Caligula
| Caligula | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Emperor of the Roman Empire | |||||
 Bust of Caligula (Ny Carlsberg Glyptotek) | |||||
| Reign | 16 March, AD 37 – 24 January, AD 41 | ||||
| Predecessor | Tiberius | ||||
| Successor | Claudius | ||||
| Burial | Rome, Italy | ||||
| Spouse | 1) Junia Claudilla, 33–34 2) Livia Orestilla, 37 or 38 3) Lollia Paulina, 38 4) Milonia Caesonia, ?–41 | ||||
| Issue | Julia Drusilla Tiberius Gemellus (adoptive) | ||||
| |||||
| Dynasty | Julio-Claudian | ||||
| Father | Germanicus | ||||
| Mother | Agrippina the Elder | ||||
Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus Germanicus (31 August AD 12 – 24 January AD 41), more commonly known by his agnomen Caligula (Template:Pron-en), was the third Roman Emperor, reigning from 16 March 37 until his assassination on 24 January 41. Caligula was a member of the house of rulers conventionally known as the Julio-Claudian dynasty.
Caligula's father, Germanicus, the nephew and adopted son of emperor Tiberius, was a very successful general and one of Rome's most beloved public figures. The young Gaius earned his nickname Caligula (the diminutive form of caliga) meaning "little [soldier's] boot", given to him by Roman soldiers, while accompanying his father on military campaigns in Germania. When Germanicus died in Antioch in AD 19, his mother Agrippina the Elder returned to Rome with her six children, where she became entangled in an increasingly bitter feud with Tiberius. This conflict eventually led to the destruction of her family, with Caligula as the sole male survivor. Unscathed by the deadly intrigues, and seemingly unmoved by the fate of his closest relatives, Caligula accepted the invitation to join the emperor on the island of Capri in AD 31, where Tiberius himself had withdrawn in AD 26. At the death of Tiberius, on 16 March AD 37, Caligula succeeded his great-uncle and adoptive grandfather.
There are few surviving sources on Caligula's reign, although he is described as a noble and moderate ruler during the first two years of his rule. After this, the sources focus upon his cruelty, extravagance, and sexual perversity, presenting him as an insane tyrant, leading many to believe he had neurosyphylis. While the reliability of these sources has been difficult to assess, what is known is that during his brief reign, Caligula worked to increase the authority of the princeps, possibly contemplating the introduction of an authoritarian system of an eastern type. He directed much of his attention to ambitious construction projects, notoriously luxurious dwellings for himself, but also two new aqueducts for the city of Rome (Aqua Claudia and Anio Novus). However, these are primarily associated with his successor Claudius, who brought these projects to completion. Caligula also annexed Mauretania.
On 24 January AD 41, Caligula was assassinated as the result of a conspiracy involving officers of the Praetorian Guard as well as members of the Roman Senate and of the imperial court. The conspirators' attempt to use the opportunity to restore the Roman Republic was thwarted, as the same day the Praetorian Guard declared Caligula's uncle and second cousin once removed Claudius emperor in his place.
Early life
Family
| Roman imperial dynasties | ||
|---|---|---|
| Julio-Claudian dynasty | ||
| Chronology | ||
|
27 BC – AD 14 |
||
|
AD 14–37 |
||
|
AD 37–41 |
||
|
AD 41–54 |
||
|
AD 54–68 |
||
|
||
Caligula was born as Gaius Julius Caesar Germanicus on 31 August AD 12, at the resort of Antium.[1] He was the third of six surviving children born to Germanicus and his second cousin Agrippina the Elder.[2] Gaius' brothers were Nero and Drusus.[2] His sisters were Julia Livilla, Julia Drusilla and Agrippina the Younger (Agrippina would be the fourth wife of Claudius, and through her Caligula was a maternal uncle to the Emperor Nero).[2] Gaius was also nephew to Claudius (the future emperor).[3]
Agrippina the Elder was the daughter of Marcus Vipsanius Agrippa and Julia the Elder.[2] She was also a granddaughter of Augustus and Scribonia.[2]
Youth and early career


As a boy of just two or three, Gaius accompanied his father, Germanicus, on campaigns in the north of Germania.[4] The soldiers were amused that Gaius was dressed in a miniature soldier's uniform, including boots and armor.[4] He was soon given his nickname Caligula, meaning "little (soldier's) boot" in Latin, after the small boots he wore as part of his uniform.[5] Gaius, though, reportedly grew to dislike this nickname.[6]
Suetonius reports that Germanicus was poisoned in Syria by an agent of Tiberius who viewed Germanicus as a political rival.[7]
After the death of his father, Caligula lived with his mother until relations between her and Tiberius deteriorated.[8] Tiberius would not allow Agrippina to remarry for fear her husband would be a rival.[9] Agrippina and Caligula's brother, Nero, were banished in AD 29 on charges of treason.[10][11]
The adolescent Caligula was then sent to live first with his great-grandmother, and Tiberius' mother, Livia.[8] Following Livia's death, he was sent to live with his grandmother Antonia.[8] In AD 30, his brother, Drusus Caesar, was imprisoned on charges of treason and his brother Nero died in exile from either starvation or suicide.[11][12] Suetonius writes that after the banishment of his mother and brothers, Caligula and his sisters were nothing more than prisoners of Tiberius under close watch of soldiers.[13]
In AD 31, Caligula was remanded to the personal care of Tiberius on Capri, where he lived for six years.[8] To the surprise of many, Caligula was spared by Tiberius.[14] According to historians, Caligula was an excellent natural actor and, recognizing danger, hid all his resentment towards Tiberius.[8][15] An observer said of Caligula, "Never was there a better servant or a worse master!"[8][15]
In AD 33, Tiberius gave Caligula an honorary quaestorship, a position he held until his reign.[16] Meanwhile, both Caligula's mother, and his brother Drusus, died in prison.[17][18] Caligula was briefly married to Junia Claudilla in 33, though she died in childbirth the following year.[19] Caligula spent time befriending the Praetorian Prefect, Naevius Sutorius Macro, an important ally.[19] Macro spoke well of Caligula to Tiberius, attempting to quell any ill will or suspicion the Emperor felt towards Caligula.[20]
