July 1932 German federal election
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 608 seats in the Reichstag 305 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Registered | 44,211,216 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Turnout | 37,162,081 (84.1%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
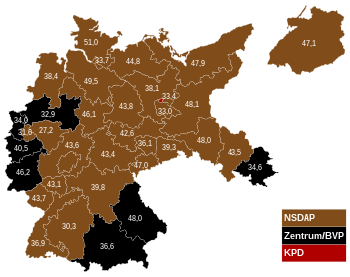 Constituencies coloured according to the party that received the largest share of the vote. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| This article is part of a series on the |
| Politics of Germany |
|---|
 |
Federal elections were held in Germany on 31 July 1932, following the premature dissolution of the Reichstag. The Nazi Party made significant gains and became the largest party in the Reichstag for the first time although they failed to win a majority.
Background
Since 1929, Germany had been suffering from the Great Depression; unemployment had risen from 8.5% to nearly 30% between 1929 and 1932,[1] while industrial production dropped by around 42%.[1] In March 1930, the governing grand coalition of the pro-republican parties (the Social Democratic Party (SPD), Centre Party and both liberal parties) collapsed. Hindenburg appointed a minority government, headed by the Centre Party's Heinrich Brüning, which could only govern by using Hindenburg's emergency powers. The September 1930 elections produced a highly fragmented Reichstag, making the formation of a stable government impossible. The elections also saw the Nazi Party rise to national prominence,[1] gaining 95 seats.
Brüning's policies, implemented via presidential decree and tolerated by parliament, failed to solve the economic crisis but weakened the parliamentary system. In March 1932, presidential elections pitted the incumbent Hindenburg, supported by pro-democratic parties, against Hitler and the Communist Ernst Thälmann. Hitler received around a third of the vote and was defeated in the second round in April by Hindenburg, who won a narrow majority.[1] However, at the end of May 1932, Hindenburg was persuaded to dismiss Brüning as chancellor and replaced him with Franz von Papen, a renegade from the Centre Party, and a non-partisan "Cabinet of Barons". Papen's cabinet had almost no support in the Reichstag. Only three days after his appointment, he was faced with the opposition and had Hindenburg dissolve the Reichstag and called for new elections for 31 July so that the Reichstag could not dismiss him immediately.[2]
Campaign
The election campaign took place under violent circumstances, as Papen lifted the token ban on the SA, the Nazi paramilitary, which Brüning had put in place during the last days of his administration. That inevitably led to clashes with the Communist paramilitary.
Results
The elections resulted in significant gains by the Nazi Party; with 230 seats, it became the largest party in parliament for the first time, but lacked an overall majority. Neither the Nazi Party nor Hindenburg had a governing majority, and the other parties refused to co-operate, meaning no coalition government with a majority could be formed.[2] Papen's minority government continued in office, leading to another early election in November.
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Votes | % | Seats | +/– |
| National Socialist German Workers' Party | 13,745,680 | 37.27 | 230 | +123 |
| Social Democratic Party of Germany | 7,959,712 | 21.58 | 133 | –10 |
| Communist Party of Germany | 5,282,636 | 14.32 | 89 | +12 |
| German Centre Party | 4,589,430 | 12.44 | 75 | +7 |
| German National People's Party | 2,178,024 | 5.91 | 37 | –4 |
| Bavarian People's Party | 1,192,684 | 3.23 | 22 | +3 |
| German People's Party | 436,002 | 1.18 | 7 | –23 |
| German State Party | 371,800 | 1.01 | 4 | –16 |
| Christian Social People's Service | 364,543 | 0.99 | 3 | –11 |
| Reich Party of the German Middle Class | 146,876 | 0.40 | 2 | –21 |
| German Farmers' Party | 137,133 | 0.37 | 2 | –4 |
| Agricultural League | 96,851 | 0.26 | 2 | –1 |
