Krill
| Euphausiacea | |
|---|---|

| |
| A northern krill (Meganyctiphanes norvegica) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Subphylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Superorder: | |
| Order: | Euphausiacea Dana, 1852
|
| Families and genera | |
|
Euphausiidae
Bentheuphausiidae
| |
Krill is the common name given to the order Euphausiacea of shrimp-like marine crustaceans. Also known as euphausiids, these small invertebrates are found in all oceans of the world. The common name krill comes from the Norwegian word [krill] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) meaning "young fry of fish",[1] which is also often attributed to other species of fish.
Krill are considered an important trophic connection—near the bottom of the food chain—because they feed on phytoplankton and to a lesser extent zooplankton, converting these into a form suitable for many larger animals for whom krill makes up the largest part of their diet. In the Southern Ocean, one species, the Antarctic krill, Euphausia superba, makes up an estimated biomass of over 500,000,000 tonnes (490,000,000 long tons; 550,000,000 short tons), roughly twice that of humans. Of this, over half is eaten by whales, seals, penguins, squid and fish each year, and is replaced by growth and reproduction. Most krill species display large daily vertical migrations, thus providing food for predators near the surface at night and in deeper waters during the day.
Commercial fishing of krill is done in the Southern Ocean and in the waters around Japan. The total global harvest amounts to 150,000–200,000 tonnes (150,000–200,000 long tons; 170,000–220,000 short tons) annually, most of this from the Scotia Sea. Most of the krill catch is used for aquaculture and aquarium feeds, as bait in sport fishing, or in the pharmaceutical industry. In Japan and Russia, krill is also used for human consumption and is known as okiami (オキアミ)[1] in Japan.
Taxonomy
Krill belong to the large arthropod subphylum, the crustacea. The most familiar and largest group of crustaceans, the class Malacostraca, includes the superorder Eucarida comprising the three orders, Euphausiacea or krill, Decapoda (shrimp, lobsters, crabs), and the planktonic Amphionides.
The order Euphasiacea comprises two families, the more well known Euphausiidae, contains ten different genera with a total of 85 species. Of these, the genus Euphausia is the largest, with 31 species.[2] The lesser known family, the Bentheuphausiidae, has only one species, Bentheuphausia amblyops, a bathypelagic krill living in deep waters below 1,000 metres (3,300 ft). It is considered the most primitive living species of all krill.[3]
Well-known species of the Euphausiidae of commercial krill fisheries include Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba), Pacific krill (Euphausia pacifica) and Northern krill (Meganyctiphanes norvegica).[4]
Distribution
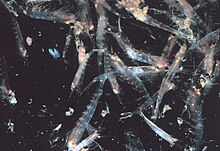
Krill occur worldwide in all oceans, although many individual species have endemic or neritic (i.e., coastal) restricted distributions. Bentheuphausia amblyops, a bathypelagic species, has a cosmopolitan distribution within its bathypelagic habitat.[5]
Species of the genus Thysanoessa occur in both the Atlantic and Pacific oceans.[6] The Pacific is home to Euphausia pacifica. Northern krill occur across the Atlantic from the Mediterranean Sea northward.
Species with neritic distibutions include the four species of the genus Nyctiphanes.[7] They are highly abundant along the upwelling regions of the California, Humboldt, Benguela, and Canarias current systems.[8][9][10] Another species having only neritic distribution is E. crystallorophias, which occurs only along the Antarctic coastline (and thus also is endemic to that region).[11]
Species with endemic distributions include Nyctiphanes capensis, which occurs only in the Benguela current,[7] E. mucronata in the Humboldt current,[12] and the six Euphausia species native to the Southern Ocean.