In AD 35, Caligula was named joint heir to Tiberius' estate along with Tiberius Gemellus.[21]
Emperor
Early reign

When Tiberius died on 16 March AD 37, his estate and the titles of the Principate were left to Caligula and Tiberius' own grandson, Gemellus, who were to serve as joint heirs. Despite Tiberius being 77 and on his death bed, some ancient historians still suppose he was murdered.[19][22] Tacitus writes that the Praetorian Prefect, Macro, smothered Tiberius with a pillow to hasten Caligula's accession, much to the joy of the Roman people,[22] while Suetonius writes that Caligula may have carried out the killing, though this is not recorded by any other ancient historian.[19] Philo, a contemporary of Tiberius's reign, and Josephus, record Tiberius dying a natural death.[23] Backed by Macro, Caligula had Tiberius’ will nullified with regards to Gemellus on grounds of insanity, but otherwise carried out Tiberius' wishes.[24]
Caligula accepted the powers of the Principate as conferred by the Senate and entered Rome on 28 March amid a crowd that hailed him as "our baby" and "our star," among other nicknames.[25] Caligula is described as the first emperor who was admired by everyone in "all the world, from the rising to the setting sun."[26] Caligula was loved by many for being the beloved son of the popular Germanicus,[25] but also because he was not Tiberius.[27] It was also said by Suetonius that over 160,000 animals were sacrificed during three months of public rejoicing to usher in his reign.[28][29] Philo describes the first seven months of Caligula's reign as completely blissful.[30]
Caligula's first acts were said to be generous in spirit, though many were political in nature.[24] To gain support, he granted bonuses to those in the military including the Praetorian Guard, city troops and the army outside of Italy.[24] He destroyed Tiberius' treason papers, declared that treason trials were a thing of the past and recalled exiles.[31] He helped those who had been harmed by the Imperial tax system, banished certain sexual deviants, and put on lavish spectacles for the public, such as gladiator battles.[32][33] Caligula also collected and brought back the bones of his mother and of his brothers and deposited their remains in the tomb of Augustus.[34]
Illness, conspiracies and a change in attitude
Following an auspicious start to his reign, Caligula fell seriously ill in October AD 37. Philo is the main historian to describe this illness,[35] though Cassius Dio mentions it in passing.[36] Philo states that Caligula's increased taking of warm baths, sex, and the consumption of alcohol and lavish meals after becoming emperor caused him to become ill.[37] It was said that the entire empire was paralyzed with sadness and sympathy over Caligula’s affliction.[38] Caligula completely recovered from this illness, but Philo highlights Caligula's near-death experience as a turning point in his reign.[39] Josephus characterizes Caligula as a noble and moderate ruler for the first two years of his rule before a turn for the worse occurred.[40]
Shortly after recovering from his illness, Caligula had several loyal individuals killed who had promised their lives for his in the event of a recovery.[41] Caligula had his wife banished and his father-in-law, Marcus Silanus, and his cousin, Tiberius Gemellus, were forced to commit suicide.[41][42]
Philo states Gemellus, in line to become emperor, plotted against Caligula while he was ill.[43] Silanus, prior to killing himself, was formally put on trial by Caligula.[44] Julius Graecinus was ordered to prosecute Silanus, but refused and was executed as well.[44] It is unknown if the plans of Gemellus and Silanus were related or separate. Suetonius considers these plots nothing more than Caligula's imagination.[45]
Public reform

In AD 38, Caligula focused his attention on political and public reform. He published the accounts of public funds, which had not been made public during the reign of Tiberius. He aided those who lost property in fires, abolished certain taxes, and gave out prizes to the public at gymnastic events. He also allowed new members into the equestrian and senatorial orders.[46]
Perhaps most significantly, he restored the practice of democratic elections.[47] Cassius Dio said that this act "though delighting the rabble, grieved the sensible, who stopped to reflect, that if the offices should fall once more into the hands of the many ... many disasters would result".[48]
During the same year, though, Caligula also was criticized for executing people without full trials and for forcing his helper Macro to commit suicide.[36]
Financial crisis and famine
According to Cassius Dio, a financial crisis emerged in AD 39.[36] Suetonius places the beginning of this crisis in 38.[49] Caligula’s political payments for support, generosity and extravagance had exhausted the state’s treasury. Ancient historians state that Caligula began falsely accusing, fining and even killing individuals for the purpose of seizing their estates.[50] A number of other desperate measures by Caligula are described by historians. In order to gain funds, Caligula asked the public to lend the state money.[51] Caligula levied taxes on lawsuits, marriage and prostitution.[52] Caligula began auctioning the lives of the gladiators at shows.[50][53] Wills that left items to Tiberius were interpreted now to leave the items to Caligula.[54] Centurions who had acquired property during plundering were forced to turn over spoils to the state.[54] The current and past highway commissioners were accused of incompetence and embezzlement and forced to repay money.[54]

A brief famine of an unknown size occurred, perhaps caused by this financial crisis, according to Suetonius due to public carriages being seized by Caligula,[50] according to Seneca because grain imports were disturbed by Caligula using boats for a pontoon bridge.[55]
Construction
Despite financial difficulties, Caligula embarked on a number of construction projects during his reign. Some were for the public good, while others were for himself.
