has changed multiple times over the decades since its adoption. In 1989, the APA revised its policies on advertising and referral fees to negotiate the end of an investigation by the Federal Trade Commission. The 1992 incarnation was the first to distinguish between "aspirational" ethical standards and "enforceable" ones. Members of the public have a five-year window to file ethics complaints about APA members with the APA ethics committee; members of the APA have a three-year window.[255]
Some of the ethical issues considered most important are the requirement to practice only within the area of competence, to maintain confidentiality with the patients, and to avoid sexual relations with them. Another important principle is informed consent, the idea that a patient or research subject must understand and freely choose a procedure they are undergoing.[255] Some of the most common complaints against clinical psychologists include sexual misconduct, and involvement in child custody evaluations.[255]
Other animals
Current ethical guidelines state that using non-human animals for scientific purposes is only acceptable when the harm (physical or psychological) done to animals is outweighed by the benefits of the research.[256] Keeping this in mind, psychologists can use certain research techniques on animals that could not be used on humans.
- An experiment by Stanley Milgram raised questions about the ethics of scientific experimentation because of the extreme emotional stress suffered by the participants. It measured the willingness of study participants to obey an authority figure who instructed them to perform acts that conflicted with their personal conscience.[257]
- Comparative psychologist Harry Harlow drew moral condemnation for isolation experiments on rhesus macaque monkeys at the University of Wisconsin–Madison in the 1970s.[258] The aim of the research was to produce an animal model of clinical depression. Harlow also devised what he called a "rape rack", to which the female isolates were tied in normal monkey mating posture.[259] In 1974, American literary critic Wayne C. Booth wrote that, "Harry Harlow and his colleagues go on torturing their nonhuman primates decade after decade, invariably proving what we all knew in advance—that social creatures can be destroyed by destroying their social ties." He writes that Harlow made no mention of the criticism of the morality of his work.[260]
References
- ^ Fernald LD (2008). Psychology: Six perspectives (pp.12–15). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications.
- ^ Hockenbury & Hockenbury. Psychology. Worth Publishers, 2010.
- ^ Although psychoanalysis and other forms of depth psychology are most typically associated with the unconscious mind, behaviorists consider such phenomena as classical conditioning and operant conditioning, while cognitivists explore implicit memory, automaticity, and subliminal messages, all of which are understood either to bypass or to occur outside of conscious effort or attention. Indeed, cognitive-behavioral therapists counsel their clients to become aware of maladaptive thought patterns, the nature of which the clients previously had not been conscious.
- ^ Cacioppo, John (September 2007). "Psychology is a Hub Science". Aps Observer. 20 (8).
psychology is a hub discipline — that is, a discipline in which scientific research is cited by scientists in many other fields. For instance, medicine draws from psychology most heavily through neurology and psychiatry, whereas the social sciences draw directly from most of the specialties within psychology.
Association for Psychological Science Observer (September 2007) - ^ O'Neil, H.F.; cited in Coon, D.; Mitterer, J.O. (2008). Introduction to psychology: Gateways to mind and behavior (12th ed., pp. 15–16). Stamford, CT: Cengage Learning.
- ^ "The mission of the APA [American Psychological Association] is to advance the creation, communication and application of psychological knowledge to benefit society and improve people's lives"; APA (2010). About APA. Retrieved 20 October 2010.
- ^ Bureau of Labor Statistics, U.S. Department of Labor, Occupational Outlook Handbook, 2010–11 Edition, Psychologists, on the Internet at bls.gov (visited 8 July 2010).
- ^ Online Etymology Dictionary. (2001). "Psychology".
- ^ "Classics in the History of Psychology – Marko Marulic – The Author of the Term "Psychology"". Psychclassics.yorku.ca. Retrieved 10 December 2011.
- ^ (Steven Blankaart, p. 13) as quoted in "psychology n." A Dictionary of Psychology. Edited by Andrew M. Colman. Oxford University Press 2009. Oxford Reference Online. Oxford University Press. oxfordreference.com
- ^ Derek Russell Davis (DRD), "psychology", in Richard L. Gregory (ed.), The Oxford Companion to the Mind, second edition; Oxford University Press, 1987/2004; ISBN 978-0-19-866224-2 (pp. 763–764).
- ^ a b Watson, John B. (1913). "Psychology as the Behaviorist Views It" (PDF). Psychological Review. 20 (2): 158–177. doi:10.1037/h0074428. hdl:21.11116/0000-0001-9182-7.
- ^ The term "folk psychology" is itself contentious: see Daniel D. Hutto & Matthew Ratcliffe (eds.), Folk Psychology Re-Assessed; Dorndrecht, the Netherlands: Springer, 2007; ISBN 978-1-4020-5557-7
- ^ Okasha, Ahmed (2005). "Mental Health in Egypt". The Israel Journal of Psychiatry and Related Sciences. 42 (2): 116–25. PMID 16342608.
- ^ "Aristotle's Psychology". Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy.
- ^ Green, C.D. & Groff, P.R. (2003). Early psychological thought: Ancient accounts of mind and soul. Westport, Connecticut: Praeger.
- ^ T.L. Brink. (2008) Psychology: A Student Friendly Approach. "Unit One: The Definition and History of Psychology." pp 9 [1].
- ^ a b Yeh Hsueh and Benyu Guo, "China", in Baker (ed.), Oxford Handbook of the History of Psychology (2012).
- ^ a b c Anand C. Paranjpe, "From Tradition through Colonialism to Globalization: Reflections on the History of Psychology in India", in Brock (ed.), Internationalizing the History of Psychology (2006).
- ^ Schwarz, K. A., & Pfister, R.: Scientific psychology in the 18th century: a historical rediscovery. In: Perspectives on Psychological Science, Nr. 11, p. 399-407.
- ^ a b c d Horst U.K. Gundlach, "Germany", in Baker (ed.), Oxford Handbook of the History of Psychology (2012).
- ^ Alan Collins, "England", in Baker (ed.), Oxford Handbook of the History of Psychology (2012).
- ^ Leahey, History of Modern Psychology (2001), p. 61.
- ^ Fechner, G. T. (1860). Elemente der Psychophysik. Breitkopf u. Härtel. (Elements of Psychophysics)
- ^ Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. (2006). "Wilhelm Maximilian Wundt".
- ^ a b c d e f Ludy T. Benjamin, Jr., and David B. Baker, "The Internationalization of Psychology: A History", in Baker (ed.), Oxford Handbook of the History of Psychology (2012).
- ^ a b c Miki Takasuna, "Japan", in Baker (ed.), Oxford Handbook of the History of Psychology (2012).
- ^ Leahey, History of Modern Psychology (2001), p. 60.
- ^ a b c d C. James Goodwin, "United States", in Baker (ed.), Oxford Handbook of the History of Psychology (2012).
- ^ The Principles of Psychology (1890), with introduction by George A. Miller, Harvard University Press, 1983 paperback, ISBN 0-674-70625-0 (combined edition, 1328 pages)
- ^ Leahey, History of Modern Psychology (2001), pp. 178–182.
- ^ Leahey, History of Modern Psychology (2001), pp. 196–200.
- ^ Cecilia Taiana, "Transatlantic Migration of the Disciplines of Mind: Examination of the Reception of Wundt's and Freud's Theories in Argentina", in Brock (ed.), Internationalizing the History of Psychology (2006).
- ^ a b c d Irina Sirotkina and Roger Smith, "Russian Federation", in Baker (ed.), Oxford Handbook of the History of Psychology (2012).
- ^ Wozniak, R.H. (1999). Introduction to memory: Hermann Ebbinghaus (1885/1913). Classics in the history of psychology
- ^ Windholz, G. (1997). "Ivan P. Pavlov: An overview of his life and psychological work". American Psychologist. 52 (9): 941–946. doi:10.1037/0003-066X.52.9.941.
- ^ a b c d e f Nancy Tomes, "The Development of Clinical Psychology, Social Work, and Psychiatric Nursing: 1900–1980s", in Wallace & Gach (eds.), History of Psychiatry and Medical Psychology (2008).
- ^ Franz Samuelson, "Organizing for the Kingdom of Behavior: Academic Battles and the Organizational Policies in the Twenties"; Journal of the History of the Behavioral Sciences 21, January 1985.
- ^ Hans Pols, "The World as Laboratory: Strategies of Field Research Developed by Mental Hygiene Psychologists in Toronto, 1920–1940" in Theresa Richardson & Donald Fisher (eds.), The Development of the Social Sciences in the United States and Canada: The Role of Philanthropy; Stamford, CT: Ablex Publishing, 1999; ISBN 1-56750-405-1
- ^ Sol Cohen, "The Mental Hygiene Movement, the Development of Personality and the School: The Medicalization of American Education"; History of Education Quarterly 23.2, Summer 1983.