In the Antarctic, seven species are known,[13] one species of the genus Thysanoessa (T. macrura) and six of the genus Euphausia. The Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba) commonly lives at depths of as much as 100 m (330 ft),[14] whereas ice krill (Euphausia crystallorophias) have been recorded at a depth of 4,000 m (13,100 ft), though they commonly live at depths of at most 300–600 m (1,000–2,000 ft).[15] Both are found at latitudes south of 55° S, with E. crystallorophias dominating south of 74° S[16] and in regions of pack ice. Other species known in the Southern Ocean are E. frigida, E. longirostris, E. triacantha and E. vallentini.[17]
Anatomy and morphology
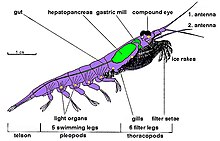
Krill are crustaceans and have a chitinous exoskeleton made up of three segments: the cephalon (head), the thorax, and the abdomen. The first two segments are fused into one segment, the cephalothorax. This outer shell of krill is transparent in most species. Krill feature intricate compound eyes; some species can adapt to different lighting conditions through the use of screening pigments.[18] They have two antennae and several pairs of thoracic legs called pereiopods or thoracopods, so named because they are attached to the thorax; their number varies among genera and species. These thoracic legs include the feeding legs and the grooming legs. Additionally all species have five swimming legs called pleopods or "swimmerets", very similar to those of a lobster or freshwater crayfish. Most krill are about 1–2 centimetres (0.4–0.8 in) long as adults, a few species grow to sizes on the order of 6–15 centimetres (2.4–5.9 in). The largest krill species is the bathypelagic Thysanopoda spinicauda.[19] Krill can be easily distinguished from other crustaceans such as true shrimp by their externally visible gills.[20]

Many krill are filter feeders:[9] their frontmost appendages, the thoracopods, form very fine combs with which they can filter out their food from the water. These filters can be very fine indeed in those species (such as Euphausia spp.) that feed primarily on phytoplankton, in particular on diatoms, which are unicellular algae. However, it is believed that krill are mostly omnivorous.[21] A few species are carnivorous, preying on small zooplankton and fish larvae.[22]
Except for Bentheuphausia amblyops, krill are bioluminescent animals having organs called photophores that can emit light. The light is generated by an enzyme-catalysed chemiluminescence reaction, wherein a luciferin (a kind of pigment) is activated by a luciferase enzyme. Studies indicate that the luciferin of many krill species is a fluorescent tetrapyrrole similar but not identical to dinoflagellate luciferin[23] and that the krill probably do not produce this substance themselves but acquire it as part of their diet, which contains dinoflagellates.[24] Krill photophores are complex organs with lenses and focusing abilities, and they can be rotated by muscles.[25] The precise function of these organs is as yet unknown; they might have a purpose in mating, social interaction or orientation. Some researchers (e.g., Lindsay & Latz and Johnsen) have proposed that krill use the light as a form of counter-illumination camouflage to compensate their shadow against the ambient light from above to make themselves less visible to predators from below.[26][27]
Behaviour
Most krill are swarming animals; the sizes and densities of such swarms vary greatly depending on the species and the region. For Euphausia superba, there have been reports of swarms of up to 10,000 to 60,000 individuals per cubic metre.[28][29] Swarming is a defensive mechanism, confusing smaller predators that would like to pick out single individuals. Krill typically follow a diurnal vertical migration. They spend the day at greater depths and rise during the night toward the surface. The deeper they go, the more they reduce their activity,[30] apparently to reduce encounters with predators and to conserve energy. Some species (e.g., Euphausia superba, E. pacifica, E. hanseni, Pseudeuphausia latifrons, and Thysanoessa spinifera) also form surface swarms during the day for feeding and reproductive purposes even though such behaviour is dangerous because it makes them extremely vulnerable to predators.[31]

Dense swarms may elicit a feeding frenzy among fish, birds and mammal predators, especially near the surface. When disturbed, a swarm scatters, and some individuals have even been observed to moult instantaneously, leaving the exuvia behind as a decoy.[32]
Krill normally swim at pace of 5–10 cm/s (2–3 body lengths per second),[33] using their swimmerets for propulsion. Their larger migrations are subject to the currents in the ocean. When in danger, they show an escape reaction called lobstering—flicking their caudal structures, the telson and the uropods, they move backwards through the water relatively quickly, achieving speeds in the range of 10 to 27 body lengths per second, which for large krill such as E. superba means around 0.8 m/s (3 ft/s).[34] Their swimming performance has led many researchers to classify adult krill as micro-nektonic life-forms, i.e., small animals capable of individual motion against (weak) currents. Larval forms of krill are generally considered zooplankton.[4]