Josephus describes as Caligula's greatest contribution to have improved the harbours at Rhegium and Sicily, there by allowing grain imports from Egypt to increase.[56] These improvements may have been made in response to the famine.[citation needed]
Caligula completed the temple of Augustus and the theatre of Pompey and began an amphitheatre beside the Saepta.[57] He also had the imperial palace expanded.[58] He began the aqueducts Aqua Claudia and Anio Novus, which Pliny the Elder considered engineering marvels.[59] He built a large racetrack known as the circus of Gaius and Nero and had an Egyptian obelisk (now known as the Vatican Obelisk) transported by sea and erected in the middle of Rome.[60] At Syracuse, he repaired the city walls and the temples of the gods.[57] He had new roads built and pushed to keep roads in good condition.[61] He had planned to rebuild the palace of Polycrates at Samos, to finish the temple of Didymaean Apollo at Ephesus and to found a city high up in the Alps.[57] He also planned to dig a canal through the Isthmus in Greece and sent a chief centurion to survey the work.[57]
In 39, Caligula performed a spectacular stunt by ordering a temporary floating bridge to be built using ships as pontoons, stretching for over two miles from the resort of Baiae to the neighboring port of Puteoli.[62] It was said that the bridge was to rival that of Persian King Xerxes' crossing of the Hellespont.[62] Caligula, a man who could not swim,[63] then proceeded to ride his favorite horse, Incitatus, across, wearing the breastplate of Alexander the Great.[62] This act was in defiance of a prediction by Tiberius' soothsayer Thrasyllus of Mendes that Caligula had "no more chance of becoming emperor than of riding a horse across the Bay of Baiae".[62]
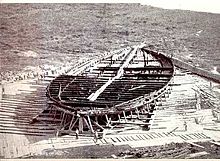
Caligula also had two large ships constructed for himself, which were found at the bottom of Lake Nemi during the dictatorship of Mussolini. The ships are among the largest vessels in the ancient world. The smaller ship was designed as a temple dedicated to Diana. The larger ship was essentially an elaborate floating palace that counted marble floors and plumbing among its amenities. Fifteen years after being raised, the ships were burned during an attack in the Second World War, and almost nothing remains of the hulls, though many archeological treasures remain intact in the museum at Lake Nemi.
Feud with the Senate
In AD 39, relations between Caligula and the Roman Senate deteriorated.[64] On what they disagreed is unknown. A number of factors, though, aggravated this feud. Prior to Caligula's appointment, the Roman Senate was accustomed to ruling without an emperor in Rome since Tiberius' departure for Capri in 26.[65] Additionally, Tiberius' treason trials had eliminated a number of pro-Julian senators such as Gallus Asinius.[66]
Caligula reviewed Tiberius' records of treason trials and decided that numerous senators, based on their actions during these trials, were not trustworthy.[64] He ordered a new set of investigations and trials.[64] He replaced the consul and had several senators put to death.[67] Suetonius reports that other senators were degraded by being forced to wait on him and run beside his chariot.[67]
Soon after his break with the Senate, Caligula was met with a number of additional conspiracies against him.[68] A conspiracy involving his brother-in-law was foiled in late 39.[68] Soon after, the governor of Germany, Gnaeus Cornelius Lentulus Gaetulicus, was executed for connections to a conspiracy.[68]
Western expansion
In AD 40, Caligula expanded the Roman Empire into Mauretania and made a significant attempt at expanding into Britannia. The later action was fully realized by his successors.
Mauretania was a client kingdom of Rome ruled by Ptolemy of Mauretania. Caligula invited Ptolemy to Rome and then had him suddenly executed.[69] Mauretania was annexed by Caligula and divided into two provinces.[70] This annexation of Mauretania led to a rebellion of some magnitude that was put down under Claudius.[71] Details on these events are unclear. Cassius Dio had written an entire chapter on the annexation of Mauretania by Caligula, but it is now lost.[72]
There also seemed to be a northern campaign to Britannia that was aborted.[72] This campaign is derided by ancient historians with accounts of Gauls dressed up as Germanic tribesmen at his triumph and Roman troops ordered to collect seashells as "spoils of the sea".[73] Due to the lack of sources, what precisely occurred and why is a matter of debate even among the primary sources for Caligula's reign. Modern historians have put forward numerous theories in an attempt to explain these actions. This trip to the English Channel could have merely been a training and scouting mission.[74] The mission may have been to accept the surrender of the British chieftain Adminius.[75] "Seashells", or conchae in Latin, may be a metaphor for something else such as female genitalia (perhaps the troops visited brothels) or boats (perhaps they captured several small British boats).[76]
Claims of divinity

In AD 40, Caligula began implementing very controversial policies that introduced religion into his political role. Caligula began appearing in public dressed as various gods and demigods such as Hercules, Mercury, Venus and Apollo.[77] Reportedly, he began referring to himself as a god when meeting with politicians and he was referred to as Jupiter on occasion in public documents.[78][79] A sacred precinct was set apart for his worship at Miletus in the province of Asia and two temples were erected for worship of him in Rome.[79] The Temple of Castor and Pollux on the Forum was linked directly to the Imperial residence on the Palatine and dedicated to Caligula.[79][80] He would appear here on occasion and present himself as a god to the public. Caligula also had several god statue's heads removed and replaced with his own in various temples.[81]
Caligula's religious policy was a departure from that of his predecessors. According to Cassius Dio, living Emperors could be worshipped as divine in the east and dead Emperors could be worshipped as divine in Rome.[82] Augustus also had the public worship his spirit on occasion, but Dio describes this as an extreme act that emperors generally shied away from.[82] Caligula took things a step further and had those in Rome, including Senators, worship him as a physical living god.[83]
Eastern policy
Caligula needed to quell several riots and conspiracies in the eastern territories during his reign. Aiding him in his actions was his good friend, Herod Agrippa, who became governor of the territories of Batanaea and Trachonitis after Caligula became emperor in AD 37.[84]
The cause of tensions in the east was complicated, involving the spread of Greek culture, Roman law and the rights of Jews.
