List of time periods: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
**[[Zhou Dynasty]] ([[China]] [[1200 BC]] - [[500 BC]]) |
**[[Zhou Dynasty]] ([[China]] [[1200 BC]] - [[500 BC]]) |
||
**([[Ancient Greece]], c:a [[1000s BC|1000 BC]]-, see [[Timeline of Ancient Greece]]) |
**([[Ancient Greece]], c:a [[1000s BC|1000 BC]]-, see [[Timeline of Ancient Greece]]) |
||
**[[Joman period]] [[Japan |
**[[Joman period]] ([[Japan]] [[800 BC]]-[[400 BC]]) |
||
**[[Timeline of Ancient Rome|Ancient Rome]] [[509 BC]] - [[476]]) |
**[[Timeline of Ancient Rome|Ancient Rome]] [[509 BC]] - [[476]]) |
||
**[[Yayoi Period]] ([[Japan]] [[400 BC]] - [[300]]) |
**[[Yayoi Period]] ([[Japan]] [[400 BC]] - [[300]]) |
||
**[[Kofun |
**[[Kofun Period]] ([[Japan]] [[300]]- [[600]]) |
||
**[[Period of the Three Kingdoms]] ([[China]], [[220]] - [[280]]) |
**[[Period of the Three Kingdoms]] ([[China]], [[220]] - [[280]]) |
||
**[[Dark Age]] {Europe, [[4th century]] - [[900]]} |
**[[Dark Age]] {Europe, [[4th century]] - [[900]]} |
||
Revision as of 03:32, 13 December 2007
This list is incomplete; you can help by adding missing items. |
The categorization of time into discrete named blocks is called periodization. This is a list of such named time periods as defined in various fields of study. Major categorization systems include cosmological (concerning the various time periods in the origin and evolution of our universe), geological (concerning time periods in the origin and evolution of earth ) and historical (concerning time periods in the origin, evolution of mankind).
Human time periods
Based on current and debatable evidence, the human species has found its origins starting from about 250,000 years ago - when homo began to develop. It is broadly divided into prehistorical (before history began to be recorded) and historical periods (when written records began to be kept).
Prehistorical periods
In archaeology and anthropology, human prehistory is subdivided around the three-age system.
- The Stone Age
- In some regions the Stone Age is divided into the Paleolithic Age (Old Stone Age) and the Neolithic Age (New Stone Age).
- In other regions the Stone Age is divided into the Paleolithic Age, the Mesolithic Age (Middle Stone Age, also called the Epipaleolithic Age), and the Neolithic Age.
- The Copper Age (aka Chalcolithic Age). The Copper Age was not part of the original three-age system.
- The Bronze Age
- The Iron Age
The dates for each age can vary by region. On the geologic time scale, the Holocene epoch starts at the end of the most recent Ice age (about 9400 BC) and continues to the present. The beginning of Mesolithic is usually considered to correspond to the beginning of the Holocene epoch.
Historical periods
- Antiquity
- Mesopotamia 6000 BC - 1100 BC
- Indus Valley Civilization 3300 BC - 1300 BC
- Old Kingdom (Egypt, 3000 BC - 2000 BC)
- Middle Kingdom (Egypt, 2000 BC - 1300 BC)
- Shang Dynasty (China 1800 BC - 1200 BC
- New Kingdom (Egypt, 1300 BC - 700 BC)
- Zhou Dynasty (China 1200 BC - 500 BC)
- (Ancient Greece, c:a 1000 BC-, see Timeline of Ancient Greece)
- Joman period (Japan 800 BC-400 BC)
- Ancient Rome 509 BC - 476)
- Yayoi Period (Japan 400 BC - 300)
- Kofun Period (Japan 300- 600)
- Period of the Three Kingdoms (China, 220 - 280)
- Dark Age {Europe, 4th century - 900}
- Middle Ages (Europe, 5th century - 15th century)
- Early Modern (Europe, 14th century - 18th century)
- The Renaissance (Europe, 14th century - 16th century)
- Age of Discovery (or Exploration) (Europe, 15th century - 17th century)
- Elizabethan period (United Kingdom, 1558 - 1603)
- The Protestant Reformation (Europe, 16th century)
- The Age of Enlightenment (Europe,18th century)
- Tokugawa shogunate (Japan, 1603 - 1868)
- Modern (Europe, 18th century - 20th century)
- Industrial Revolution (Europe, United States, elsewhere 18th and 19th centuries)
- Napoleonic Era (1799 - 1815)
- Victorian era (United Kingdom, 1837 - 1901)
- Edwardian period (United Kingdom, 1901 - 1910)
- Meiji era (Japan, 1868 - 1912)
- Machine Age(1900 - 1945)
- World War I (Much of Earth, 1914 - 1918)
- Interwar period (Earth, 1918 - 1939 or 1937)
- World War II (Earth, 1937 or 1939 - 1945)
- Atomic Age (after 1945)
- Cold War (Soviet Union and United States, as well their allied states, 1945 - 1989 or 1991)
- Space Age (after 1957)
- Information Age (1971 - Present)
Calendar systems
Various societies in the past have created calendars to record events, such as religious observances and agricultural tasks. A common characteristic of most known calendars is that they measure time in relation to a particular point in history, known as the epoch date. A period between epoch dates is known as a calendar era.