Ecology and life history

Krill are an important element of the food chain. Antarctic krill feed directly on phytoplankton, converting the primary production energy into a form suitable for consumption by larger animals that cannot feed directly on the minuscule algae. Some species like the Northern krill have a relatively small filtering basket and actively hunt for copepods and larger zooplankton.[22] Many animals feed on krill, ranging from smaller animals like fish or penguins to larger ones like seals and even baleen whales.[35]
Disturbances of an ecosystem resulting in a decline in the krill population can have far-reaching effects. During a coccolithophore bloom in the Bering Sea in 1998,[36] for instance, the diatom concentration dropped in the affected area. Krill cannot feed on the smaller coccolithophores, and consequently the krill population (mainly E. pacifica) in that region declined sharply. This in turn affected other species: the shearwater population dropped, and the incident was even thought to have been a reason for salmon not returning to the rivers of western Alaska that season.[37]
Other factors besides predation and food availability can influence the mortality rate in krill populations. As temperatures have risen over the past couple decades, Antarctic sea ice has melted. In this way, climate change poses a threat to krill populations as they feed on algae beneath the ice.[38] There are several single-celled endoparasitoidic ciliates of the genus Collinia that can infect different species of krill and cause massive decline in affected populations. Such diseases have been reported for Thysanoessa inermis in the Bering Sea and also for E. pacifica, Thysanoessa spinifera, and T. gregaria off the North American Pacific coast.[39] There are also some ectoparasites of the family Dajidae (epicaridean isopods) that afflict krill (and also shrimp and mysids); one such parasite is Oculophryxus bicaulis, which has been found on the krill Stylocheiron affine and S. longicorne. It attaches itself to the eyestalk of the animal and sucks blood from its head; it is believed that it inhibits the reproduction of its host, as none of the afflicted animals found reached maturity.[40]
Life history

The general life cycle of krill has been the subject of several studies (e.g., Gurney 1942[41] and Mauchline & Fisher 1969[9]) performed on a variety of species and is thus relatively well understood, although there are minor variations in detail from species to species. After krill hatch from the egg, they go through several larval stages called the nauplius, pseudometanauplius, metanauplius, calyptopsis, and furcilia stages, each of which is sub-divided into several sub-stages. The pseudometanauplius stage is exclusive to species that lay their eggs within an ovigerous sac: so-called "sac-spawners". The larvae grow and moult multiple times as they develop, shedding their rigid exoskeleton whenever it becomes too small and growing a new one. Smaller animals moult more frequently than larger ones. Up through the metanauplius stage, the larvae are nourished by yolk reserves within their body. Only by the calyptopsis stages has differentiation progressed far enough for them to develop a mouth and a digestive tract, and they begin to feed upon phytoplankton. By that time, the larvae must have reached the photic zone, the upper layers of the ocean where algae flourish, for their yolk reserves are exhausted by then and they would starve otherwise. During the furcilia stages, segments with pairs of swimmerets are added, beginning at the frontmost segments. Each new pair becomes functional only at the next moult. The number of segments added during any one of the furcilia stages may vary even within one species depending on environmental conditions.[42] After the final furcilia stage, the krill emerges in a shape similar to an adult, but it is still an immature juvenile, that only subsequently develops gonads and matures.[43]
During the mating season, which varies depending on the species and the climate, the male deposits a sperm sack at the genital opening (named thelycum) of the female. The females can carry several thousand eggs in their ovary, which may then account for as much as one third of the animal's body mass.[44] Krill can have multiple broods in one season, with interbrood periods in the order of days.[10][45]

There are two types of spawning mechanism.[10] The 57 species of the genera Bentheuphausia, Euphausia, Meganyctiphanes, Thysanoessa, and Thysanopoda are "broadcast spawners": the female releases the fertilised eggs into the water, where they usually sink into deeper waters, disperse, and are on their own. These species generally hatch in the nauplius 1 stage, but have recently been discovered to hatch sometimes as metanauplius or even as calyptopis stages.[46] The remaining 29 species of the other genera are "sac spawners", where the female carries the eggs with her, attached to the rearmost pairs of thoracopods until they hatch as metanauplii, although some species like Nematoscelis difficilis may hatch as nauplius or pseudometanauplius.[47]