Caligula did not trust the prefect of Egypt, Aulus Avilius Flaccus. Flaccus had been loyal to Tiberius, had conspired against Caligula's mother and had connections with Egyptian separatists.[85] In 38, Caligula sent Agrippa to Alexandria unannounced to check on Flaccus.[86] According to Philo, the visit was met with jeers from the Greek population who saw Agrippa as the king of the Jews.[87] Flaccus tried to placate both the Greek population and Caligula by having statues of the emperor placed in Jewish synagogues.[88] As a result, riots broke out in the city.[89] Caligula responded by removing Flaccus from his position and executing him.[90]
In 39, Agrippa accused Herod Antipas, the tetrarch of Galilee and Perea, of planning a rebellion against Roman rule with the help of Parthia. Herod Antipas confessed and Caligula exiled him. Agrippa was awarded with his territories.[40]
Riots again erupted in Alexandria in AD 40 between Jews and Greeks.[91] Jews were accused of not honoring the emperor.[91] Also, disputes occurred in the city of Jamnia.[92] Jews were angered by the erection of a clay altar and destroyed it.[92] In response, Caligula ordered the erection of a statue of himself in the Jewish Temple of Jerusalem,[93] a demand in conflict with Jewish monotheism.[94] In this context, Philo wrote that Caligula "regarded the Jews with most especial suspicion, as if they were the only persons who cherished wishes opposed to his".[94]
Fearing civil war if the order were carried out, it was delayed for nearly a year by the governor of Syria, Publius Petronius.[95] Agrippa finally convinced Caligula to reverse the order.[91]
Scandals

Surviving sources present a number of stories about Caligula that illustrate cruelty and insanity.
The contemporaneous sources, Philo of Alexandria and Seneca the Younger, describe an insane emperor who was self-absorbed, angry, killed on a whim, and who indulged in too much spending and sex.[96] He is accused of sleeping with other men's wives and bragging about it,[97] killing for mere amusement,[98] purposely wasting money on his bridge, causing starvation,[99] and wanting a statue of himself erected in the Temple of Jerusalem for his worship.[93] Once at some games at which he was presiding, he ordered his guards to throw an entire section of the crowd into the arena during intermission to be eaten by animals because there were no criminals to be prosecuted and he was bored.[100]
While repeating the earlier stories, the later sources of Suetonius and Cassius Dio add additional tales of insanity. They accuse Caligula of incest with his sisters, Agrippina the Younger, Drusilla and Livilla, and say he prostituted them to other men.[101] They state he sent troops on illogical military exercises,[72][102] turned the palace into a brothel,[51] and most famously, tried to make his horse, Incitatus, a consul and a priest.[103]
The validity of these accounts is debatable. In Roman political culture, insanity and sexual perversity were often presented hand-in-hand with poor government.[104]
Assassination and aftermath

Caligula's actions as Emperor were described as being especially harsh to the Senate, the nobility and the equestrian order.[105] According to Josephus, these actions led to several failed conspiracies against Caligula.[106] Eventually, a successful murder was planned by officers within the Praetorian Guard led by Cassius Chaerea.[107] The plot is described as having been planned by three men, but many in the Senate, army and equestrian order were said to have been informed of it and involved in it.[108]
According to Josephus, Chaerea had political motivations for the assassination.[109] Suetonius sees the motive in Caligula calling Chaerea derogatory names.[110] Caligula considered Chaerea effeminate because of a weak voice and for not being firm with tax collection.[111] Caligula would mock Chaerea with watchwords like "Priapus" and "Venus".[112]
On 24 January 41, Chaerea and other guardsmen accosted Caligula while he was addressing an acting troupe of young men during a series of games and dramatics held for the Divine Augustus.[113] Details on the events vary somewhat from source to source, but they agree that Chaerea was first to stab Caligula followed by a number of conspirators.[114] Suetonius records that Caligula's death was similar to that of Julius Caesar. He states that both the elder Gaius Julius Caesar (Julius Caesar) and the younger Gaius Julius Caesar (Caligula) were stabbed 30 times by conspirators led by a man named Cassius (Cassius Longinus and Cassius Chaerea).[115] The cryptoporticus (underground corridor) where this event would have taken place was discovered beneath the imperial palaces on the Palatine Hill.[116] By the time Caligula's loyal Germanic guard responded, the emperor was already dead. The Germanic guard, stricken with grief and rage, responded with a rampaging attack on the assassins, conspirators, innocent senators and bystanders alike.[117]
The Senate attempted to use Caligula's death as an opportunity to restore the Republic.[118] Chaerea attempted to convince the military to support the Senate.[119] The military, though, remained loyal to the office of the emperor.[119] The grieving Roman people assembled and demanded that Caligula's murderers be brought to justice.[120] Uncomfortable with lingering imperial support, the assassins sought out and stabbed Caligula's wife, Caesonia, and killed their young daughter, Julia Drusilla, by smashing her head against a wall.[121] They were unable to reach Caligula's uncle, Claudius, who was spirited out of the city to a nearby Praetorian camp.[122] Claudius became emperor after procuring the support of the Praetorian guard and ordered the execution of Chaerea and any other known conspirators involved in the death of Caligula.[123] According to Suetonius, Caligula's body was placed under turf until it was burned and entombed by his sisters. He was buried within the Mausoleum of Augustus; in 410 during the Sack of Rome the tomb's ashes were scattered.