- ^ Vern L. Bullough, "The Rockefellers and Sex Research"; Journal of Sex Research 21.2, May 1985. "Their importance is hard to overestimate. In fact, in the period between 1914 and 1954, the Rockefellers were almost the sole support of sex research in the United States. The decisions made by their scientific advisers about the nature of the research to be supported and how it was conducted, as well as the topics eligible for research support, shaped the whole field of sex research and, in many ways, still continue to support it."
- ^ a b Guthrie, Even the Rat was White (1998), Chapter 4: "Psychology and Race" (pp. 88–110). "Psychology courses often became the vehicles for eugenics propaganda. One graduate of the Record Office training program wrote, 'I hope to serve the cause by infiltrating eugenics into the minds of teachers. It may interest you to know that each student who takes psychology here works up his family history and plots his family tree.' Harvard, Columbia, Brown, Cornell, Wisconsin, and Northwestern were among the leading academic institutions teaching eugenics in psychology courses."
- ^ Dorwin Cartwright, "Social Psychology in the United States During the Second World War", Human Relations 1.3, June 1948, p. 340; quoted in Cina, "Social Science For Whom?" (1981), p. 269.
- ^ Catherine Lutz, "Epistemology of the Bunker: The Brainwashed and Other New Subjects of Permanent War", in Joel Pfister & Nancy Schnog (eds.), Inventing the Psychological: Toward a Cultural History of Emotional Life in America; Yale University Press, 1997; ISBN 0-300-06809-3
- ^ Cina, "Social Science For Whom?" (1981), pp. 315–325.
- ^ Herman, "Psychology as Politics" (1993), p. 288. "Had it come to fruition, CAMELOT would have been the largest, and certainly the most generously funded, behavioral research project in U.S. history. With a $4–6 million contract over a period of 3 years, it was considered, and often called, a veritable Manhattan Project for the behavioral sciences, at least by many of the intellectuals whose services were in heavy demand."
- ^ Cocks, Psychotherapy in the Third Reich (1997), pp. 75–77.
- ^ Cocks, Psychotherapy in the Third Reich (1997), p. 93.
- ^ Cocks, Psychotherapy in the Third Reich (1997), pp. 86–87. "For Schultz-Hencke in this 1934 essay, life goals were determined by ideology, not by science. In the case of psychotherapy, he defined health in terms of blood, strong will, proficiency, discipline, (Zucht und Ordnung), community, heroic bearing, and physical fitness. Schultz-Hencke also took the opportunity in 1934 to criticize psychoanalysis for providing an unfortunate tendency toward the exculpation of the criminal."
- ^ Jürgen Brunner, Matthias Schrempf, & Florian Steger, "Johannes Heinrich Schultz and National Socialism", Israel Journal of Psychiatry & Related Sciences 45.4, 2008. "Bringing these people to a right and deep understanding of every German's duty in the New Germany, such as preparatory mental aid and psychotherapy in general and in particular for persons to be sterilized, and for people having been sterilized, is a great, important and rewarding medical duty."
- ^ Cocks, Psychotherapy in the Third Reich (1997), Chapter 14: "Reconstruction and Repression", pp. 351–375.
- ^ a b Kozulin, Psychology in Utopia (1984), pp. 84–86. "Against such a background it is not at all surprising that psychoanalysis, as a theory that ventured to approach the forbidden but topical theme of sexual relations, was embraced by the newborn Soviet psychology. Psychoanalysis also attracted the interest of Soviet psychology as a materialist trend that had challenged the credentials of classical introspective psychology. The reluctance of the pre-Revolutionary establishment to propagate psychoanalysis also played a positive role in the post-Revolutionary years; it was a field uncompromised by ties to old-regime science." Though c.f. Hannah Proctor, "Reason Displaces All Love", The New Inquiry, 14 February 2014.
- ^ Kozulin, Psychology in Utopia (1984), p. 22. "Stalin's purges of the 1930s did not spare Soviet psychologists. Leading Marxist philosophers earlier associated with psychology—including Yuri Frankfurt, Nikolai Karev, and Ivan Luppol—were executed in prison camps. The same fate awaited Alexei Gastev and Isaak Shipilrein. Those who survived lived in an atmosphere of total suspicion. [...] People who dominated their fields yesterday might be denounced today as traitors and enemies of the people, and by tomorrow their names might disappear from all public records. Books and newspapers were constantly being recalled from libraries to rid them of 'obsolete' names and references."
- ^ Kozulin, Psychology in Utopia (1984), pp. 25–26, 48–49.
- ^ Kozulin, Psychology in Utopia (1984), pp. 27–33. "Georgy Schedrovitsky, who is currently at the Moscow Institute of Psychology, can be singled out as the most prominent theorist working in the context of systems research. [...] This is Schedrovitsky's second major thesis: Activity should not be regarded as an attribute of the individual but rather as an all-embracing system that 'captures' individuals and 'forces' them to behave a certain way. This approach may be traced back to the assertion of Wilhelm Humboldt that it is not man who has language as an attribute, but rather language that 'possesses' man. [...] Schedrovitsky's activity approach has been applied successfully to the design of man-machine systems and to the evaluation of human factors in urban planning."
- ^ Chin & Chin, Psychological Research in Communist China (1969), pp. 5–9.
- ^ Chin & Chin, Psychological Research in Communist China (1969), pp. 9–17. "The Soviet psychology that Peking modeled itself upon was a Marxist-Leninist psychology with a philosophical base in dialectical materialism and a newly added label, Pavlovianism. This new Soviet psychology leaned heavily on Lenin's theory of reflection, which was unearthed in his two volumes posthumously published in 1924. Toward the late twenties, a group of Soviet research psychologists headed by Vygotskii, along with Luria and Leont'ev, laid the groundwork for a Marxist-Leninist approach to psychic development."
- ^ Chin & Chin, Psychological Research in Communist China (1969), pp. 18–24.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Wade Pickren & Raymond D. Fowler, "Professional Organizations", in Weiner (ed.), Handbook of Psychology (2003), Volume 1: History of Psychology.
- ^ a b Irmingard Staeuble, "Psychology in the Eurocentric Order of the Social Sciences: Colonial Constitution, Cultural Imperialist Expansion, Postcolonial Critique" in Brock (ed.), Internationalizing the History of Psychology (2006).
- ^ For example, see Oregon State Law, Chapter 675 (2013 edition) at Statutes & Rules Relating to the Practice of Psychology.
- ^ a b c Judy E. Hall and George Hurley, "North American Perspectives on Education, Training, Licensing, and Credentialing", in Weiner (ed.), Handbook of Psychology (2003), Volume 8: Clinical Psychology.
- ^ T.S. Kuhn, The Structure of Scientific Revolutions, 1st. ed., Chicago: Univ. of Chicago Pr., 1962.
- ^ Beveridge, Allan (2002). "Time to abandon the subjective–objective divide?". Psychiatric Bulletin. 26 (3): 101–103. doi:10.1192/pb.26.3.101.
- ^ Peterson, C. (2009, 23 May). "Subjective and objective research in positive psychology: A biological characteristic is linked to well-being". Psychology Today. Retrieved 20 April 2010.
- ^ Panksepp, J. (1998). Affective neuroscience: The foundations of human and animal emotions. New York: Oxford University Press, p. 9.
- ^ Teo, The Critique of Psychology (2005), pp. 36–37. "Methodologism means that the method dominates the problem, problems are chosen in subordination to the respected method, and psychology has to adopt without question, the methods of the natural sciences. [...] From an epistemological and ontological-critical as well as from a human-scientific perspective the experiment in psychology has limited value (for example, only for basic psychological processes), given the nature of the psychological subject matter, and the reality of persons and their capabilities."
- ^ Teo, The Critique of Psychology (2005), p. 120. "Pervasive in feminist critiques of science, with the exception of feminist empiricism, is the rejection of positivist assumptions, including the assumption of value-neutrality or that research can only be objective if subjectivity and emotional dimensions are excluded, when in fact culture, personality, and institutions play significant roles (see Longino, 1990; Longino & Doell, 1983). For psychology, Grimshaw (1986) discussed behaviorism's goals of modification, and suggested that behaviorist principles reinforced a hierarchical position between controller and controlled and that behaviorism was in principle an antidemocratic program."
- ^ Edwin R. Wallace, IV, "Two 'Mind'–'Body' Models for a Holistic Psychiatry" and "Freud on 'Mind–Body' I: The Psychoneurobiological and 'Instinctualist' Stance; with Implications for Chapter 24, and Two Postscripts", in Wallace & Gach (eds.), History of Psychiatry and Medical Psychology (2008).
- ^ a b c Richard F. Thompson & Stuart M. Zola, "Biological Psychology", in Weiner (ed.), Handbook of Psychology (2003), Volume 1: History of Psychology.