Some high-latitude species of krill can live for more than six years (e.g., Euphausia superba); others, such as the mid-latitude species Euphausia pacifica, live for only two years.[4] Subtropical or tropical species' longevity is still shorter, e.g., Nyctiphanes simplex, which usually lives for only six to eight months.[48]
Moulting occurs whenever the animal outgrows its rigid exoskeleton. Young animals, growing faster, moult more often than older and larger ones. The frequency of moulting varies widely from species to species and is, even within one species, subject to many external factors such as the latitude, the water temperature, and the availability of food. The subtropical species Nyctiphanes simplex, for instance, has an overall inter-moult period in the range of two to seven days: larvae moult on the average every four days, while juveniles and adults do so on average every six days. For E. superba in the Antarctic sea, inter-moult periods ranging between 9 and 28 days depending on the temperature between −1 and 4 °C (30 and 39 °F) have been observed, and for Meganyctiphanes norvegica in the North Sea the inter-moult periods range also from 9 and 28 days but at temperatures between 2.5 and 15 °C (36.5 and 59.0 °F).[49] E. superba is able to reduce its body size when there is not enough food available, moulting also when its exoskeleton becomes too large.[50] Similar shrinkage has also been observed for E. pacifica, a species occurring in the Pacific Ocean from polar to temperate zones, as an adaptation to abnormally high water temperatures. Shrinkage has been postulated for other temperate-zone species of krill as well.[51]
Economy

Krill has been harvested as a food source for humans (okiami) and domesticated animals since the 19th century, in Japan maybe even earlier. Large-scale fishing developed only in the late 1960s and early 1970s, and now occurs only in Antarctic waters and in the seas around Japan. Historically, the largest krill fishery nations were Japan and the Soviet Union, or, after the latter's dissolution, Russia and Ukraine. A peak in krill harvest had been reached in 1983 with more than 528,000 tonnes in the Southern Ocean alone (of which the Soviet Union produced 93%). In 1993, two events led to a drastic decline in krill production: first, Russia abandoned its operations, and second, the Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources (CCAMLR) defined maximum catch quotas for a sustainable exploitation of Antarctic krill. The annual catch in Antarctic waters seems to have stabilised around 100,000 tonnes of krill, which is roughly one fiftieth of the CCAMLR catch quota.[52] The main limiting factor is probably the high cost associated with Antarctic operations, although there are some political and legal issues as well.[53] The fishery around Japan appears to have saturated at some 70,000 tonnes.[54]
Experimental small-scale harvesting is being carried out in other areas, for example, fishing for Euphausia pacifica off British Columbia and harvesting Meganyctiphanes norvegica, Thysanoessa raschii and Thysanoessa inermis in the Gulf of St. Lawrence. These experimental operations produce only a few hundred tonnes of krill per year. Nicol & Foster consider it unlikely that any large-scale harvesting operations in these areas will be started due to opposition from local fishing industries and conservation groups.[54]
Krill tastes salty and somewhat stronger than shrimp. For mass-consumption and commercially prepared products they must be peeled, because their exoskeleton contains fluorides, which are toxic in high concentrations.[55] There is a small but growing market for krill oil as a dietary supplement ingredient. Two clinical trials have been published; tests included lipid lowering, arthritis pain and function, and C-reactive protein.[56][57]
Footnotes
^ The scientific name Euphausiacea in Japanese is okiami moku (オキアミ目).
References
- ^ "Krill". Online Etymology Dictionary. Retrieved 22 June 2010.
- ^ "Euphausiacea". Integrated Taxonomic Information System.
- ^ E. Brinton (1962). "The distribution of Pacific euphausiids". Bull. Scripps Inst. Oceanogr. 8 (2): 51–270.
- ^ a b c Nicol, S.; Endo, Y.: "Krill fisheries: Development, management and ecosystem implications", Aquat. Living Resour. 12, pp. 105–120, 1999. Cite error: The named reference "nicol" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ^ Torres and Childress (1985). "Respiration and chemical composition of the bathypelagic euphausiid Bentheuphausia amblyops". Marine Biology. 87 (3): 267–272.
{{cite journal}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Check date values in:|accessdate=(help); Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ World Register of Marine Species: Thysanoessa, plus the entries at WoRMS for all the species. Retrieved 2010-06-03.