Legacy
Historiography
The history of Caligula’s reign is extremely problematic as only two sources contemporary with Caligula have survived — the works of Philo and Seneca. Philo’s works, On the Embassy to Gaius and Flaccus, give some details on Caligula’s early reign, but mostly focus on events surrounding the Jewish population in Judea and Egypt with whom he sympathizes. Seneca’s various works give mostly scattered anecdotes on Caligula’s personality. Seneca was almost put to death by Caligula in 39 likely due to his associations with conspirators.[124]
At one time, there were detailed contemporaneous histories on Caligula, but they are now lost. Additionally, the historians who wrote them are described as biased, either overly critical or praising of Caligula.[125] Nonetheless, these lost primary sources, along with the works of Seneca and Philo, were the basis of surviving secondary and tertiary histories on Caligula written by the next generations of historians. A few of the contemporaneous historians are known by name. Fabius Rusticus and Cluvius Rufus both wrote condemning histories on Caligula that are now lost. Fabius Rusticus was a friend of Seneca who was known for historical embellishment and misrepresentation.[126] Cluvius Rufus was a senator involved in the assassination of Caligula.[127] Caligula’s sister, Agrippina the Younger, wrote an autobiography that certainly included a detailed explanation of Caligula’s reign, but it too is lost. Agrippina was banished by Caligula for her connection to Marcus Lepidus, who conspired against Caligula.[68] The inheritance of Nero, Agrippina's son and the future emperor, was seized by Caligula. Gaetulicus, a poet, produced a number of flattering writings about Caligula, but they too are lost.
The bulk of what is known of Caligula comes from Suetonius and Cassius Dio. Suetonius wrote his history on Caligula 80 years after his death, while Cassius Dio wrote his history over 180 years after Caligula’s death. Though Cassius Dio’s work is invaluable because it alone gives a loose chronology of Caligula’s reign, his surviving work is only a summary written by John Xiphilinus, an 11th century monk.
A handful of other sources also add a limited perspective on Caligula. Josephus gives a detailed description of Caligula’s assassination. Tacitus provides some information on Caligula’s life under Tiberius. In a now lost portion of his Annals, Tacitus gave a detailed history of Caligula. Pliny the Elder’s Natural History also has a few brief references to Caligula.
There are few surviving sources on Caligula and no surviving source paints Caligula in a favorable light. The paucity of sources has resulted in significant gaps in the reign of Caligula. Little is written on the first two years of Caligula’s reign. Additionally, there are only limited details on later significant events, such as the annexation of Mauretania, Caligula’s military actions in Britannia, and his feud with the Roman Senate.
Health
All surviving sources, except Pliny the Elder, characterize Caligula as insane. However it is not known whether they are speaking figuratively or literally. Additionally, given Caligula's unpopularity among the surviving sources, it is difficult to separate fact from fiction. Recent sources are divided in attempting to ascribe a medical reason for Caligula's behavior, citing as possibilities encephalitis, epilepsy or meningitis. The question of whether or not Caligula was insane remains unanswered.
Philo of Alexandria, Josephus and Seneca also state Caligula was insane, but describe this madness as a personality trait that came through experience.[40][128][129] Seneca states that Caligula became arrogant, angry and insulting once becoming emperor and uses his personality flaws as examples his readers can learn from.[130] According to Josephus, power made Caligula incredibly conceited and led him to think he was a god.[40] Philo of Alexandria reports that Caligula became ruthless after nearly dying of his illness in 39.[131] Juvenal reports he was given a magic potion that drove him insane.
Suetonius said that Caligula suffered from "falling sickness", or epilepsy, when he was young.[132] Modern historians have theorized that Caligula lived with a daily fear of seizures.[133] Despite swimming being a part of imperial education, Caligula could not swim.[134] Epileptics are encouraged not to swim because light reflecting off water can induce seizures.[135] Additionally, Caligula reportedly talked to the full moon.[67] Epilepsy was also long associated with the moon.[136]
Some modern historians think that Caligula suffered from hyperthyroidism.[137] This diagnosis is mainly attributed to Caligula's irritability and his "stare" as described by Pliny the Elder.
A recent study of Caligula's life has argued that his illness may have been an indication of lead poisoning. The Romans believed that pure wine could only be brewed in lead bowls, and Caligula's drinking was reputed to be excessive. A contemporaneous bowl artifact was tested and revealed high amounts of lead.[138]
Ancestry
| 16. Drusus Claudius Nero | |||||||||||||||||||
| 8. Tiberius Claudius Nero | |||||||||||||||||||
| 17. Claudia | |||||||||||||||||||
| 4. Nero Claudius Drusus | |||||||||||||||||||
| 18. Marcus Livius Drusus Claudianus | |||||||||||||||||||
| 9. Livia Drusilla | |||||||||||||||||||
| 19. Aufidia | |||||||||||||||||||
| 2. Germanicus | |||||||||||||||||||
| 20. Marcus Antonius Creticus | |||||||||||||||||||
| 10. Mark Antony | |||||||||||||||||||
| 21. Julia Antonia | |||||||||||||||||||
| 5. Antonia Minor | |||||||||||||||||||
| 22. Gaius Octavius (=28) | |||||||||||||||||||
| 11. Octavia Minor | |||||||||||||||||||
| 23. Atia Balba Caesonia (=29) | |||||||||||||||||||
| 1.Caligula | |||||||||||||||||||
| 12. Lucius Vipsanius Agrippa | |||||||||||||||||||
| 6. Marcus Vipsanius Agrippa | |||||||||||||||||||
| 3. Agrippina the Elder | |||||||||||||||||||
| 28. Gaius Octavius (=22) | |||||||||||||||||||
| 14. Augustus | |||||||||||||||||||
| 29. Atia Balba Caesonia (=23) | |||||||||||||||||||
| 7. Julia the Elder | |||||||||||||||||||
| 30. Lucius Scribonius Libo | |||||||||||||||||||
| 15. Scribonia | |||||||||||||||||||
| 31. Sentia | |||||||||||||||||||
In popular culture
Caligula, by French author Albert Camus, is a play in which Caligula returns after deserting the palace for three days and three nights following the death of his beloved sister, Drusilla. The young emperor then uses his unfettered power to 'bring the impossible into the realm of the likely'.