- ^ Michela Gallagher & Randy J. Nelson, "Volume Preface", in Weiner (ed.), Handbook of Psychology (2003), Volume 3: Biological Psychology.
- ^ Luria, "The Working Brain" (1973), pp. 20–22.
- ^ Pinel, John (2010). Biopsychology. New York: Prentice Hall. ISBN 978-0-205-83256-9.
- ^ Richard Frankel; Timothy Quill; Susan McDaniel (2003). The Biopsychosocial Approach: Past, Present, Future. Boydell & Brewer. ISBN 978-1-58046-102-3.
- ^ a b McGue M, Gottesman II (2015). "Behavior Genetics". pp. 1–11. doi:10.1002/9781118625392.wbecp578. ISBN 978-1-118-62539-2.
{{cite book}}:|journal=ignored (help); Missing or empty|title=(help) - ^ Guthrie, Even the Rat was White (1998), Chapter 1: "'The Noble Savage' and Science" (pp. 3–33)
- ^ Guthrie, Even the Rat was White (1998), Chapter 5: "The Psychology of Survival and Education" (pp. 113–134)
- ^ Guthrie, Even the Rat was White (1998), Chapter 2: "Brass Instruments and Dark Skins" (pp. 34–54)
- ^ Leahey, History of Modern Psychology (2001), pp. 212–215.
- ^ Leahey, History of Modern Psychology (2001), pp. 218–227.
- ^ J.B. Watson & R. Rayner, "Conditioned emotional responses", Journal of Experimental Psychology 3, 1920; in Hock, Forty Studies (2002), pp. 70–76.
- ^ Overskeid, Geir (2007). "Looking for Skinner and finding Freud". American Psychologist. 62 (6): 590–595. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.321.6288. doi:10.1037/0003-066X.62.6.590. PMID 17874899.
- ^ Miller, S.; Konorski, J. (1928). "Sur une forme particulière des reflexes conditionels" [On a particular form of conditional reflexes]. Comptes Rendus des Séances de la Société de Biologie et de Ses Filiales (in French). 99: 1155–1157.
- ^ Skinner, B.F. (1932) The Behavior of Organisms[page needed]
- ^ a b Schlinger, H.D. (2008). "The long good-bye: why B.F. Skinner's Verbal Behavior is alive and well on the 50th anniversary of its publication". The Psychological Record. 58 (3): 329–337. doi:10.1007/BF03395622. S2CID 18114690.
- ^ Leahey, History of Modern Psychology (2001), pp. 282–285.
- ^ Chomsky, N.A. (1959) A Review of Skinner's Verbal Behavior
- ^ Seligman M.E.P.; Maier S.F. (1967). "Failure to escape traumatic shock". Journal of Experimental Psychology. 74 (1): 1–9. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.611.8411. doi:10.1037/h0024514. PMID 6032570.
- ^ Overmier J.B.; Seligman M.E.P. (1967). "Effects of inescapable shock upon subsequent escape and avoidance responding". Journal of Comparative and Physiological Psychology. 63 (1): 28–33. doi:10.1037/h0024166. PMID 6029715. S2CID 17310110.
- ^ Tolman, Edward C. (1948). "Cognitive maps in rats and men". Psychological Review. 55 (4): 189–208. doi:10.1037/h0061626. PMID 18870876. S2CID 42496633.
- ^ a b Ruben Ardila, "Behavior Analysis in an International Context", in Brock (ed.), Internationalizing the History of Psychology (2006).
- ^ a b Mandler, G. (2007). A history of modern experimental psychology: From James and Wundt to cognitive science. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.[page needed]
- ^ Bandura, A. (1973). Aggression: A social learning analysis. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall.
- ^ Aidman, Eugene; Galanis, George; Manton, Jeremy; Vozzo, Armando; Bonner, Michael (2002). "Evaluating human systems in military training". Australian Journal of Psychology. 54 (3): 168–173. doi:10.1080/00049530412331312754.
- ^ Juslin, Peter (2013), "Availability Heuristic", Encyclopedia of the Mind, SAGE Publications, Inc., doi:10.4135/9781452257044.n39, ISBN 978-1-4129-5057-2
- ^ Jain, Dr Abha; Nisha, Ms (22 May 2020). Sports Psychology. Friends Publications India. ISBN 978-93-88457-75-0.
- ^ Moore, B.E.; Fine, B.D. (1968), A Glossary of Psychoanalytic Terms and Concepts, Amer Psychoanalytic Assn, p. 78, ISBN 978-0-318-13125-2
- ^ Freud, S (1900). "The Interpretation of Dreams". IV and V (2nd ed.). Hogarth Press, 1955.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Freud, S (1915). "The Unconscious". XIV (2nd ed.). Hogarth Press, 1955.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Karl Popper, Conjectures and Refutations, London: Routledge and Keagan Paul, 1963, pp. 33–39; from Theodore Schick, ed., Readings in the Philosophy of Science, Mountain View, CA: Mayfield Publishing Company, 2000, pp. 9–13. Faculty.washington.edu
- ^ a b June 2008 study by the American Psychoanalytic Association, as reported in The New York Times, "Freud Is Widely Taught at Universities, Except in the Psychology Department" by Patricia Cohen, 25 November 2007.
- ^ For example, scientists have related brain structures to Freudian concepts such as libido, drives, the unconscious, and repression. The contributors to neuro-psychoanalysis include António Damásio (Damásio, A. (1994). Descartes' error: Emotion, reason, and the human brain; Damásio, A. (1996). The somatic marker hypothesis and the possible functions of the prefrontal cortex; Damásio, A. (1999). The feeling of what happens: Body and emotion in the making of consciousness; Damásio, A. (2003). Looking for Spinoza: Joy, sorrow, and the feeling brain); Eric Kandel; Joseph E. LeDoux (LeDoux, J.E. (1998). The emotional brain: The mysterious underpinnings of emotional life (Touchstone ed.). Simon & Schuster. Original work published 1996. ISBN 0-684-83659-9); Jaak Panksepp (Panksepp, J. (1998). Affective neuroscience: The foundations of human and animal emotions. New York and Oxford: Oxford University Press); Oliver Sacks (Sacks, O. (1984). A leg to stand on. New York: Summit Books/Simon and Schuster); Mark Solms (Kaplan-Solms, K., & Solms, M. (2000). Clinical studies in neuro-psychoanalysis: Introduction to a depth neuropsychology. London: Karnac Books; Solms, M., & Turnbull, O. (2002). The brain and the inner world: An introduction to the neuroscience of subjective experience. New York: Other Press); and Douglas Watt.
- ^ "Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs". Honolulu.hawaii.edu. Archived from the original on 11 February 2010. Retrieved 10 December 2011.
- ^ Gazzaniga, Michael (2010). Psychological Science. New York: W.W. Norton & Company. p. 23. ISBN 978-0-393-93421-2.
- ^ Rowan, John. (2001). Ordinary Ecstasy: The Dialectics of Humanistic Psychology. London, UK: Brunner-Routledge. ISBN 0-415-23633-9
- ^ A.J. Sutich, American association for humanistic psychology, Articles of association. Palo Alto, CA (mimeographed): August 28, 1963; in Severin (ed.), Humanistic Viewpoints in Psychology (1965), pp. xv–xvi.
- ^ Hergenhahn, B.R. (2005). An introduction to the history of psychology. Belmont, California: Thomson Wadsworth. pp. 528–536.
- ^ Hergenhahn, B.R. (2005). An introduction to the history of psychology. Belmont, California: Thomson Wadsworth. pp. 546–547.
- ^ Hergenhahn, B.R. (2005). An introduction to the history of psychology. Belmont, California: Thomson Wadsworth. pp. 523–532.
- ^ Frankl, V.E. (1984). Man's search for meaning (rev. ed.). New York: Washington Square Press. p. 86.
- ^ Seidner, Stanley S. (10 June 2009) "A Trojan Horse: Logotherapeutic Transcendence and its Secular Implications for Theology". Mater Dei Institute. p 2.
- ^ Carver, C., & Scheier, M. (2004). Perspectives on Personality (5th ed.). Boston: Pearson.
- ^ Haggbloom, Steven J.; Warnick, Renee; Warnick, Jason E.; Jones, Vinessa K.; Yarbrough, Gary L.; Russell, Tenea M.; Borecky, Chris M.; McGahhey, Reagan; Powell, John L., III; Beavers, Jamie; Monte, Emmanuelle (2002). "The 100 most eminent psychologists of the 20th century" (PDF). Review of General Psychology. 6 (2): 139–152. doi:10.1037/1089-2680.6.2.139. S2CID 145668721.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Cattell, R.B. (1995). "The fallacy of five factors in the personality sphere". The Psychologist, May, 207–208.