| German Country People | 90,554 | 0.25 | 1 | –18 |
| Socialist Workers' Party of Germany | 72,630 | 0.20 | 0 | New |
| German-Hanoverian Party | 46,927 | 0.13 | 0 | –3 |
| People's Justice Party | 40,825 | 0.11 | 1 | +1 |
| Poland List | 33,436 | 0.09 | 0 | New |
| Nationalsozialistische Kleinrentner, Inflationsgeschädigte und Vorkriegsgeldbesitzer | 14,816 | 0.04 | 0 | New |
| Worker and Farmer Party of Germany/Christian Radical People's Front | 13,950 | 0.04 | 0 | New |
| Free Economy Party of Germany | 12,247 | 0.03 | 0 | New |
| Farmers, House and Property Owners | 9,465 | 0.03 | 0 | New |
| Radical Middle Class | 8,637 | 0.02 | 0 | New |
| Kampfgemeinschaft der Arbeiter und Bauern | 4,551 | 0.01 | 0 | New |
| Interessengemeinschaft der Kleinrentner und Inflationsgeschädigten | 2,932 | 0.01 | 0 | New |
| National Socialist People's Alliance for Truth and Justice | 2,436 | 0.01 | 0 | New |
| Nationalsozialistische Handwerker, Handels- und Gewerbetreibende | 2,221 | 0.01 | 0 | New |
| Nationalsozialistische Kriegsteilnehmer, Kriegsbeschädigte und Kriegshinterbliebene | 2,213 | 0.01 | 0 | New |
| Nationalsozialistischer enteigneter Mittelstand | 2,186 | 0.01 | 0 | New |
| Gerechtigkeitsbewegung für Parteienverbot – gegen Lohn-, Gehalts- und Rentenkürzungen – für Arbeitsbeschaffung | 2,035 | 0.01 | 0 | New |
| German Free Economy Party | 1,916 | 0.01 | 0 | New |
| Deutsche Einheitspartei für wahre Volkswirtschaft, Unterstützungsempfänger- Partei Deutschlands | 1,709 | 0.00 | 0 | New |
| Schleswig Home | 1,511 | 0.00 | 0 | New |
| Partei der Unzufriedenen | 1,341 | 0.00 | 0 | New |
| Höchstgehalt der Beamten 5000 M. Für die Arbeitslosen und bis jetzt abgewiesenen Kriegsbeschädigten | 1,141 | 0.00 | 0 | New |
| German Socialist Struggle Movement | 947 | 0.00 | 0 | New |
| Liste gegen Kürzung der Invaliden-, Sozial- und Kriegsbeschädigtenrenten | 887 | 0.00 | 0 | New |
| Unemployed Front | 853 | 0.00 | 0 | New |
| Kampfbund gegen Hauszinssteuer | 790 | 0.00 | 0 | New |
| German People's Community | 618 | 0.00 | 0 | New |
| Greater Germany Schmalix List | 610 | 0.00 | 0 | 0 |
| Schlesiens Handwerk und Gewerbe | 598 | 0.00 | 0 | New |
| Der ernste evangelisch-lutherische Christ (Gerechtigkeits-Bewegung) | 587 | 0.00 | 0 | New |
| Bund Bayerisches Handwerk und Gewerbe, Haus- und Grundbesitz und Landwirtschaft | 577 | 0.00 | 0 | New |
| Kampfgemeinschaft der Rentner, Sparer und Inflationsgeschädigten | 532 | 0.00 | 0 | New |
| Nationale Rentner, Sparer und Inflationsgeschädigte | 522 | 0.00 | 0 | New |
| Party of the Unemployed for Work and Bread | 492 | 0.00 | 0 | New |
| Freiheitliche National-Soziale Deutsche Mittelstandsbewegung | 480 | 0.00 | 0 | New |
| National Freedom Party of Germany | 392 | 0.00 | 0 | New |
| National-Soziale Partei gegen die Hauszinssteuer | 376 | 0.00 | 0 | New |
| Nationalsoziale Kampfgemeinschaft für Handwerk, Gewerbe, Hausbesitz und Landwirtschaft | 334 | 0.00 | 0 | New |
| General Social-National Unity Worker Party of Germany | 277 | 0.00 | 0 | New |
| Freiwirtschaftsbewegung für Freiland, Freigeld, Festwährung | 270 | 0.00 | 0 | New |
| German Workers Party | 257 | 0.00 | 0 | New |
| Nationaler Bürger- und Wirtschaftsblock | 226 | 0.00 | 0 | New |
| Kampfbund der Lohn- und Gehaltsabgebauten und Auslandsgeschädigten | 177 | 0.00 | 0 | New |
| Radical Party | 154 | 0.00 | 0 | New |
| Kampfgemeinschaft der Lohn- und Gehaltsabgebauten | 128 | 0.00 | 0 | New |
| Unitarianist Union of Germany | 81 | 0.00 | 0 | New |
| Mieter- und Volks-Reichspartei | 69 | 0.00 | 0 | New |
| German Social Monarchist Party | 66 | 0.00 | 0 | New |
| German Reform Party | 59 | 0.00 | 0 | New |
| Invalid/blank votes | 279,727 | – | – | – |
| Total | 37,162,081 | 100 | 608 | +31 |
| Registered voters/turnout | 44,211,216 | 84.1 | – | – |
| Source: Gonschior.de | ||||
See also
References
- ^ a b c d The Holocaust Chronicle PROLOGUE: Roots of the Holocaust. 2002.
- ^ a b Hornberger, Jacob G. How Hitler became a Dictator Archived 18 February 2008 at the Wayback Machine. 2004.