In the novel I, Claudius by English writer Robert Graves, Caligula is presented as being a murderous sociopath from his childhood, who became clinically insane early in his reign. At the age of only seven, he drove his father Germanicus to despair and death by secretly terrorizing him.
American actor Jay Robinson famously portrayed a sinister and scene-stealing Caligula in two epic films of the 1950s, The Robe (1953) and its sequel Demetrius and the Gladiators (1954).
Caligula also has been played by Ralph Bates in the 1968 ITV television series The Caesars; John Hurt in the 1976 BBC television series I, Claudius; John McEnery in the 1985 miniseries A.D.; Szabolcs Hajdu in the 1996 film Caligula; and John Simm in the 2004 miniseries Imperium Nerone. In Muriel Spark's 1976 novel The Takeover the eccentric Hubert Mallindaine believes himself to be a direct descendant of Caligula.
A feature-length historical film Caligula was completed in 1979, in which Malcolm McDowell played the lead role. The film alienated audiences with extremely explicit sex and violence and received extremely negative reviews.[139] Emlyn Williams was cast as Caligula in the never-completed 1937 film I, Claudius, and Courtney Love appeared as Caligula in a fake trailer for Gore Vidal's Caligula, ostensibly a remake of the 1979 film, but actually a parodic short film by conceptual artist Francesco Vezzoli.[140]
The play The Reckoning of Kit and Little Boots by Nat Cassidy, examines the lives of the Elizabethan playwright Christopher Marlowe and Caligula, with the fictional conceit that Marlowe was working on a play about Caligula around the time of his own murder. It emphasizes the similarities between the two characters—both stabbed to death at 29, both in part as a result to their controversial perspectives on religion. The play also focuses on Caligula's love for his sister Drusilla, and his deep-rooted loathing for Tiberius. It received its world premiere in New York City in June 2008.[141][142]
In Melissa de la Cruz's series Blue Bloods, Caligula is the vampire reincarnation of Lucifer, the Prince of Heaven, who later became Satan in the fall from Paradise.
References
Notes
- ^ Suetonius, The Lives of Twelve Caesars, Life of Caligula 8.
- ^ a b c d e Suetonius, The Lives of Twelve Caesars, Life of Caligula 7.
- ^ Cassius Dio, Roman History LIX.6.
- ^ a b Suetonius, The Lives of Twelve Caesars, Life of Caligula 9.
- ^ "Caligula" is formed from the Latin word caliga, meaning soldier's boot, and the diminutive infix -ul.
- ^ Seneca the Younger, On the Firmness of a Wise Person XVIII 2-5. See also Malloch, 'Gaius and the nobiles', Athenaeum (2009).
- ^ Suetonius, The Lives of Twelve Caesars, Life of Caligula 2.
- ^ a b c d e f Suetonius, The Lives of Twelve Caesars, Life of Caligula 10.
- ^ Tacitus, Annals IV.52.
- ^ Tacitus, Annals V.3.
- ^ a b Suetonius, The Lives of Twelve Caesars, Life of Tiberius 54.
- ^ Tacitus, Annals V.10.
- ^ Suetonius, The Lives of Twelve Caesars, Life of Tiberius 64.
- ^ Suetonius, The Lives of Twelve Caesars, Life of Tiberius 62.
- ^ a b Tacitus, Annals VI.20.
- ^ Cassius Dio, Roman History LVII.23.
- ^ Tacitus, Annals VI.25.
- ^ Tacitus, Annals VI.23.
- ^ a b c d Suetonius, The Lives of Twelve Caesars, Life of Caligula 12.
- ^ Philo of Alexandria, On the Embassy to Gaius VI.35.
- ^ Suetonius, The Lives of Twelve Caesars, Life of Tiberius 76.
- ^ a b Tacitus, Annals VI.50.
- ^ Philo of Alexandria, On the Embassy to Gaius IV.25; Josephus, Antiquities of the Jews XIII.6.9.
- ^ a b c Cassius Dio, Roman History LIX.1.
- ^ a b Suetonius, The Lives of Twelve Caesars, Life of Caligula 13.
- ^ Philo of Alexandria, On the Embassy to Gaius II.10.
- ^ Suetonius, The Lives of Twelve Caesars, Life of Tiberius 75.
- ^ Suetonius, The Lives of Twelve Caesars, Life of Caligula 14.
- ^ Philo mentions widespread sacrifice, but no estimation on the degree, Philo of Alexandria, On the Embassy to Gaius II.12.
- ^ Philo of Alexandria, On the Embassy to Gaius II.13.
- ^ Suetonius, The Lives of Twelve Caesars, Life of Caligula 15.
- ^ Suetonius, The Lives of Twelve Caesars, Life of Caligula 16.
- ^ Suetonius, The Lives of Twelve Caesars, Life of Caligula 18.
- ^ Cassius Dio, Roman History LIX.3.
- ^ Philo of Alexandria, On the Embassy to Gaius II–III.
- ^ a b c Cassius Dio, Roman History LIX.10.
- ^ Philo of Alexandria, On the Embassy to Gaius II.14.
- ^ Philo of Alexandria, On the Embassy to Gaius III.16.