- ^ Cattell, Raymond B.; Nichols, K. Ernest (1972). "An Improved Definition, from 10 Researchers, of Second Order Personality Factors in Q Data (with Cross-Cultural Checks)". The Journal of Social Psychology. 86 (2): 187–203. doi:10.1080/00224545.1972.9918617.
- ^ Block, Jack (1995). "A contrarian view of the five-factor approach to personality description". Psychological Bulletin. 117 (2): 187–215. doi:10.1037/0033-2909.117.2.187. PMID 7724687.
- ^ Boyle, G.J. (2008). Critique of Five-Factor Model (FFM). In G.J. Boyle, G. Matthews, & D.H. Saklofske. (Eds.), The SAGE handbook of personality theory and assessment: Vol. 1 – Personality theories and models. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE. ISBN 978-1-4129-4651-3
- ^ Boyle, G.J. (2011). Changes in personality traits in adulthood. In D. Westen, L. Burton, & R. Kowalski (Eds.), Psychology: Australian and New Zealand 3rd edition (pp. 448–449). Milton, Queensland: Wiley. ISBN 978-1-74216-644-5
- ^ Cattell, Raymond B.; Boyle, Gregory J.; Chant, David (2002). "Enriched behavioral prediction equation and its impact on structured learning and the dynamic calculus". Psychological Review. 109 (1): 202–205. doi:10.1037/0033-295X.109.1.202. PMID 11863038.
- ^ Boyle, Gregory J. (1995). "Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI): Some Psychometric Limitations". Australian Psychologist. 30: 71–74. doi:10.1111/j.1742-9544.1995.tb01750.x.
- ^ Leslie C. Morey, "Measuring Personality and Psychopathology" in Weiner (ed.), Handbook of Psychology (2003), Volume 2: Research Methods in Psychology.
- ^ Helmes, Edward; Reddon, John R. (1993). "A perspective on developments in assessing psychopathology: A critical review of the MMPI and MMPI-2". Psychological Bulletin. 113 (3): 453–471. doi:10.1037/0033-2909.113.3.453.
- ^ Charles Sanders Peirce & Joseph Jastrow, "On Small Differences in Sensation", Memoirs of the National Academy of Sciences 3, 17 October 1884; cited in William P. Banks & Ilya Farber, "Consciousness", in Weiner (ed.), Handbook of Psychology (2003), Volume 4: Experimental Psychology; and in Deber, James A; Jacoby, Larry L. (1994). "Unconscious Perception: Attention, Awareness, and Control". Journal of Experimental Psychology. 20 (2): 304–317. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.412.4083. doi:10.1037/0278-7393.20.2.304. PMID 8151275.
- ^ a b John F. Kihlstrom, "The Psychological Unconscious", in Lawrence Pervin & Oliver John (eds.), Handbook of Personality; New York: Guilford Press, 1999. Also see web version Archived 9 October 2016 at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ a b William P. Banks & Ilya Farber, "Consciousness", in Weiner (ed.), Handbook of Psychology (2003), Volume 4: Experimental Psychology.[page needed]
- ^ a b Bargh, John A.; Chartrand, Tanya L. (1999). "The unbearable automaticity of being". American Psychologist. 54 (7): 462–479. doi:10.1037/0003-066X.54.7.462. S2CID 5726030. Also see: John A. Bargh, "The Automaticity of Everyday Life", in Robert S. Wyer Jr. (ed.), The Automaticity of Everyday Life, Advances in Social Cognition, Volume X; Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 1997; ISBN 978-0-8058-1699-0[page needed]
- ^ a b John F. Kihlstrom, "The Automaticity Juggernaut—or, Are We Automatons After All?", in John Baer, James C. Kaufmna, & Roy F. Baumeister (eds.), Are We Free? Psychology and Free Will; Oxford University Press, 2008. ISBN 978-0-19-518963-6
- ^ Soon, Chun Siong; Brass, Marcel; Heinze, Hans-Jochen; Haynes, John-Dylan (2008). "Unconscious determinants of free decisions in the human brain". Nature Neuroscience. 11 (5): 543–545. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.520.2204. doi:10.1038/nn.2112. PMID 18408715. S2CID 2652613.
- ^ Baumeister, Roy F. (2008). "Free Will in Scientific Psychology". Perspectives on Psychological Science. 3 (1): 14–19. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.476.102. doi:10.1111/j.1745-6916.2008.00057.x. PMID 26158665. S2CID 9630921.
- ^ a b Forgas, Williams, & Laham, "Social Motivation: Introduction and Overview", in Forgas, Williams, & Laham, Social Motivation (2005).
- ^ Weiner, Human Motivation (2013), Chapter 2, "The Psychoanalytic Theory of Motivation" (pp. 9–84).
- ^ a b c Bill P. Godsil, Matthew R. Tinsley, & Michael S. Fanselow, "Motivation", in Weiner (ed.), Handbook of Psychology (2003), Volume 4: Experimental Psychology.
- ^ Weiner, Human Motivation (2013), Chapter 3, "Drive Theory" (pp. 85–138).
- ^ E. Tory Higgins, Beyond Pleasure and Pain: How Motivation Works; Oxford University Press, 2012; ISBN 978-0-19-976582-9[page needed]
- ^ Shah & Gardner, Handbook of Motivation Science (2008), entire volume.[page needed]
- ^ Hank Aarts, Ap Dijksterhuis, & Giel Dik, "Goal Contagion: Inferring goals from others' actions—and what it leads to", in Shah & Gardner, Handbook of Motivation Science (2008). "In short, then, the studies presented above indicate that humans are keen to act on the goals of other social beings that are implied in behavioral scenarios or scripts." Also see: Aarts; Hassin; Gollwitzer (2004). "Goal Contagion: Perceiving is for Pursuing". Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 87 (1): 23–37. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.312.5507. doi:10.1037/0022-3514.87.1.23. PMID 15250790.
- ^ Kathleen D. Vohs & Roy F. Baumeister, "Can Satisfaction Reinforce Wanting? A new theory about long-term changes in strength of motivation", in Shah & Gardner, Handbook of Motivation Science (2008).
- ^ Polderman, Tinca J C.; Benyamin, Beben; De Leeuw, Christiaan A.; Sullivan, Patrick F.; Van Bochoven, Arjen; Visscher, Peter M.; Posthuma, Danielle (2015). "Meta-analysis of the heritability of human traits based on fifty years of twin studies" (PDF). Nature Genetics. 47 (7): 702–709. doi:10.1038/ng.3285. PMID 25985137. S2CID 205349969.
- ^ Turkheimer, Eric (2000). "Three Laws of Behavior Genetics and What They Mean". Current Directions in Psychological Science. 9 (5): 160–164. doi:10.1111/1467-8721.00084. S2CID 2861437.
- ^ Visscher, Peter M.; Brown, Matthew A.; McCarthy, Mark I.; Yang, Jian (2012). "Five Years of GWAS Discovery". The American Journal of Human Genetics. 90 (1): 7–24. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.11.029. PMC 3257326. PMID 22243964.
- ^ Ripke, Stephan; Neale, Benjamin M.; Corvin, Aiden; Walters, James T. R.; Farh, Kai-How; Holmans, Peter A.; Lee, Phil; Bulik-Sullivan, Brendan; Collier, David A.; Huang, Hailiang; Pers, Tune H.; Agartz, Ingrid; Agerbo, Esben; Albus, Margot; Alexander, Madeline; Amin, Farooq; Bacanu, Silviu A.; Begemann, Martin; Belliveau, Richard A.; Bene, Judit; Bergen, Sarah E.; Bevilacqua, Elizabeth; Bigdeli, Tim B.; Black, Donald W.; Bruggeman, Richard; Buccola, Nancy G.; Buckner, Randy L.; Byerley, William; Cahn, Wiepke; et al. (2014). "Biological insights from 108 schizophrenia-associated genetic loci". Nature. 511 (7510): 421–427. Bibcode:2014Natur.511..421S. doi:10.1038/nature13595. PMC 4112379. PMID 25056061.
- ^ Lee, S Hong; Decandia, Teresa R.; Ripke, Stephan; Yang, Jian; Sullivan, Patrick F.; Goddard, Michael E.; Keller, Matthew C.; Visscher, Peter M.; Wray, Naomi R. (2012). "Estimating the proportion of variation in susceptibility to schizophrenia captured by common SNPs". Nature Genetics. 44 (3): 247–250. doi:10.1038/ng.1108. PMC 3327879. PMID 22344220.
- ^ Sullivan, Patrick F.; Daly, Mark J.; O'Donovan, Michael (2012). "Genetic architectures of psychiatric disorders: The emerging picture and its implications". Nature Reviews Genetics. 13 (8): 537–551. doi:10.1038/nrg3240. PMC 4110909. PMID 22777127.
