Policresulen
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | topical |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
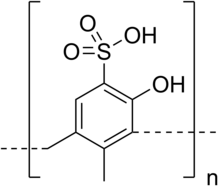
| Formula | (C9H8O4S)n |
| Molar mass | variable |
| | |
Policresulen is the polycondensation product of metacresol sulfonic acid and formaldehyde.[1] It is used as a topical hemostatic and antiseptic[2] in infectious and other lesions of the mucous membranes, like gynecological infections, anal hemorrhoids as well as ulcers of the oral cavity including canker sores. In some countries it is marketed under the trade name Albothyl or Polilen (Taiwan) or Faktu (combination with Cinchocaine).
Medical uses
Policresulen is used in the treatment of gynecological infections since the 1950s.[3] The range of applications soon widened to include the therapy of other mucous membrane and skin lesions. The mechanism of action is twofold: next to its antiseptic effect, policresulen promotes the selective coagulation of necrotic and pathologically altered tissues while leaving healthy tissues intact.[1] The shedding of necrotic tissues is accompanied by the reepithelialization of the mucosal (or dermal) wound tissues.[1]
References
- ^ a b c Kim EC, Park JB, Hong JY, Kang KL (April 2015). "Extensive gingival necrosis and sequestration of the alveolar bone caused by methimazole-induced neutropenia and three-year follow-up". Journal of Periodontal & Implant Science. 45 (2): 76–80. doi:10.5051/jpis.2015.45.2.76.
- ^ "Policresulen". drugs.com.
- ^ Renner, Alfred (December 1954). "Albothyl, a substance with a new mechanism of action in the treatment of gynecological diseases". Medizinische Klinik. 49 (50): 1998–1999. PMID 13235222.