- ^ Philo of Alexandria, On the Embassy to Gaius IV.22.
- ^ a b c d Josephus, Antiquities of the Jews XVIII.7.2.
- ^ a b Cassius Dio, Roman History LIX.8.
- ^ Philo of Alexandria, On the Embassy to Gaius V.29.
- ^ Philo of Alexandria, On the Embassy to Gaius V.28.
- ^ a b Tacitus, Agricola 4.
- ^ Suetonius, The Lives of Twelve Caesars, Life of Caligula 23.
- ^ Cassius Dio, Roman History LIX.9–10.
- ^ Suetonius, The Lives of Twelve Caesars, Life of Caligula 16.2.
- ^ Cassius Dio, Roman History LIX.9.7.
- ^ Suetonius, The Lives of Twelve Caesars, Life of Caligula 37.
- ^ a b c Suetonius, The Lives of Twelve Caesars, Life of Caligula 38.
- ^ a b Suetonius, The Lives of Twelve Caesars, Life of Caligula 41.
- ^ Suetonius, The Lives of Twelve Caesars, Life of Caligula 40.
- ^ Cassius Dio, Roman History LIX.14.
- ^ a b c Cassius Dio, Roman History LIX.15.
- ^ Seneca the Younger, On the Shortness of Life XVIII.5.
- ^ Josephus, Antiquities of the Jews XIX.2.5.
- ^ a b c d Suetonius, The Lives of Twelve Caesars, Life of Caligula 21.
- ^ Suetonius, The Lives of Twelve Caesars, Life of Caligula 22.
- ^ Suetonius, The Lives of Twelve Caesars, Life of Caligula 21, Life of Claudius 20; Pliny the Elder, Natural History XXXVI.122.
- ^ Pliny the Elder, Natural History XVI.76.
- ^ Cassius Dio, Roman History LIX.15; Suetonius, The Lives of Twelve Caesars, Life of Caligula 37.
- ^ a b c d Suetonius, The Lives of Twelve Caesars, Life of Caligula 19.
- ^ Suetonius, The Lives of Twelve Caesars, Life of Caligula 54.
- ^ a b c Cassius Dio, Roman History LIX.16; Suetonius, The Lives of Twelve Caesars, Life of Caligula 30.
- ^ Tacitus, Annals IV.41.
- ^ Tacitus, Annals' IV.41.
- ^ a b c Suetonius, The Lives of Twelve Caesars, Life of Caligula 26.
- ^ a b c d Cassius Dio, Roman History LIX.22.
- ^ Suetonius, The Lives of Twelve Caesars, Life of Caligula 35.
- ^ Pliny the Elder, Natural History V.2.
- ^ Cassius Dio, Roman History LX.8, LX.24; Pliny the Elder, Natural History V.11.
- ^ a b c Cassius Dio, Roman History LIX.25.
- ^ Suetonius, The Lives of Twelve Caesars, Life of Caligula 45-47.
- ^ P. Bicknell, "The Emperor Gaius' Military Activities in AD 40", Historia 17 (1968), 496-505.
- ^ R.W. Davies, "The Abortive Invasion of Britain by Gaius", Historia 15 (1966), 124-128; S.J.V.Malloch, 'Gaius on the Channel Coast', Classical Quarterly 51 (2001) 551-56; See Suetonius, The Lives of Twelve Caesars, Life of Caligula 44.
- ^ D. Wardle, Suetonius' Life of Caligula: a Commentary (Brussels, 1994), 313; David Woods "Caligula's Seashells", Greece and Rome (2000), 80-87.
- ^ Philo of Alexandria, On the Embassy to Gaius XI-XV.
- ^ Cassius Dio, Roman History LIX.26.
- ^ a b c Cassius Dio, Roman History LIX.28.
- ^ Sanford, J.: "Did Caligula have a God complex?, Stanford Report, 10 September 2003.[dead link]
- ^ Farquhar, Michael (2001). A Treasure of Royal Scandals, p. 209. Penguin Books, New York. ISBN 0739420259.
- ^ a b Cassius Dio, Roman History LI.20.
- ^ Cassius Dio, Roman History LIX.26-28.
- ^ Josephus, Antiquities of the Jews XVIII.6.10; Philo of Alexandria, Flaccus V.25.
- ^ Philo of Alexandria, Flaccus III.8, IV.21.
- ^ Philo of Alexandria, Flaccus V.26-28.
- ^ Philo of Alexandria, Flaccus V.29.
- ^ Philo of Alexandria, Flaccus VI.43.
- ^ Philo of Alexandria, Flaccus VII.45.
- ^ Philo of Alexandria, Flaccus XXI.185.
- ^ a b c Josephus, Antiquities of the Jews XVIII.8.1.
- ^ a b Philo of Alexandria, On the Embassy to Gaius XXX.201.
- ^ a b Philo of Alexandria, On the Embassy to Gaius XXX.203.
- ^ a b Philo of Alexandria, On the Embassy to Gaius XVI.115.
- ^ Philo of Alexandria, On the Embassy to Gaius XXXI.213.
- ^ Seneca the Younger, On Anger xviii.1, On Anger III.xviii.1; On the Shortness of Life xviii.5; Philo of Alexandria, On the Embassy to Gaius XXIX.
- ^ Seneca the Younger, On Firmness xviii.1.
- ^ Seneca the Younger, On Anger III.xviii.1.
- ^ Seneca the Younger, On the Shortness of Life xviii.5.
- ^ "Daily life in the Roman City". Aldrete, Gregory.
- ^ Cassius Dio, Roman History LIX.11, LIX.22; Suetonius, The Lives of Twelve Caesars, Life of Caligula 24.
- ^ Suetonius, The Lives of Twelve Caesars, Life of Caligula 46-47.