- ^ De Moor, Marleen H. M.; Van Den Berg, Stéphanie M.; Verweij, Karin J. H.; Krueger, Robert F.; Luciano, Michelle; Arias Vasquez, Alejandro; Matteson, Lindsay K.; Derringer, Jaime; Esko, Tõnu; Amin, Najaf; Gordon, Scott D.; Hansell, Narelle K.; Hart, Amy B.; Seppälä, Ilkka; Huffman, Jennifer E.; Konte, Bettina; Lahti, Jari; Lee, Minyoung; Miller, Mike; Nutile, Teresa; Tanaka, Toshiko; Teumer, Alexander; Viktorin, Alexander; Wedenoja, Juho; Abecasis, Goncalo R.; Adkins, Daniel E.; Agrawal, Arpana; Allik, Jüri; Appel, Katja; et al. (2015). "Meta-analysis of Genome-wide Association Studies for Neuroticism, and the Polygenic Association with Major Depressive Disorder". JAMA Psychiatry. 72 (7): 642–50. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2015.0554. PMC 4667957. PMID 25993607.
- ^ Gregory, Psychological Testing (2011), pp. 41–42.
- ^ Gregory, Psychological Testing (2011), pp. 42–43.
- ^ Gregory, Psychological Testing (2011), pp. 44–45.
- ^ a b Gregory, Psychological Testing (2011), pp. 45–46.
- ^ Gregory, Psychological Testing (2011), p. 50–56.
- ^ a b Guthrie, Even the Rat was White (1998), Chapter 3: "Psychometric Scientism" (pp. 55–87)
- ^ Gregory, Psychological Testing (2011), p. 61.
- ^ Berry, Robert M. (2012). "From Involuntary Sterilization to Genetic Enhancement: The Unsettled Legacy of Buck v. Bell". Notre Dame Journal of Law, Ethics, & Public Policy. 12.
- ^ Gregory, Psychological Testing (2011), p. 2. "From birth to old age, we encounter tests at almost every turning point in life. […] Tests are used in almost every nation on earth for counseling, selection, and placement. Testing occurs in settings as diverse as schools, civil service, industry, medical clinics, and counseling centers. Most persons have taken dozens of tests and thought nothing of it. Yet, by the time the typical individual reaches retirement age, it is likely that psychological test results will have helped to shape his or her destiny."
- ^ Gregory, Psychological Testing (2011), pp. 4–6.
- ^ a b George Stricker & Thomas A. Widiger, "Volume Preface", in Weiner (ed.), Handbook of Psychology (2003), Volume 8: Clinical Psychology.
- ^ Brain, Christine. (2002). Advanced psychology: applications, issues and perspectives. Cheltenham: Nelson Thornes. ISBN 0-17-490058-9
- ^ Nancy McWilliams and Joel Weinberger, "Psychodynamic Psychotherapy", in Weiner (ed.), Handbook of Psychology (2003), Volume 8: Clinical Psychology.
- ^ W. Edward Craighead & Linda Wilcoxon Craighead, "Behavioral and Cognitive-Behavioral Psychotherapy" in Weiner (ed.), Handbook of Psychology (2003), Volume 8: Clinical Psychology.
- ^ Teri L. Elliott, "Disaster Psychology: Keep Clients out of Your Office—Get into the Field!" in Morgan et al. (ed.), Life After Graduate School in Psychology (2005). "...it is the disaster psychologist's role to utilize crisis intervention processes with the goal of preventing natural distress due to the critical event from developing into a more harmful, long-term psychological condition."
- ^ Leichsenring, Falk; Leibing, Eric (2003). "The effectiveness of psychodynamic therapy and cognitive behavior therapy in the treatment of personality disorders: A meta-analysis". The American Journal of Psychiatry. 160 (7): 1223–1233. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.160.7.1223. PMID 12832233.
- ^ Reisner, Andrew (2005). "The common factors, empirically validated treatments, and recovery models of therapeutic change". The Psychological Record. 55 (3): 377–400. doi:10.1007/BF03395517. S2CID 142840311.
- ^ Jensen, J.P.; Bergin, A.E.; Greaves, D.W. (1990). "The meaning of eclecticism: New survey and analysis of components". Professional Psychology: Research and Practice. 21 (2): 124–130. doi:10.1037/0735-7028.21.2.124.
- ^ Palmer, S.; Woolfe, R. (eds.) (1999). Integrative and eclectic counselling and psychotherapy. London: Sage.
- ^ Clarkson, P. (1996). The eclectic and integrative paradigm: Between the Scylla of confluence and the Charybdis of confusion. In Handbook of Counselling Psychology (R. Woolfe & W.L. Dryden, eds.). London: Sage, pp. 258–283. ISBN 0-8039-8991-1
- ^ Goldfried, M.R.; Wolfe, B.E. (1998). "Toward a more clinically valid approach to therapy research" (PDF). Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology. 66 (1): 143–150. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.475.7156. doi:10.1037/0022-006X.66.1.143. PMID 9489268.
- ^ Seligman, M.E.P. (1995). "The effectiveness of psychotherapy: The Consumer Reports study" (PDF). American Psychologist. 50 (12): 965–974. doi:10.1037/0003-066X.50.12.965. PMID 8561380.
- ^ Peter E. Nathan & James Langenbucher, "Diagnosis and Classification", in Weiner (ed.), Handbook of Psychology (2003), Volume 8: Clinical Psychology.
- ^ National Association of School Psychologists. "Who are school psychologists?". Archived from the original on 17 May 2008. Retrieved 1 June 2008.
- ^ a b c Laura L. Koppes, "Industrial-Organizational Psychology", in Weiner (ed.), Handbook of Psychology (2003), Volume 1: History of Psychology.
- ^ Yeh Hsueh, "The Hawthorne experiments and the introduction of Jean Piaget in American industrial psychology, 1929–1932"; History of Psychology 5.2, May 2002.
- ^ Myers (2004). Motivation and work. Psychology. New York, NY: Worth Publishers
- ^ Steven Williams, "Executive Management: Helping Executives Manage Their Organizations through Organizational and Market Research" in Morgan et al. (ed.), Life After Graduate School in Psychology (2005).
- ^ See also for example Baden Eunson: Behaving – Managing Yourself and Others. McGraw-Hill, Sidney/New York City 1987, ISBN 978-0-0745-2022-2.
- ^ Robert M. Yerkes, "Measuring the Mental Strength of an Army"; Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 4.10, 15 October 1918.
- ^ Joshua N. Friedlander, "Military Psychology: An Army Clinical Psychologist" in Morgan et al. (ed.), Life After Graduate School in Psychology (2005).
- ^ Paul M.A. Linebarger, Psychological Warfare; Washington: Combat Forces Press, 1954.
- ^ See "Project MKULTRA, the CIA's Program of Research in Behavioral Modification"; Joint Hearing before the Senate Committee on Intelligence and the Subcommittee on Health and Scientific Research of the Committee on Human Resources, United States Senate, Ninety Fifth Congress, First Session, 3 August 1997; and John D. Marks, The Search for the Manchurian Candidate, New York: Times Books, 1979.
- ^ Alfred Paddock, Jr., "PSYOP: On a Complete Change in Organization, Practice, and Doctrine Archived 12 July 2015 at the Wayback Machine", Small Wars Journal 2010.
- ^ US torture report: psychologists should no longer aid military, group says The Guardian, 2015-07-11
- ^ Marilu Price Berry, "Interdisciplinary Medical Setting: The Multiple Roles of a Health Psychologist" in Morgan et al. (ed.), Life After Graduate School in Psychology (2005).
- ^ Monica L. Baskin, "Public Health: Career Opportunities for Psychologists in Public Health", in Morgan et al. (ed.), Life After Graduate School in Psychology (2005). "Prevention strategies of late have largely concentrated on community-based interventions, which have been shown to be effective in changing the health of large populations. Behavioral and social scientists, such as psychologists, are helpful in this arena as we are trained to view individuals as belonging to complex and dynamic social systems, including immediate and extended family systems, acquaintance and friendship networks, neighborhood and community systems, and cultural groups (Schneiderman & Spee4, 2001)."
- ^ Guthrie, Even the Rat was White (1998), Chapter 7: "Production of Black Psychologists in America" (pp. 155–213).
- ^ John A. Schinka & Wayne F. Velicer, "Volume Preface" in Weiner (ed.), Handbook of Psychology (2003), Volume 2: Research Methods in Psychology.
- ^ Schulz, K.F.; Altman, D.G.; Moher, D.; for the CONSORT Group (2010). "CONSORT 2010 Statement: updated guidelines for reporting parallel group randomised trials". BMJ. 340: c332. doi:10.1136/bmj.c332. PMC 2844940. PMID 20332509.
- ^ Milgram, Stanley (1963). "Behavioral Study of Obedience". Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology. 67 (4): 371–378. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.599.92. doi:10.1037/h0040525. PMID 14049516. Full-text PDF. Archived 11 June 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Evelyn S. Behar & Thomas D. Borkovec, "Psychotherapy Outcome Research", in Weiner (ed.), Handbook of Psychology (2003), Volume 2: Research Methods in Psychology.