- ^ a b D'Amato, M.E. et al.: "Molecular dating and biogeography of the neritic krill Nyctiphanes", in Marine Biology vol. 155, no. 2, pp. 243-247, August 2008.
- ^ World Register of Marine Species: Nyctiphanes, plus the entries at WoRMS for the four species. Retrieved 2010-06-03.
- ^ a b c J. Mauchline & L. R. Fisher (1969). "The biology of euphausiids". Advances in Marine Biology. 7.
- ^ a b c Gómez-Gutiérrez, J.; Robinson, C. J.: "Embryonic, early larval development time, hatching mechanism and interbrood period of the sac-spawning euphausiid Nyctiphanes simplex Hansen", Journal of Plankton Research 27(3), 2005; pp. 279–295; doi:10.1093/plankt/fbi003. Retrieved 2010-06-04.
- ^ Jarman, S.N. et al.: "Genetic differentiation in the Antarctic coastal krill Euphausia crystallorophias", in Heredity (2002) 88, pp. 280–287.
- ^ Escribano, R. et al.: "Distribution of Euphausia mucronata at the upwelling area of Peninsula Mejillones, northern Chile: the influence of the oxygen minimum layer", Sci. Mar. 64(1), pp. 69-77, 2000.
- ^ P. Brueggeman. "Euphausia crystallorophias". Underwater Field Guide to Ross Island & McMurdo Sound, Antarctica. University of California, San Diego.
- ^ "Krill, Euphausia superba". MarineBio.org. Retrieved 25 February 2009.
- ^ J. A. Kirkwood (1984). "A Guide to the Euphausiacea of the Southern Ocean". ANARE Research Notes. 1: 1–45.
- ^ A. Sala, M. Azzali & A. Russo (2002). "Krill of the Ross Sea: distribution, abundance and demography of Euphausia superba and Euphausia crystallorophias during the Italian Antarctic Expedition (January–February 2000)". Scientia Marina. 66 (2): 123–133.
- ^ G. W. Hosie, M. Fukuchi & S. Kawaguchi (2003). "Development of the Southern Ocean Continuous Plankton Recorder survey" (PDF). Progress in Oceanography. 58: 263–283. doi:10.1016/j.pocean.2003.08.007.
- ^ E. Gaten. "Meganyctiphanes norvegica". University of Leicester. Retrieved 25 February 2009.
- ^ E. Brinton (1953). "Thysanopoda spinicauda, a new bathypelagic giant euphausiid crustacean, with comparative notes on T. cornuta and T. egregia". Journal of the Washington Academy of Sciences. 43: 408–412.
- ^ Tasmanian Aquaculture & Fisheries Institute: Euphausiacea. Retrieved 2010-06-06.
- ^ Cripps, G. C.; Atkinson, A.: "Fatty acid composition as an indicator of carnivory in Antarctic krill, Euphausia superba", Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 57(S3), pp. 31–37; 2000.
- ^ a b Saether, O. et al.: "Lipids of North Atlantic krill", in Journal of Lipid Research vol. 27 (1986), pp. 274–285.
- ^ O. Shimomura (1995). "The roles of the two highly unstable components F and P involved in the bioluminescence of euphausiid shrimps". Journal of Bioluminescence and Chemiluminescence. 10 (2): 91–101. doi:10.1002/bio.1170100205. PMID 7676855.
- ^ J. C. Dunlap, J. W. Hastings & O. Shimomura (1980). "Crossreactivity between the light-emitting systems of distantly related organisms: novel type of light-emitting compound". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 77 (3): 1394–1397. doi:10.1073/pnas.77.3.1394.
- ^ P. J. Herring, E. A. Widder (2001). "Bioluminescence in Plankton and Nekton". In J. H. Steele, S. A. Thorpe & K. K. Turekian (ed.). Encyclopedia of Ocean Science. Vol. 1. Academic Press, San Diego. pp. 308–317. ISBN 0-12-227430-X.
- ^ S. M. Lindsay & M. I. Latz (1999). Experimental evidence for luminescent countershading by some euphausiid crustaceans. American Society of Limnology and Oceanography (ASLO) Aquatic Sciences Meeting. Santa Fe.
- ^ S. Johnsen (2005). "The Red and the Black: bioluminescence and the color of animals in the deep sea" (PDF). Integrative and Comparative Biology. 4 (2): 234–246.