- ^ Suetonius, The Lives of Twelve Caesars, Life of Caligula 55; Cassius Dio, Roman History LIX.14, LIX.28.
- ^ Younger, John G. (2005). Sex in the Ancient World from A to Z. Routledge. xvi. ISBN 0415242525.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|nopp=ignored (|no-pp=suggested) (help) - ^ Josephus, Antiquities of the Jews XIX.1.1.
- ^ Suetonius, The Lives of Twelve Caesars, Life of Caligula 56; Tacitus, Annals 16.17; Josephus, Antiquities of Jews XIX.1.2.
- ^ Josephus, Antiquities of the Jews XIX.1.3.
- ^ Josephus, Antiquities of the Jews XIX.1.10, XIX.1.14.
- ^ Josephus, Antiquities of the Jews XIX.1.6.
- ^ Suetonius, The Lives of Twelve Caesars, Life of Caligula 56.
- ^ Seneca the Younger, On Firmness xviii.2; Josephus, Antiquities of the Jews XIX.1.5.
- ^ Seneca the Younger, On Firmness xviii.2; Suetonius, The Lives of Twelve Caesars, Life of Caligula 56.
- ^ Suetonius, The Lives of Twelve Caesars, Life of Caligula 58.
- ^ Seneca the Younger, On Firmness xviii.2; Suetonius, The Lives of Twelve Caesars, Life of Caligula 58; Josephus, Antiquities of the Jews XIX.1.14.
- ^ Suetonius, The Lives of Twelve Caesars, Life of Caligula 57, 58.
- ^ Archaeologists unearth place where Emperor Caligula met his end by Richard Owen, October 17, 2008. Retrieved 2010-03-05.
- ^ Josephus, Antiquities of the Jews XIX.1.15; Suetonius, Life of Caligula 58.
- ^ Josephus, Antiquities of the Jews XIX.2.
- ^ a b Josephus, Antiquities of the Jews XIX.4.4.
- ^ Tacitus, Annals XI.1; Josephus, Antiquities of the Jews XIX.1.20.
- ^ Suetonius, The Lives of Twelve Caesars, Life of Caligula 59.
- ^ Josephus, Antiquities of the Jews XIX.2.1.
- ^ Josephus, Antiquities of the Jews XIX.3.1.
- ^ Cassius Dio, Roman History LIX.19.
- ^ Tacitus, Annals I.1.
- ^ Tacitus, Life of Gnaeus Julius Agricola X, Annals XIII.20.
- ^ Josephus, Antiquities of the Jews XIX.1.13.
- ^ Philo of Alexandria, On the Embassy to Gaius XIII.
- ^ Seneca the Younger, On the Firmness of the Wise Person XVIII.1; Seneca the Younger, On Anger I.xx.8.
- ^ Seneca the Younger, On the Firmness of the Wise Person XVII-XVIII; Seneca the Younger, On Anger I.xx.8.
- ^ Philo of Alexandria, On the Embassy to Gaius III-IV.
- ^ Suetonius, The Lives of Twelve Caesars, Life of Caligula 50.
- ^ D. Thomas Benediktson, "Caligula's Phobias and Philias: Fear of Seizure?", The Classical Journal (1991) pp. 159-163.
- ^ Suetonius, The Lives of Twelve Caesars, Life of Augustus 64, Life of Caligula 54.
- ^ J.H. Pearn, "Epilepsy and Drowning in Childhood," British Medical Journal (1977) pp. 1510-11.
- ^ O. Temkin, The Falling Sickness (2nd ed., Baltimore 1971) 3-4, 7, 13, 16, 26, 86, 92-96, 179.
- ^ R.S. Katz, "The Illness of Caligula" CW 65(1972),223-25, refuted by M.G. Morgan, "Caligula’s Illness Again", CW 66(1973), 327-29.
- ^ Ancients Behaving Badly. Retrieved 2010-03-05.
- ^ Caligula > Overview - AllMovie.com. Retrieved 2010-03-05.
- ^ 'Caligula' Gives a Toga Party (but No One's Really Invited).
- ^ [1][dead link]
- ^ nytheatrecast » Blog Archive » Episode #223 - The Reckoning of Kit & Boots and Hope’s Arbor.
Bibliography
- Primary sources
- Cassius Dio, Roman History, Book 59
- Josephus, Antiquities of the Jews, (trans. W.Whiston), Books XVIII–XIX
- Philo of Alexandria, (trans. C.D.Yonge, London, H. G. Bohn, 1854–1890):
- Seneca the Younger
- Suetonius, The Lives of Twelve Caesars, Life of Caligula
- Tacitus, Annals, Book 6
- Secondary material
- Caligula: the corruption of power by Anthony A. Barrett (Batsford 1989) ISBN 0-7134-5487-3
- Grant, Michael, The Twelve Caesars. New York: Charles Scribner's Sons. 1975
- Hurley, Donna W., An Historical and Historiographical Commentary on Suetonius' "Life of C. Caligula". Atlanta, Georgia: Scholars Press. 1993.
- Biography from De Imperatoribus Romanis
- Biography of Gaius Caligula
- Straight Dope article
- Caligula
- A chronological account of his reign
- A critical account of a number of his reported activities
- Caligula at BBC History
Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA
- Julio-Claudian dynasty
- Articles needing cleanup from February 2010
- Cleanup tagged articles without a reason field from February 2010
- Wikipedia pages needing cleanup from February 2010
- 12 births
- 41 deaths
- 41 crimes
- 1st-century Roman emperors
- Capri
- Julio-Claudian Dynasty
- Roman emperors to suffer posthumous denigration or damnatio memoriae
- Roman emperors murdered by the Praetorian Guard
- People from the Province of Rome
- Deaths by stabbing