- ^ Melvin M. Mark, "Program Evaluation" in Weiner (ed.), Handbook of Psychology (2003), Volume 2: Research Methods in Psychology.
- ^ Roger E. Kirk, "Experimental Design" in Weiner (ed.), Handbook of Psychology (2003), Volume 2: Research Methods in Psychology.
- ^ Russell M. Bauer, Elizabeth C. Leritz, & Dawn Bowers, "Neuropsychology", in Weiner (ed.), Handbook of Psychology (2003), Volume 2: Research Methods in Psychology.
- ^ John T. Behrens and Chong-Ho Yu, "Exploratory Data Analysis" in Weiner (ed.), Handbook of Psychology (2003), Volume 2: Research Methods in Psychology.
- ^ Frank L. Schmidt and John E. Hunter, "Meta-Analysis", Handbook of Psychology (2003), Volume 2: Research Methods in Psychology.
- ^ Rösler, Frank (2005). "From Single-Channel Recordings to Brain-Mapping Devices: The Impact of Electroencephalography on Experimental Psychology" (PDF). History of Psychology. 8 (1): 95–117. doi:10.1037/1093-4510.8.1.95. PMID 16021767. Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 September 2015. Retrieved 24 April 2015.
- ^ Moran, Joseph M.; Zaki, Jamil (2013). "Functional Neuroimaging and Psychology: What Have You Done for Me Lately?". Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience. 25 (6): 834–842. doi:10.1162/jocn_a_00380. PMID 23469884. S2CID 12546790.
- ^ Cacioppo, John T.; Berntson, Gary G.; Nusbaum, Howard C. (2008). "Neuroimaging as a New Tool in the Toolbox of Psychological Science" (PDF). Current Directions in Psychological Science. 17 (2): 62–67. doi:10.1111/j.1467-8721.2008.00550.x. S2CID 14565940. Archived from the original (PDF) on 31 October 2014.
- ^ Aue, Tatjana; Lavelle, Leah A.; Cacioppo, John T. (2009). "Great expectations: What can fMRI research tell us about psychological phenomena?" (PDF). International Journal of Psychophysiology. 73 (1): 10–16. doi:10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2008.12.017. PMID 19232374. Archived from the original (PDF) on 9 January 2016.
- ^ Ron Sun, (2008). The Cambridge Handbook of Computational Psychology. Cambridge University Press, New York. 2008.
- ^ "Ncabr.Org: About Biomedical Research: Faq". Archived from the original on 8 July 2008. Retrieved 1 July 2008.
- ^ Shettleworth, S.J. (2010) Cognition, Evolution and Behavior (2nd Ed), New York: Oxford.
- ^ Wilson, E.O. (1978) On Human Nature p. x, Cambridge, Ma: Harvard
- ^ Glaser, B. & Strauss, A. (1967). The discovery of grounded theory: Strategies for qualitative research. Chicago: Aldine.
- ^ Harlow (1868), Fig. 2, p. 347 Harlow, John Martyn (1868). "Recovery from the Passage of an Iron Bar through the Head." Publications of the Massachusetts Medical Society 2:327–347 (Republished in Macmillan 2000).
- ^ Administration for Children and Families (2010) The Program Manager's Guide to Evaluation. Chapter 2: What is program evaluation?.
- ^ Shackman, Gene (11 February 2018). "What Is Program Evaluation: A Beginner's Guide". The Global Social Change Research Project. SSRN 3060080.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Franco, Annie; Malhotra, Neil; Simonovits, Gabor (1 January 2016). "Underreporting in Psychology Experiments: Evidence From a Study Registry". Social Psychological and Personality Science. 7 (1): 8–12. doi:10.1177/1948550615598377. ISSN 1948-5506. S2CID 143182733.
- ^ Munafò, Marcus (29 March 2017). "Metascience: Reproducibility blues". Nature. 543 (7647): 619–620. Bibcode:2017Natur.543..619M. doi:10.1038/543619a. ISSN 1476-4687.
- ^ StokstadSep. 20, Erik (19 September 2018). "This research group seeks to expose weaknesses in science—and they'll step on some toes if they have to". Science | AAAS. Retrieved 24 May 2019.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ Stevens, Jeffrey R. (2017). "Replicability and Reproducibility in Comparative Psychology". Frontiers in Psychology. 8: 862. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2017.00862. ISSN 1664-1078. PMC 5445189. PMID 28603511.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Arjo Klamer; Robert M. Solow; Donald N. McCloskey (1989). The Consequences of economic rhetoric. Cambridge University Press. pp. 173–174. ISBN 978-0-521-34286-5.
- ^ Lehrer, Jonah (13 December 2010). "The Truth Wears Off". The New Yorker. Retrieved 10 April 2011.
- ^ Sterling, Theodore D. (March 1959). "Publication decisions and their possible effects on inferences drawn from tests of significance—or vice versa". Journal of the American Statistical Association. 54 (285): 30–34. doi:10.2307/2282137. JSTOR 2282137.
- ^ Fanelli, Daniele (2010). Enrico Scalas (ed.). "'Positive' Results Increase Down the Hierarchy of the Sciences". PLOS ONE. 5 (4): e10068. Bibcode:2010PLoSO...510068F. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0010068. PMC 2850928. PMID 20383332.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Marcus, Gary (1 May 2013). "The Crisis in Social Psychology That Isn't". The New Yorker. Advance Publications. Retrieved 19 December 2018.
- ^ Meyer, Michelle N.; Chabris, Christopher (31 July 2014). "Why Psychologists' Food Fight Matters". Slate. The Slate Group. Retrieved 19 December 2018.
- ^ Aschwanden, Christie (27 August 2015). "Psychology Is Starting To Deal With Its Replication Problem". FiveThirtyEight. Retrieved 19 December 2018.
- ^ a b Open Science Collaboration (2015). "Estimating the reproducibility of psychological science" (PDF). Science. 349 (6251): aac4716. doi:10.1126/science.aac4716. hdl:10722/230596. PMID 26315443. S2CID 218065162.
- ^ Hunt, Earl B. (2011). Human Intelligence. Cambridge University Press. p. 94. ASIN B004V9O6CE.
- ^ Baumeister, Roy (September 2016), "Charting the future of social psychology on stormy seas: Winners, losers, and recommendations", Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 66: 153–158, doi:10.1016/j.jesp.2016.02.003,
...shifting the dominant conceptual paradigm from Freudian psychoanalytic theory to Big Five research has reduced the chances of being wrong but palpably increased the fact of being boring. In making that transition, personality psychology became more accurate but less broadly interesting.
- ^ Plomin, Robert; Defries, John C.; Knopik, Valerie S.; Neiderhiser, Jenae M. (2016). "Top 10 Replicated Findings from Behavioral Genetics". Perspectives on Psychological Science. 11 (1): 3–23. doi:10.1177/1745691615617439. PMC 4739500. PMID 26817721.
- ^ Duncan, Laramie E.; Keller, Matthew C. (2011). "A Critical Review of the First 10 Years of Candidate Gene-by-Environment Interaction Research in Psychiatry". American Journal of Psychiatry. 168 (10): 1041–1049. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2011.11020191. PMC 3222234. PMID 21890791.
- ^ Camerer, C. F.; Dreber, A.; Forsell, E.; Ho, T.-H.; Huber, J.; Johannesson, M.; Kirchler, M.; Almenberg, J.; Altmejd, A.; Chan, T.; Heikensten, E.; Holzmeister, F.; Imai, T.; Isaksson, S.; Nave, G.; Pfeiffer, T.; Razen, M.; Wu, H. (2016). "Evaluating replicability of laboratory experiments in economics". Science. 351 (6280): 1433–1436. Bibcode:2016Sci...351.1433C. doi:10.1126/science.aaf0918. PMID 26940865.
- ^ Leichsenring, F.; Abbass, A.; Hilsenroth, M. J.; Leweke, F.; Luyten, P.; Keefe, J. R.; Midgley, N.; Rabung, S.; Salzer, S.; Steinert, C. (2017). "Biases in research: Risk factors for non-replicability in psychotherapy and pharmacotherapy research". Psychological Medicine. 47 (6): 1000–1011. doi:10.1017/S003329171600324X. PMID 27955715. S2CID 1872762.