- ^ U. Kils & P. Marshall (1995). "Der Krill, wie er schwimmt und frisst – neue Einsichten mit neuen Methoden ("The Antarctic krill – how it swims and feeds – new insights with new methods")". In I. Hempel & G. Hempel (ed.). Biologie der Polarmeere – Erlebnisse und Ergebnisse (Biology of the Polar Oceans Experiences and Results). Fischer Verlag. pp. 201–210. ISBN 3-334-60950-2.
- ^ R. Piper (2007). Extraordinary Animals: An Encyclopedia of Curious and Unusual Animals. Greenwood Press. ISBN 0313339228.
- ^ J. S. Jaffe, M. D. Ohmann & A. de Robertis (1999). "Sonar estimates of daytime activity levels of Euphausia pacifica in Saanich Inlet" (PDF). Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences. 56: 2000–2010. doi:10.1139/cjfas-56-11-2000.
- ^ Howard, D.: "Krill", pp. 133–140 in Karl, H.A. et al. (eds): Beyond the Golden Gate – Oceanography, Geology, Biology, and Environmental Issues in the Gulf of the Farallones, USGS Circular 1198, 2001. URLs last accessed 2010-06-04.
- ^ D. Howard. "Krill in Cordell Bank National Marine Sanctuary". NOAA. Retrieved 15 June 2005.
- ^ David A. Demer & Stéphane G. Conti (2005). "New target-strength model indicates more krill in the Southern Ocean". ICES Journal of Marine Science: Journal du Conseil. 62 (1): 25–32. doi:10.1016/j.icesjms.2004.07.027.
- ^ U. Kils (1982). "Swimming behavior, swimming performance and energy balance of Antarctic krill Euphausia superba". BIOMASS Scientific Series 3, BIOMASS Research Series: 1–122.
- ^ Schramm, M. J.: Tiny Krill: Giants in Marine Food Chain, NOAA National Marine Sanctuary Program, 2007-10-10. Retrieved 2010-06-04.
- ^ J. Weier (1999). "Changing currents color the Bering Sea a new shade of blue". NOAA Earth Observatory. Retrieved 15 June 2005.
- ^ R. D. Brodeur, G. H. Kruse; et al. (1998). Draft Report of the FOCI International Workshop on Recent Conditions in the Bering Sea. NOAA. pp. 22–26.
{{cite book}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help) - ^ R. Dornin (6 July 1997). "Antarctic krill populations decreasing". CNN.
- ^ J. Roach (17 July 2003). "Scientists discover mystery krill killer". National Geographic News.. See also the base article: J. Gómez-Gutiérrez, W. T. Peterson, A. de Robertis, R. D. Brodeur (2003). "Mass mortality of krill caused by parasitoid ciliates". Science. 301 (5631): 339. doi:10.1126/science.1085164.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ J. D. Shields & J. Gómez-Gutiérrez (1996). "Oculophryxus bicaulis, a new genus and species of dajid isopod parasitic on the euphausiid Stylocheiron affine Hansen". International Journal for Parasitology. 26 (3): 261–268. doi:10.1016/0020-7519(95)00126-3.
- ^ R. Gurney (1942). "Larvae of decapod crustacea". Royal Society Publications. 129.
- ^ M. D. Knight (1984). "Variation in larval morphogenesis within the Southern California Bight population of Euphausia pacifica from Winter through Summer, 1977–1978" (PDF). CalCOFI Report. XXV.
- ^ FAO: Species factsheet: Euphausia superba. Retrieved 2010-06-04.
- ^ R. M. Ross & L. B. Quetin (1986). "How productive are Antarctic krill?". BioScience. 36: 264–269. doi:10.2307/1310217.
- ^ Cuzin-Roudy, J. "Seasonal reproduction, multiple spawning, and fecundity in northern krill, Meganyctiphanes norvegica, and Antarctic krill, Euphausia superba", Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 57(S3), 200, pp. 6–15.
- ^ J. Gómez-Gutiérrez (2002). "Hatching mechanism and delayed hatching of the eggs of three broadcast spawning euphausiid species under laboratory conditions". Journal of Plankton Research. 24 (12): 1265–1276. doi:10.1093/plankt/24.12.1265.