Mythological and astrological time periods
- Greek mythology
- Golden Age, self-sufficient
- Silver Age, self-indulgent
- Bronze Age, warlike
- Heroic Age, nobly aspirant
- Iron Age, violent
- Aztec mythology
- Nahui-Ocelotl, Destroyed by Jaguars
- Nahui-Ehécatl, Destroyed by Hurricane
- Nahuiquiahuitl, Destroyed by rain of Fire
- Nahui-Atl, Destroyed by Flood
- Nahui-Ollin, Destroyed by Earthquakes
Cosmological time periods
13.7 billion years ago: The Big Bang.
Because of the scales involved (both very large and very small), cosmological time periods are usually described in seconds. In this table, each row is defined in seconds after the Big Bang, with earliest at the top of the chart.
| Seconds after the Big Bang | Period |
|---|---|
| 5.4 × 10−44 | Planck time |
| 10−43 to 10−35 | Planck Epoch |
| 10−35 to 10−33 | Inflationary epoch |
| 10−35 to 10−12 | Epoch of Grand Unification |
| 10−12 to 10−6 | Electroweak Epoch |
| 10−6 to 100 | Hadron Epoch |
| 1 to 100 | Lepton Epoch |
100 seconds to 300,000 years after the big bang - Epoch of Nucleosynthesis
300,000 years on from the Big Bang - Epoch of Galaxies
Formation of Population III stars
The first stars were formed from the Hydrogen and Helium formed in the Big Bang were short lived massive Population III stars. Nuclear processes in these stars converted the Hydrogen and Helium into metals and other heavier elements. As the Population III stars died these heavier elements were released.
Formation of Population II stars
Population II stars contain metals formed in the Population III stars. These were longer lived than the Population III stars and some of them are still around. In addition to the metals these inherited from the Population III stars the Population II stars also formed metals by nuclear reactions and when the stars died much of that material was returned to be used as the building blocks for the next generation of stars.
5 Billion Years ago - Formation of Population I stars
Population I stars are also known as metal rich stars. Our own sun is a Population I star and was formed about 5 billion years ago.
Geologic time periods
The geologic time scale covers the extent of the existence of Earth, from about 4600 million years ago to the present day. It is marked by Global Boundary Stratotype Sections and Points. Geologic time units are (in order of descending specificity) eons, eras, periods, epochs, and ages; and the corresponding chronostratigraphic units, which measure "rock-time", are eonothems, erathems, systems, series, and stages.
The second and third timelines are each subsections of their preceding timeline as indicated by asterisks. The Cenozoic is sometimes divided into the Quaternary and Tertiary periods, although their use is no longer official.
The following five timelines show the geologic time scale to scale. The first shows the entire time from the formation of the Earth to the present, but this gives little space for the most recent eon. The second timeline shows an expanded view of the most recent eon. In a similar way, the most recent era is expanded in the third timeline, the most recent period is expanded in the fourth timeline, and the most recent epoch is expanded in the fifth timeline.
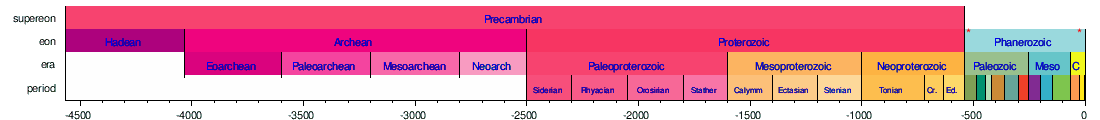



Horizontal scale is Millions of years (above timelines) / Thousands of years (below timeline)

See also
- Periodization for a discussion of the tendency to try to fit history into non-overlapping periods.
- Exponential timeline shows all history on one page in ten lines.
- List of timelines
- List of fossil sites (with link directory)
References
This article needs additional citations for verification. (December 2006) |