- ^ Hengartner, Michael P. (2018). "Raising Awareness for the Replication Crisis in Clinical Psychology by Focusing on Inconsistencies in Psychotherapy Research: How Much Can We Rely on Published Findings from Efficacy Trials?". Frontiers in Psychology. 9: 256. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2018.00256. PMC 5835722. PMID 29541051.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Frank, Michael C.; Bergelson, Elika; Bergmann, Christina; Cristia, Alejandrina; Floccia, Caroline; Gervain, Judit; Hamlin, J. Kiley; Hannon, Erin E.; Kline, Melissa; Levelt, Claartje; Lew-Williams, Casey; Nazzi, Thierry; Panneton, Robin; Rabagliati, Hugh; Soderstrom, Melanie; Sullivan, Jessica; Waxman, Sandra; Yurovsky, Daniel (2017). "A Collaborative Approach to Infant Research: Promoting Reproducibility, Best Practices, and Theory-Building". Infancy. 22 (4): 421–435. doi:10.1111/infa.12182. PMC 6879177. PMID 31772509.
- ^ Harris, Judith Rich (2009) [1998]. The Nurture Assumption: Why Children Turn Out the Way They Do (2nd ed.). New York: Free Press. ISBN 978-1439101650.
- ^ Harris, Judith Rich (2006). No Two Alike: Human Nature and Human Individuality. New York: W. W. Norton & Company. ISBN 978-0393329711.
- ^ Tyson, Charlie (14 August 2014). "Failure to Replicate". Inside Higher Ed. Retrieved 19 December 2018.
- ^ Makel, Matthew C.; Plucker, Jonathan A. (2014). "Facts Are More Important Than Novelty". Educational Researcher. 43 (6): 304–316. doi:10.3102/0013189X14545513. S2CID 145571836.
- ^ Kirschner, Paul A.; Sweller, John; Clark, Richard E. (2006). "Why Minimal Guidance During Instruction Does Not Work: An Analysis of the Failure of Constructivist, Discovery, Problem-Based, Experiential, and Inquiry-Based Teaching". Educational Psychologist. 41 (2). Routledge: 75–86. doi:10.1207/s15326985ep4102_1. S2CID 17067829.
- ^ Foundations for Success: The Final Report of the National Mathematics Advisory Panel (PDF) (Report). United States Department of Education. 2008. pp. 45–46. Retrieved 3 November 2020.
- ^ Simmons, Joseph P.; Nelson, Leif D.; Simonsohn, Uri (2011). "False-Positive Psychology". Psychological Science. 22 (11): 1359–1366. doi:10.1177/0956797611417632. PMID 22006061.
- ^ Stroebe, Wolfgang; Strack, Fritz (2014). "The Alleged Crisis and the Illusion of Exact Replication" (PDF). Perspectives on Psychological Science. 9 (1): 59–71. doi:10.1177/1745691613514450. PMID 26173241. S2CID 31938129.
- ^ Aschwanden, Christie (6 December 2018). "Psychology's Replication Crisis Has Made The Field Better". FiveThirtyEight. Retrieved 19 December 2018.
- ^ Chartier, Chris; Kline, Melissa; McCarthy, Randy; Nuijten, Michele; Dunleavy, Daniel J.; Ledgerwood, Alison (December 2018), "The Cooperative Revolution Is Making Psychological Science Better", Observer, 31 (10), retrieved 19 December 2018
- ^ Allen, Christopher P G.; Mehler, David Marc Anton. "Open Science challenges, benefits and tips in early career and beyond". doi:10.31234/osf.io/3czyt.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Cohen, Jacob (1994). "The earth is round (p < .05)". American Psychologist. 49 (12): 997–1003. doi:10.1037/0003-066X.49.12.997. S2CID 380942.
- ^ a b Arnett, J. J. (2008). "The neglected 95%: Why American psychology needs to become less American". American Psychologist. 63 (7): 602–614. doi:10.1037/0003-066X.63.7.602. PMID 18855491.
- ^ Henrich, Joseph; Heine, Steven J.; Norenzayan, Ara (2010). "The weirdest people in the world?". Behavioral and Brain Sciences. 33 (2–3): 61–83. doi:10.1017/S0140525X0999152X. PMID 20550733.
- ^ Collins, L. H.; Machizawa, S.; Rice, J. K. (2019). Transnational Psychology of Women: Expanding International and Intersectional Approaches. Washington, D. C.: American Psychological Association. ISBN 978-1-4338-3069-3.
- ^ Altmaier, E. M.; Hall, J. E. (2008). Global promise: Quality assurance and accountability in professional psychology. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-530608-8.
- ^ Morgan-Consoli, M. L.; Inman, A. G.; Bullock, M.; Nolan, S. A. (2018). "Framework for competencies for U.S. psychologists engaging internationally". International Perspectives in Psychology: Research, Practice, Consultation. 7 (3): 174–188. doi:10.1037/ipp0000090. S2CID 159028411.
- ^ Rad, Mostafa Salari; Martingano, Alison Jane; Ginges, Jeremy (2018). "Toward a psychology of Homo sapiens: Making psychological science more representative of the human population". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 115 (45): 11401–11405. doi:10.1073/pnas.1721165115. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 6233089. PMID 30397114.
- ^ Schulz, Jonathan F.; Bahrami-Rad, Duman; Beauchamp, Jonathan P.; Henrich, Joseph (8 November 2019). "The Church, intensive kinship, and global psychological variation". Science. 366 (6466): eaau5141. doi:10.1126/science.aau5141. PMID 31699908. S2CID 207943472.
- ^ Brian Connolly, Hans Hummer, and Sara McDougall, "Weird Science: Incest and History" Perspectives on History (May 2020)
- ^ Kurtis, T.; Adams, G. (2015). "Decolonizing liberation: Toward a transnational feminist psychology" (PDF). Journal of Social and Political Psychology. 3 (2): 388–413. doi:10.5964/jspp.v3i1.326. JSTOR 3178747.
- ^ Bhatia, S. (2010). "Theorizing indigenous psychology". Theory & Psychology. 20: 137–140. doi:10.1177/0959354309345640.
- ^ a b Collins, L. H.; Machizawa, S.; Rice, K. "Introduction". Transnational psychology of women : expanding international and intersectional approaches (PDF). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association. ISBN 1-4338-3124-4. OCLC 1090706835.
- ^ Machizawa, S.; Enns, C. (2015). "Transnational psychological practice with women: Perspectives from East Asia and Japan". In Enns, C.; Rice, J.; Nutt, R. (eds.). Psychological practice with women: Guidelines, diversity, empowerment. APA Division 35 Psychology of Women Book Series. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association. pp. 225–256. ISBN 978-1433818127.
- ^ Collins, L. H. (2019). "Teaching cultural and transnational psychology: Taking intersectionality across the globe.". In Mena, J.; Quina, K. (eds.). Integrating multiculturalism and intersectionality into the psychology curriculum: Strategies for instructors. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association (published 2015). pp. 181–196. ISBN 978-1433830075.
- ^ Dawes, Robyn (1994). House of Cards – Psychology and Psychotherapy Built on Myth. Free Press. ISBN 978-0-02-907205-9.
- ^ Beyerstein, Barry L. (Spring 2001). "Fringe Psychotherapies: The Public at Risk". The Scientific Review of Alternative Medicine. 5 (2): 70–9. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.462.3147.
- ^ "SRMHP: Our Raison d'Être". Retrieved 1 July 2008.
- ^ Neuringer, A. (November 1984). "Melioration and Self-Experimentation". J Exp Anal Behav. 42 (3): 397–406. doi:10.1901/jeab.1984.42-397. PMC 1348111. PMID 16812398. in 1966, and in 1974 ad
- ^ Elliot Robert (1998). "Editor's Introduction: A Guide to the Empirically Supported Treatments Controversy". Psychotherapy Research. 8 (2): 115–125. doi:10.1080/10503309812331332257.
- ^ The American Psychological Society: Responsible Conduct of Research
- ^ a b c Stanley E. Jones, "Ethical Issues in Clinical Psychology", in Weiner (ed.), Handbook of Psychology (2003), Volume 8: Clinical Psychology.
- ^ Sherwin, C.M.; Christionsen, S.B.; Duncan, I.J.; Erhard, H.W.; Lay Jr., D.C.; Mench, J.A.; O'Connor, C.E.; Petherick, J.C. (2003). "Guidelines for the Ethical use of animals in the applied ethology studies". Applied Animal Behaviour Science. 81 (3): 291–305. doi:10.1016/s0168-1591(02)00288-5.
- ^ Milgram, Stanley. (1974), Obedience to Authority; An Experimental View. Harpercollins (ISBN 0-06-131983-X).
- ^ Blum 1994, p. 95, Blum 2002, pp. 218–219. Blum 1994, p. 95: "... the most controversial experiment to come out of the Wisconsin laboratory, a device that Harlow insisted on calling the 'pit of despair.'"