- ^ E. Brinton, M. D. Ohman, A. W. Townsend, M. D. Knight & A. L. Bridgeman (2000). Euphausiids of the World Ocean. World Biodiversity Database CD-ROM Series, Springer Verlag. ISBN 3-540-14673-3.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ J. G. Gómez (1995). "Distribution patterns, abundance and population dynamics of the euphausiids Nyctiphanes simplex and Euphausia eximia off the west coast of Baja California, Mexico" (PDF). Marine Ecology Progress Series. 119: 63–76.
- ^ F. Buchholz (2003). "Experiments on the physiology of Southern and Northern krill, Euphausia superba and Meganyctiphanes norvegica, with emphasis on moult and growth – a review". Marine and Freshwater Behaviour and Physiology. 36 (4): 229–247. doi:10.1080/10236240310001623376.
- ^ H.–C. Shin & S. Nicol (2002). "Using the relationship between eye diameter and body length to detect the effects of long-term starvation on Antarctic krill Euphausia superba". Marine Ecology Progress Series. 239: 157–167. doi:10.3354/meps239157.
- ^ B. Marinovic, & M. Mangel (1999). "Krill can shrink as an ecological adaptation to temporarily unfavourable environments" (PDF). Ecology Letters. 2: 338–343.
- ^ "Harvested species: krill (Eupausia superba)". Convention for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources. Retrieved 20 June 2005.
- ^ M. Wright (1987). "The Ownership of Antarctica, its Living and Mineral Resources". Journal of Law and the Environment.
- ^ a b S. Nicol & J. Foster (2003). "Recent trends in the fishery for Antarctic krill". Aquatic Living Resources. 16: 42–45. doi:10.1016/S0990-7440(03)00004-4.
- ^ K. Haberman (26 February 1997). "Answers to miscellaneous questions about krill". NASA. Retrieved 6 September 2007.
- ^ Bunea, R.; El Farrah, K.; Deutsch, L.: "Evaluation of the effects of Neptune Krill Oil on the clinical course of hyperlipidemia", Altern Med Rev., vol. IX, 2004; pp. 420–428.
- ^ Deutsch, L: "Evaluation of the effect of Neptune Krill Oil on chronic inflammation and arthritic symptoms"., J Am Coll Nutr., vol. 26, 2007; pp. 39–48.
Further reading
- Boden, Brian P.; Johnson, Martin W.; Brinton, Edward: Euphausiacea (Crustacea) of the North Pacific. Bulletin of the Scripps Institution of Oceanography. Volume 6 Number 8, 1955.
- Brinton, Edward: Euphausiids of Southeast Asian waters. Naga Report volume 4, part 5. La Jolla: University of California, Scripps Institution of Oceanography, 1975.
- Conway, D. V. P.; White, R. G.; Hugues-Dit-Ciles, J.; Galienne, C. P.; Robins, D. B.: Guide to the coastal and surface zooplankton of the South-Western Indian Ocean, Order Euphausiacea, Occasional Publication of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom No. 15, Plymouth, UK, 2003.
- Everson, I. (ed.): Krill: biology, ecology and fisheries. Oxford, Blackwell Science; 2000. ISBN 0-632-05565-0.
- Mauchline, J.: Euphausiacea: Adults, Conseil International pour l'Exploration de la Mer, 1971. Identification sheets for adult krill with many line drawings. PDF file, 2 Mb.
- Mauchline, J.: Euphausiacea: Larvae, Conseil International pour l'Exploration de la Mer, 1971. Identification sheets for larval stages of krill with many line drawings. PDF file, 3 Mb.
- Tett, P.: The biology of Euphausiids, lecture notes from a 2003 course in Marine Biology from Napier University. Last accessed 18 July 2005.
- Tett, P.: Bioluminescence, lecture notes from the 1999/2000 edition of that same course. Last accessed 18 July 2005.
External links
![]() Media related to Krill at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Krill at Wikimedia Commons
![]() Data related to Euphausia at Wikispecies
Data related to Euphausia at Wikispecies
- Webcam of Krill Aquarium at Australian Antarctic Division
 The dictionary definition of krill at Wiktionary
The dictionary definition of krill at Wiktionary- 'Antarctic Energies' animation by Lisa Roberts