- ^ Blum, Deborah. Love at Goon Park: Harry Harlow and the Science of Affection. Perseus Publishing, 2002. ISBN 0-7382-0278-9
- ^ Booth, Wayne C. Modern Dogma and the Rhetoric of Assent, Volume 5, of University of Notre Dame, Ward-Phillips lectures in English language and literature, University of Chicago Press, 1974, p. 114. Booth is explicitly discussing this experiment. His next sentence is, "His most recent outrage consists of placing monkeys in 'solitary' for twenty days—what he calls a 'vertical chamber apparatus .... designed on an intuitive basis' to produce 'a state of helplessness and hopelessness, sunken in a well of despair.'"
Sources
- Baker, David B. (ed.). The Oxford Handbook of the History of Psychology. Oxford University Press (Oxford Library of Psychology), 2012. ISBN 978-0-19-536655-6
- Brock, Adrian C. (ed.). Internationalizing the History of Psychology. New York University Press, 2006. ISBN 978-0-8147-9944-4
- Chin, Robert, and Ai-li S. Chin. Psychological Research in Communist China: 1949–1966. Cambridge: M.I.T. Press, 1969. ISBN 978-0-262-03032-8
- Cina, Carol. "Social Science for Whom? A Structural History of Social Psychology." Doctoral dissertation, accepted by the State University of New York at Stony Brook, 1981.
- Cocks, Geoffrey. Psychotherapy in the Third Reich: The Göring Institute, second edition. New Brunswick, NJ: Transaction Publishers, 1997. ISBN 1-56000-904-7
- Forgas, Joseph P., Kipling D. Williams, & Simon M. Laham. Social Motivation: Conscious and Unconscious Processes. Cambridge University Press, 2005. ISBN 0-521-83254-3
- Gregory, Robert J. Psychological Testing: History, Principles, and Applications. Sixth edition. Boston: Allyn & Bacon (Pearson), 2011. ISBN 978-0-205-78214-7
- Guthrie, Robert. Even the Rat was White: A Historical View of Psychology. Second edition. Boston, Allyn and Bacon (Viacon), 1998. ISBN 0-205-14993-6
- Leahey, A History of Modern Psychology. Third Edition. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall (Pearson), 2001.
- Luria, A. R. (1973). The Working Brain: An Introduction to Neuropsychology. Translated by Basil Haigh. Basic Books. ISBN 0-465-09208-X
- Herman, Ellen. "Psychology as Politics: How Psychological Experts Transformed Public Life in the United States 1940–1970." Doctoral dissertation accepted by Brandeis University, 1993.
- Hock, Roger R. Forty Studies That Changed Psychology: Explorations Into the History of Psychological Research. Fourth edition. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall, 2002. ISBN 978-0-13-032263-0
- Kozulin, Alex. Psychology in Utopia: Toward a Social History of Soviet Psychology. Cambridge: MIT Press, 1984. ISBN 0-262-11087-3
- Morgan, Robert D., Tara L. Kuther, & Corey J. Habben. Life After Graduate School in Psychology: Insider's Advice from New Psychologists. New York: Psychology Press (Taylor & Francis Group), 2005. ISBN 1-84169-410-X
- Severin, Frank T. (ed.). Humanistic Viewpoints in Psychology: A Book of Readings. New York: McGraw Hill, 1965. ISBN
- Shah, James Y., and Wendi L. Gardner. Handbook of Motivation Science. New York: The Guilford Press, 2008. ISBN 978-1-59385-568-0
- Teo, Thomas. The Critique of Psychology: From Kant to Postcolonial Theory. New York: Springer, 2005. ISBN 978-0-387-25355-8
- Wallace, Edwin R., IV, & John Gach (eds.), History of Psychiatry and Medical Psychology; New York: Springer, 2008; ISBN 978-0-387-34708-0
- Weiner, Bernard. Human Motivation. Hoboken, NJ: Taylor and Francis, 2013. ISBN 978-0-8058-0711-0
- Weiner, Irving B. Handbook of Psychology. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons, 2003. ISBN 0-471-17669-9
- Volume 1: History of Psychology. Donald K. Freedheim, ed. ISBN 0-471-38320-1
- Volume 2: Research Methods in Psychology. John A. Schinka & Wayne F. Velicer, eds. ISBN 0-471-38513-1
- Volume 3: Biological Psychology. Michela Gallagher & Randy J. Nelson, eds. ISBN 0-471-38403-8
- Volume 4: Experimental Psychology. Alice F. Healy & Robert W. Proctor, eds. ISBN 0-471-39262-6
- Volume 8: Clinical Psychology. George Stricker, Thomas A. Widiger, eds. ISBN 0-471-39263-4
Further reading
- Badcock, Christopher R. (2015). "Nature-Nurture Controversy, History of". International Encyclopedia of the Social & Behavioral Sciences. pp. 340–344. doi:10.1016/B978-0-08-097086-8.03136-6. ISBN 978-0-08-097087-5.
- Cascio, Wayne F. (2015). "Industrial–Organizational Psychology: Science and Practice". International Encyclopedia of the Social & Behavioral Sciences. pp. 879–884. doi:10.1016/B978-0-08-097086-8.22007-2. ISBN 978-0-08-097087-5.
- Chryssochoou, Xenia (2015). "Social Psychology". International Encyclopedia of the Social & Behavioral Sciences. pp. 532–537. doi:10.1016/B978-0-08-097086-8.24095-6. ISBN 978-0-08-097087-5.
- Deakin, Nicholas (2015). "Philosophy, Psychiatry, and Psychology". International Encyclopedia of the Social & Behavioral Sciences. pp. 31–36. doi:10.1016/B978-0-08-097086-8.27049-9. ISBN 978-0-08-097087-5.
- Demetriou, Andreas (2015). "Intelligence in Cultural, Social and Educational Context". International Encyclopedia of the Social & Behavioral Sciences. pp. 313–322. doi:10.1016/B978-0-08-097086-8.92147-0. ISBN 978-0-08-097087-5.
- Gelso, Charles J. (2015). "Counseling Psychology". International Encyclopedia of the Social & Behavioral Sciences. pp. 69–72. doi:10.1016/B978-0-08-097086-8.21073-8. ISBN 978-0-08-097087-5.
- Henley, Tracy B. (2015). "Psychology, History of (Early Period)". International Encyclopedia of the Social & Behavioral Sciences. pp. 406–411. doi:10.1016/B978-0-08-097086-8.03235-9. ISBN 978-0-08-097087-5.
- Knowland, Victoria C.P.; Purser, Harry; Thomas, Michael S.C. (2015). "Cross-Sectional Methodologies in Developmental Psychology". International Encyclopedia of the Social & Behavioral Sciences. pp. 354–360. doi:10.1016/B978-0-08-097086-8.23235-2. ISBN 978-0-08-097087-5.
- Louw, Dap (2015). "Forensic Psychology". International Encyclopedia of the Social & Behavioral Sciences. pp. 351–356. doi:10.1016/B978-0-08-097086-8.21074-X. ISBN 978-0-08-097087-5.
- McWilliams, Spencer A. (2015). "Psychology, History of (Twentieth Century)". International Encyclopedia of the Social & Behavioral Sciences. pp. 412–417. doi:10.1016/B978-0-08-097086-8.03046-4. ISBN 978-0-08-097087-5.
- Pe-Pua, Rogelia (2015). "Indigenous Psychology". International Encyclopedia of the Social & Behavioral Sciences. pp. 788–794. doi:10.1016/B978-0-08-097086-8.24067-1. ISBN 978-0-08-097087-5.
- Peterson, Roger L.; Peterson, Donald R.; Abrams, Jules C.; Stricker, George; Ducheny, Kelly (2015). "Training in Clinical Psychology in the United States: Practitioner Model". International Encyclopedia of the Social & Behavioral Sciences. pp. 517–523. doi:10.1016/B978-0-08-097086-8.21086-6. ISBN 978-0-08-097087-5.
- Poortinga, Ype H. (2015). "Cross-Cultural Psychology". International Encyclopedia of the Social & Behavioral Sciences. pp. 311–317. doi:10.1016/B978-0-08-097086-8.24011-7. ISBN 978-0-08-097087-5.
- Spinath, Frank M.; Spinath, Birgit; Borkenau, Peter (2015). "Developmental Behavioral Genetics and Education". International Encyclopedia of the Social & Behavioral Sciences. pp. 320–325. doi:10.1016/B978-0-08-097086-8.92009-9. ISBN 978-0-08-097087-5.
- Smith, Edward E. (2015). "Cognitive Psychology: History". International Encyclopedia of the Social & Behavioral Sciences. pp. 103–109. doi:10.1016/B978-0-08-097086-8.03028-2. ISBN 978-0-08-097087-5.
- Staerklé, Christian (2015). "Political Psychology". International Encyclopedia of the Social & Behavioral Sciences. pp. 427–433. doi:10.1016/B978-0-08-097086-8.24079-8. ISBN 978-0-08-097087-5.
- Gelder, Mayou & Geddes (2005). Psychiatry. New York: Oxford University Press Inc.

